The methods of fracture prediction based on structural strain analysis and its application
-
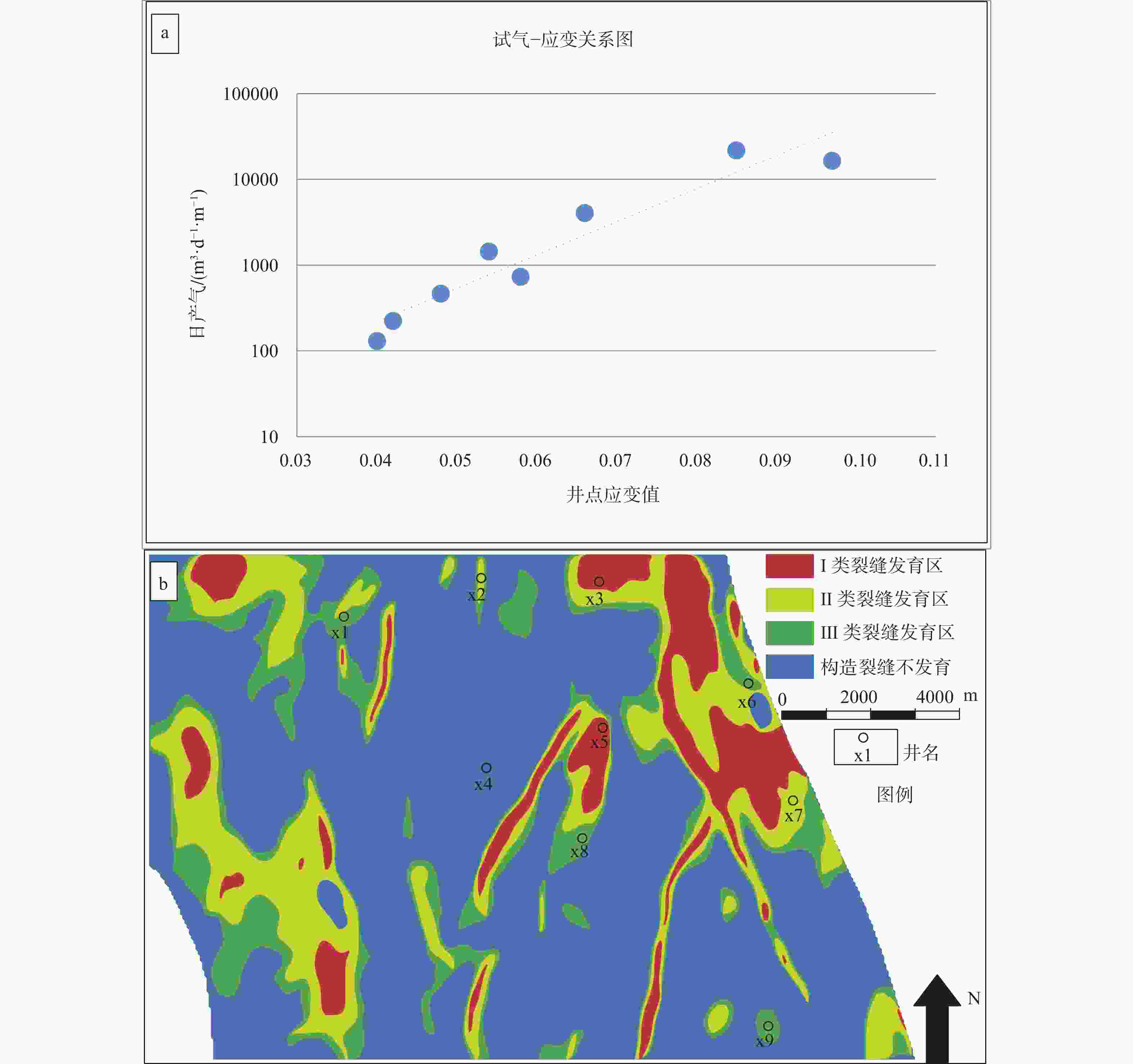
摘要: 地层应变是构造裂缝产生的直接因素,根据构造应变大小可以预测构造裂缝发育的位置和强度,对研究区的主要裂缝发育区进行划分。文章以松辽盆地徐家围子断陷徐中地区营城组四段(简称营四段)为研究对象,在建立研究区精细的三维构造模型基础上,利用“构造恢复”方法实现研究区古构造恢复,通过开展有限应变值计算来预测构造裂缝的平面分布。研究表明:研究区营四段主要包括3个造缝期,即营城组末期、泉头组—青山口组时期、嫩江组时期,其中,营城组末期与泉头组—青山口组时期的构造变形较为强烈,是裂缝的主要形成时期。根据应变大小与试气产量的关系,将研究区划分为3类裂缝发育区,Ⅰ类裂缝发育区已钻井验证,表明利用构造应变对裂缝的预测结果可靠,Ⅱ类裂缝发育区可作为深层天然气的下一步挖潜的重要方向,Ⅲ类裂缝发育区产能较低,裂缝对储层的改造作用有限。Abstract: Formation strain can directly affect the generation of structural fractures. According to the magnitude of structural strain, the location and intensity of structural fracture development can be predicted, and the chief fracture development areas in the study area can be divided. This paper takes the fourth member of the Yingcheng formation (referred to as the YING-4 section) in the Xuzhong area of the Xujiaweizi rift in the Songliao basin as the research object. Based on establishing a detailed 3D structural model of the study area, we used the “structural restoration” method to restore the paleo-structure of the study area and calculated finite strain values to predict the planar distribution of structural fractures. The research shows that the YING-4 section in the study area mainly includes three fracture-making periods, namely the end of the Yingcheng formation, the Quantou–to–Qingshankou formation, and the Nenjiang formation. Among them, the tectonic deformation at the end of the Yingcheng formation and the Quantou–to–Qingshankou formation is relatively strong, which is the main formation period of the fracture. The study area is divided into three types of fracture development zones according to the relationship between strain size and test gas production. Type I fracture development zone has been verified by well-drilling, indicating that the prediction results of fractures using structural strain are reliable. Type Ⅱ fracture development zone can be used as an important direction for the next step of deep natural gas exploration. Type Ⅲ fracture development zone has low productivity, and the fractures have limited effect on reservoir reconstruction.
-
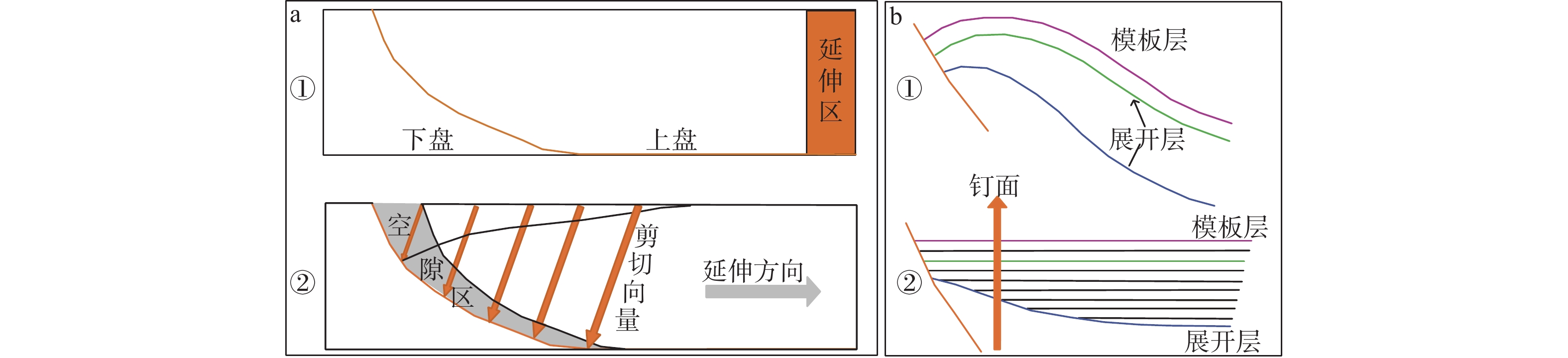
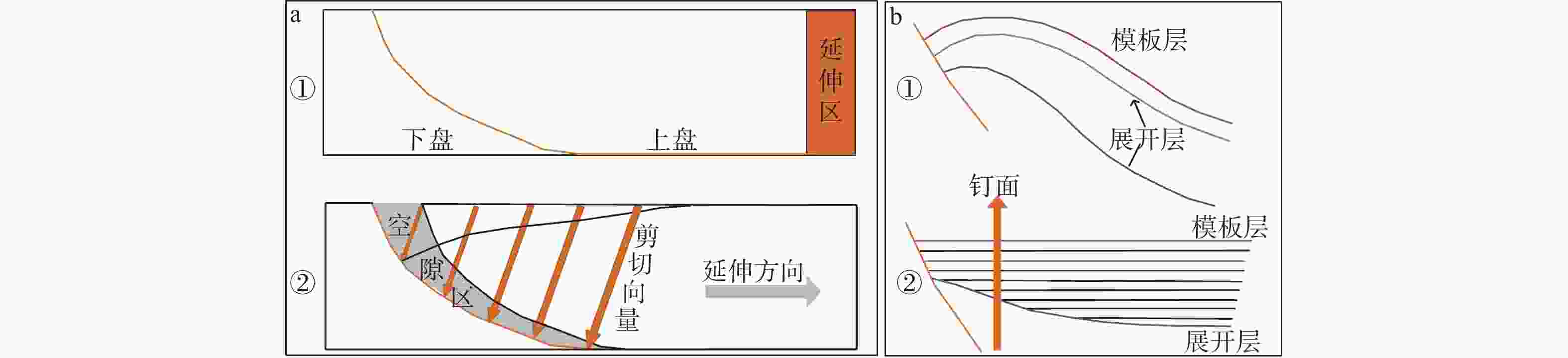
图 1 构造恢复方法示意图
a—斜剪切法恢复断层示意图(①—伸展断层形成前;②—伸展断层形成过程);b—弯滑去褶皱法恢复褶皱示意图(①—现今地层形态;②—弯滑去褶皱恢复后地层形态)
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the structural restoration methods
(a) Schematic diagram of the fault restoration by the oblique shear method (①–Before the extensional fault formation; ②–Formation process of the extensional fault); (b) Schematic diagram of the fold restoration by the flexural slip unfolding method (①–Current stratigraphic morphology; ②–Stratigraphic morphology after the fold restoration)
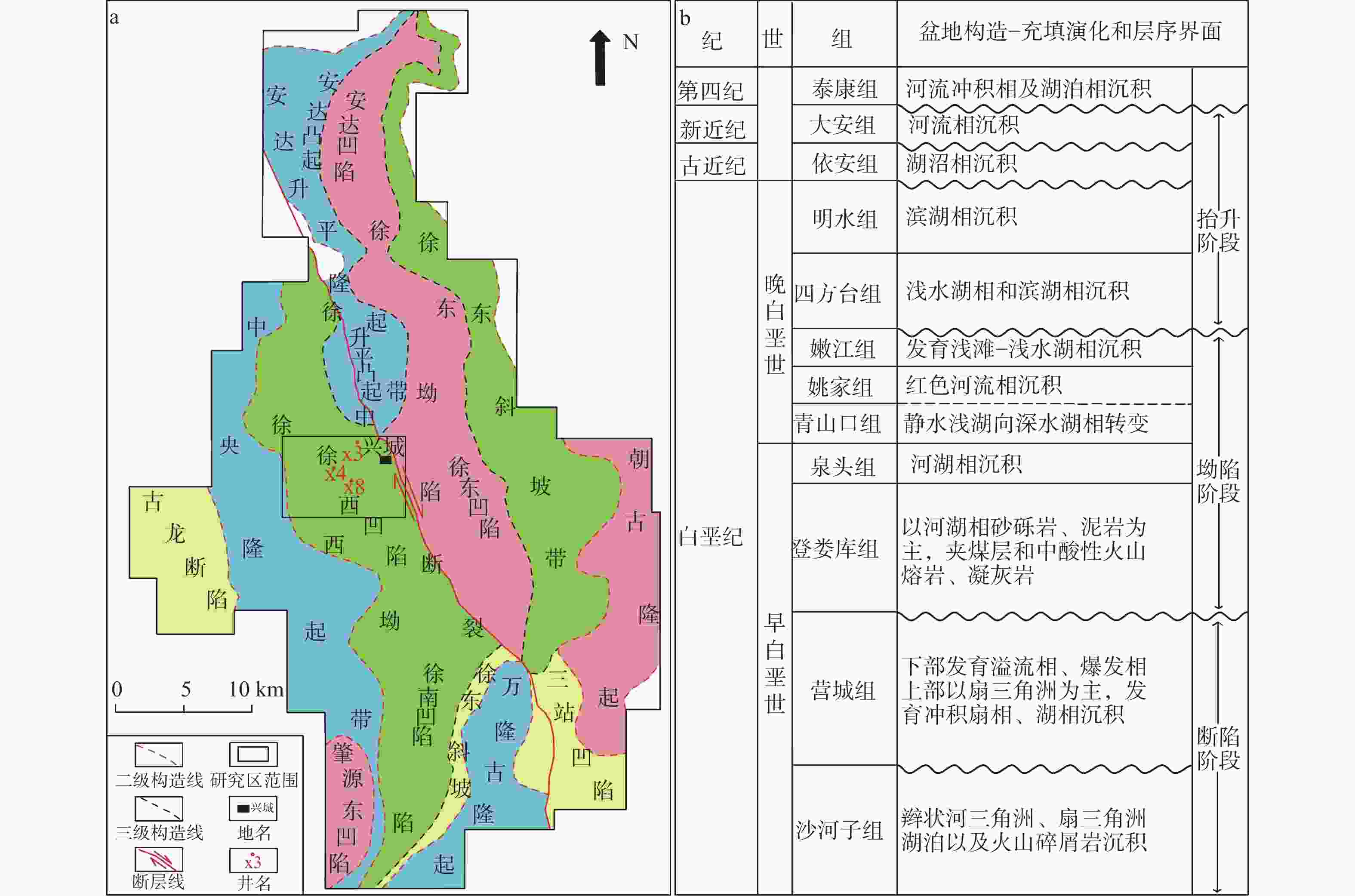
图 2 研究区构造位置及地层沉积序列图
a—研究区构造位置图(据刘国平等,2016修改);b—研究区地层沉积序列图
Figure 2. Structural location and stratigraphic sedimentary sequence map of the study area
(a) Tectonic location map of the study area (modified from Liu et al., 2016); (b) Stratigraphic sedimentary sequence map of the study area
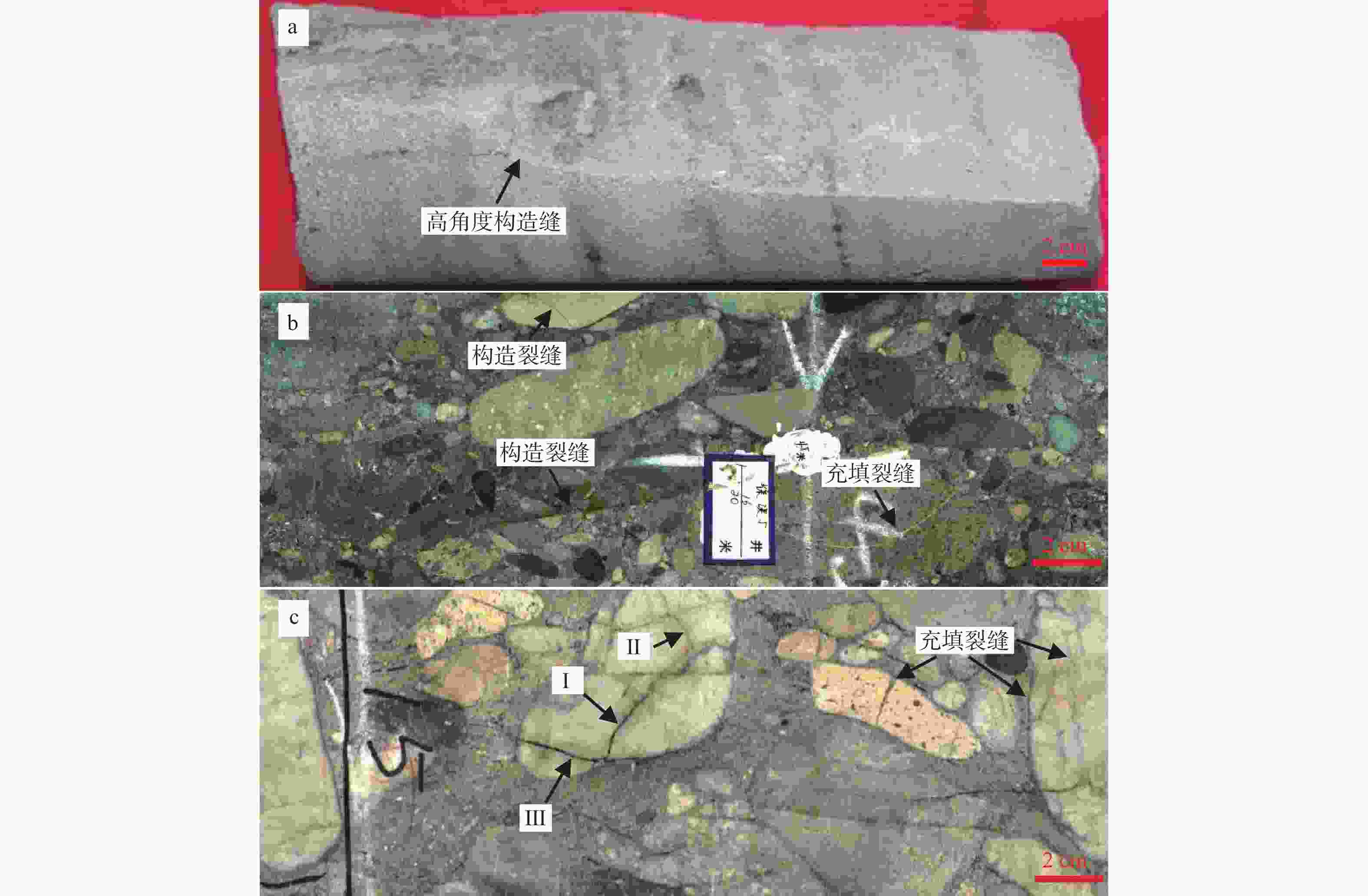
图 3 研究区构造裂缝照片
a—高角度构造裂缝,XS601井,3646.60 m;b—3组构造裂缝,早期构造裂缝被方解石完全充填,XS5井,3480.10 m;c—多组构造裂缝,构造裂缝(Ⅱ)发育受到构造裂缝(Ⅰ)限制,构造裂缝(Ⅰ)又被构造裂缝(Ⅲ)切割,部分裂缝被泥质完全充填,XS5井,3488.30 m
Figure 3. Photos of structural fractures in the study area
(a) High-angle structural fractures (Well XS601 at 3646.60 m); (b) Three groups of structural fractures, and the early structural fractures are filled by calcite (Well XS5 at 3480.10 m); (c) Multiple groups of structural fractures; Structural fracture (I) limits the development of Structural fracture (II), and Structural fracture (Ⅲ) cut Structural fracture (I); Some of the fractures are filled by mud (Well XS5 at 3488.30 m)
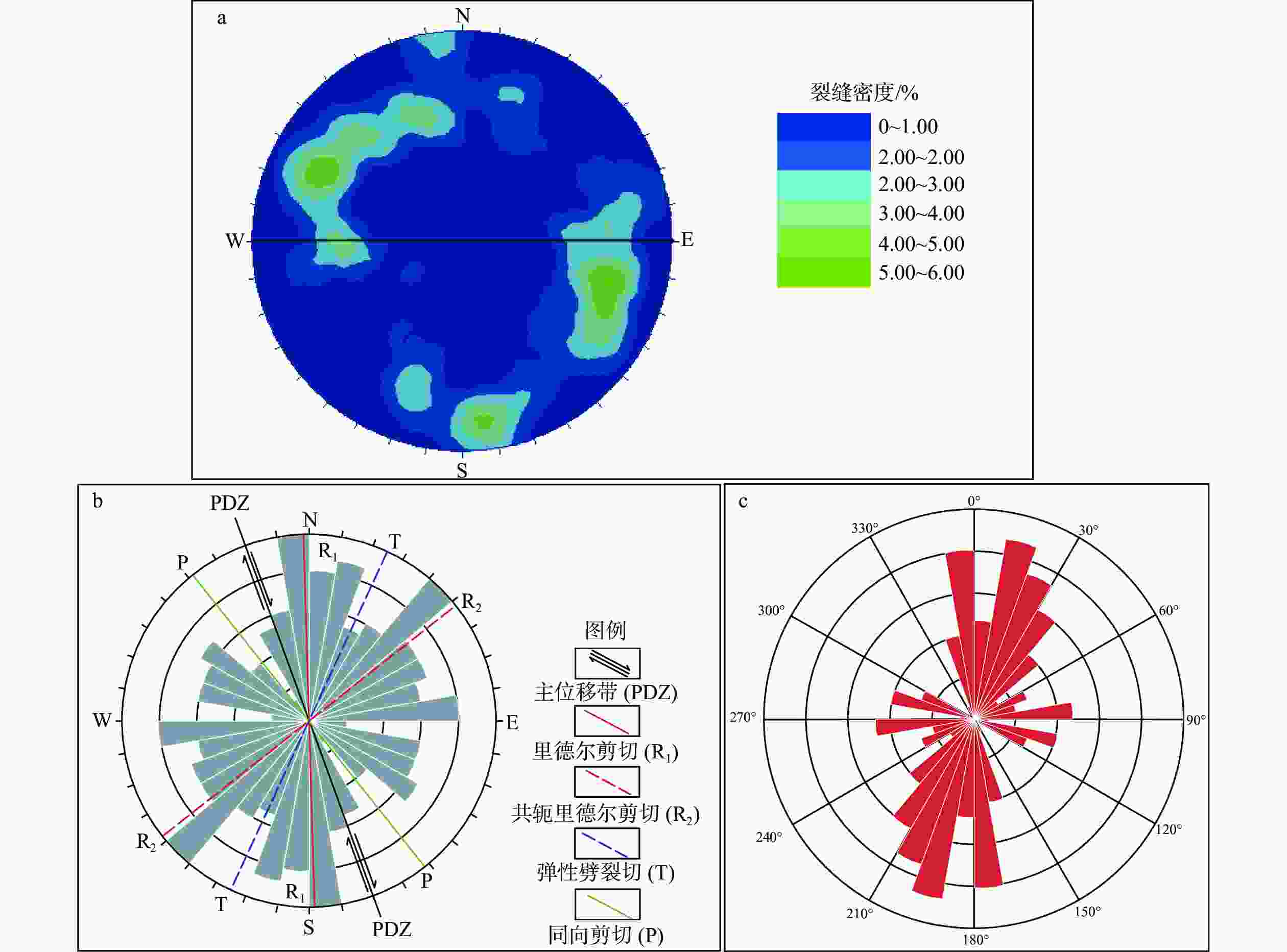
图 4 研究区裂缝产状分布图
a—构造裂缝倾向倾角等密图(n=242);b—构造裂缝走向玫瑰花图(n=242);c—充填裂缝走向玫瑰花图(n=35)
Figure 4. Distribution map of fracture occurrence in the study area
(a) Isometric map of the dip and dip direction of structural fractures (n=242); (b) Rose diagram of the strike of structural fractures (n=242); (c) Rose diagram of the strike of filling fractures (n=35)
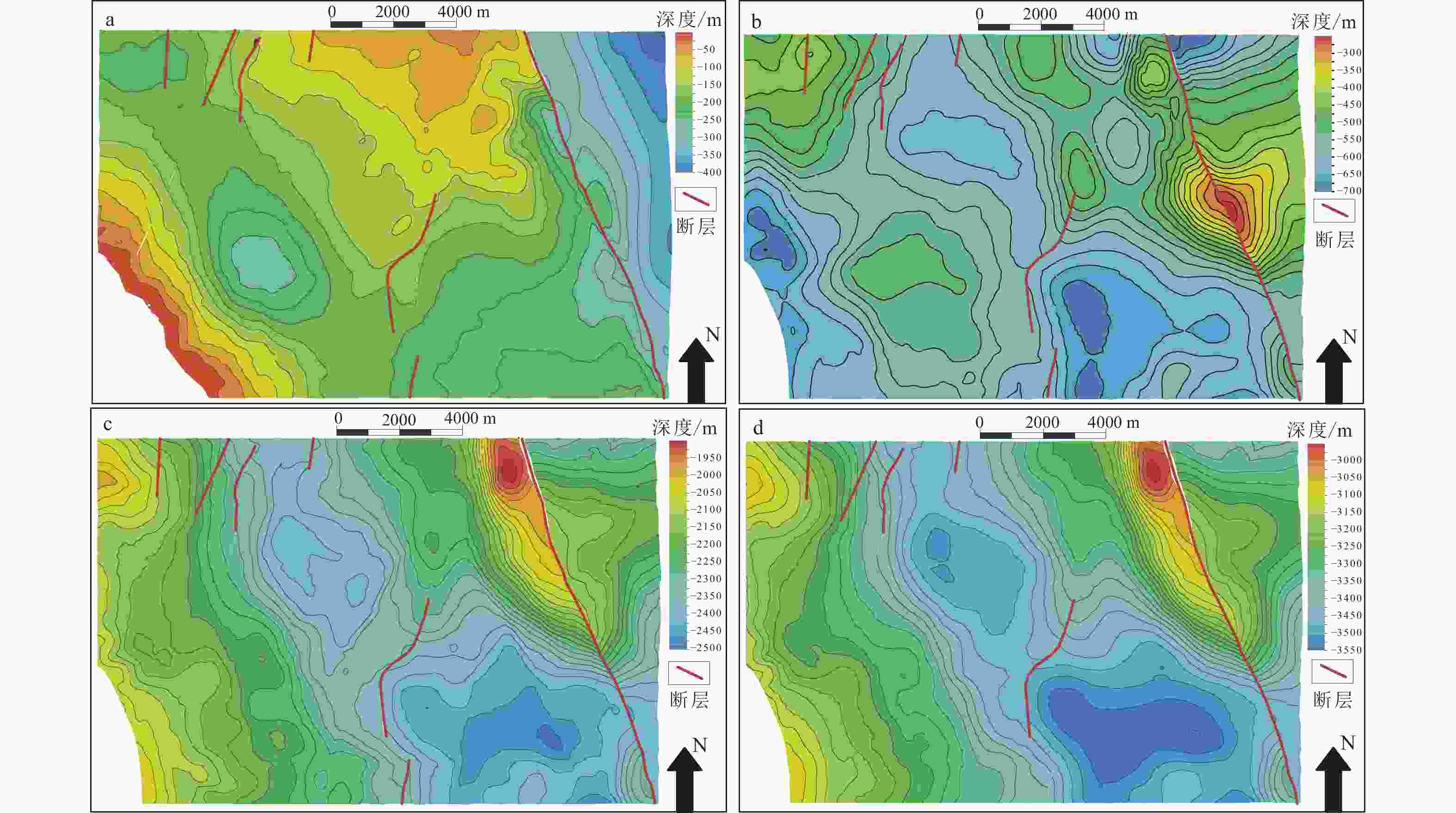
图 6 各时期研究区营四段构造图
a—营四段沉积末期底面构造图;b—登娄库组沉积末期营四段顶面构造图;c—嫩江组沉积末期营四段顶面构造图;d—现今营四段顶面构造图
Figure 6. Structural map of the YING-4 section of different periods in the study area
(a) The bottom structure of the YING-4 section at the end of the deposition; (b) The top structure of the YING-4 section at the end of the deposition of the Denglouku formation; (c) The top structure of the YING-4 section at the end of the deposition of the Nenjiang formation; (d) The top structure of the present YING-4 section
图 7 研究区有限应变分布图
a—营城末期—登娄库期有限应变分布图;b—泉头—青山口期有限应变分布图;c—嫩江期—现今有限应变图;d—三期叠加总有限应变分布图
Figure 7. Finite strain distribution in the study area
(a) Finite strain distribution map of the late Yingcheng–Denglouku period; (b) Finite strain distribution map of the Quantou–Qingshankou period; (c) Finite strain distribution map of the Nenjiang period–present; (d) Distribution map of the three-phase superimposed total finite strain
表 1 徐家围子兴城地区营四段致密气储集层渗透率与产能对应关系表(冯子辉等,2013)
Table 1. Corresponding relationship between permeability and productivity of the tight gas reservoir in the Ying-4 section of the Xingcheng area, Xujiaweizi Rift(Feng et al.,2013)
井名 井段/m 渗透率/×10-3μm2 产能(压裂后)/(m3/d) xs601 3461~3472 1.28 262641 fs5 3186~3210 0.25 49191 xs1 4435~4480 0.39 70000 3364~3379 0.31 54758 xs5 3411~3422 0.16 6619 -
BARTLETT W L, FRIEDMAN M, LOGAN J M, 1981. Experimental folding and faulting of rocks under confining pressure Part IX. Wrench faults in limestone layers[J]. Tectonophysics, 79(3-4): 255-277. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(81)90116-5 BORKOVIĆ A, KOVAČEVIĆ S, RADENKOVIĆ G, et al. , 2018. Rotation-free isogeometric analysis of an arbitrarily curved plane Bernoulli–Euler beam[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 334: 238-267. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2018.02.002 CARDOZO N, ALLMENDINGER R W, 2009. SSPX: A program to compute strain from displacement/velocity data[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 35(6): 1343-1357. CHEMENDA A I, CAVALIÉ O, VERGNOLLE M, et al. , 2016. Numerical model of formation of a 3-D strike-slip fault system[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 348(1): 61-69. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2015.09.008 CHEN S M, JIANG C J, LIU L, et al. , 2014. Fracture formation mechanism of volcanic rocks in Xujiaweizi fault depression of Songliao basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(6): 1816-1826. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHENG G Y, PANG J Y, ZHANG C S, 1988. Predicting method of the reservoir fracture system of the maukou formation in southern Sichuan[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 9(1): 32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHO Y, GIBSON R L, VASILYEVA M, et al. , 2018. Generalized multiscale finite elements for simulation of elastic-wave propagation in fractured media[J]. Geophysics, 83(1): WA9-WA20. doi: 10.1190/geo2017-0076.1 CIL M B, ALSHIBLI K A, KENESEI P, 2017. 3D experimental measurement of lattice strain and fracture behavior of sand particles using synchrotron X-ray diffraction and tomography[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 143(9): 04017048. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001737 DOOLEY T P, SCHREURS G, 2012. Analogue modelling of intraplate strike-slip tectonics: A review and new experimental results[J]. Tectonophysics, 574-575: 1-71. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.05.030 DURIEZ J, SCHOLTÈS L, DONZÉ F V, 2016. Micromechanics of wing crack propagation for different flaw properties[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 153: 378-398. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.12.034 FENG Z H, YIN C H, LU J M, et al. , 2013. Formation and accumulation of tight sandy conglomerate gas: a case from the Lower Cretaceous Yingcheng formation of Xujiaweizi fault depression, Songliao basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(6): 650-656. (in Chinese with English abstract) FISK J C, MARFURT K J, COOKE D, 2010. Correlating heterogeneous production to seismic curvature attributes in an Australian coalbed methane field[C]//2010 SEG annual meeting. Denver: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts: 2323-2328. FOSSEN H, SCHULTZ R A, SHIPTON Z K, et al. , 2007. Deformation bands in sandstone: a review[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(4): 755-769. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-036 FU X F, SHA W, YU D, et al. , 2010. Lateral sealing of faults and gas reservoir formation in volcanic rocks in Xujiaweizi fault depression[J]. Geological Review, 56(1): 60-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) GIBBS A D, 1983. Balanced cross-section construction from seismic sections in areas of extensional tectonics[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 5(2): 153-160. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(83)90040-8 GONG L, FU X F, WANG Z S, et al. , 2019. A new approach for characterization and prediction of natural fracture occurrence in tight oil sandstones with intense anisotropy[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 103(6): 1383-1400. doi: 10.1306/12131818054 GONG L, GAO S, WU J P, et al. , 2017. Natural gas accumulation and fractures in volcanic rocks of Yingcheng formation in Xujiaweizi fault depression[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 41(2): 283-290. (in Chinese with English abstract) HASAN A, ALSHIBLI K, 2012. Three dimensional fabric evolution of sheared sand[J]. Granular Matter, 14(4): 469-482. doi: 10.1007/s10035-012-0353-0 HOU G T, FENG D C, WANG W M, et al. , 2004. Reverse structures and their impacts on hydrocarbon accumulation in Songliao basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 25(1): 49-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU M, FU G, LV Y F, et al. , 2010. The fault activity period and its relationship to deep gas accumulation in the Xujiaweizi depression, Songliao basin[J]. Geological Review, 56(5): 710-718. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUDSON J A, HARRISON J P, POPESCU M E, 2002. Engineering rock mechanics: an introduction to the principles[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 55(2): B30. JACOBI R, STARR J, ECKERT C, et al. , 2021. Relay ramps and rhombochasms in the northern Appalachian Basin: extensional and strike-slip tectonics in the Marcellus Formation and Utica Group[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 105(10): 2093-2124. JIANG D W, ZHANG S M, DING R, 2020. Surface deformation and tectonic background of the 2019 Ms 6.0 Changning earthquake, Sichuan basin, SW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 200: 104493. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104493 JIANG R, ZHAO L, XU A Z, et al. , 2022. Sweet spots prediction through fracture genesis using multi-scale geological and geophysical data in the karst reservoirs of Cambrian Longwangmiao carbonate formation, Moxi-Gaoshiti area in Sichuan basin, South China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 12(5): 1313-1328. doi: 10.1007/s13202-021-01390-0 LAUBACH S E, EICHHUBL P, HARGROVE P, et al. , 2014. Fault core and damage zone fracture attributes vary along strike owing to interaction of fracture growth, quartz accumulation, and differing sandstone composition[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 68: 207-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2014.08.007 LIU G P, ZENG L B, LEI M S, et al. , 2016. Fracture development characteristics and main controlling factors of the volcanic reservoir in Xujiaweizi fault depression[J]. Geology in China, 43(1): 329-337. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J Z, HAN L, SHI L, et al. , 2021. Seismic prediction of tight sandstone reservoir fractures in XC area, western Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 42(3): 747-754. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU K, LI Y F, GUO H W, et al. , 2021. Determination of surface rupture length and analysis of Riedel shearstructure of the Litang M7.3 earthquake in west Sichuan in 1948[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(8): 2346-2360. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU X Y, JI Y F, HUANG S M, et al. , 2011. Analysis of invariants in strain tensor matrixes of crustal deformation[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 31(4): 66-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) LUO J, EVANS S G, PEI X J, et al. , 2020. Anomalous co-seismic surface effects produced by the 2014 Mw 6.2 Ludian earthquake, Yunnan, China: an example of complex faulting related to Riedel shear structures[J]. Engineering Geology, 266: 105476. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105476 LYU W Y, MIAO F B, ZHANG B J, et al. , 2020. Fracture characteristics and their influence on natural gas production: a case study of the tight conglomerate reservoir in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation in Jian’gearea, Sichuan basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 41(3): 484-491, 557. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA R H, WANG A Z, 2006. Mapping palaeostructural evolution with tectonic reconstruction theory[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 26(1): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) MARRETT R, GALE J F W, GÓMEZ L A, et al. , 2018. Correlation analysis of fracture arrangement in space[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 108: 16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2017.06.012 MEANS W D, 1976. Stress and strain[M]. New York: Springer. OLIVEIRA L S B, NOGUEIRA F C C, VASCONCELOS D L, 2022. Mechanical stratigraphy influences deformation band pattern in arkosic sandstones, Rio do Peixe Basin, Brazil[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 155: 104510. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2022.104510 OZKAYA S I, 2019. Validating predicted fracture corridors by statistical comparison with well data[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering, 22(4): 1385-1398. QIU Y X, 2000. On the method of tectonic sieving[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 6(1): 33-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) RAO G, LI A M, YAN B, et al. , 2011. Co-seismic Riedel shear structures produced by the 2010 Mw 6.9 Yushu earthquake, central Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 507(1-4): 86-94. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.05.011 REN H L, LIU C L, LIU W P, et al. , 2020. Stress field simulation and fracture development prediction of the Wufeng formation—Longmaxi formation in the Fushun-Yongchuan block, Sichuan basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(1): 74-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) RENANI H R, MARTIN C D, 2018. Cohesion degradation and friction mobilization in brittle failure of rocks[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 106: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.04.003 SCHULTZ R A, FOSSEN H, 2008. Terminology for structural discontinuities[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 92(7): 853-867. doi: 10.1306/02200807065 SUN Q C, SUN X M, WANG P J, et al. , 2007. Joint structure features, distribution regularity and reservoir prediction of Yingcheng formation in Eastern Songliao basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 37(6): 1091-1096. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG X D, WANG R, SHI W Z, et al. , 2022. Tectonic characteristics and evolution of typical rift basins in eastern China: a case study in the Gudian area, Songliao basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 41(3): 85-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Z S, DONG S Q, MENG N N, et al. , 2020. Fracture network in the low-permeability fault block reservoirs in deep-buried Gaoshangpu oilfield, Bohai Bay basin, and its controlling factors[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 41(3): 534-542, 626. (in Chinese with English abstract) WEN H J, SHU P, FAN C W, et al. , 2008. Reservoir space type and control factors of the deep conglomerate reservoir in Xingcheng gas field[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 32(3): 101-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) WITHJACK M O, PETERSON E T, 1993. Prediction of normal-fault geometries-a sensitivity analysis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 77(11): 1860-1873. WU M, YANG F L, LU J L, 2010. Predication of fractures in the volcanic reservoirs in the east of the Songliao basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 17(5): 60-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIAO F S, CHEN K, RAN Q, et al. , 2018. New understandings of the seismic modes of high productivity wells in the Sinian Dengying Fm gas reservoirs in the Gaoshiti area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 5(5): 499-507. doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2018.02.004 XIE J T, QIN Q R, FAN C H, 2019. Quantitative prediction of fracture distribution of the Longmaxi formation in the Dingshan area, China using FEM numerical simulation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(6): 1662-1672. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13815 ZENG L B, QI J F, WANG Y X, 2007. Origin type of tectonic fractures and geological conditions in low-permeability reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 28(4): 52-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZENG L B, SU H, TANG X M, et al. , 2013a. Fractured tight sandstone oil and gas reservoirs: a new play type in the Dongpu depression, Bohai bay basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 97(3): 363-377. doi: 10.1306/09121212057 ZENG W T, ZHANG J C, DING W L, et al. , 2013b. Fracture development in Paleozoic shale of Chongqing area (South China). Part one: fracture characteristics and comparative analysis of main controlling factors[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 75: 251-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.07.014 ZHANG J B, LIU S L, DAI J S, et al. , 2019. The quantitative prediction of structural fractures in ordovician reservoir in Yu-bei area, Tarim basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(2): 177-186. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y G, CHEN S M, ZHANG E H, et al. , 2010. The new progress of Xujiaweizi fault depression characteristics of structural geology research[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(1): 142-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) 陈树民, 姜传金, 刘立, 等, 2014. 松辽盆地徐家围子断陷火山岩裂缝形成机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(6): 1816-1826. 程光瑛, 庞加研, 张长盛, 1988. 川南地区茅口组储层裂缝系统预测方法探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 9(1): 32-39. 冯子辉, 印长海, 陆加敏, 等, 2013. 致密砂砾岩气形成主控因素与富集规律: 以松辽盆地徐家围子断陷下白垩统营城组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 40(6): 650-656. 付晓飞, 沙威, 于丹, 等, 2010. 松辽盆地徐家围子断陷火山岩内断层侧向封闭性及与天然气成藏[J]. 地质论评, 56(1): 60-70. 巩磊, 高帅, 吴佳朋, 等, 2017. 徐家围子断陷营城组火山岩裂缝与天然气成藏[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 41(2): 283-290. 侯贵廷, 冯大晨, 王文明, 等, 2004. 松辽盆地的反转构造作用及其对油气成藏的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 25(1): 49-53. 胡明, 付广, 吕延防, 等, 2010. 松辽盆地徐家围子断陷断裂活动时期及其与深层气成藏关系分析[J]. 地质论评, 56(5): 710-718. 刘国平, 曾联波, 雷茂盛, 等, 2016. 徐家围子断陷火山岩储层裂缝发育特征及主控因素[J]. 中国地质, 43(1): 329-337. 刘俊州, 韩磊, 时磊, 等, 2021. 致密砂岩储层多尺度裂缝地震预测技术: 以川西XC地区为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 42(3): 747-754. 刘亢, 李岩峰, 郭辉文, 等, 2021. 1948年川西理塘M7.3地震地表破裂特征及Riedel剪切构造分析[J]. 地质学报, 95(8): 2346-2360. 刘序俨, 季颖锋, 黄声明, 等, 2011. 地形变应变张量矩阵的不变量分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 31(4): 66-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2011.04.015 吕文雅, 苗凤彬, 张本键, 等, 2020. 四川盆地剑阁地区须家河组致密砾岩储层裂缝特征及对天然气产能的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 41(3): 484-491, 557. 马如辉, 王安志, 2006. 利用构造恢复原理制作古构造演化图[J]. 天然气工业, 26(1): 34-36. 丘元禧, 2000. 论构造筛分[J]. 地质力学学报, 6(1): 33-43. 任浩林, 刘成林, 刘文平, 等, 2020. 四川盆地富顺-永川地区五峰组: 龙马溪组应力场模拟及裂缝发育区预测[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(1): 74-83. 孙庆春, 孙晓猛, 王璞珺, 等, 2007. 松辽盆地东缘营城组节理构造特征、分布规律及其储层预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 37(6): 1091-1096. 王向东, 王任, 石万忠, 等, 2022. 中国东部典型裂谷盆地构造活动特征及演化: 以松辽盆地孤店断陷为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 41(3): 85-95. 王兆生, 董少群, 孟宁宁, 等, 2020. 渤海湾盆地高尚堡深层低渗透断块油藏缝网系统及其主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 41(3): 534-542, 626. 文慧俭, 舒萍, 范传闻, 等, 2008. 兴城气田深层砾岩储层储集空间类型及控制因素[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 32(3): 101-104. 吴满, 杨风丽, 陆建林, 2010. 松辽盆地东部地区火山岩储层裂缝预测研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 17(5): 60-62. 曾联波, 漆家福, 王永秀, 2007. 低渗透储层构造裂缝的成因类型及其形成地质条件[J]. 石油学报, 28(4): 52-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2007.04.010 张继标, 刘士林, 戴俊生, 等, 2019. 塔里木盆地玉北地区奥陶系储层构造裂缝定量预测[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(2): 177-186. 张元高, 陈树民, 张尔华, 等, 2010. 徐家围子断陷构造地质特征研究新进展[J]. 岩石学报, 26(1): 142-148. -




 下载:
下载: