Geologic characteristics of the Naqiong Sb-Au deposit and prospecting prediction for Au-polymetallic deposits in Longzi County, Tibet
-
摘要: 那穷锑金矿是近年来通过区域地质矿产调查在西藏自治区隆子县新发现的金多金属矿床,其矿化带受断裂构造控制。目前该矿床研究程度相对较低,若对其成矿地质条件、地质特征及找矿潜力等内容进行专门性和系统性研究,可为该矿床的下步找矿勘探工作提供依据。文章通过总结区域成矿地质背景,分析了该矿床地质特征、地球物理与地球化学异常特征、包裹体地球化学特征,并结合遥感地质特征和异常查证开展相关研究工作,结果表明:矿体主要产于上三叠统涅如组中,受东西向次级断裂构造带控制,目前共发现3条破碎蚀变带;土壤地球化学剖面测量工作中,选择了Sb、Au、As、Bi、Cu作为Sb及多金属成矿指示元素,共圈定单元素异常10处,各元素异常套合较好;激电中梯测量共圈定极化体2条,视极化率异常3处;与成矿有关的流体包裹体类型主要为富液包裹体,并推测矿区流体为含微量CO2、N2气体的中低温低盐度NaCl-H2O热液体系。综合分析认为那穷锑金矿区具备优越的成矿条件,具有寻找金多金属矿的潜力。
-
关键词:
- 那穷锑金矿 /
- 地球化学和地球物理特征 /
- 地质特征 /
- 找矿前景分析 /
- 西藏
Abstract: The Naqiong Sb-Au deposit is a newly discovered Au-polymetallic deposit in Longzi county, Tibet. Recent years of regional geological surveys reveal that its mineralized zone is controlled by fault structure. In view of the relatively low research degree of this deposit, specialized and systematic research on its metallogenic geologic conditions, geologic characteristics and prospecting potentials will lay a foundation for further prospecting and exploration work of this deposit. The geologic characteristics, geophysical and geochemical anomaly characteristics, and inclusion geochemical characteristics are analyzed based on the regional metallogenic geological background. The analysis results in combination with the remote sensing geologic characteristics and anomaly verification work show that the ore bodies mainly occur in the Nieru formation of the upper Triassic and are controlled by the EW-trending secondary fault structural belt. Three fractured alteration zones have been found. Through the soil geochemical profile survey, Sb, Au, As, Bi and Cu are selected as the indicator elements for Sb and polymetallic mineralization. Altogether there are ten single element anomalies, showing good match with each other. Two polarization bodies and three apparent polarizability anomalies are defined by induced polarization intermediate gradient measurement. The fluid inclusions related to mineralization are mainly liquid-rich inclusions. It is inferred that the fluid in the mining area belongs to a medium-low temperature and low salinity NaCl-H2O hydrothermal system containing traces of CO2 and N2. Overall, the available data support the notion that the Naqiong Sb-Au mining area has superior metallogenic conditions for Au-polymetallic deposits. -
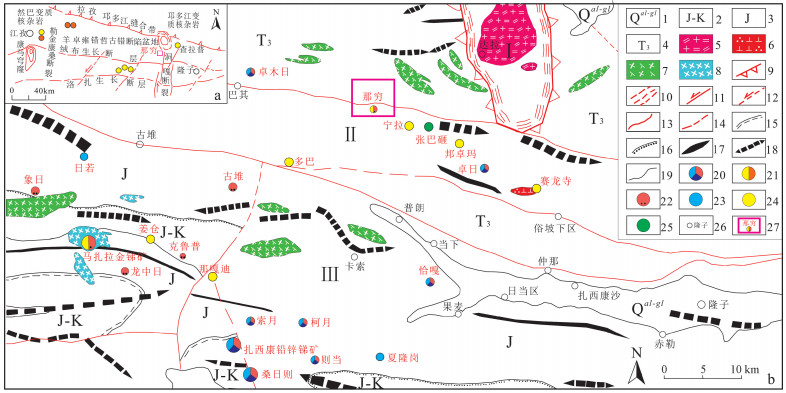
图 1 西藏古堆-隆子地区区域构造纲要及矿产分布图(据娄元林等,2019;许云鹏,2021修改)
1—第四纪冲积、冰积堆积;2—侏罗纪-白垩纪滨浅海碎屑岩建造,含火山碎屑岩建造;3—侏罗纪海相碎屑岩建造,含火山碎屑岩建造、碳酸盐岩建造;4—晚三叠世海相碎屑岩建造,含火山碎屑岩建造;5—中新世二云二长花岗岩;6—始新世石英闪长岩;7—晚白垩世辉绿玢岩;8—未分岩脉;9—伸展剥离断层;10—韧性剪切带;11—实测平推断层;12—推测平推断层;13—实测断层线;14—推测断层线;15—平行不整合界线;16—角度不整合界线;17—背斜轴线;18—向斜轴线;19—地质界线;20—典型锑铅锌矿;21—典型锑金矿;22—典型锑矿;23—典型锌矿;24—典型金矿;25—典型铜矿;26—地名;27—那穷锑金矿及矿区范围;Ⅰ—雅拉香波变质核杂岩;Ⅱ—卓木日-俗坡下逆冲推覆带;Ⅲ—甲坞-多日褶皱冲断带
a—古堆-隆子地区大地构造略图;b—那穷锑金矿周边矿产分布图Figure 1. Regional tectonics and mine distribution in the Gudui-Longzi area, Tibet (modified from Lou et al., 2019; Xu, 2021)
(a) Sketch map showing the tectonic units in the Gudui-Longzi area; (b) Distribution of mines in the Naqiong Sb-Au deposit and surrounding areas
1-Quaternary alluvial-glacial accumulation; 2-Jurassic-Cretaceous littoral and shallow sea clastic rock formation, volcanic clastic rock formation; 3-Jurassic marine clastic rock formation, volcanic clastic rock formation, carbonate rock formation; 4-Late Triassic marine clastic rock formation, volcanic clastic rock formation; 5-Miocene Ermo-feldspar granite; 6-Eocene quartz diorite; 7-Late Cretaceous diabase porphyrite; 8-Undetermined dikes; 9-Extensional detachment fault; 10-Ductile shear zone; 11-Measured transcurrent fault; 12-Inferred transcurrent fault; 13-Measured fault line; 14-Inferred fault line; 15-Parallel unconformity boundary; 16-Angular unconformity boundary; 17-Anticline axis; 18-Syncline axis; 19-Geologic boundary; 20-Typical Sb-Pn-Zn deposit; 21-Typical Sb-Au deposit; 22-Typical Sb deposit; 23-Typical Zn deposit; 24-Typical Au deposit; 25-Typical Cu deposit; 26-Place names; 27-The Naqiong Sb-Au deposit and its mining areas; Ⅰ-Yalashangbo metamorphic core complex; Ⅱ-Zhuomuri-Supoxia thrust nappe belt; Ⅲ-Jiawu-Duori fold and thrust belt图 2 那穷锑金矿综合地质图
1—第四系;2—上三叠统涅如组第三段;3—上三叠统涅如组第二段;4—上三叠统涅如组第一段;5—辉绿岩;6—玄武安山岩;7—地质界线;8—断层及编号;9—视极化率异常及编号;10—1:50000水系沉积物测量金异常及编号;11—1:50000水系沉积物测量锑异常及编号;12—土壤地球化学剖面测量金异常及编号;13—土壤地球化学剖面测量砷异常及编号;14—土壤地球化学剖面测量锑异常及编号;15—土壤地球化学剖面测量铋异常及编号;16—土壤地球化学剖面测量银异常及编号;17—土壤地球化学剖面测量铜异常及编号;18—破碎蚀变带及编号;19—探槽及编号;20—金品位/厚度;21—激电中梯剖面测量测线及编号
Figure 2. A generalized geological map of the Naqiong Sb-Au deposit
1-Quaternary; 2-The third member of the Upper Triassic Nieru Formation; 3-The sccond member of the Triassic Nieru Formation; 4-The first member of the Upper Triassic Nieru Formation; 5-Diabase; 6-Basaltic andesite; 7-Geologic boundary; 8-Fault and number; 9-Apparent polarizability anomaly and number of geophysical prospecting; 10-Au anomaly and number in 1:50000-scale stream sediment survey; 11-Sb anomaly and number in 1:50000-scale stream sediment survey; 12-Au anomaly and number in soil geochemical profile survey; 13-As anomaly and number in soil geochemical profile survey; 14-Sb anomaly and number in soil geochemical profile survey; 15-Bi anomaly and number in soil geochemical profile survey; 16-Ag anomaly and number in soil geochemical profile survey; 17-Cu anomaly and number in soil geochemical profile survey; 18-Fractured alteration zone and number; 19-Exploration trench and number; 20-Au grade/thickness; 21-Lines and numbers of the induced polarization intermediate gradient survey profile
图 5 那穷锑金矿激电中梯视极化率剖面平面图及等值线异常图
a—视极化率剖面平面图;b—视极化率等值线异常图
Figure 5. Intermediate gradient apparent polarizability profile plane and contour anomaly diagram in induced polarization of the Naqiong Sb-Au deposit
(a) Apparent polarizability profile plane; (b) Apparent polarizability contour anomaly diagram
图 6 那穷锑金矿流体包裹体显微镜下照片
L—液相; V—气相
a—包裹体成带状分布;b—包裹体成群分布;c—富液包裹体和气体包裹体;d—富液包裹体Figure 6. Microscope photos of fluid inclusions in the Naqiong deposit
(a) Banded distribution of inclusions; (b) Clustered distribution of inclusions; (c) Liquid-rich inclusions and gas inclusions; (d) Liquid-rich inclusions
L-Liquid phase; V-Vapor phase表 1 那穷锑金矿土壤剖面测量异常特征表
Table 1. Anomaly characteristics of the soil profile survey in the Naqiong Sb-Au deposit
异常编号 异常下限 面积/km2 形状 浓度分带 最高值 平均值 衬度 规模/km2 异常点数/个 Au-1 2.5 0.06 椭圆状 外 8.25 4.75 1.90 0.12 7 Au-2 2.5 0.02 椭圆状 外 4.42 3.45 1.38 0.02 6 Au-3 2.5 0.01 椭圆状 外 4.65 3.79 1.52 0.02 6 As-1 50.0 0.28 不规则状 外 144.00 80.61 1.61 0.45 36 As-2 50.0 0.10 椭圆状 外、中、内 324.00 163.01 3.26 0.31 18 Sb-1 2.5 0.21 不规则状 外、中 10.20 6.03 2.41 0.50 31 Sb-2 2.5 0.07 椭圆状 外、中 7.58 5.43 2.17 0.15 18 Cu-1 54.0 0.17 不规则状 外 65.60 60.58 1.12 0.19 13 Cu-2 54.0 0.08 条带状 外 68.20 61.41 1.14 0.10 7 Bi-1 1.0 0.17 椭圆状 外、中 5.21 1.91 1.91 0.32 28 注:Au/×10-9,其他元素/×10-6 表 2 那穷锑金矿激电中梯异常特征表
Table 2. Anomaly characteristics of intermediate gradient in induced polarization(IP) in the Naqiong Sb-Au deposit
异常编号 形态特征 地质特征 异常分类 ηs-1 位于矿区西南部,串珠状分布,北东走向,长约800 m,宽约200 m,南西端未封闭;视极化率异常下限7.9%,最大值14%,平均值约为13%,极化较强,视电阻率平均值约为120 Ω·m 异常位置出露岩性为上三叠统涅如组(T3n)灰色粉砂质绢云母板岩夹中厚层状细粒岩屑杂砂岩 丙2 ηs-2 位于矿区南部,条带状分布,长约2000 m,宽约200 m,南端未封闭;视极化率异常下限7.9%,最大值14.5%,平均值13%,极化较强,视电阻率平均值为120 Ω·m 乙3 ηs-3 位于矿区东南部,条带状分布,长约1600 m,宽约100 m,南东端未封闭;视极化率异常下限7.9%,最大值14.8%,平均值13.5%,极化较强,视电阻率平均值为120 Ω·m 乙3 -
BIAN S, YU Z Q, GONG J F, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal distribution and geodynamic mechanism of the nearly NS-trending rifts in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 178-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN D T, CHEN W, HU K W, et al., 2016. Geological characteristics and geochemical anomaly of Bangzhuoma Gold Deposit in Longzi County, Tibet[J]. Gold, 37(8): 25-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Z L, LIU Y P, 1996. The South Tibetan detachment system[J]. Tethyan Geology(20): 31-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) DONG F Q, LI W Y, HU K W, et al., 2015. Geological characteristics and prospecting potentiality of Qiaga village stibnite property in Longzi county, Tibet[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 30(1): 98-102. (in Chinese with English abstract) DU Z Z, GU X X, LI G Q, et al., 2011. Sulfur, lead isotope composition characteristics and the relevant instructive significance of the Lamuyouta Sb(Au) Deposit, South Tibet[J]. Geoscience, 25(5): 853-860. (in Chinese with English abstract) FENG X L, DU G S, 1999. The distribution, mineralization types and prospecting and exploration of the gold deposits in Xizang[J]. Tethyan Geology(23): 31-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) FU W, ZHOU Y Z, YANG Z J, et al., 2005. Characteristics of multi-horizon ore-bearing formations in southern Tibet Au-Sb metallogenic belt and its controlling factors[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 29(3): 321-327. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG X D, 2011. Study on Metallogenic regularity and ore-prospecting direction of Gyantse-Lhunze Gold-antimony Metallogenic Belt in the South Tibetan Detachment System[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIANG Y S, XU T D, ZHAO Y N, 2009. Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic magmatic portfolio analysis in Cuoqin area of the Middle Gangdise[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(4): 336-348. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI H L, LI G M, LI Y X, et al., 2017. A study on ore geological characteristics and fluid inclusions of Jienagepu Gold Deposit in Zhaxikang Ore concentration district, southern Tibet, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 37(6): 684-696. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Y X, LI G M, DONG L, et al., 2018. Geology and exploration potential of the Mazhala gold deposit, Cuomei, Xizang: an approach[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 38(3): 88-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIANG W, ZHENG Y C, YANG Z S, et al., 2014. Multiphase and polystage metallogenic process of the Zhaxikang large-size Pb-Zn-Ag-Sb polymetallic deposit in southern Tibet and its implications[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 33(1): 64-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) LOU Y L, 2016. Analysis on the geochemical characteristics and prospecting of Zhegu-Gudui area, Tibet[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) LOU Y L, CHEN W, CHEN D T, et al., 2016. The primary halo characteristics of No. 4 vein and related depth prospecting prediction of the Qiaga Dtibnite deposit in Longzi County, Tibet[J]. Northwestern Geology, 49(4): 146-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) LOU Y L, CHEN W, LI Z W, et al., 2018a. Application of integrated prospecting methods on Xiangri stibnite deposit, Tibet[J]. Mineral Exploration, 9(1): 117-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) LOU Y L, CHEN W, CHEN D T, et al., 2018b. Geological characteristics and prospecting potentiality of Nagadi gold polymetallic deposit in Longzi county, Tibet[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 33(1): 15-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) LOU Y L, CHEN W, YUAN Y S, et al., 2018c. Fluid inclusion and H, O, and S isotopic composition of Qiaga stibnite deposit in Longzi county, Tibet[J]. Mineral Deposits, 37(5): 1124-1140. (in Chinese with English abstract) LOU Y L, CHEN W, YANG T, 2019. Metallogenic model and prospecting pattern of the Bangzhuoma gold deposit in Longzi County, Tibet[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 38(2-3): 449-461. (in Chinese with English abstract) PAN G T, DING J, YAO D S, et al., 2005. The Manual of Geology Map (1:1500000) Tibetan Plateau and its Surrounding areas[M]. Chengdu: Chengdu Map Press. (in Chinese) QI X X, LI T F, MENG X J, et al., 2008. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Tethyan Himalayan foreland fault-fold belt in southern Tibet, and its constraint on antimony-gold polymetallic minerogenesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(7): 1638-1648. (in Chinese with English abstract) REN C, MA F Z, ZHU Z H, et al., 2015. U-Pb SHRIMP zircon ages of the mafic-ultramafic rocks from Chigu Co of South Tibet and their geological significances[J]. Geology in China, 42(4): 881-890. (in Chinese with English abstract) REN C, 2015. Geochemistry, geochronology and its geological significances of Early Cretaceous magmatic rocks of Comei district in Tibet[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG J, ZHANG J, 2001. Metallogenic characters and prospecting direction of the Mazhala gold-antimony deposit, southern Tibet[J]. Gold Geology, 7(3): 15-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG J, ZHANG J, ZHENG Y Y, 2001. Exploration on metallogenic regularity of gold-antimony deposit in Mazhala, South Tibet[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 9(3-4): 5-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG J, ZHU L X, MA S M, et al., 2019. The application of the integrated geological, geophysical and geochemical prospecting method in the discovery of the Longtoushan lead polymetallic deposit in northern Hebei province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(1): 9-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) XI W J, XIAO K Y, 2016. Geological features and resource potential of the Gangdise-Southern Tibet Cu-Ag-Pb-Zn-Mo Metallogenic Belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(7): 1636-1649. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE Y L, YANG K J, LI Y X, et al., 2019. Mazhala gold-antimony deposit in southern Tibet: the characteristics of ore-forming fluids and the origin of gold and antimony[J]. Earth Science, 44(6): 1998-2016. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU G Y, 2020. Metallogenic fluid characteristics and Implications for ore genesis of Chalapu gold deposit in South Tibet[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Y P, 2021. Analysis of ore-forming depth and exploration potential of gold-antimony polymetallic deposits in Gudui area, South Tibet[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 35(2): 202-210. (in Chinese with English abstract) XUE Y S, WANG R T, WANG C, et al., 2020. Ore-controlling rules of fault structures in the Wangjiaping gold deposit in Shanyang County, Shaanxi province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(3): 391-404. (in Chinese with English abstract) YIN A, 2001. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen in the context of phanerozoic continental growth of Asia[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 22(3): 193-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) YU M, 2015. Characteristics of ore geology and ore-forming fluid in the Zhaxikang Sb-Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, Southern Tibet, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG D, LI F, HE X L, et al., 2021. Mesozoic tectonic deformation and its rock/ore-control mechanism in the important metallogenic belts in South China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(4): 497-528. (in Chinese with English abstract) Zhang G Y, 2012. Metallogenic Model and Prospecting Potential in Southern Tibet Au-Sb Polymetallic Belt[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG H R, HOU Z Q, YANG Z M, 2010. Metallogenesis and Geodynamics of Tethyan metallogenic domain: a review[J]. Mineral Deposits, 29(1): 113-133. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J F, ZHENG Y Y, ZHANG G Y, et al., 2011. Geologic characteristic and mineralization of Mazhala gold-antimony deposit in Northern Himalaya[J]. Gold, 32(1): 20-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG Y Y, DUO J, MA G T, et al., 2007. Mineralization characteristics, discovery and age restriction of Chalapu hardrock gold deposit, southern Tibet[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32(2): 185-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG Y Y, LIU M Y, SUN X, et al., 2012. Type, discovery process and significance of Zhaxikang antimony polymetallic ore deposit, Tibet[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 37(5): 1003-1014. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU T C, SUN X, ZHENG Y Y, et al., 2015. Characteristics of gold-bearing minerals and modes of occurrence of gold in Chalapu gold deposit, southern Tibet[J]. Mineral Deposits, 34(3): 521-532. (in Chinese with English abstract) 卞爽, 于志泉, 龚俊峰, 等, 2021. 青藏高原近南北向裂谷的时空分布特征及动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 178-194. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.018 陈东太, 陈武, 胡可卫, 等, 2016. 西藏隆子县邦卓玛金矿床地质特征及地球化学异常特征[J]. 黄金, 37(8): 25-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201608006.htm 陈智梁, 刘宇平, 1996. 藏南拆离系[J]. 特提斯地质(20): 31-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD600.001.htm 董富权, 李武毅, 胡可卫, 等, 2015. 西藏隆子县恰嘎村辉锑矿地质特征及找矿潜力[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 30(1): 98-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201501014.htm 杜泽忠, 顾雪祥, 李关清, 等, 2011. 藏南拉木由塔锑(金)矿床S、Pb同位素组成及指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 25(5): 853-860. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.05.004 冯孝良, 杜光树, 1999. 西藏金矿资源分布规律、矿化类型及找矿方向[J]. 特提斯地质(23): 31-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD199900002.htm 付伟, 周永章, 杨志军, 等, 2005. 藏南多层位金锑含矿建造特征及其控矿因素制约[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 29(3): 321-327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2005.03.005 黄小东, 2011. 藏南拆离系江孜—隆子金—锑成矿带成矿规律与找矿方向研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学. 江元生, 徐天德, 赵友年, 2009. 冈底斯构造岩浆带中段措勤地区中新生代岩浆岩构造组合分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(4): 336-348. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.04.003 李洪梁, 李光明, 李应栩, 等, 2017. 藏南扎西康矿集区姐纳各普金矿床地质与流体包裹体特征[J]. 矿物学报, 37(6): 684-696. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201706002.htm 李应栩, 李光明, 董磊, 等, 2018. 西藏马扎拉金矿区外围地质特征与找矿方向[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 38(3): 88-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2018.03.010 梁维, 郑远川, 杨竹森, 等, 2014. 藏南扎西康铅锌银锑多金属矿多期多阶段成矿特征及其指示意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 33(1): 64-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2014.01.005 娄元林, 2016. 西藏哲古—古堆地区地球化学特征及找矿前景分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 娄元林, 陈武, 陈东太, 等, 2016. 西藏隆子县恰嘎锑矿4号脉原生晕特征及深部找矿预测[J]. 西北地质, 49(4): 146-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2016.04.006 娄元林, 陈武, 李致伟, 等, 2018a. 综合找矿方法在西藏象日锑矿床的应用[J]. 矿产勘查, 9(1): 117-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201801016.htm 娄元林, 陈武, 陈东太, 等, 2018b. 西藏隆子县那嘎迪金多金属矿地质特征及找矿潜力[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 33(1): 15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201801002.htm 娄元林, 陈武, 袁永盛, 等, 2018c. 西藏隆子县恰嘎锑矿床流体包裹体及H、O、S同位素组成特征[J]. 矿床地质, 37(5): 1124-1140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201805014.htm 娄元林, 陈武, 杨桃, 2019. 西藏隆子县邦卓玛金矿床成矿模式与找矿模型[J]. 地质通报, 38(2-3): 449-461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2019Z1027.htm 潘桂棠, 丁俊, 姚冬生, 等, 2004. 青藏高原及邻区地质图(1:1500000)说明书[M]. 成都: 成都地图出版社. 戚学祥, 李天福, 孟祥金, 等, 2008. 藏南特提斯喜马拉雅前陆断褶带新生代构造演化与锑金多金属成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 24(7): 1638-1648. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200807021.htm 任冲, 马飞宙, 朱振华, 等, 2015. 藏南哲古基性岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 42(4): 881-890. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.04.007 任冲, 2015. 西藏措美地区早白垩世岩浆岩地质年代学、地球化学及地质意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 王建, 朱立新, 马生明, 等, 2019. 冀北地区龙头山铅多金属矿床的发现及地物化综合找矿模型的建立[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(1): 9-18. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.01.002 王军, 张均, 2001. 西藏南部马扎拉金锑矿成矿特征及找矿方向[J]. 黄金地质, 7(3): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJDZ200103002.htm 王军, 张均, 郑有业, 2001. 西藏南部马扎拉金锑矿成矿规律初探[J]. 黄金科学技术, 9(3-4): 5-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ2001Z1001.htm 席伟杰, 肖克炎, 2016. 冈底斯-藏南Cu-Au-Pb-Zn-Mo成矿带成矿地质特征与资源潜力分析[J]. 地质学报, 90(7): 1636-1649. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.07.026 谢玉玲, 杨科君, 李应栩, 等, 2019. 藏南马扎拉金-锑矿床: 成矿流体性质和成矿物质来源[J]. 地球科学, 44(6): 1998-2016. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201906019.htm 许国雨, 2020. 藏南查拉普金矿床成矿流体特征及其对矿床成因的指示[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 许云鹏, 2021. 藏南古堆地区金锑多金属矿床形成深度及找矿潜力分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 35(2): 202-210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD202102004.htm 薛玉山, 王瑞廷, 汪超, 等, 2020. 陕西省山阳县王家坪金矿断裂构造控矿规律[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(3): 391-404. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.03.034 尹安, 2001. 喜马拉雅-青藏高原造山带地质演化: 显生宙亚洲大陆生长[J]. 地球学报, 22(3): 193-230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2001.03.001 于淼, 2015. 藏南扎西康锑铅锌银矿床地质及成矿流体特征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 张达, 李芳, 贺晓龙, 等, 2021. 华南重要成矿区带中生代构造变形及其控岩控矿机理[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(4): 497-528. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.04.045 张刚阳. 2012. 藏南金锑多金属成矿带成矿模式与找矿前景研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉). 张洪瑞, 侯增谦, 杨志明, 2010. 特提斯成矿域主要金属矿床类型与成矿过程[J]. 矿床地质, 29(1): 113-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.01.011 张建芳, 郑有业, 张刚阳, 等, 2011. 西藏北喜马拉雅马扎拉金锑矿床地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 黄金, 32(1): 20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1277.2011.01.005 郑有业, 多吉, 马国桃, 等, 2007. 藏南查拉普岩金矿床特征、发现及时代约束[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 32(2): 185-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200702004.htm 郑有业, 刘敏院, 孙祥, 等, 2012. 西藏扎西康锑多金属矿床类型、发现过程及意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 37(5): 1003-1014. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201205015.htm 周天成, 孙祥, 郑有业, 等, 2015. 藏南查拉普金矿床载金矿物特征与金的赋存状态[J]. 矿床地质, 34(3): 521-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201503006.htm -





 下载:
下载: