Sedimentary paleo-environment and organic matter enrichment in the Lucaogou Formation of the Jimsar Sag
-
摘要:
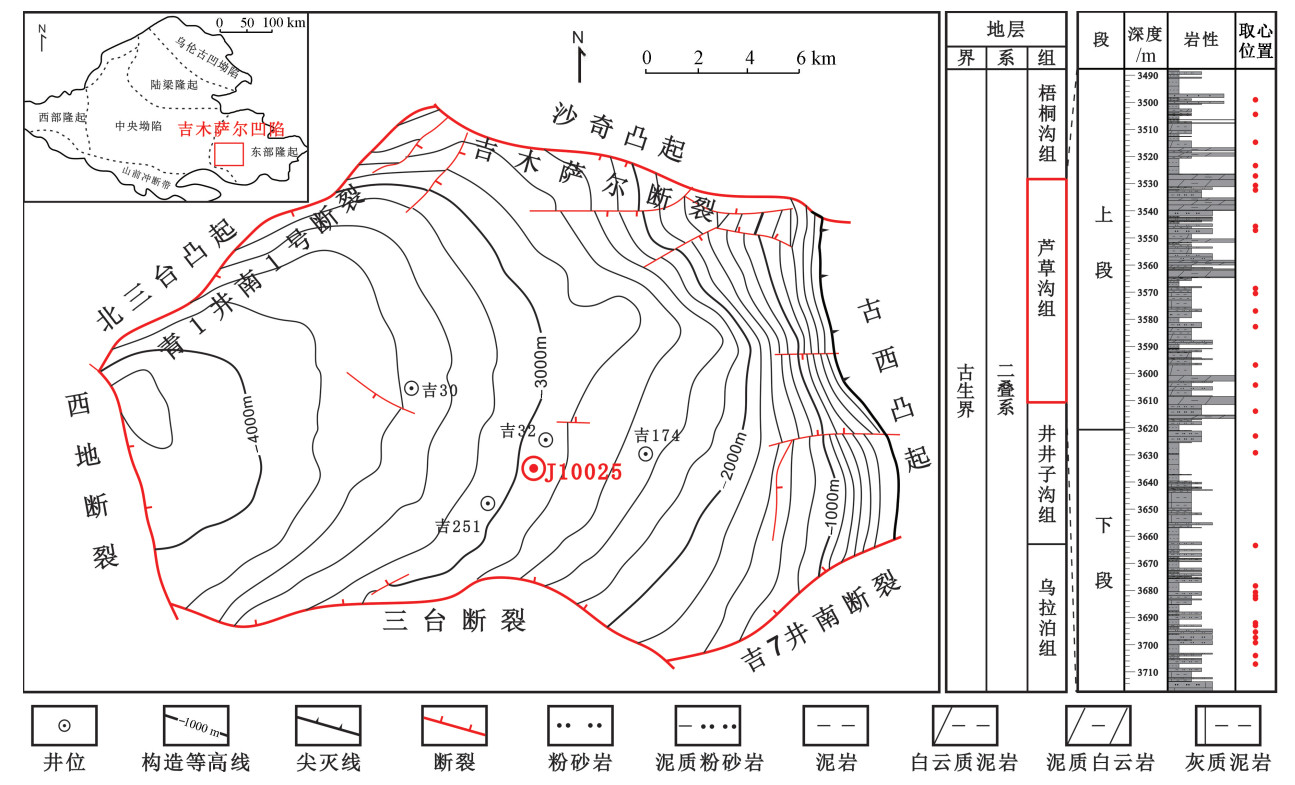
吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组是陆相盆地页岩油勘探开发的主力层位, 但其古环境信息与有机质富集机理尚不明确。为了深入研究二叠系芦草沟组的沉积古环境, 在岩心和薄片观察的基础上, 通过X射线荧光光谱(XRF)和电感耦合等离子质谱(ICP-MS)对J10025井26块烃源岩样品进行主微量元素测试, 并结合GC-MS生物标志化合物数据与典型沉积构造反映芦草沟组古环境特征。古气候指数C值、Sr/Cu、Sr/Ba、V/Cr、Pr/Ph、P、Co元素等地化指标表明, 芦草沟组整体上为干旱—半干旱的咸化湖泊沉积环境, 沉积时期水体较深, 且为贫氧—缺氧的状态。其中, 芦草沟组上段整体为半干旱气候、微咸水环境, 还原性相对较弱, 水体较深, 生产力较高, 但环境波动较大; 芦草沟组下段环境比较稳定, 气候极度干旱, 盐度较高, 还原性相对较强, 水体较浅, 生产力较低。古环境指标与TOC含量的相关性分析结果显示, 有机质的保存条件以及稀释速率对芦草沟组有机质富集的影响比较有限, 而初级生产力大小是芦草沟组有机质富集的主控因素。
Abstract:The Lucaogou Formation in the Jimsar Sag is the main target layer of shale oil exploration and development in continental basins. However, its paleo-environmental information and organic matter enrichment mechanism still need to be determined. In order to investigate the paleo-environment of the Permian Lucaogou Formation, based on core and thin section observation, we carried out major and trace element analyses on 26 source rocks from Well J10025 by using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy(XRF) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry(ICP-MS). This analysis, combined with GC-MS biomarker data and typical sedimentary structures, reflects the paleo-environmental characteristics of the Luchaogou Formation. Geochemical indicators such as C-value, Sr/Ba, V/Cr, Pr/Ph, P, and Co show that the Lucaogou Formation was generally developed in a saline lake environment under an arid to semi-arid climate, with relatively deep water during deposition and hypoxic to anoxic conditions. The upper member was deposited in a semi-arid, brackish lake with weak reducibility, deep water body, and high productivity. In contrast, the lower member was deposited in an extremely dry, highly saline, and strongly reductive shallow lake with low productivity. The paleo-environment of the upper member fluctuated wildly, while that of the lower member was relatively stable. The correlation analyses between paleo-environmental indicators and TOC show that the preservation conditions and dilution rate of organic matter have limited influence on organic matter enrichment of the Lucaogou Formation. At the same time, the primary productivity is the main controlling factor.
-
Key words:
- Jimsar /
- the Lucaogou Formation /
- shale oil /
- sedimentary paleo-environment /
- organic matter enrichment
-
图 2 J10025井芦草沟组岩心与岩石薄片特征
a、d、g、j为岩心照片;b、e、h、k为透射光;c、f、i、l为正交偏光
a—c—泥岩,可见鱼鳞化石,上段顶部,3530.8 m;d—f—云质岩屑细砂岩,上段中部,3549.3 m;g—i—白云质泥岩,发育白云石纹层,上段底部,3603.1 m;j—l—灰质泥岩,下段,3685.5 m,下半部分用茜素红染色Figure 2. Photographs of cores and thin sections of the Lucaogou Formation in Well J10025
(a-c)Mudstone with fish scales, the top of the upper member, 3530.8 m; (d-f)Dolomitic lithic fine sandstone, the middle of the upper member, 3549.3 m; (g-i)Dolomitic mudstone with dolomitic lamina, the bottom of the upper member, 3603.1 m; (j-l)Calcareous mudstone, half of the sample is alizarin red stained, the lower member, 3685.5 m
Core photos in the left column, transmitted light in the middle and orthogonal light in the right表 1 J10025井芦草沟组TOC含量与主量元素含量
Table 1. Contents of TOC and major elements of the Lucaogou Formation in Well J10025
层位 样品 深度/m TOC含量/% SiO2/% Al2O3/% MgO/% Na2O/% K2O/% P2O5/% TiO2/% CaO/% Fe2O3/% MnO/% 上段 J-26 3499.5 5.77 18.68 4.58 0.67 0.52 0.53 0.13 0.18 1.10 2.46 0.03 J-25 3506.8 1.81 62.71 11.69 2.44 0.54 1.94 0.23 0.56 7.47 6.21 0.16 J-24 3515.0 7.76 65.33 11.85 1.68 1.18 3.29 0.40 0.62 2.84 3.92 0.09 J-23 3523.7 6.81 18.08 4.16 0.42 1.58 0.61 0.10 0.14 1.05 1.51 0.03 J-22 3526.1 5.74 16.46 4.34 0.49 2.02 0.91 0.27 0.20 0.64 1.91 0.04 J-21 3530.8 14.93 14.84 3.70 0.62 1.25 0.70 0.29 0.14 1.08 2.33 0.05 J-20 3547.8 5.53 15.49 4.16 0.81 1.81 1.01 0.09 0.17 0.41 2.01 0.02 J-19 3569.2 3.10 10.76 3.34 2.01 1.69 0.87 0.03 0.13 1.96 1.54 0.04 J-18 3570.5 6.75 10.24 3.05 2.06 1.82 0.48 0.03 0.11 1.07 1.32 0.02 J-17 3574.2 19.60 55.68 8.74 1.26 2.82 1.99 0.46 0.41 4.54 2.81 0.13 J-16 3576.6 16.97 6.10 2.44 0.41 1.20 0.51 0.09 0.10 1.48 1.86 0.04 J-15 3595.4 15.80 46.24 8.64 4.52 3.22 2.05 0.13 0.39 5.67 2.67 0.08 J-14 3603.1 7.04 38.92 7.12 8.42 2.26 1.66 0.22 0.28 13.85 3.29 0.15 J-13 3613.7 6.98 53.72 9.84 5.56 4.38 1.75 0.10 0.48 6.00 4.65 0.13 平均值 8.90 30.94 6.26 2.24 1.88 1.31 0.18 0.28 3.51 2.75 0.07 下段 J-12 3624.3 3.62 49.98 9.74 6.05 4.64 1.99 0.07 0.51 6.98 3.34 0.13 J-11 3629.2 2.29 55.41 9.74 2.88 4.40 1.71 0.08 0.44 8.92 2.13 0.12 J-10 3664.3 4.20 52.01 8.90 4.46 3.55 1.79 0.11 0.34 9.94 2.90 0.12 J-09 3679.5 3.11 49.71 8.56 6.69 3.67 1.44 0.07 0.35 10.32 4.08 0.13 J-08 3681.6 2.44 52.87 9.50 5.16 3.92 2.29 0.06 0.39 7.39 4.30 0.13 J-07 3684.5 3.48 39.19 7.97 8.09 3.62 1.68 0.09 0.38 12.67 3.56 0.13 J-06 3685.5 5.82 58.81 11.19 2.51 4.00 3.39 0.15 0.60 3.45 2.67 0.08 J-05 3695.3 2.50 39.14 8.19 5.27 3.04 2.66 0.17 0.44 15.44 3.59 0.12 J-04 3696.9 1.95 42.57 8.35 9.31 3.01 2.33 0.04 0.36 11.31 2.98 0.18 J-03 3699.9 5.73 50.47 9.43 4.90 3.10 2.80 0.08 0.43 8.43 3.05 0.13 J-02 3701.3 7.87 29.90 6.37 8.39 2.52 1.66 0.11 0.28 17.03 2.67 0.09 J-01 3708.3 4.85 43.00 8.09 7.35 2.99 1.95 0.09 0.36 12.42 2.83 0.15 平均值 3.99 46.92 8.83 5.92 3.54 2.14 0.09 0.41 10.36 3.17 0.13 平均值 6.63 38.32 7.45 3.94 2.64 1.69 0.14 0.34 6.67 2.95 0.10 上地壳(UCC) — 49.50 15.80 4.40 3.20 1.88 0.20 0.70 6.40 6.60 0.14 表 2 J10025井芦草沟组微量元素特征
Table 2. Trace elements characteristics of the Lucaogou Formation in Well J10025
层位 样品 深度/m B/(μg/g) Ga/(μg/g) Sr/(μg/g) V/(μg/g) Cr/(μg/g) Co/(μg/g) Ni/(μg/g) Th/(μg/g) U/(μg/g) Cu/(μg/g) Ba/(μg/g) 上段 J-26 3499.5 196.0 12.0 169.0 78.3 26.6 10.40 28.9 4.4 2.16 36.3 170 J-25 3506.8 300.0 11.6 265.0 80.3 25.3 4.61 11.4 5.7 1.21 24.2 189 J-24 3515.0 363.0 13.5 321.0 108.0 33.0 12.20 42.5 7.0 4.26 57.2 425 J-23 3523.7 60.7 12.3 229.0 70.5 181.0 13.20 93.5 4.9 2.65 98.0 370 J-22 3526.1 74.3 17.1 293.0 91.9 373.0 16.70 209.0 7.4 6.81 79.6 598 J-21 3530.8 69.9 10.9 223.0 77.2 419.0 15.90 187.0 4.2 5.61 66.2 261 J-20 3547.8 128.0 20.0 116.0 136.0 52.0 12.70 45.0 5.6 3.05 60.7 445 J-19 3569.2 132.0 13.3 161.0 74.1 37.0 10.60 24.5 4.1 1.50 33.1 337 J-18 3570.5 74.1 11.1 304.0 55.2 225.0 5.21 95.3 1.5 1.53 112.0 508 J-17 3574.2 83.7 9.0 223.0 68.5 29.1 7.82 22.0 8.2 3.88 28.5 204 J-16 3576.6 88.7 10.2 293.0 70.0 28.2 7.66 25.7 5.2 2.78 31.0 281 J-15 3595.4 91.8 6.8 429.0 62.1 20.4 5.21 17.8 52.3 7.04 21.9 199 J-14 3603.1 51.1 5.7 683.0 65.3 146.0 6.34 57.8 13.5 3.68 51.5 324 J-13 3613.7 129.0 12.6 159.0 87.9 35.4 9.76 35.3 3.3 1.44 29.2 252 平均值 131.6 11.9 276.3 80.4 116.5 9.90 64.0 9.1 3.40 52.1 326 下段 J-12 3624.3 112.0 7.4 604.0 67.2 22.2 6.80 19.2 21.7 3.79 31.9 288 J-11 3629.2 106.0 7.3 433.0 40.4 26.9 7.29 19.0 3.6 1.52 8.3 377 J-10 3664.3 98.1 8.6 506.0 86.2 21.7 5.82 15.2 7.8 2.72 24.5 292 J-09 3679.5 136.0 7.2 343.0 63.0 22.7 4.46 12.7 2.8 1.47 15.7 218 J-08 3681.6 118.0 11.4 523.0 87.9 32.8 6.20 19.4 3.0 2.29 15.5 234 J-07 3684.5 89.9 6.7 710.0 91.3 20.5 4.84 15.8 2.1 1.08 16.3 250 J-06 3685.5 82.5 9.5 579.0 91.2 23.5 8.63 30.6 10.5 2.43 43.0 459 J-05 3695.3 112.0 9.6 771.0 130.1 38.9 11.01 31.1 18.0 6.00 38.1 426 J-04 3696.9 172.0 8.7 614.0 83.3 27.5 9.46 24.9 2.1 2.29 18.9 269 J-03 3699.9 128.0 10.0 489.0 113.0 37.6 7.16 25.9 2.9 1.39 50.3 377 J-02 3701.3 55.2 5.7 832.0 93.9 163.0 10.50 109.0 11.7 2.84 103.0 327 J-01 3708.3 103.0 5.2 885.0 95.5 19.6 5.48 17.0 4.6 1.14 22.1 202 平均值 109.4 8.1 607.4 86.9 38.1 7.30 28.3 7.6 2.40 32.3 310 平均值 121.3 10.1 429.1 83.4 80.3 8.70 47.5 8.4 2.90 43.0 319 上地壳(UCC) — 16.0 325.0 131.0 119.0 25.00 51.0 5.6 1.40 24.0 390 表 3 J10025井芦草沟组古气候与古盐度指标
Table 3. Paleo-climate and paleo-salinity proxies of the Lucaogou Formation in Well J10025
层位 古气候指标 古盐度指标 Sr/Cu C值 CIA Sr/Ba B/Ga GI 上段 $\frac{1.91 \sim 19.59}{6.83}$ $\frac{0.11 \sim 1.14}{0.54}$ $\frac{44 \sim 79}{58}$ $\frac{0.26 \sim 2.16}{0.96}$ $\frac{4.35 \sim 26.89}{11.32}$ $\frac{0.10 \sim 0.24}{0.19}$ 下段 $\frac{8.08 \sim 52.23}{26.25}$ $\frac{0.07 \sim 0.21}{0.13}$ $\frac{46 \sim 52}{49}$ $\frac{1.15 \sim 4.38}{2.10}$ $\frac{8.72 \sim 19.85}{13.85}$ $\frac{0.20 \sim 0.26}{0.23}$ 芦草沟组 $\frac{1.91 \sim 52.23}{15.79}$ $\frac{0.07 \sim 1.14}{0.35}$ $\frac{44 \sim 79}{54}$ $\frac{0.26 \sim 4.38}{1.49}$ $\frac{4.35 \sim 26.89}{12.49}$ $\frac{0.10 \sim 0.26}{0.21}$ 注:$\frac{{ 最小值 \sim 最大值 }}{\text { 平均值 }}$ 表 4 J10025井芦草沟组氧化还原条件指标
Table 4. Paleo-redox proxies of the Lucaogou Formation in Well J10025
层位 氧化还原指标 V/Cr V/(V+Ni) Pr/Ph β-胡萝卜烷指数 上段 $\frac{0.18 \sim 3.27}{1.85}$ $\frac{0.29 \sim 0.88}{0.62}$ $\frac{0.47 \sim 1.50}{1.00}$ $\frac{1.19 \sim 66.47}{21.84}$ 下段 $\frac{0.54 \sim 4.87}{3.09}$ $\frac{0.46 \sim 0.85}{0.77}$ $\frac{0.19 \sim 1.14}{0.64}$ $\frac{2.86 \sim 34.69}{10.01}$ 芦草
沟组$\frac{0.18 \sim 4.87}{2.42}$ $\frac{0.29 \sim 0.88}{0.69}$ $\frac{0.19 \sim 1.50}{0.82}$ $\frac{1.19 \sim 66.47}{15.93}$ 注:$\frac{{ 最小值 \sim 最大值 }}{\text { 平均值 }}$ 表 5 Co元素计算J10025井芦草沟组古水深参数
Table 5. Paleo-water depth parameters of the Lucaogou Formation by Co calculation
层位 样品 深度/m SCo/(μg/g) SLa/(μg/g) t Vs/(mm/a) h/m 上段 J-26 3499.5 10.40 13.90 0.36 0.46 31.11 J-25 3506.8 4.61 20.30 0.52 1.84 3.86 J-24 3515.0 12.20 31.60 0.81 0.48 29.39 J-23 3523.7 13.20 22.90 0.59 0.38 40.73 J-22 3526.1 16.70 26.60 0.68 0.30 59.85 J-21 3530.8 15.90 16.40 0.42 0.29 62.69 J-20 3547.8 12.70 31.40 0.81 0.45 32.18 J-19 3569.2 10.60 19.50 0.50 0.48 28.62 J-18 3570.5 5.21 17.90 0.46 1.31 6.46 J-17 3574.2 7.82 13.80 0.35 0.65 18.45 J-16 3576.6 7.66 17.00 0.44 0.71 16.06 J-15 3595.4 5.21 26.90 0.69 2.02 3.36 J-14 3603.1 6.34 14.90 0.38 0.88 11.71 J-13 3613.7 9.76 17.90 0.46 0.53 25.32 下段 J-12 3624.3 6.80 22.80 0.58 0.98 9.87 J-11 3629.2 7.29 17.00 0.44 0.76 14.50 J-10 3664.3 5.82 18.60 0.48 1.12 8.19 J-09 3679.5 4.46 12.40 0.32 1.35 6.18 J-08 3681.6 6.20 19.30 0.49 1.03 9.23 J-07 3684.5 4.84 10.60 0.27 1.12 8.12 J-06 3685.5 8.63 37.70 0.97 0.97 10.03 J-05 3695.3 11.01 10.55 0.27 0.41 36.67 J-04 3696.9 9.46 17.10 0.44 0.54 24.31 J-03 3699.9 7.16 21.00 0.54 0.86 12.05 J-02 3701.3 10.50 18.40 0.47 0.48 28.78 J-01 3708.3 5.48 16.00 0.41 1.12 8.10 表 6 J10025井芦草沟组古水深、古生产力与碎屑输入指标
Table 6. Paleo-water depth, paleo-productivity and detrital input proxies of the Lucaogou Formation in Well J10025
层位 古水深/m 古生产力 碎屑输入 Mn/Fe分析 Co分析 TOC含量/% P含量/% P/Ti Al2O3/TiO2 上段 $\frac{0.01 \sim 0.04}{0.03}$ $\frac{3.36 \sim 62.69}{26.41}$ $\frac{1.81 \sim 19.60}{8.90}$ $\frac{0.01 \sim 0.20}{0.08}$ $\frac{0.05 \sim 1.05}{0.38}$ $\frac{19 \sim 29}{24}$ 下段 $\frac{0.03 \sim 0.05}{0.04}$ $\frac{6.18 \sim 36.67}{14.67}$ $\frac{1.95 \sim 7.87}{3.99}$ $\frac{0.02 \sim 0.07}{0.04}$ $\frac{0.09 \sim 0.37}{0.24}$ $\frac{19 \sim 26}{22}$ 芦草沟组 $\frac{0.01 \sim 0.05}{0.03}$ $\frac{3.36 \sim 62.69}{20.99}$ $\frac{1.81 \sim 19.60}{6.63}$ $\frac{0.01 \sim 0.20}{0.06}$ $\frac{0.05 \sim 1.05}{0.31}$ $\frac{19 \sim 29}{23}$ 注:$\frac{{ 最小值 \sim 最大值 }}{\text { 平均值 }}$ -
ALGEO T J, KUWAHARA K, SANO H, et al., 2011. Spatial variation in sediment fluxes, redox conditions, and productivity in the Permian-Triassic Panthalassic Ocean[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 308(1-2): 65-83. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.07.007 ALGEO T J, LIU J S, 2020. A re-assessment of elemental proxies for paleoredox analysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 540: 119549. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119549 BOYNTON W V, 1984. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 2: 63-114. CHENG L M, LI Y F, LU M, et al. 2022. Identification method of shale deformation structure based on whole core CT scanning: a case study of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang oil & Gas, 18(3): 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) ESKENAZY G M, 1987. Rare earth elements in a sampled coal from the Pirin deposit, Bulgaria[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 7(3): 301-314. doi: 10.1016/0166-5162(87)90041-3 FANG S H, XU H M, SONG Y, et al., 2005. Characteristics and evolution of the composite petroleum system in Jimsar depression, eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 26(3): 259-264. (in Chinese with English abstract) FENG W P, WANG F Y, WANG Z X, et al., 2020. Characteristics and origin of crude oils in the Wulanhua sag[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(6): 932-940. (in Chinese with English abstract) GE H K, CHEN Y K, TENG W W, et al., 2021. Micro-Mechanism of Production and Method of Enhanced Oil Recovery for Jimsar Shale Oil[J]. Xinjiang oil & Gas, 17(3): 84-90 (in Chinese with English abstract). GUO X G, HE W J, YANG S, et al., 2019. Evaluation and application of key technologies of "Sweet Area" of shale oil in Junggar Basin: case study of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 30(8): 1168-1179. (in Chinese with English abstract) HATCH J R, LEVENTHAL J S, 1992. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U.S.A. [J]. Chemical Geology, 99(1-3): 65-82. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(92)90031-Y HU J J, MA Y S, WANG Z X, et al., 2017. Palaeoenvironment and palaeoclimate of the middle to late Jurassic revealed by geochemical records in northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 19(3): 480-490. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIA C Z, 2017. Breakthrough and significance of unconventional oil and gas to classical petroleum geological theory[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(1): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30002-2 JIANG Y H, HOU D J, LI H, et al., 2020. Impact of the paleoclimate, paleoenvironment, and algae bloom: organic matter accumulation in the lacustrine Lucaogou Formation of Jimsar Sag, Junggar basin, NW China[J]. Energies, 13(6): 1488. doi: 10.3390/en13061488 JIANG Z F, DING X J, WANG Z Q, et al., 2020. Sedimentary paleoenvironment of source rocks of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 32(6): 109-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIANG Z X, ZHANG W Z, LIANG C, et al., 2014. Characteristics and evaluation elements of shale oil reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 35(1): 184-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIN Z J, ZHU R K, LIANG X P, et al., 2021. Several issues worthy of attention in current lacustrine shale oil exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(6): 1276-1287. (in Chinese with English abstract) JONES B, MANNING D A C, 1994. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 111(1-4): 111-129. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X KUANG L C, TANG Y, LEI D W, et al., 2012. Formation conditions and exploration potential of tight oil in the Permian saline lacustrine dolomitic rock, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(6): 657-667. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIAO K X, WANG M A, PENG H, et al. 2021. Analysis of Factors Affecting the Dehydration Effect of Shale Gas Triethylene Glycol Dehydration Unit[J]Journal of Liaoning Petrochemical University, 41(5): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIN X H, ZHAN Z W, ZOU Y R, et al., 2019. Elemental geochemical characteristics of the Lucaogou Formation oil shale in the southeastern Junggar Basin and its depositional environmental implications[J]. Geochimica, 48(1): 67-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU H, CAO G, 2022. Opportunities and challenges for scientific and technological innovation and development of oil and gas production engineering in the new era[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 44(5): 529-539. DOI: 10.13639/j.odpt.2022.05.001.(in Chinese with English abstract) LIU D D, FAN Q Q, ZHANG C, et al., 2022. Paleoenvironment evolution of the Permian Lucaogou Formation in the southern Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 603: 111198. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111198 LUO J C, TIAN J J, MA J H, et al., 2022. Sedimentary environment and organic matter enrichment mechanism of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jiye-1 well area, Jimsar Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 34(5): 73-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA W L, JIANG X Q, LI X, et al., 2021. Geochemical characteristics and paleoenvironment paleoclimate significance of mudstone in the Shang-Gan-Chai-Gou Formation at the northwestern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 40(5): 1166-1180. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA Z L, TAN J Q, ZHAO H, et al., 2020. Organic geochemistry and geological significance of oil seepage from the Devonian of Luquan area, Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(6): 952-960. (in Chinese with English abstract) MCLENNAN S M, 1993. 100th Anniversary symposium: evolution of the earth's surface ‖ weathering and global denudation[J]. Journal of Geology, 101(2): 295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222 MCLENNAN S M, 2001. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2(4): 2000GC000109. MORADI A V, SARI A, AKKAYA P, 2016. Geochemistry of the Miocene oil shale (Hançili Formation) in the Çankırı-Çorum Basin, Central Turkey: Implications for Paleoclimate conditions, source-area weathering, provenance and tectonic setting[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 341: 289-303. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.05.002 MUKHOPADHYAY P K, GORMLY J R, 1984. Hydrocarbon potential of two types of resinite[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 6: 439-454. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(84)90067-6 PAN Y S, HUANG Z L, LI T J, et al., 2020. Environmental response to volcanic activity and its effect on organic matter enrichment in the Permian Lucaogou Formation of the Malang Sag, Santanghu Basin, Northwest China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 560: 110024. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.110024 PENG X F, WANG L J, JIANG L P, 2012. Geochemical characteristics of the Lucaogou Formation oil shale in the southeastern margin of the Junggar Basin and its environmental implications[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 31(2): 121-127, 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) PETERS K E, WALTERS C C, MOLDOWAN J M, 2005. The biomarker guide[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. QU C S, QIU L W, YANG Y Q, et al., 2017. Carbon and oxygen isotope compositions of carbonatic rock from Permian Lucaogou Formation in the Jimsar Sag, NW China and their paleolimnological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(3): 605-616. (in Chinese with English abstract) REN X C, XIU J L, LIU L, et al., 2023. Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic structural style, deformation sequence, and formation process and mechanism of the checkboard structure in the eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 29(2): 155-173. (in Chinese with English abstract) ROHLING E J, 2000. Paleosalinity: confidence limits and future applications[J]. Marine Geology, 163(1-4): 1-11. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00097-3 SCHOELL M, HWANG R J, CARLSON R M K, et al., 1994. Carbon isotopic composition of individual biomarkers in gilsonites (Utah)[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 21(6-7): 673-683. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(94)90012-4 SHI H, LI Z X, YANG Y Y, et al., 2022. The factors influencing the enrichment of organic matters in the Carboniferous source rocks, Ounan depression, eastern Qaidam basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(2): 203-216. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHI Z S, CHEN K Y, SHI J, et al., 2003. Feasibility analysis of the application of the ratio of strontium to barium on the identifying sedimentary environment[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 10(2): 12-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) SI C S, CHEN N G, YU C F, et al., 2013. Sedimentary characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 35(5): 528-533. (in Chinese with English abstract) SU Y, ZHA M, DING X J, et al., 2019. Petrographic, palynologic and geochemical characteristics of source rocks of the Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China: origin of organic matter input and depositional environments[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 183: 106364. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106364 TANG Y, ZHENG M L, WANG X T, et al., 2022. Sedimentary paleoenvironment of source rocks of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 33(5): 677-692. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAO S, TANG D Z, ZHOU C Y, et al., 2009. Element Geochemical Characteristics of the Lower Assemblage Hydrocarbon Source Rocks in Southeast Sichuan-Central Guizhou (Chuandongnan-Qianzhong) Region and Its Periphery Areas and Their Implications to Sedimentary Environments[J]. Geology in China, 36(2): 397-403. (in Chinese with English abstract) TRIBOVILLARD N, ALGEO T J, LYONS T, et al., 2006. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update[J]. Chemical Geology, 232(1-2): 12-32. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012 WANG F, LIU X C, DENG X Q, et al., 2017. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of trace elements of Zhifang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 35(6): 1265-1273. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG H, MA S Z, NIU D L, et al., 2022. Elemental geochemical characteristics of fine grained sedimentary rocks of the Lucaogou Formation in the western Jimusar Sag of the Junggar Basin and their paleo-environmental significances[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 41(1): 143-150. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Z W, FU X G, FENG X L, et al., 2017. Geochemical features of the black shales from the Wuyu Basin, southern Tibet: implications for palaeoenvironment and palaeoclimate[J]. Geological Journal, 52(2): 282-297. doi: 10.1002/gj.2756 WEI W, ALGEO T J, 2020. Elemental proxies for paleosalinity analysis of ancient shales and mudrocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 287: 341-366. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2019.06.034 WU H G, HU W X, CAO J, et al., 2016. A unique lacustrine mixed dolomitic-clastic sequence for tight oil reservoir within the middle Permian Lucaogou Formation of the Junggar Basin, NW China: reservoir characteristics and origin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 76: 115-132. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.05.007 WU X Z, HE D F, YANG D S, et al., 2012. Structural character and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Luliang uplift, Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 47(1): 73-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2012.01.007 WU Z P, ZHOU Y Q, 2000. Using the characteristic elements from meteoritic must in strata to calculate sedimentation rate[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 18(3): 395-399. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2000.03.012 XIE W Q, TAN J Q, WANG W H, et al., 2021. Middle Jurassic lacustrine source rocks controlled by an aridification event: a case study in the northern Qaidam Basin (NW China)[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 242: 103779. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2021.103779 XU Y B, SUN P C, LI Z, et al., 2022. The geochemical characteristics and metallogenic condition of Permian Lucaogou Formation oil shale in Jimsar, Junggar Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Geology in China, 49(1): 311-323. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J C, LIN L M, LI Y X, et al., 2012. Classification and evaluation of shale oil[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(5): 322-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG S, LIU Y Q, JIAO X, et al., 2018. Sedimentary environment and Formation mechanisim of dolomitic rocks in the middle Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimusar Depression, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 20(1): 33-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG W W, HAN C C, TIAN J J, et al., 2021. Sequence stratigraphy division and evolutionary features of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 33(5): 45-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG X, ZHUANG X G, TU Q J, et al., 2018. Depositional process and mechanism of organic matter accumulation of Lucaogou Shale in Southern Junggar Basin, Northwest China[J]. Earth Science, 43(2): 538-550. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y S, YANG Y Q, QI Z X, et al., 2003. Sedimentary characteristics and environments of the salt-bearing series of Qianjiang Formation of the Paleogene in Qianjiang Sag of Jianghan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 5(1): 29-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2003.01.003 ZHANG Y Y, HE Z L, JIANG S, et al., 2017. Marine redox stratification during the early Cambrian (ca. 529~509 Ma) and its control on the development of organic-rich shales in Yangtze Platform[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 18(6): 2354-2369. doi: 10.1002/2017GC006864 ZHAO D F, GUO Y H, WANG G, et al., 2023. Organic matter enrichment mechanism of Youganwo Formation oil shale in the Maoming Basin[J]. Heliyon, 9(2): e13173. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13173 ZHAO W Z, HU S Y, HOU L H, et al., 2020. Types and resource potential of continental shale oil in China and its boundary with tight oil[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60001-5 ZHI D M, SONG Y, HE W J, et al., 2019. Geological characteristics, resource potential and exploration direction of shale oil in middle-lower Permian, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 40(4): 389-401. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHONG H L, PU R H, YAN H, et al., 2012. Analysis on paleosalinity and paleoenvironment of late Paleozoic in Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 42(1): 74-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU C N, YANG Z, CUI J W, 2013. Formation mechanism, geological characteristics and development strategy of Nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(1): 14-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU C N, PAN S Q, JING Z H, et al., 2020. Shale oil and gas revolution and its impact[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 41(1): 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0299-4 程垒明, 李一凡, 吕明, 等, 2022. 基于全直径岩心CT扫描的页岩变形构造识别方法: 以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 18(3): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY202203004.htm 方世虎, 徐怀民, 宋岩, 等, 2005. 准噶尔盆地东部吉木萨尔凹陷复合含油气系统特征及其演化[J]. 地球学报, 26(3): 259-264. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2005.03.011 冯伟平, 王飞宇, 王宗秀, 等, 2020. 乌兰花凹陷原油特征及成因[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(6): 932-940. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.06.074 葛洪魁, 陈玉琨, 滕卫卫, 等, 2021. 吉木萨尔页岩油微观产出机理与提高采收率方法探讨[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 17(3): 84-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY202103015.htm 郭旭光, 何文军, 杨森, 等, 2019. 准噶尔盆地页岩油"甜点区"评价与关键技术应用: 以吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 30(8): 1168-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201908010.htm 胡俊杰, 马寅生, 王宗秀, 等, 2017. 地球化学记录揭示的柴达木盆地北缘地区中—晚侏罗世古环境与古气候[J]. 古地理学报, 19(3): 480-490. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201703008.htm 贾承造, 2017. 论非常规油气对经典石油天然气地质学理论的突破及意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 44(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701002.htm 姜在兴, 张文昭, 梁超, 等, 2014. 页岩油储层基本特征及评价要素[J]. 石油学报, 35(1): 184-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201401027.htm 蒋中发, 丁修建, 王忠泉, 等, 2020. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组烃源岩沉积古环境[J]. 岩性油气藏, 32(6): 109-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202006010.htm 金之钧, 朱如凯, 梁新平, 等, 2021. 当前陆相页岩油勘探开发值得关注的几个问题[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 48(6): 1276-1287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202106021.htm 匡立春, 唐勇, 雷德文, 等, 2012. 准噶尔盆地二叠系咸化湖相云质岩致密油形成条件与勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 39(6): 657-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206004.htm 廖柯熹, 王敏安, 彭浩, 等. 页岩气三甘醇脱水装置脱水效果影响因素分析[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSSX202105001.htm 林晓慧, 詹兆文, 邹艳荣, 等, 2019. 准噶尔盆地东南缘芦草沟组油页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境意义[J]. 地球化学, 48(1): 67-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201901006.htm 刘合, 曹刚. 新时期采油采气工程科技创新发展的挑战与机遇[J]. 2022, 石油钻采工艺, 44(5): 529-539. DOI: 10.13639/j.odpt.2022.05.001. 罗锦昌, 田继军, 马静辉, 等, 2022. 吉木萨尔凹陷吉页1井区二叠系芦草沟组沉积环境及有机质富集机理[J]. 岩性油气藏, 34(5): 73-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202205006.htm 马万里, 江小青, 李璇, 等, 2021. 柴达木盆地西北缘上干柴沟组泥岩地球化学特征与古环境古气候意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 40(5): 1166-1180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202105019.htm 马中良, 谭静强, 赵晗, 等, 2020. 云南禄劝地区泥盆系油苗地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(6): 952-960. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.06.076 彭雪峰, 汪立今, 姜丽萍, 2012. 准噶尔盆地东南缘芦草沟组油页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境指示意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 31(2): 121-127, 151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201202004.htm 曲长胜, 邱隆伟, 杨勇强, 等, 2017. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素特征及其古湖泊学意义[J]. 地质学报, 91(3): 605-616. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201703008.htm 任新成, 修金磊, 刘林, 等, 2023. 准噶尔东部晚古生代—中生代构造样式、变形序列及棋盘格构造的形成过程与机制[J]. 地质力学学报, 29(2): 155-173. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2022113 施辉, 李宗星, 杨元元, 等, 2022. 柴东欧南凹陷石炭系烃源岩有机质富集的影响因素[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(2): 203-216. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021135 史忠生, 陈开远, 史军, 等, 2003. 运用锶钡比判定沉积环境的可行性分析[J]. 断块油气田, 10(2): 12-16. 斯春松, 陈能贵, 余朝丰, 等, 2013. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储层沉积特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 35(5): 528-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201305011.htm 唐勇, 郑孟林, 王霞田, 等, 2022. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组烃源岩沉积古环境[J]. 天然气地球科学, 33(5): 677-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202205001.htm 陶树, 汤达祯, 周传祎, 等, 2009. 川东南-黔中及其周边地区下组合烃源岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境意义[J]. 中国地质, 36(2): 397-403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200902014.htm 王峰, 刘玄春, 邓秀芹, 等, 2017. 鄂尔多斯盆地纸坊组微量元素地球化学特征及沉积环境指示意义[J]. 沉积学报, 35(6): 1265-1273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706017.htm 王欢, 马世忠, 牛东亮, 等, 2022. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷西区芦草沟组细粒岩元素地球化学特征及古环境意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 41(1): 143-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202201010.htm 吴晓智, 何登发, 杨迪生, 等, 2012. 准噶尔盆地陆梁隆起构造特征与油气成藏[J]. 地质科学, 47(1): 73-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201201008.htm 吴智平, 周瑶琪, 2000. 一种计算沉积速率的新方法: 宇宙尘埃特征元素法[J]. 沉积学报, 18(3): 395-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200003011.htm 徐银波, 孙平昌, 李昭, 等, 2022. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔地区二叠系芦草沟组油页岩地球化学特征与成矿条件[J]. 中国地质, 49(1): 311-323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202201020.htm 张金川, 林腊梅, 李玉喜, 等, 2012. 页岩油分类与评价[J]. 地学前缘, 19(5): 322-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205032.htm 张帅, 柳益群, 焦鑫, 等, 2018. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷中二叠统芦草沟组云质岩沉积环境及白云石成因探讨[J]. 古地理学报, 20(1): 33-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201801003.htm 张文文, 韩长城, 田继军, 等, 2021. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组层序地层划分及演化特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 33(5): 45-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202105005.htm 张逊, 庄新国, 涂其军, 等, 2018. 准噶尔盆地南缘芦草沟组页岩的沉积过程及有机质富集机理[J]. 地球科学, 43(2): 538-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201802015.htm 张永生, 杨玉卿, 漆智先, 等, 2003. 江汉盆地潜江凹陷古近系潜江组含盐岩系沉积特征与沉积环境[J]. 古地理学报, 5(1): 29-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200301002.htm 赵文智, 胡素云, 侯连华, 等, 2020. 中国陆相页岩油类型、资源潜力及与致密油的边界[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 47(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202001002.htm 支东明, 宋永, 何文军, 等, 2019. 准噶尔盆地中—下二叠统页岩油地质特征、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 40(4): 389-401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201904002.htm 钟红利, 蒲仁海, 闫华, 等, 2012. 塔里木盆地晚古生代古盐度与古环境探讨[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 42(1): 74-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201201017.htm 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等, 2013. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 40(1): 14-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201301003.htm 邹才能, 潘松圻, 荆振华, 等, 2020. 页岩油气革命及影响[J]. 石油学报, 41(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202001001.htm -





 下载:
下载: