MULTI-LEVEL GEOLOGICAL MAPPING APPROACHES OF THE PLANE AREA AND APPLICATIONS: A CASE STUDY IN 1: 50000 SHEETS OF GANGKOU, TAIXIAN, ZHANGDIANGONGSHE, TAIXINGXIAN AND SHENGCITANGZHEN
-
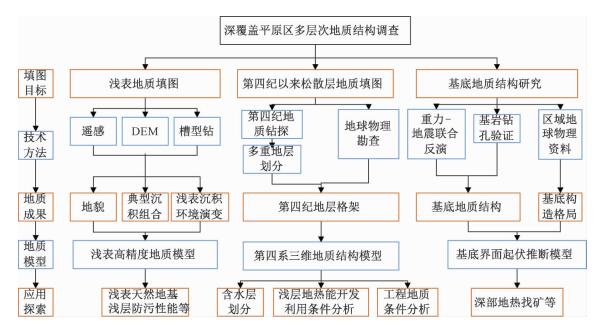
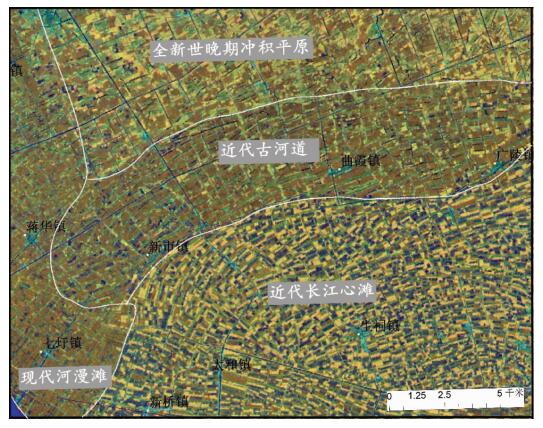
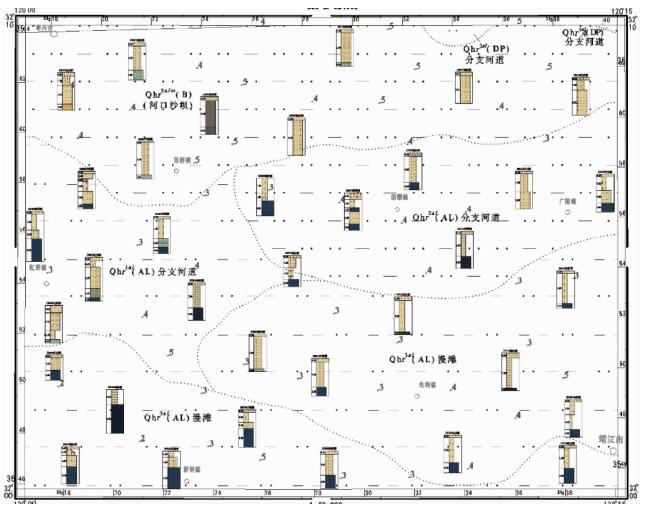
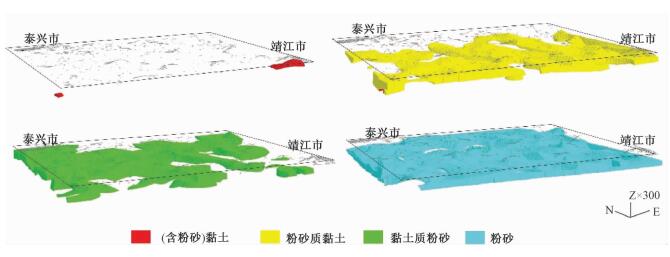
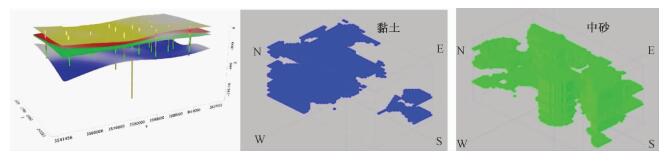
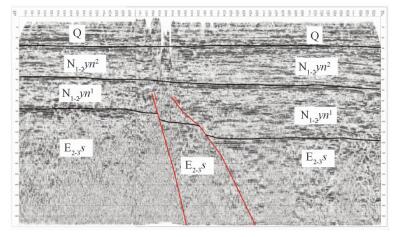
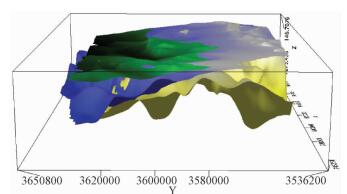
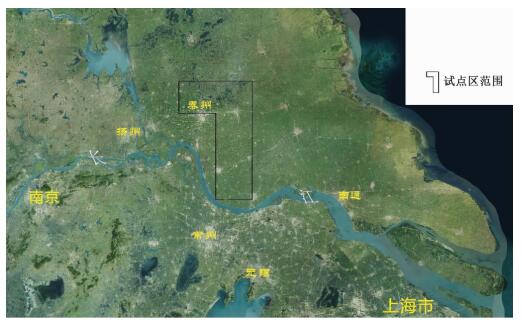
摘要: 以江苏港口、泰县、张甸公社、泰兴县、生祠堂镇幅平原区1:50000填图试点为例,围绕深覆盖平原区1:50000基础地质填图的不同深度层次目标任务,采取多种有效技术方法组合,分别对浅表(0~4 m)沉积物、第四纪以来松散层、以及基岩地质等3个深度层次的有效地质填图技术方法进行研究。浅表采用槽型钻+DEM+RS的综合填图方法,第四纪以来松散层采用钻孔、综合地球物理测井相结合的方法建立地层格架,基底地质特征通过区域重磁资料结合浅层地震勘查研究,有效填绘各层次地质信息。基于多种信息源,建立了不同深度、不同精度的多尺度三维地质模型,通过三维建模客观表达多层次地质结构特征,丰富了平原区1:50000填图成果图件体系。最后,探索了不同层次填图成果的应用领域,为平原区1:50000填图的地质图件表达及成果应用提供示范。Abstract: To take geological survey of 1:50000 sheets of Gangkou, Taixian, Zhangdiangongshe, Taixingxian and Shengcitangzhen for an example, geological mapping technologies for three depth levels of shallow (0 to 4 m), Quaternary and bedrock depth have been discussed in this paper. Different combination of effective mapping methods should be selected to determine different mapping targets of different depths. Shallow deposits are mapped by the methods of groove drilling, DEM analyzing and RS (remote sensing) image interpretation. The stratigraphic framework of Quaternary deposits is established by combination of drilling and integrated geophysical logging. The bedrock geological characteristics are studied according to the regional magnetic data combined with the shallow seismic exploration method. These geological methods could obtain geological information effectively. The multi-scale three-dimensional geological models of different depth and precision are established based on a variety of geological information. The multi-level geological structure characteristics are presented by three-dimensional modeling, which enriches 1:50000 geological mapping results. Finally, the applications of different level mapping results are discussed, leading the way of expression and application of 1:50000 geological mapping results in plane area.
-
Key words:
- plane area /
- 1:50000 mapping /
- 3D geological structure /
- results application
-
1. 区域地质概况
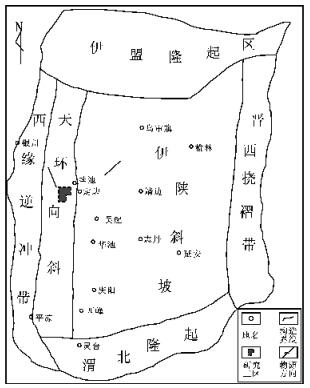
麻黄山西区位于鄂尔多斯盆地天环坳陷西部[1](图 1)。区域上,延长组为大型湖泊沉积,砂体主要为三角洲类型。本次研究的目的层段三叠系延长组长4 + 5至长6段,共分5个油层组,分别为长4 + 51、长4 + 52、长61、长62、长63。本区总体沉积属于鄂尔多斯盆地西部三角洲体系,长4 + 5、长6段为三角洲前缘亚相[1-2],岩性主要为粉细砂岩与泥岩互层,埋深大约在2170m~2650m之间,油气显示普遍,但试油水多油少,目前处于勘探评价阶段,尚未进行开发生产。
本区储层属低孔低渗一致密型储层,因此储层的含油气较差,造成储层物性及含油气差的原因除储层的沉积类型之外,成岩作用是一个不可忽视的因素。本文从研究区成岩作用类型、成岩阶段划分等方面论述了成岩作用对储层物性与含油气性的影响,为今后该区有利储层勘探开发提供参考。
2. 储层岩石学及物性特征
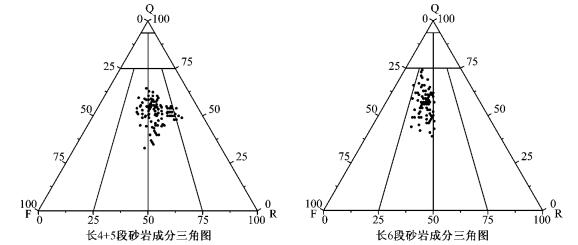
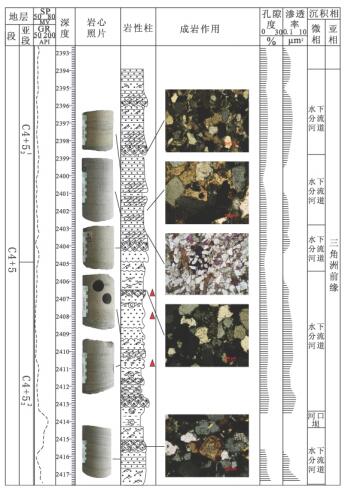
根据岩心观察及薄片鉴定结果,长4 + 5段储层岩性主要为浅灰色、灰色长石岩屑砂岩(图 2)。碎屑岩中石英含量51% ~ 73%,长石主要为钾长石和斜长石,含量6.8%~20.4%,岩屑见变质岩岩屑、火成岩岩屑和沉积岩岩屑,含量19.1% ~ 27.3%,以变质岩岩屑为主。
长6段储层岩性主要为浅灰色岩屑长石细砂岩(图 2)。碎屑岩中石英含量55.8% ~ 75.5%,长石主要为钾长石和斜长石,含量5.5% ~ 26.3%,岩屑见变质岩岩屑、火成岩岩屑和沉积岩岩屑,含量17%~27.8%。
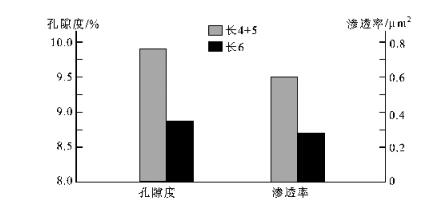
长4 + 5段储层平均孔隙度为9.9%,平均渗透率为0.6×10-3μm2; 长6段储层平均孔隙度为8.6%,平均渗透率为0.36×10-3μm2。可见,储层类型为低孔低渗一致密型,其中长4+ 5段储层物性略好于长6段储层(图 3)。
3. 成岩作用及特征
利用偏光显微镜对研究区取心井的岩石薄片样品进行观察描述和分析鉴定,认为该地区影响储层性质的成岩作用主要有机械压实与压溶作用、胶结作用、交代作用及溶蚀作用,其特征如下:
3.1 机械压实及压溶作用
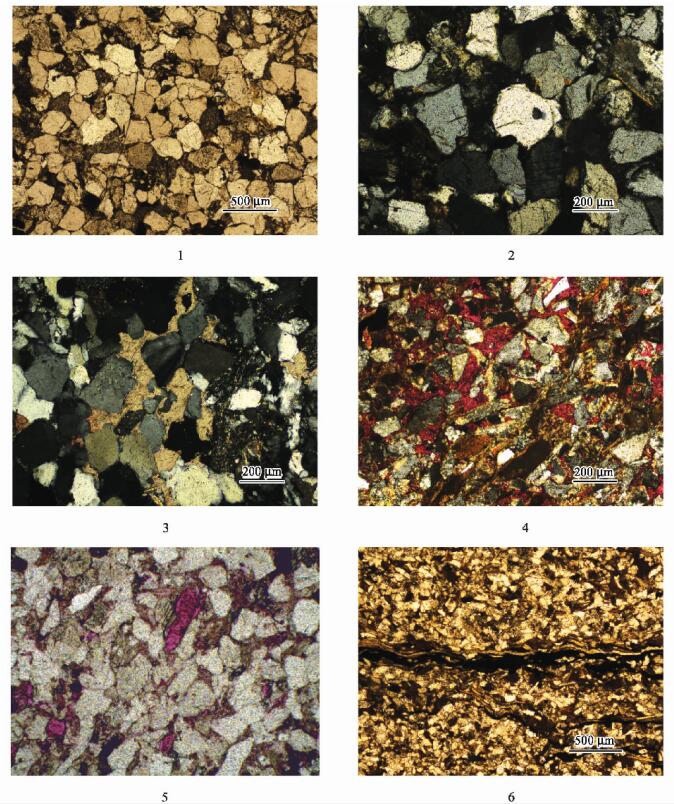
研究区长4 + 5及长6段砂岩的支撑类型主要为颗粒支撑,接触类型主要为点一线接触及线接触(图版-1)。泥质岩屑呈假杂基状充填于岩石孔隙之中,云母等片状矿物受挤压发生变形。砂岩压溶作用明显,如ND14井可见石英颗粒次生加大现象(图版-2),一般加大边环绕石英颗粒或局部分布,为Ⅱ级加大。这些现象表明本区压实与压溶作用都较强,本区储层原生孔隙几乎损失殆尽,导致在本区原生孔隙很少发育。所以压实作用是本区储层物性变差的主要原因,现今已发现的油气储集空间主要是由后期成岩改造所形成。
3.2 胶结作用
长4 + 5及长6储层砂岩的胶结类型主要为孔隙式胶结。成岩前期的泥质、钙质胶结伴随压实作用使岩石孔隙急剧减少;后期压实作用使孔隙度的减少速率变小,储层岩石物性变差的原因主要是孔隙被自生粘土及碳酸盐类矿物所充填。
3.2.1 碳酸盐胶结作用
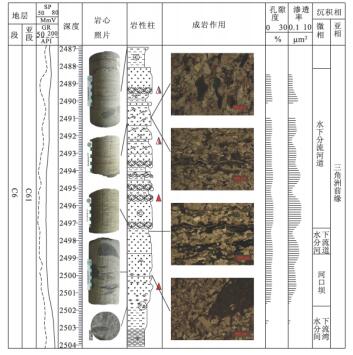
研究区长4 + 5及长6储层砂岩碳酸盐胶结非常普遍(图版-3),主要矿物有含铁的方解石、白云石,以及少量的菱铁矿。从ND14井可见,在水下分流河道砂岩中碳酸盐胶结较严重(图 4),这可能是由于水下分流河道砂岩孔渗相对较好,地层水活跃,溶解作用强烈,更有利于自生碳酸盐的沉淀。方解石呈微晶或亮晶结构,部分或完全交代碎屑颗粒,铁白云石具明显的铁质环带,由此可见该碳酸盐胶结物形成于主压实期以后的埋藏成岩作用,因为在深埋作用下,蒙一伊转变和钙斜长石溶解产生的Ca2+、Mg2+、及Fe2+结合能形成白云石及铁白云石[3]。
3.2.2 自生粘土矿物胶结
研究区自生粘土矿物胶结以绿泥石胶结为主,其平均相对含量高达49.95% (表 1)。绿泥石主要沿颗粒边缘生长,在颗粒表面形成环边或包壳,对岩石的孔隙起到保护的作用。绿泥石的一种成因是由于云母的风化所致,该区常见黑云母及云母化的千枚岩屑,且大多绿泥石化,故绿泥石部分来自云母及岩屑。也有学者认为,大量绿泥石胶结物多出现于三角洲前缘环境,其形成可能与入湖的河流带来的溶解铁有关[4]。
表 1 长4 + 5及长6段砂岩粘土矿物相对含量①Table 1. The relative content of clay mineral of sandstone of 4th + 5th-6th Members of Yanchang Formation
① 麻黄山西区块北部延长组储层非均质性与储层评价研宄.中国地质大学(北京),2008.
自生高岭石也是主要的粘土胶结矿物,其平均相对含量为25.6%。高岭石呈蠕虫状集合体充填于岩石孔隙之中,其形成与长石的大量溶解有关。
3.2.3 其他矿物胶结
硅质胶结主要是自生石英,显微镜下常见石英颗粒次生加大,加大边的形成可能与压溶作用及长石向粘土矿物转化作用有关。长石的溶解可以形成次生孔隙以及促使形成石英胶结物[5]。
研究区还见少量的浊沸石和硬石膏胶结。浊沸石的形成与火山物质的水化、长石及岩屑等不稳定组分溶蚀以及粘土矿物转化等关系密切[6]。
3.3 交代作用
研究区常见碳酸盐矿物交代其它组分,主要是方解石交代石英及长石,使石英及长石颗粒的边缘呈港湾状,见亮晶方解石(图版-4)。方解石交代石英,主要控制因素为pH值和温度。据Siever的计算[5],SiO2与CaCO3的平衡条件是pH = 9.8,t = 25℃。所以,当地层温度升高,pH > 9.8时,SiO2就会溶解,CaCO3而就会沉淀,这样方解石就交代了石英。
交代作用也主要发生于水下分流河道等钙质胶结严重的区域(图 5),强烈的钙质胶结导致方解石交代石英颗粒。交代作用过程中,溶解作用会产生部分次生孔隙,而且交代形成的方解石也较易被孔隙水溶解形成次生空隙。从整个成岩作用来说,交代作用对本区储层物性影响程度不大。
3.4 溶蚀作用
溶蚀作用是本区普遍的成岩作用,它对储层的孔隙度有着重要的影响。研究区的长石见不同程度的溶蚀,形成粒内溶孔及铸模孔(图版-5),千枚岩屑及泥质杂基溶蚀现象也较普遍,形成粒间溶孔。由于千枚岩屑呈片状且顺层理分布(图 6),所以在水下分流河道及河口坝等砂岩的平行层理及交错层理的纹层中常见溶蚀缝(图版-6)。碳酸盐矿物溶解较少,仅局部见方解石溶解,形成部分次生孔隙。这是由于在淡水一半咸水湖盆碎屑岩中,有机酸溶液铝硅酸盐组分的溶蚀要比碳酸盐组分的溶蚀强烈得多[7]。
研究区长4 + 5及长6段砂岩的溶蚀作用主要有大气淡水的淋滤作用及埋藏(溶蚀)成岩作用两种方式。
该地区延长组缺失长2及长1段地层,与上覆地层延安组呈不整合接触,说明该地区延长组在地质历史时期曾遭受抬升剥蚀。另据罗静兰等、陈瑞银等所做的埋藏史研究:鄂尔多斯盆地延长组在晚三叠世(208~203Ma)有明显的抬升剥蚀,剥蚀量在100~400m[8-9]。故研究区长4 + 5及长6段砂岩在成岩早期受到过大气淡水淋滤作用。由于大气淡水为酸性水,含CO2,pH值较低,对碳酸盐、长石及黑云母等都有溶蚀作用,易于形成次生孔隙。
后期埋藏(溶蚀)成岩作用主要由碳酸及有机酸引起的溶蚀作用。碳酸主要溶解岩石中的钙质组分,如对方解石的溶解:

但在正常压力下,随着深度的增加,温度的升高,CO2含量逐渐降低,方解石是难溶的,所以埋深较大的地层中,方解石很少被碳酸溶解[10]。有机酸主要溶蚀岩石中的硅酸盐组分,如长石与草酸的反应为:

由以上分析可以看出研究区储层岩石孔隙多为长石、岩屑溶蚀形成的次生孔隙,碳酸盐矿物溶解程度较低的原因在于有机酸的选择性溶蚀作用。
溶蚀作用形成大量的次生孔隙,使岩石物性变好,但也有溶解出来的化学成分发生再沉淀,形成胶结物,堵塞孔隙,使岩石物性变差,尤其是溶蚀作用析出的Ca、Mg等元素,在后期形成的含铁碳酸盐胶结,又使储层物性变差。
3.5 成岩相划分
由以上单因素成岩作用研究,结合含砂率、孔隙度以及碳酸盐含量平面展布,并以单井成岩作用特征为控制,根据邹才能等[11],季汉成等[12]的成岩相划分标准,将研究区的成岩相划分为:低孔渗中细粒长石岩屑砂岩压实相、低孔渗中细粒长石岩屑砂岩碳酸盐胶结相、低孔渗中细粒长石岩屑砂岩长石溶蚀相、低孔渗中细粒长石岩屑砂岩碳酸盐溶解相、低孔渗中细粒长石岩屑砂岩层理缝溶蚀相等。
4. 成岩阶段的确定
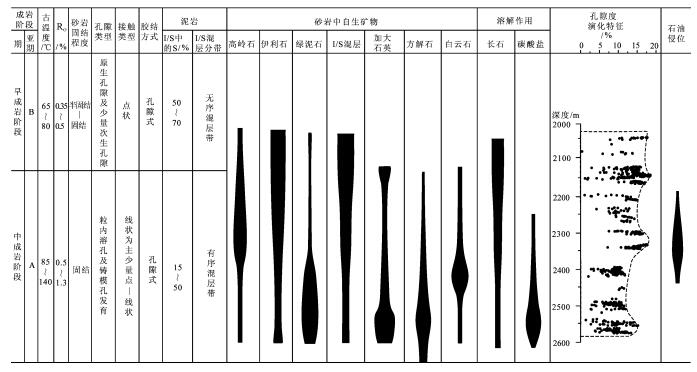
研究区储层属于淡水一半咸水湖盆碎屑岩,其古地温、有机质成熟度、自生粘土矿物及岩石结构和孔隙类型等特征如下(图 7)。
长4 + 5、长6储层埋深在1650m~2500m之间,古地温大约在75~120℃之间。鄂尔多斯盆地内延长组烃源岩镜质体反射率为0.7%~1.0%[13]; 颗粒间以点一线及线接触为主,局部呈凹凸接触;石英次生加大现象普遍,属Ⅱ级加大;胶结类型为孔隙式胶结,胶结物主要为含铁的碳酸盐矿物;长石大量被溶蚀,次生溶蚀孔隙发育,局部见少量溶蚀缝;砂岩中自生粘土矿物主要为绿泥石、伊利石及高岭石。
根据以上各种特征,按照中国石油天然气集团总公司规范(2003年)①,初步判断研究区长4+ 5、长6储层目前主要处于中成岩A期,局部处于早成岩B期。
① 中国石油天然气集团总公司,SY/T5477碎屑岩成岩阶段划分规范,2003.
5. 成岩演化史及对储集物性的影响
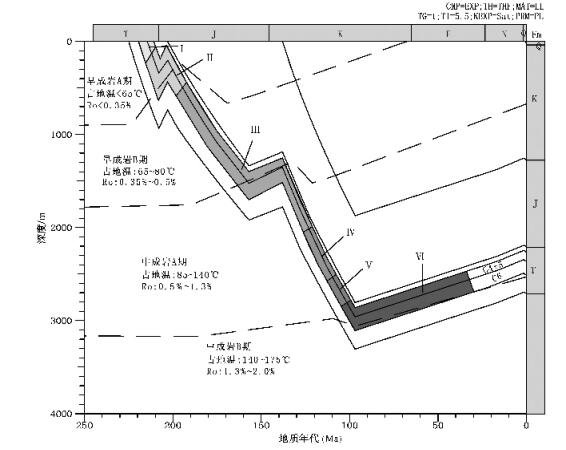
根据研究区的全井资料,运用PRA盆地模拟软件对盆地埋藏进行了模拟恢复[14],根据目的层段的埋藏曲线结合古地温和Ro等资料划分了研究区的成岩阶段及演化序列(图 8):
早成岩A期:有机质未成熟,古温度小于65℃。地层持续沉降,储层主要以机械压实为主,颗粒以点接触,岩石弱固结一半固结,岩石孔隙迅速减少,孔隙类型主要为原生粒间孔隙,此阶段为早期机械压实、胶结作用阶段(Ⅰ阶段)。
早成岩B期:有机质未成熟一低成熟,古温度范围为65~80℃。在早成岩B期早期,地层继续沉降,储层主要受机械压实作用和胶结作用,早期胶结物较少,局部出现方解石胶结,由于胶结作用较弱,压实作用使原生孔隙损失较多,颗粒呈点一线接触。受晚三叠世(208 ~203Ma)构造抬升的影响,延长组顶部出露地表,遭受剥蚀,储层受到大气淡水淋滤作用,部分长石及碳酸盐矿物受到溶蚀,形成次生孔隙带,埋深分布于2100m ~ 2200m之间,但由于抬升时间较短(只有约5Ma),所以溶蚀强度有限,对储集物性影响不大,该阶段为大气淡水淋滤作用阶段(Ⅱ阶段)。随后地层连续沉降(在侏罗纪晚期短暂抬升),受到强烈的压实及胶结作用,在早成岩B期末期,石英次生加大开始出现,此阶段为中期强烈压实、胶结作用阶段(Ⅲ阶段)。
中成岩A期:随着地层的继续埋深,有机质开始进入生烃门限,有机质成熟阶段为低熟一成熟。由于油气的生成,有机酸大量出现,处于相对封闭的酸性环境,古温度范围为85~140℃。在中成岩A期早期,地层继续受到压实作用,但由于胶结作用的影响,压实强度逐渐减弱,颗粒以线接触为主,局部见凹凸接触,石英次生加大现象较普遍。该期有机酸开始大量出现,铝硅酸盐矿物受到强烈的溶蚀,部分碳酸盐也被溶蚀,形成大量次生溶蚀孔隙,分布于2250m~2350m之间,为主要的储集空间,该阶段为有机酸溶蚀作用阶段(Ⅳ阶段)。随后一段时期有机质进入储层,是油气侵位的主要阶段(Ⅴ阶段)。在中成岩A期末期,有机质成熟,进入生油高峰,有机酸浓度降低,铁方解石及铁白云石大量出现,成为储层的主要胶结物,同时碳酸盐矿物交代石英及长石颗粒,此阶段为铁方解石、铁白云石胶结阶段(Ⅵ阶段)。
中成岩B期:长6底部以下为中成岩B期,但由于不在研究目标层段,缺乏资料,未作分析。
由以上分析可以看出,在成岩演化过程中,Ⅲ阶段的强烈压实和胶结作用及Ⅵ阶段的碳酸盐胶结使研究区长4 + 5、长6储层的原生孔隙损失殆尽,故该区主要为致密型储层。目前本区研究层段的储层平均孔隙度为9.15%,且主要Ⅳ阶段形成的次生溶蚀孔隙,因此不同成岩作用的演化阶段对储层物性有着重要的影响。
6. 结论
(1) 研究区长4 + 5、长6储层岩性主要为细粒一极细粒岩屑长石砂岩及长石岩屑砂岩,结构及成分成熟度较低。平均孔隙度为9.15(,平均渗透率为0.67×10-3μm2, 属低孔特低渗一超低渗的致密储层。
(2) 根据压实作用、胶结作用及交代溶蚀作用等成岩作用特征,结合粘土矿物分析化验资料及盆地埋藏史研究,综合判断长4 + 5、长6储层总体处于中成岩A期,局部为早成岩B期。所经历的成岩演化序列为:Ⅰ.早期机械压实及胶结作用阶段;Ⅱ.大气淡水淋滤作用阶段;Ⅲ.中期强烈压实压溶及胶结作用阶段;Ⅳ.有机酸溶蚀作用阶段;Ⅴ.石油侵位阶段;Ⅵ.铁方解石及铁白云石胶结作用阶段。
(3) 研究区储层砂岩粒度较细,含油性差,加上压实压溶、胶结等作用,特别是后期的碳酸盐胶结作用,使岩石孔隙急剧减少,总体上该区储层物性较差。而大气淡水的淋滤作用及有机酸溶蚀作用,尤其是有机酸对长石及顺层理分布的泥质岩屑的溶蚀,形成一些次生孔隙,改善了储层物性,故该区较好储层应为粒度稍粗、层理发育的水下分流河道及河口坝砂体,这些具有较好次生孔隙的储层是今后油气勘探开发的重点。
-
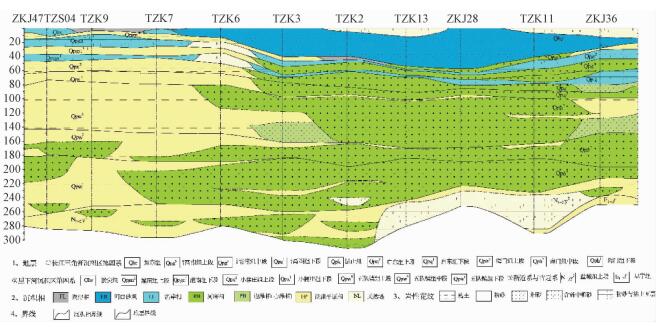
表 1 试点图幅第四纪地层简表
Table 1. Quaternary lithostratigraphy of mapping area
年代 里下河沉积区(东台地层小区) 长江三角洲沉积区(南通地层小区) 组名 深度/m 岩性特征 沉积相 组名 深度/m 岩性特征 沉积相 全新世 淤尖组 3~6 灰、灰黄色黏土; 黏土质粉砂 湖沼相
滨岸相如东组 20~50 灰色粉砂与黏土互层, 粉砂 河口砂坝 晚更
新世灌南组 20~40 灰黄、棕黄色黏土; 灰色粉砂与黏土互层 泛滥相
滨岸相滆湖组 35~75 灰色中粗砂、含砾中粗砂; 细砂 河床相
滨岸相昆山组 50~80 灰、青灰、灰黄色粉砂夹黏土、粉砂、细砂 滨岸相 中更
新世小腰庄组 75~95 灰黄、棕黄色黏土为主 泛滥相 启东组 80~110 灰色、灰黄色砂砾层、含砾粗砂、细砂 河床相
边滩相早更
新世五队镇组 190~270 灰、灰绿、灰黄色黏土、含粉砂黏土, 局部夹粉砂、细砂 泛滥相 海门组 200~270 灰、灰黄色粉砂、细砂、中粗砂、含砾中粗砂、砾石层, 局部夹薄层灰黄、灰褐色黏土 河床相 -
[1] 张智勇, 张克信, 于庆文, 等.造山带区1/25万区域地质调查方法[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27(4):377~385. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200204004.htmZHANG Zhi-yong, ZHANG Ke-xin, YU Qing-wen, et al. Method of 1:250000 regional geological surveying in orogenic belts[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2002, 27(4):377~385. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200204004.htm [2] 邱鸿坤, 陈忠大, 汪庆华, 等.厚覆盖区1:25区域地质调查工作方法研究[J].资源调查与环境, 2004, 25(2):79~87. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ200402001.htmQIU Hong-kun, CHEN Zhong-da, WANG Qing-hua, et al. Methodological study of the heavy-cover area in 1:250000 regional geological survey[J]. Resources Survey & Environment, 2004, 25(2):79~87. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ200402001.htm [3] Weertsa H J T, Westerhoffa W E, Cleveringaa P. Quaternary geological mapping of the lowlands of the Netherlands, a 21st century perspective[J]. Quaternary International, 2005, 133/134:159~178. [4] 李继军.天津城市三维地质结构调查工作方法的应用[J].地质调查与研究, 2006, 29(3):233~240. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200603010.htmLI Ji-jun. Working method of 3-D geological structure investigation of Tianjin[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2006, 29(3):233~240. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ200603010.htm [5] 缪卫东, 周国兴, 冯金顺, 等.二维地震勘探方法在南通区调工作中的应用[J].地震地质, 2010, 32(3):520~531. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201003022.htmMIAO Wei-dong, ZHOU Guo-xing, FENG Jin-shun, et al. Application of 2nd seismic method in regional geological survey in Nantong[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2010, 32(3):520~531. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201003022.htm [6] Bierkens M F P, Weerts H J T. Application of indicator simulation to modelling the lithological properties of a complex confining layer[J].Geoderma, 1994, 62:265~284. doi: 10.1016/0016-7061(94)90040-X [7] 郑翔, 吴志春, 张洋洋, 等.国外三维地质填图的新进展[J].东华理工大学学报:社会科学版, 2013, 32(3):397~402. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZSZ201303039.htmZHENG Xiang, WU Zhi-chun, ZHANG Yang-yang, et al. The new progress of overseas 3D-geological mapping[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology:Social Science, 2013, 32(3):397~402. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZSZ201303039.htm [8] Koichi Suzuki, Shinji Toda, Kenichiro Kusunoki, et al. Case studies of electrical and electromagnetic methods applied to mapping active faults beneath the thick quaternary[J]. Engineering Geology, 2000, 56:29~45. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(99)00132-5 [9] 金永念, 季克其.地质调查中物探资料的开发应用[J].中国区域地质, 2001, 20(4):422~443. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200104014.htmJIN Yong-nian, JI Ke-qi. Development and application of geophysical data in geological survey[J]. Regional Geology of China, 2001, 20(4):422~443. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200104014.htm [10] 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 辛后田, 等.平原区1:5万区域地质调查在生态文明建设中的作用——以渤海湾北岸为例[J].地质调查与研究, 2014, 37(2):85~89. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201402002.htmXU Qin-mian, YUAN Gui-bang, XIN Hou-tian, et al. Functions of 1:50000 regional geological survey in ecological civilization construction:acase study on northern coast of Bohai Bay[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2014, 37(2):85~89. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201402002.htm [11] 安守林, 黄敬军, 张丽, 等.海绵城市建设下城市地质调查工作方向与支撑作用——以徐州市为例[J].城市地质, 2015, 10(4):6~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ201504002.htmAN Shou-lin, HUANG Jing-jun, ZHANG Li, et al. The urban geological survey working direction and supporting role on sponge city construction:Take Xuzhou City as an example[J]. City Geology, 2015, 10(4):6~10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSDZ201504002.htm -






 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载: