Two pillar theories of structural geology in the new century: the MEM criterion and the deformation partitioning
-
摘要: 传统构造地质学用摩尔-库伦准则和贝克尔的应变椭球体理念分别解释地壳中的脆性断层和塑性变形,将变形局部化的韧性剪切带形成解释为平行应变椭球体的圆切面,却无法解释变形局部化的共轭剪切带稳定夹角~110°面对应缩短方向。变形局部化是独立于脆性和塑性变形外的变形领域,受最大有效力矩准则控制。20世纪末提出的变位形分解理念,摆脱连续介质力学的束缚,合理地说明广泛存在的走滑断层平行俯冲带或逆冲断层带。非均匀变形和非连续介质力学理念的建立,为地质学与力学的结合开辟了新的前景。文章试用上述两理念概略分析中国和邻区中新生代构造格局,以期引发讨论。Abstract: Geologists used the Mohr-Coulomb criterion and Becker's strain ellipsoid to explain brittle fractures and plastic deformation, respectively, in traditional structural geology, and considered that formation of ductile shear zones was parallel to the circular sections of a strain ellipsoid. However, they failed to explain the stable angle ~110° facing contraction direction between conjugate ductile shear zones due to deformation localization. In fact, deformation localization is an independent deformation category controlled by MEM-criterion besides brittle fracturing and plastic deformation. The concept of deformation partitioning put forward at the end of twentieth century got rid of the bondage of continuum mechanics, and successfully explained the widespread phenomenon, strike-slip faults parallel to subduction zones or fold-and-thrust belts. The establishment of inhomogeneous and discontinuous medium mechanics opens up a new prospect for the combination of geology and mechanics.
-
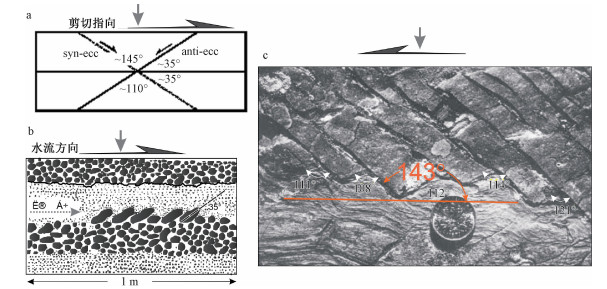
图 1 自然界常见的两类钝角(~110°和~145°)
a—切割糜棱面理的共轭剪切条带(White, 1979);b—河床中的叠瓦状砾石(施罗克, 1955);c—多米诺骨牌构造(Ramsay and Huber, 1987)
Figure 1. Common two obtuse angles, ~110° and ~145° in nature
(a) Conjugate shear bands truncating mylonitic foliation (White, 1979); (b) Imbricate pebbles in the river bed (Shi et al., 1955) (c) Domino structure by Ramsay and Huber (1987)
图 2 最大有效力矩准则
a、b—有限方块边界的应力状态及相应的应力莫尔圆; c—最大有效力矩准则的数学表达式与图示(深浅阴影区表示全部实验和自然观测值范围); d—英格兰地下1 km处钾盐矿柱的共轭剪切带(黑色粗线表示剪切带;虚线表示早期开采时挖掘机开采时的挖掘痕迹,注意发生错动;Watterson, 1999)
Figure 2. Mathematical expression and graphical representation of the MEM-criterion
(a-c) Mathematic expression and diagram of the MEM-criterion (grey shallow areas presenting the ranges of all experimental and natural observations); (d) Conjugate shear zones in a potash pillar underground (1000 m depth) in England (Watterson, 1999)
图 3 变形局部化(110°不随递进变形而变,菱形块体内基本无应变)
a—千枚岩轴向压缩实验(Paterson and Weiss, 1966);b—赛璐璐数值模拟(Liao et al., 2013)
Figure 3. Deformation localization (Note that 110° is an invariant and that there is almost no strain in rhombic blocks or lozenges)
(a) Axial compression test for phyllite (Paterson and Weiss, 1966); (b) Results by numerical simulation (Liao et al., 2013)
图 4 变形局部化与准均匀变形的应力与应变曲线(Peltzer and Tapponnier, 1988)
a为应力降和共轭伸展剪切带,110°面对缩短方向;b中的共轭褶皱也是钝角面对缩短方向,但未形成清晰的不连续面,故应力-应变曲线近似均匀变形
Figure 4. Difference in stress-strain curves in various deformation types (Peltzer and Tapponnier, 1988)
(a) Conjugate extensional shear zones with 110° in the shortening direction in deformation localization; (b) An obtuse angle between conjugate fold sets in sub-homogeneous deformation
图 5 走滑边界变位形分解程度图解(Tikoff and Teyssier, 1994; Teyssier et al., 1995)
α—汇聚方向;θ—σ1或${\dot S_3}$(最小瞬时伸长度)与边界的夹角;图中①、②、③分别代表圣安德烈斯断层、苏门答腊断层和新西兰阿尔派恩断层的变位形分解,96%~98%、30%和0;黑星和白星分别是文中圣安德烈斯断层和怒江-实皆断层求解的走滑分解量
Figure 5. Diagram for deformation partitioning% (Tikoff and Teyssier, 1994; Teyssier et al., 1995)
图 7 实验学所揭示的变位形分解的两个端元
a—层状塑性泥斜向缩短实验(Gómez Rivas, 2008),显示100%变位形分解;b—千枚岩斜向挤压实验(Paterson and Weiss, 1966),显示无变位形分解
Figure 7. Two types of deformation partitioning by experiments
(a) Results from layered plasticine experiment (Gómez Rivas, 2008); (b) Deformed phyllite (Paterson and Weiss, 1966), showing 100% and zero-deformation partitioning, respectively
图 8 中国及邻区构造分区与格局图(白色箭头代表变质核杂岩上盘伸展运动方向;图中角度为大型共轭走滑断裂钝夹角角度;据任纪舜(1989)、潘桂棠等(2009)、杨巍然等(2012)和万天丰(2013)修编)
Figure 8. Tectonic units and network of China and its adjacent regions (Adapted from Ren, 1989 with referring to these works)
图 9 青藏高原中的摩尔-库伦断裂与宽V形共轭走滑断层系及所显示的应力状态(底图据Kapp et al., 2008; 断层走向玫瑰图据Zhang et al., 2012)
BS—班公缝合带(北缝合带);IYS—印度-雅鲁藏布缝合带(南缝合带)
Figure 9. Mohr-Coulomb-type fractures and wide-open V-shaped conjugate strike-slip fault system in Tibet and the related stress state (Tectonic frame by From Kapp et al., 2008, and rose diagram of fautt strike by Zhang et al., 2012)
BS-The Bangong suture belt (The northern suture belt); IYS-The Indian-Yarlung Zangbo suture belt
图 10 高黎贡怒江段右行韧性剪切带不同尺度构造面理几何特征
a—露头尺度的长石碎斑指示右行剪切;b—显微尺度S/C指示右行剪切(Zhang et al., 2010);c—怒江东侧千枚状板岩中的共轴叠加褶皱
Figure 10. Various-scale structures in the Gaoligong shear zone (Nujiang section)
(a) σ-type feldspar porphyroblast showing dextral shearing on outcrop-scale within the Gaoligong shear zone. (b) S/C structures in the microstructures in the shear zone (Zhang et al., 2010). (c) Coaxial superimpose folds on the eastern side of the shear zone
图 11 中南半岛新生代区域规模走滑断裂体系空间展布
a—中南半岛的主要断层带(Kanjanapayont et al., 2012);b—几何特征、运动学和应力状态分析
Figure 11. Structure frame and major strike-slip fault systems in the Indo-China Peninsular
(a) Main faults in Indo-China Peninsular (Kanjanapayont et al., 2012); (b) Geometric, kinematic, stress-state and their transformation in Tertiary
图 12 东亚新生代构造与应力体系分析
a—最大有效力矩方向取代滑移线的东亚新生代挤出构造(图中角度为大型共轭走滑断裂钝夹角度数;底图引自Zheng et al., 2011);b—滑移线方向;c—最大有效力矩方向(红线右行走滑,红蓝相间为左右交替,印度板块东侧先左后右,①、②表示断裂活动先后)
Figure 12. Tectonics and stress analysis of eastern Asia
(a) Extrusion tectonics in eastern Asia with MEM-directions (Tectonic frame by Zheng et al., 2011); (b) Tectonic interpretation by slip lines; (c) Tectonic interpretation by MEM-directions
图 13 东亚中、新生代构造的概略分析
a—东亚巨型构造边界及应力体系;b—Maruyama et al.(1997)提出的模型;c—Müller et al. (2016)模式
Figure 13. Summary analysis on tectonics in eastern Asia region
(a) Major tectonic boundaries and stress system in eastern Asia; (b) Mesozoic tectonic evolution by Maruyama et al., 1997; (c) Cenozoic tectonic evolution by Müller et al., 2016
-
ANDERSON E M, 1951. The dynamics of faulting and dyke formation with applications to Britain[M]. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd. BECKER G F, 1893. Finite homogeneous strain, flow and rupture of rocks[J]. GSA Bulletin, 4(1): 13-90. BOUCHON M, 1997. The state of stress on some faults of the San Andreas system as inferred from near-field strong motion data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 102(B6): 11731-11744. doi: 10.1029/97JB00623 CAO S Y, LIU J L, LEISS B, et al., 2009. Timing of initiation of left-lateral slip along the Ailao Shan-Red River Shear Zone: microstructural, texture and thermochronological evidence from high temperature mylonites in Diancang Shan, SW China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(10): 1388-1400. (in Chinese with English abstract) CAO X Z, FLAMENT N, LI S Z, et al., 2021. Spatio-temporal evolution and dynamic origin of Jurassic-Cretaceous magmatism in the South China Block[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 217: 103605. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103605 CARRERAS J, COSGROVE J W, DRUGUET E, 2013. Strain partitioning in banded and/or anisotropic rocks: implications for inferring tectonic regimes[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 50: 7-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2012.12.003 CHARLES N, GUMIAUX C, AUGIER R, et al., 2011. Metamorphic core complexes vs. synkinematic plutons in continental extension setting: insights from key structures (Shandong Province, eastern China)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(1): 261-278. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.07.006 CHIKOV B M, ZINOVIEV S V, DEYEV E V, 2012. Post-late Paleozoic collisional framework of southern Great Altai[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 86(5): 1093-1104. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00733.x COLLETTINI C, 2011. The mechanical paradox of low-angle normal faults: current understanding and open questions[J]. Tectonophysics, 510(3-4): 253-268. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.07.015 CONEY P J, 1980. Cordilleran metamorphic core complexes: an overview[M]//CRITTENDEN M D JR, CONEY P J, DAVIS G H. Cordilleran metamorphic core complexes. Tulsa: Geological Society of America: 7-31. DAVIS G A, ZHENG Y D, 1988. A possible Cordilleran-type metamorphic core complex beneath the Great Wall near Hefangkou, Huairou Country, northern China[J]. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 20: A324. DAVIS G A, WANG C, ZHENG Y D, et al., 1998. The enigmatic Yinshan fold-and-thrust belt of northern China: new views on its intraplate contractional styles[J]. Geology, 26(1): 43-46. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0043:TEYFAT>2.3.CO;2 DAVIS G A, XU B, ZHENG Y D, et al., 2004. Indosinian extension in the Solonker suture zone: the Sonid Zuoqi metamorphic core complex, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(3): 135-144. DAVIS G H, 1980. Structural characteristics of metamorphic core complexes, southern Arizona[M]//CRITTENDEN M D JR, CONEY P J, DAVIS G H. Cordilleran metamorphic core complexes. Tulsa: Geological Society of America: 35-77. DONG S W, WU X H, WU Z H, et al., 2000. On tectonic seesawing of the East Asia continent-Global implication of the Yanshanian Movement[J]. Geological Review, 46(1): 8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) DONG S W, ZHANG Y Q, CHEN X H, et al., 2008. The formation and deformational characteristics of East Asia multi-direction convergent tectonic system in Late Jurassic[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29(3): 306-317. (in Chinese with English abstract) DONG S W, GAO R, YIN A, et al., 2013. What drove continued continent-continent convergence after ocean closure? Insights from high-resolution seismic-reflection profiling across the Daba Shan in central China[J]. Geology, 41(6): 671-674. doi: 10.1130/G34161.1 DONG S W, ZHANG Y Q, LI H L, et al., 2018. The Yanshan orogeny and late Mesozoic multi-plate convergence in East Asia-Commemorating 90th years of the "Yanshan Orogeny"[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(12): 1888-1909. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9297-y DRUGUET E, CZECK D M, ALSOP G I, et al., 2013. Preface: deformation localization[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 50: 1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2013.04.002 DWIVEDI S K, HAYASHI D, 2010. Modeling the contemporary stress field and deformation pattern of eastern Mediterranean[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 21(4): 365-381. doi: 10.1007/s12583-010-0100-6 FAURE M, LIN W, CHEN Y, 2012. Is the Jurassic (Yanshanian) intraplate tectonics of North China due to westward indentation of the North China block?[J] Terra Nova, 24(6): 456-466. doi: 10.1111/ter.12002 FAURE M, LEPVRIER C, VAN NGUYEN V, et al., 2014. The South China Block-Indochina collision: where, when, and how?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79: 260-274. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.022 GÓMEZ RIVAS E, 2008. Localización de deformación en medios dúctiles y anisótropos: estudio de campo, experimental y numérico[D]. Barcelona: Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. GILLEY L D, HARRISON T M, LELOUP P H, et al., 2003. Direct dating of left-lateral deformation along the Red River shear zone, China and Vietnam[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(B2): 2127. GOMEZ-RIVAS E, GRIERA A, 2012. Shear fractures in anisotropic ductile materials: an experimental approach[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 34: 61-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2011.10.007 HILL R, 1950. The mathematical theory of plasticity[M]. Oxford: Clarendon Press. HUBERT-FERRARI A, KING G, MANIGHETTI I, et al., 2003. Long-term elasticity in the continental lithosphere; modelling the Aden Ridge propagation and the Anatolian extrusion process[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 153(1): 111-132. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01872.x KANJANAPAYONT P, GRASEMANN B, EDWARDS M A, et al., 2012. Quantitative kinematic analysis within the Khlong Marui shear zone, southern Thailand[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 35: 17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2011.12.002 KAPP P, TAYLOR M, STOCKLI D, et al., 2008. Development of active low-angle normal fault systems during orogenic collapse: insight from Tibet[J]. Geology, 36(1): 7-10. doi: 10.1130/G24054A.1 LEE J S, 1939. The geology of China[M]. London: Thomas Murby & Co. LEE J S, 1973. Introduction to geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) LELOUP P H, LACASSIN R, TAPPONNIER P, et al., 1995. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone (Yunnan, China), Tertiary transform boundary of Indochina[J]. Tectonophysics, 251(1-4): 3-84. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(95)00070-4 LI C C, JIANG D Z, 2011. A critique of vorticity analysis using rigid clasts[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 33(3): 203-219. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2010.09.001 LI J H, HOU G T, HUANG X N, 2001. The constraint for the supercontinental cycles: evidence from Precambrian geology of North China Block[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 17(2): 177-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI J H, 2013. The Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution of South China-Constraints from tectonic deformation and chronology of northern Daba Shan, central Yuanma Basin and Hengshan[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI J H, DONG S W, CAWOOD P A, et al., 2018. An Andean-Type Retro-Arc foreland system beneath northwest South China revealed by SINOPROBE profiling[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 490: 170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2018.03.008 LI Z X, LI X H, 2007. Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: a flat-slab subduction model[J]. Geology, 35(2): 179-182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1 LIANG H, RAN Q, DI G D, et al., 2019. Kink folds discovered in Qixia Formation of the buried structural belt, northwestern Sichuan Basin: their significance to oil and gas[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 42(4): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIAO S F, ZHENG Z J, YU J L, 2013. Dynamic crushing of 2D cellular structures: Local strain field and shock wave velocity[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 57: 7-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.01.008 LIN W, WANG Q C, CHEN K, 2008. Phanerozoic tectonics of South China Block: new insights from the polyphase deformation in the Yunkai massif[J]. Tectonics, 27(6): TC6004. LIN W, WANG J, LIU F, et al., 2013. Late Mesozoic extension structures on the North China Craton and adjacent regions and its geodynamics[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(5): 1791-1810. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIN W, WEI W, 2020. Late Mesozoic extensional tectonics in the North China Craton and its adjacent regions: a review and synthesis[J]. International Geology Review, 62(7-8): 811-839. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2018.1477073 LIN Y, ZHANG C H, LI C M, et al., 2020. From dextral contraction to sinistral extension of intracontinental transform structures in the Yanshan and northern Taihang Mountain belts during Early Cretaceous: implications to the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 189: 104139. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104139 LIU K, ZHANG J J, XIAO W J, et al., 2020. A review of magmatism and deformation history along the NE Asian margin from ca. 95 to 30 Ma: transition from the Izanagi to Pacific plate subduction in the early Cenozoic[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 209: 103317. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103317 MALUSKI H, LEPVRIER C, JOLIVET L, et al., 2001. Ar-Ar and fission-track ages in the Song Chay massif: early Triassic and Cenozoic tectonics in Northern Vietnam[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 19(1-2): 233-248. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00038-9 MARUYAMA S, ISOZAKI Y, KIMURA G, et al., 1997. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: plate Tectonic synthesis from 750 Ma to the present[J]. Island Arc, 6(1): 121-142. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1738.1997.tb00043.x MOLNAR P, TAPPONNIER P, 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: effects of a continental collision[J]. Science, 189(4201): 419-426. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419 MOUNT V S, SUPPE J, 1987. State of stress near the San Andreas fault: Implications for wrench tectonics[J]. Geology, 15(12): 1143-1146. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1987)15<1143:SOSNTS>2.0.CO;2 MÜLLER R D, SETON M, ZAHIROVIC S, et al., 2016. Ocean basin evolution and global-scale plate reorganization events since Pangea breakup[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 44: 107-138. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060115-012211 NIE T C, ZHU G L, 2004. On the characteristics and evolution of geological structures in the intermediate section of the Zhenghe-Dapu deep faulted zone[J]. Geology of Fujian, 23(4): 186-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) PAN G T, XIAO Q H, LU S N, et al., 2009. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 36(1): 1-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) PARK R G, 2004. Foundations of structural geology[M]. London: Routledge. PASSCHIER C W, ZHANG J S, KONOPÁSEK J, 2005. Geometric aspects of synkinematic granite intrusion into a ductile shear zone-an example from the Yunmengshan core complex, northern China[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 245: 65-80. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2005.245.01.04 PATERSON M S, WEISS L E, 1966. Experimental deformation and folding in phyllite[J]. GSA Bulletin, 77(4): 343-374. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1966)77[343:EDAFIP]2.0.CO;2 PELTZER G, TAPPONNIER P, 1988. Formation and evolution of strike-slip faults, rifts, and basins during the India-Asia collision: an experimental approach[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 93(B12): 15085-15117. doi: 10.1029/JB093iB12p15085 PONCE C, DRUGUET E, CARRERAS J, 2013. Development of shear zone-related lozenges in foliated rocks[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 50: 176-186. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2012.04.001 RAMSAY J G, GRAHAM R H, 1970. Strain variation in shear belts[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 7(3): 786-813. doi: 10.1139/e70-078 RAMSAY J G, HUBER M I, 1987. The techniques of modern structural geology. Volume 2: folds and fractures[M]. London: Academic Press. REN J S, 1989. Some new ideas on tectonic evolution of eastern China and adjacent areas[J]. Regional Geology of China(4): 289-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) REN J S, 1996. The continental tectonics of China[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 13(3-5): 197-204. doi: 10.1016/0743-9547(96)00026-8 ROGER F, LELOUP P H, JOLIVET M, et al., 2000. Long and complex thermal history of the Song Chay metamorphic dome (Northern Vietnam) by multi-system geochronology[J]. Tectonophysics, 321(4): 449-466. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00085-8 SENGÖR A M C, 1991. Plate tectonics and orogenic research after 25 years: synopsis of a Tethyan perspective[J]. Tectonophysics, 187(1-3): 315-330, 337-344. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(91)90427-T SENGÖR A M C, NATALIN B A, BURTMAN V S, 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Pala[J]. Nature, 364(6435): 299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0 SHARP W D, CLAGUE D A, 2006. 50-Ma initiation of Hawaiian-Emperor bend records major change in Pacific Plate motion[J]. Science, 313(5791): 1281-1284. doi: 10.1126/science.1128489 SHROCK R R, 1955. Sequence in layered rocks[M]. WENG W H, trans. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) SHU L S, ZHOU X M, 2002. Late Mesozoic tectonism of southeast China[J]. Geological Review, 48(3): 249-260. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHU L S, FAURE M, JIANG S Y, et al., 2006. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age, litho-and biostratigraphic analyses of the Huaiyu Domain in South China-Evidence for a Neoproterozoic orogen, not Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic collision[J]. Episodes, 29(4): 244-252. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i4/002 SHU L S, 2012. An analysis of principal features of tectonic evolution in South China Block[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 31(7): 1035-1053. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHU L S, WANG B, CAWOOD P A, et al., 2015. Early Paleozoic and early Mesozoic intraplate tectonic and magmatic events in the Cathaysia block, South China[J]. Tectonics, 34(8): 1600-1621. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003835 SIBSON R H, 1977. Fault rocks and fault mechanisms[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 133(3): 191-213. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.133.3.0191 SIBSON R H, ROBERT F, POULSEN K H, 1988. High-angle reverse faults, fluid-pressure cycling, and mesothermal gold-quartz deposits[J]. Geology, 16(6): 551-555. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0551:HARFFP>2.3.CO;2 SONG S G, JI J Q, WEI C J, et al., 2007. Early Paleozoic granite in Nujiang River of northwest Yunnan in southwestern China and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(17): 2402-2406. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0301-2 TAPPONNIER P, MOLNAR P, 1976. Slip-line field theory and large-scale continental tectonics[J]. Nature, 264(5584): 319-324. doi: 10.1038/264319a0 TAYLOR M, YIN A, RYERSON F J, et al., 2003. Conjugate strike-slip faulting along the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone accommodates coeval east-west extension and north-south shortening in the interior of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 22(4): 1044. TEYSSIER C, TIKOFF B, MARKLEY M, 1995. Oblique plate motion and continental tectonics[J]. Geology, 23(5): 447-450. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0447:OPMACT>2.3.CO;2 TIKOFF B, TEYSSIER C, 1994. Strain modeling of displacement-field partitioning in transpressional orogens[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 16(11): 1575-1588. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(94)90034-5 TORSVIK T H, DOUBROVINE P V, STEINBERGER B, et al., 2017. Pacific plate motion change caused the Hawaiian-Emperor Bend[J]. Nature Communications, 8(1): 15660. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15660 TOWNEND J, ZOBACK M D, 2004. Regional tectonic stress near the San Andreas fault in central and southern California[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(15). VALLI F, LELOUP P H, PAQUETTE J L, et al., 2008. New U-Th/Pb constraints on timing of shearing and long-term slip-rate on the Karakorum fault[J]. Tectonics, 27(5): TC5007. WAN T F, ZHU H, ZHAO L, et al., 1996. Formation and evolution of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone: a review[J]. Geoscience, 10(2): 159-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) WAN T F, 2013. A new Asian tectonic unit map[J]. Geology in China, 40(5): 1351-1365. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG T, ZHENG Y D, ZHANG J J, et al., 2011. Pattern and kinematic polarity of Late Mesozoic extension in continental NE Asia: perspectives from metamorphic core complexes[J]. Tectonics, 30(6): TC6007. WANG T, GUO L, ZHENG Y D, et al., 2012. Timing and processes of late Mesozoic mid-lower-crustal extension in continental NE Asia and implications for the tectonic setting of the destruction of the North China Craton: mainly constrained by zircon U-Pb ages from metamorphic core complexes[J]. Lithos, 154: 315-345. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.07.020 WANG Z H, LU H F, 1997. Evidence and Dynamics for the change of strike-slip direction of the Changle-Nanao ductile shear zone, southeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 15(6): 507-515. doi: 10.1016/S0743-9547(97)00035-4 WANG Z H, LU H F, 2000. Ductile deformation and 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Changle-Nanao ductile shear zone, southeastern China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 22(5): 561-570. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(99)00179-0 WATTERSON J, 1999. The future of failure: stress or strain?[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 21(8-9): 939-948. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(99)00012-7 WERNICKE B, 1981. Low-angle normal faults in the Basin and Range Province: nappe tectonics in an extending orogen[J]. Nature, 291(5817): 645-648. doi: 10.1038/291645a0 WHITE S, 1979. Large strain deformation: report on a Tectonic Studies Group discussion meeting held at Imperial College, London on 14 November 1979[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1(4): 333-339. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(79)90008-7 WRIGHT T J, PARSONS B, ENGLAND P C, et al., 2004. InSAR observations of low slip rates on the major faults of western Tibet[J]. Science, 305(5681): 236-239. doi: 10.1126/science.1096388 WU G Y, 2002. The Yanshanian orogeny and Late Mesozoic activation in China continent[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 37(4): 453-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU J T J, WU J, 2019. Izanagi-Pacific ridge subduction revealed by a 56 to 46 Ma magmatic gap along the northeast Asian margin[J]. Geology, 47(10): 953-957. doi: 10.1130/G46778.1 XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, SUN S, et al., 2015. A Tale of Amalgamation of Three Permo-Triassic Collage Systems in Central Asia: Oroclines, Sutures, and Terminal Accretion[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43: 477-507. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105254 XU J W, ZHU G, TONG W X, et al., 1987. Formation and evolution of the Tancheng-Lujiang wrench fault system: a major shear system to the northwest of the Pacific Ocean[J]. Tectonophysics, 134(4): 273-310. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(87)90342-8 XU J W, MA G F, TONG W X, et al., 1993. Displacement of the Tancheng-Lujiang wrench fault system and its geodynamic setting in the northwestern circum-Pacific[M]//XU J W. The Tancheng-Lujiang wrench fault system. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons: 51-74. YAN D P, ZHOU M F, SONG H L, et al., 2003. Origin and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic multi-layer over-thrust system within the Yangtze block (South China)[J]. Tectonophysics, 361(3-4): 239-254. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00646-7 YAN D P, ZHANG B, ZHOU M F, et al., 2009. Constraints on the depth, geometry and kinematics of blind detachment faults provided by fault-propagation folds: an example from the Mesozoic fold belt of South China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 31(2): 150-162. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2008.11.005 YANG W R, WANG J, LIANG X, 2012. The major characteristics of geotectonics of Asia and regularities of evolution[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(5): 1-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) YIN A, 2010. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Asia: a preliminary synthesis[J]. Tectonophysics, 488(1-4): 293-325. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.06.002 YIN A, TAYLOR M H, 2011. Mechanics of V-shaped conjugate strike-slip faults and the corresponding continuum mode of continental deformation[J]. GSA Bulletin, 123(9-10): 1798-1821. doi: 10.1130/B30159.1 ZHANG B, ZHANG J J, ZHONG D L, 2010. Structure, kinematics and ages of transpression during strain-partitioning in the Chongshan shear zone, western Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 32(4): 445-463. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2010.02.001 ZHANG C H, SONG H L, WANG G H, et al., 2001. Mesozoic dextral strike-slip structural system in middle segment of intraplate Yanshan Orogenic Belt, Northern China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 26(5): 464-472. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG C H, LI C M, DENG H L, et al., 2011. Mesozoic contraction deformation in the Yanshan and northern Taihang mountains and its implications to the destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(6): 798-822. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4180-7 ZHANG G W, GUO A L, 2019. Thoughts on continental tectonics[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 44(5): 1464-1475. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.971 ZHANG J J, SANTOSH M, WANG X X, et al., 2012. Tectonics of the northern Himalaya since the India-Asia collision[J]. Gondwana Research, 21(4): 939-960. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.004 ZHANG K J, CAI J X, 2009. NE-SW-trending Hepu-Hetai dextral shear zone in southern China: penetration of the Yunkai Promontory of South China into Indochina[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 31(7): 737-748. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2009.04.012 ZHANG P, MOLNAR P, XU X, 2007. Late Quaternary and present-day rates of slip along the Altyn Tagh Fault, northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 26(5): TC5010. ZHANG Y, SHI W, 2018. Advances in continental scape structures[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(2): 145-156. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y Q, DONG S W, LI J H, et al., 2012. The new progress in the study of Mesozoic tectonics of South China[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 33(3): 257-279. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y Q, DONG S W, 2019. East Asia multi-plate convergence in Late Mesozoic and the development of continental tectonic systems[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 613-641. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Z K, LING M X, LIN W, et al., 2020. "Yanshanian Movement" induced by the westward subduction of the paleo-Pacific plate[J]. Solid Earth Sciences, 5(2): 103-114. doi: 10.1016/j.sesci.2020.04.002 ZHENG J P, DAI H K, 2018. Subduction and retreating of the western Pacific plate resulted in lithospheric mantle replacement and coupled basin-mountain respond in the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(4): 406-424. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9166-8 ZHENG Y D, WANG Y F, LIU R X, et al., 1988. Sliding-thrusting tectonics caused by thermal uplift in the Yunmeng Mountains, Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 10(2): 135-144. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(88)90111-3 ZHENG Y D, ZHANG Q, WANG Y Y, et al., 1996. Great Jurassic thrust sheets in Beishan (North Mountains)-Gobi areas of China and southern Mongolia[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 18(9): 1111-1126. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(96)00038-7 ZHENG Y D, WANG T, MA M B, et al., 2004. Maximum effective moment criterion and the origin of low-angle normal faults[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 26(2): 271-285. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00079-8 ZHENG Y D, WANG T, 2005. Kinematics and dynamics of the Mesozoic orogeny and late-orogenic extensional collapse in the Sino-Mongolian border areas[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 48(7): 849-862. doi: 10.1360/03yd0552 ZHENG Y D, WANG T, WANG X S, 2006. The maximum effective moment criterion (MEMC) and its implications in structural geology[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 80(1): 70-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2006.tb00797.x ZHENG Y D, MO W L, ZHANG W T, et al., 2007. A new idea for petroleum exploration in Qaidam Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 34(1): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG Y D, ZENG L S, LI J B, et al., 2009. Mesozoic orogeniccontractional decollement and late-orogenic extensional detachment in the southern Liaoning Peninsula[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 44(3): 811-824. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG Y D, WANG E, ZHANG J J, et al., 2011. A challenge to the concept of slip-lines in extrusion tectonics[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2(1): 23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2010.11.006 ZHENG Y D, ZHANG J J, WANG T, 2014. Interpretation of the experimental data provided by Gómez-Rivas and Griera (2012) in terms of the MEM-criterion[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 57(11): 2819-2824. doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4972-7 ZHOU D, SUN Z, CHEN H Z, et al., 2005. Mesozoic lithofacies, paleo-geography, and tectonic evolution of the South China Sea and surrounding areas[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(3): 204-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU X M, SUN T, SHEN W Z, et al., 2006. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in south China: a response to tectonic evolution[J]. Episodes, 29(1): 26-33. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i1/004 ZHU G, WANG D X, LIU G S, et al., 2004. Evolution of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone and its responses to plate movements in west Pacific Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 39(1): 36-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU G, WANG W, GU C C, et al., 2016. Late Mesozoic evolution history of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone and its indication to destruction processes of the North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(4): 935-949. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU R X, XU Y G, ZHU G, et al., 2012. Destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 55(10): 1565-1587. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4516-y ZOU H P, WANG J H, QIU Y X, 2000. 40Ar/39Ar ages of the Nan'ao Shear Zone and the Lianhuashan Shear Zone in Guangdong province and their geological significance[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 21(4): 356-364. (in Chinese with English abstract) 曹淑云, 刘俊来, LEISS B, 等, 2009. 哀牢山-红河剪切带左行走滑作用起始时间约束: 点苍山高温糜棱岩的显微构造与热年代学证据[J]. 地质学报, 83(10): 1388-1400. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.10.003 董树文, 吴锡浩, 吴珍汉, 等, 2000. 论东亚大陆的构造翘变: 燕山运动的全球意义[J]. 地质论评, 46(1): 8-13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.01.002 董树文, 张岳桥, 陈宣华, 等, 2008. 晚侏罗世东亚多向汇聚构造体系的形成与变形特征[J]. 地球学报, 29(3): 306-317. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.03.005 李建华, 2013. 华南中生代大地构造过程-源于北部大巴山和中部沅麻盆地、衡山的构造变形及年代学约束[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院. 李四光, 1973. 地质力学概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 梁瀚, 冉崎, 狄贵东, 等, 2019. 川西北地区双鱼石区块栖霞组膝折褶皱的发现及其油气意义[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 42(4): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT201904002.htm 林伟, 王军, 刘飞, 等, 2013. 华北克拉通及邻区晚中生代伸展构造及其动力学背景的讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 29(5): 1791-1810. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201305025.htm 聂童春, 朱根灵, 2004. 政和-大埔深(大)断裂带中段地质构造特征及其演化探讨[J]. 福建地质, 23(4): 186-194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2004.04.003 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等, 2009. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 36(1): 1-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200901004.htm 任纪舜, 1989. 中国东部及邻区大地构造演化的新见解[J]. 中国区域地质(4): 289-300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD198904000.htm 施罗克, 1955. 层状岩石的层序[M]. 翁文灏, 译. 北京: 地质出版社. 舒良树, 周新民, 2002. 中国东南部晚中生代构造作用[J]. 地质论评, 48(3): 249-260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.03.004 舒良树, 2012. 华南构造演化的基本特征[J]. 地质通报, 31(7): 1035-1053. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.07.003 万天丰, 朱鸿, 赵磊, 等, 1996. 郯庐断裂带的形成与演化: 综述[J]. 现代地质, 10(2): 159-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ602.002.htm 万天丰, 2013. 新编亚洲大地构造区划图[J]. 中国地质, 40(5): 1351-1365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.05.002 吴根耀, 2002. 燕山运动和中国大陆晚中生代的活化[J]. 地质科学, 37(4): 453-461. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.04.009 杨巍然, 王杰, 梁晓, 2012. 亚洲大地构造基本特征和演化规律[J]. 地学前缘, 19(5): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205003.htm 张长厚, 宋鸿林, 王根厚, 等, 2001. 燕山板内造山带中段近东西向中生代右行走滑构造系统[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 26(5): 464-472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200105005.htm 张国伟, 郭安林, 2019. 关于大陆构造研究的一些思考与讨论[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 44(5): 1464-1475. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201905005.htm 张宇, 施炜, 2018. 大陆逃逸构造研究现状[J]. 地质力学学报, 24(2): 145-156. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.02.016 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等, 2012. 华南中生代大地构造研究新进展[J]. 地球学报, 33(3): 257-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201203001.htm 张岳桥, 董树文, 2019. 晚中生代东亚多板块汇聚与大陆构造体系的发展[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(5): 613-641. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.05.059 郑亚东, 莫午零, 张文涛, 等, 2007. 柴达木盆地油气勘探新思路[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 34(1): 13-18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2007.01.003 郑亚东, 曾令森, 李健波, 等, 2009. 辽南中生代造山期缩短滑脱与晚造山伸展拆离构造[J]. 地质科学, 44(3): 811-824. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2009.03.003 周蒂, 孙珍, 陈汉宗, 等, 2005. 南海及其围区中生代岩相古地理和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 12(3): 204-218. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.022 朱光, 王道轩, 刘国生, 等, 2004. 郯庐断裂带的演化及其对西太平洋板块运动的响应[J]. 地质科学, 39(1): 36-49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.01.005 朱光, 王薇, 顾承串, 等, 2016. 郯庐断裂带晚中生代演化历史及其对华北克拉通破坏过程的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 32(4): 935-949. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201604001.htm 朱日祥, 徐义刚, 朱光, 等, 2012. 华北克拉通破坏[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 42(8): 1135-1159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201208002.htm 邹和平, 王建华, 丘元禧, 2000. 广东南澳和莲花山韧性剪切带40Ar/39Ar年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 21(4): 356-364. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.04.004 -





 下载:
下载: