Research on multi-source heterogeneous data fusion algorithm of landslide monitoring based on BP neural network
-
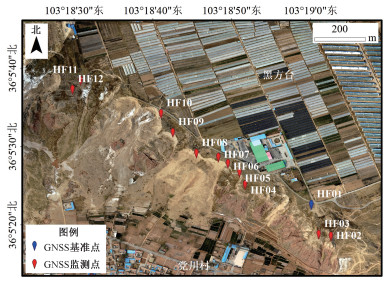
摘要: 针对滑坡监测中的多源异构数据融合问题,论文提出了一种基于BP神经网络的多源异构监测数据融合算法。该算法将影响滑坡变形的温度、湿度、风力、云量、单日降水量和累计降水量等多环境因子变量作为输入变量,以滑坡位移变化量数据作为期望输出数据,并利用各环境因子变量和滑坡位移变化量的相关性及显著性进行环境因子变量筛选,以提高算法的预测精度。论文采用甘肃省永靖县黑方台党川滑坡的实测数据进行了试验,结果表明:反向传播(Back-Propagation,BP)神经网络数据融合算法适用于具有多源异构监测数据的滑坡变形预测;在进行环境变量因子筛选后,BP神经网络数据融合算法的决定系数达到0.985,均方根误差(RMSE)达到0.4787 mm,从而有效提高了变形预测结果的精度。Abstract: Aiming at the multi-source heterogeneous data fusion problem of landslide monitoring,a multi-source heterogeneous monitoring data fusion algorithm based on BP neural network is proposed in this paper. The temperature,humidity,wind power,cloudiness,precipitation and accumulated precipitation which affect the landslide deformation are taken as the input variables,and the landslide displacement changes data are taken as the expected output data in this algorithm. And the prediction accuracy of this algorithm can be effectively improved by filtering the environmental factor variables with calculating the correlation and significance of the environmental factor variables and the landslide displacement changes. This algorithm is verified by the monitoring data of the Dangchuan landslide in Heifangtai,Yongjing County,Gansu Province. The results show that the BP neural network data fusion algorithm can be used in the landslide displacement prediction with multi-source heterogeneous monitoring data. After the environmental factor variable filtering,the determination coefficient of the BP neural network data fusion algorithm can achieve 0.985 and the RMSE can achieve 0.4787 mm. Thus the accuracy of deformation prediction can be effectively improved.
-
Key words:
- landslide monitoring /
- multi-source heterogeneous data /
- data fusion /
- BP neural network /
- prediction
-
表 1 多环境因子变量及GNSS位移量样本数据
Table 1. Sample data of multiple environmental factor variables and GNSS displacement
序号 温度/℃ 湿度/% 风力/级 云量/% 单日降水量/mm 累计降水量/mm 位移变化量/(mm/d) 1 -6 54.5 6 53 0.5 0.5 2.35 2 -7.5 72.5 6 89 17.7 18.2 3.15 3 -7 74.5 5 66 13.6 31.8 2.77 19 -2.5 83.5 5 71 3.9 54.3 4.13 20 -1.5 79.5 5 55 3.6 57.9 3.80 表 2 环境因子变量相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficients of environmental factor variables
相关系数 温度/℃ 湿度/% 风力/级 云量/% 单日降水量/mm 累计降水量/mm 温度/℃ 1 -0.197 -0.764 -0.468 -0.625 0.428 湿度/% -0.197 1 -0.081 0.818 0.508 0.521 风力/级 -0.764 -0.081 1 0.267 0.239 -0.466 云量/% -0.468 0.818 0.267 1 0.597 0.169 单日降水量/mm -0.625 0.508 0.239 0.597 1 -0.171 累计降水量/mm 0.428 0.521 -0.466 0.169 -0.171 1 表 3 各环境因子变量和滑坡位移变化量的相关性及显著性
Table 3. Correlation and significance of various environmental factor variables and landslide displacement changes
变量 温度/℃ 湿度/% 风力/级 云量/% 单日降水量/mm 累计降水量/mm 相关性 -0.190 0.598 0.063 0.465 0.206 0.475 显著性 0.423 0.005 0.792 0.039 0.383 0.034 表 4 两种方案下融合模型的预测位移变化量和实际位移变化量的对比
Table 4. Comparison of the predicted displacement change and the actual displacement change of the fusion model under two schemes
序号 预测位移变化量/mm 实际位移变化量/mm 方案一 方案二 16 2.09 2.53 2.69 17 2.50 2.74 3.03 18 2.20 2.89 3.15 19 3.07 3.35 4.13 20 2.80 3.20 3.80 MAE 0.8280 0.4180 / RMSE 0.8564 0.4787 / 表 5 两种方案下融合模型的决定系数与残差平方和
Table 5. The residual sum of squares and the determination coefficient of the fusion model under two schemes
R2 RSS 方案一 0.890 0.073 方案二 0.985 0.006 -
CHEN M J, OUYANG Z X, FAN G S, et al., 2007. On information extraction method based on data fusion for integrated landslide monitoring[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 27(6):77-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200706014.htm CHENG J, ZHANG W J, 2018. Analysis on the changes and correlation of precipitation and cloud in northwest china in the past 40 years[J]. Journal of Qinghai Meteorology, (3):1-5. (in Chinese) DING J X, SHANG Y J, YANG Z F, et al., 2004. New method of predicting rainfall-induced landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 23(21):3738-3743. (in Chinese with English abstract) DONG W W, ZHU H H, SUN Y J, et al., 2016. Current status and new progress on slope deformation monitoring technologies[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 24(6):1088-1095. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201606007.htm DU G L, ZHANG Y S, GAO J C, et al., 2016. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on GIS in Bailongjiang watershed, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(1):1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLX201601001.htm FAN J Q, 2015. Research on multi-source heterogeneous sensor information fusion for landslide monitoring[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) FENG Z, LI B, ZHAO C Y, et al., 2016. Geological hazards monitoring and application in mountainous town of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(3):685-694. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201603022.htm GAO Y, LI B, FENG Z, et al., 2017. Global climate change and geological disaster response analysis[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(1):65-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201701002.htm GUMILAR I, FATTAH A, ABIDIN H Z, et al., 2017. Landslide monitoring using terrestrial laser scanner and robotic total station in Rancabali, West Java (Indonesia)[C]//American Institute of Physics Conference Series, 1857: 060001. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/318705997_Landslide_monitoring_using_terrestrial_laser_scanner_and_robotic_total_station_in_Rancabali_West_Java_Indonesia GUO K, PENG J B, XU Q, 2005. Realization of the extraction of comprehensive information of multi-station monitoring data of landslide with the technique of multisensor target tracking[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 20(3):808-813. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200503036.htm GUO K, PENG J B, XU Q, et al., 2006. Application of multi-sensor target tracking to multi-station monitoring data fusion in landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 27(3):479-481. (in Chinese with English abstract) HIBERT C, GRANDJEAN G, BITRI A, et al., 2012. Characterizing landslides through geophysical data fusion:Example of the La Valette landslide (France)[J]. Engineering Geology, 128:23-29. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.05.001 JIANG H Q, LI Z X, LI X S, et al., 2006. Discussion on the prediction theory and method of landslide disaster caused by meteorological change[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 13(5):20-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-STBY200605006.htm LIAO M S, ZHANG L, SHI X G, et al., 2017. Remote sensing monitoring method and practice of landslide deformation radar[M]. Beijing:Science Press. (in Chinese) LIU C Y, YIN X B, ZHANG B, 2015. Analysis and prediction of landslide deformations based on data fusion technology of Kalman-filter[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 26(4):30-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGDH201504007.htm LIU X H, YAO X, ZHOU Z K, et al., 2018. Study of the technique for landslide rapid recognition by InSAR[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(2):229-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLX201802067.htm MO Y S, DONG X M, WEN R H, 2010. Analysis of the influence of meteorological factors on the formation of landslide[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 22(6):51-52, 55. (in Chinese) NI X J, 2005. Application of wavelet theory to the denoising and the combinatorial predetermination for landslide[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) PENG H, HUANG B Z, YANG Y, 2012. Study on technical methods of landslide monitoring[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 26(1):45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK201201010.htm PENG P, SHAN Z G, DONG Y F, et al., 2011. Application of multi-sensor valuation fusion theory to monitoring dynamic deformation of landslides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 19(6):928-934. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GCDZ201106023.htm PRADHAN B, JEBUR M N, SHAFRI H Z M, et al., 2016. Data fusion technique using wavelet transform and Taguchi methods for automatic landslide detection from airborne laser scanning data and QuickBird satellite imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 54(3):1610-1622. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2484325 QI X, HUANG B L, LIU G N, et al., 2017. Landslide susceptibility assessment in the Three Gorges area, China, Zigui synclinal basin, using GIS technology and frequency ratio model[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(1):97-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) QI X, XU Q, ZHAO K Y, et al., 2018. Analysis on law of response from irrigation to groundwater level at Heifangtai Tableland in Gansu Province[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 49(9):205-209. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIU D D, 2017. Landslide risk analysis based on multi-source data fusion[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN B, 2012. Method research on comprehensive treatment and data fusion of multiple monitoring data[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences. (in Chinese) SUN Y P, ZHANG S P, CHEN W K, et al., 2018. Risk assessment of landslides caused by Wenchuan Earthquakes:a case study in the Wudu District and Wenxian County, Gansu Province[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 40(5):1084-1091. (in Chinese with English abstract) VILLALPANDO F, TUXPAN J, RAMOS-LEAL J A, et al., 2020. New framework based on fusion information from multiple landslide data sources and 3D visualization[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 31(1):159-168. doi: 10.1007/s12583-019-1243-8 WANG J, 2013. 3D geological modeling of landslide mass based on QuantyView and multi-source data[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG L, ZHANG Q, ZHAO C Y, et al., 2005. The application study of GPS multi-antenna monitoring technique in the monitoring of road slope disaster[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 22(6):163-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK2005S1042.htm WANG L, ZHANG Q, LI X C, et al., 2011. Dynamic and real time deformation monitoring of landslide with GPS-RTK technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 19(2):193-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=c717bdc0a7a24a19b42883c5496f8f78&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn WANG Y M, FENG Q, LI Z X, 2014. Analysis of low cloud amount variations in the northwest China during 1960-2005[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 34(5):635-640. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=09089b50bb335a6a0f0c0a0ee8f013eb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn WU W, WANG S G, DENG L T, et al., 2010. Four-season distribution of cloud and its correlation with precipitation in northern China[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 46(3):32-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=adf29f12b2346c2630ca9ea66d022dfb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn XU Q, FENG D L, QI X, et al., 2016. Dangchuan 2# landslide of April 29, 2015 in Heifangtai area of Gansu Province:characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 24(2):167-180. (in Chinese with English abstract) YIN J X, HE Y Q, YAO Y S, et al., 2019. Research on deformation of plateau landslide based on meteorological conditions[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying(1):184-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-CSKC201901052.htm ZHANG W Q, 2019. Research on high-precision deformation monitoring and prediction methods for loess landslide[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University. (in Chinese) ZHANG X Y, ZHANG C S, MENG H J, et al., 2018. Landslide susceptibility assessment of new Jing-Zhang high-speed railway based on GIS and information value model[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(1):96-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y J, 2006. Research on detection and recognition of underwater target based on network and data fusion[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y Z, 2007. Study on the theory of structural damage identification based on neural network and data fusion[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University. (in Chinese) ZHAO C Y, LIU X J, ZHANG Q, et al., 2019. Research on loess landslide identification, monitoring and failure mode with InSAR technique in Heifangtai, Gansu[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 44(7):996-1007. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-WHCH201907005.htm ZHAO S Q, ZHU S J, 2013. On forecasting typical landslides in the Three-Gorge Reservoir[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 13(6):259-264. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU F, 2015. Study on the deformation characteristics of loess slope and mechanism of landslide in Heifangtai, Gansu Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU Z M, ZHOU K R, TAN C H, et al., 2013. Study on technology of slope/landslide stability analysis and early warning under heavy rainfall[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 19(4):423-430. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=022cb0e78d567d546d7dc2f0dde56d44&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn 陈明金, 欧阳祖熙, 范国胜, 2007.基于数据融合的滑坡综合监测信息提取方法[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 27(6):77-81. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=26071326 成静, 张文军, 2018.西北地区近40年降水量和云量的变化及其相互关系分析[J].青海气象(3):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-QHQX201803001.htm 丁继新, 尚彦军, 杨志法, 等, 2004.降雨型滑坡预报新方法[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 23(21):3738-3743. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb200421030 董文文, 朱鸿鹄, 孙义杰, 等, 2016.边坡变形监测技术现状及新进展[J].工程地质学报, 24(6):1088-1095. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCDZ201606007.htm 杜国梁, 张永双, 高金川, 等, 2016.基于GIS的白龙江流域甘肃段滑坡易发性评价[J].地质力学学报, 22(1):1-11. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160101&journal_id=dzlxxb 樊俊青, 2015.面向滑坡监测的多源异构传感器信息融合方法研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1016061177.htm 冯振, 李滨, 赵超英, 等, 2016.三峡库区山区城镇重大地质灾害监测预警示范研究[J].地质力学学报, 22(3):685-694. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20160322&journal_id=dzlxxb 高杨, 李滨, 冯振, 等, 2017.全球气候变化与地质灾害响应分析[J].地质力学学报, 23(1):65-77. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20170102&journal_id=dzlxxb 郭科, 彭继兵, 许强, 2005.应用多传感器目标跟踪融合技术实现滑坡多点监测数据综合信息的提取[J].地球物理学进展, 20(3):808-813. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWJ200503036.htm 郭科, 彭继兵, 许强, 等, 2006.滑坡多点数据融合中的多传感器目标跟踪技术应用[J].岩土力学, 27(3):479-481. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/94551X/200603/21629942.html 姜海泉, 黎祖贤, 李细生, 等, 2006.论气象类滑坡灾害的预报原理和方法[J].水土保持研究, 13(5):20-22. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=23089748 廖明生, 张路, 史绪国, 等, 2017.滑坡变形雷达遥感监测方法与实践[M].北京:科学出版社. 刘超云, 尹小波, 张彬, 2015.基于Kalman滤波数据融合技术的滑坡变形分析与预测[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 26(4):30-35. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdzzhyfzxb201504006 刘星洪, 姚鑫, 周振凯, 等, 2018.滑坡灾害InSAR应急排查技术方法研究[J].地质力学学报, 24(2):229-237. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180209&journal_id=dzlxxb 莫运松, 董雪梅, 文日海, 2010.气象因素对滑坡形成的影响分析[J].西部探矿工程, 22(6):51-52, 55. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbtkgc201006019 倪秀静, 2005.小波理论在滑坡降噪和组合预测中的应用[D].成都: 成都理工大学. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y759169 彭欢, 黄帮芝, 杨永, 2012.滑坡监测技术方法研究[J].资源环境与工程, 26(1):45-50. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBDK201201010.htm 彭鹏, 单治钢, 董育烦, 等, 2011.多传感器估值融合理论在滑坡动态变形监测中的应用研究[J].工程地质学报, 19(6):928-934. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCDZ201106023.htm 齐信, 黄波林, 刘广宁, 等, 2017.基于GIS技术和频率比模型的三峡地区秭归向斜盆地滑坡敏感性评价[J].地质力学学报, 23(1):97-104. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20170105&journal_id=dzlxxb 亓星, 许强, 赵宽耀, 等, 2018.甘肃黑方台灌溉与地下水位响应规律分析[J].水利水电技术, 49(9):205-209. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SJWJ201809028.htm 邱丹丹, 2017.基于多源数据融合的滑坡风险分析研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1018714830.htm 孙波, 2012.多传感器融合估计算法的研究及在滑坡中的应用[D].武汉: 中国地质大学. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis_Y2188880.aspx 孙艳萍, 张苏平, 陈文凯, 等, 2018.汶川地震滑坡危险性评价:以武都区和文县为例[J].地震工程学报, 40(5):1084-1091. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=ZBDZ201805032 王静, 2013.基于QuantyView和多源数据的滑坡体三维地质建模技术研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1014164902.htm 王利, 张勤, 赵超英, 等, 2005. GPS一机多天线技术在公路边坡灾害监测中的应用研究[J].公路交通科技, 22(6):163-166. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91479X/2005S1/4000368954.html 王利, 张勤, 李寻昌, 等, 2011. GPS RTK技术用于滑坡动态实时变形监测的研究[J].工程地质学报, 19(2):193-198. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCDZ201102008.htm 王亚敏, 冯起, 李宗省, 2014. 1960-2005年西北地区低云量的时空变化及成因分析[J].地理科学, 34(5):635-640. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=663134564 吴伟, 王式功, 邓莲堂, 等, 2010.中国北方云量的四季分布与降水[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 46(3):32-40. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=34377940 许强, 彭大雷, 亓星, 等, 2016. 2015年4.29甘肃黑方台党川2#滑坡基本特征与成因机理研究[J].工程地质学报, 24(2):167-180. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98122X/201602/668435894.html 尹继鑫, 何永晴, 姚永顺, 等, 2019.高原滑坡变形与气象因素相关性研究[J].城市勘测(1):184-188. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CSKC201901052.htm 张伟琪, 2019.黄土滑坡高精度变形监测及预测方法研究[D].西安: 长安大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1019674872.htm 张向营, 张春山, 孟华君, 等, 2018.基于GIS和信息量模型的京张高铁滑坡易发性评价[J].地质力学学报, 24(1):96-105. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180111&journal_id=dzlxxb 张亚军, 2006.基于神经网络数据融合的水下目标检测识别研究[D].西安: 西北工业大学. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y930415 张育智, 2007.基于神经网络与数据融合的结构损伤识别理论研究[D].成都: 西南交通大学. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1237418 赵超英, 刘晓杰, 张勤, 等, 2019.甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡InSAR识别、监测与失稳模式研究[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 44(7):996-1007. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-WHCH201907005.htm 赵松琴, 朱思军, 2013.三峡库区典型滑坡预测预报研究[J].安全与环境学报, 13(6):259-264. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/83738X/201306/48277161.html 周飞, 2015.甘肃省黑方台黄土斜坡变形特征与滑坡机理研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10616-1015312387.htm 朱志铭, 周凯睿, 谭春洪, 等, 2013.强降雨作用下边(滑)坡稳定性分析及预警技术研究[J].地质力学学报, 19(4):423-430. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_csjsllyj201408874.aspx -





 下载:
下载: