Metallogenic regularity of Meso-Cenozoic stratabound glutenite-type Cu-Pb-Zn deposits in the southwestern Tianshan Mountains
-
摘要: 西南天山是新疆中—新生界层控砂砾岩型铜铅锌矿的重要产出地区,以萨热克铜矿、乌拉根铅锌矿、花园铜矿、伽师铜矿为代表,均产于隆起剥蚀区边缘的红层盆地中并严格受层位控制,赋矿盆地的下部为煤系生烃岩,中部为渗透性良好的砂砾岩铜铅锌矿储集层,上覆膏岩及泥岩等密闭盖层,具有铜铅锌-铀-煤-天然气同盆共存富集的成矿特征。文章总结了西南天山赋矿盆地沉积-构造演化及赋矿层位特征,研究了铜铅锌典型矿床的控矿条件和成矿作用特征。通过对比分析,总结了中—新生界砂砾岩型铜铅锌矿的区域成矿规律,认为有机质与铜铅锌成矿关系密切,推测在原始矿源层的基础上,在隆起部位经油田卤水叠加形成铜铅锌贫矿体,喜马拉雅期断裂构造沟通深源成矿流体再次叠加形成铜铅锌富矿体。总结构建了西南天山中—新生界层控砂砾岩型铜铅锌矿的成矿模式,以期为已知矿山深边部勘查及区域找矿工作部署提供依据。Abstract: The southwestern Tianshan Mountains is an important producing area of the Meso-Cenozoic stratabound glutenite-type Cu-Pb-Zn deposits in Xinjiang. Sareke copper mine, Wulagen lead-zinc mine, Huayuan copper mine and Jiashi copper mine are the representative deposits, which all occur in the red bed basin on the edge of the uplift denudation area and are strictly controlled by strata. The lower part of the ore-bearing basin is composed of coal-bearing hydrocarbon-generating rocks, the middle part is well-permeable glutenites as the Cu-Pb-Zn reservoir, and the overlying layer is a sealed cap formed by gypsum rocks and mudstones, showing the ore-forming characteristics of co-enrichment of Cu-Pb-Zn-Uranium-coal-natural gas in the same basin. In this paper, we summarized the sedimentary-tectonic evolution of these ore-bearing basins and the characteristics of ore-bearing layers, and analyzed the ore-controlling conditions and metallogenic characteristics of typical copper, lead and zinc deposits. Combining with comparative analysis, we summarized the regional metallogenic regularity of the Meso-Cenozoic glutenite-type Cu-Pb-Zn deposit, and hold the view that organic matter is closely related to Cu-Pb-Zn mineralization. Moreover, it is inferred that Cu-Pb-Zn-lean ore bodies were formed over the original source layer in the uplift caused by the superimposition of oilfield brine; Cu-Pb-Zn-rich ore bodies were formed by the superimposition of deep-source ore-forming fluids from the Himalayan fault structure. The metallogenic model of the middle Cenozoic stratabound glutenite-type Cu-Pb-Zn deposits in the southwestern Tianshan Mountains provides a basis for the exploration of the known mines in their deep and edge, and also provides guidance for the regional prospecting work.
-
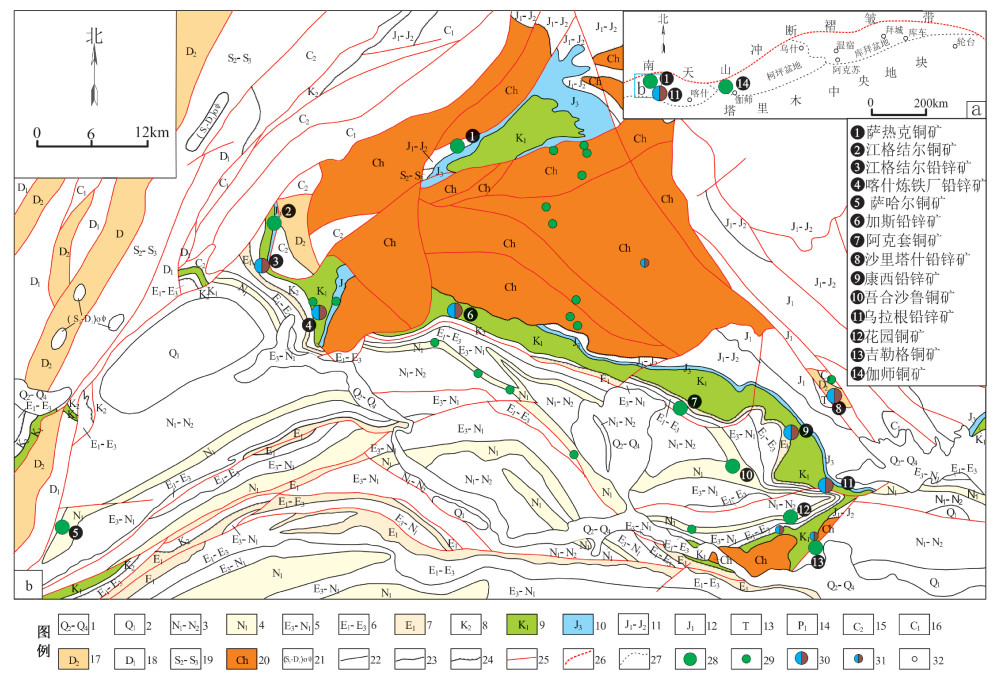
图 1 西南天山乌恰地区苏鲁铁列克-乌拉根隆起周缘区域地质图
1—中更新世—全新世冲洪积堆积; 2—早更新世冲洪积相碎屑岩建造; 3—中新世—上新世滨浅湖、冲积扇相粗-细碎屑岩建造; 4—中新世滨浅湖相碎屑岩建造; 5—渐新世—中新世滨浅湖相细碎屑岩夹膏盐建造; 6—古新世—渐新世浅海相碳酸盐岩、细碎屑岩夹膏盐建造; 7—古新世海湾相膏盐建造; 8—晚白垩世潮坪-海湾相碳酸盐岩、细碎屑岩、膏盐建造; 9—早白垩世辫状河三角洲相碎屑岩建造; 10—晚侏罗世冲积扇相粗碎屑岩建造; 11—早—中侏罗世滨浅湖相含煤碎屑岩建造; 12—晚侏罗世冲积扇相粗碎屑岩建造; 13—三叠纪滨浅湖相碎屑岩建造; 14—早二叠世滨浅湖相碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩建造; 15—晚石炭世滨浅海相碳酸盐岩、碎屑岩建造; 16—早石炭世浅海-半深海相碳酸盐岩建造; 17—中泥盆世滨浅海相碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩建造; 18—早泥盆世浅海-半深海相变质碎屑岩建造; 19—中—晚志留世浅海-半深海相碎屑岩建造; 20—长城纪半深海-深海相变质碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩建造; 21—晚志留世—早泥盆世超镁铁质岩建造; 22—整合接触界线; 23—角度不整合接触界线; 24—平行不整合接触界线; 25—断层; 26—南天山冲断褶皱带; 27—盆地边界; 28—铜矿床; 29—铜矿(化)点; 30—铅锌矿床; 31—铅锌矿(化)点; 32—城镇
a—南天山冲断褶皱带含铜铅锌矿盆地分布; b—苏鲁铁列克-乌拉根隆起周缘砂砾岩型铜铅锌矿分布Figure 1. Regional geological map of the Sulutilek-Wulagan uplift in the Wuqia area, southwestern Tianshan Mountains
(a) Distribution of Cu-Pb-Zn-bearing basins in the thrust-fold belt of the southern Tianshan Mountains; (b) Distribution map of glutenite-type Cu-Pb-Zn deposits in the periphery of the Sulutilek-Wulagan uplift
1-Meso-pleistocene-Holocene alluvial-pluvial accumulation; 2-Early pleistocene alluvial-pluvial clastic formation; 3-Coarse-fine clastic formation of Miocene-Pliocene coastal shallow-lake facies and alluvial fan facies; 4-Clastic formation of Miocene coastal shallow-lake facies; 5-Fine clastic rock with gypsum salt formation of Oligocene-Miocene coastal shallow-lake facies; 6-Carbonate rock-fine clastic rock-gypsum salt formation of Paleocene-Oligocene neritic facies; 7-Gypsum salt formation of Paleocene bay facies; 8-Carbonate rock-fine clastic rock-gypsum salt formation of Late Cretaceous tidal flat-bay facies; 9-Clastic formation of early Cretaceous braided fluvial-delta facies; 10-Coarse clastic formation of Late Jurassic alluvial fan facies; 11-Coal-bearing clastic formation of early Jurassic-middle Jurassic coastal shallow-lake facies; 12-Coarse clastic formation of Late Jurassic alluvial fan facies; 13-Clastic formation of Triassic coastal shallow-lake facies; 14-Clastic formation with carbonate formation of early Permian coastal shallow-lake facies; 15-Marine carbonate and clastic formation of late Carboniferous littoral-neritic facies; 16-Carbonate formation of early Carboniferous neritic-bathyal facies; 17-Carbonate formation with clastic formation of middle Devonian littoral-neritic facies; 18-Metamorphic clastic formation of early Devonian neritic-bathyal facies; 19-Clastic formation of middle-late Silurian neritic-bathyal facies; 20-Metamorphic clastic formation with carbonate formation of neritic-bathyal facies in the Changcheng period; 21-Late Silurian-early Devonian ultramafic formation; 22-Conformable geologic boundary; 23-Angular unconformable geological boundary; 24-Parallel unconformable geological boundaries; 25-Fault; 26-Thrust-fold belt of the Southern Tianshan Mountains; 27-Basin boundary; 28-Copper deposit; 29-Copper (mineralization) occurrence; 30-Lead-Zinc deposit; 31-Lead-Zinc (mineralization) occurrence; 32-town图 2 萨热克盆地沉积-构造演化图
1—砾岩; 2—石英砾岩; 3—粗砂岩; 4—细砂岩; 5—粉砂岩; 6—石英砂岩; 7—泥质砂岩; 8—泥质粉砂岩; 9—粉砂质泥岩; 10—泥岩; 11—灰岩; 12—云母片岩; 13—云母石英片岩; 14—含砾砂岩透镜体; 15—煤层; 16—铜矿
Figure 2. Sedimentary-tectonic evolution of the Sareke basin
1-Conglomerate; 2-Quartz conglometate; 3-Gritstone; 4-Fine sandstone; 5-Siltstone; 6-Silicarenite; 7-Argillaceous sandstone; 8-Muddy siltstone; 9-Silty mudstone; 10-Mudstone; 11-Limestone; 12-Mica-schist; 13-Mica quartz schist; 14-Gravel sandstone lens; 15-Coal bed; 16-Copper ore
图 3 喀什凹陷北缘乌恰洼陷沉积-构造演化图
1—砾岩; 2—石英砾岩; 3—砂砾岩; 4—粗砂岩; 5—细砂岩; 6—粉砂岩; 7—石英砂岩; 8—泥质砂岩; 9—泥质粉砂岩; 10—粉砂质泥岩; 11—泥岩; 12—灰岩; 13—介壳灰岩; 14—云母片岩; 15—云母石英片岩; 16—含砾砂岩透镜体; 17—石膏层; 18—煤层; 19—铜矿; 20—铅锌矿
Figure 3. Sedimentary-tectonic evolution of the Wuqia subsag in the northern margin of the Kashi Sag
1-Conglomerate; 2-Quartz conglometate; 3-Sandy conglomerates; 4-Gritstone; 5-Fine sandstone; 6-Siltstone; 7-Silicarenite; 8-Argillaceous sandstone; 9-Muddy siltstone; 10-Silty mudstone; 11-Mudstone; 12-Limestone; 13-Shell limestone; 14-Mica-schist; 15-Mica quartz schist; 16-Gravel sandstone lens; 17-Gypsum bed; 18-Coal bed; 19-Copper ore; 20-Lead-zinc ore
图 4 萨热克铜矿、乌拉根铅锌矿有机质成矿表现形式
a—萨热克铜矿油田卤水造成含砾砂岩褪色蚀变; b—萨热克铜矿断裂破碎带中充填的沥青与辉铜矿; c—乌拉根铅锌矿石中的有机气泡(含闪锌矿)(单偏光); d—乌拉根北矿带破碎带中与方铅矿、黄铁矿共同产出的沥青
Figure 4. Organic mineralization forms of the Sareke copper deposit and the Wulagen lead-zinc deposit
(a) The fade alteration of pebbly sandstone caused by brine in the Sareke copper deposit; (b)Bitumen and chalcocite filled in fractures of the Sareke copper deposit; (c) Organic bubbles in the Wulagan lead-zinc ore (containing sphalerite) (single polarized light); (d) Bitumen produced together with galena and pyrite in the fracture zone of the northern Wulagen ore belt
图 5 中—新生界砂砾岩型铅锌铜矿成矿模式图
1—白云岩; 2—石膏; 3—泥岩; 4—粉砂质泥岩; 5—砂岩; 6—粗砂岩; 7—砂砾岩; 8—砾岩; 9—坍塌角砾岩; 10—古近系/白垩系; 11—侏罗系/长城系; 12—断裂构造; 13—深源成矿流体; 14—深源成矿流体/油田卤水; 15—盆地卤水; 16—铅锌富/贫矿体; 17—铜富/贫矿体
Figure 5. Metallogenic model of Meso-Cenozonic glutenite-type Pb-Zn-Cu deposit
1-Dolomite; 2-Gypsum; 3-Mudstone; 4-Silty mudstone; 5-Sandstone; 6-Gritstone; 7-Glutenite; 8-Conglomerate; 9-Collapse breccia; 10-Paleogene system/Cretaceous system; 11-Jurassic system/Changcheng system; 12-Fracture; 13-Deep source ore-forming fluid; 14-Deep source ore-forming fluid/Oilfield brine; 15-Basin brine; 16-Lead-zinc-rich ore bodies/Lead-zinc lean ore bodies; 17-Copper-rich ore bodies/Copper-lean ore bodies
表 1 新疆萨热克铜矿床与云南六苴铜矿床对比表
Table 1. Comparison of the Sareke copper deposit in Xinjiang and the Liuju copper deposit in Yunnan
矿床 萨热克铜矿床 六苴铜矿床 大地构造位置 费尔干纳拉分断陷盆地之萨热克盆地。红层盆地下部为煤系烃源岩, 组成"煤-铜-泥岩"建造组合 扬子陆块西南缘云南楚雄中—新生界陆相红层盆地。盆地下部为煤系烃源岩, 组成"煤-铜-盐"建造组合 赋矿层位与岩石组合 上侏罗统库孜贡苏组上段(J3k2)灰绿色冲积扇相砾岩与下白垩统克孜勒苏群第一岩性段(K1kz1)褐红色泥岩组合 下—上白垩统高峰寺组凹地苴段(K1gw)、马头山组六苴段(K2ml)与大村段(K2md)高渗透率石英砂岩、含砾砂岩与泥岩组合 控矿构造特征 苏鲁铁列克隆起、萨热克向斜及向斜南北翼基底断裂及其横向次级断裂, 断裂构造交接部位为富矿体形成部位 大雪山背斜及其次级褶皱构造和南北、东北向次级构造控矿 矿体特征 层状、似层状、透镜状、脉状 层状、似层状、透镜状、脉状 蚀变特征 方解石化、黄铁矿化及碎裂化、褪色蚀变 褪色化、硅化、碳酸岩化、黄铁矿化 矿石矿物 辉铜矿、黄铜矿、斑铜矿、蓝铜矿以及黄铁矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿、辉钼矿等, 脉石矿物为方解石 辉铜矿、斑铜矿、黄铜矿、蓝辉铜矿、黄铁矿及辉银矿、方铅矿等, 脉石矿物为石英、长石等 结构构造特征 砾状结构、他形粒状结构、镶嵌结构、胶状结构、交代结构等; 浸染状、碎裂状、细脉状、团块状构造等 自形/他形粒状结构、交代结构、镶嵌结构等, 具稠密浸染状、星点状、条带状、细脉状构造 矿物分带 垂向上具"辉铜矿-斑铜矿-黄铜矿-黄铁矿"分带, 平面具"辉铜矿-辉铜矿+斑铜矿-黄铜矿+辉铜矿+斑铜矿-黄铜矿+黄铁矿-黄铁矿"分带 垂向上具"赤铁矿-辉铜矿-斑铜矿-黄铜矿-黄铁矿"分带, 平面具"赤铁矿-赤铁矿+辉铜矿-辉铜矿+斑铜矿-辉铜矿+斑铜矿+黄铜矿-黄铜矿+黄铁矿-黄铁矿"分带 油气显示 油迹、沥青与轻质油, 油田卤水造成浅-砖红色交互带, 包裹体为油气烃类-盐水、含烃类盐水、含轻质油及甲烷-CO2包裹体 矿区斑点状"原生"有机质发育, 形成浅-砖红色交互带, 包裹体为富含烃类、沥青的有机包裹体 硫同位素特征 δ34S全为负值, 集中于-15.4‰~-24.7‰之间, 硫主要来自硫酸盐细菌与有机质还原, 部分源于有机硫 δ34S分布范围较广, δ34S值为-31.4‰~-5.8‰, 主要为硫酸盐生物细菌还原成因 铅同位素特征 铅同位素投点图位于上地壳与造山带之间, 靠近造山带演化线 铅同位素投影集中于上地壳附近及造山带线之间 成矿流体特征 成矿流体为来自于沉积盆地中的建造水及富含有机烃类的油田卤水和深源成矿流体 成矿流体为含有机质的还原性流体及高盐度氧化性流体, 发生水-岩相互作用沉淀成矿 成矿期次 原始矿源层成矿期, 乌恰构造运动及地幔柱热源驱动盆地油田卤水向隆起区迁移聚集与地表水发生氧化-还原作用成矿期、喜马拉雅构造运动沟通深源成矿流体形成富矿体成矿期、表生成矿期 沉积-成岩期、喜马拉雅早期构造-热演化富含有机质流体与氧化流体水-岩作用期、喜马拉雅中期断裂构造沟通深源成矿流体上侵形成脉状铅锌矿体、表生成矿期 注: 六苴铜矿床资料据韩润生等(2010) 表 2 新疆乌拉根铅锌矿床与云南金顶铅锌矿床对比表
Table 2. Comparison of the Wulagen Pb-Zn deposit in Xinjiang and the Jinding Pb-Zn deposit in Yunnan
矿床 乌拉根铅锌矿床 金顶铅锌矿床 大地构造位置 塔里木盆地西缘喀什凹陷北部之乌恰洼陷, 盆地下部为侏罗系煤系烃源岩, 组成"煤-铅锌-膏岩"建造组合 兰坪-思茅中—新生代盆地北段 赋矿层位与岩石组合 下白垩统克孜勒苏群第五岩性段(K1kz5)辫状河三角洲相砂砾岩及古新统阿尔塔什组(E1a)石膏夹白云岩 赋矿层为古新统云龙组上段(E1yb)含灰岩角砾砂岩、砂岩和下白垩统景星组(K1j)石英砂岩和粉砂岩 控矿构造特征 吾合沙鲁断裂、基底断裂及近南北向小型断裂与节理, 上部石膏不透水层与赋矿砂砾岩透水层组成的储-盖系统 金顶穹窿为最重要的控矿构造 矿体特征 层状、似层状及透镜状 层状、脉状和透镜状 蚀变特征 褪色化、黄铁矿化、天青石化 以天青石化强烈发育为特征 矿石矿物 矿石矿物以闪锌矿、方铅矿为主, 脉石矿物主要为黄铁矿、方解石、白云石; 成矿元素以Zn为主, Pb/Zn≥1∶4 金属矿物为方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铁矿、白铁矿; 非金属矿物为天青石、重晶石等; 成矿元素以Zn为主, Pb/Zn≥1∶4 结构构造特征 粒状结晶结构、胶状结构、结核状结构、交代溶蚀结构、嵌晶结构、粗晶结构及条带状、浸染状、草莓状、角砾状、块状、脉状、皮壳状、多孔状构造 浸染状、层纹状、同生角砾状、块状构造; 霉球状、细粒状、乳滴状、胶状等结构 有机质特征 矿区及外围见原油、沥青等有机质, 形成浅—砖红色交互带 金顶穹窿中多见油气显示和轻油、重油、沥青等有机质 硫同位素特征 δ34S分布范围较广, 北矿带δ34S值为-25.9‰~-7.0‰, 南矿带δ34S值为-18.4‰~+15.0‰ 以负值为主、分布范围广, δ34S值为-48.43‰~-1.71‰; 源于有机质或细菌参与下的碳酸盐还原 铅同位素特征 不同矿石的铅同位素投影集中于造山带铅演化线附近, 大部分落入造山带区, 个别落入下地壳与地幔混合区 85%的样品显示幔源铅, 15%的样品显示壳-幔混源铅 成矿流体特征 油气包裹体成分测试结果成矿流体为低温中—高盐度的流体, 均一温度78~410 ℃, 盐度为3.55%~23.37% 成矿流体为中—低温、中—低盐度流体, 超压含烃富CO2的流体可能是深部富CO2含矿流体注入 成矿期次 原始矿源层形成期、油田卤水叠加成矿期(贫矿体)、深源成矿流体叠加成矿期(富矿体)、表生成矿期 盆地卤水与有机质还原成矿期、幔源流体上侵叠加成矿期、表生成矿期 注: 金顶矿床资料据薛春纪等(2017) -
CAI H Y, DENG G A, ZHENG Y P, 2002. Genetic discussion on Wulagen lead-zinc deposit of Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 16(1): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200201000.htm CHEN H Y, ZHANG L, LI D F, et al., 2013. Characteristics of rare earth and trace elements of the Sawayaerdun gold deposit, Southwest Tianshan: implications for ore genesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(1): 159-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) FANG W X, JIA R X, GUO Y Q, et al., 2016. Hydrocarbon-rich basin fluid with reductibility and metallogenic mechanism for glutenite-type Cu-Pb-Zn-U deposits in the Western of Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 38(6): 727-752. (in Chinese with English abstract) FANG W X, JIA R X, WANG L, 2017. Types of basin fluids, mechanism of discolored alterations and metal mineralizations of glutenite-type Cu-Pb-Zu-U deposits in intercontinental red-bed basin of the Western Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 39(5): 585-619. (in Chinese with English abstract) FANG W X, WANG L, GUO Y Q, et al., 2018a. Tectonic patterns in the Sarekebayi apart-pull Basin and their ore-controlling regularities for the sareke glutenite-type copper deposit in Xinjiang, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(3): 240-259. (in Chinese with English abstract) FANG W X, WANG L, JIA R X, 2018b. Mosaic tectonics of Mesozoic to Cenozoic basin-mountain-plateau in the Western Tarim Basin, China: glutenite-type Cu-Pb-Zn-celesite-U-coal metallogenic system[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 40(6): 663-705. (in Chinese with English abstract) FANG W X, WANG L, WANG S C, et al., 2019. Metallogenic regularity and prospecting forecast of the western Tarim Basin glutenite Cu-Pb-Zn deposi[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-424. (in Chinese) FANG W X, WANG L, LU J, et al., 2020. Mesozoic-Cenozoic sedimentary basin, foreland fold-and-thrust meralization reglarities of copper-lead-zinc-celesite-uranium-coal in Wulagen, Xinjiang, China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 44(5): 881-912. (in Chinese with English abstract) FU X G, LIN L, PANG Y C, et al., 2006. The characteristics of organic matter and its mineralization in the Jinding lead-zinc deposit, Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 33(6): 621-630. (in Chinese with English abstract) GAO R Z, 2018. Mineralization of mesozoic-cenozoic sandstone-hosted Zn-Pb deposits in the Southwstern Tianshan, Xingjiang, NW China: examplified by the Uragen Zn-Pb deposit[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences: 66-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN B F, WANG X C, HE G Q, et al., 1999. Discovery of mantle and lower crust xenoliths from early Cretaceous volcanic rocks of southwestern Tianshan, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(12): 1119-1123. doi: 10.1007/BF02886139 HAN F B, 2012. Study on Metallogensis of Wulagen Lead-zinc deposit in Wuqia, Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences: 45-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN F B, CHEN Z L, LIU Z R, et al., 2013. Organic geochemistry of Wulagen Pb-Zn deposit in Southwest Tianshan Mountains and its implications[J]. Mineral Deposits, 32(3): 591-602. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN R S, ZOU H J, WU P, et al., 2010. Coupling tectonic-fluid metallogenic model of the sandstone-type copper deposit in the Chuxiong Basin, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(10): 1438-1447. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUO H L, CHEN Z L, CHEN G M, et al., 2019. The U-Pb geochronology and geochemical characteristics of the Saergan mafic rocks in the Keping area, Southwest Tianshan, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(S1): 60-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIA R X, FANG W X, HU L L, et al., 2017a. Sulfur, lead, hydrogen, oxygen and carbon isotopic geochemical characteristics of Sareke copper deposit, Wuqia county, the Xingjiang Uygur Autonumous region, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 37(5): 630-637. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIA R X, FANG W X, WANG L, et al., 2017b. Hydrocarbon-rich Reducing Basin Fluid with in Sareke Glutenite Type Copper Deposit, Wuqia, Xinjiang[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 41(4): 721-733. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIA R X, FANG W X, LI J X, et al., 2018. Re-Os isotopic dating and its geological significance from Sareke copper deposit in Wuqia, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 37(1): 151-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIA R X, FANG W X, 2021. The migration rule of the ore-forming fluids in the Meso-Cenozoic Basins, Southwestern Tianshan, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(4): 529-541. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI F S, WANG W, YANG J M, 2005. Geological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Wulagen lead and zinc deposit in Wuqia County, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 19(4): 335-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Y A, LI Q, ZANG H, et al., 1995. Palaeomagnetic Study of Tarim and its Adjacent area as well as the Formation and Evolution of Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 13(4): 293-378. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Z D, XUE C J, XIN J, et al., 2011. Geological characteristics and S-, Pb-isotope geochemistry of Sareke copper deposit in Wuqia County, Xinjiang[J]. Geoscience, 25(4): 720-729. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIANG T, LUO Z H, LI W T, et al., 2005. Geologic features and tectonic implications of the Tuyon volcano group[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 23(2): 105-110. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Z R, TIAN P R, ZHU X Y, et al., 2011. Ore-forming geological characteristics and metallogenic model on Wulagen lead-zinc deposit, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2(6): 669-680. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Z R, QI S J, TIAN P R, et al., 2014a. Determination of age and its significance of ore-bearing strata of the Meso-Cenozoic glutenite type lead-zinc-copper deposit in the northwestern edge of Tarim basin, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Exploration, 5(2): 149-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Z R, QI S J, TIAN P R, et al., 2014b. Ore-forming geological characteristics and optimization selection of the prospecting targets of the Wulagen lead-zinc metallogenic belt, Wuqia county, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Exploration, 5(5): 689-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Z R, CHEN Z L, HAN F B, et al., 2016. Optimization and evaluation of prospecting target area in glutenite copper, lead and zinc metallogenic belt in the western margin of Tarim Basin[R]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Institute of Geological Survey, China Non-ferrous Metals Resource Geological Survey: 166-170. (in Chinese) LIU Z R, YE L, WANG L, et al., 2019. Geological and mineral survey of Hoshbluk-Ulagen in southwest Tianshan metallogenic belt[R]. Beijing: Internal Information of China Non-ferrous Metals Resource Geological Survey: 33-529. (in Chinese) LU J L, ZHUANG H P, LIU W J, 1997. The experimental studies on the role of organic matter in formation of strata-bound Pb-Zn deposit[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 15(2): 226-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) PENG S J, ZHANG X X, ZHOU Z C, 1985. The lead-zine ore types, ore forming law and direction of prospecting, XinJang[J]. XinJiang Geology, 3(3): 86-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) TU G C, 1988. Geochemistry of stratabound deposits in China Vol. 3[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 27-35. (in Chinese) WANG S C, XUE C J, LI Z D, 2011. Geology and S-, Pb-isotopic geochemistry of the Jiashi sandstone-type copper deposit, Xinjiang, China[J]. Geoscience, 25(2): 219-227. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG W, LI W Y, GAO M X, et al., 2018. Constraints on tectonic, fluid and metallogenic system evolution for the formation of Sareke sandstone copper deposit in northwestern Tarim block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 37(7): 1315-1324. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Y B, WANG Y, LIU X, et al., 2000. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of late cretaceous to paleoene basalts in Tuyon basin, South Tianshan Mountain[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 19(2): 131-139, 173. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE S Y, MO J P, YANG J G, et al., 2002. Geological characteristics and ore forming mechanism of Wu Lagen hot brine exhalogene lead-zinc deposit of cenozoic era, Wuqia, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 21(S1): 495-498. (in Chinese) XU X Y, XIA L Q, XIA Z C, et al., 2003. Geochemistry and genesis of cretaceous-paleogene basalts from the Tuoyun Basin, Southwest Tianshan Mountains[J]. Geochimica, 32(6): 551-560. (in Chinese with English abstract) XUN C J, CHI G X, CHEN Y C, et al., 2017. Giant Jingding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-119. (in Chinese) YANG B, 2018. Red bed Cu-Pb-Zn deposits and mineralization of hot brine in continental red bed basin[J]. Geology in China, 45(3): 441-455. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J, 2011. Geological characteristics of Jiashi Cu deposit in Xinjiang and the genetic Model[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 26(4): 373-377. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG T, CHEN Z L, HUANG H Y, et al., 2020. Geochemical characteristics of gold-bearing minerals and its geological significance in the Ashawayi gold deposit in the southwestern Tianshan Orogen[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(3): 443-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y Y, ZWINGMANN H, TODD A, et al., 2004. K-Ar dating of authigenic illite and its applications to study of oil-gas charging histories of typical sandstone reservoirs, Tarim basin, Northwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(4): 637-648. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.xml-data.org/ZGSYKT/html/2018/3/20180306.htm ZHANG Z L, FENG X J, DONG F C, et al., 2014. Type, genesis and exploration direction of glutenite-hosted ore deposits in the southwestern Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 47(3): 70-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO L T, MA Z M, 2021. Geological characteristics of Huayuan Cu deposit in Xijiang and Prospecting Marks[J]. Xinjiang Youse Jinshu, 44(1): 46-49. (in Chinese) ZHOU X Y, HU Y Z, LIU S, et al., 2003. Petroleum geology of outcrops areas in the northern part of Kashi Sag in Tarim Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press: 184-221. (in Chinese) ZHU H Y, ZHANG B C, ZHANG L, et al., 2021. Geological characteristics of Cenozoic stratabound sandstone type copper deposits in northwest margin of Tarim Basin[J]. Mineral Exploration, 12(7): 1539-1547. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU X Y, WANG J B, LIU Z R, et al., 2010. Geologic characteristics and the genesis of the Wulagen lead-zinc deposit, Xinjiang, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(5): 694-702. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU X Y, WANG J B, WANG Y J, et al., 2011. The geologic characteristics of Sareke copper deposit, Xinjiang, China: ore genesis related to basin brines[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2(1): 28-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHUANG H P, RAN C Y, HE M Q, et al., 1996. Organic geochemical evidence and meachanism of the genetic relationship between organic matter, evaporite, and sandstone-hosted copper deposits in Chuxiong Basin, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 14(3): 131-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) 蔡宏渊, 邓贵安, 郑跃鹏, 2002. 新疆乌拉根铅锌矿床成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质, 16(1): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2002.01.001 陈华勇, 张莉, 李登峰, 等, 2013. 南天山萨瓦亚尔顿金矿床稀土微量元素特征及其成因意义[J]. 岩石学报, 29(1): 159-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201301013.htm 方维萱, 贾润幸, 郭玉乾, 等, 2016. 塔西地区富烃类还原性盆地流体与砂砾岩型铜铅锌-铀矿床成矿机制[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 38(6): 727-752. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2016.06.001 方维萱, 贾润幸, 王磊, 2017. 塔西陆内红层盆地中盆地流体类型、砂砾岩型铜铅锌-铀矿床的大规模褪色化围岩蚀变与金属成矿[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 39(5): 585-619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2017.05.001 方维萱, 王磊, 郭玉乾, 等, 2018a. 新疆萨热克巴依盆内构造样式及对萨热克大型砂砾岩型铜矿床控制规律[J]. 地学前缘, 25(3): 240-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201803025.htm 方维萱, 王磊, 贾润幸, 2018b. 塔西地区中-新生代盆-山-原镶嵌构造区: 砂砾岩型铜铅锌-天青石-铀-煤成矿系统[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 40(6): 663-705. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201806002.htm 方维萱, 王磊, 王寿成, 等, 2019. 塔西砂砾岩型铜铅锌矿床成矿规律与找矿预测[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-424. 方维萱, 王磊, 鲁佳, 等, 2020. 新疆乌拉根中-新生代沉积盆地和前陆冲断褶皱带对铜铅锌-天青石-铀-煤成矿控制规律[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 44(5): 881-912. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202005008.htm 付修根, 林丽, 庞艳春, 等, 2006. 云南金顶铅锌矿床中的有机质特征及成矿作用探讨[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 33(6): 621-630. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2006.06.013 高荣臻, 2018. 新疆西南天山中-新生界砂岩容矿铅锌成矿作用: 以乌拉根铅锌矿床为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学: 66-101. 韩宝福, 王学潮, 何国琦, 等, 1998. 西南天山早白垩世火山岩中发现地幔和下地壳捕虏体[J]. 科学通报, 43(23): 2544-2547. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.23.019 韩凤彬, 2012. 新疆乌恰乌拉根铅锌矿床成因研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院: 45-124. 韩凤彬, 陈正乐, 刘增仁, 等, 2013. 西南天山乌拉根铅锌矿床有机地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 32(3): 591-602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.03.010 韩润生, 邹海俊, 吴鹏, 等, 2010. 楚雄盆地砂岩型铜矿床构造-流体耦合成矿模型[J]. 地质学报, 84(10): 1438-1447. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201010005.htm 霍海龙, 陈正乐, 陈贵民, 等, 2019. 西南天山柯坪地区萨尔干基性岩脉U-Pb年代学及地球化学特征[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(S1): 60-65. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.S1.011 贾润幸, 方维萱, 胡雷雷, 等, 2017a. 新疆萨热克铜矿床硫铅氢氧碳同位素地球化学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 37(5): 630-637. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201705014.htm 贾润幸, 方维萱, 王磊, 等, 2017b. 新疆萨热克砂砾岩型铜矿床富烃类还原性盆地流体特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 41(4): 721-733. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201704009.htm 贾润幸, 方维萱, 李建旭, 等, 2018. 新疆萨热克铜矿床铼-锇同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 37(1): 151-162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201801011.htm 贾润幸, 方维萱, 2021. 西南天山中新生代盆地成矿流体运移规律[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(4): 529-541. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.04.046 李丰收, 王伟, 杨金明, 2005. 新疆乌恰县乌拉根铅锌矿床地质地球化学特征及其成因探讨[J]. 矿产与地质, 19(4): 335-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2005.04.002 李永安, 李强, 张慧, 等, 1995. 塔里木及其周边古地磁研究与盆地形成演化[J]. 新疆地质, 13(4): 293-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI199504000.htm 李志丹, 薛春纪, 辛江, 等, 2011. 新疆乌恰县萨热克铜矿床地质特征及硫、铅同位素地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 25(4): 720-729. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.04.013 梁涛, 罗照华, 李文韬, 等, 2005. 托云火山群的火山地质特征及其构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 23(2): 105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2005.02.001 刘增仁, 田培仁, 祝新友, 等, 2011. 新疆乌拉根铅锌矿成矿地质特征及成矿模式[J]. 矿产勘查, 2(6): 669-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2011.06.005 刘增仁, 漆树基, 田培仁, 等, 2014a. 塔里木盆地西北缘中新生代砂砾岩型铅锌铜矿赋矿层位的时代厘定及意义[J]. 矿产勘查, 5(2): 149-158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201402006.htm 刘增仁, 漆树基, 田培仁, 等, 2014b. 新疆乌拉根铅锌成矿带地质特征与找矿靶区优选[J]. 矿产勘查, 5(5): 689-698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201405002.htm 刘增仁, 陈正乐, 韩凤彬, 等, 2016. 塔里木盆地西缘砂砾岩型铜铅锌成矿带找矿靶区优选评价研究报告[R]. 乌鲁木齐: 有色金属矿产地质调查中心新疆地质调查所: 166-170. 刘增仁, 叶雷, 王磊, 等, 2019. 西南天山成矿带霍什布拉克-乌拉根地质矿产调查报告[R]. 北京: 有色金属矿产地质调查中心: 33-529. 卢家烂, 庄汉平, 刘文均, 1997. 有机质在层控铅锌矿床中作用的实验研究[J]. 沉积学报, 15(2): 226-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB702.047.htm 彭守晋, 张希宣, 周自成, 1985. 新疆铅锌矿类型、成矿规律及找矿方向[J]. 新疆地质, 3(3): 86-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI198503007.htm 涂光炽, 1988. 中国层控矿床地球化学-第三卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 27-35. 王思程, 薛春纪, 李志丹, 2011. 新疆伽师砂岩型铜矿床地质及S、Pb同位素地球化学[J]. 现代地质, 25(2): 219-227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.02.004 王伟, 李文渊, 高满新, 等, 2018. 塔里木陆块西北缘萨热克砂岩型铜矿床构造-流体演化对成矿的制约[J]. 地质通报, 37(7): 1315-1324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201807015.htm 王彦斌, 王永, 刘训, 等, 2000. 南天山托云盆地晚白垩世-早第三纪玄武岩的地球化学特征及成因初探[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 19(2): 131-139, 173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2000.02.005 谢世业, 莫江平, 杨建功, 等, 2002. 新疆乌恰县乌拉根新生代热卤水喷流沉积铅锌矿地质特征及成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 21(S1): 495-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2002S1136.htm 徐学义, 夏林圻, 夏祖春, 等, 2003. 西南天山托云地区白垩纪-早第三纪玄武岩地球化学及其成因机制[J]. 地球化学, 32(6): 551-560. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.06.005 薛春纪, 池国祥, 陈毓川, 等, 2017. 云南金顶超大型铅锌矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-119. 杨兵, 2018. 陆相红层型铜铅锌矿床与红层盆地热卤水成矿作用[J]. 中国地质, 45(3): 441-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201803003.htm 张江, 2011. 新疆伽师铜矿床地质特征及成因模式[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 26(4): 373-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201104004.htm 张涛, 陈正乐, 黄宏业, 等, 2020. 西南天山阿沙哇义金矿载金矿物地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(3): 443-458. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.03.038 张有瑜, ZWINGMANN H, TODD A, 等, 2004. 塔里木盆地典型砂岩油气储层自生伊利石K-Ar同位素测年研究与成藏年代探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 11(4): 637-648. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.031 张振亮, 冯选洁, 董福辰, 等, 2014. 西南天山砂砾岩容矿矿床类型及找矿方向[J]. 西北地质, 47(3): 70-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2014.03.011 赵路通, 马忠美, 2021. 新疆花园铜矿床地质特征及及找矿标志[J]. 新疆有色金属, 44(1): 46-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJYS202101020.htm 周新源, 胡煜昭, 刘胜, 等, 2003. 塔里木盆地喀什凹陷北部露头区油气地质[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 184-221. 朱红英, 张宝琛, 张磊, 等, 2021. 西南天山新生代层控砂岩型铜矿成矿地质特征[J]. 矿产勘查, 12(7): 1539-1547. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2021.07.006 祝新友, 王京彬, 刘增仁, 等, 2010. 新疆乌拉根铅锌矿床地质特征与成因[J]. 地质学报, 84(5): 694-702. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201005009.htm 祝新友, 王京彬, 王玉杰, 等, 2011. 新疆萨热克铜矿: 与盆地卤水作用有关的大型矿床[J]. 矿产勘查, 2(1): 28-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2011.01.007 庄汉平, 冉祟英, 何明勤, 等, 1996. 楚雄盆地有机质、膏盐与砂岩铜矿生成关系的有机地球化学证据与机理[J]. 沉积学报, 14(3): 131-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB603.016.htm -





 下载:
下载: