Karst groundwater enrichment law in Laiwu Basin
-
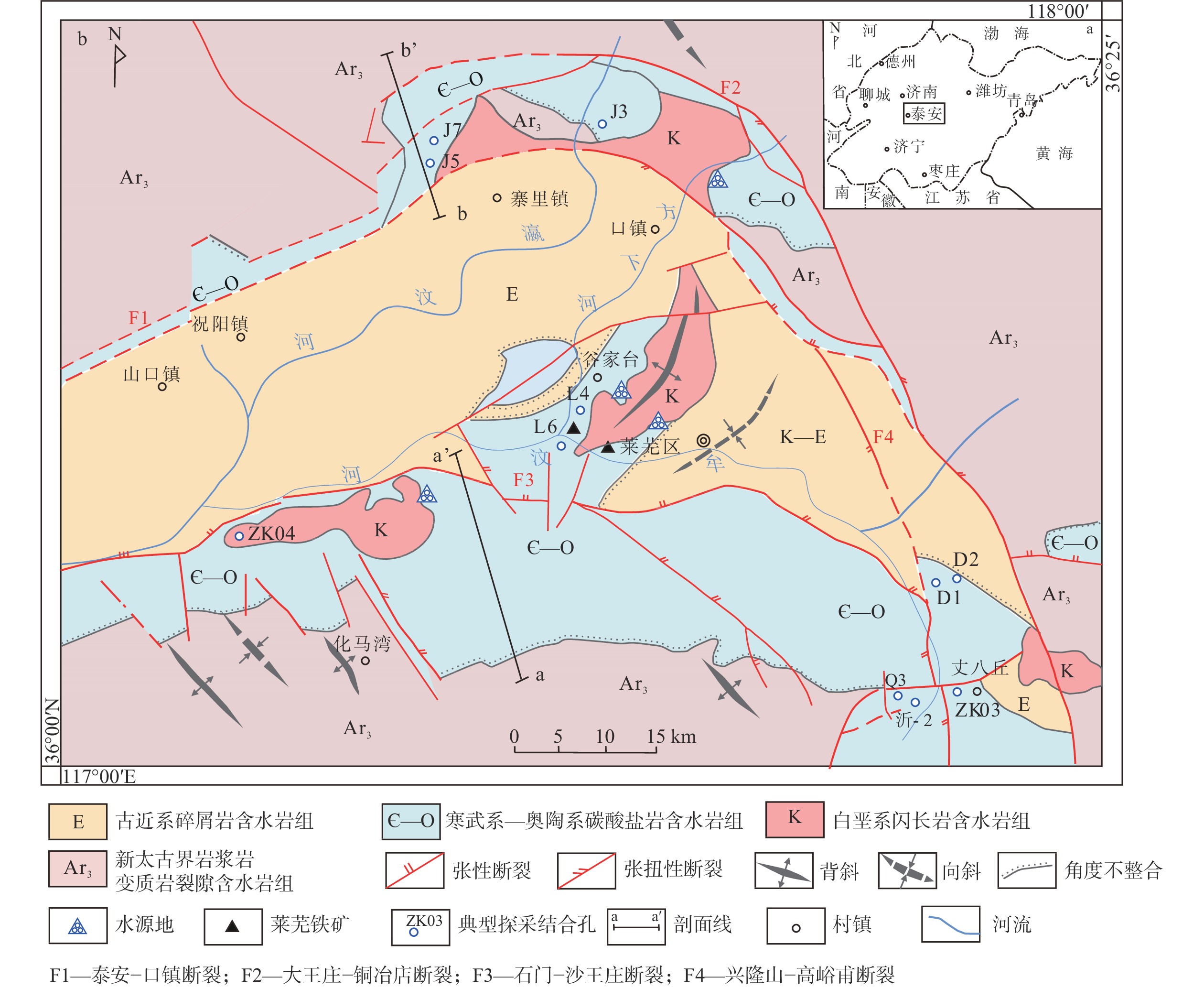
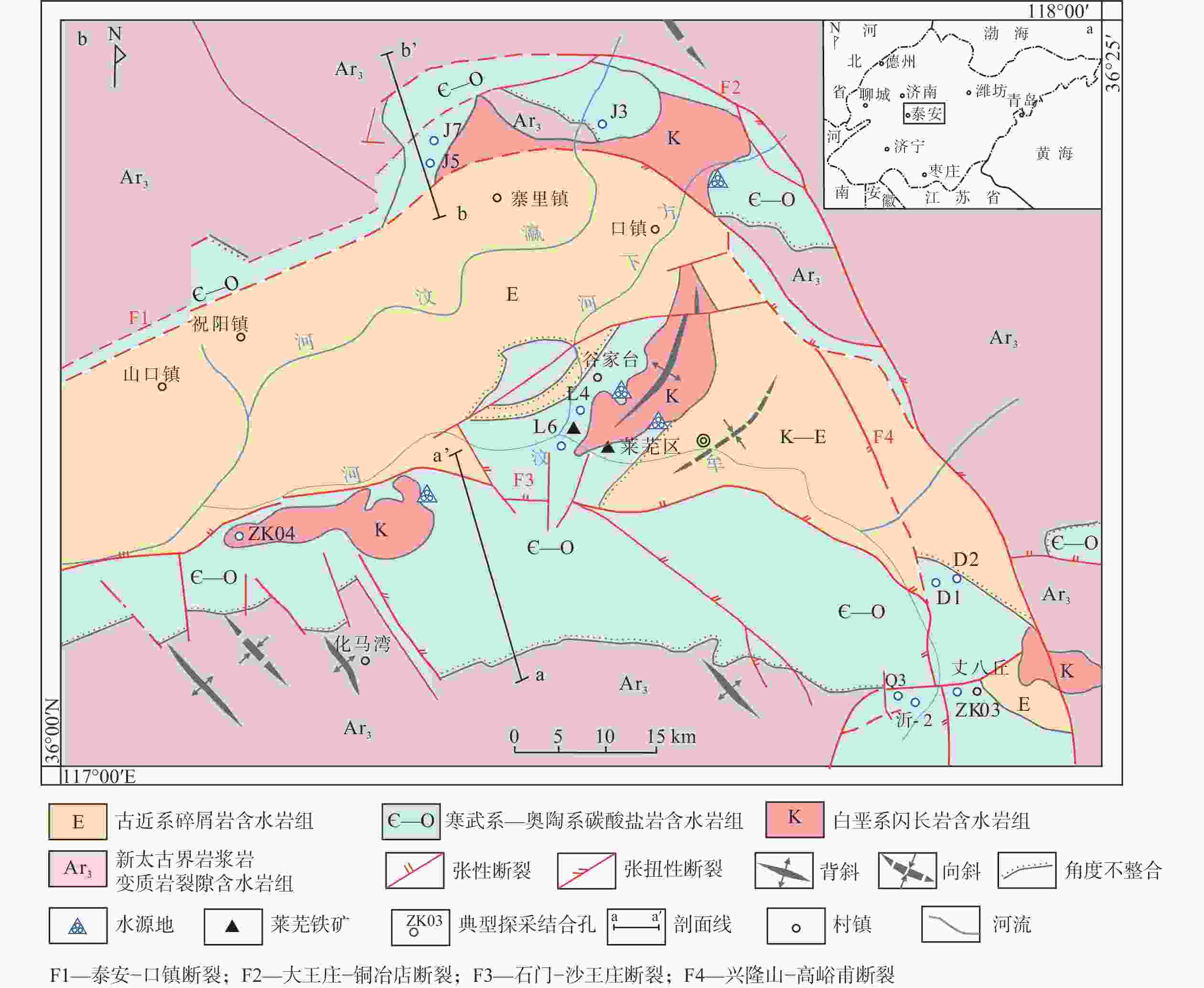
摘要: 基于在莱芜盆地开展的水文地质调查与泉水保护工作,通过资料收集、野外地质调查、水文地质钻探及岩矿测试,对区内碳酸盐岩岩溶发育特征及富水规律进行研究。结果表明:莱芜盆地碳酸盐岩分布受构造控制明显,集中分布在盆地南部,呈单斜状产出,在盆地北缘、东缘地区零星分布;岩溶发育受地层岩性、地质构造、地下水动力条件及岩浆侵入等多因素影响;地表岩溶形态以溶沟、溶槽为主,地下岩溶以溶蚀裂隙、溶孔溶洞为主,主要发育400 m以浅;岩溶水主要富集在多期构造断块区域、阻水断裂形成的上盘、地下水承压排泄区及莱芜矿山背斜两翼岩溶发育区。研究结果可为鲁中南缺水山区地下水资源开发与利用提供科学技术支撑。Abstract:
Objective The Laiwu Basin is a typical monocline fault basin in the central and southern regions of Shandong Province. It has a complex geological structure and an uneven distribution of groundwater resources within the region. Previous researchers have conducted a large number of hydrogeological and spring water protection studies, but no relevant research has been conducted on the relationship between the development laws of fissure karst and the distribution of karst groundwater. Methods In this study, karstification and groundwater enrichment characteristics were investigated in the Laiwu Basin through research methods of data collection, field geological surveys, hydrogeological drilling, and rock and mineral testing. Results Carbonate strata are concentrated in the southern part of the Laiwu Basin, with a monoclinal structure controlled by the geological structure, which is scattered sporadically in the northern and eastern regions. Karst development is affected by many factors, such as formation lithology, geological structure, groundwater dynamic conditions, and magma intrusion. The principal surface karst features are grikes and karst valleys. In addition, the principal underground karst features were dominated by dissolution fissures and holes at 400 m depth. Karst groundwater is primarily concentrated in multistage structural fault basins, hanging walls formed by water-blocking faults, groundwater pressure discharge areas, and karst development areas on the anticlinal flank of the mine. Conclusion The karst water cycle in the Laiwu Basin has a general regularity of monoclinic basins but is influenced by multiple factors, forming karst water systems of varying sizes that are relatively independent. Significant differences were observed in the development characteristics and water abundance patterns of karsts in different regions. Fault structures and geological water-blocking areas have relatively abundant karst water, whereas the shallow karst water has a strong runoff cycle. [ Significance ] This study provides scientific and technical support for the exploitation and utilization of groundwater resources in water-scarce mountainous areas of central and southern Shandong Province. -
Key words:
- Laiwu Basin /
- karstification /
- groundwater /
- enrichment pattern /
- hydrogeololgy
-
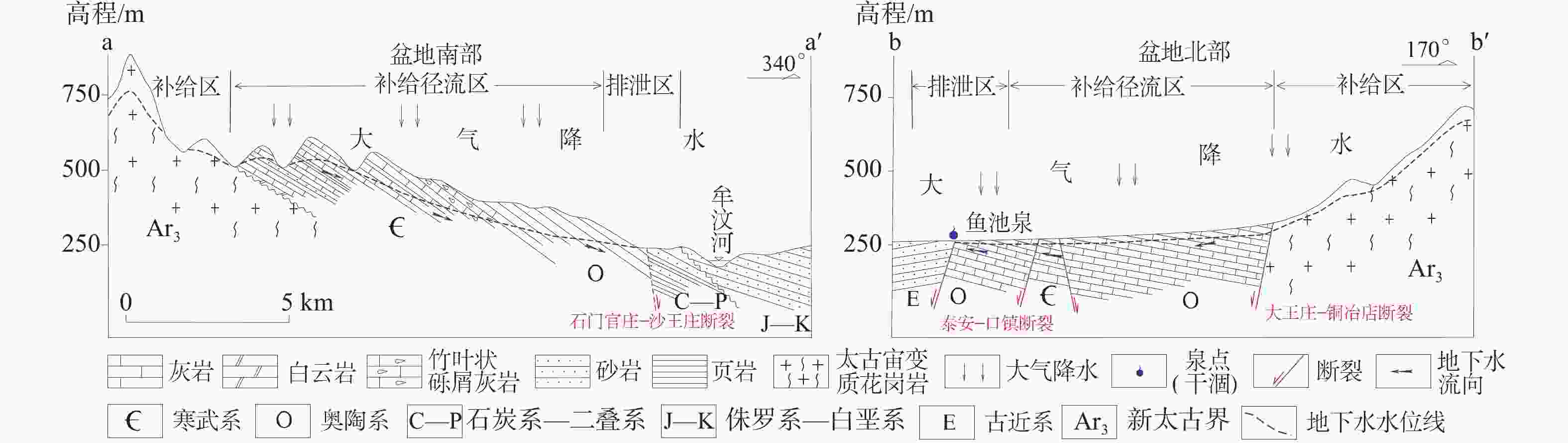
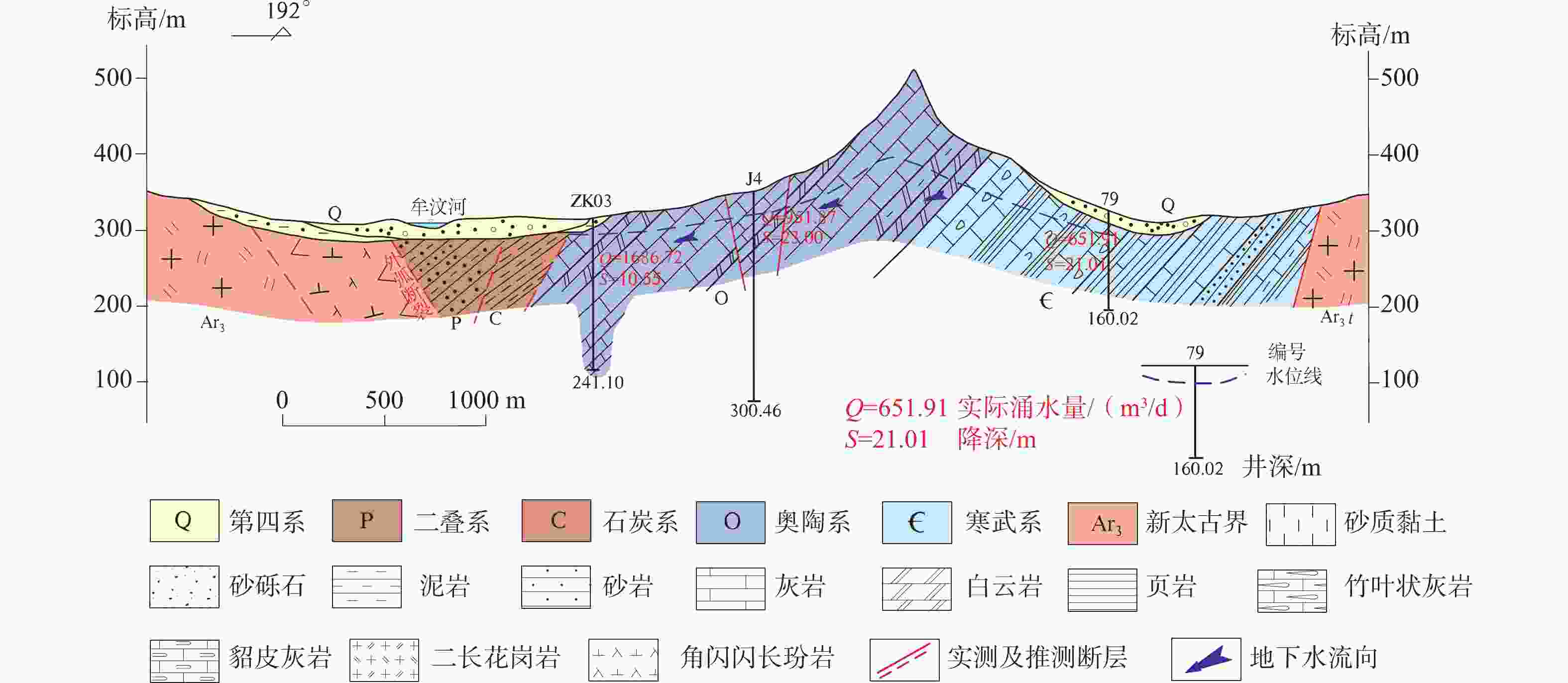
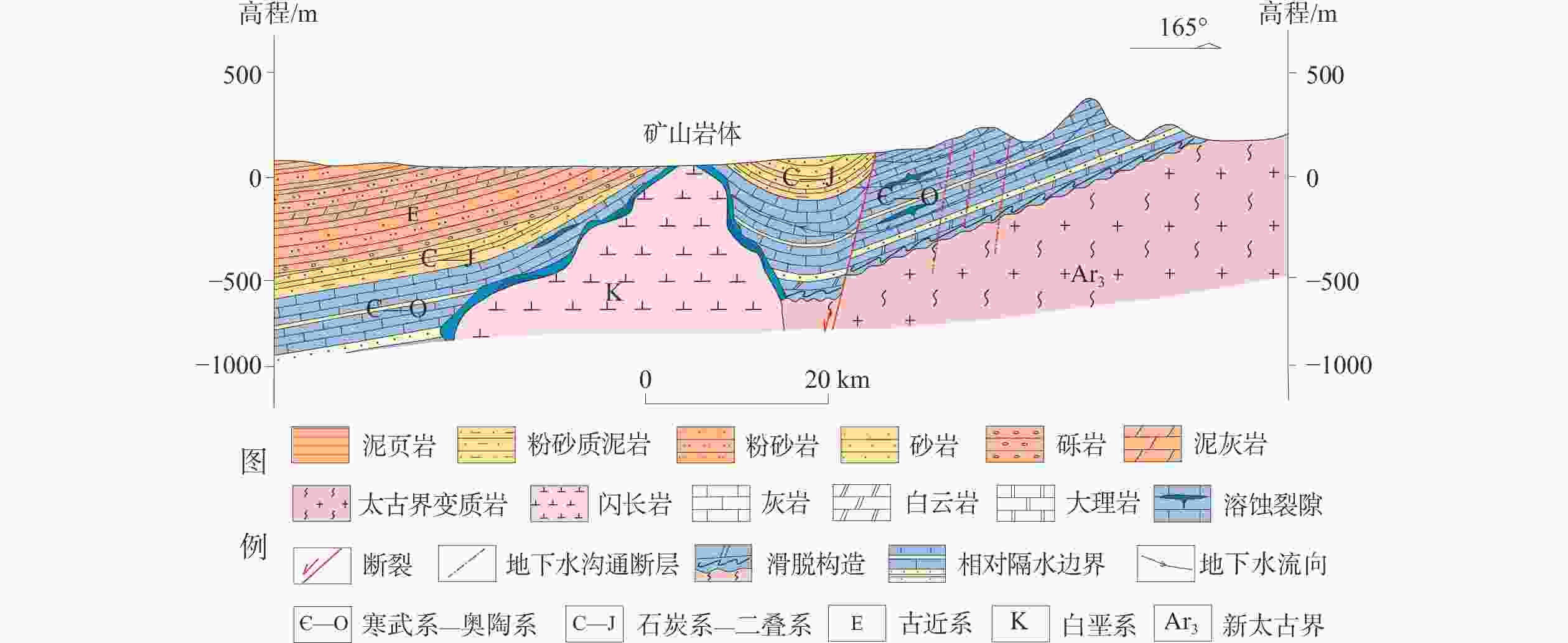
图 2 莱芜盆地水文地质结构图(剖面位置见图1)
a−盆地南部水文地质剖面图;b−盆地北部水文地质剖面图
Figure 2. Hydrogeological Structure Map of Laiwu Basin (The profile position is shown in Figure 1)
(a)Hydrogeological profile map of the southern basin;(b)Hydrogeological profile map of the northern basin
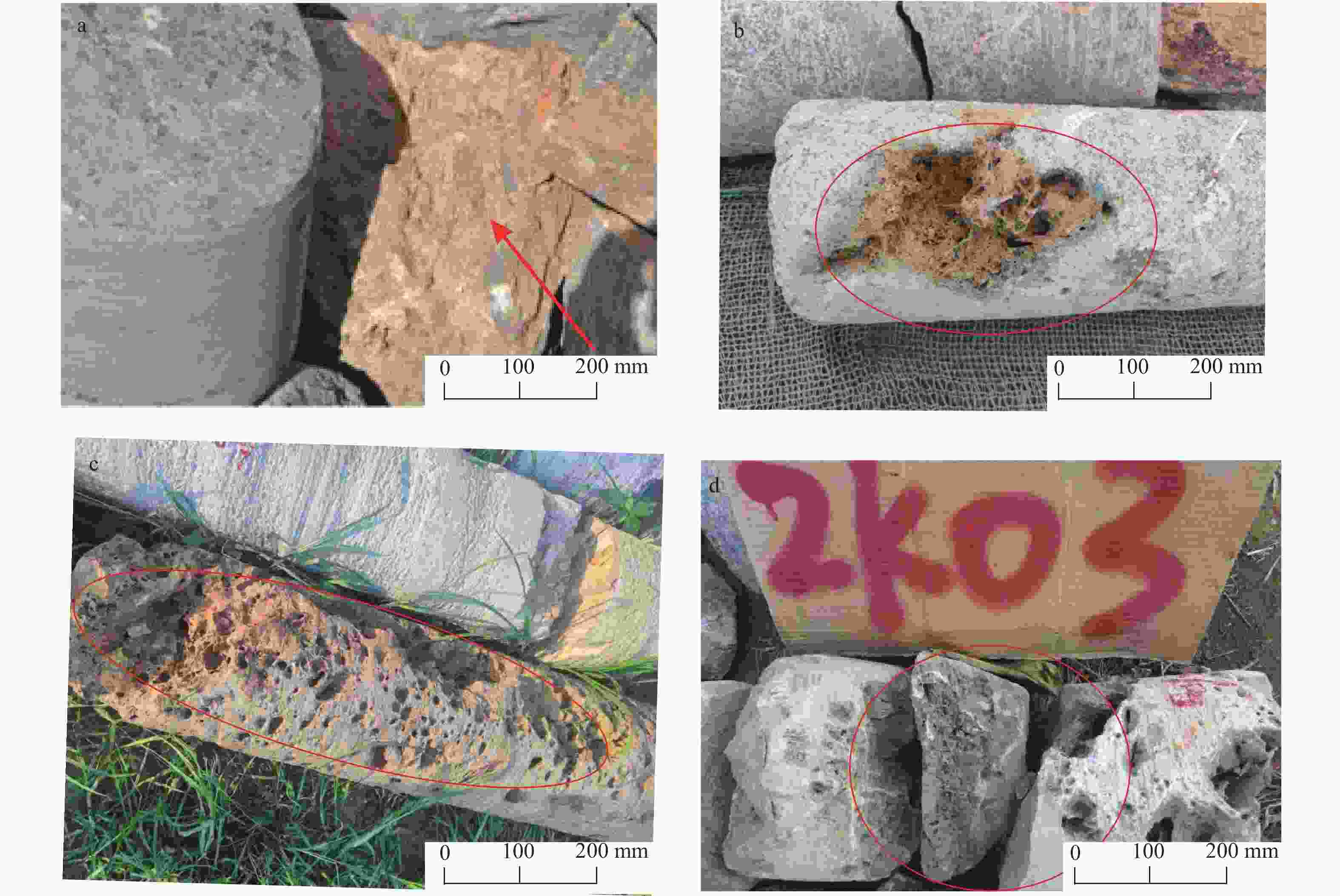
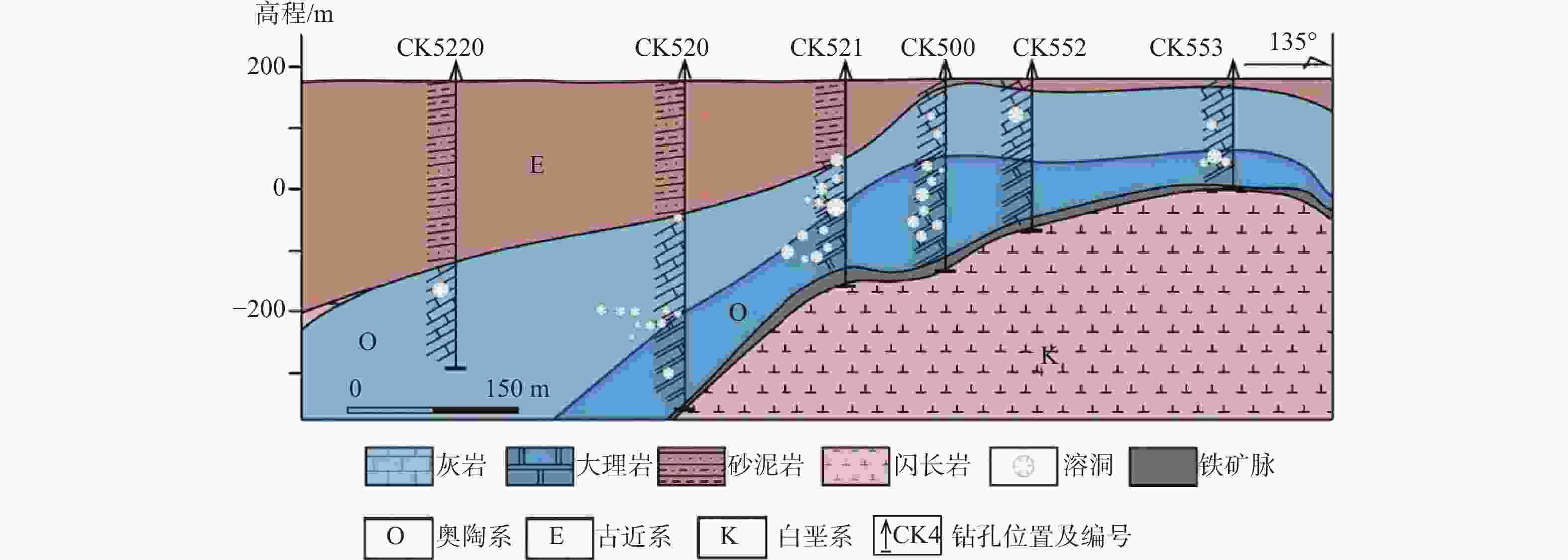
图 5 谷家台侵入接触带岩溶发育示意图(据刘元晴等,2020a修改)
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of intrusion contact zone and karst development in Gujiatai (modified from Liu et al.,2020a)
表 1 岩溶层组类型划分表
Table 1. Classification of karst strata groups
岩溶层组类型 碳酸盐
岩占比/%地层 主要岩性 分布区域 纯碳酸盐岩组 灰岩层组 >70 奥陶系马家沟群八陡组、五阳山组、
北庵庄组,寒武系张夏组中厚层灰岩、微晶灰岩,云斑灰岩、
生物碎屑灰岩等莱芜盆地牛泉镇—高
庄镇一带白云岩层组 奥陶系马家沟群阁庄组、土峪组、东黄
山组,寒武系三山子组,寒武系朱砂洞组中厚层白云岩、灰质白云岩 莱芜盆地牛泉镇—高
庄镇一带不纯碳酸盐岩组 碳酸盐岩夹碎屑岩层组 30~70 寒武系炒米店组 中薄层灰岩、疙瘩状灰岩夹泥质页岩 清泥沟—老君堂 碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩层组 <30 寒武系崮山组、馒头组 黄绿色、紫红色页岩夹薄层灰岩 清泥沟—老君堂 表 2 岩矿测试分析结果统计表
Table 2. Statistical table of rock test analysis results
地层 主要岩性 CaO含量/% 可溶岩含量/% 可溶岩均值/% 线岩溶率/% 白垩系 安山岩、辉绿岩等 2.95~8.25 6.50~11.74 9.12 / 古近系朱家沟组 灰质砾岩、砂泥岩等 1.19~49.27 2.81~49.69 29.33 8.5 奥陶系马家沟群 灰岩、白云岩、微晶灰岩等 44.54~52.55 49.50~54.56 52.48 23.5 奥陶系三山子组 白云岩、微晶白云岩等 29.53~50.91 48.30~51.67 49.92 22.5 寒武系炒米店组 灰岩、竹叶状灰岩等 24.31~51.56 40.11~52.10 49.50 20.6 寒武系崮山组 瘤状灰岩、页岩等 42.02~52.26 38.56~52.80 46.25 17.8 寒武系张夏组 石灰岩、泥晶灰岩等 14.66~46.72 22.37~48.23 37.70 15.6 鲕粒灰岩 46.88~52.43 47.82~53.99 51.95 22.8 寒武系馒头组 薄层页岩夹灰岩等 1.58~19.50 3.89~21.44 20.51 10.6 泥质灰岩、灰岩等 10.66~53.32 19.48~53.81 38.48 13.5 寒武系朱砂洞组 白云岩、微晶白云岩等 25.68~46.82 38.08~53.04 47.18 19.7 -
[1] CHEN C W, HE X, ZAI J X, 2021. Karst development feature and contrl factor analysis of Jinchanghe orefield in W Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 40(4): 479-483. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] DUAN Z, GAO M B, GAO J L, et al., 2022. Phlogopite 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Zhangjiawa iron deposit, Laiwu district, Shandong Province: implications for regional iron skarn mineralization of North China Craton[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(4): 1279-1296. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] GAO F, WANG Z T, JIN F S, et al., 2016. Risk assessment of karst collapse in the Laiwu of Shandong Province[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 26(S2): 359-362. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] LI B, WANG J X, ZHAO W J, et al., 2019. Analysis on isotopic characteristics of water body of Muwen River Basin in Laiwu Basin[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 35(7): 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] LI B, WANG J X, WU X, et al., 2020. Hydrogeological conditions and characteristics of water-rich sections in the eastern Laiwu basin, Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 39(5): 637-649. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] LI B, SONG Y X, GAO H, et al., 2021. Hydrogeological characteristics and water yield pattern of the Paleogene Zhujiagou formation in South-central Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(1): 117-126. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] LI G H, FENG J G, LU T M, et al. , 2019. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of groundwater in Tailai Basin[J]. Water Resources and Power, 37(4): 52-55, 121. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] LI S Z, SUO Y H, ZHOU J, et al., 2022. Tectonic evolution of the South China Ocean-Continent Connection Zone: transition and mechanism of the Tethyan to the Pacific tectonic domains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 683-704. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] LIANG Y P, WANG W T, 2010. The division and characteristics of karst water systems in northern China[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 31(6): 860-868. (in Chinese) [10] LIAO Z S, 1985. On the development and management of karst water resource in North China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 4(1-2): 107-114. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] LIU S F, 2020. Characteristics of the Mesozoic intrusive complexes and their relation to metallogeny in Laiwu area, Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Geology, 44(S1): 34-47. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] LIU Y Q, ZHOU L, LI W, et al., 2018. The characteristics and genetic analysis of the Paleogene semi-consolidated water-bearing Formation on the northwestern Margin of Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 39(6): 737-748. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] LIU Y Q, ZHOU L, LI W, et al., 2020a. Characteristics and hydrogeological significance of hydrothermal dissolution in carbonate rocks from Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Geoscience, 34(1): 199-206. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] LIU Y Q, ZHOU L, MA X M, et al., 2020b. Environmental geological problems and causes during development and utilization of groundwater in Laiwu Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 34(11): 118-124. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] MA M, GAO J L, GAO M B, et al., 2020. Geophysical characteristics of Laiwu Area in western Shandong Province and establishment of exploration model for iron rich deposits[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 38(2): 13-20. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] MA Z M, LIU L C, CHEN H H, et al., 2002. Hydrochemical environmental evolution of Karst Water System in Tai’an, Shandong Province[J]. Geoscience, 16(4): 423-428. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] NIU S Y, HU H B, MAO J W, et al., 2004. Structure in western Shandong and its genetic mechanism[J]. Geology in China, 31(1): 34-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] SHI X P, LI L, HU Q Y, et al., 2010. Characteristics of NW-trending normal faults and physical modeling since Late Mesozoic in West Shandong Uplift, China[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 49(2): 130-137. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] SUN X, WANG K H, SUN Q T, et al., 2010. Types and distribution of Karst fissure water in central and southern Shandong Province[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 38(2): 52-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] WANG C, ZHANG L C, WANG Y Q, et al. , 2021. Study on groundwater pollution in Laiwu region[J]. Ground Water, 43(6): 21-24, 229. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] WANG W T, LIANG Y P, WANG Z H, et al. , 2012. Characteristics of climate change in northern China and its effect on groundwater in karst areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 39(6): 6-10, 28. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] WANG Y, YANG H B, ZHENG M Q, et al., 2019. Study on characteristics of groundwater storage structures and well explorating and locating within Tailai Basin[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 50(3): 52-65. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] WANG Y L, CHEN W Q, JIANG X Z, et al., 2015. Development features and formation mechanisms of karst collapses in the Tailai Basin, Shandong Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 34(5): 495-506. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] YU X F, LI D P, SHAN W, et al., 2022. Yanshanian gold metallogenic system and metallogenic model of the Guilaizhuang gold ore field, western Shandong[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 821-841. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] ZHAI M G, MENG Q R, LIU J M, et al., 2004. Geological features of Mesozoic tectonic regime inversion in eastern North China and implication for geodynamics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 11(3): 285-297. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] ZHAI M G, 2019. Tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 722-745. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] ZHANG F Q, LI B T, 1990. Karst groundwater system in North China and problems of its development and utilization[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 9(1): 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] ZHANG Q Q, ZHANG S H, 2019. Devonian magmatism in the northern margin of the North China Block and its tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(1): 125-138. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] ZHANG X M, ZHANG Y Q, JI W, 2007. Fault distribution patterns of the luxi block, Shandong, and Mesozoic sedimentary-magmatic-structural evolution sequence[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 13(2): 163-172. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] ZHAO Y B, LIU Q J, HUANG X J, 2022. Characteristics of karst development and the law of groundwater enrichment in Shazhouba area of Ruijin City[J]. East China Geology, 43(2): 227-234. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] ZHOU L, LIU Y Q, LI W, et al. , 2020. Tectonic evolutionary characteristics and their hydrological geological significance in Laiwu Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 20(2): 519-526. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] ZHOU X G, SUN B S, SHAO Z G, et al., 2004. Evolutionary characteristics of the boundary fault of the Wenxi Depression, Shandong, and its control on sedimentary sand bodies[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 10(3): 235-244. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] ZHU J, ZHAO D P, HE Q, 2023. Study on water pressure law and structural safety of tunnel lining in Karst weakly developed strata[J]. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 49(5): 137-142, 157. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 陈朝稳,和祥,宰家宪,2021. 滇西金厂河矿区岩溶发育特征及控制因素分析[J]. 云南地质,40(4):479-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2021.04.015 [35] 段壮,高明波,高继雷,等,2022. 山东莱芜张家洼铁矿床金云母40Ar/39Ar定年及其对成矿构造背景的启示[J]. 地质学报,96(4):1279-1296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.04.010 [36] 高峰,王振涛,靳丰山,等,2016. 山东省莱芜盆地岩溶塌陷风险性评价[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境,26(S2):359-362. [37] 李波,王金晓,赵无忌,等,2019. 莱芜盆地牟汶河流域水体同位素特征与分析[J]. 山东国土资源,35(7):58-63. [38] 李波,王金晓,吴璇,等,2020. 山东莱芜盆地东部水文地质条件及富水块段特征[J]. 中国岩溶,39(5):637-649. doi: 10.11932/karst2020y34 [39] 李波,宋一心,高菡,等,2021. 鲁中南地区古近系朱家沟组水文地质特征及富水模式[J]. 地质力学学报,27(1):117-126. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.01.012 [40] 李贵恒,冯建国,鲁统民,等,2019. 泰莱盆地地下水水化学特征及水质评价[J]. 水电能源科学,37(4):52-55,121. [41] 李三忠,索艳慧,周洁,等,2022. 华南洋陆过渡带构造演化:特提斯构造域向太平洋构造域的转换过程与机制[J]. 地质力学学报,28(5):683-704. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222809 [42] 梁永平,王维泰,2010. 中国北方岩溶水系统划分与系统特征[J]. 地球学报,31(6):860-868. [43] 廖资生,1985. 论北方岩溶水资源的开发与管理问题[J]. 中国岩溶,4(1-2):107-114. [44] 刘书锋,2020. 山东莱芜地区中生代侵入杂岩特征与成矿关系[J]. 地质学刊,44(S1):34-47. [45] 刘元晴,周乐,李伟,等,2018. 山东莱芜盆地西北缘古近系半固结含水岩组的特征及其成因[J]. 地球学报,39(6):737-748. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.080801 [46] 刘元晴,周乐,李伟,等,2020a. 山东莱芜盆地碳酸盐岩热液溶蚀特征及水文地质意义[J]. 现代地质,34(1):199-206. [47] 刘元晴,周乐,马雪梅,等,2020b. 莱芜盆地地下水开发利用中的环境地质问题及成因[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,34(11):118-124. [48] 马明,高继雷,高明波,等,2020. 鲁西莱芜地区地球物理特征及富铁矿床勘查模型建立[J]. 华北地震科学,38(2):13-20. [49] 马振民,刘立才,陈鸿汉,等,2002. 山东泰安岩溶水系统地下水化学环境演化[J]. 现代地质,16(4):423-428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2002.04.015 [50] 牛树银,胡华斌,毛景文,等,2004. 鲁西地区地质构造特征及其形成机制[J]. 中国地质,31(1):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.01.004 [51] 时秀朋,李理,胡秋媛,等,2010. 鲁西隆起晚中生代以来北西向正断层特征及物理模拟[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),49(2):130-137. [52] 孙逊,王克红,孙启堂,等,2010. 鲁中南山区岩溶裂隙水富水带类型及分布特征[J]. 工程勘察,38(2):52-56. [53] 王超,张立川,王应强,等,2021. 莱芜地区地下水污染研究[J]. 地下水,43(6):21-24,229. [54] 王维泰,梁永平,王占辉,等,2012. 中国北方气候变化特征及其对岩溶水的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,39(6):6-10,28. [55] 王延岭,陈伟清,蒋小珍,等,2015. 山东省泰莱盆地岩溶塌陷发育特征及形成机理[J]. 中国岩溶,34(5):495-506. doi: 10.11932/karst201505y01 [56] 汪云,杨海博,郑梦琪,等,2019. 泰莱盆地地下水蓄水构造特征及勘查定井研究[J]. 水利水电技术,50(3):52-65. [57] 于学峰,李大鹏,单伟,等,2022. 鲁西归来庄金矿田燕山期金成矿系统及成矿模式[J]. 地质力学学报,28(5):821-841. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222815 [58] 翟明国,孟庆任,刘建明,等,2004. 华北东部中生代构造体制转折峰期的主要地质效应和形成动力学探讨[J]. 地学前缘,11(3):285-297. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.03.027 [59] 翟明国,2019. 华北克拉通构造演化[J]. 地质力学学报,25(5):722-745. [60] 张凤岐,李博涛,1990. 中国北方岩溶地下水系统和开发利用中的几个问题[J]. 中国岩溶,9(1):9-16. [61] 张琪琪,张拴宏,2019. 华北地块北缘泥盆纪岩浆活动及其构造背景[J]. 地质力学学报,25(1):125-138. [62] 张锡明,张岳桥,季玮,2007. 山东鲁西地块断裂构造分布型式与中生代沉积—岩浆—构造演化序列[J]. 地质力学学报,13(2):163-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2007.02.009 [63] 赵毅斌,刘前进,黄旭娟,2022. 瑞金市沙洲坝地区岩溶发育特征与地下水富集规律[J]. 华东地质,43(2):227-234. [64] 周乐,刘元晴,李伟,等,2020. 莱芜盆地构造演化特征及水文地质意义[J]. 科学技术与工程,20(2):519-526. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.02.012 [65] 周新桂,孙宝珊,邵兆刚,等,2004. 山东汶西凹陷边界断裂演化特征及其对沉积砂体的控制[J]. 地质力学学报,10(3):235-244. [66] 朱君,赵东平,和琦,2023. 岩溶弱发育地层隧道衬砌水压规律及结构安全性研究[J]. 铁道勘察,49(5):137-142,157. -




 下载:
下载: