-
-
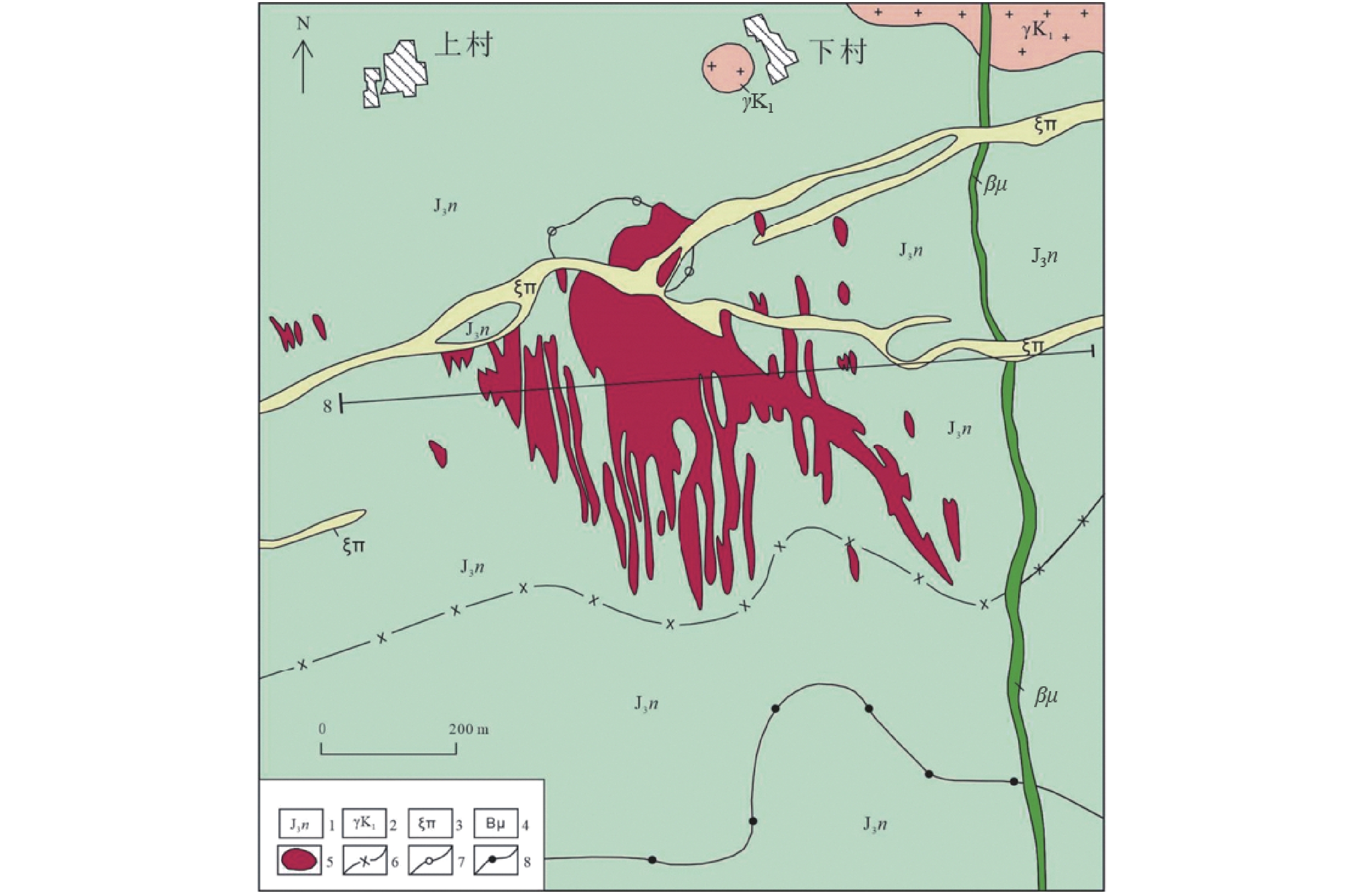
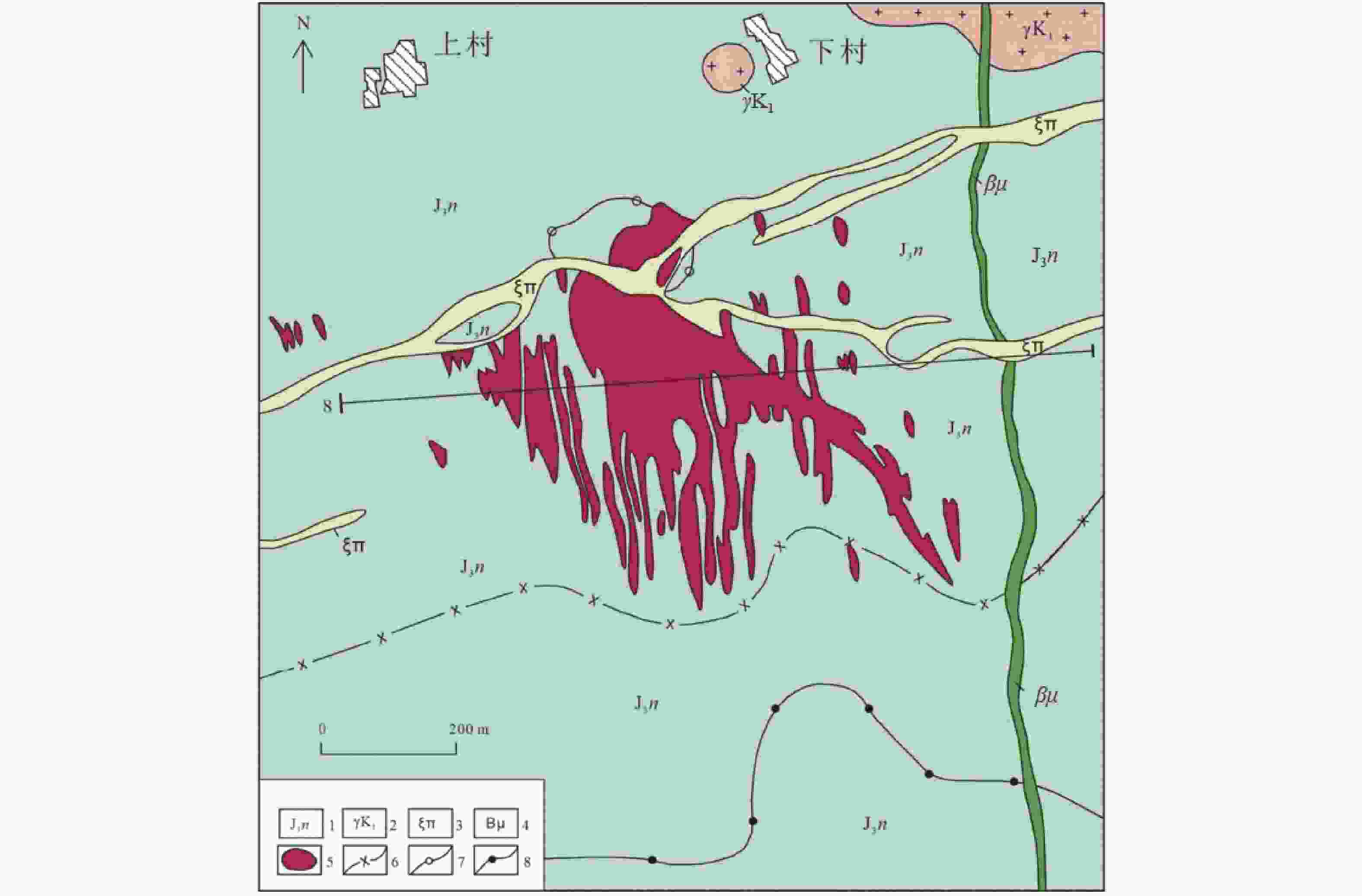
图 1 福建福安赤路矿区地质略图(据福建省地质四队四〇三分队,1976修改)
1—南园组流纹质晶屑凝灰熔岩及流纹质角砾凝灰熔岩;2—微细粒似斑状花岗岩;3—正长斑岩;4—辉绿玢岩;5—钼矿体;6—云英岩化带与绢英岩化带分界线;7—钾长石化与云英岩化带界线;8—绢英岩化带与青盘岩化带分界线
Figure 1. Geological sketch of the Chilu mining area in Fu'an(revised from Fujian Provincial Geological Team 403 Division, 1976)
1–rhyolitic crystal lapilli tuff and rhyolitic brecciated lapilli tuff of the Nanyuan Group; 2–fine-grained porphyritic granite; 3–syenite porphyry; 4–diabase; 5–molybdenum ore body; 6–boundary between greisenization zone and sericite alteration zone; 7–boundary between potassic alteration zone and greisenization zone; 8–boundary between sericite alteration zone and propylitization zone
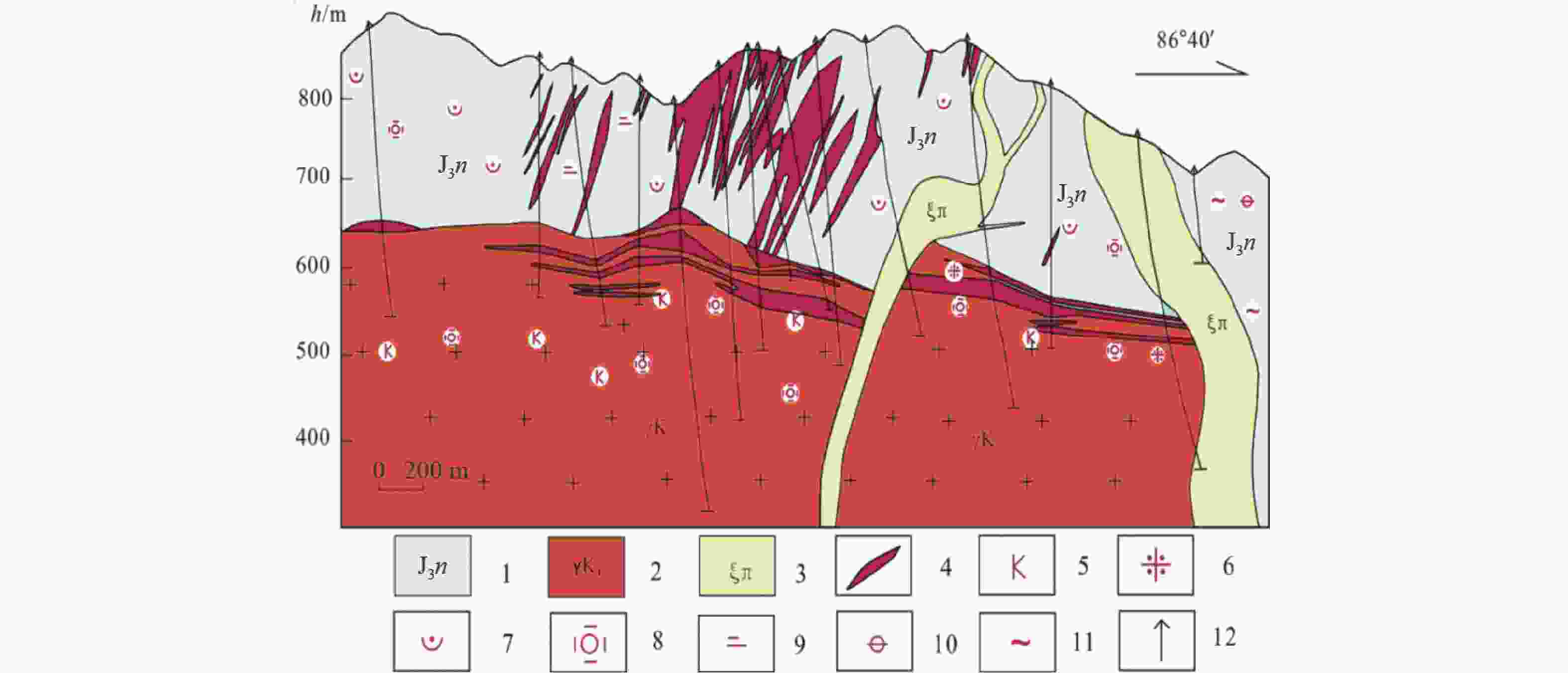
图 2 福建福安赤路矿区8线地质剖面图(据福建省地质四队四〇三分队,1976改编)
1—南园组;2—花岗岩;3—正长斑岩;4—钼矿体;5—钾长石化;6—云英岩化;7—绢英岩化;8—硅化;9—绢云母化;10—绿帘石化;11—绿泥石化;12—钻孔
Figure 2. Geological profile of Line 8 in the Chilu mining area in Fu'an(revised from the Fujian Provincial Geological Team 403 Division, 1976)
1–Nanyuan Group; 2–granite; 3–syenite porphyry; 4–molybdenum ore body; 5–potassic alteration; 6–greisenization; 7–silication and sericitization; 8–silicification; 9–sericitization; 10–epidotization; 11–chloritization; 12–drill hole
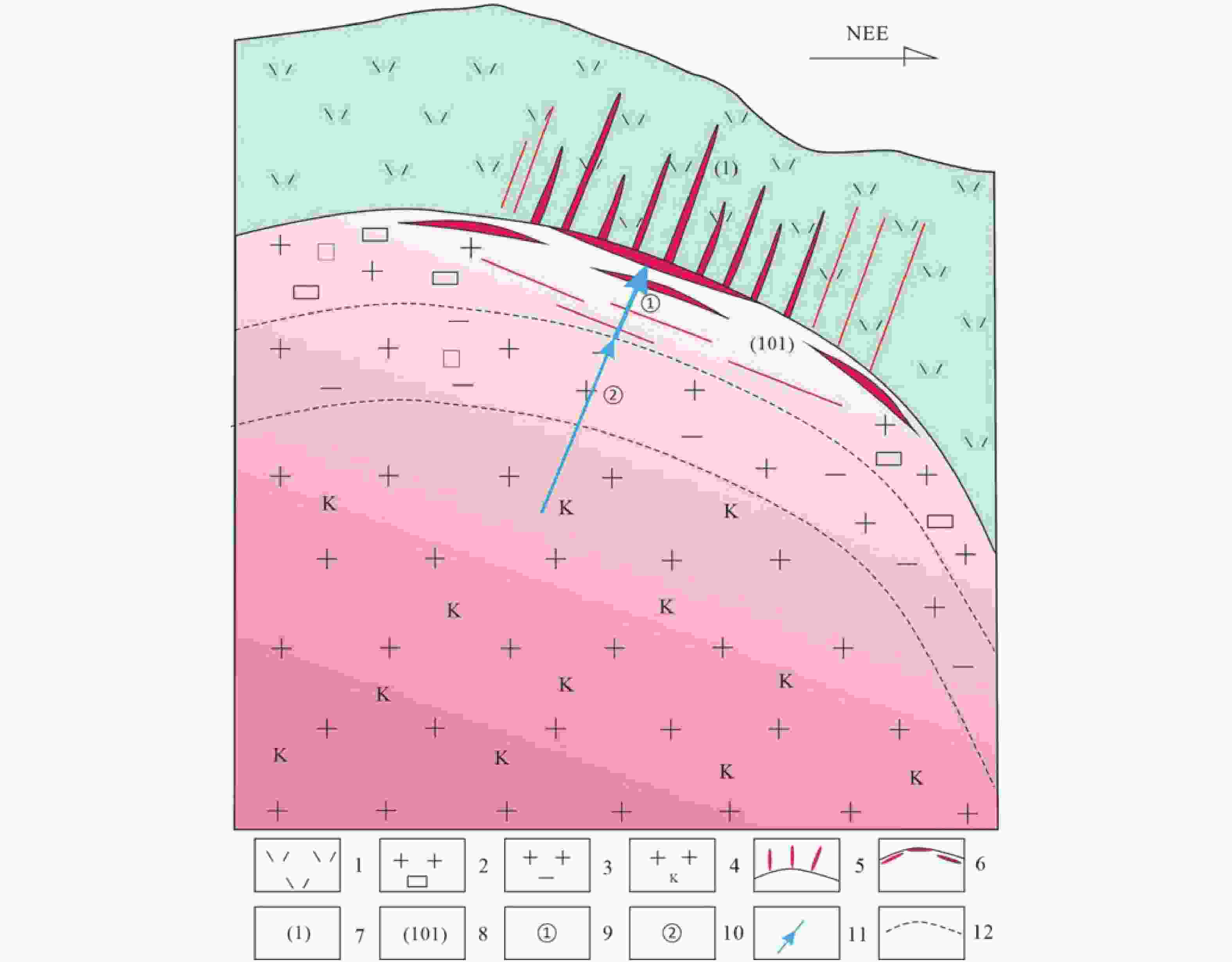
图 3 赤路钼矿床成矿模式
1—上侏罗统南园组第三段(J3nc)流纹质晶屑凝灰熔岩和流纹质角砾熔岩;2—中细粒似斑状花岗岩;3—二长花岗岩;4—钾长花岗岩;5—接触面及其以上陡倾斜矿体;6—接触面及其以下平行接触面的缓倾斜矿体;7—1号矿体;8—101号矿体;9—第一期岩浆动力作用;10—第二期岩浆动力作用;11—同源二期岩浆动力作用方式、方向;12—不同花岗岩之间的界线
Figure 3. Metallogenic Model of the Chilu Molybdenum Deposit
1–rhyolitic crystalline tuff lava and rhyolitic breccia lava (J3nc) from the third member of the Nanyuan Group of the Upper Jurassic; 2–medium to fine grained porphyritic granite; 3–monzogranite; 4–orthogonal granite; 5–steep inclined ore bodies at and above the contact surface; 6–gently inclined ore bodies with parallel contact surfaces at and below the contact surface; 7–No.1 ore body; 8–No.101 ore body; 9–the first stage of magmatic dynamic process; 10–the second stage of magmatic dynamic process; 11–the mode and direction of the second stage of magmatic dynamic process from the same source; 12–the boundary between different granites
表 1 赤路钼矿床主要控矿构造特征表
Table 1. Main ore-controlling structural characteristics of the Chilu molybdenum deposit
位置 构造特征 力学性质 产状 与接触面关系 与岩浆上冲力方向关系 接触面以上 张性或张剪性 NNW/SWW∠70°± 垂直或近垂直 平行或近平行(NNW/SWW∠70°±) 接触面 压性或压剪性 NEE/SSE∠20°± 同一 垂直或近垂直 接触面以下 压性或压剪性 NEE/SSE∠20°± 平行或近平行 垂直或近垂直 表 2 岩浆动力成因构造控矿主要类型及其特征表
Table 2. The main types and characteristics of structures associated with intrusion and mineralization
特征 主要类型 直立树枝状−
对称弧形倾斜平行−
不对称弧形陡倾斜平行−
缓倾斜平行弧形平行 倾向相向平行夹X
形−弧形平行形态 直立树枝状石英脉型钨矿 倾斜平行石英脉型钨矿 陡倾斜石英脉型钼矿平行分布 弧形石英脉型、硅化脉带型钼矿层(体)叠层平行分布 两侧倾向相向平行中间夹X形石英脉型钨矿 产状 平行或近平行接触面矽卡岩型、砂岩细脉型钨矿层(体) 矽卡岩型钨矿
平行或近平行接触面分布结构面 接触面 接触面 接触面 (隐形)接触面 接触面 类型 伟晶岩型、云英岩型矿体(层)平行叠层分布 云英岩型矿层(体)平行接触面分布 缓倾斜云英岩层(体)平行接触面及以下平行分布 ? 与接触面平行云英岩型、细脉浸染型、浸染型钨矿层(体)叠层平行分布 典型矿床 湖南瑶岗仙钨(钼)矿床(李顺庭,2011)等 江西徐山钨矿床(王显华和龙细文,2010)等 福建赤路钼矿床(福建省地质四队四〇三分队,1976)等 福建古田西朝钼矿床(石礼炎,2009)等 江西茅坪钨锡矿床(王定生等,2011)等 -
[1] ANDERSON E M, 1936. The dynamics of the formation of cone sheets, ring dykes and cauldron subsidence[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 56: 128-163. [2] Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Fujian Province, 1985. Regional geology of Fujian Province[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) [3] CARACCIOLO A, BALI E, GUÐFINNSSON G H, et al. , 2020. Temporal evolution of magma and crystal mush storage conditions in the Bárðarbunga-Veiðivötn volcanic system, iceland[J]. Lithos, 352-353: 105234. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105234 [4] CHAMBERS M, MEMETI V, EDDY M P, et al. , 2020. Half a million years of magmatic history recorded in a K-feldspar megacryst of the tuolumne intrusive complex, California, USA[J]. Geology, 48(4): 400-404. doi: 10.1130/G46873.1 [5] CHEN L L, NI P, LI W S, et al. , 2018. The link between fluid evolution and vertical zonation at the Maoping tungsten deposit, Southern Jiangxi, China: fluid inclusion and stable isotope evidence[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 192: 18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.01.001 [6] CHEN M S, LIU X H, 2000. Metallogenic model and resource general capacity forecast of Furong Sn field in Chenzhou[J]. Hunan Geology, 19(1): 43-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] COLEMAN D S, GRAY W, GLAZNER A F, 2004. Rethinking the emplacement and evolution of zoned plutons: geochronologic evidence for incremental assembly of the Tuolumne intrusive suite, California[J]. Geology, 32(5): 433-436. doi: 10.1130/G20220.1 [8] FENG Z H, WANG C Z, WANG B H, 2009. Granite magma ascent and emplacement mechanisms and their relation to mineralization process[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 29(2): 183-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] Fujian Provincial Geological Team 403 Division, 1976. The detailed geological survey and evaluation report of the Chilu molybdenum mining area in Fujian Province[M]. Fuzhou: Fujian Geological Center Laboratory. (in Chinese) [10] GLGXYQZH, 2015. The origin of the five story model[EB/OL]. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/eb909bc0f121dd36a22d8236.html?_wkts_=1709082736687&needWelcomeRecommand=1. (in Chinese) [11] Guangdong Nonferrous Metal Geological Exploration Company 932 Team, 1966. How do we use the 'five story building' law to search, evaluate, and explore wolframite quartz vein deposits[J]. Geology and Prospecting(5): 15-19. (in Chinese) [12] GUDMUNDSSON A, 2020. Volcanotectonics: understanding the structure, deformation and dynamics of volcanoes[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [13] LEE J S, 1973. Introduction to geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [14] LI G F, 1995. Basic characteristic of Mo metallogenic belt in east Fujian[J]. Journal of East China Geological Institute, 18(4): 330-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] LI S T, 2011. Characteristics and genesis of the Yaogangxian tungsten polymetallic deposits in Hunan Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] LI W S, NI P, PAN J Y, et al. , 2023. The genetic association between vein and skarn type tungsten mineralization in the Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, South China: constraints from LA-ICP-MS analysis of individual fluid inclusion[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 159: 105544. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105544 [17] MA C Q, ZOU B W, GAO K, et al. , 2020. Crystal mush storage, incremental pluton assemblyand granitic petrogenesis[J]. Earth Science, 45(12): 4332-4351. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] MEI Y W, 1985. Distribution pattern of tungsten deposits in the Xihuashan Zongshukeng area[J]. Geology and Prospecting(4): 11-16. (in Chinese) [19] MICHEL J, BAUMGARTNER L, PUTLITZ B, et al. , 2008. Incremental growth of the Patagonian Torres del Paine laccolith over 90 k. y. [J]. Geology, 36(6): 459-462. doi: 10.1130/G24546A.1 [20] MILLER J S, 2008. Assembling a pluton…one increment at a time[J]. Geology, 36(6): 511-512. doi: 10.1130/focus062008.1 [21] SCHALTEGGER U, SCHOENE B, PEYTCHEVA I, 2008. Tracking the growth of plutons: the contribution of high-precision U-Pb zircon dating[J]. Geophysical Research Abstract, 10: EGU 2008-A-01909. [22] SHI L Y, 2009. The metallotectonic characteristics and the ore-finding target of the Xichao molybdenum deposit in Gutian County, Fujian Province[J]. Geology of Fujian, 28(3): 167-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] WANG D S, LU S M, HU B Y, et al. , 2011. The geological characteristics and mineralization model of a tungsten-tin deposit[J]. China Tungsten Industry, 26(2): 6-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] WANG X H, LONG X W, 2010. Structural superposition and metallogenic structural evolution model of the Xushan tungsten deposit in Fengcheng City, Jiangxi Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 22(12): 147-151. (in Chinese)(未找到本条文献英文翻译信息, 请确认) [25] WEI L M, LIN J F, LI W Q, et al. , 2008. Discussion on “five stored” superposed model of Meiziwo tungsten deposit, Guangdong[J]. Journal of Geology, 82(7): 888-893. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] Wuhan College of Geology, Chengdu College of Geology, Department of Geology, Nanjing University, et al. , 1979. Structural geology[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) [27] XIAO Q H, ZHOU Y Q, LI X B, et al. , 1988. Recent progress in the study of granite tectonics abroad[R]. Information Research Institute, Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources. (in Chinese) [28] XU K L, ZHU Z C, 1989. Structural geology[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) [29] YANG M G, 2015-02-03. On the origin of the "five story building" deposit model[N]. China Mining Daily. (in Chinese) [30] YUAN G X, 2018. The great story hidden in this supplement[R]. Jiangxi Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration. (in Chinese) [31] ZHANG K Y, WANG J P, DU A D, et al. , 2009. Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenite from the Chilu molybdenum deposit in Fu'an, Fujian Province[J]. Geology of China, 36(1): 147-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] ZHANG Q L, HE G H, XIE G, 2007. The geological characteristics of tungsten-tin ore deposit in Baxiannao, Chongyi Jiangxi[J]. Resource Survey and Environment, 28(1): 40-45. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] ZHAO B, 2013. A study on metallogenic depths of Piaotang quartz vein type Wolframite deposits in Jiangxi Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese) [34] ZHOU H N, HE Y J, 1983. Discussion on the characteristics of isotope geology of porphyry molybdenum at Chilu and its source of ore material[J]. Geology of Fujian(2): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] ZHOU J Y, 1976. Method for identification of mechanical properties of structural planes[M]. Chengdu: Chengdu College of Geology. (in Chinese) [36] ZHOU J Y, 1989. Introduction to geomechanics[M]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press: 37. (in Chinese) [37] ZHOU J Y, CUI B F, CHEN H M, et al. , 2000. Metallogenic regularities and prognosis of copper and tin deposits in the area of Hongshan-Xikengjing, south of Jiangxi Province[M]. Beijing: Geology Press: 31-61. (in Chinese) [38] ZHOU J Y, XIAO H L, 2006. Metallostructural system and its significance of search for tungsten deposit[J]. Resources Survey & Environment, 27(2): 110-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] ZHOU J Y, CUI B F, 2018. New progress in research and application of metallogenic system[J]. East China Geology, 39(4): 271-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] ZHU Z C, SONG H L, 1990. Structural geology[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press. (in Chinese) [41] 陈民苏, 刘星辉, 2000. 郴州芙蓉锡矿田成矿模式及资源总量预测[J]. 湖南地质, 19(1): 43-47. [42] 冯佐海, 王春增, 王葆华, 2009. 花岗岩侵位机制与成矿作用[J]. 桂林工学院学报, 29(2): 183-194. [43] 福建省地质矿产局, 1985. 福建省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [44] 福建省地质四队四〇三分队, 1976. 福建福安赤路钼矿区地质详查评价报告[M]. 福州: 福建省地质中心实验室. [45] GLGXYQZH, 2015. 五层楼模式的由来[EB/OL]. https://wenku.baidu.com/view/eb909bc0f121dd36a22d8236.html?_wkts_=1709082736687&needWelcomeRecommand=1. [46] 广东有色金属地质勘探公司九三二队, 1966. 我们是怎样用“五层楼”规律寻找、评价和勘探黑钨石英脉矿床的[J]. 地质与勘探(5): 15-19. [47] 李观富, 1995. 闽东地区钼成矿带的基本特征[J]. 华东地质学院学报, 18(4): 330-334. [48] 李顺庭, 2011. 湖南瑶岗仙钨多金属矿床特征与成因[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). [49] 李四光, 1973. 地质力学概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [50] 马昌前, 邹博文, 高珂, 等, 2020. 晶粥储存、侵入体累积组装与花岗岩成因[J]. 地球科学, 45(12): 4332-4351. [51] 梅勇文, 1985. 西华山-棕树坑地区钨矿分布规律[J]. 地质与勘探(4): 11-16. [52] 石礼炎, 2009. 福建古田西朝钼矿床成矿构造特征及找矿方向[J]. 福建地质, 28(3): 167-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2009.03.001 [53] 王定生, 陆思明, 胡本语, 等, 2011. 江西茅坪钨锡矿床地质特征及成矿模式[J]. 中国钨业, 26(2): 6-11. [54] 王显华, 龙细文, 2010. 江西省丰城市徐山钨矿床构造迭加及成矿构造演化模式[J]. 西部探矿工程, 22(12): 147-151. [55] 韦龙明, 林锦富, 李文铅, 等, 2008. 广东梅子窝钨矿“五层楼”叠加现象探讨[J]. 地质学报, 82(7): 888-893. [56] 武汉地质学院, 成都地质学院, 南京大学地质系, 等, 1979. 构造地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [57] 肖庆辉, 周玉泉, 李晓波, 等, 1988. 国外花岗岩体构造研究的新进展[R]. 地质矿产部情报研究所. [58] 徐开礼, 朱志澄, 1989. 构造地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [59] 杨明桂, 2015-02-03. 关于“五层楼”矿床模式的由来[N]. 中国矿业报. [60] 袁赣湘, 2018. 这本《增刊》蕴藏的大故事[R]. 江西省地质矿产勘查局. [61] 张克尧, 王建平, 杜安道, 等, 2009. 福建福安赤路钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 36(1): 147-155. [62] 张庆林, 何桂红, 谢刚, 2007. 崇义县八仙脑钨锡矿床特征[J]. 资源调查与环境, 28(1): 40-45. [63] 赵波, 2013. 江西漂塘石英脉型黑钨矿床成矿深度估算[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). [64] 周鸿年, 何耀基, 1983. 赤路斑岩钼矿床同位素地质特征及其物质来源探讨[J]. 福建地质(2): 1-12. [65] 周济元, 1976. 结构面力学性质鉴定方法[M]. 成都: 成都地质学院. [66] 周济元, 1989. 地质力学引论[M]. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社: 37. [67] 周济元, 崔炳芳, 陈宏明, 等, 2000. 赣南红山—錫坑迳地区铜锡矿地质及预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 31-61. [68] 周济元, 肖惠良, 2006. 成矿结构体系及其钨矿找矿意义[J]. 资源调查与环境, 27(2): 110-119. [69] 周济元, 崔炳芳, 2018. 成矿体系研究和应用新进展[J]. 华东地质, 39(4): 271-278. [70] 朱志澄, 宋鸿林, 1990. 构造地质学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社. -




 下载:
下载: