IN-SITU SOAKING TEST ON THE DISTURBED LOESS SITE AT LANZHOU METRO, GANSU PROVINCE, CHINA
-
摘要: 由于受长期地表降水与排水下渗、前期施工、拆迁等加卸载作用及车辆交通荷载的扰动影响,城市拆迁场地土体的特性与处于原始地形地貌和地层分布的土体情况有所不同。目前尽管已经发表了大量黄土浸水试验的成果,但基本都是在原状黄土场地进行,而在这类扰动场地黄土中开展浸水试验的研究尚不多见。在兰州东岗轨道交通车辆段建设场地进行了累计观测时间超过100天的试坑原位浸水试验。结合室内土工试验和现场测试结果,讨论了该扰动场地黄土浸水产生沉降变形的特征。结果表明:该扰动场地浸水发生沉降变形的时间发展过程具有"缓慢增长-突增-趋于稳定"的特点,其总沉降也远小于既有原状黄土场地的实测结果,应理解为广义的浸水增湿湿陷,其变形包括压缩变形和湿陷变形两部分,二者比例近似为7:3;前期扰动导致的较低的孔隙比和试坑开挖造成的卸荷是其总变形量较小的原因,但是其浸水沉降变形增长过程中突增的湿陷变形和土层空间分布不均匀引起的差异沉降值得引起注意。研究结果对于进一步加深对黄土湿陷变形与水稳定性的理解,选择扰动场地黄土地基处理和防排水措施具有一定的参考价值。Abstract: The underlying soil under the engineering construction on the levy and removing sites in cities is quite different from the soil on the sites with primitive landform and strata distributions due to the disturbing influence of loading and reloading caused by long-term water seepage from precipitation and drainage, previous construction & demolition, traffic loading and so on. Although there are a lot of published researches on the in-situ soaking test for loess sites, most of which are for the intact loess sites, very little research has been devoted to the disturbed loess sites. An in-situ soaking test on the loess test pit were carried out on the construction site of car depot of rail transit in Donggang, Lanzhou and the observation last for over 100 days. Combined with the laboratory experiments and the in-situ test, the settlement deformation patterns due to the soaking of the loess at this disturbed site were discussed. The results indicate that the characteristics of the settlement deformation of the loess site can be generalized as the process of 'slow increasing-sudden increasing-tending to be stable', and the total settlements are much less than those obtained from other similar studies, which can be interpreted as the broadly-defined humidifying collapsibility including the compressive deformation and collapsible deformation with the approximate proportion of 7:3 between them. The relatively low void ratio caused by previous disturbances and unloading resulted from excavation of test pit are the main reasons that the total settlements are quite small, but much attentions should be paid to the sudden collapsibility settlement during the development of settlement deformation due to soaking and differential settlement due to uneven distribution of soil strata. The result would help to comprehend the collapsible deformation and water stability of loess and provide reference to select the measures of foundation treatment and waterproof & drainage for loess site.
-
Key words:
- Lanzhou /
- disturbed site /
- loess /
- in-situ soaking test
-
表 1 试验场地黄土物理力学参数汇总表
Table 1. The physical and mechanical parameters of loess in the test site
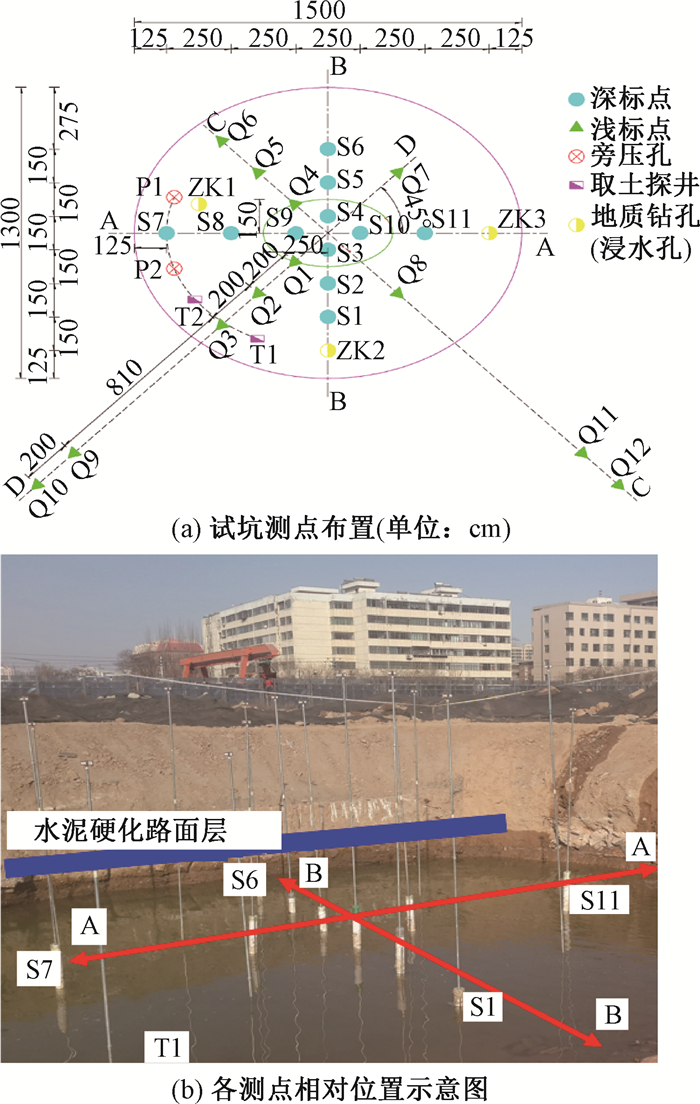
深度/m 密度/(g/cm3) 含水率/% 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性指数 液性指数 颗粒比重 初始孔隙比 饱和度/% 粘聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 标贯击数 自重湿陷系数 2 1.65 7.6 28.1 18.6 8.5 0.8 2.70 0.76 26.9 61.86 30.25 26 0.025 3 1.65 8.4 30.3 19.9 10.4 -0.92 2.71 0.78 29.2 63.23 26.65 26 0.034 4 1.6 8.9 25.8 16.8 9.0 0.44 2.70 0.84 28.7 71.71 30.49 24 0.026 5 1.65 10.5 25.9 16.8 9.1 -0.28 2.70 0.81 35.1 95.29 31.6 23 0.030 6 1.7 12.2 25.7 16.8 9.0 0.42 2.70 0.78 42.0 76.42 32.22 27 0.027 7 1.7 13.1 25.5 16.7 8.8 -0.83 2.70 0.80 44.4 74.54 29.68 20 0.047 8 1.85 17.3 25.6 16.7 8.9 0.33 2.70 0.71 65.5 79.25 27.34 19 0.049 9 1.9 21.3 26.7 17.2 9.5 0.09 2.70 0.73 79.4 99.8 25.00 22 0.045 10 1.95 23.0 27.0 17.3 9.7 -0.04 2.70 0.71 88.2 92.46 36.61 19 0.037 11 1.9 21.9 26.8 17.2 9.6 0.2 2.70 0.73 80.5 74 27.03 17 0.025 12 1.92 22.3 26.6 17.1 9.4 -0.15 2.70 0.72 83.6 80.47 26.83 16 0.034 表 2 深标点和浅标点位置最终沉降量汇总表
Table 2. The summary of the monitoring points and the related total settlements
序号 浅标点编号 灌水结束沉降量/mm 观测结束沉降量/mm 灌水结束沉降量占总沉降比值/% 深标点编号 埋设深度/m 灌水结束沉降量/mm 观测结束沉降量/mm 灌水结束沉降量占总沉降比值/% 1 Q1 96 105 91.4 S1 6 73 72 101.4 2 Q2 207 215 96.3 S2 7 70 77 90.9 3 Q3 226 236 95.8 S3 8 84 84 100.0 4 Q4 261 268 97.4 S4 9 76 75 101.3 5 Q5 260 268 97.0 S5 5 86 84 102.4 6 Q6 280 288 97.2 S6 4 97 100 97.0 7 Q7 370 381 97.1 S7 12 86 81 106.2 8 Q8 66 70 94.3 S8 11 78 82 95.1 9 Q9 51 61 83.6 S9 10 98 85 115.3 10 Q10 47 58 81.0 S10 3 80 83 96.4 11 Q11 79 92 85.9 S11 2 92 88 104.5 12 Q12 55 69 79.7 注:浅标点埋设深度统一为自然地面以下2.6 m,试坑表面以下0.3 m。 表 3 各测点最大沉降速率及其对应时间
Table 3. The maximum settlement velocities and their corresponding time
深标点编号 埋深/m 最大沉降速率/mm 最大沉降发生时间/d 占总沉降比值/% 浅标点编号 最大沉降速率/mm 最大沉降速率发生时间/d 占总沉降比值/% 湿陷变形占总变形比例/% S1 6 15 23 80.6 Q1 32 26 84.8 30.5 S2 7 13 11 74.0 Q2 65 26 80.5 30.2 S3 8 11 11 42.9 Q3 81 26 88.6 34.3 S4 9 12 12 48.0 Q4 87 26 96.3 32.5 S5 5 12 10 65.5 Q5 75 26 95.5 28.0 S6 4 10 15 78.0 Q6 110 26 94.4 38.2 S7 12 15 14 56.8 Q7 109 25 66.9 28.6 S8 11 14 13 56.1 Q8 17 27 100 24.3 S9 10 10 13 62.4 Q9 16 26 60.7 26.2 S10 3 12 6 44.6 Q10 16 26 72.4 27.6 S11 2 11 20 88.6 Q11 32 28 78.3 34.8 Q12 16 23 52.2 30.5 -
[1] 黄雪峰, 陈正汉, 哈双, 等. 大厚度自重湿陷性黄土场地湿陷变形特征的大型现场浸水试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2006, 28(3): 382~389. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.03.019HUANG Xuefeng, CHEN Zhenghan, HA Shuang, et al. Large area field immersion tests on characteristics of deformation of self weight collapse loess under overburden pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 28(3): 382~389. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.03.019 [2] 黄雪峰, 杨校辉. 湿陷性黄土现场浸水试验研究进展[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(S2): 222~228. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx2013z2036HUANG Xuefeng, YANG Xiaohui. A study progress on in-situ soaking test on collapsible loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(S2): 222~228. (in Chinese with English abstract http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx2013z2036 [3] 王小军, 米维军, 熊治文, 等. 郑西客运专线黄土地基湿陷性现场浸水试验研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2012, 34(1): 83~90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.01.015WANG Xiaojun, MI Weijun, XIONG Zhiwen, et al. Water immersion field tests of collapsibility of loess foundation of Zhengzhou-Xi’an passenger dedicated line[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2012, 34(1): 83~90. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2012.01.015 [4] 马闫, 王家鼎, 彭淑君, 等. 大厚度黄土自重湿陷性场地浸水湿陷变性特征研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(3): 537~546. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1017803828.htmMA Yan, WANG Jiading, PENG Shujun, et al. Immersion tests on characteristics of deformation of self-weight collapsible loess under overburden pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(3): 537~546. (in Chinese with English abstract http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1017803828.htm [5] 邢义川, 金松丽, 赵卫全, 等. 基于离心模型试验的黄土湿陷试验新方法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(3): 389~398. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201703002XING Yichuan, JIN Songli, ZHAO Weiquan, et al. New experimental method for loess collapsibility using centrifugal model tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(3): 389~398. (in Chinese with English abstract http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201703002 [6] 邵生俊, 王丽琴, 邵帅, 等. 黄土的结构屈服及湿陷变形的分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(8): 1357~1365. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201708002SHAO Shengjun, WANG Liqin, SHAO Shuai, et al. Structural yield and collapse deformation of loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(8): 1357~1365. (in Chinese with English abstract http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201708002 [7] 黄雪峰, 刘长玲, 姚志华, 等. 采用TDR水分计研究非饱和黄土入渗及自重湿陷变形规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(S1): 3231~3238. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2012z1086HUANG Xuefeng, LIU Changling, YAO Zhihua, et al. Study of infiltration and collapsible deformation law of unsaturated loess under over burden pressure by using TDR soil water probe[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(S1): 3231~3238 (in Chinese with English abstract http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2012z1086 [8] 邵生俊, 李骏, 邵将, 等. 大厚度湿陷性黄土地层的现场砂井浸水试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(9): 1549~1558. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201609002SHAO Shengjun, LI Jun, SHAO Jiang, et al. In-situ sand well immersion tests on self-weight collapsible loess site with large depth[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(9): 1549~1558. (in Chinese with English abstract http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201609002 [9] 孔洋, 阮怀宁, 黄雪峰. DDC法复合黄土地基的原位浸水试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2017, 50(11): 125~132. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201711013.htmKONG Yang, RUAN Huaining, HUANG Xuefeng. In-situ soaking test on composite loess foundation with down-hole dynamic compaction (DDC)[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2017, 50(11): 125~132. (in Chinese with English abstract http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC201711013.htm [10] 邵生俊, 李骏, 李国良, 等. 大厚度自重湿陷黄土湿陷变形评价方法的研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(6): 956~978. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201506002SHAO Shengjun, LI Jun, LI Guoliang, et al. Evaluation method for self-weight collapsible deformation of large thickness loess foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(6): 956~978. (in Chinese with English abstract http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcxb201506002 [11] 李开超, 高虎艳, 邓建国, 等. 西安地铁四号线南段大厚度湿陷性黄土浸水试验研究[J]. 地下水, 2017, 39(2): 133~137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2017.02.056LI Kaichao, GAO Huyan, DENG Jianguo, et al. Xi'an metro line four South Thick Collapsible Loess of water immersion tests[J]. Ground Water, 2017, 39(2): 133~137. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2017.02.056 [12] 张国伟, 范寒光, 张常亮, 等. 西安地铁五号线湿陷性黄土浸水特性研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(S): 400~407. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10700-1018834815.htmZHANG Guowei, FAN Hanguang, ZHANG Changliang, et al. Immeision characteristics of collapsed loess in Xi’an Metro Line 5[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 24(S): 400~407. (in Chinese with English abstract http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10700-1018834815.htm [13] 甘肃省建工一局建筑科学研究所. 自重湿陷性黄土的试验研究[R]. 1975, 4.Gansu Province Building Research Institute. Test research on collapsible loess under overburden pressure[R]. 1975, 4. (in Chinese) [14] 第八冶金建设公司建筑科学研究所. 湿陷性黄土地区桩基负摩擦力的初步研究[R]. 1977, 1.Building Research Institute of No 8th Metallurgical Construction Company. Preliminary research on the negative skin friction of pile foundation in collapsible loess area[R]. 1977, 1. (in Chinese) [15] 中华人民共和国建设部. GB 50025-2004 湿陷性黄土地区建筑规范[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2004.Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China. GB 50025-2004 Code for building construction in collapsible loess regions[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2004. (in Chinese) [16] 刘明振. 湿陷性黄土间歇浸水试验[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1985, 7(1): 47~54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1985.01.005LIU Mingzhen. Collapsible loess intermittent water immersion test[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1985, 7(1): 47~54. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1985.01.005 [17] 钱鸿缙, 罗宇生. 湿陷性黄土地基[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1985.QIAN Hongjin, LUO Yusheng. Collapsed loess foundation[M]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 1985 (in Chinese) [18] 谢定义. 黄土力学特性与应用研究的过去、现在与未来[J]. 地下空间, 1999, 19(4): 273~284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.1999.04.003XIE Dingyi. The past, present and future of the research on mechanical characteristics and application of loess[J]. Underground Space, 1999, 19(4): 273~284. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0836.1999.04.003 [19] 谢定义. 试论我国黄土力学研究中的若干新趋向[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2001, 23(1): 3~13. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.01.002XIE Dingyi. Exploration of some new tendencies in research of loess soil mechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(1): 3~13. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.01.002 [20] 郅彬, 郭洁, 彭敏, 等. 增湿减湿对黄土湿陷性的影响研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(28): 273~276, 287. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.28.050ZHI Bin, GUO Jie, PENG Min, et al. Research on the impact of humidification and dehumidification on the loess collapsibility[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(28): 273~276, 287 (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.28.050 -





 下载:
下载: