Accumulation model of the Sinian-Cambrian shale gas in western Hubei Province, China
-
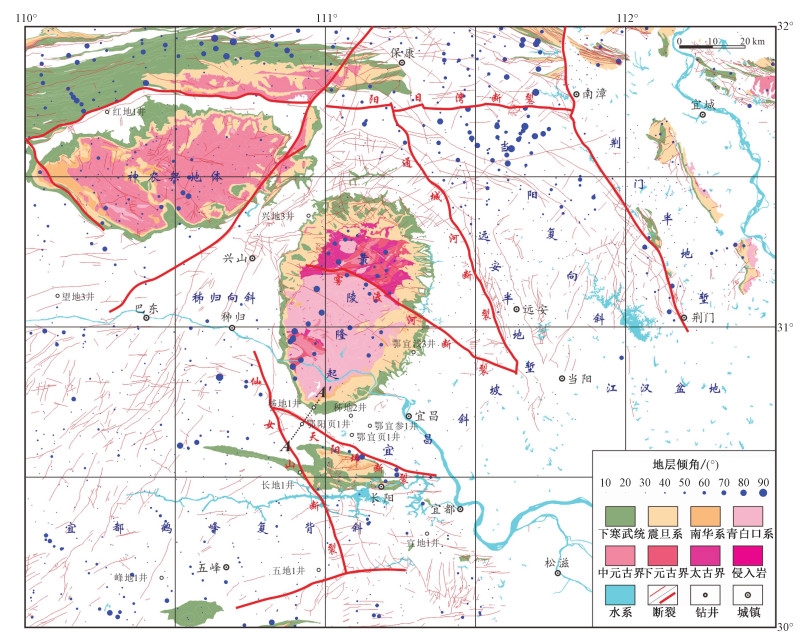
摘要: 通过对鄂西震旦系陡山沱组和寒武系牛蹄塘组页岩气勘查大量实际资料总结研究,创新性地提出了针对鄂西地区震旦系和寒武系"岩相控炭、成岩控烃、构造控藏"的页岩气成藏理论认识。震旦系陡山沱组和寒武系牛蹄塘组富有机质页岩沉积受控于鄂西裂陷海槽,富有机质页岩甜点层段主要形成于海侵体系域和早期高水位体系域。黄陵古隆起周缘震旦纪—三叠纪长期浅埋,为生油提供了充足时间,三叠纪短暂快速深埋,为页岩气生成的主峰期。古隆起刚性基底、区域性泥页岩盖层以及后期逆冲推覆构造,为页岩气保存提供了良好的条件。从而建立了鄂西震旦—寒武系"深水海槽控炭、古隆起浅埋控烃、古隆起+逆冲断裂控藏"的页岩气成藏模式。Abstract: Based on the study of a large number of real data of shale gas exploration in the Sinian Doushantuo Formation and the Cambrian Niutitang Formation in western Hubei Province, the theoretical understanding of shale gas accumulation in the Sinian and Cambrian that lithofacies controls carbon, diagenesis controls hydrocarbon and structure controls reservoir is put forward innovatively. The deposition of organic-rich shales in the Sinian Doushantuo Formation and the Cambrian Niutitang Formation were controlled by the rift trough in western Hubei. Sweet spots of organic-rich shales were mainly formed in the transgressive system tract and the early high water-level system tract. The long-term shallow burial in the Sinian and Triassic around the Huangling paleo-uplift provided sufficient time for the oil generation. The Triassic is a short-term and rapid burial period, which is the main peak period of shale gas generation. The rigid basement of paleo-uplift, regional shale cap rock and later thrust nappe structure provided good conditions for the shale gas preservation. Thus, the shale gas accumulation model of the Sinian and Cambrian in western Hubei Province is established, which includes carbon control by deep-water trough, hydrocarbon control by shallow burial of paleo-uplift, reservoir control by paleo-uplift and thrust fault.
-
表 1 鄂西地区陡山沱组和牛蹄塘组钻井实测TOC含量统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of measured TOC content in drilling of the Doushantuo Formation and Niutetang Formation in western Hubei Province
井号 陡山沱组页岩TOC含量/% 牛蹄塘组页岩TOC含量/% 鄂阳页1井 1.00~2.90/1.70(295) 4.42~6.65/5.34(16) 鄂宜参1井 0.13~4.0/0.92(?) 0.52~5.96/2.26(32) 秭地1 0.72~2.91/1.63(19) 0.53~8.72/2.95(40) 秭地2 0.07~1.78/0.66(22) 0.30~9.59/2.34(44) 注:表中1.00~2.90为TOC测试样品值范围;1.70为TOC平均值;(295)为测试样品数 表 2 鄂西地区震旦系陡山沱组与牛蹄塘组实测有机质成熟度统计表
Table 2. Statistics of measured organic matter maturity in the Doushantuo Formation and Niutitang Formation of Sinian system in western Hubei Province
测试方法 陡山沱组Ro/% 牛蹄塘组Ro/% 固体沥青反射率 3.09~3.49/3.21(9) 2.84~3.24/3.02(11) 干酪根红外光谱 2.3~3.3 1.7~2.6 干酪根激光拉曼 /2.84(13) /3.08 注:表中3.09~3.49为测试样品值范围;3.21为平均值;(9)为测试样品数 表 3 鄂阳页1井陡山沱组和牛蹄塘组页岩裂缝脉体样品信息表
Table 3. Information table of shale fractured vein samples from the Doushantuo Formation and Jiutitang Formation in the Eyangye No.1 well
样品编号 采样层位 深度/m 脉体类型 脉体产状 N-2 牛蹄塘组( 
2942.56 方解石脉 高角度 N-4 3062.00 D-5 陡山沱组(Z1ds) 3357.72 石英脉为主 D-7 3363.64 D-10 3371.68 D-12 3374.84 D-20 3381.45 D-21 3392.42 -
DENG M Z, 2018. Structural modeling of the Huangling anticline and its peripheral structural belt[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) DENG M Z, HE D F, ZHANG Y Y, 2018. Tectonic evolution of Xiannüshan fault and its influence on hydrocarbon traps in Changyang anticline, Western Hubei fold belt[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 40(2):177-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201802007 GAO J, HE S, ZHAO J X, et al., 2017. Geothermometry and geobarometry of overpressured lower Paleozoic gas shales in the Jiaoshiba field, Central China:Insight from fluid inclusions in fracture cements[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 83:124-139. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.02.018 GE X H, WANG M P, LIU J L, 2010. Redefining the Sichuan Movement and the age and background of Qingzang Plateau's first uplift:The implication of Huangling anticline and its enlightenment[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(4):206-217. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO X S, 2014. Rules of two-factor enrichiment for marine shale gas in Southern China-understanding from the Longmaxi Formation shale gas in Sichuan Basin and its surrounding area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(7):1209-1218. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201407001 HAN S B, ZHANG J C, LI Y X, et al., 2013. The optimum selecting of shale gas well location for geological investigation in Niutitang Formation in Lower Cambrian, northern Guizhou area[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 24(1):182-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201301026 HE C F, ZHANG C G, WANG Q L, et al., 2017. Micro-morphology characteristics and dating implications of the Gouge Quartz of Xiannüshan-Jiuwanxi fault[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 37(4):355-360. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz201704006 HU J M, CHEN H, QU H J, et al., 2012. Mesozoic deformations of the Dabashan in the southern Qinling orogen, central China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 47:171-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.015 HU L, ZHU Y M, CHEN S B, et al., 2012. Resource potential analysis of shale gas in Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in Middle & Upper Yangtze region[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 37(11):1871-1877. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mtxb201211018 HUANG J L, ZOU C N, LI J Z, et al., 2012. Shale gas generation and potential of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in Southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(1):69-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201201008 JIN Z J, HU Z Q, GAO B, et al., 2016. Controlling factors on the enrichment and high productivity of shale gas in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(1):1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201601001 LI W, HE S, ZHANG B Q, et al., 2018. Characteristics of paleo-temperature and paleo-pressure of fluid inclusions in shale composite veins of Longmaxi Formation at the western margin of Jiaoshiba anticline[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 39(4):402-415. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201804004 LI X M, SHAN Y H, 2011. Diverse exhumation of the Mesozoic tectonic belt within the Yangtze Plate, China, determined by apatite fission-track thermochronology[J]. Geosciences Journal, 15(4):349-357. doi: 10.1007/s12303-011-0037-5 LIANG D G, GUO T L, BIAN L Z, et al., 2009. Some progresses on studies of hydrocarbon generation and accumulation in marine sedimentary regions, Southern China (part 3):Controlling factors on the sedimentary facies and development of Palaeozoic marine source rocks[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 14(2):1-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU B, FU Y W, 2016. Practice on shale gas volume fracturing for Qiongzhusi Formation in JY1 HF well[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 9(3):69-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fzyqc201603015 LIU S G, RAN B, GUO T L, et al., 2014. Lower Palaeozoic organic-matter-rich black shale in the Sichuan Basin and its periphery:From oil-prone source rock to gas-producting shale reservoir[M]. Beijing:Science Press:42-294. (in Chinese) MA Y S, CAI X Y, ZHAO P R, 2018. China's shale gas exploration and development:understanding and practice[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(4):561-574. (in Chinese with English abstract) MOU C L, ZHOU K K, LIANG W, et al., 2011. Early Paleozoic sedimentary environment of hydrocarbon source rocks in the Middle-Upper Yangtze region and petroleum and gas exploration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(4):526-532. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201104008 SHEN C B, MEI L F, LIU Z Q, et al., 2009. Apatite and zircon fission track data, evidences for the Mesozoic-Cenozoic uplift of Huangling Dome, central China[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 29(2):54-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwys200902009 SHU L S, 2012. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J] Geological Bulletin of China, 31(7):1035-1053. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201207003 WANG Y F, ZHAI G Y, LENG J G, et al., 2017. Well TX1 fracturing effect evaluation of Niutitang formation shale in Cengong, Guizhou[J]. Earth Science, 42(7):1107-1115. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201707007 WANG Y F, ZHAI G Y, HU Z F, 2018. Stable and high-yield shale gas flow has been obtained in Niutitang Formation of Eyangye1hf well in Yichang, Hubei province. The project of "strategic investigation of shale gas favorable area in Zigui Changyang, Hubei Province" has achieved important achievements[J]. Management and Research of Scientific and Technological achievements(4):79-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Y F, ZHAI G Y, ZHANG J Z, 2019. Shale gas breakthrough of Sinian Doushantuo Formation in well Eyangye 2hf, Yichang, Hubei province. The project of "strategic investigation of shale gas favorable area in Zigui Changyang, Hubei Province" has achieved important achievements[J]. Management and Research of Scientific and Technological achievements(7):70-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) WEN L, HU S Y, TIAN H Q, 2001. A study on hydrocarbon source rock of Cambrian in Yangtze area, China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 34(2):67-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200102012 XIONG C Y, WEI C S, JIN G F, et al., 2004. Pre-sinian paleostructural framework and major geological events in the Huangling Anticline, Western Hubei[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 10(2):97-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200402001 XU C H, ZHOU Z Y, CHANG Y, et al., 2010. Genesis of Daba Arcuate structural belt related to adjacent basement upheavals:constraints from fission-track and (U-Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Science China Earth Science, 53(11):1634-1646. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4112-y XU D L, PENG L H, LIU H, et al., 2013. Meso-Cenozoic tectono-sedimentary response of multi-phased uplifts of Huangling Anticline, Central China[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 29(2):90-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hndzykc201302002 ZHAI G Y, BAO S J, WANG Y F, et al., 2017. Reservoir accumulation model at the edge of Palaeohigh and Significant discovery of shale gas in Yichang area, Hubei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 38(4):441-447. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201704001 ZHAI G Y, WANG Y F, ZHOU Z, et al., 2018. "Source-Diagenesis-Accumulation" enrichment and accumulation regularity of marine shale gas in southern China[J]. China Geology, 1(3):319-330. doi: 10.31035/cg2018059 ZHANG H D, 1986. Analysis of the formation and tectonics of the Huangling anticline[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute(1):29-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J K, HE S, YI J Z, et al., 2014. Rock thermos-acoustic emission and basin modeling technologies applied to the study of maximum paleotemperatures and thermal maturity histories of Lower Paleozoic marine shales in the western middle Yangtze area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 35(1):58-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.122 ZHAO W Z, LI J Z, YANG T, et al., 2016. Geological difference and its significance of marine shale gases in South China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 43(4):499-510. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201604001 ZOU C N, DONG D Z, WANG Y M, et al., 2015. Shale gas in China:characteristics, challenges and prospects (I)[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 42(6):689-701. (in Chinese with English abstract) 邓铭哲, 2018.黄陵背斜及邻区构造建模[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 邓铭哲, 何登发, 张煜颖, 2018.鄂西仙女山断裂构造演化及其对长阳背斜圈闭性的影响[J].石油实验地质, 40(2):177-184. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201802007 葛肖虹, 王敏沛, 刘俊来, 2010.重新厘定"四川运动"与青藏高原初始隆升的时代、背景:黄陵背斜构造形成的启示[J].地学前缘, 17(4):206-217. 郭旭升, 2014.南方海相页岩气"二元富集"规律:四川盆地及周缘龙马溪组页岩气勘探实践认识[J].地质学报, 88(7):1209-1218. 韩双彪, 张金川, 李玉喜, 等, 2013.黔北地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩气地质调查井位优选[J].天然气地球科学, 24(1):182-187. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201301026 何超枫, 张春光, 王秋良, 等, 2017.仙女山-九畹溪断裂带断层泥石英微形貌特征及其年代学意义[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 37(4):355-360. 胡琳, 朱炎铭, 陈尚斌, 等, 2012.中上扬子地区下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩气资源潜力分析[J].煤炭学报, 37(11):1871-1877. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=mtxb201211018 黄金亮, 邹才能, 李建忠, 等, 2012.川南下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩气形成条件及资源潜力[J].石油勘探与开发, 39(1):69-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201201008 金之钧, 胡宗全, 高波, 等, 2016.川东南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气富集与高产控制因素[J].地学前缘, 23(1):1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201601001 李文, 何生, 张柏桥, 等, 2018.焦石坝背斜西缘龙马溪组页岩复合脉体中流体包裹体的古温度及古压力特征[J].石油学报, 39(4):402-415. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201804004 梁狄刚, 郭彤楼, 边立曾, 等, 2009.中国南方海相生烃成藏研究的若干新进展(三)南方四套区域性海相烃源岩的沉积相及发育的控制因素[J].海相油气地质, 14(2):1-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz200902001 刘斌, 付育武, 2016. JY1HF井筇竹寺组页岩气体积压裂实践[J].复杂油气藏, 9(3):69-73. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fzyqc201603015 刘树根, 冉波, 郭彤楼, 等, 2014.四川盆地及周缘下古生界富有机质黑色页岩:从优质烃源岩到页岩气产层[M].北京:科学出版社:42-294. 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣, 2018.中国页岩气勘探开发理论认识与实践[J].石油勘探与开发, 45(4):561-574. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201804003 牟传龙, 周恳恳, 梁薇, 等, 2011.中上扬子地区早古生代烃源岩沉积环境与油气勘探[J].地质学报, 85(4):526-532. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201104008 沈传波, 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 等, 2009.黄陵隆起中-新生代隆升作用的裂变径迹证据[J].矿物岩石, 29(2):54-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwys200902009 舒良树, 2012.华南构造演化的基本特征[J].地质通报, 31(7):1035-1053. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201207003 王玉芳, 翟刚毅, 冷济高, 等, 2017.贵州岑巩TX1井牛蹄塘组页岩压裂效果评价[J].地球科学, 42(7):1107-1115. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201707007 王玉芳, 翟刚毅, 胡志方, 2018.湖北宜昌鄂阳页1HF井牛蹄塘组获稳定高产页岩气流:"湖北秭归-长阳页岩气有利区战略调查"项目取得重要阶段性成果[J].科技成果管理与研究(4):79-81. 王玉芳, 翟刚毅, 张家政, 2019.湖北宜昌鄂阳页2HF井震旦系陡山沱组页岩气重大突破:"湖北秭归-长阳页岩气有利区战略调查"项目取得重要阶段成果[J].科技成果管理与研究(7):70-72. 文玲, 胡书毅, 田海芹, 2001.扬子地区寒武系烃源岩研究[J].西北地质, 34(2):67-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200102012 熊成云, 韦昌山, 金光富, 等, 2004.鄂西黄陵背斜地区前南华纪古构造格架及主要地质事件[J].地质力学学报, 10(2):97-112. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20040201&journal_id=dzlxxb 徐大良, 彭练红, 刘浩, 等, 2013.黄陵背斜中新生代多期次隆升的构造-沉积响应[J].华南地质与矿产, 29(2):90-99. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hndzykc201302002 翟刚毅, 包书景, 王玉芳, 等, 2017.古隆起边缘成藏模式与湖北宜昌页岩气重大发现.地球学报, 38(4):441-447. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201704001 张或丹, 1986.黄陵背斜的形成和构造发展初析[J].江汉石油学院学报, (1):29-40. 张建坤, 何生, 易积正, 等, 2014.岩石热声发射和盆模技术研究中扬子区西部下古生界海相页岩最高古地温和热成熟史[J].石油学报, 35(1):58-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201401006 赵文智, 李建忠, 杨涛, 等, 2016.中国南方海相页岩气成藏差异性比较与意义[J].石油勘探与开发, 43(4):499-510. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201604001 邹才能, 董大忠, 王玉满, 等, 2015.中国页岩气特征、挑战及前景(一)[J].石油勘探与开发, 42(6):689-701. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201506001 -





 下载:
下载: