Electrical characteristics and metallogenic prediction of Baishawo rare metal deposit in northeast Hunan Province
-
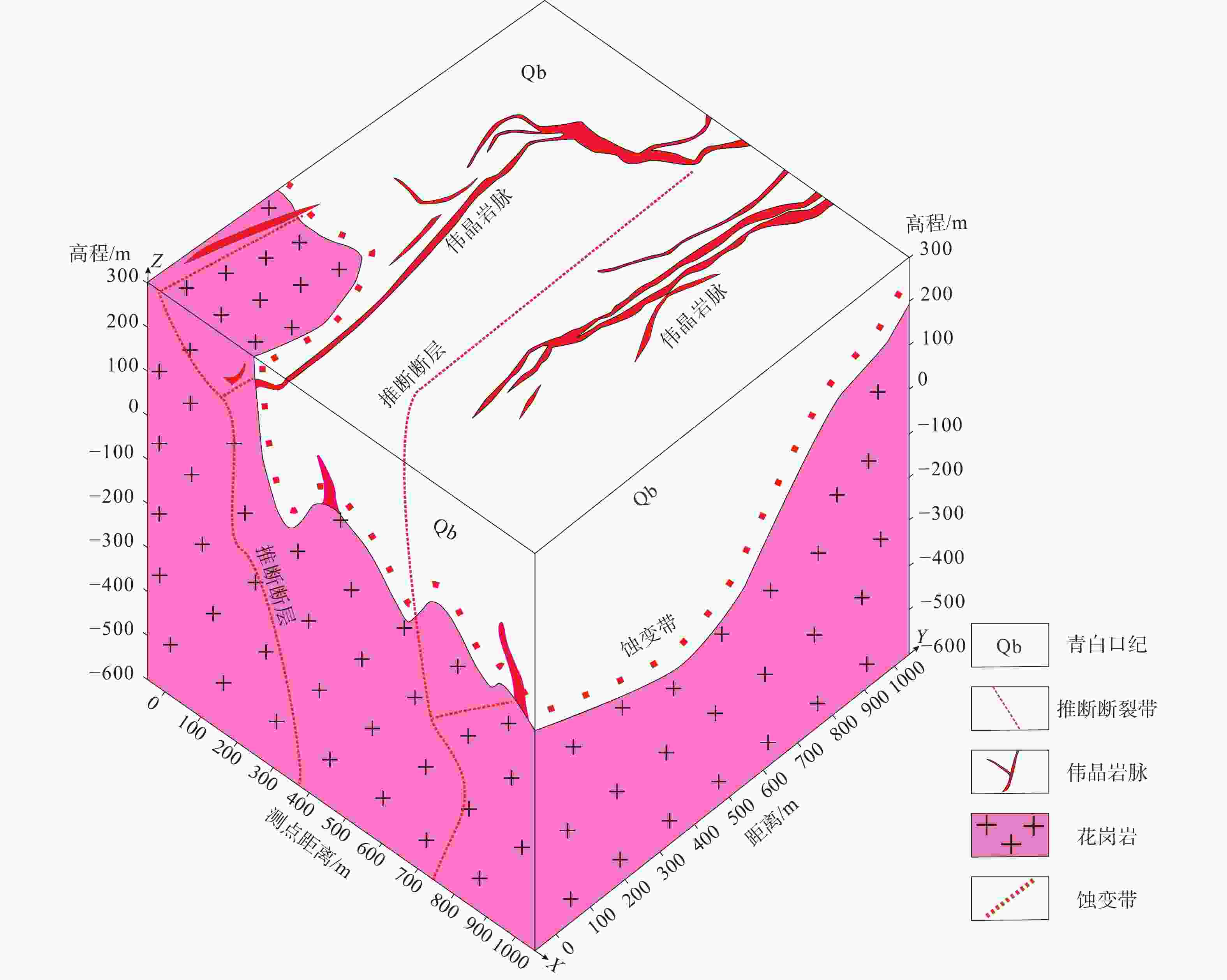
摘要: 花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床是最重要的稀有金属矿床类型之一。连云山东部新发现了白沙窝伟晶岩型矿床,初步评估白沙窝矿床深部稀有金属资源潜力巨大,但该矿床的矿产开采程度很低,围绕深部隐伏花岗伟晶岩脉的研究程度不高。通过研究白沙窝伟晶岩型矿床的深部电性结构特征,探讨稀有金属成矿模型及赋矿载体的空间分布,阐明矿脉就位关系,旨为稀有金属找矿预测提供依据。通过可控源音频大地电磁法(CSAMT)在白沙窝岩体东南方向开展深部隐伏岩(矿)体的探测工作,采用共轭梯度法反演实测3条探测剖面数据,探测深部隐伏岩(矿)体,并结合钻孔信息和元素地球化学异常特征信息进行综合分析,揭示隐伏岩脉的分布及成矿特征。研究结果表明,隐伏伟晶岩脉主要位于冷家溪群中,集中分布在花岗岩体顶部及构造裂隙周围,埋深在50~300 m;伟晶岩脉的成矿地球物理标志为深部高阻体侵入浅部低阻体中的高阻脉状地质体。研究成果为白沙窝矿床后续勘查工作提供了科学依据,揭示了伟晶岩脉的形成机理,并为湘东北及华南地区的稀有金属勘查提供了可靠的物探预测技术和经验。Abstract:
Objective The aim of this study is to characterize the deep electrical structure of the Baishawo pegmatite-type deposits, explore the spatial distribution of rare metal mineralization models and ore-conferring carriers, and elucidate the relationship between the location of ore veins to provide a basis for prediction in rare metal mineral exploration. Methods Through the controlled-source audio-geomagnetic method (CSAMT) and the conjugate gradient method of inverse measurement of three exploration profiles, deep hidden rock (ore) bodies were detected. Then, by combining these results with the information from drill holes and elemental geochemical anomalies, a comprehensive analysis was carried out to reveal the distribution of the hidden dikes and the mineralization characteristics. Results The study showed that the concealed pegmatite veins are mainly located in the Lengjiaxi Group, where they are concentrated on the top of the granite body and around tectonic fissures and have burial depths ranging from 50 to 300 m. The geophysical signature of pegmatite vein mineralization is a high-resistance vein-like geologic body intruded from a deep high-resistance body into a shallow low-resistance body. Conclusion The determined distribution and burial depth of concealed pegmatite veins, identified potential concealed veins in the study area, and geophysical characteristics of the pegmatite vein mineralization provide a basis for understanding the formation mechanism of fracture zone-constrained pegmatite veins. Significance The research results provide a scientific basis for follow-up exploration of the Baishawo deposit, reveal the formation mechanism of the pegmatite veins, and provide reliable physical exploration and prediction technology and experience useful for rare metal exploration in northeast Hunan and south China. -
Key words:
- pegmatite /
- Lianyunshan mountain /
- CSAMT /
- lithium-beryllium-niobium-tantalum deposit /
- rare metal
-
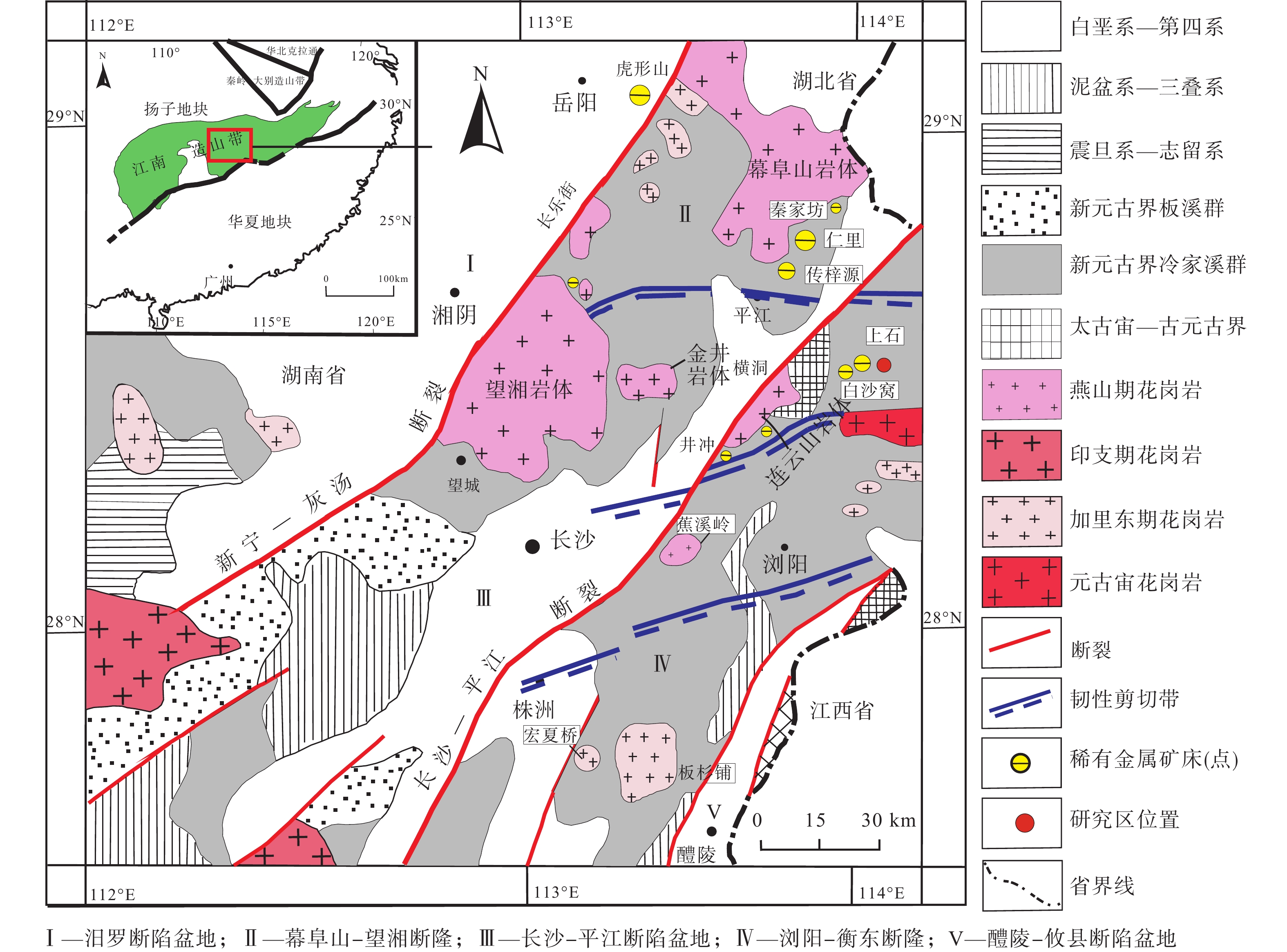
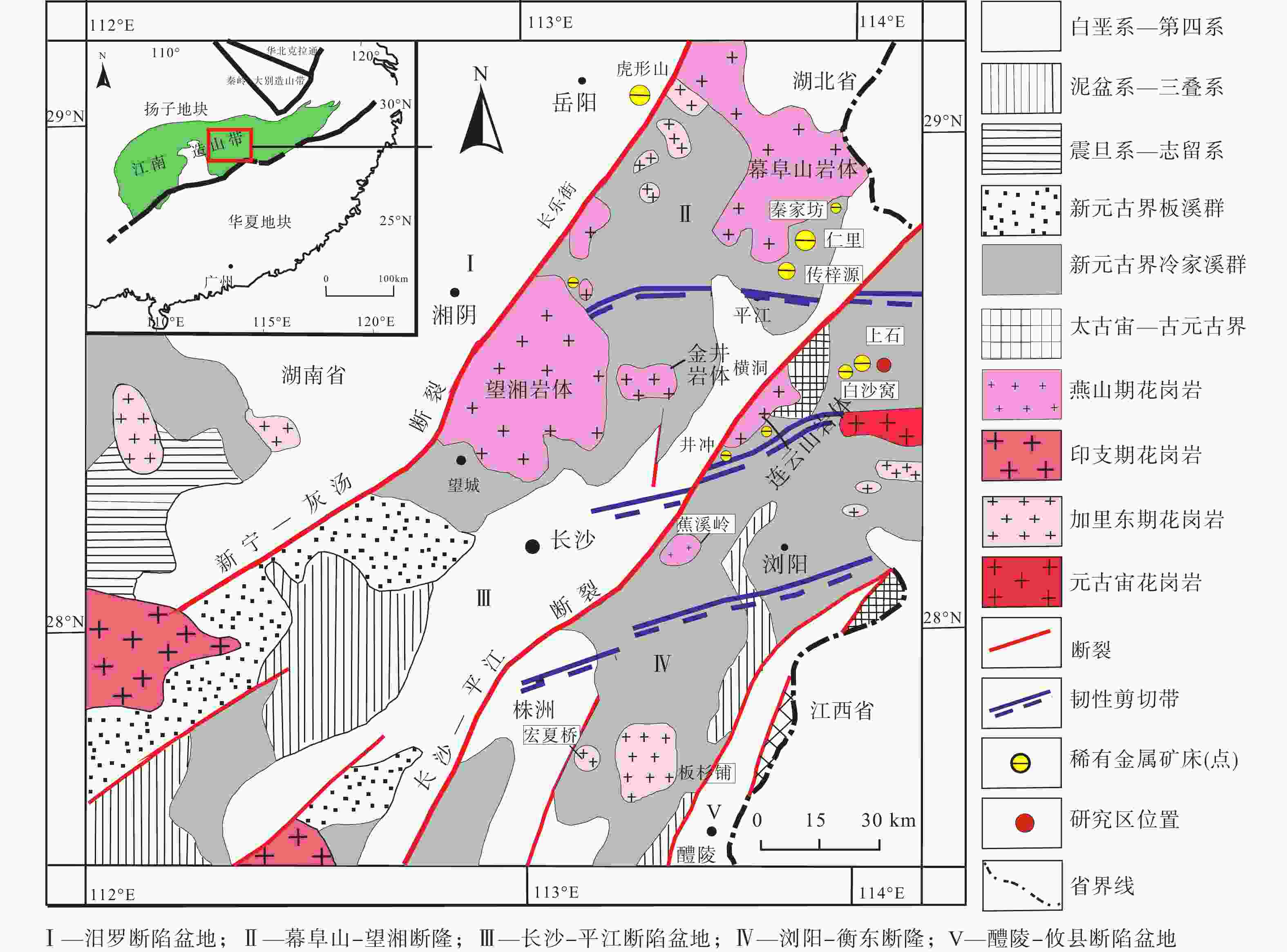
图 1 湘东北地区地质简图
a—华南构造划分图(Chen and Jahn,1998);b—湘东北地区大地构造图(许德如等,2009)
Figure 1. Generalized geological map of northeast Hunan Province in the Jiangnan Orogen Belt
(a) Tectonic division map of South China (Chen and Jahn, 1998); (b) Geotectonic map of northeast Hunan (Xu et al., 2009)
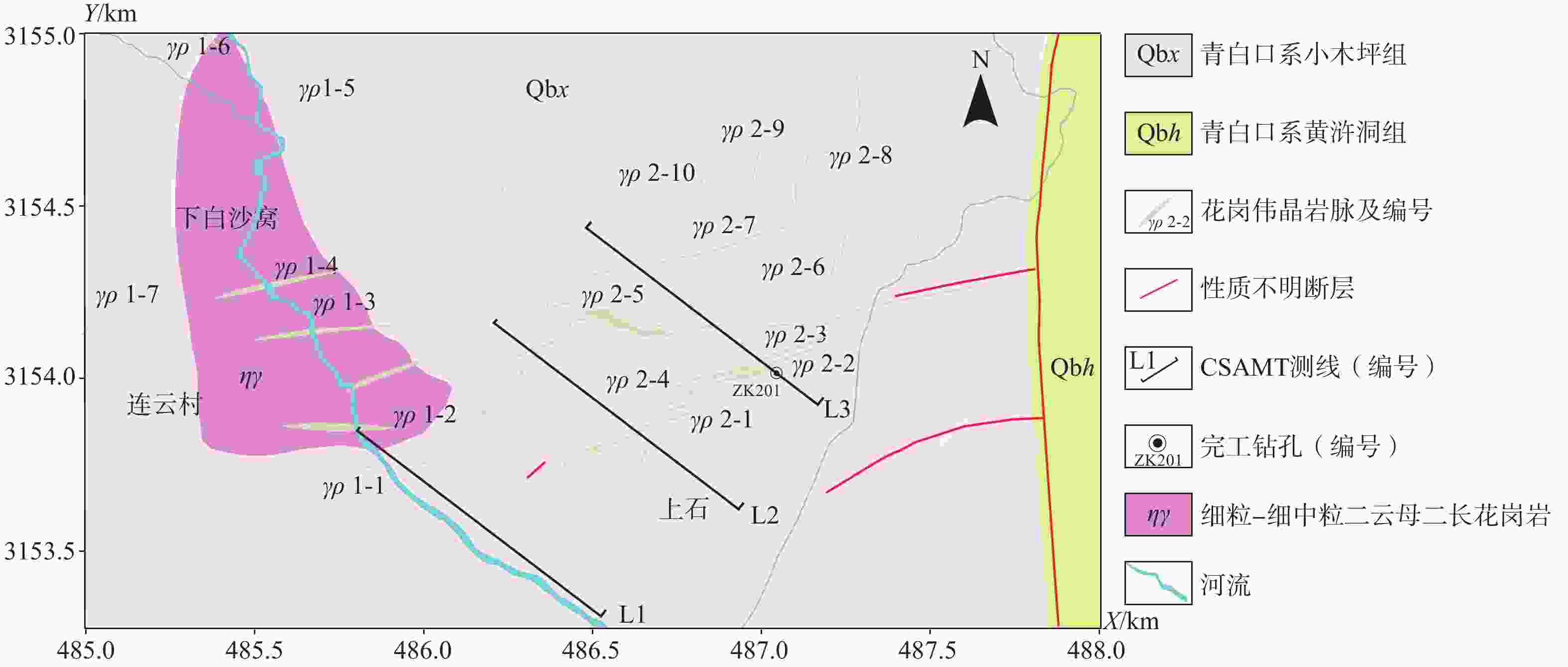
图 2 白沙窝矿床测线布置图(据曹创华等,2020修改)
Figure 2. Map of CSAMT survey line layout in the research area (modified after Cao et al., 2020)
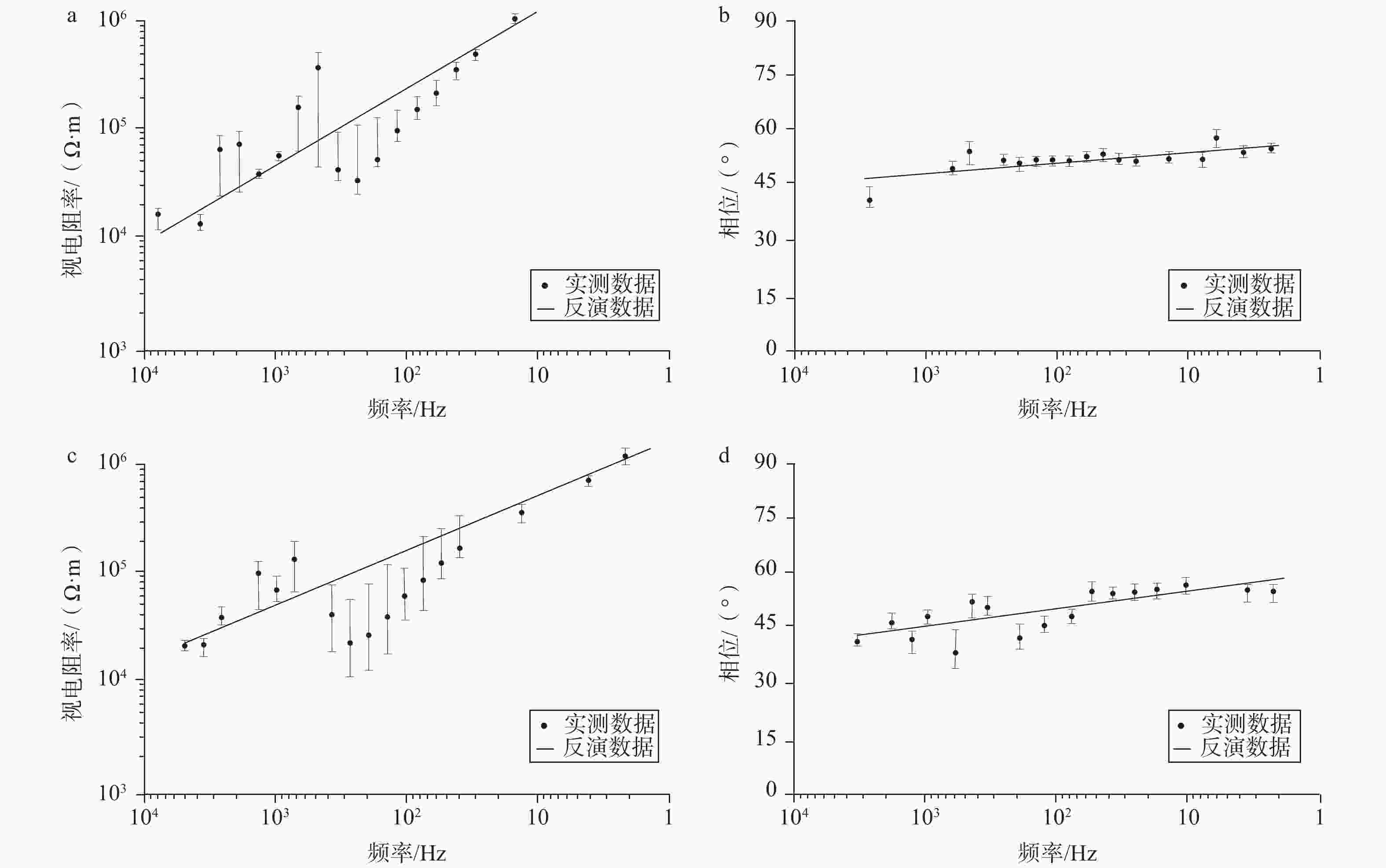
图 3 测线实测数据和二维反演模型数据
a—测线L1中170号点的视电阻率曲线;b—测线L1中170号点的相位曲线;c—测线L2中870号点的视电阻率曲线;d—测线L2中870号点的相位曲线
Figure 3. Data of line measurement and two-dimensional inversion model
(a) Apparent resistivity curve at point 170 in Line 1; (b) Phase curve at point 170 in Line 1; (c) Apparent resistivity curve at point 870 in Line 2; (d) Phase curve at point 870 in Line 2
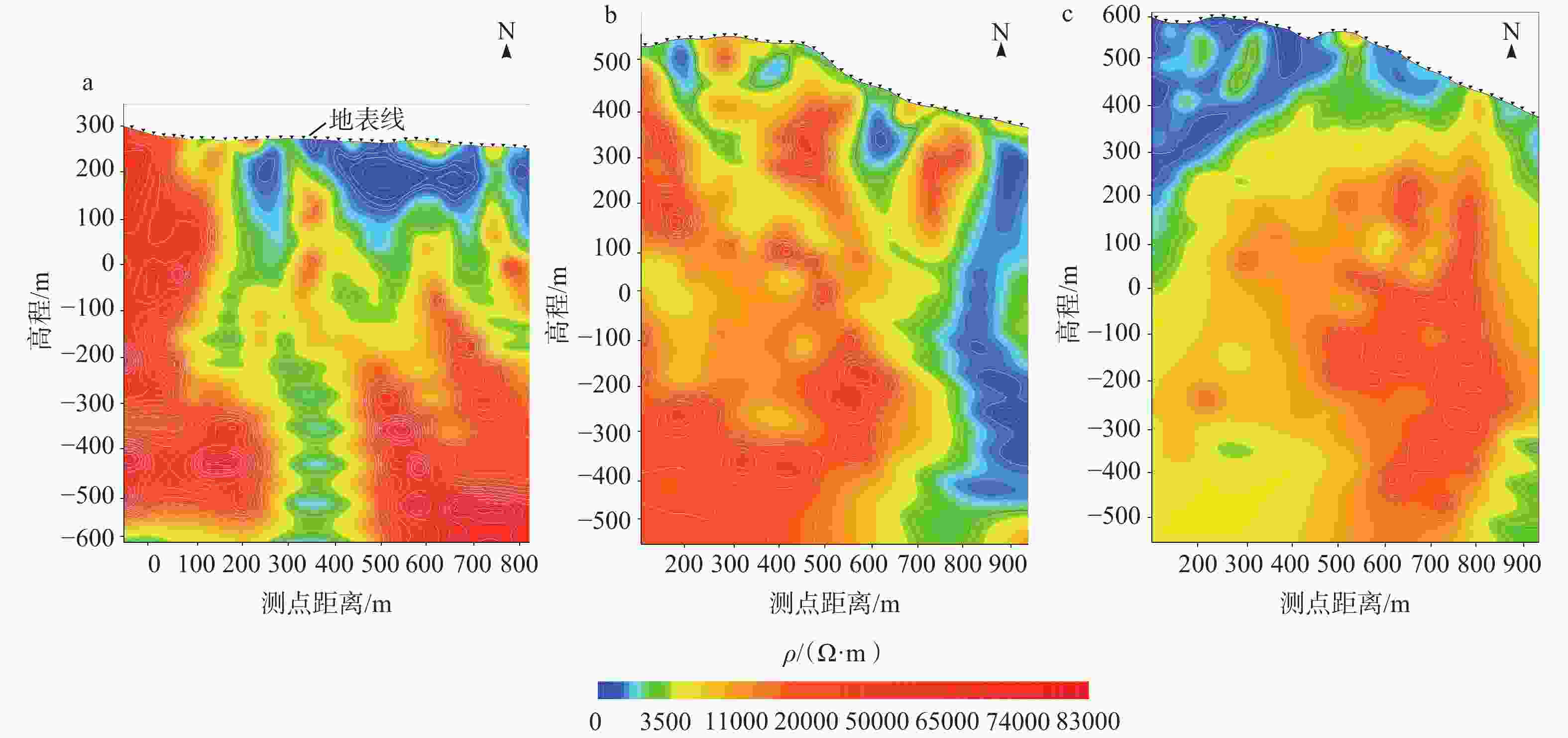
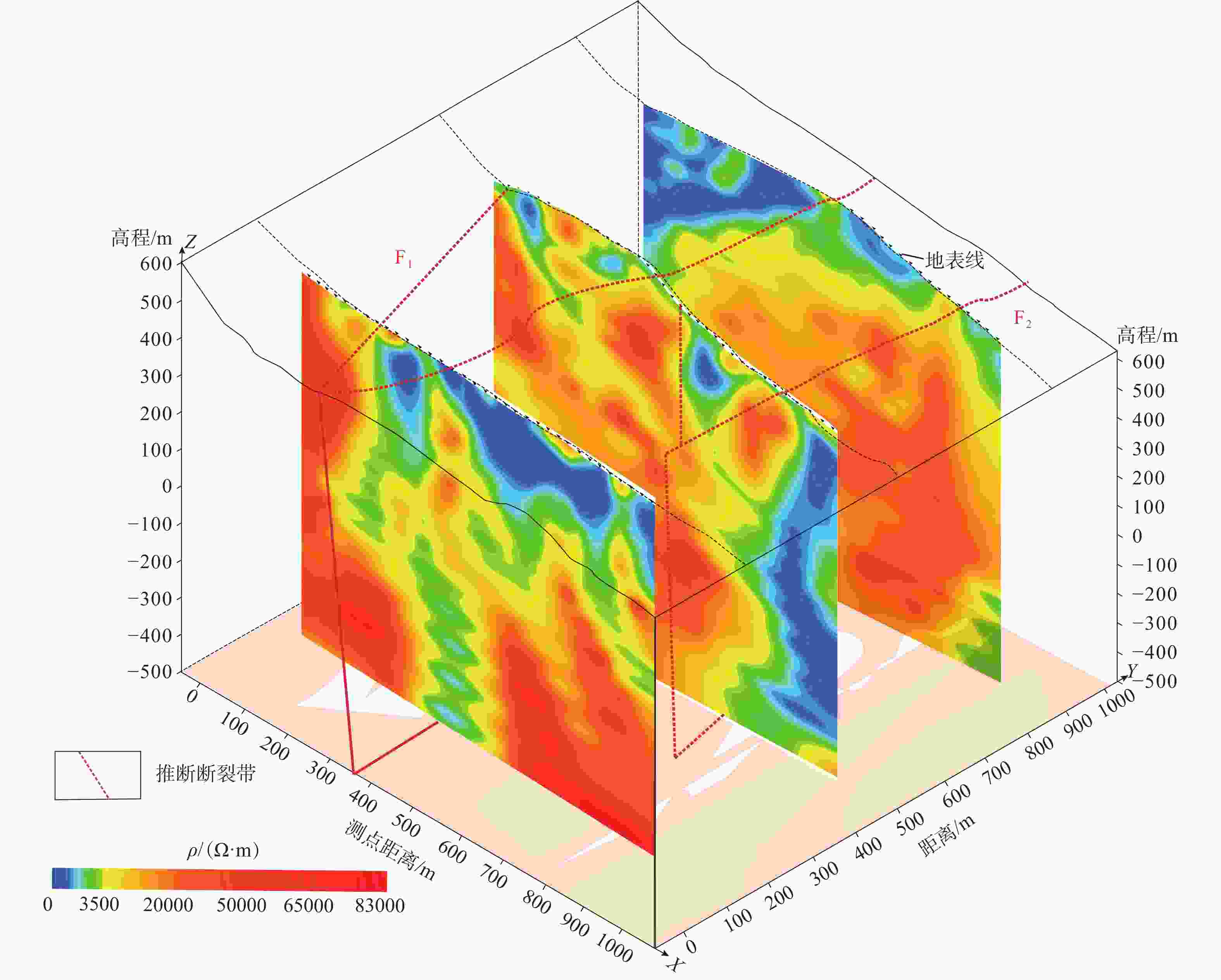
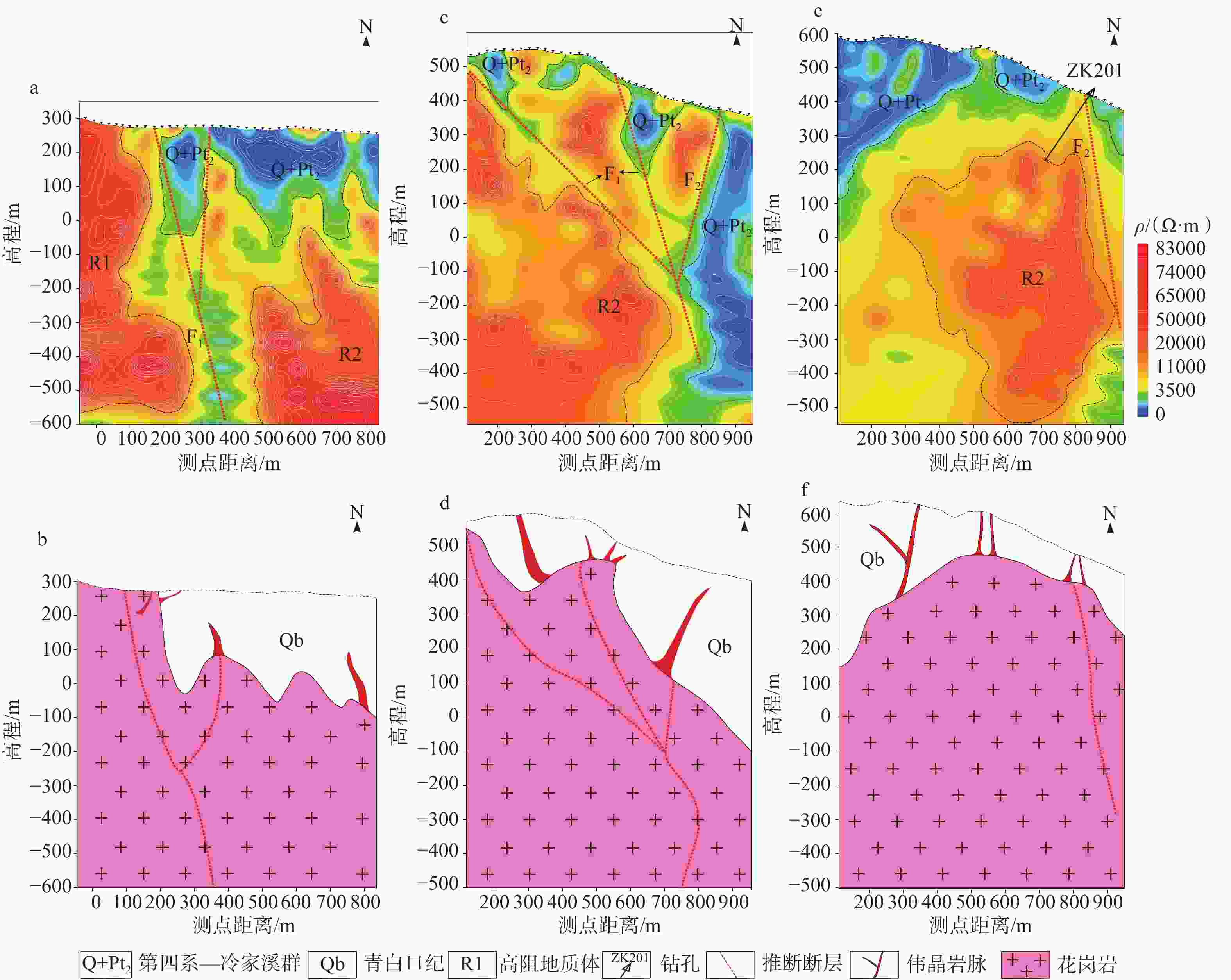
图 6 白沙窝矿床测线L1—L3的电性结构和地质解释图
a—测线L1电性结构图;b—测线L1地质解释图;c—测线L2电性结构图;d—测线L2地质解释图;e—测线L3电性结构图;f—测线L3地质解释图
Figure 6. L1–L3 electrical structure and geological interpretation map of the Baishawo mining area
(a) Electrical structure diagram of measuring Line 1; (b) Geological interpretation map of survey Line 1; (c) Electrical structure diagram of measuring Line 2; (d) Geological interpretation map of survey Line 2; (e) Electrical structure diagram of measuring Line 3; (f) Geological interpretation map of survey Line 3
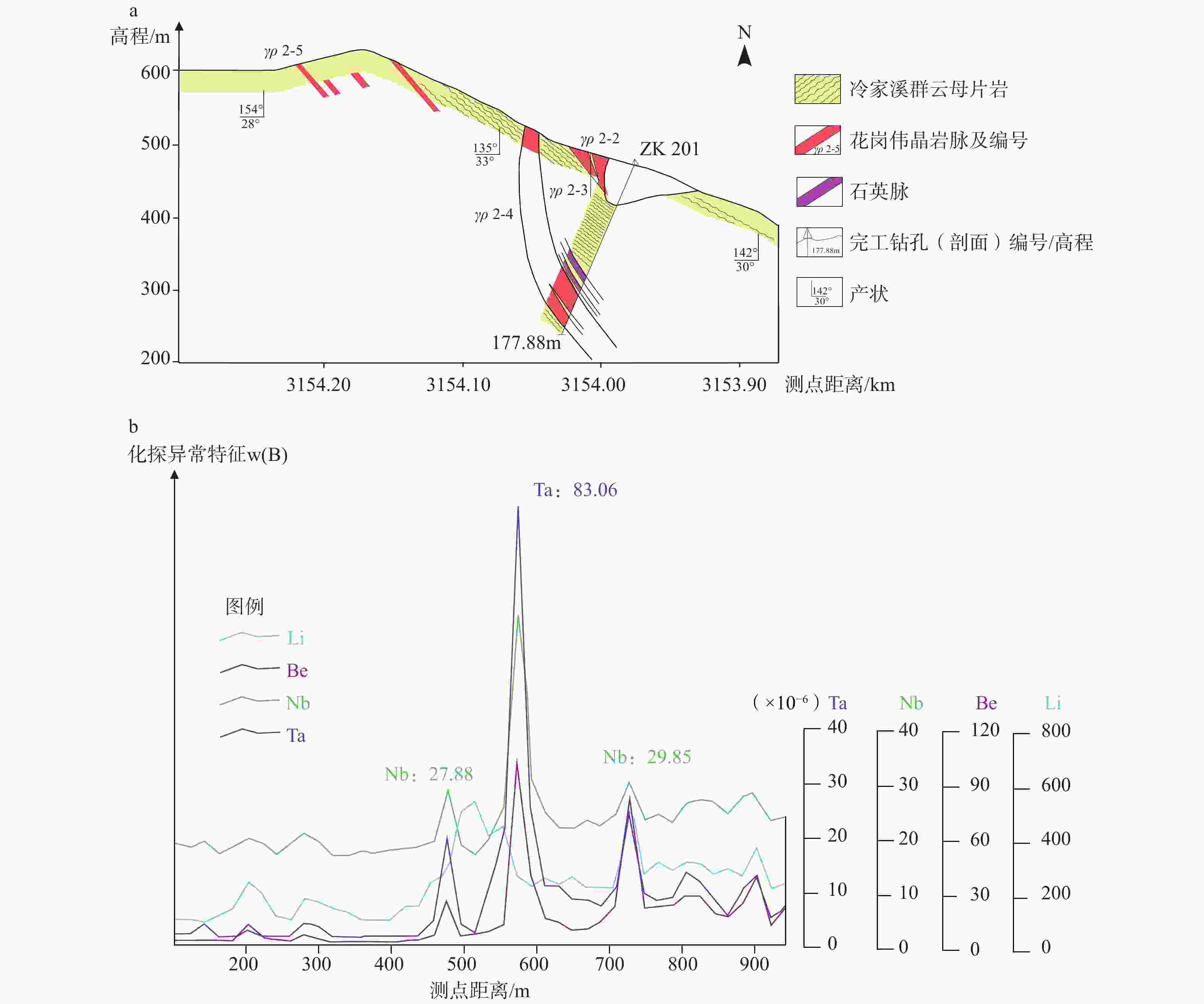
图 7 钻孔地质剖面与地球化学元素解译图
a—ZK201钻孔地质剖面图; b—测线L3元素地球化学异常特征图(Wen et al.,2021)
Figure 7. Comprehensive geological and geochemical results interpretation map
(a) Geological profile of drill hole ZK201; (b) Characterization of L3 elemental geochemical anomalies in the survey line (Wen et al., 2021)
表 1 白沙窝矿床主要地层与岩浆岩物性参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of main strata and magmatic rocks in the Baishawo mining area
地质体类型 样品数量 电阻率/(Ω·m) 最小值 最大值 平均值 地层 第四系 532 1.21 211.12 112.22 冷家溪群 388 118.66 1988.31 886.53 花岗岩 白沙窝岩体 331 5633.23 33552.83 24388.22 含矿体 伟晶岩 111 4568.66 26953.77 17683.41 -
[1] CAO C H, WEN C H, LOU F S, et al., 2020. Geophysical responses of typical rare metal deposits and implications on geophysical prospecting in Hunan province, China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 44(6): 1096-1112. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] CAO X Z, ZHANG W S, SUN H S, 2009. Progress in the study of deep exploration in China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 28(2): 104-109. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] ČERNÝ P, ERCIT T S, 2005. The classification of granitic pegmatites revisited[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 43(6): 2005-2026. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.43.6.2005 [4] CHEN J F, JAHN B M, 1998. Crustal evolution of southeastern China: Nd and Sr isotopic evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 284(1-2): 101-133. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00186-8 [5] CHENG C G, LI Y, ZHANG K, et al., 2011. A preliminary study on prospecting deep-seated hidden ore body in the Yueshan intrusion using CSAMT[J]. Geology of Anhui, 21(1): 52-59. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] DE GROOT-HEDLIN C D, CONSTABLE S C, 1990. Occam’s inversion to generate smooth, two-dimensional models from magnetotelluric data[J]. Geophysics, 55(12): 1613-1624. doi: 10.1190/1.1442813 [7] DI Q Y, MARTYN UNSWORTH, WANG M Y, 2006.2. 5-Dimensional Finite Element Method CSAMT Numerical Inversion[J]. Petroleum Geophysical Exploration, (01): 100-106+122+129. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] DONG H, WEI W B, YE G F, et al., 2012. Study of two dimensional magnetotelluric inversions of complex three dimensional structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(12): 4003-4014, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.012 [9] FAN J B, YANG R, HAO X F, et al., 2022. Application of audio-frequency magnetotelluric sounding to deep prospecting and prediction of rare metal deposit in Jiajika area[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 37(1): 111-117. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] GUO Z W, XUE G Q, LIU J X, et al., 2020. Electromagnetic methods for mineral exploration in China: A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 118: 103357. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103357 [11] HE H Y, WANG J R, WEN W, et al., 2024. Deep structure of epithermal deposits in Youxi area: insights from CSAMT and dual-frequency IP data[J]. Minerals, 14(1): 27. [12] HE M X, HU X Y, CHEN Y P, et al. 2008. Application of one-dimensional inversion of CSAMT Occam[J]. Journal of Engineering Geophysics, (04): 439-443. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] HOU Z Q, CHEN J, ZHAI M G, 2020. Current status and frontiers of research on critical mineral resources[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 65(33): 3651-3652. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-1417 [14] HUANG N, SHAO K, ZHANG B S, et al., 2014. The application of CSAMT and induced electric medium gradient method to one lead—zinc polymetallic ore in one district of Guangdong[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 11(6): 797-801. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] JIAO Y J, HUANG X R, LIANG S X, et al., 2021. Deep structure and prospecting significance of the Cuonadong dome, Tethys Himalaya, China: geophysical constraints[J]. Geological Journal, 56(1): 253-264. doi: 10.1002/gj.3962 [16] LEI D, 2010. Studies and applications of 2-D CSAMT modeling and inversion with a dipole source and topography[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(4): 982-993. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] LI B, DING Y H, ZHANG Z H, et al., 2014. Application of CSAMT to deep iron ore exploration in Wuyang area, Henan province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 29(1): 108-113. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] LI T D, 2022. Development history of geological and mineral survey in China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 653-682. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] LIN C H, TAN H D, SHU Q, et al., 2012. Three-dimensional conjugate gradient inversion of CSAMT data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(11): 3829-3838. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] LIU G D, 1992. Comprehensive study of geophysics for shallow layer[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 7(4): 1-3. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] LIU J X, LIU R, GUO R W, et al., 2023. Research progress of electromagnetic method in nonferrous metal mineral exploration[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 33(1): 261-284. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] LIU J X, ZHOU K K, LIU H D, et al., 2023. Metallogenic prediction of magnetite in the Pandian area at the northwest margin of Luxi uplift, China: constraints of wide-field electromagnetic data[J]. Remote Sensing, 15(5): 1217. doi: 10.3390/rs15051217 [23] LU H F, WANG Z F, WANG H, et al., 2013. The application of CSAMT and GS on prospecting and evaluation in Baishan molybdenum deposit, Hami, Xinjiang[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 28(3): 1547-1556. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] LV H Q, XU L Y, YANG B, et al., 2022. Mineralization based on CSAMT and SIP sounding data: a case study on the Hadamengou gold deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Minerals, 12(11): 1404. doi: 10.3390/min12111404 [25] MAO J W, YUAN S D, XIE G Q, et al., 2019. New advances on metallogenic studies and exploration on critical minerals of China in 21st century[J]. Mineral Deposits, 38(5): 935-969. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] RODI W, MACKIE R L, 2001. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysics, 66(1): 174-187. doi: 10.1190/1.1444893 [27] SHEN P, PAN H D, LI C H, et al., 2023. Lithium deposits in the Central Asian Metallogenic Domain: Metallogenic regularity and model[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 39(11): 3185-3209. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.11.01 [28] STRANGWAY D W, SWIFT JR C M, HOLMER R C, 1973. The application of audio-frequency magnetotellurics (AMT) to mineral exploration[J]. Geophysics, 38(6): 1159-1175. doi: 10.1190/1.1440402 [29] WANG D H, 2016. A discussion on some problems concerning deep exploration of mineral resources in South China[J]. Geology in China, 43(5): 1585-1598. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] WANG D H, WANG R J, SUN Y, et al., 2016. A review of achievements in the three-type rare mineral resources (rare resources, rare earth and rarely scattered resources) survey in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 37(5): 569-580. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] WANG D H, DAI H Z, LIU S B, et al., 2022. New progress and trend in ten aspects of lithium exploration practice and theoretical research in China in the past decade[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 743-764. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] WANG R T, 1999. Characteristics of geophysical and geochemical anomalies in main gold deposits of devonian strata along the Qinling orogenic belt(Shaanxi part)and indicators for prospecting[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 23(1): 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] WANG R, WANG M Y, 2007. One-dimensional full data CSAMT inversion[J]. Petroleum Geophysical Exploration, (01): 107-114+132-133+125. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] WANG X L, ZHOU J C, CHEN X, et al., 2017. Formation and evolution of the Jiangnan orogen[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 36(5): 714-735+696. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] WANG Y F, GUO R W, LIU J X, et al., 2024. A divergence-free vector finite-element method for efficient 3D magnetotelluric forward modeling[J]. Geophysics, 89(1): E1-E11. doi: 10.1190/geo2023-0037.1 [36] WEI W B, 2002. New advance and prospect of magnetotelluric sounding (MT) in China[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 17(2): 245-254. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] WEN C H, CHEN J F, LIN B H, LUO X Y. 2018a. 2018 Implementation Program of the Survey and Evaluation of Rare Metals in Key Mining Aggregation Areas of Hunan. Changsha: Hunan Geological Survey Institute: 1-55. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] WEN C H, CHEN J F, LUO X Y. 2018b. Report on the results of the survey and evaluation of rare metals in key mining concentration areas of Hunan. Changsha: Hunan Geological Survey Institute: 1-124. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] WEN C H, CHEN J F, CAO C H, 2020. Study on the mineralization of rare metal pegmatite in Lianyunshan ore district, Hunan Province[J]. Geological Review, 66(S1): 135-136. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] WEN C H, SHAO Y J, XIONG Y Q, et al., 2021. Ore genesis of the Baishawo Be-Li-Nb-Ta deposit in the northeast Hunan Province, south China: Evidence from geological, geochemical, and U-Pb and Re-Os geochronologic data[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 129: 103895. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103895 [41] WEN Z L, HUANG M, XU G F, et al., 2024. Discovery and significance of pegmatitic rare metal deposits in Shangshi area, Lianyunshan, Northeast Hunan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 59(4): 961-970. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2024.068 [42] XU D R, WANG L, LI P C, et al., 2009. Petrogenesis of the Lianyunshan granites in northeastern Hunan Province, South China, and its geodynamic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(5): 1056-1078. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] XUE G Q, DENG X, 2007. Detectability of thin layers by transient electromagnetic method[J]. Petroleum Geophysical Exploration, (06): 709-713+733+609. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] YANG N F, HE Y J, YANG L T, 2014. Application of CSAMT method in deep prospecting of Cuihongshan Fe polymetallic deposit[J]. Global Geology, 33(4): 880-888. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] ZHAI M G, WU F Y, HU R Z, et al, 2019. Strategic key metal mineral resources: Current status and problems[J]. China Science Foundation, 33(02): 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] ZHOU J J, QIANG J K, TANG J T, et al., 2010. 1-D optimization inversion of CSAMT data with intervention mechanism[J]. Seismology and Geology, 32(3): 453-464. (in Chinese with English abstract [47] 曹创华,文春华,楼法生,等,2020. 湖南省典型稀有金属矿床地球物理响应特征及物探找矿方法研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,44(6):1096-1112. [48] 曹新志,张旺生,孙华山,2009. 我国深部找矿研究进展综述[J]. 地质科技情报,28(2):104-109. [49] 程长根,李勇,张凯,等,2011. 在月山岩体利用大地音频电磁测深(CSAMT)法寻找深部隐伏矿体的初步研究[J]. 安徽地质,21(1):52-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2011.01.012 [50] 董浩,魏文博,叶高峰,等,2012. 大地电磁测深二维反演方法求解复杂电性结构问题的适应性研究[J]. 地球物理学报,55(12):4003-4014, doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.012. [51] 底青云,Martyn Unsworth,王妙月,2006.2. 5维有限元法CSAMT数值反演[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,(01):100-106+122+129. [52] 范俊波,杨荣,郝雪峰,等,2022. 音频大地电磁测深在甲基卡深部找矿预测中的应用研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛,37(1):111-117. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2022.01.015 [53] 何梅兴,胡祥云,陈玉萍,等,2008. CSAMT奥克姆一维反演的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报,(04):439-443. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7940.2008.04.011 [54] 侯增谦,陈骏,翟明国,2020. 战略性关键矿产研究现状与科学前沿[J]. 科学通报,65(33):3651-3652. [55] 雷达,2010. 起伏地形下CSAMT二维正反演研究与应用[J]. 地球物理学报,53(4):982-993. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2010.04.023 [56] 李冰,丁云河,张智慧,等,2014. CSAMT法在河南舞阳地区寻找深部铁矿中的应用[J]. 地质找矿论丛,29(1):108-113. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2014.01.015 [57] 李廷栋,2022. 中国地质矿产调查事业发展历程[J]. 地质力学学报,28(5):653-682. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222818 [58] 林昌洪,谭捍东,舒晴,等,2012. 可控源音频大地电磁三维共轭梯度反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报,55(11):3829-3838. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.11.030 [59] 刘光鼎,1992. 浅层地球物理综合研究[J]. 地球物理学进展,7(4):1-3. [60] 柳建新,童孝忠,郭荣文,等,2012. 大地电磁测深法勘探:资料处理、反演与解释[M]. 北京:科学出版社. [61] 柳建新,刘嵘,郭荣文,等,2023. 电磁法在有色金属矿产勘查中的研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报,33(1):261-284. doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2022-43043 [62] 毛景文,袁顺达,谢桂青,等,2019. 21世纪以来中国关键金属矿产找矿勘查与研究新进展[J]. 矿床地质,38(5):935-969. [63] 王登红,2016. 对华南矿产资源深部探测若干问题的探讨:以若干超大型矿床深部找矿突破为例[J]. 中国地质,43(5):1585-1598. doi: 10.12029/gc20160509 [64] 王登红,王瑞江,孙艳,等,2016. 我国三稀(稀有稀土稀散)矿产资源调查研究成果综述[J]. 地球学报,37(5):569-580. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.05.06 [65] 王登红,代鸿章,刘善宝,等,2022. 中国锂矿十年来勘查实践和理论研究的十个方面新进展新趋势[J]. 地质力学学报,28(5):743-764. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222811 [66] 王若,王妙月,2007. 一维全资料CSAMT反演[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,(1):107-114+132-133+125 [67] 王孝磊,周金城,陈昕,等,2017. 江南造山带的形成与演化[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,36(5):714-735 [68] 魏文博,2002. 我国大地电磁测深新进展及瞻望[J]. 地球物理学进展,17(2):245-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2002.02.009 [69] 文春华,陈剑锋,林碧海,罗小亚. 2018a. 湖南重点矿集区稀有金属调查评价2018年实施方案. 长沙:湖南省地质调查院:1–55. [70] 文春华,陈剑锋,罗小亚. 2018b. 湖南重点矿集区稀有金属调查评价成果报告. 长沙:湖南省地质调查院:1–124. [71] 文春华,陈剑锋,曹创华,2020. 湖南连云山矿集区稀有金属伟晶岩成矿作用研究[J]. 地质论评,66(S1):135-136. [72] 文志林,黄明,许国锋,等,2024. 湘东北连云山上石地区伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床的发现及意义[J]. 地质科学,59(4):961-970. [73] 许德如,王力,李鹏春,等,2009. 湘东北地区连云山花岗岩的成因及地球动力学暗示[J]. 岩石学报,25(5):1056-1078. [74] 薛国强,邓湘,2007. 瞬变电磁法对薄层的探测能力[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,(06):709-713+733+609. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2007.06.018 [75] 杨乃峰,何英杰,杨李汀,2014. CSAMT法在翠宏山铁多金属矿床深部找矿中的应用[J]. 世界地质,33(4):880-888. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2014.04.016 [76] 翟明国,吴福元,胡瑞忠,等,2019. 战略性关键金属矿产资源:现状与问题[J]. 中国科学基金,33(02):106-111. [77] 周俊杰,强建科,汤井田,等,2010. 具有干预机制的CSAMT数据一维最优化反演[J]. 地震地质,32(3):453-464. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2010.03.012 -




 下载:
下载: