Characteristics and geological significance of the palynological assemblages of the Qingshuiying Formation in the Beilianchi section, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau
-
摘要:
青藏高原隆升是新生代最重要的地质事件之一,对邻区乃至全球的气候变化都产生了深远的影响,已有学者研究认为该期隆升与气候冷暖变化之间具有较好的耦合关系。北联池剖面在区域构造位置上隶属于青藏高原东北缘弧形构造带后缘六盘山以西,古近系清水营组主要为一套紫红色泥岩夹薄层石膏层为主的浅湖相沉积,蕴含了丰富的古环境和古气候信息。文章系统研究了剖面的孢粉组合特征,共鉴定出孢粉类型60属65种及若干未定种,其孢粉组合特征中被子植物花粉占绝对优势,裸子植物花粉和蕨类植物孢子含量很少。结合现有区域孢粉的研究成果,综合分析认为清水营组沉积的地质时代属于中晚渐新世—中新世早期。孢粉植物群以桦木科、胡桃科和榆科等落叶阔叶植物为主,组合中还出现了数量不多但种类繁多的热带—亚热带植物的花粉,而典型干旱的灌木和草本植物分子含量少,总体上反映了暖温带较温和湿润的古环境古气候背景。孢粉组合中几乎不见耐寒山地针叶植物花粉的出现,说明该时期区域气候环境尚未发生由暖转冷的重大变化,青藏高原向东北方向的隆升扩展尚未影响到六盘山地区。研究成果为约束青藏高原东北缘清水营组的沉积时代以及青藏高原隆升过程对区域古生态古气候的影响提供新的证据。
Abstract:The uplift of the Tibetan Plateau is one of the most important geological events in the Cenozoic era, which has had a far-reaching impact on climate change in neighboring regions and even the world. Scholars have already considered that the uplift of this period has a good coupling with the warm and cold climate changes. The Beilianchi section is west of Liupan Mountain, the back edge of the arcuate tectonic belt on the northeast margin of the Tibetan Plateau. The Paleocene Qingshuiying Formation is mainly a set of shallow lacustrine deposits dominated by purple-red mudstone with thin gypsum layers containing rich paleoenvironmental and paleoclimatic information. The article systematically studied the palynological assemblage of the Beilianchi section and identified 60 genera and 65 species of sporopollen types as well as several undetermined species. The assemblage is characterized by dominant angiosperm pollen grains and rare gymnosperm pollen and fern spores. Based on the existing research results of regional sporopollen, the geologic age of the Qingshuiying Formation is believed to be the middle-late Oligocene–early Miocene. The sporopollen flora is dominated by deciduous broad-leaved plants such as Betulaceae, Juglandaceae, and Ulmaceae, and pollens from a few but diverse tropical-subtropical plants also occur in the assemblage. In contrast, the pollen content of typical arid shrubs and herbaceous plants is small, generally reflecting the warm-temperate zone's milder and wetter paleoenvironmental and paleoclimatic background. The absence of pollen from cold-tolerant mountain conifers in the palynological assemblage indicates that the regional climatic environment had not yet changed from warm to cold during this period and that the uplift and expansion of the Tibetan Plateau to the northeast had not yet affected the Liupanshan area. The results of this study provide new evidence to constrain the depositional age of the Qingshuiying Formation on the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and the impact of the uplift process of the Tibetan Plateau on the paleoecology and paleoclimate of the region.
-
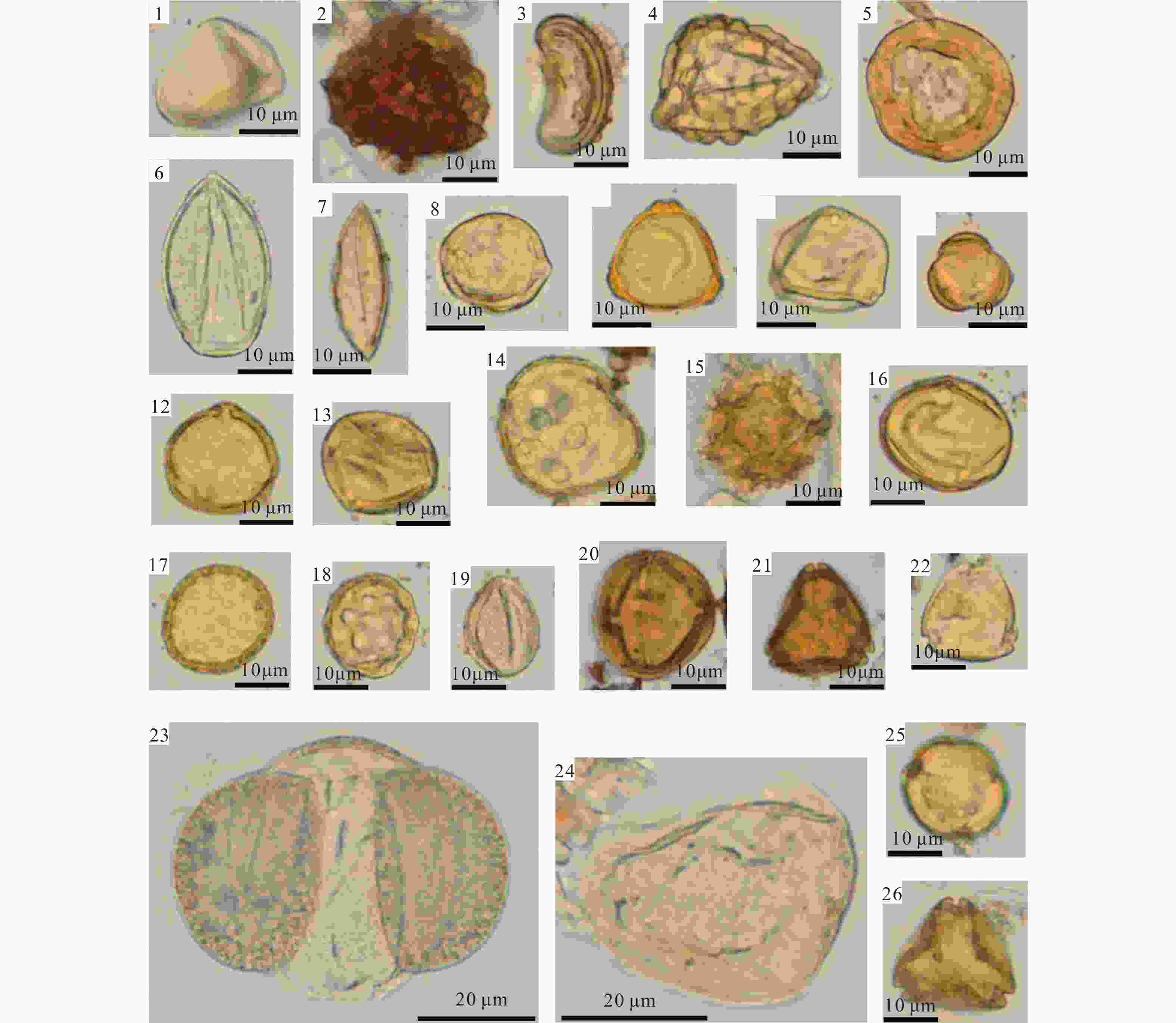
图 3 青藏高原东北缘北联池剖面清水营组蕨类、裸子和被子植物主要孢粉类型
1—三角孢;2—莱蕨孢;3—水龙骨单缝孢;4—凤尾蕨孢;5—环圈克拉梭粉;6—苏铁粉;7—小银杏粉;8—槭粉;9—拟桦粉;10—褶皱肋桦粉;11—普通蒿粉;12—圆形枥粉;13—四孔枥粉;14—短三沟粉;15—纤细拟菊苣粉;16—小孔栗粉;17—小孔藜粉;18—多坑藜粉;19—小十字花粉;20—西里拉粉;21—胡颓子粉;22—小黄杞粉;23—双束松粉;24—许里兹莎草粉;25—平凡山毛榉粉;26—华美高腾粉
Figure 3. Photomicrographs of selected spore-pollen from the Qingshuiying Formation in the Beilianchi section, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau
(1) Deltoidospora sp.; (2) Leptolepidites sp.; (3) Polypodiaceaesporites sp.; (4) Pterisisporites sp.; (5) Classopollis annulatus; (6) Cycadopites cycadoides; (7) Ginkgoretectina minor; (8) Aceripollenites sp.; (9) Betulaceoipollenites bituitus; (10) Betulaepollenites plicoides; (11) Artemisiaepollenites communis; (12) Carpinipites orbicularis; (13) Carpinipites tetraporus; (14) Brecolpites sp.; (15) Cichorieacidites gracilis; (16) Cupuliferoipollenites minitrimatus; (17) Chenopodipollis microporatus; (18) Chenopodipollis multiplex; (19) Cruciferaeipites minor; (20) Cyrillaceaepollenites megaexactus; (21) Elaeangnacites sp.; (22) Engelhardtioidites levis; (23) Pinuspollenites sp.; (24) Cyperaceaepolliss cholitzensis; (25) Faguspollenites mediocris; (26) Gothanipollis elegans
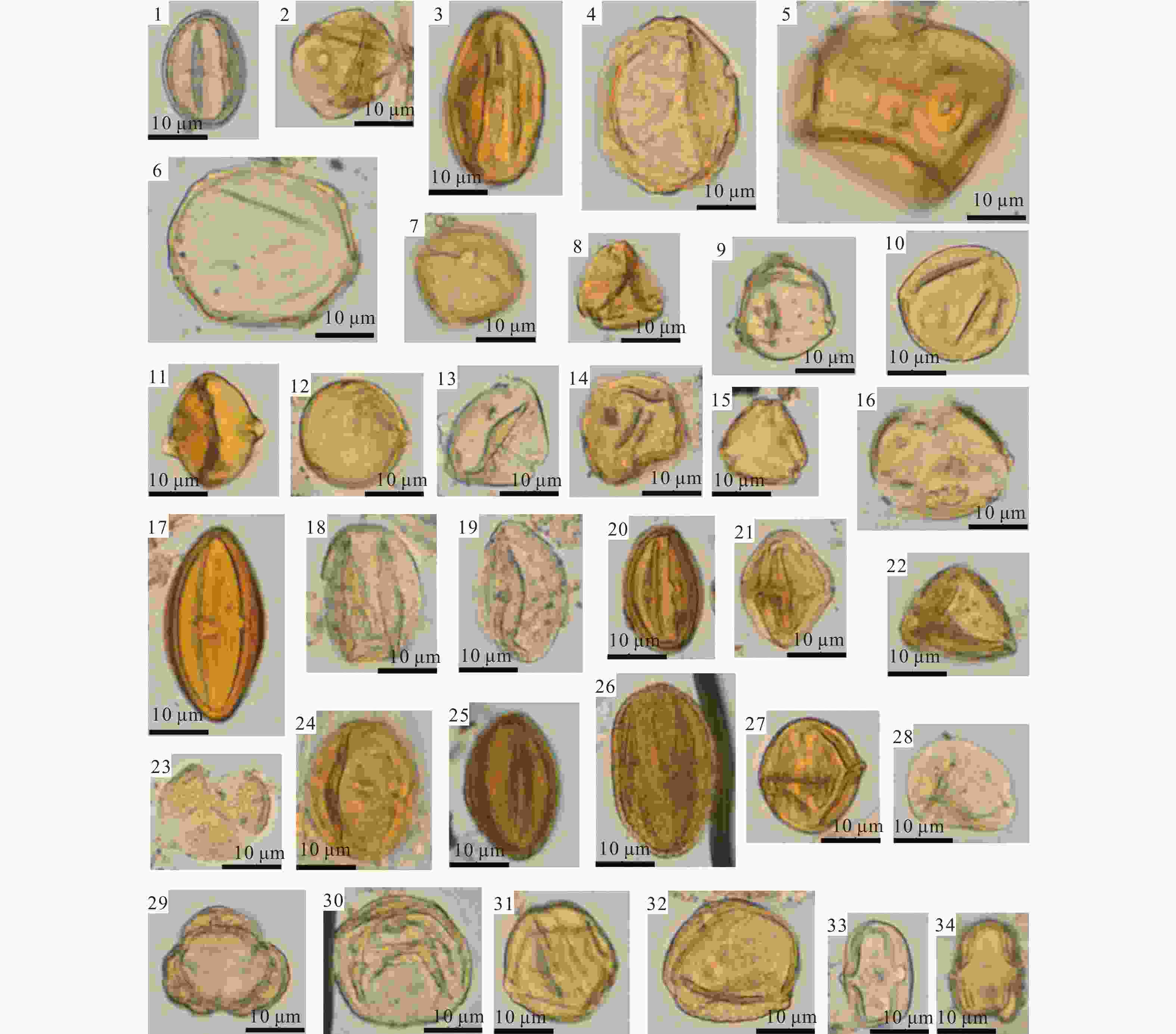
图 4 青藏高原东北缘北联池剖面清水营组被子植物主要孢粉类型
1—卵形梣粉;2—纤弱禾本粉;3—唇形三沟粉;4—圆形胡桃粉;5—大型禾本粉;6—真胡桃粉; 7—圆楝粉;8—三射莫米粉;9—拟榛莫米粉;10—薄极莫米粉;11—菱形南岭粉;12—桑粉;13—极面紫树粉;14—异常桤木粉;15—混合紫树粉;16—海龙井毛茛粉;17—坡氏粉;18—致密栎粉(比较种);19—小亨氏栎粉;20—青海粉;21—柴达木漆树粉;22—细波无患子粉;23—平常毛茛粉;24—芸香粉;25—锦致柳粉;26—假孔柳粉;27—扁圆芸香粉;28—椴粉;29—微刺管花菊粉;30—圆形榆粉;31—刺榆型脊榆粉;32—三肋脊榆粉;33、34—小拟伞形粉
Figure 4. Photomicrographs of selected spore-pollen from the Qingshuiying Formation in the Beilianchi section, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau
(1) Fraxinoipollenites ovatus; (2) Graminidites gracilis; (3) Labitricolpites stenosus; (4) Juglanspollenite srotundus; (5) Graminidites major; (6) Juglanspollenites verus; (7) Meliaceoidites orbicularis; (8) Momipites triradiatus; (9) Momipites coryloides; (10) Momipites tenuipolus; (11) Nanlingpollis rhombiformis; (12) Moraceoipollenites sp.; (13) Nyssapollenites pseudolaesus; (14) Paraalnipollenites sp.; (15) Nyssapollenites commixtus; (16) Ranunculacidites hailongjingensis; (17) Pokrovskajaoriginalis; (18) Quercoidites cf. densus; (19) Quercoidites microhenrici; (20) Qinghaipollis elegans; (21) Rhoipites qaidamensis; (22) Sapindaceidites microrugosus; (23) Ranunculacidites vulgaris; (24) Rutaceoipollis sp.; (25) Salixipollenites elegans; (26) Salixipollenites pseudoporites; (27) Rutaceoipollenites oblatus; (28) Tiliaepollenites sp.; (29) Tubulifloridites inispinulosus; (30) Ulmipollenites rotundatus; (31) Ulmoideipites planeraeformis; (32) Ulmoideipites tricostatus; (33 and 34) Umbelliferaepites minutus
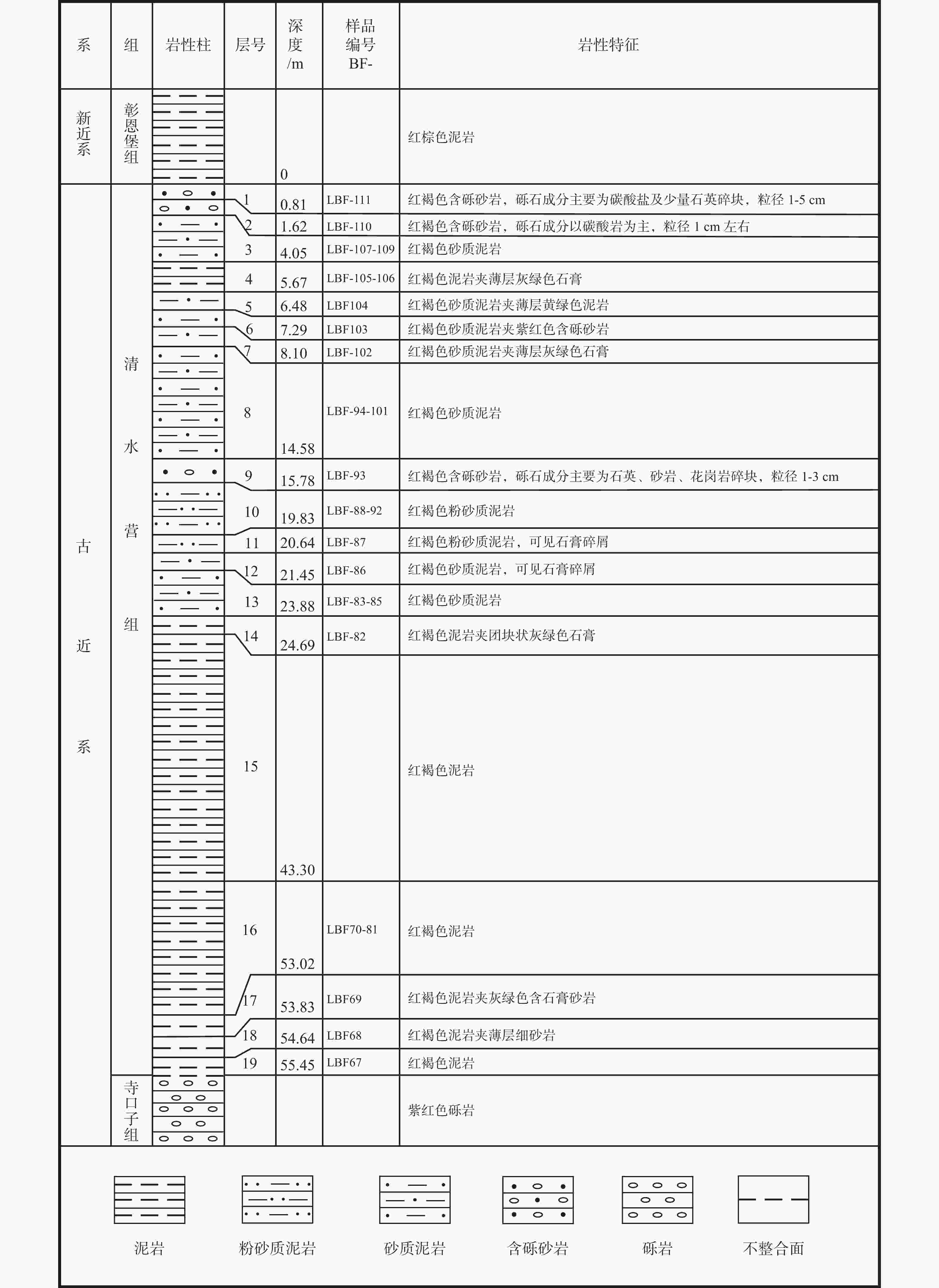
表 1 青藏高原东北缘北联池剖面清水营组孢粉统计表
Table 1. Statistics of sporopollens from the Qingshuiying Formation of the Beilianchi section, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau
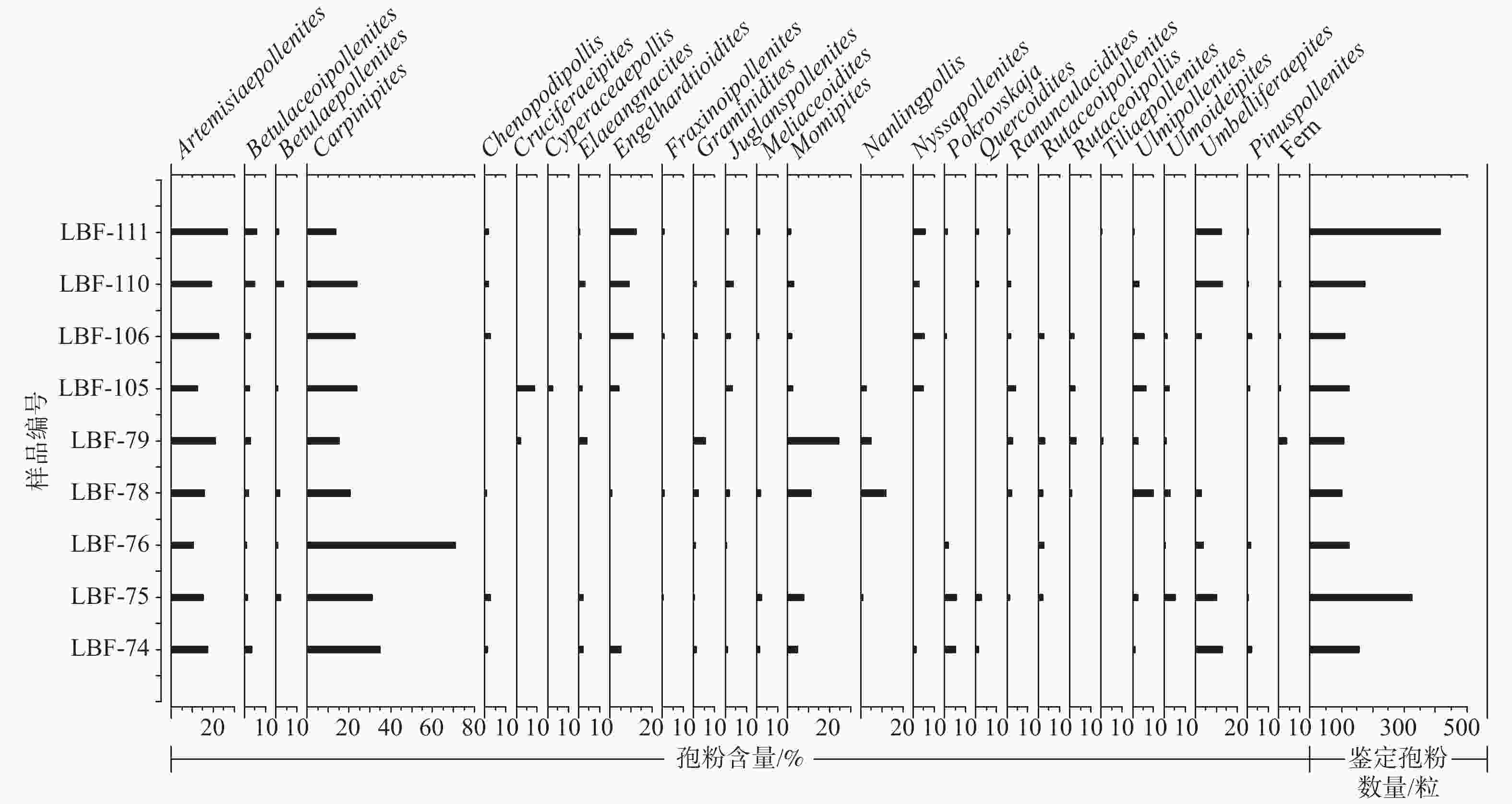
孢粉属种 中文名称 亲缘关系 不同样品的孢粉含量/% LBF-74 LBF-75 LBF-76 LBF-78 LBF-79 LBF-105 LBF-106 LBF-110 LBF-111 蕨类植物孢子 3.8 0.8 0.9 1.1 Deltoidospora sp. 三角孢 ? 0.9 0.8 Lygodioisporites sp. 瘤面海金沙孢 海金沙科 0.9 Polypodiaceaesporites sp. 水龙骨单缝孢 水龙骨科 1.9 0.9 1.1 裸子植物花粉 1.9 0.3 1.6 0.9 0.8 1.8 0.6 1.2 Classopollisannulatus 环圈克拉梭粉 希默杉亚科 0.0 0.9 Cycadopitescycadoides 苏铁粉 苏铁科 0.2 Ginkgoretectina minor 小银杏粉 银杏科 0.2 Keteleeriaepollenites sp. 油杉粉 油杉属 0.2 Pinuspollenites sp. 双束松粉 松属 1.9 0.3 1.6 0.8 1.8 0.6 0.5 被子植物花粉 96.8 99.7 98.4 97.1 95.3 98.4 97.3 96.6 98.3 Aceripollenites sp. 槭粉 槭树科 0.2 Alnipollenitesmetaplasmus 变形桤木粉 桦木科 0.3 Artemisiaepollenites communis 普通蒿粉 菊科蒿属 17.2 15.1 10.6 15.7 20.8 12.3 22.7 19.0 26.9 Betulaceoipollenitesbituitus 拟桦粉 桦木科 3.2 1.2 2.0 2.8 2.5 2.7 4.6 5.8 B. prominens 显环桦粉 桦木科 0.3 0.8 Betulaepollenitesclaripites 明亮肋桦粉 桦木科 1.5 0.8 0.6 B. microrugusus 微隆肋桦粉 桦木科 0.9 0.8 2.9 B. plicoides 褶皱肋桦粉 桦木科 2.0 1.2 Brevitricolpites sp. 短三沟粉 ? 0.3 Carpinipites orbicularis 圆形枥粉 桦木科 18.5 24.1 44.7 7.8 10.4 13.9 10.0 8.6 6.7 C. spackmanii 斯氏枥粉 桦木科 0.3 2.8 0.0 2.3 C. tetraporus 四孔枥粉 桦木科 16.6 6.5 26.0 12.7 1.9 9.8 12.7 12.6 7.2 Caryophyllidites sp. 石竹粉 石竹科 1.3 Chenopodipollismicroporatus 小孔藜粉 藜科 1.3 1.9 1.0 1.8 1.7 1.9 C. multiplex 多坑藜粉 藜科 0.9 0.9 Cruciferaeipites minor 小十字花粉 十字花科 0.3 1.9 C. pusillus 小栗粉 栗亚科 9.0 Cyperaceaepollisscholitzensis 许里兹莎草粉 莎草科 1.6 C. sp. 莎草粉 莎草科 0.3 0.8 Cyrillaceaepollenitesmegaexactus 西里拉粉 西里拉科或栗亚科 0.6 0.8 0.5 Echitricolporitesmicroechinatus 细刺刺三孔沟粉 菊科紫菀族 1.0 Elaeangnacites sp. 胡颓子粉 胡颓子科 1.9 1.9 3.8 1.6 0.9 2.9 0.5 Engelhardtioiditeslevis 小黄杞粉 胡桃科 5.1 1.0 4.1 10.9 9.2 12.5 Faguspollenites mediocris 平凡山毛榉粉 山毛榉科 0.6 Fraxinoipollenitesovatus 卵形梣粉 木犀科 0.3 1.0 0.9 F. sp. 梣粉 木犀科 0.7 Gothanipollis elegans 华美高腾粉 桑寄生科? 1.9 0.3 0.8 1.2 Graminiditesgracilis 纤弱禾本粉 禾本科 1.3 0.3 0.8 2.0 2.8 1.8 0.6 G. major 大型禾本粉 禾本科 2.8 0.6 Juglanspollenitesrotundus 圆形胡桃粉 胡桃科 0.8 3.3 0.9 1.1 J. tetraporus 四孔胡桃粉 胡桃科 1.7 0.7 J. verus 真胡桃粉 胡桃科 1.3 2.0 1.8 1.1 0.7 Lonicerapollis sp. 忍冬粉 忍冬科 0.2 Meliaceoidites orbicularis 圆楝粉 楝科 1.3 2.5 2.0 0.9 1.7 Momipitescoryloides 拟榛莫米粉 胡桃科 1.9 2.0 1.8 1.1 M. polanulatus 极环莫米粉 胡桃科 0.9 M. tenuipolus 薄极莫米粉 胡桃科 4.0 1.2 M. triradiatus 三射莫米粉 胡桃科 4.5 0.9 7.5 2.5 M. spp. 莫米粉 胡桃科 8.8 17.0 1.7 Moraceoipollenites sp. 桑粉 桑科 0.3 Nanlingpollisrhombiformis 菱形南岭粉 伞形科 0.9 11.8 4.7 2.5 Nyssapollenitesanalepticus 待壮紫树粉 珙桐科 0.5 N. commixtus 混合紫树粉 珙桐科 1.3 4.9 2.7 2.9 1.9 N. pseudolaesus 极面紫树粉 珙桐科 2.7 3.4 Paraalnipollenites sp. 异常桤木粉 桦木科 0.9 Pokrovskajaoriginalis 坡氏粉 蒺藜科白刺属 5.1 5.6 1.6 0.9 1.4 Qinghaipollis elegans 青海粉 伞形科 1.1 Quercoidites cf. densu 致密栎粉(比较种) 山毛榉科 0.6 1.1 1.4 Q. microhenrici 小亨氏栎粉 山毛榉科 1.3 1.9 Ranunculaciditeshailongjingensis 海龙井毛茛粉 毛茛科 1.6 1.8 0.5 R. vulgaris 平常毛茛粉 毛茛科 0.6 2.5 R. sp. 毛茛粉 毛茛科 0.6 2.0 2.8 1.7 0.7 Rhoipitesqaidamensis 柴达木漆树粉 漆树科 0.9 Rutaceoipollenitesoblatus 扁圆芸香粉 芸香科 1.9 2.4 2.0 2.8 2.7 Rutaceoipollis sp. 芸香粉 芸香科 1.0 2.8 2.5 1.8 Salixipollenites elegans 锦致柳粉 杨柳科柳属 0.8 S. pseudoporites 假孔柳粉 杨柳科柳属 1.8 Sapindaceiditesmicrorugosus 细波无患子粉 无患子科 0.9 1.6 Tiliaepollenites sp. 椴粉 椴科 0.9 0.5 Tricolpopollenitespsilatus 光三沟粉 ? 0.3 0.8 Tricolporopollenites spp. 三孔沟粉 ? 3.9 5.7 0.9 Tubulifloriditesminispinulosus 微刺管花菊粉 菊科管花菊族 2.4 2.6 T. minumus 微小管花菊粉 菊科管花菊族 1.1 1.7 Ulmipollenitesgranulatus 粒纹榆粉 榆科 1.3 0.9 6.9 0.9 U. rotundatus 圆形榆粉 榆科 0.9 2.9 2.8 4.1 4.5 2.9 0.7 U. triangulatus 三角榆粉 榆科 0.9 2.5 Ulmoideipiteskrempii 克氏脊榆粉 榆科 1.5 0.8 2.0 0.9 2.5 1.8 U. planeraeformis 刺榆型脊榆粉 榆科 1.9 U. tricostatus 三肋脊榆粉 榆科 1.9 1.0 Umbelliferaepitesminutus 小拟伞形粉 伞形科 11.5 9.0 4.1 1.0 13.2 12.5 U. sp. 拟伞形粉 伞形科 1.3 0.9 2.0 2.7 Vaclavipollis radiatus 辐射法克拉维粉 石竹科 1.9 4.9 0.5 不能鉴定的孢粉 1.3 2.9 1.7 0.5 鉴定孢粉数量/粒 157 324 123 102 106 122 110 174 416 -
[1] DUPONT-NIVET G, KRIJGSMAN W, LANGEREIS C G, et al. , 2007. Tibetan Plateau aridification linked to global cooling at the Eocene-Oligocene transition[J]. Nature, 445(7128): 635-638. doi: 10.1038/nature05516 [2] Exploration and Development Institute of Qinghai Petroleum Administration, Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1985. Tertiary palynology of Qaidam Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press. (in Chinese) [3] FANG X M, 2017. Phased uplift of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science & Technology Review, 35(6): 42-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] GESHIDEKOVA, GRICHUK, ZAKLINSKAYA, et al. , 1956. Pollen analysis[M]. WANG F X, ZHANG J T, MA Y Q, et al. , trans. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [5] JIANG F Y, JI L Y, ZHAO Q, 2021. Numerical simulation of the present seismic risk of the Haiyuan-Liupanshan fault zone[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 230-240. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] JIANG H C, DING Z L, 2008. A 20Ma pollen record of east-Asian summer monsoon evolution from Guyuan, Ningxia, China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 265(1-2): 30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.04.016 [7] JIANG H C, JI J L, GAO L, et al. , 2008. Cooling-driven climate change at 12-11Ma: multiproxy records from a long fluviolacustrine sequence at Guyuan, Ningxia, China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 265(1-2): 148-158. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.05.006 [8] KOU L L, LI Z H, DONG X P, et al. , 2021. The age sequence of the detrital zircons from the Guanyindian section in Longde, the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(6): 1051-1064. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] LI M T, LI L M, LIANG Z R, 2020. Geochemical characteristics and their significances of the Paleogene-Neogene sedimentary rocks in the Tongxin area, Ningxia, China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 39(2): 304-318. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] MIAO Y F, FANG X M, SONG Z C, et al. , 2008. Eocenesporopollen records and paleo-environmental changes in northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 38(2): 187-196. (in Chinese) [11] Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, 1990. Regional geology of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) [12] Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Geological Survey Institute, 2017. Regional geology of China: Ningxia[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) [13] Palynology Section, Morphological Department, Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1960. Plant pollen morphology in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [14] PAN J L, MA X D, MA Y X, et al. , 2022. Geochemistry characteristics of Paleogene-Neogene sedimentary rocks in the Lingwu area of Yinchuan Basin, Ningxia and its enlightenment for paleoenvironmental evolution[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 41(2-3): 296-305. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] SHEN X H, TIAN Q J, DING G Y, et al. , 2001. The Late Cenozxic stratigraphic sequence and its implication to Tectuic evolution Hejiakouzi area Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 17(2): 156-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] SHI W, DONG S W, HU J M, 2020. Neotectonics around the Ordos Block, North China: a review and new insights[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 200: 102969. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102969 [17] SONG Z C, ZHENG Y H, LI M Y, et al. , 1999. Fossil spores and pollen of China (vol. 1)[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [18] SUN S Y, 1982. Oligocene spore and pollen assemblages from the Tongxin district of Ningxia[C]//Collected Works of Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (4). Beijing: Geology Press: 130-141. (in Chinese) [19] SUN X Y, ZHAO Y N, HE Z S, 1984. The Oligocene-Miocene palynological assemblages from the Xining-Minghe Basin, Qinghai Province[J]. Geological Review, 30(3): 207-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] TAO M H, WANG K F, ZHENG G G, et al. , 2001. Early Tertiary sporopollen assemblages from Jizhong depression and their stratigraphic implication[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 18(3): 274-292. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] WANG B Y, YAN Z Q, LU Y J, et al. , 1994. Discovery of two Mid-Tertiary mammalian faunas from Haiyuan, Ningxia, China[J]. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 32(4): 285-296. (in Chinese) [22] WANG W T, ZHANG P Z, ZHANG G L, et al. , 2010. Cenozoic sedimentary evolution of the Sikouzi Basin on the northeastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 45(2): 440-452. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] WANG W T, 2012. Sedimentary evolution of Cenozoic basin in southern Ningxia and its response to tectonic deformation in northeast corner of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology(10): 40-43. (in Chinese) [24] WANG W T, ZHENG D D, PANG J Z, 2013. Provenancial tracing for the Cenozoic Sikouzi section in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(10): 1551-1569. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] WANG X Z, ZHOU S F, XU S J, 1979. Discussions on the palaeogeography and palaeoclimatology of the Late Eocene epoch and Oligocene epoch North Jiangsu[J]. Acta Botanica Sinica, 21(2): 149-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] WU F L, FANG X M, YANG Y B, et al. , 2022. Reorganization of Asian climate in relation to Tibetan Plateau uplift[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 3(10): 684-700. [27] WU X L, LI R X, HU J M, et al. , 2017. Late Paleogene saline lake evolution of the Ningnan Basin, Northern China, and its regional geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(4): 954-967. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] WU X L, LI R X, HU J M, et al. , 2018. Late Paleogene saline lake evolution of the Ningnan Basin and its response to the regional paleoclimate and uplift of the Tibetan Plateau: evidence from sedimentary strata, and S and Sr isotopes[J]. Geological Journal, 53(S2): 405-416. [29] WU X L, LI R X, LI X G, et al. , 2023. Late Paleogene climate change and its driving mechanism in the Ningnan Basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 41(1): 206-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] WU Z H, WU Z H, YE P S, et al. , 2006. Late Cenozoic environmental evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau as indicated by the evolution of sporopollen assemblages[J]. Geology in China, 33(5): 966-979. (in Chinese with English abstract) [31] XIAO L, LI C P, WANG W T, et al. , 2019. Climate evolution since 29 Ma recorded by sediment color on Sikouzi Section, Guyuan, Ningxia[J]. Geological Review, 65(3): 623-631. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] XU Q H, WU N, WANG J, et al. , 2023. Sedimentary characteristics and lake basin evolution of salinized lake basin of Qingshuiying formation in Yinchuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 48(1): 317-328. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] YIN A, RUMELHART P E, BUTLER R, et al. , 2002. Tectonic history of the Altyn Tagh fault system in northern Tibet inferred from Cenozoic sedimentation[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 114(10): 1257-1295. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2002)114<1257:THOTAT>2.0.CO;2 [34] ZHANG J, MA Z J, REN W J, 2005. The sedimentary characteristics of Cenozoic strata in central and southern Ningxia and their relationships with the development of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(6): 757-773. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] ZHANG Y Y, 1990. Discovery of some forerunner species of Momipites from Lower Tertiary of China[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 29(3): 300-308. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] ZHAO Y, LIU C Y, ZHANG D D, et al. , 2016. Geochemical characteristics of Paleogene sedimentary rocks in Ningnan Basin and their implications for sedimentary environments[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 35(5): 27-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] ZHENG W J, ZHANG P Z, YUAN D Y, et al. , 2019. Basic characteristics of active tectonics and associated geodynamic processes in continental China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 699-721. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] ZHENG W J, ZHANG B X, YUAN D Y, et al. , 2021. Tectonic activity in the southern Alashan Block and the latest boundary of outward expansion on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 43(2): 224-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] 方小敏, 2017. 青藏高原隆升阶段性[J]. 科技导报, 35(6): 42-50. [40] 格刺德科娃, 格里丘克, 札克苓斯卡娅, 等, 1956. 花粉分析[M]. 王伏雄, 张金谈, 马毓泉, 等译. 北京: 科学出版社. [41] 蒋锋云, 季灵运, 赵强, 2021. 海源-六盘山断裂带现今地震危险性的数值模拟分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 230-240. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.022 [42] 寇琳琳, 李振宏, 董晓朋, 等, 2021. 青藏高原东北缘隆德观音店剖面碎屑锆石年龄序列及地质意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(6): 1051-1064. [43] 李明涛, 李黎明, 梁志荣, 2020. 宁夏同心地区古近纪-新近纪沉积岩地球化学特征及意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 39(2): 304-318. doi: 10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2020.39.018 [44] 苗运法, 方小敏, 宋之琛, 等, 2008. 青藏高原北部始新世孢粉记录与古环境变化[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 38(2): 187-196. [45] 宁夏回族自治区地质矿产局, 1990. 宁夏回族自治区区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [46] 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院, 2017. 中国区域地质志·宁夏志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [47] 潘进礼, 马学东, 马玉学, 等, 2022. 宁夏银川盆地灵武地区古近纪—新近纪沉积岩地球化学特征及对古环境演化的启示[J]. 地质通报, 41(2-3): 296-305. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.2-3.009 [48] 青海石油管理局勘探开发研究院, 中国科学院南京地质古生物研究所, 1985. 柴达木盆地第三纪孢粉学研究[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社. [49] 申旭辉, 田勤俭, 丁国瑜, 等, 2001. 宁夏贺家口子地区晚新生代地层序列及其构造意义[J]. 中国地震, 17(2): 156-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2001.02.006 [50] 宋之琛, 郑亚惠, 李曼英, 等, 1999. 中国孢粉化石(第一卷): 晚白垩世和第三纪孢粉[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [51] 孙素英, 1982. 宁夏同心地区渐新世孢粉组合[C]//中国地质科学院地质研究所文集(4). 北京: 地质出版社: 130-141. [52] 孙秀玉, 赵英娘, 何卓生, 1984. 青海西宁-民和盆地渐新世至中新世孢粉组合[J]. 地质论评, 30(3): 207-216. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.1984.03.002 [53] 陶明华, 王开发, 郑国光, 等, 2001. 冀中拗陷早第三纪孢粉组合及地质时代讨论[J]. 微体古生物学报, 18(3): 274-292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2001.03.008 [54] 王伴月, 阎志强, 陆彦俊, 等, 1994. 宁夏海原两个第三纪中期哺乳动物群的发现[J]. 古脊椎动物学报, 32(4): 285-296. doi: 10.19615/j.cnki.1000-3118.1994.04.013 [55] 王伟涛, 张培震, 张广良, 等, 2010. 青藏高原东北缘寺口子盆地新生代沉积演化及其构造意义[J]. 地质科学, 45(2): 440-452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2010.02.007 [56] 王伟涛, 2012. 宁夏南部新生代盆地沉积演化及其对青藏高原东北角构造变形的响应[J]. 国际地震动态(10): 40-43. [57] 王伟涛, 郑德文, 庞建章, 2013. 青藏高原东北缘寺口子剖面碎屑锆石示踪及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 87(10): 1551-1569. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2013.10.006 [58] 王宪曾, 周山富, 徐淑娟, 1979. 江苏北部早第三纪晚期孢粉植物群及其古气候、古地理意义[J]. 植物学报, 21(2): 149-156. [59] 吴小力, 李荣西, 胡建民, 等, 2017. 中国北方宁南盆地古近纪晚期咸化湖盆演化及其区域地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 91(4): 954-967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.04.018 [60] 吴小力, 李荣西, 李小刚, 等, 2023. 青藏高原东北缘宁南盆地晚古近纪气候变化及其驱动机制[J]. 沉积学报, 41(1): 206-218. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2021.082 [61] 吴珍汉, 吴中海, 叶培盛, 等, 2006. 青藏高原晚新生代孢粉组合与古环境演化[J]. 中国地质, 33(5): 966-979. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.05.004 [62] 肖霖, 李朝鹏, 王伟涛, 等, 2019. 宁夏固原寺口子剖面色度记录的29 Ma以来气候演化[J]. 地质论评, 65(3): 623-631. [63] 徐清海, 吴楠, 王健, 等, 2023. 银川盆地清水营组咸化湖盆沉积特征与湖盆演化[J]. 地球科学, 48(1): 317-328. [64] 张进, 马宗晋, 任文军, 2005. 宁夏中南部新生界沉积特征及其与青藏高原演化的关系[J]. 地质学报, 79(6): 757-773. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.06.005 [65] 张一勇, 1990. Momipites的几个先驱种在我国下第三系的发现: 兼评Carya的北美起源说[J]. 古生物学报, 29(3): 300-308. [66] 赵岩, 刘池洋, 张东东, 等, 2016. 宁南盆地古近纪沉积岩地球化学特征对沉积环境的反映[J]. 地质科技情报, 35(5): 27-33. [67] 郑文俊, 张培震, 袁道阳, 等, 2019. 中国大陆活动构造基本特征及其对区域动力过程的控制[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(5): 699-721. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.05.062 [68] 郑文俊, 张博譞, 袁道阳, 等, 2021. 阿拉善地块南缘构造活动特征与青藏高原东北缘向外扩展的最新边界[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 43(2): 224-236. doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2021.01039 [69] 中国科学院植物研究所形态室孢粉组, 1960. 中国植物花粉形态[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. -





 下载:
下载: