STUDY ON QUATERNARY TECTONIC-SEDIMENTARY EVOLUTION OF LUJIAO AREA, EAST EDGE OF YUANJIANG SAG, DONGTING BASIN
-
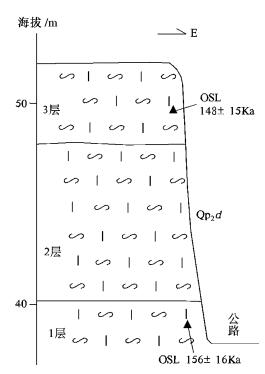
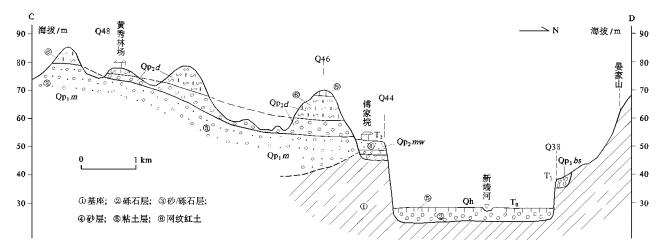
摘要: 沅江凹陷为第四纪洞庭盆地东部的一个次级凹陷。通过地表地质调查和钻孔资料,在沅江凹陷东缘北部鹿角地区第四纪构造、沉积及地貌特征研究基础上,探讨并提出其构造一沉积演化过程:早更新世早期洪湖一湘阴断裂和荣家湾断裂相继活动,断裂以西地区断陷沉降并沉积,以东地区则构造抬升而遭受风化剥蚀。早更新世末期凹陷区东部构造反转抬升并遭受侵蚀。中更新世早期和中期凹陷区断陷沉降并接受沉积。中更新世晚期研究区整体抬升而遭受剥蚀。晚更新世西部主凹陷区在稳定或弱沉降并形成泥质沉积,东部间歇性抬升。在上述中更新世晚期开始的构造抬升的同时,研究区东部产生了自东向西、自南向北的构造掀斜。全新世构造总体稳定,西部洞庭湖区形成湖冲积。区域上,第四纪洞庭盆地构造性质经历了早期断陷到晚期坳陷的转变。Abstract: Quaternary Yuanjiang sag is an eastern one of the secondary tectonic units of the Dongting basin. Detailed geologic mapping and bore data were taken to reveal the Quaternary tectonic, sedimentary and geomorphic characteristics and tectonic-sedimentary evolution of Lujiao area, northeast Yuanjiang sag. The Honghu-Xiangyin fault and Rongjiawan fault formed in succession during Early Pleistocene, which caused that the west walls of the faults subsided and received alluvial and lacustrine deposits, while the east walls rose and were denuded. Eastern area of the sag uplifted and was denuded in the end of Early Pleistocene. The sag subsided and received alluvial and lacustrine deposits during early-middle Middle Pleistocene. The study area rose as a whole and was denuded during late Middle Pleistocene. The western main depressional area was stable or subsided weakly and formed clay deposits in Late Pleistocene, when east area rose by fits. In the same time of above tectonic uplift since late Middle Pleistocene, east of the area tilted westward and northward. The area was under tectonic stable state in Holocene, forming alluvial-lacustrine deposits in western Dongting lake area.
-
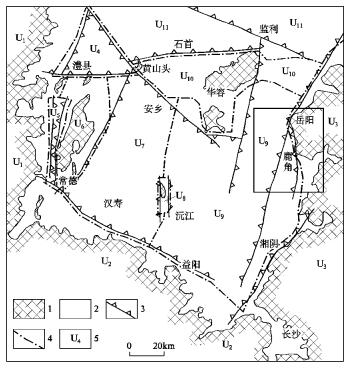
图 1 第四纪洞庭盆地构造格局
1.前第四纪地层出露区;2.第四纪地层出露区;3.第四纪正断裂,齿向示下降盘;4.构造单元分界线;5.构造单元代号。构造单元名称:U1-武陵隆起;U2-雪峰隆起;U3-幕阜山隆起;4-澧县凹陷;U5-临澧凹陷;U6-太阳山隆起;U7-安乡凹陷;U8-赤山隆起;U9-沅江凹陷;U10-华容隆起;U11-江汉盆地。方框示图 2范围
Figure 1. Tectonic framework map of Quaternary Dongting Basin
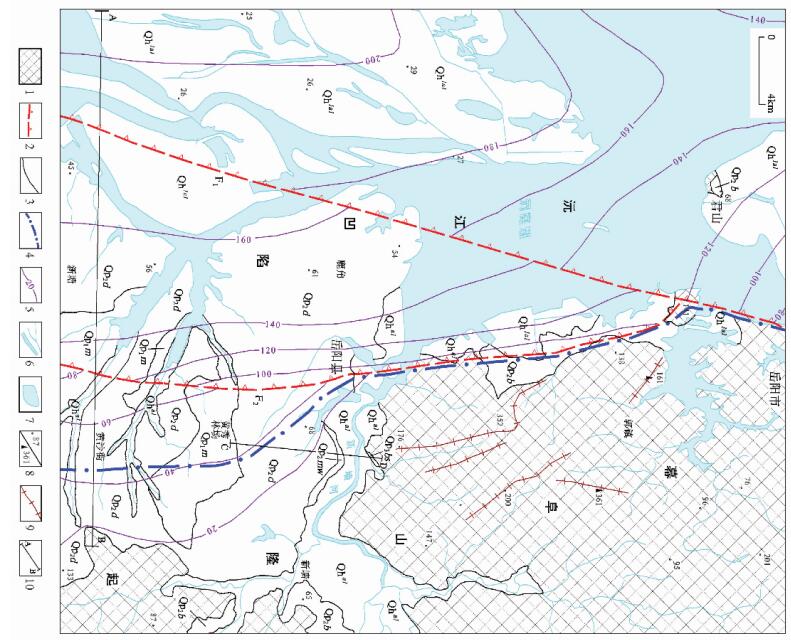
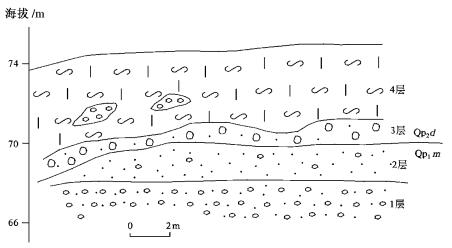
图 2 鹿角地区综合地质地貌图
1.前第四纪基岩;2.控盆控凹正断裂,齿向示下降盘;3.地质体界线;4.第四纪构造单元分界;5.第四纪沉积等厚线及厚度值;6.河流;7.湖泊水面;8.高程点与高程值/山峰与高程;9.山脊线;10.第四纪地质剖面位置,A-B对应图 3,C-D对应图 5。Qhal-全新世冲积;Qhlal-全新世湖冲积;Qp3bs-晚更新世白水江组;Qp2mw-中更新世马王堆组;Qp2b-中更新世白沙井组;Qp2d-中更新世洞庭湖组;Qp1m-早更新世汨罗组;F1-洪湖一湘阴断裂;F2-荣家湾断裂
Figure 2. Geological-geomorphologic sketch map of Lujiao area
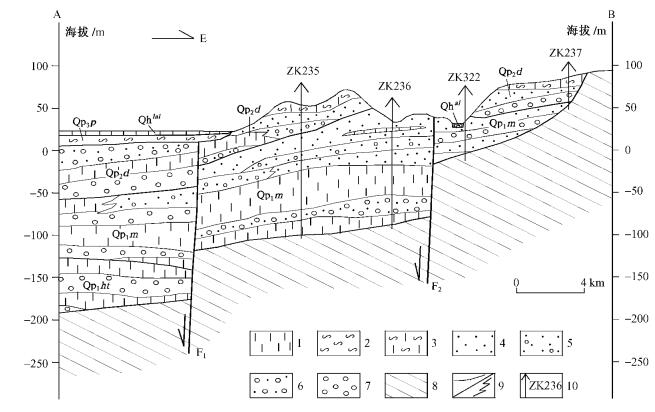
图 3 阳罗一黄沙街第四纪地质剖面(剖面位置见图 2中A—B剖面线)
1.粘土;2.淤泥;3.网纹红土;4.砂层;5.含砾砂层;6.砂砾层;7.砾石层;8.基座;9.地层单位界线/相变界线;10.钻孔位置及编号。Qhal全新世冲积;Qhlal-全新世湖冲积;Qp3bs-晚更新世白水江组;Qp2mw-中更新世马王堆组;Qp2b-中更新世白沙井组;Qp2d-中更新世洞庭湖组;Qp1m-早更新世汨罗组;F1-洪湖一湘阴断裂;F2-荣家湾断裂
Figure 3. Yangluo-Huangshajie Quaternary geological section (location is shown with A-B line in fig.2)
表 1 洞庭盆地及周缘第四纪地层划分对比表
Table 1. Subdivision and correlation of the Quaternary strata in Dongting basin and its adjacent areas

-
[1] 林承坤.洞庭湖的演变与治理(上)Ⅰ洞庭湖的沉积[J].地理学与国土研究, 1985, 1 (4): 28~35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1618213LIN Cheng-kun. Evolution of the Dongting lake and the way of management: I Sediments of the Dongting lake[J]. Geography and Territorial Research, 1985, 1 (4): 28~35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1618213 [2] 景存义.洞庭湖的形成与演变[J].南京师院学报自然科学版, 1982, (2): 52~60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stbcyj200102014JIN Cun-yi. Formation and evolution of the Dongting basin[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 1982, (2): 52~60. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stbcyj200102014 [3] 蔡述明, 官子和, 孔昭宸, 等.从岩相特征和孢粉组合探讨洞庭盆地第四纪自然环境的变迁[J].海洋与湖沼, 1984, 15 (6): 527~539.CAI Shu-ming, GUAN Zi-he, KONG Zhao-chen, et al. Natural environment as reflected in sedimentary Dongting basin in Quaternary[ J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1984, 15 (6): 527~539. [4] 杨达源.洞庭湖的演变及其整治[J].地理研究, 1986, 5 (3): 39~46. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10532-2007051213.htmYANG Da-yuan. On the evolution of the Dongting Lake during holocene and the way of management[J]. Geographical Research, 1986, 5 (3): 39~46. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10532-2007051213.htm [5] 张晓阳, 蔡明述, 孙顺才.全新世以来洞庭湖的演变[J].湖泊科学, 1994, 6 (1): 13~21. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10511-2009159420.htmZHANG Xiao-yang, CAI Shu-ming, SUN Shun-cai. Eevolution of Dongting Lake since Holocene[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 1994, 6 (1): 13~21. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10511-2009159420.htm [6] 皮建高, 张国梁, 梁杏, 等.洞庭盆地第四纪沉积环境演变的初步分析[J].地质科技情报, 2001, 20 (2): 6~10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.02.002PI Jian-gao, ZHANG Guo-liang, LIANG Xing, et al. Preliminary research on sedimentary environment evolution Dongting Basin in the Quaternary period[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2001, 20 (2): 6~10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2001.02.002 [7] 杜耘, 殷鸿福.洞庭湖历史时期环境研究[J].地球科学--中国地质大学学报, 2003, 28 (2): 214~218. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200302017DU Yun, YIN Hong-fu. Study on historical environment in Dongting Lake area[J]. Earth Science一Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2003, 28 (2): 214~218. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200302017 [8] 来红州, 莫多闻, 李新坡.洞庭盆地第四纪红土层及古气候研究[J].沉积学报, 2005, 23 (1): 130~137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.017LAI Hong-zhou, MO Duo-wen, LI Xin-po. Research on the Quaternary laterite and paleoclimate in the Dongting Basin[J]. Acta sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23 (1) : 130~137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.017 [9] 林承坤.洞庭湖的演变与治理(下): Ⅱ洞庭湖的演变及治理设想[J].地理学与国土研究, 1986, 2 (1): 40~46. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1533512LIN Cheng-kun. Evolution of the Dongting lake and the way of management : Ⅱ Evolution of the Dongting lake and proposal about the way of management[J]. Geography and Territorial Research, 1986, 2 (1): 40~46. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1533512 [10] 刘锁旺, 甘家思, 李蓉川, 等.江汉洞庭盆地的非对称扩张与潜在地震危险性[J].地壳形变与地震, 1994, 14 (2): 56~66.LIU Suo-wang, GAN Jia-si, LI Rong-chuan, et al. Asymmetric extension and hidden earthquake risk in Jianghan-Dongting basin (JDB)[J]. Crustal Deformation and Earthquake, 1994, 14 (2): 56~66. [11] 薛宏交, 耿爱玲, 龚平.江汉洞庭盆地水系展布特征与新构造运动[J].地壳形变与地震, 1996, 16 (4): 58~65.XUE Hong-jiao, GEN Ai-lin, GONG Ping. Extension characteristics of river system and neotectonic movement in the Jianghan- Dongting basin[J]. Crustal Deformation and Earthquake, 1996, 16 (4): 58~65. [12] 李春初.构造沉降是控制近代洞庭湖演变的关键因素吗?一一评《洞庭湖地质环境系统分析》[J].海洋与湖沼, 2000, 31 (4) : 460~464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.04.019LI Chun-chu. Tectonic subsidence in relation to modern Dongting Lake evolution : review on " Dongting Lake geology environmental system analysis"[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2000, 31 (4): 460~464. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.04.019 [13] 王道经, 黄怀勇.洞庭湖现代构造与湖盆演变[J].湖南地质, 2000, 19 (1): 30~36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1209433WANG Dao-jing, HUANG Huai-yong. Dongtinghu modern tectonics and its basin evolution[J]. Hunan Geology, 2000, 19 (1): 30~36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1209433 [14] 梁杏, 张人权, 皮建高, 等.洞庭盆地第四纪构造活动特征[J].地质科技情报, 2001, 20 (2): 11~14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200102003LIANG Xing, ZHANG Ren-quan, PI Jian-gao, et al. Characteristics of tectonic movement of Dongting basin in the Quaternary period [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2001, 20 (2): 11~14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200102003 [15] 梁杏, 张人权, 皮建高, 等.构造沉降对近代洞庭湖区演变的贡献[J].海洋与湖沼, 2001, 32 (6): 690~696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.06.016LIANG Xing, ZHANG Ren-quan, PI Jian-gao, et al. Contributions of tectonic subsidence to the modern Dongting lake area evolution [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2001, 32 (6): 690~696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2001.06.016 [16] 苏成, 莫多闻, 王辉.洞庭湖的形成、演变与洪涝灾害[J].水土保持研究, 2001, 8 (2): 52~55, 87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2001.02.014SU Cheng, MO Duo-wen, WANG Hui. Evolution of Lake Dongting and its flood disasters[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2001, 8 (2): 52~55, 87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3409.2001.02.014 [17] 来红州, 莫多闻.构造沉降和泥沙淤积对洞庭湖区防洪的影响[J].地理学报, 2004, 59 (4): 574~580. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.04.011LAI Hong-zhou, MO Duo-wen. Influences of the tectonic subsidence and the siltationon flood disaster prevention situation in the region of Dongting Lake [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2004, 59 (4): 574~580. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.04.011 [18] 来红州, 莫多闻, 李新坡.洞庭盆地红土地层中网纹的成因探讨[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 41 (2) 240~248. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2005.02.010LAI Hong-zhou, MO Duo-wen, LI Xin-po. Genesis of reticulate clay in the laterite of the Dongting basin[ J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2005, 41 (2) : 240~248. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2005.02.010 [19] 蒋复初, 吴锡浩, 肖华国, 等.九江地区网纹红土的时代[J].地质力学学报, 1997, 3 (4): 27~32. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19970443&journal_id=dzlxxbJIANG Fu-chu, WU Xi-hao, XIAO Hua-guo, et al. Age of the vermiculated red soil in Jiujiang area, central China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1997, 3 (4): 27~32. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19970443&journal_id=dzlxxb [20] 乔彦松, 郭正堂, 郝青振, 等.皖南风尘堆积一土壤序列的磁性地层学研究及其古环境意义[J].科学通报, 2003, 48 (13): 1465~1469. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.13.022QIAO Yan-song, GUO Zhen-tang, HAO Qing-zhen, et al. Magnetostratigraphy studies on the eolian deposits-soil chronosequence in south Anhui and its paleoenvironmental significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48 (13): 1465~1469. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.13.022 [21] 杨浩, 赵其国, 李小平, 等.安徽宣城风成沉积一红土系列剖面ESR年代学研究[J].土壤学报, 1996, 33 (3): 293~300. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.1996.03.009YASG Hao, ZHAO Qi-guo, LI Xiao-ping, et al. ESR dating of eolian sediment and red earth series from Xuancheng profile in Anhui Province[J]. Acta PedologicaSinica, 1996, 33 (3): 293~300. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.1996.03.009 [22] 赵志中, 乔彦松, 王燕, 等.成都平原红土堆积的磁性地层学及古环境记录[J].中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 2007, 37 (3): 370~377. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200703010ZHAO Zhi-zhong, QIAO yan-song, WASG Yan, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and records of paleoenvironment of the Red Earth Formation in the Chendu Plain[J]. Science in China (Series D), 2007, 37 (3): 370~377. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200703010 [23] 尹秋珍, 郭正堂.中国南方的网纹红土与东亚季风的异常强盛期[J].科学通报, 2006, 51 (2): 186~193. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.02.012YIN Qiu-zhen, GUO Zhen-tang. Vermicular red earth in South China and abnormal puissant period of East Asia monsoon[J]. Chinese Scienc Bulletin, 2006, 51 (2): 186~193. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.02.012 -





 下载:
下载: