InSAR monitoring and analysis of landslide deformation after the earthquake in the Zhangmu Port, Tibet
-
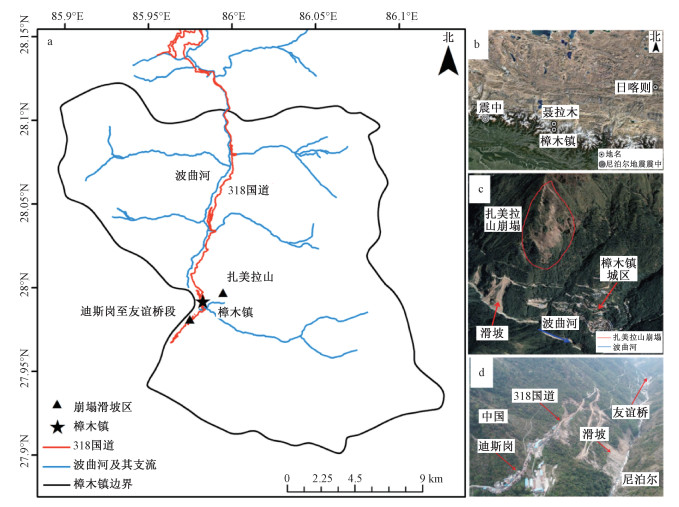
摘要: 位于中国和尼泊尔边境的西藏樟木口岸是国家一类陆路通商口岸,也是西藏最大的边贸中心口岸。2015年尼泊尔大地震之后,西藏樟木口岸因多次发生滑坡灾害,而导致口岸关闭。为了调查樟木口岸区域滑坡灾害的分布和变形情况及更好的服务于区域减灾防灾,利用InSAR技术对覆盖该区域的Sentinel-1A和ALOS-2两种卫星影像数据进行了处理,并通过分析视线向年均形变速率图,圈定了17处疑似滑坡,并对其中的5处典型滑坡进行时间序列形变特征分析,监测识别出的滑坡基本沿318国道所在一侧的波曲河左岸分布。InSAR调查结果表明受地震影响樟木地区的滑坡多分布在沿波曲河左岸的陡峭山体上,中尼公路迪斯岗至友谊桥段的古滑坡出现了局部复活的现象,同时樟木镇居民所在的城区也发育有扎美拉山危岩体崩塌滑坡灾害。Abstract: The Zhangmu Port,located on the border between China and Nepal,is a national first-class land trading port and the largest border trade port in Tibet. After the Nepal earthquake in 2015, the Zhangmu port was closed due to multiple landslide disasters. In order to investigate the distribution and deformation of landslide disasters in the Zhangmu port area so as to serve regional disaster mitigation and prevention,the InSAR technology was used to process the satellite image data of Sentinel-1A and ALOS-2 covering the area,and by analyzing the annual average rate map of line-of-sight deformation,17 suspected landslides were delineated,and the time series deformation characteristics of 5 typical landslides were analyzed. From the distribution point of view,the landslides identified by monitoring are basically distributed along the left bank of the Boiqu River on the side of National Highway 318. InSAR survey results show that the landslides in the Zhangmu area affected by the earthquake are mostly distributed on the steep hills along the left bank of the Boiqu River. The ancient landslides on the section of Disigang to Youyi Bridge on the China-Nepal Highway have partially resurrected,and the Zhameila dangerous rock mass collapses and landslides are also developed in the urban area where residents live in Zhangmu Town.
-
表 1 SAR数据集的基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of the SAR datasets
SAR传感器 Sentinel-1A ALOS-2 轨道 121 157 轨道方向 Descending Ascending 入射角/(°) 39.276 40.560 方位角/(°) -169.936 -10.096 分辨率/(方位向m×距离向m) 13.969×2.329 3.256×4.290 影像数量 51 20 获取时间/yyyymmdd 20170413~20181228 20150627~20191012 -
BAI Y J, NI H Y, GE H, 2019. Advances in research on the geohazard effect of active faults on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6):1116-1128. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQXB201603004.htm BERARDINO P, FORNARO G, LANARI R, et al., 2002. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 40(11):2375-2383. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1166596 CHEN J, WANG Q C, LI B, 2016. Characteristics and cause analysis of Zhangmu landslide in Tibet[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 25(2):103-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZRZH201602012.htm CUI P, CHEN X Q, CHENG Z L, et al., 2010. Monitoring and prevention of debris-flows and landslides in Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 32(1):19-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_chinese-journal-nature_thesis/020121195509.html DU X P, GUO H D, FAN X T, et al., 2013. Vertical accuracy assessment of SRTM and ASTER GDEM over typical regions of China using ICESat/GLAS[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 38(4):887-897. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.087 HU G S, CHEN N S, SU P C, et al., 2016. Secondary mountain disasters induced by the "4·25" Nepal earthquake in Nyalam County and disaster prevention and mitigation countermeasures[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 25(4):70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZRZH201604009.htm HU R L, ZHANG X Y, MA F S, et al., 2015. Structure and Stability of Tibetan Camphor Wood Accumulation[C]//Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Compilation of Papers for the 2014(14th) Annual Academic Meeting of Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Engineering Geology Water Resources Laboratory, 2015. Beijing: Division of Science and Technology and Achievement Transformation, Institute of Geology and Geophysics. Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015: 8. (in Chinese) KANG Y, 2016. Landslides detection and monitoring over southwestern mountainous areas with InSAR[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University. (in Chinese with English abstract) KRISHNAN P V S, KIM D J, JUNG J, 2018. Subsidence in the Kathmandu Basin, before and after the 2015 Mw7.8 Gorkha Earthquake, Nepal Revealed from small baseline subset-DInSAR analysis[J]. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 55(4):604-621. LI W, 2018. DInSAR technology of subsidence monitoring in Changbai Mountain area based on sentinel satellite[J]. Beijing Surveying and Mapping, 32(9):1073-1077. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI X, LI X Z, HE S M, et al., 2018. Characteristics and stability evaluation of the Zhameilashan unstable rock in Zham, Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 38(2):310-316. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J, ZHAO G M, WU Z H, 2017. The evolution of seismic activity image in the Himalaya belt before and after 2015 Nepal M 8.1 great earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(1):173-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU X H, YAO X, ZHOU Z K, et al., 2018. Study of the technique for landslide rapid recognition by InSAR[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(2):229-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLX201802067.htm LUO Y H, LI S Q, WANG Z L, 2017. Geohazards development characteristics and influence factors analysis induced by Nepal earthquake[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 28(3):33-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB201703008.htm MAO C W, 2008. Analyzing and evaluating the stability of welfare-institute landslide in Zhangmu town of Tibet[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) ONN F, 2006. Modeling water vapor using GPS with application to mitigating InSAR atmospheric distortions[D]. Stanford: Stanford University. SANDWELL D T, SICHOIX L, 2000. Topographic phase recovery from stacked ERS interferometry and a low-resoiution digital elevation mode[J]. Geophys. Res. Sdid Earth, 105(B12):28211-28222. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900340 SHAN X J, ZHANG G H, WANG C S, et al., 2015. Joint inversion for the spatial fault slip distribution of the 2015 Nepal MW7.9 earthquake based on InSAR and GPS observations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(11):4266-4276. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG J, 2018. Research on monitoring of landslide geological disters using time series spaceborne InSAR technology[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG J S, ZHAO N Y, 2020. Seismogenic structure of 2018 Xietongmen, Tibet MW5.6 earthquake inferred from InSAR data[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 42(2):384-390. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG R C, KONG J M, CUI Y, et al., 2019. Characteristics of secondary hazards in severely damaged region of Tibet by MS 8. 1 Earthquake, April 25, 2015, Nepal and recommendations on reconstruction[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan(1):32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG X Q, HUANG S S, DING X, et al., 2015. The application of remote sensing and GIS in the investigation and evaluation of earthquake disasters in Nepal[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology(9):119. (in Chinese) WRIGHT T, PARSONS B, FIELDING E, et al., 2001. Measurement of interseismic strain accumulation across the North Anatolian Fault by satellite radar interferometry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 28(6):2117-2120. doi: 10.1029/2000GL012850 WRIGHT T J, PARSONS B, ENGLAND P C, et al., 2004. INSAR observations of low slip rateson the major faults of westem Tibet[J]. SCIENCE, 305(5681):236-239. doi: 10.1126/science.1096388 WU X N, YI J M, ZHOU S L, et al., 2017. A study on the active faults structures and geohazards triggered by the Ms8.1 earthquake in Nepal[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 44(4):137-144. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG C S, HAN B Q, ZHAO C Y, et al., 2019. Co-and post-seismic deformation mechanisms of the MW 7.3 Iran Earthquake (2017) revealed by Sentinel-1 InSAR observations[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(4):418. YANG Z H, ZHANG Y S, GUO C B, et al., 2017. Landslide hazard rapid assessment in the MS 8.1 Nepal earthquake-impacted area, based on Newmark model[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(1):115-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLX201701007.htm YAO Z Y, 2017. Main problems in engineering geology and geological alignment in Xiamude-Katmandu Section of China-Nepal Railway[J]. Railway Standard Design, 61(9):21-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-TDBS201709007.htm YI S M, TANG H M, 1996. The fractal feature of Zhangmu landslides group in Tibet and its significance[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Geology, 26(4):392-397. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ604.006.htm ZEBER H A, VILLASENOR J, 1992. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 30(5):950-959. doi: 10.1109/36.175330 ZENG Z, 2019. Analysis of the surface deformation of the Heifangtai sliding and potential landslide area in Gansu based on InSAR technology[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. (in Chinese) ZHANG X G, QIANG B, 2003. Analysis of development characteristics of Youyiqiao landslide along China-Nepal Highway[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 21(S1):139-142, 160. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SDYA2003S1027.htm ZHANG Y, WANG Y J, YAN S Y, 2016. Ground subsidence detection of Peibei mining area based on stacking InSAR technology[J]. Coal Technology, 35(7):102-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_coal-technology_thesis/0201215840581.html ZHAO C Y, 2009. Differential interferometric radar technology for discontinuous deformation monitoring[D]. Xi'an: Changan University. (in Chinese) ZHAO G M, WU Z H, LIU J, et al., 2019. The time space distribution characteristics and migration law of large earthquakes in the Indian-Eurasian plate collision deformation area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(3):324-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU J, LEI Y, ZHAO J, 2008. Mechanism analysis of the outsized ancient landslide of Zhangmu port in Tibet[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 35(1):49-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200801013.htm ZHU J, CAI Q E, JIANG H B, 2010. Deformation monitoring & analysis of ancient landslide at Zhangmu port in Tibet[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 18(1):66-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201001012.htm 白永健, 倪化勇, 葛华, 2019.青藏高原东南缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究现状[J].地质力学学报, 25(6):1116-1128. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190613&journal_id=dzlxxb 陈剑, 王全才, 李波, 2016.西藏樟木滑坡特征及成因研究[J].自然灾害学报, 25(2):103-109. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zrzhxb201602012 崔鹏, 陈晓清, 程尊兰, 等, 2010.西藏泥石流滑坡监测与防治[J].自然杂志, 32(1):19-25. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1001258258 杜小平, 郭华东, 范湘涛, 等, 2013.基于ICESat/GLAS数据的中国典型区域SRTM与ASTER GDEM高程精度评价[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 38(4):887-897. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94035X/201304/46627065.html 胡桂胜, 陈宁生, 苏鹏程, 等, 2016.西藏聂拉木县"4·25"尼泊尔地震次生山地灾害与防灾减灾对策[J].自然灾害学报, 25(4):70-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zrzhxb201604009 胡瑞林, 张小艳, 马凤山, 等, 2015.西藏樟木堆积体结构及其稳定性[C]//中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所.中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所2014年度(第14届)学术年会论文汇编: 工程地质与水资源研究室.北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所科技与成果转化处, 2015: 8. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCDZ201404025.htm 康亚, 2016. InSAR技术在西南山区滑坡探测与监测的应用[D].西安: 长安大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1016748892.htm 李旺, 2018.基于哨兵卫星的长白山地区地表形变监测DInSAR技术[J].北京测绘, 32(9):1073-1077. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BJCH201809016.htm 李鑫, 李秀珍, 何思明, 等, 2018.西藏樟木扎美拉山危岩特征与稳定性评价[J].四川地质学报, 38(2):310-316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SCDB201802028.htm 刘杰, 赵根模, 吴中海, 2017. 2015年尼泊尔8.1级大地震前后喜马拉雅带地震活动图像演变[J].地质力学学报, 23(1):173-181. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20170113&journal_id=dzlxxb 刘星洪, 姚鑫, 周振凯, 等, 2018.滑坡灾害InSAR应急排查技术方法研究[J].地质力学学报, 24(2):229-237. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180209&journal_id=dzlxxb 罗永红, 李石桥, 王梓龙, 2017.尼泊尔地震诱发地质灾害发育特征及影响因素分析[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 28(3):33-40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZHB201703008.htm 毛成文, 2008.西藏樟木镇福利院滑坡稳定性分析与评价[D].西安: 西安科技大学. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/Y1321998 单新建, 张国宏, 汪驰升, 等, 2015.基于InSAR和GPS观测数据的尼泊尔地震发震断层特征参数联合反演研究[J].地球物理报, 58(11):4266-4276. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX201511032.htm 王京, 2018.长时序星载InSAR技术滑坡地质灾害监测研究[D].北京: 北京交通大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10004-1018131393.htm 王金烁, 赵宁远, 2020.利用InSAR技术研究2018年西藏谢通门MW5.6地震发震构造[J].地震工程学报, 42(2):384-390. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_china-earthquake-engineering-journal_thesis/0201278553502.html 王仁超, 孔纪名, 崔云, 等, 2019.尼泊尔MS8.1地震西藏重灾区震害特征分析及灾后重建对策[J].四川地震(1):32-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SCHZ201901007.htm 王晓青, 黄树松, 丁香, 等, 2015.遥感与GIS在尼泊尔地震现场灾害调查与评估中的应用[J].国际地震动态(9):119. http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_8841539.aspx 武新宁, 易俊梅, 周淑丽, 等, 2017.尼泊尔Ms8.1级地震活动构造及次生地质灾害研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 44(4):137-144. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90596X/201704/672705570.html 杨志华, 张永双, 郭长宝, 等, 2017.基于Newmark模型的尼泊尔Ms8.1级地震滑坡危险性快速评估[J].地质力学学报, 23(1):115-124. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20170107&journal_id=dzlxxb 姚志勇, 2017.中尼铁路夏木德至加德满都段主要工程地质问题及地质比选[J].铁道标准设计, 61(9):21-25. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TDBS201709007.htm 易顺民, 唐辉明, 1996.西藏樟木滑坡群的分形特征及其意义[J].长春地质学院学报, 26(4):392-397. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ604.006.htm 曾珠, 2019.基于InSAR技术分析甘肃黑方台已滑及潜在滑坡区地表形变[D].成都: 电子科技大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10614-1019850781.htm 张小刚, 强巴, 2003.中尼公路友谊桥滑坡的发育特征分析[J].山地学报, 21(S1):139-142, 160. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SDYA2003S1027.htm 张洋, 汪云甲, 闫世勇, 2016.基于Stacking InSAR技术的沛北矿区沉降监测[J].煤炭技术, 35(7):102-105. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-MTJS201607042.htm 赵超英, 2009.差分干涉雷达技术用于不连续形变的监测研究[D].西安: 长安大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-2009176708.htm 赵根模, 吴中海, 刘杰, 等, 2019.印度-欧亚板块碰撞变形区的大地震时空分布特征与迁移规律[J].地质力学学报, 25(3):324-340. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190303&journal_id=dzlxxb 祝建, 雷英, 赵杰, 2008.西藏樟木口岸特大型古滑坡形成机理分析[J].水文地质工程地质, 35(1):49-52. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/swdzgcdz200801011 祝建, 蔡庆娥, 姜海波, 2010.西藏樟木口岸古滑坡变形监测分析[J].工程地质学报, 18(1):66-71. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201001009 -





 下载:
下载: