Application of geomechanics in risk prevention and control for the geosafety of major projects on the Tibetan Plateau
-
摘要: 青藏高原是全球构造活动最强烈的地区之一,内外动力耦合作用下地质灾害和复杂工程地质问题频现,给国家重大工程规划建设地质安全带来重大威胁。文章结合作者团队20余年来在青藏高原开展的工程地质与地质灾害研究工作,总结了地质力学理论在重大工程地质安全风险防控中的应用和成效,具体包括:继承和发展了区域地壳稳定性评价理论,提出了区域地壳稳定性−工程地质稳定性−场地稳定性调查评价方法,有效服务重大工程选线选址;提出了活动构造带工程地质研究框架,阐明了活动断裂的地质灾害效应,构建了高位滑坡地质力学模式,揭示了岩体结构与特殊岩性联合控滑机制;开展了基于实测地应力的深埋隧道岩爆机理研究,对比分析了不同构造环境下隧道岩爆特征的差异,提出了高地应力环境下隧道岩爆风险防控对策。在以上研究总结的基础上,提出了地质力学理论创新和工程应用的发展方向。相关研究有助于进一步推动地质力学发展,为国家重大工程规划建设和防灾减灾提供新的理论价值与技术支撑。Abstract:
Objective The Tibetan Plateau is one of the most tectonically active regions in the world. The coupled effects of endogenic and exogenic processes result in frequent geological hazards and complex engineering geological problems, posing a significant threat to the geological safety of major engineering projects. Method This paper summarizes the application of geomechanics theories in the prevention and control of geological safety risks for major engineering projects, based on over two decades of research conducted on the Tibetan Plateau by our team. Results Specific contributions include: (1) The theory of regional crustal stability evaluation was advanced, and a methodology was proposed for investigating and assessing regional crustal stability, engineering geological stability, and site stability; this has been effectively applied to the route selection and site planning of major projects; (2) An engineering geological research framework was established for active tectonic zones, the geohazard effects of active faults were clarified, geomechanical models for high-position landslides were developed, and the combined control mechanism of rock mass structure and special lithology on landslide formation was revealed; (3) Research on rockburst mechanisms in deeply buried tunnels was conducted based on in-situ stress measurements, the characteristics of rockbursts under different tectonic settings were compared and analyzed, and strategies for rockburst prevention and control in high-stress environments were proposed. Building upon the aforementioned research findings, future directions for the innovation of geomechanical theories and their engineering applications are proposed. Conclusion The research on the application of engineering geology can further promote the advance of geomechanics and provide new theoretical and technical support for the planning and construction of major national projects, as well as disaster prevention and mitigation. -
Key words:
- geomechanics /
- engineering geology /
- geohazards /
- active faults /
- in-situ stress
-
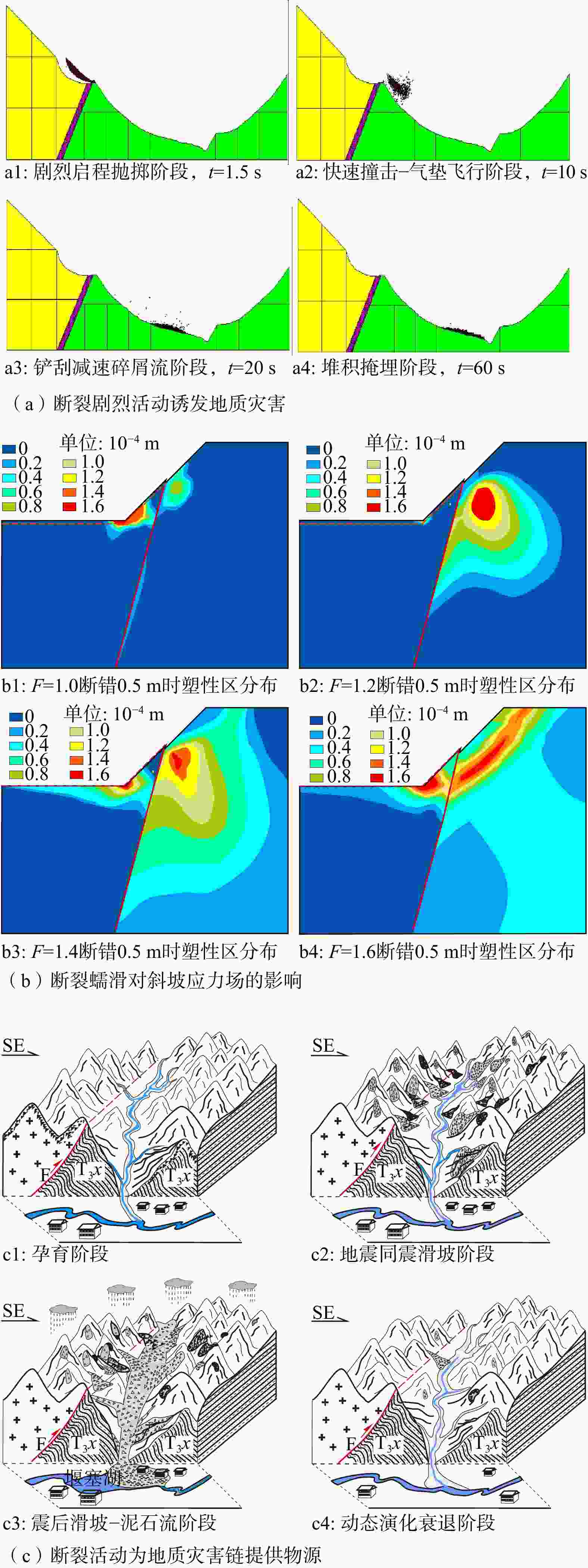
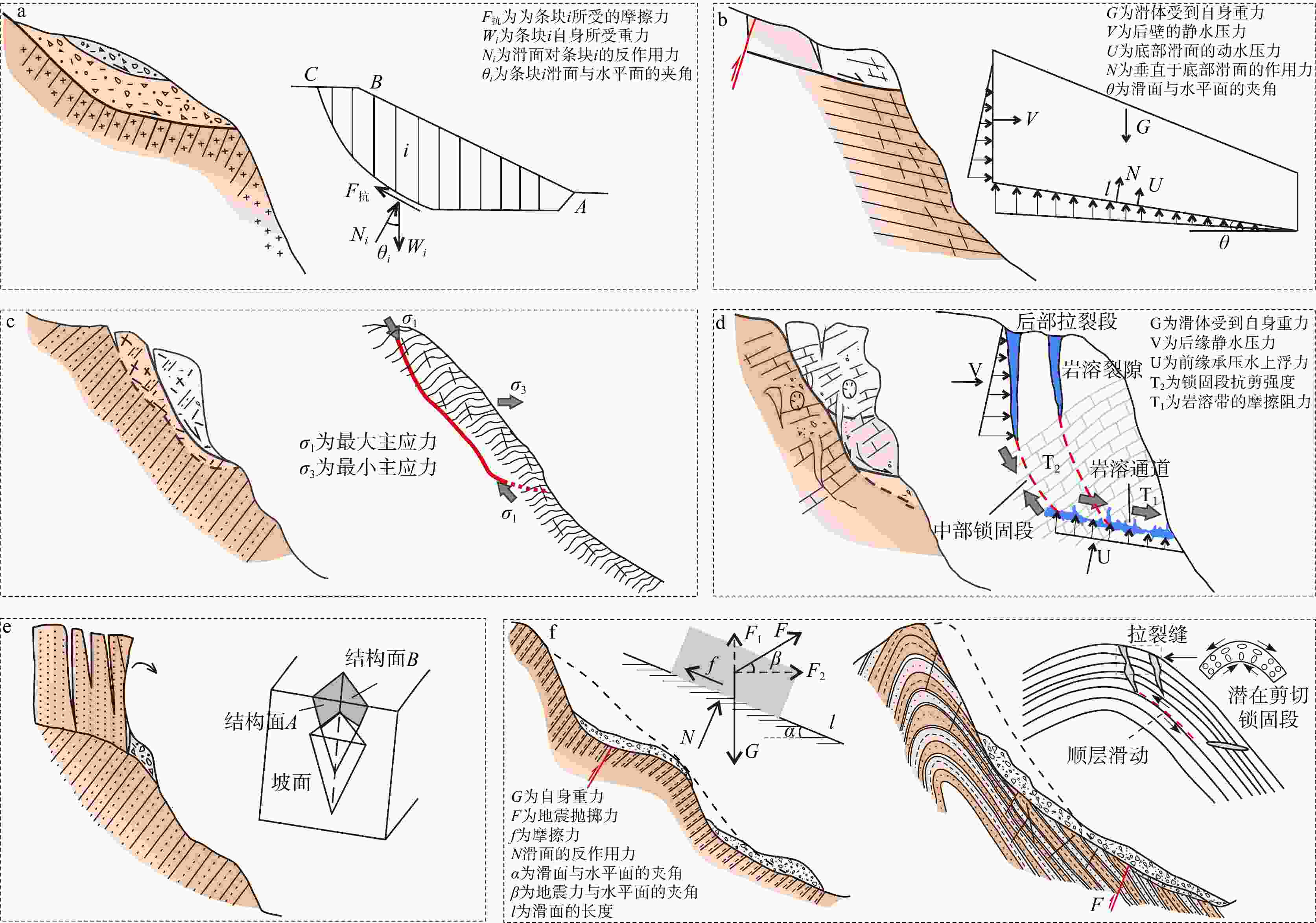
图 6 高位滑坡启动的地质力学模式示意图(据张永双等,2021修改)
a—堆积体滑移型; b—顺层滑移拉裂型;c—卸荷剪断型;d—岩溶贯通拉裂型;e—崩滑溃散型;f—构造控制型
Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the geomechanical model for high-position landslide initiation (after Zhang et al., 2021)
(a) Accumulation body slide type; (b)Bedding-plane slip and tension crack type; (c) Unloading and shearing type; (d) Karst penetration and tension crack type; (e) Collapse-slide and disintegration type; (f) Structurally controlled type.
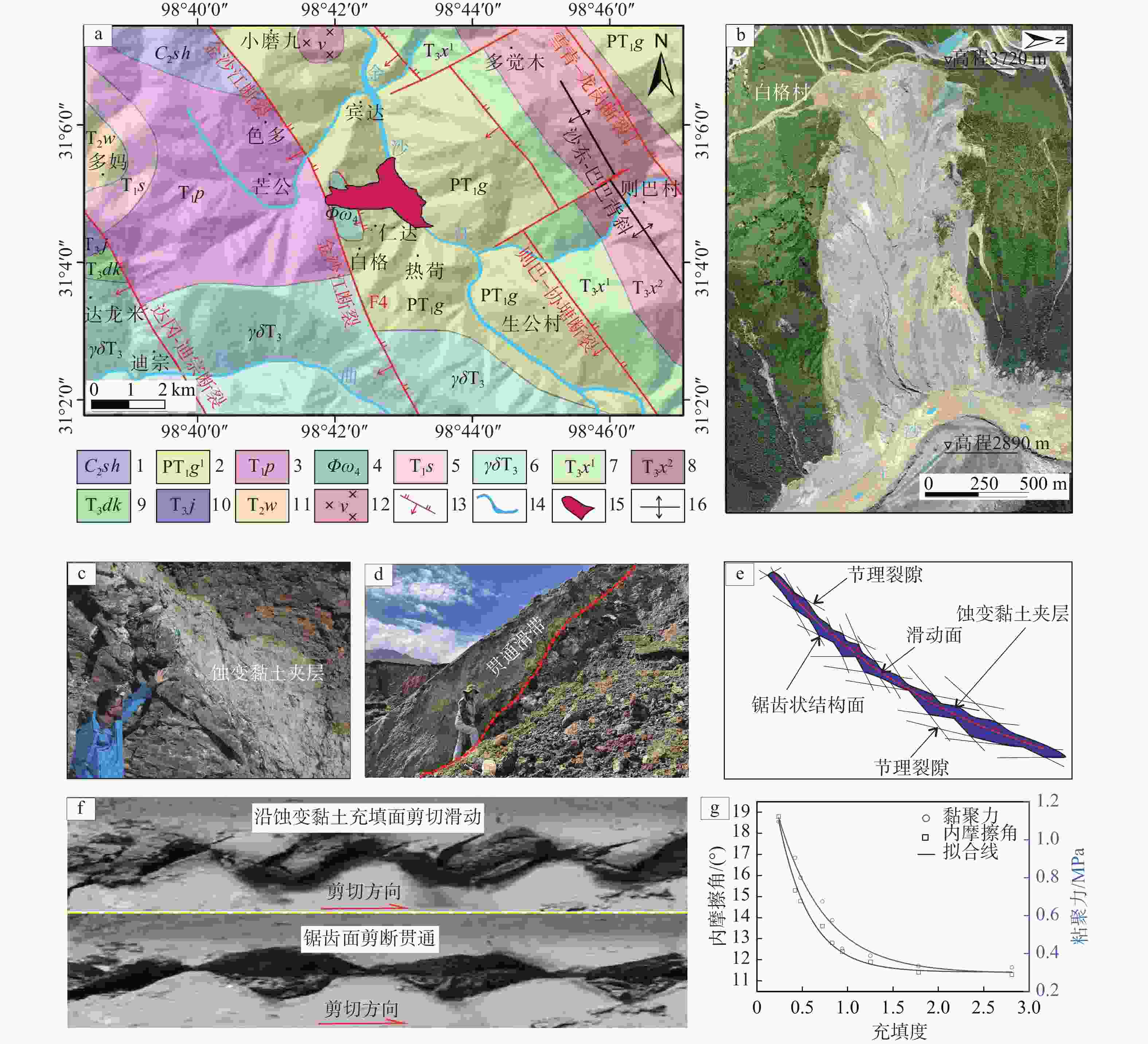
图 7 地质构造与蚀变黏土联合控制滑坡演化
a—白格滑坡所在区域地质构造位置(1—上石炭统生帕群;2—二叠系—三叠系岗托岩组;3—下三叠统普水桥组;4—华力西期金沙江超镁铁质岩带、蛇纹岩;5—下三叠统色容寺组;6—三叠系花岗闪长岩;7—上三叠统下逆松多组下段;8—上三叠统下逆松多组上段;9—上三叠统洞卡组;10—上三叠统甲丕拉组;11—三叠系中统瓦拉寺组;12—三叠系辉长岩岩块;13—逆断裂;14—水系;15—白格滑坡;16—背斜); b—白格滑坡影像;c—充填蚀变黏土结构面野外特征;d—蚀变黏土结构面贯通形成滑带;e—结构面贯通示意图;f—含蚀变黏土夹层结构面循环剪切试验剪切破坏过程;g—蚀变黏土充填结构面抗剪强度参数与充填度关系曲线
Figure 7. Geological structure and altered clay jointly control of landslide evolution
(a) Geological structure of the Baige landslide (1–Upper Carboniferous Shengpa Group; 2–Permian–Triassic Gangtuo Group; 3–Lower Triassic Pushuiqiao Group; 4–Jinsha River ultramafic belt and serpentine; 5–Lower Triassic Serongsi Group; 6–Triassic granodiorite; 7–Lower Songduo Group, Upper Triassic; 8–Upper Songduo Group, Upper Triassic; 9–Upper Triassic Dongka Group; 10–Upper Triassic Jiapira Group; 11–Middle Triassic Walasi Group; 12–Triassic gabbro block; 13–Faults; 14–Water system; 15–Baige Landslide; 16–Anticline); (b) Image of the Baige landslide; (c) Field characteristics of altered clay-filled structural planes; (d) Slip zone formation by interconnecting altered clay structural planes; (e) Schematic diagram of structural plane interconnection; (f) Shear failure process in cyclic shear tests on structural planes containing altered clay interlayers; (g) Relationship between shear strength parameters and degree to which structural planes are filled with altered clay
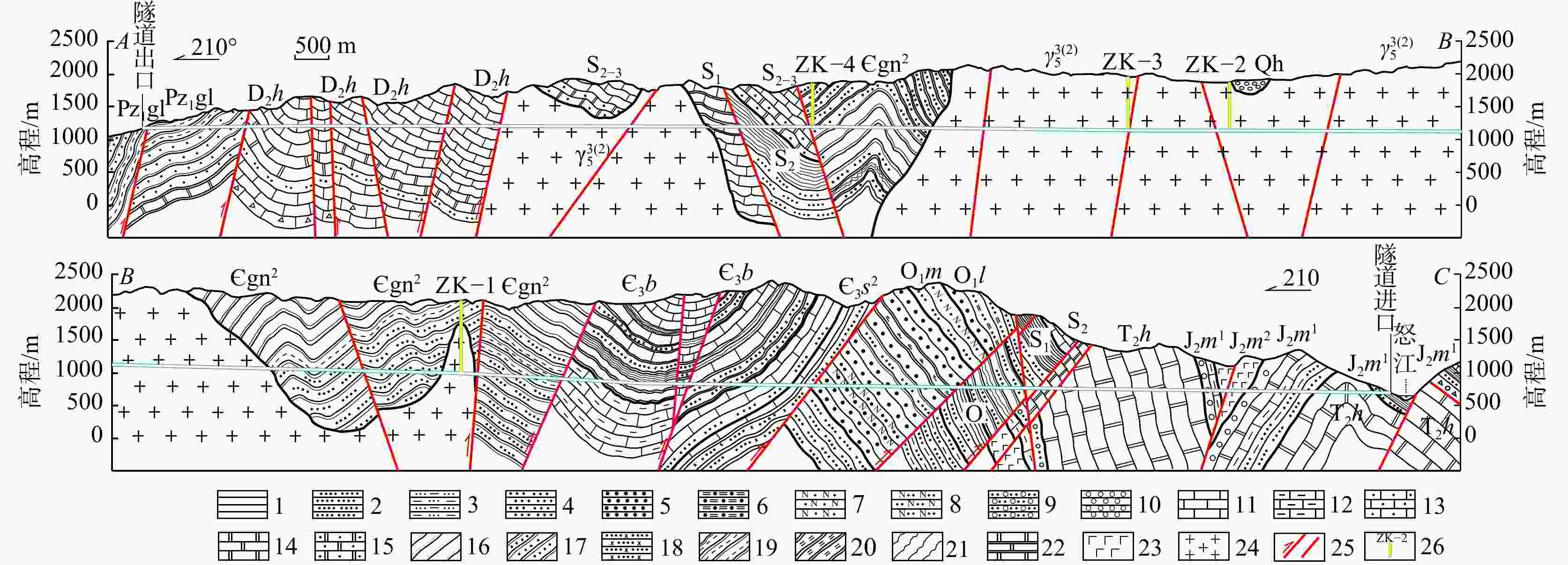
图 8 高黎贡隧道区工程地质剖面图(AB段和BC段)
Qh—全新世冲洪积物;J2m1—中侏罗统勐戛组下段砂泥岩、泥灰岩;J2m2—中侏罗统勐戛组上段玄武岩夹砂、泥岩;T2h—中二叠统河湾街组白云岩;D2h—中泥盆统回贤组灰岩;O1l—下奥陶统亮甲山组页岩、粉砂岩;O1m—下奥陶统马家沟组砂岩、粉砂岩; O—奥陶统细砂岩、粉砂岩、石英砂岩、板岩;S1—下志留统笔石页岩、粉砂岩;S2—中志留统条带状、网纹状灰岩、砂质泥灰岩;S2-3—中上志留统条带状、网纹状灰岩、砂质泥灰岩;${\rlap{--} {\mathrm{C}}}_3 $b—上寒武统保山组灰岩、砂岩、粉砂岩及页岩;${\rlap{--} {\mathrm{C}}}_3 $s2—上寒武统沙河厂组上段砂板岩、粉砂岩夹灰岩;${\rlap{--} {\mathrm{C}}} $gn2—寒武统公养河群绢云板岩夹石英岩、轻变质砂岩;Pz1gl—下古生界高黎贡山群黄灰色、褐灰色板岩、变质砂岩夹变粒岩;γ53(2)—燕山期黑云母花岗岩1—泥岩;2—粉砂岩;3—泥质粉砂岩;4—细砂岩;5—粗砂岩;6—杂砂岩;7—长石砂岩;8—长石石英砂岩;9—砂砾岩;10—砾岩;11—灰岩;12—泥质灰岩;13—砂质灰岩;14—白云岩;15—砂质白云岩;16—泥质板岩;17—砂质板岩;18—变质砂岩;19—千枚状板岩;20—石英片岩;21—片岩;22—大理岩;23—玄武岩;24—花岗岩(斑岩);25—断裂;26—钻孔及编号
Figure 8. Engineering geological section of the Gaoligong tunnel (Sections AB and BC)
1−Mudstone; 2−Siltstone; 3−Silty mudstone; 4−Fine sandstone; 5−Coarse sandstone; 6−Greywacke; 7−Arkose; 8−Feldspathic quartz sandstone; 9−Sandy conglomerate; 10−Conglomerate; 11−Limestone; 12−Argillaceous limestone; 13−Sandy limestone; 14−Dolomite; 15−Sandy dolomite; 16−Argillaceous slate; 17−Sandy slate; 18−Metasandstone; 19−Phyllitic slate; 20−Quartz schist; 21−Schist; 22−Marble; 23−Basalt; 24−Granite (porphyry); 25−Fault; 26−Borehole and number Qh−Holocene alluvial-pluvial deposits; J2m1−Middle Jurassic Mengga Formation lower member sandstone and mudstone, marl; J2m2−Middle Jurassic Mengga Formation upper member basalt interbedded with sandstone and mudstone; T2h−Middle Triassic Hewanjie Formation dolomite; D2h−Middle Devonian Huixian Formation limestone; O1l−Lower Ordovician Liangjiashan Formation shale, siltstone; O1m−Lower Ordovician Majiagou Formation sandstone, siltstone; O−Ordovician fine sandstone, siltstone, quartz sandstone, slate; S1−Lower Silurian graptolite shale, siltstone; S2−Middle Silurian banded and reticulated limestone, sandy marl; S2-3−Middle-Upper Silurian banded and reticulated limestone, sandy marl; ${\rlap{--} {\mathrm{C}}}_3 $b−Upper Cambrian Baoshan Formation limestone, sandstone, siltstone, and shale; ${\rlap{--} {\mathrm{C}}}_3 $s2−Upper Cambrian Shahechang Formation upper member slate, siltstone interbedded with limestone; ${\rlap{--} {\mathrm{C}}} $gn2−Cambrian Gongyanghe Group sericite slate interbedded with quartzite and lightly metamorphosed sandstone; Pz1gl−Lower Paleozoic Gaoligongshan Group yellow-gray and brown-gray slate, metamorphosed sandstone interbedded with granulite; γ53(2) −Yanshanian biotite granite.
表 1 花岗斑岩试件岩爆模拟试验过程和岩爆特征一览表
Table 1. Overview of rockburst simulation test procedures and rockburst characteristics of granite porphyry specimens
试件
编号破坏应力/MPa 岩爆过程描述 加载方式 试件初始
受力状态σV σh1 σh2 Y1 88.5 40.7 7.7 卸荷后41 s 时触发岩爆,历时 0.551 s;顶部先出现碎屑剥离
并伴脆性声响,继而碎屑/颗粒弹射;属局部滞后型岩爆卸载后保持 
Y2 100.8 19.8 8.8 卸载后再垂向加载,5.2 min 后发生岩爆,历时0.69 s;下部首先弹射破坏,
大量碎屑/块体飞出,颗粒在空中有旋转;为局部滞后型岩爆卸载后增加垂直方向
荷载
105.7 19.6 0.0 Y3 30.1 119.8 10.4 卸载后47.7 min 发生岩爆;右下部率先弹射,随后中部形成多条
破裂面,试件被分割成块体并整体塌落;为整体滞后型岩爆卸载后保持 
Y4 10.0 90.0 40.0 从卸载到破坏约 11 min,历时 0.699 s;前兆为上部少量碎屑下坠,随后
偏右中部出现沿前表面平行飞出的碎屑(单向弹射);为局部滞后型岩爆卸载后增加水平最大主应力 
117.0 10.0 0.0 Y5 23.4 80.7 8.8 卸载后再水平向加载,9 min 触发岩爆并全面爆裂;
前兆为上部小颗粒掉落/飞出,约 1 s 后转入整体破坏,
伴密集弹裂声与细碎屑喷出;全过程 1.36 s;为整体滞后型卸载后增加水平荷载 
-
[1] CHEN Q X, 1986. Some problems deserving of special attention in the analysis of rock deformation and tectonic stress field[J]. Bulletin of the Institute of Geomechanics Cags(8): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] DU D J, 1994. Establishment and development of regional stability engineering geology in Chinese[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2(3): 21-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] FAN X M, SCARINGI G, KORUP O, et al., 2019. Earthquake-induced chains of geologic hazards: patterns, mechanisms, and impacts[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 57(2): 421-503. doi: 10.1029/2018RG000626 [4] FENG X T, XIAO Y X, FENG G L, et al., 2019. Study on the development process of rockbursts[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 38(4): 649-673. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] GONG F Q, DAI J H, WANG M Y, et al., 2022. "Strength & stress" coupling criterion and its grading standard for high geostress[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(6): 1893-1913. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] GU D Z, 1979. Fundamentals of rock mass engineering geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [7] GUO C B, 2011. Research on the major engineering geological problems of the Dali-Ruili Railway through Gaoligong Mt. [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] HE M C, REN S L, TAO Z G, 2022. Disaster prevention and control methods for deep buried tunnels[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(6): 1777-1797. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] HEAP M J, BAUMANN T S, ROSAS-CARBAJAL M, et al., 2021. Alteration-induced volcano instability at La Soufrière de Guadeloupe (Eastern Caribbean)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(8): e2021JB022514. doi: 10.1029/2021JB022514 [10] HU H T, YIN Y P, 1996. Theory and evaluation methods of regional crust stability "Safety Island"[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 3(1-2): 57-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] HUANG R Q, 2008. Geodynamical process and stability control of high rock slope development[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 27(8): 1525-1544. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] LI B, YIN Y P, TAN C X, et al., 2022. Geo-safety challenges against the site selection of engineering projects in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(6): 907-918. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] LI S G, 1945. Fundamentals and methods of geomechanics[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press. (in Chinese) [14] LIU G C, 1979. Regional stability and earthquakes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 6(2): 1-7. (in Chinese) [15] MAEDA H, SASAKI T, FURUTA K, et al., 2012. Relationship between landslides, geologic structures, and hydrothermal alteration zones in the Ohekisawa-Shikerebembetsugawa Landslide Area, Hokkaido, Japan[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Engineering, 2(6): 317-327. [16] PENG J B, MAO Y L, FAN W, 2001. Study on regional stability dynamics[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [17] PENG J B, CUI P, ZHUANG J Q, 2020. Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan—Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 39(12): 2377-2389. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] REN S S, ZHANG Y S, LI J Q, et al., 2023. A new type of sliding zone soil and its severe effect on the formation of giant landslides in the Jinsha River tectonic suture zone, China[J]. Natural Hazards, 117(2): 1847-1868. doi: 10.1007/s11069-023-05931-0 [19] SHUGAR D H, JACQUEMART M, SHEAN D, et al., 2021. A massive rock and ice avalanche caused the 2021 disaster at Chamoli, Indian Himalaya[J]. Science, 373(6552): eabh4455. [20] SUN G Z, 1988. Rock mass structure mechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [21] SUN G Z, SUN Y, 2004. Rock mass structure mechanics[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) [22] SUN Y, TAN C X, WANG R J, et al., 1996. An assessment and zonation of regional crustal stability in and around the dam region of the Three Gorges Project on the Yangtze River[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 17(3): 258-268. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] SUN Y K, 1997. Rockmass structural mechanism - a new advance in rock engineering - geological mechanicas[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 5(4): 292-294. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] TAN C X, SUN W F, SUN Y, et al., 2006. A consideration on in-situ crustal stress measuring and its underground engineering application[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(10): 1627-1632. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] WANG S J, 2002. Coupling of earth's endogenic and exogenic geological processes and origins on serious geological disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 10(2): 115-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] WU F Q, WANG S J, PAN B T, 2022. Statistical mechanics of rock masses(SMRM): inheriting and developing of engineering geomechanics of rock masses[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(1): 1-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] WU S R, WANG R J, 1996. Some development trends in the study of geological hazards and regional crustal stability[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2(3): 78-80. (in Chinese) [28] WU Z H, YE P S, WU Z H, et al., 2003. Hazard effects of active faulting along the Golmud-Lhasa railway across the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geoscience, 17(1): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] WU Z H, ZHAO G M, LONG C X, et al., 2014. The seismic hazard assessment around south-east area of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau: a preliminary results from active tectonics system analysis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(8): 1401-1416. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] XU Q, LI W L, 2010. Distribution of large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 18(6): 818-826. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] YI M C, HU H T, YIN Y P, et al., 2006. Developing Li Siguang's "safety island" thought and making serious evaluation and research on regional crustal stability in areas of engineering works[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 12(2): 105-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] YIN Y P, 2008. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 16(4): 433-444. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] YIN Y P, LI B, GAO Y, et al., 2023. Geostructures, dynamics and risk mitigation of high-altitude and long-runout rockslides[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 15(1): 66-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.11.001 [34] ZHANG Y S, QU Y X, LIU J R, et al., 2007. Engineering geological research on altered rocks in the area of NW Yunnan along Yunnan-Tibet railway line[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 29(4): 531-536. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] ZHANG Y S, LEI Z W, SHI J S, et al., 2008. General characteristics of 5.12 earthquake-induced geohazards in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 14(2): 109-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] ZHANG Y S, XIONG T Y, DU Y B, et al., 2009. Geostress characteristic and simulation experiment of rockburst of a deep-buried tunnel in Gaoligong mountain[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 28(11): 2286-2294. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] ZHANG Y S, SHI J S, SUN P, et al., 2013. Surface ruptures induced by the Wenchuan earthquake: their influence widths and safety distances for construction sites[J]. Engineering Geology, 166: 245-254. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.09.010 [38] ZHANG Y S, CHENG Y L, YIN Y P, et al., 2014. High-position debris flow: a long-term active geohazard after the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Engineering Geology, 180: 45-54. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.05.014 [39] ZHANG Y S, GUO C B, YAO X, et al. , 2014. Seismic engineering geology of the east marginal region of Tibetan Plateau[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) [40] ZHANG Y S, GUO C B, YAO X, et al., 2016. Research on the geohazard effect of active fault on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 37(3): 277-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] ZHANG Y S, REN S S, GUO C B, et al., 2019. Research on engineering geology related with active fault zone[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(4): 763-775. (in Chinese with English abstract) [42] ZHANG Y S, DU G L, GUO C B, et al., 2021. Research on typical geomechanical model of high-position landslides on the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(3): 605-617. (in Chinese with English abstract) [43] ZHANG Y S, LI J Q, REN S S, et al., 2022a. Development characteristics of clayey altered rocks in the Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor and their promotion to large-scale landslides[J]. Earth Science, 47(6): 1945-1956. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] ZHANG Y S, WU R A, GUO C B, et al., 2022b. Geological safety evaluation of railway engineering construction in plateau mountainous region: ideas and methods[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(5): 1736-1751. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] 陈庆宣, 1986. 岩石形变与构造应力场分析中值得引起注意的几个问题[J]. 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所所刊(8): 1-8. [46] 杜东菊, 1994. 中国区域稳定工程地质学产生与发展[J]. 工程地质学报, 2(3): 21-26. [47] 冯夏庭, 肖亚勋, 丰光亮, 等, 2019. 岩爆孕育过程研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 38(4): 649-673. [48] 宫凤强, 代金豪, 王明洋, 等, 2022. 高地应力“强度&应力”耦合判据及其分级标准[J]. 工程地质学报, 30(6): 1893-1913. [49] 谷德振, 1979. 岩体工程地质力学基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [50] 郭长宝, 2011. 大瑞铁路高黎贡山越岭段重大工程地质问题研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院. [51] 何满潮, 任树林, 陶志刚, 2022. 深埋隧道灾变防控方法[J]. 工程地质学报, 30(6): 1777-1797. [52] 胡海涛, 殷跃平, 1996. 区域地壳稳定性评价“安全岛”理论及方法[J]. 地学前缘, 3(1-2): 57-68. [53] 黄润秋, 2008. 岩石高边坡发育的动力过程及其稳定性控制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 27(8): 1525-1544. [54] 李滨, 殷跃平, 谭成轩, 等, 2022. 喜马拉雅东构造结工程选址面临的地质安全挑战[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(6): 907-918. [55] 李四光, 1945. 地质力学之基础与方法[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社. [56] 刘国昌, 1979. 区域稳定性与地震[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 6(2): 1-7. [57] 彭建兵, 毛彦龙, 范文, 2001. 区域稳定动力学研究: 黄河黑山峡大型水电工程例析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [58] 彭建兵, 崔鹏, 庄建琦, 2020. 川藏铁路对工程地质提出的挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 39(12): 2377-2389. [59] 孙广忠, 1988. 岩体结构力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [60] 孙广忠, 孙毅, 2004. 地质工程学原理[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [61] 孙叶, 谭成轩, 王瑞江, 等, 1996. 长江三峡工程坝区及外围地壳稳定性评价与分区研究[J]. 地球学报, 17(3): 258-268. [62] 孙玉科, 1997. 岩体结构力学: 岩体工程地质力学的新发展[J]. 工程地质学报, 5(4): 292-294. [63] 谭成轩, 孙炜锋, 孙叶, 等, 2006. 地应力测量及其地下工程应用的思考[J]. 地质学报, 80(10): 1627-1632. [64] 王思敬, 2002. 地球内外动力耦合作用与重大地质灾害的成因初探[J]. 工程地质学报, 10(2): 115-117. [65] 伍法权, 王思敬, 潘别桐, 2022. 统计岩体力学(SMRM): 岩体工程地质力学的传承与发展[J]. 工程地质学报, 30(1): 1-20. [66] 吴树仁, 王瑞江, 1996. 地质灾害与区域地壳稳定性研究的某些发展趋势[J]. 地质力学学报, 2(3): 78-80. [67] 吴珍汉, 叶培盛, 吴中海, 等, 2003. 青藏铁路沿线断裂活动的灾害效应[J]. 现代地质, 17(1): 1-7. [68] 吴中海, 赵根模, 龙长兴, 等, 2014. 青藏高原东南缘现今大震活动特征及其趋势: 活动构造体系角度的初步分析结果[J]. 地质学报, 88(8): 1401-1416. [69] 许强, 李为乐, 2010. 汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 18(6): 818-826. [70] 易明初, 胡海涛, 殷跃平, 等, 2006. 发扬李四光“安全岛”思想, 认真做好工程建设地区的区域地壳稳定性评价研究工作[J]. 地质力学学报, 12(2): 105-118. [71] 殷跃平, 2008. 汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 16(4): 433-444. [72] 张永双, 曲永新, 刘景儒, 等, 2007. 滇藏铁路滇西北段蒙脱石化蚀变岩的工程地质研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 29(4): 531-536. [73] 张永双, 雷伟志, 石菊松, 等, 2008. 四川5.12地震次生地质灾害的基本特征初析[J]. 地质力学学报, 14(2): 109-116. [74] 张永双, 熊探宇, 杜宇本, 等, 2009. 高黎贡山深埋隧道地应力特征及岩爆模拟试验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 28(11): 2286-2294. [75] 张永双, 郭长宝, 姚鑫, 等, 2014. 青藏高原东缘地震工程地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [76] 张永双, 郭长宝, 姚鑫, 等, 2016. 青藏高原东缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究[J]. 地球学报, 37(3): 277-286. [77] 张永双, 任三绍, 郭长宝, 等, 2019. 活动断裂带工程地质研究[J]. 地质学报, 93(4): 763-775. [78] 张永双, 杜国梁, 郭长宝, 等, 2021. 川藏交通廊道典型高位滑坡地质力学模式[J]. 地质学报, 95(3): 605-617. [79] 张永双, 李金秋, 任三绍, 等, 2022a. 川藏交通廊道黏土化蚀变岩发育特征及其对大型滑坡的促滑作用[J]. 地球科学, 47(6): 1945-1956. [80] 张永双, 吴瑞安, 郭长宝, 等, 2022b. 高原山区铁路工程建设地质安全评价: 思路与方法[J]. 地质学报, 96(5): 1736-1751. -




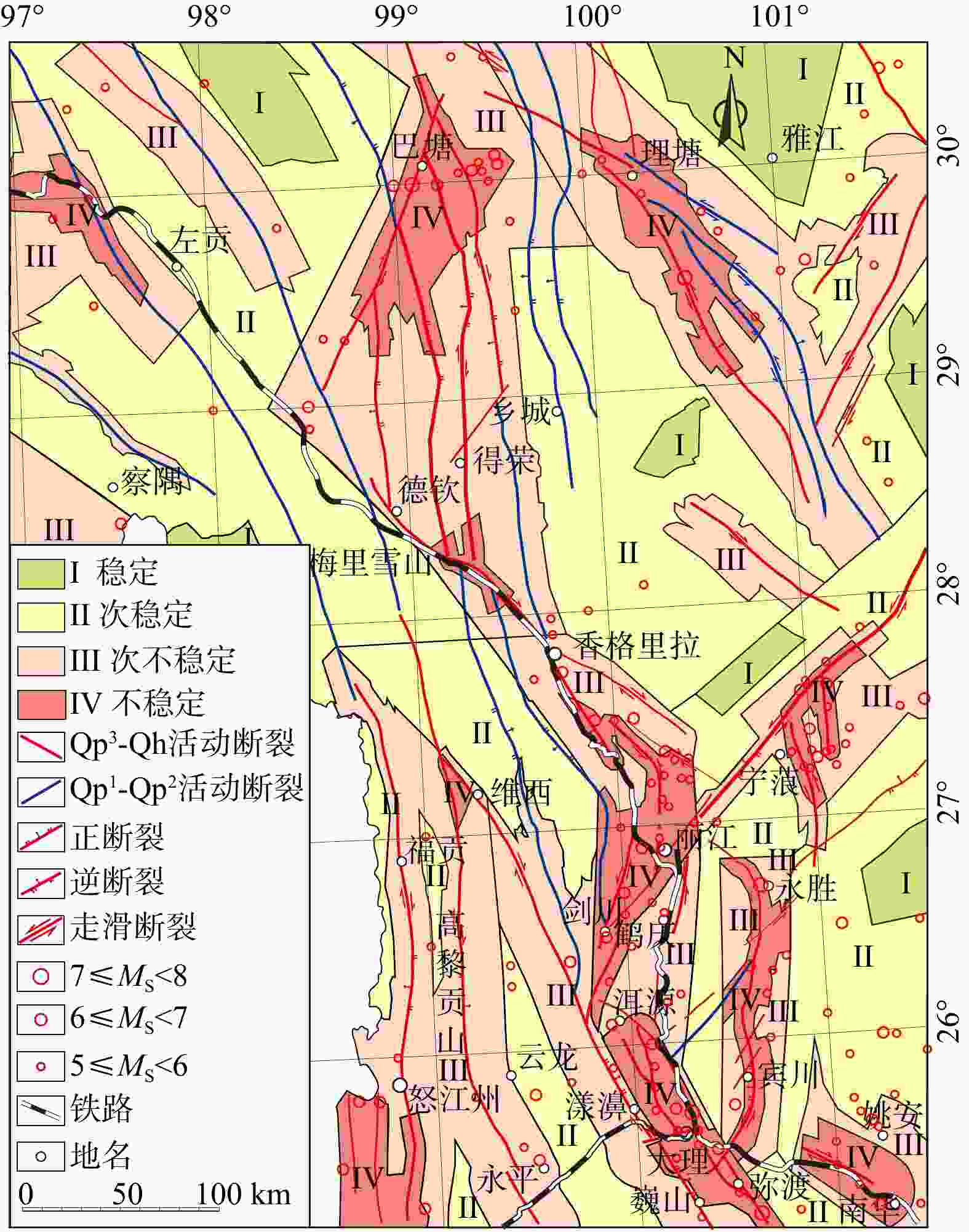
 下载:
下载: