Using historical aerial images to accurately locate the urban "invisible" active faults: A case study of the Shuiyu fault of the Datong Basin in Shanxi province
-
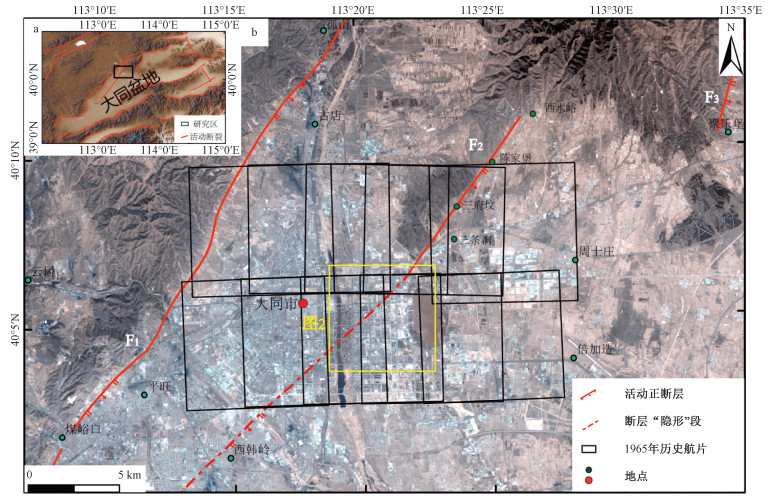
摘要: 活动断层是城市地震灾害的重要风险源,准确厘定活动断层的空间几何展布是有效降低城市地震灾害和开展活动断层避让的基础。而城市化建设对原始地貌的严重改造使得原先出露地表的活动断层成为"隐形"断层,难以准确确定断层的几何展布。大同盆地中部的水峪断裂北段位于马铺山东缘,断错地貌明显,但南段进入大同市御东新区被城市建筑物覆盖,成为"隐形"断层。研究基于大同地区1965年历史航片影像资料,结合1∶10000地形图,运用航片像对和航空立体摄影的方法重建了该地区的数字高程模型(DEM)和正射影像(DOM),重点对水峪断裂"隐形"段进行识别和定位,厘定了水峪断裂断层陡坎的几何展布特征。研究结果表明,水峪断裂北段山前陡坎线性特征明显,由影像可以准确解译出断层几何展布位置;水峪断裂南段可基于2000年之前的Keyhole历史遥感影像、DOM与DEM资料,根据断层两侧的颜色差异及陡坎高度差异,精确厘定该段的断层几何展布位置;DEM提取的地形剖面表明"隐形"段陡坎高度在19 m左右。同时,基于野外调查的断层剖面与浅层人工地震剖面证明该陡坎就是水峪断裂的位置,这也表明利用历史航卫片对城市"隐形"活动断层进行精确定位的方法是可行的。该研究不仅为大同地区的地震危险性评估提供了重要依据,而且为城市"隐形"活动断层探测提供了一个新的思路和途径。Abstract: Active fault is a major risk source of urban earthquake disaster. Accurately identifying the spatial geometry distribution features of active fault is the basis for urban seismic risk migration. However, due to the large-scale and deep urban renewal by human activities and urbanization, the traces of active faults are obscure and invisible on the surface, which makes it hard to identify the surface geometry of this kind of active faults. Though the northern Shuiyu fault in the central part of the Datong Basin is bounded by the eastern edge of the Mapu Mountain and characterized by linear displaced landforms, the southern section of the Shuiyu fault crossing the Yudong District of Datong City is covered by dense buildings and roads, becoming an "invisible" fault. In this study, based on the 1965 historical aerial photos of the Datong region in the 1960's and the 1∶10000 topographic maps, we reconstructed the original DEM and DOM of this region using the aerial photo stereopair and stereoscopic photography. These original data revealed the geometry distribution characteristics of the Shuiyu fault. Our results show that the piedmont fault scarps are marked by prominent linear features along the northern Shuiyu fault. We can accurately locate the fault by the images. Based on the previous Keyhole satellite images, DOM and DEM data, the geometric distribution of the fault in the southern Shuiyu fault can be accurately determined. Topographic profiles extracted from the original DEM show that the vertical offset on terrace T3 along the Shuiyu fault is about 19 meters. On this basis, the fault natural exposures and shallow seismic reflection data demonstrate that it is feasible to accurately locate the "invisible" active fault in the city by using historical aerial photos and stereoscopic photography. This study provides not only an important basis for the seismic hazard assessment in the Datong region but a useful technique for the detection of "invisible" active faults beneath a city.
-
图 4 大同水峪断裂历史影像
a—2020年Google earth影像(黄色虚实线为水峪断裂);b—1985年美国锁眼(Keyhole)卫星影像;c—1965年历史航片正射影像(DOM);d—1965年历史航片数字高程模型(DEM;红色箭头指示断层陡坎位置)
Figure 4. Historical images of the Shuiyu fault. (a)Google earth image of 2020. (b) Keyhole satellite image of 1985. (c) DOM data of 1965. (d) DEM data of 1965
The yellow pseudo-solid line is the Shuiyu fault, and the red arrows indicate the position of the fault scarps
图 7 跨水峪断裂的浅层人工地震探测剖面(位置见图 6b)
FPk8, FPk20—断层点;TN,Tg—地震波反射界面
a—KL2测线;b—KL1测线Figure 7. Shallow seismic reflection profiles across the Shuiyu fault (The sites are shown in Fig. 6.)
(a) Surveyline KL2. (b) Surveyline KL1
FPk8 and FPk20 are the fault points; TN, Tg are the reflection interfaces of seismic waves -
DENG Q D, 1991. Research on active fault[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) DENG Q D, NOBUYUKI Y, XU X W, et al., 1994. Study on the late Quaternary kinematics of the northern piedmont fault of the Liuleng Mountain[J]. Seismology and Geology, 16(4): 339-343. (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ404.006.htm DENG Q D, XU X W, ZHANG X K, et al., 2003. Methods and techniques for surveying and prospecting active faults in urban areas[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(1): 93-104. (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200301019.htm DENG Q D, CHEN L C, RAN Y K, 2004. Quantitative studies and applications of active tectonics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(4): 383-392. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/304335743_Quantitative_studies_and_applications_of_active_tectonics DENG Q D, LU Z X, YANG Z E, 2007. Remarks on urban active faults exploration and associated activity assessment[J]. Seismology and Geology, 29(2): 189-200. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/292658777_Remarks_on_urban_active_faults_exploration_and_associated_activity_assessment DENG Q D, WEN X Z, 2008. A review on the research of active tectonics-history, progress and suggestions[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(1): 1-30. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZDZW200901002.htm DUAN R T, FANG Z J, 1995. Neotectonic characteristics of the northern piedmont fault of the Liuleng mountain[J]. Seismology and Geology, 17(3): 207-213. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10024498661/ FANG S M, ZHANG X K, LIU B J, et al. 2002. Geophysical methods for the exporation of urban active faults[J]. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 606-613. (in Chinese) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/289973418_Geophysical_methods_for_the_exporation_of_urban_active_faults FENG X Y, 1986. On seismic geomorphology[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 4(8): 66-71. (in Chinese) FENG X Y, 1991. Earthquake dislocation geomorphy[J]. Inland Earthquake, 5(1): 17-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-LLDZ199101002.htm FRANKEL K L, DOLAN J F, 2007. Characterizing arid region alluvial fan surface roughness with airborne laser swath mapping digital topographic data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 112(F2): F02025. doi: 10.1029/2006JF000644/full GUAN Y X, LU J T, HE T J, et al., 2016. The application of CSAMT exploration to detecting buried faults in city[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 37(1): 90-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201601021.htm HOOPER D M, BURSIK M I, WEBB F H, 2003. Application of high-resolution, interferometric DEMs to geomorphic studies of fault scarps, Fish Lake Valley, Nevada-California, USA[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 84(2): 255-267. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00110-4 JIANG W L, XIE X S, WANG H Z, et al., 2003. Holocene palaeoseismic activities along the northern piedmont fault of Hengshan mountain, Datong basin, Shanxi province[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 19(1): 8-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGZD200301001.htm LEI Q Y, CHAI C Z, MENG G K, et al., 2011. Method of locating buried active fault by composite drilling section doubling exploration[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(1): 45-55. (in Chinese) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/289945007_Method_of_locating_buried_active_fault_by_composite_drilling_section_doubling_exploration LI J H, SONG F M, LIANG X H, et al., 1998. Evaluation of active fault in the engineering site area for Datong power plant 2[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 6(1): 79-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GCDZ801.008.htm LI Y H, WANG Q L, CUI D X, et al., 2013. Research on fault motion and segmentation charateristic of Kouquan fault in Datong basin by numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 33(4): 9-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/302971107_Research_on_fault_motion_and_segmentation_characteristic_of_Kouquan_Fault_in_Datong_Basin_by_numerical_simulation LIU B J, CHAI C Z, FENG S Y, et al., 2008. Seismic exploration method for buried fault and its up-breakpoint in Quaternary sediment area-an example of Yinchuan buried active fault[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(5): 1475-1483. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.oalib.com/paper/1569358 MICHELETTI N, LANE S N, CHANDLER J H, 2015. Application of archival aerial photogrammetry to quantify climate forcing of alpine landscapes[J]. The Photogrammetric Record, 30(150): 143-165. doi: 10.1111/phor.12099 OSKIN M E, LE K, STRANE M D, 2007. Quantifying fault-zone activity in arid environments with high-resolution topography[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(23): L23S05. doi: 10.1029/2007GL031295/full PARSONS T, 2007. Persistent earthquake clusters and gaps from slip on irregular faults[J]. Nature Geoscience, 1(1): 59-63. http://www.nature.com/articles/ngeo.2007.36 SIEH K E, JAHNS R H, 1984. Holocene activity of the San Andreas fault at Wallace Creek, California[J]. GSA Bulletin, 95(8): 883-896. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1984)95<883:HAOTSA>2.0.CO;2 WANG S S, AI M, WU C Y, et al., 2018. Application of DEM generation technology from high resolution satellite image in quantitative active tectonics study: a case study of fault scarps in the southern margin of Kumishi basin[J]. Seismology and Geology, 40(5): 999-1017. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_seismology-geology_thesis/0201270242403.html WU J B, GAO P F, W J H, et al., 2019. Application of integrated geophysical methods to the detection of buried faults in Liuzhou, Guangxi[J]. Geology and Exploration, 55(4): 1026-1035. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZKT201904012.htm XIE X S, JIANG W L, WANG R, et al., 2003. Holocene paleo-seismic activities on the Kouquan fault zone, Datong basin, Shanxi province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 25(3): 359-374. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200303001.htm XU W M, CHEN X, WANG L, 2012. Technology and methods of historical aerial photo data processing[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying(6): 93-95, 102. (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CSKC201206027.htm XU X W, YU G H, MA W T, et al., 2002. Evidence and methods for determining the safety distance from the potential earthquake surface rupture on active fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 470-483. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZDZ200204001.htm XU X W, 2006. Active faults, associated earthquake disaster distribution and policy for disaster reduction[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 1(1): 7-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZZFY200601001.htm YAN R H, LI J W, ZHU W, et al., 2004. Preliminary research on the digitalization and database construction of historical aerophotograph[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 19(2): 102-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=YGJS200402007&dbcode=CJFD&year=2004&dflag=pdfdown YANG H B, YANG X P, HUANG X N, et al., 2016. Data comparative analysis between SFM data and DGPS data: a case study from fault scarp in the east bank of Hongshuiba river, northern margin of the Qilian shan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(4): 1030-1046. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313597914_Data_comparative_analysis_between_SfM_data_and_DGPS_data_A_case_study_from_fault_scarp_in_the_east_bank_of_Hongshuiba_River_northern_margin_of_the_Qilian_Shan YIN Y G, SHI W, GONG W B, et al., 2017. The application of ground penetrating radar technology in geological mapping of shallow covered active tectonics region: a case study of 1: 50000 mapping of neotectonic zone and active tectonic zone in Qing Tongxia area, Ningxia[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(2): 214-223. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201702005.htm ZHANG D, LI J C, WU Z H, et al., 2021. Using terrestrial LiDAR to accurately measure the microgeomorphologic geometry of active fault: A case study of fault scarp on the Maoyaba fault zone[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(1): 63-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/350159033_Using_terrestrial_LiDAR_to_accurately_measure_the_microgeomorphologic_geometry_of_active_fault_A_case_study_of_fault_scarp_on_the_Maoyaba_fault_zone ZHANG D, WU Z H, LI J C, et al, 2019. The application of multi-frequency GPR antenna for imaging the shallow subsurface features in the Yushu active fault[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6): 1138-1149. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/350324240_THE_APPLICATION_OF_MULTI-FREQUENCY_GPR_ANTENNA_FOR_IMAGING_THE_SHALLOW_SUBSURFACE_FEATURES_IN_THE_YUSHU_ACTIVE_FAULT/download ZHANG L, BAI L Y, CAI X M, et al., 2014. Study on the position of north west section of Nankou-Sunhe fault in Beijing and its activity[J]. Geoscience, 28(1): 234-242. (in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/xddz201401027 ZHANG S M, WANG D D, LIU X D, et al., 2008. Using borehole core analysis to reveal Late Quaternary paleoearthquakes along the Nankou-Sunhe Fault, Beijing[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 38(7): 881-895. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=29096125 ZIELKE O, ARROWSMITH J R, LUDWIG L G, et al., 2010. Slip in the 1857 and Earlier Large Earthquakes Along the Carrizo Plain, San Andreas Fault[J]. Science, 327(5969): 1119-1122. doi: 10.1126/science.1182781 ZIELKE O, KLINGER Y, ARROWSMITH J R, 2015. Fault slip and earthquake recurrence along strike-slip faults: Contributions of high-resolution geomorphic data[J]. Tectonophysics, 638: 43-62. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.11.004 ZOU X B, YUAN D Y, SHAO Y X, et al., 2017. Using stereo-pair and differential GPS to reveal surface deformation characteristics of the Minle-Yongchang fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(6): 1198-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/327514441_Using_stereo-pair_and_differential_GPS_to_reveal_surface_deformation_characteristics_of_the_Minle-Yongchang_fault 邓起东, 1991. 活动断裂研究[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. 邓起东, 米仓伸之, 徐锡伟, 等, 1994. 山西高原六棱山北麓断裂晚第四纪运动学特征初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 16(4): 339-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ404.006.htm 邓起东, 徐锡伟, 张先康, 等, 2003. 城市活动断裂探测的方法和技术[J]. 地学前缘, 10(1): 93-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200301019.htm 邓起东, 陈立春, 冉勇康, 2004. 活动构造定量研究与应用[J]. 地学前缘, 11(4): 383-392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200404006.htm 邓起东, 卢造勋, 杨主恩, 2007. 城市活动断层探测和断层活动性评价问题[J]. 地震地质, 29(2): 189-200. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200702000.htm 邓起东, 闻学泽, 2008. 活动构造研究: 历史、进展与建议[J]. 地震地质, 30(1): 1-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200801002.htm 段瑞涛, 方仲景, 1995. 六棱山北麓断裂新活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 17(3): 207-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ503.002.htm 方盛明, 张先康, 刘保金, 等, 2002. 探测大城市活断层的地球物理方法[J]. 地震地质, 24(4): 606-613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200204016.htm 冯先岳, 1986. 论地震地貌[J]. 华北地震科学, 4(8): 66-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDKD198603007.htm 冯先岳, 1991. 地震断错地貌[J]. 内陆地震, 5(1): 17-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LLDZ199101002.htm 关艺晓, 卢进添, 何泰健, 等, 2016. 可控音频大地电磁测深在城市隐伏断层探测中的应用[J]. 上海国土资源, 37(1): 90-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201601021.htm 江娃利, 谢新生, 王焕贞, 等, 2003. 山西大同盆地恒山北缘断裂全新世古地震活动[J]. 中国地震, 19(1): 8-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD200301001.htm 雷启云, 柴炽章, 孟广魁, 等, 2011. 隐伏活断层钻孔联合剖面对折定位方法[J]. 地震地质, 33(1): 45-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201101007.htm 李建华, 宋方敏, 梁小华, 等, 1998. 大同二电厂扩建厂址工程区活动构造评价[J]. 工程地质学报, 6(1): 79-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ801.008.htm 李煜航, 王庆良, 崔笃信, 等, 2013. 大同盆地口泉断裂的活动性及分段特征的数值模拟[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 33(4): 9-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201304003.htm 刘保金, 柴炽章, 酆少英, 等, 2008. 第四纪沉积区断层及其上断点探测的地震方法技术: 以银川隐伏活动断层为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1475-1483. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200805022.htm 汪思抒, 艾明, 吴传勇, 等, 2018. 高分辨率卫星影像提取DEM技术在活动构造定量研究中的应用: 以库米什盆地南缘断裂陡坎为例[J]. 地震地质, 40(5): 999-1017. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201805005.htm 吴教兵, 高鹏飞, 陆俊宏, 等, 2019. 综合物探方法在广西柳州隐伏断裂探测中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 55(4): 1026-1035. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201904012.htm 谢新生, 江娃利, 王瑞, 等, 2003. 山西大同盆地口泉断裂全新世古地震活动[J]. 地震地质, 25(3): 359-374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200303001.htm 徐卫民, 陈香, 王琳, 2012. 历史航片数据处理技术及方法探讨[J]. 城市勘测(6): 93-95, 102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSKC201206027.htm 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 马文涛, 等, 2002. 活断层地震地表破裂"避让带"宽度确定的依据与方法[J]. 地震地质24(4): 470-483. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200204001.htm 徐锡伟, 2006. 活动断层、地震灾害与减灾对策问题[J]. 震灾防御技术, 1(1): 7-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZFY200601001.htm 严荣华, 李京伟, 朱武, 等, 2004. 历史航空影像数字化与建库技术初探[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 19(2): 102-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGJS200402007.htm 杨海波, 杨晓平, 黄雄南, 等, 2016. 移动摄影测量数据与差分GPS数据的对比分析: 以祁连山北麓洪水坝河东岸断层陡坎为例[J]. 地震地质, 38(4): 1030-1046. 尹艳广, 施炜, 公王斌, 等, 2017. 地质雷达探测技术在浅覆盖活动构造区填图中的应用: 以宁夏青铜峡地区1: 5万新构造与活动构造区填图为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 23(2): 214-223. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20170204&journal_id=dzlxxb 张迪, 李家存, 吴中海, 等, 2021. 利用地面LiDAR精细化测量活断层微地貌形态: 以毛垭坝断裂禾尼处断层崖为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(1): 63-72. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20210107&journal_id=dzlxxb 张迪, 吴中海, 李家存, 等, 2019. 综合多频率地质雷达天线探测活断层浅层结构: 以玉树活动断裂为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(6): 1138-1149. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190615&journal_id=dzlxxb 张磊, 白凌燕, 蔡向民, 等, 2014. 北京南口-孙河断裂北西段综合物探剖面定位及其活动性研究[J]. 现代地质, 28(1): 234-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201401027.htm 张世民, 王丹丹, 刘旭东, 等, 2008. 北京南口-孙河断裂晚第四纪古地震事件的钻孔剖面对比与分析[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 38(7): 881-895. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200807010.htm 邹小波, 袁道阳, 邵延秀, 等, 2017. 采用立体像对和差分GPS揭示民乐-永昌隐伏断裂地表变形特征[J]. 地震地质, 39(6): 1198-1212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201706008.htm -





 下载:
下载: