STUDY OF DISASTER-INDUCING GEOLOGICAL CONDITIONS OF COLLAPSE AND LANDSLIDE ALONG LULANG-TONGMAI IN SE TIBET
-
摘要: 藏东南的喜马拉雅东构造结地区作为青藏高原隆升最快的地区之一,其复杂的地质背景条件决定了该区工程地质问题具有复杂性和特殊性,并孕育了多种地质灾害。利用测窗、节理裂隙分期配套等野外调查方法以及遥感影像解译,分析总结了藏东南地区鲁朗至通麦不同区段崩塌滑坡地质灾害的孕灾地质背景,据此将研究区划分为四段,分别为鲁朗-东久段、东久-拉月段、拉月-排龙段、排龙-通麦段,每一区段分别对应了不同的孕灾地质条件特征,由此也决定了区段内崩滑地质灾害的性质、变形破坏模式、规模。相关成果可用于藏东南崩塌滑坡地质灾害的早期识别和风险评价。Abstract: Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis, as one of the fastest uplifting region in Tibetan Plateau, its complex geological environment determines that the engineering geological problems have complexity and particularity and give birth to a variety of geo-hazards. Based on the survey results of the project "Geo-hazards investigation in main towns and major highways in SE Tibet", the geological conditions of landslides along Lulang-Tongmai were analyzed. According to the analysis, the study area could be divided into four sections, respectively, which are Lulang-Dongjiu section, Dongjiu-Layue section, Layue-Pailong section, Pailong-Tongmai section. Each section corresponds to different disaster-inducing geological conditions, which determines the nature, deformation and failure mode and scale of landslide in the section. The conclusion could be used in risk assessment and early identification of landslides in SE Tibet.
-
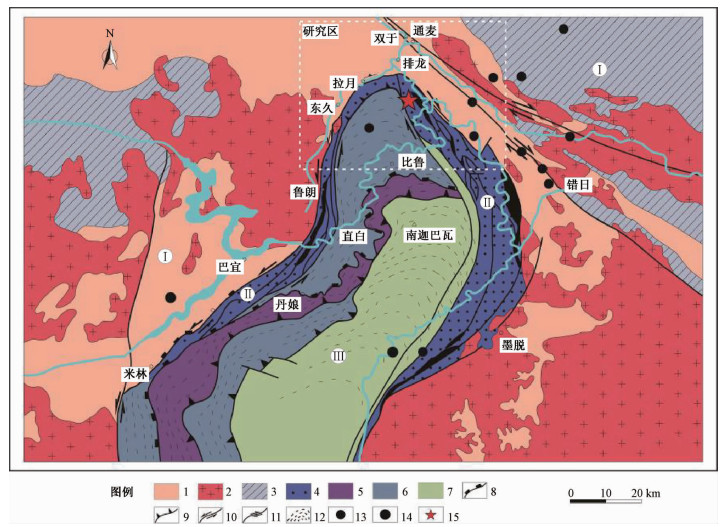
图 1 喜马拉雅东构造结区域地质、历史地震图[4]
Ⅰ—拉萨地体;Ⅱ—雅鲁藏布江缝合带;Ⅲ—喜马拉雅东构造结;1—念青唐古拉变质岩系;2—冈底斯花岗岩带;3—古生代岩石;4—雅鲁藏布江蛇绿混杂岩带;5—直白组高压麻粒相带;6—派乡组角闪岩相变质岩;7—多雄拉组混合岩化角闪岩相变质岩;8—拆离断裂;9—逆冲断裂;10—左行走滑断裂;11—右行走滑断裂;12—面理产状;13—里氏6.0~7.0级地震;14—大于里氏7.0级地震;15—11.18米林6.9级地震震中
Figure 1. Regional geology and historical earthquake distribution of Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis[4]
表 1 鲁朗—通麦崩滑地质灾害类型、孕灾地质条件对比
Table 1. Contrastive analysis of the geologic conditions and disaster-inducing features along Lulang-Tongmai
区段名称 崩滑灾害类型及规模 岩性组合 斜坡结构 变形破坏模式 鲁朗—东久段 小型土质滑坡 高陡边坡坡脚的坡积物 类均质土质斜坡 蠕滑—拉裂式 东久—拉月段 小型崩塌 节理裂隙发育的块状变质岩 类反向坡 倾倒、拉裂式 拉月—排龙段 大型—特大型岩质滑坡 节理裂隙发育的块状变质岩 类顺向坡 滑移—拉裂式 排龙—通麦段 小—中型崩塌 节理裂隙发育的块状变质岩 类横向坡 倾倒、拉裂式 -
[1] 尚彦军, 杨志法, 廖秋林, 等.雅鲁藏布江大拐弯北段地质灾害分布规律及防治对策[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2001, 12(4):30~40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdzzhyfzxb200104007SHANG Yanjun, YANG Zhifa, LIAO Qiulin, et al. Geological hazard distribution and prevention in North of Yalu Canyon, Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2001, 12(4):30~40. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdzzhyfzxb200104007 [2] 丁继新, 杨志法, 尚彦军.川藏公路然乌-鲁朗段泥石流灾害成因分析及定量化分区[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12(2):203~210, 226. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20060230&journal_id=dzlxxbDING Jixin, YANG Zhifa, SHANG Yanjun. Cause analysis and quantitative zonation of mudflow hazards along the Rawu-Lunang section, Sichuan-Tibet highway[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(2):203~210, 226. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20060230&journal_id=dzlxxb [3] 宋章, 张广泽, 蒋良文, 等.川藏铁路主要地质灾害特征及地质选线探析[J].铁道标准设计, 2016, 60(1):14~19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tdbzsj201601003SONG Zhang, ZHANG Guangze, JIANG Liangwen, et al. Analysis of the characteristics of major geological disasters and Geological alignment of Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2016, 60(1):14~19. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tdbzsj201601003 [4] 许志琴, 蔡志慧, 张泽明, 等.喜马拉雅东构造结——南迦巴瓦构造及组构运动学[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(7):1463~1476. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DGYK200603006.htmXU Zhiqin, CAI Zhihui, ZHANG Zeming, et al. Tectonics and fabric kinematics of the Namche Barwa terrane, Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(7):1463~1476. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/DGYK200603006.htm [5] 何易平, 胡凯衡, 韦方强, 等.川藏公路迫隆藏布流域段泥石流活动特征[J].水土保持学报, 2001, 15(3):76~80. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96166X/200103/5841132.htmlHE Yiping, HU Kaiheng, WEI Fangqiang, et al. Characteristics of debris flow in Polongzangbu basin of Sichuan-Tibet highway[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2001, 15(3):76~80. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96166X/200103/5841132.html [6] 程尊兰, 田金昌, 张正波, 等.西藏江河堵溃灾害及成灾环境分析[J].灾害学, 2009, 24(1):26~30.CHENG Zunlan, TIAN Jinchang, ZHANG Zhengbo, et al. Analysis on environment of disasters resulting from river blockage in Tibet[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2009, 24(1):26~30. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 张佳佳, 刘建康, 高波, 等.藏东南嘎龙曲冰川泥石流的物源特征及其对扎墨公路的影响[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(1):106~115. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.01.012ZHANG Jiajia, LIU Jiankang, GAO Bo, et al. Characteristics of material sources of Galongqu glacial debris flow and the influence to Zhamo road[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(1):106~115. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.01.012 [8] 蒋忠信.西藏帕隆藏布河谷崩塌滑坡、泥石流的分布规律[J].地理研究, 2002, 21(4):495~503.JIANG Zhongxin. Differential distribution regularity of collapse-landslides and debris flows along Palong Zangbu River Valley in Tibet[J]. Geographical Research, 2002, 21(4):495~503. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 中国科学院-水利部成都山地灾害与环境研究所, 西藏自治区交通厅科学研究所.西藏泥石流与环境[M].成都:成都科技大学出版社, 1999, 1~245.Chinese Academy of Sciences-Chengdu Institute of Mountain Disasters and Environment, Ministry of Water Resources, Institute of Science, Ministry of Communications, Tibet Autonomous Region. Debris flow and environment in Tibet[M]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Science and Technology University Press, 1999, 1~245. (in Chinese) [10] 中国科学院-水利部, 西藏交通科学研究院.川藏公路典型山地灾害研究[M].成都:成都科技大学出版社, 1999, 1~243.Chinese Academy of Sciences-Ministry of Water Resources, Tibet Institute of Transportation Science. Study on typical mountain hazards along Sichuan-Tibet highway[M]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Science and Technology University Press, 1999, 1~243. (in Chinese) [11] 廖秋林, 李晓, 尚彦军, 等.水岩作用对雅鲁藏布大拐弯北段滑坡的影响[J].水文地质工程地质, 2002, 29(5):19~21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdzgcdz200205006LIAO Qiulin, LI Xiao, SHANG Yanjun, et al. Effect of water-rock interaction on the slope in the north of the great turn of Yaluzangbu[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2002, 29(5):19~21. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdzgcdz200205006 [12] 丁林, 钟大赉.印度与欧亚板块碰撞以来东喜马拉雅构造结的演化[J].地质科学, 2013, 48(2):317~333. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e20b394d964bcf84b9d57b99.htmlDING Lin, ZHONG Dalai. The tectonic evolution of the eastern Himalaya syntaxis since the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2013, 48(2):317~333. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e20b394d964bcf84b9d57b99.html [13] 张永双, 郭长宝, 姚鑫, 等.青藏高原东缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究[J].地球学报, 2016, 37(3):277~286. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.03.03ZHANG Yongshuang, GUO Changbao, YAO Xin, et al. Research on the Geohazard effect of active fault on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2016, 37(3):277~286. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.03.03 [14] 唐方头, 宋键, 曹忠权, 等.最新GPS数据揭示的东构造结周边主要断裂带的运动特征[J].地球物理学报, 2010, 53(9):2119~2128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.09.012TANG Fangtou, SONG Jian, CAO Zhongquan, et al. The movement Characters of main faults around Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis revealed by the latest GPS data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(9):2119~2128. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.09.012 [15] 孔纪名.川藏公路拉月滑坡破坏过程模型试验研究[J].山地学报, 2003, 21(S1):133~138. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/SDYA200302014.htmKONG Jiming. The model test research of breakdown process of Layue landslide on the highway from Sichuan to Tibet[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2003, 21(S1):133~138. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/SDYA200302014.htm -





 下载:
下载: