Mechanism of rockfall coupled with endogenic and exogenic geological processes: A case study in the upper Triassic limestone mines in the Qamdo area, eastern Tibet
-
摘要:
石灰石矿山采场崩塌是藏东昌都地区常见的地质灾害类型, 是矿山企业安全生产和铁路工程建设面临的主要地质安全问题之一。文章采用基础地质、构造地质和灾害地质相结合的方法, 通过详实的地质灾害调查, 查明崩塌发育规律, 分析岩体结构面特征, 探讨崩塌灾害的形成机理, 并建立其破坏模式。结果表明: 藏东昌都地区上三叠统石灰石矿山采场崩塌沿区内褶冲带呈线状展布; 岩体内发育纵张节理(S1)、横张节理(S2)、"X"型共轭剪节理(S3、S4)及层间剪节理(S5)共5组与区域褶皱和对冲系断裂配套的陡倾构造结构面, 将岩体切割为破碎的块体; 研究区崩塌地质灾害是内、外动力地质作用耦合的产物。晚三叠世(T3)早期, 昌都地区陆内裂谷盆地环境沉积形成的上三叠统波里拉组(T3b)灰岩是崩塌发育的沉积建造基础; 新生代(Cz)印度-欧亚大陆碰撞引发的强烈褶皱造山运动奠定了区内构造格架, 是崩塌发育的必要条件; 第四纪(Q)以来的强烈新构造运动和晚更新世(Q3)以来的湿-热气候频繁交替、充沛降雨、现代人类活动等做为内和外动力的耦合作用是崩塌灾害的主要诱发因素。研究区内崩塌灾害存在倾倒式、坠落式和滑移式3种破坏模式。研究成果对岩溶区崩塌灾害防治与相关铁路建设具有一定指导意义。
Abstract:Rockfall in limestone mines is a common geohazard in the Changdu area of eastern Tibet and one of the leading geo-safety issues that mining enterprises and railway projects are faced with. We carried out a detailed geohazard survey using the methods of general geology, structural geology, and geohazard geology. We found the rockfall development pattern, characterized rock mass structural planes, discussed the collapse's mechanism, and established its failure mode. The results show that rockfall sites in the study area show a linear spreading along the fold and thrust zone. Five groups of steep-dip structural planes have developed in the rock body, including the longitudinal joint (S1), the transverse joint (S2), the X-type conjugate shear joints (S3 and S4), and the interlayer shear joint (S5). Paired with regional folds and hedging faults, these structural planes cut the rock mass into broken blocks. The collapses are the product of coupled internal and external dynamic geological processes. The sedimentary foundation of the rockfalls in the Qamdo area is the limestone from the upper Triassic Bolila Formation (T3b) formed in the intracontinental rift basin. The strongly folded orogeny triggered by the Cenozoic (Cz) India-Eurasia collision laid down the tectonic framework in the region, which is the essential condition for rockfall development. The strong Neotectonic movement since the Quaternary (Q), frequent hot and humid climate alternations with abundant rainfall since the Late Pleistocene (Q3), everyday human activities, and other internal and external dynamic coupling effects are the main triggering factors of the rockfall disaster. Three failure modes of rockfall are identified, namely toppling, falling, and sliding. The research results have specific guiding significance for rockfall prevention and control in the karst area and the railway construction in the Sichuan-Tibet area.
-
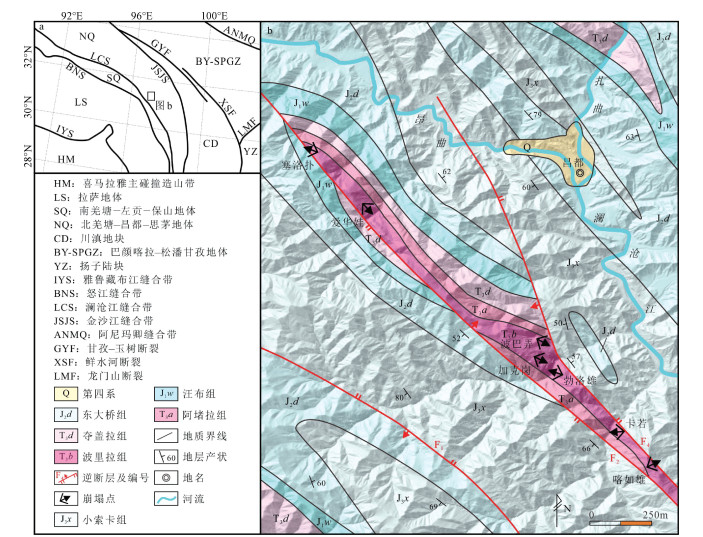
图 1 昌都地区大地构造位置图与区域地质简图
a—昌都地区大地构造位置图(许志琴等,2013);b—区域地质简图
Figure 1. Geotectonic map of the Qamdo area and regional geological sketchmap
(a) Geotectonic map of the Qamdo area (Xu et al., 2013); (b) Regional geological sketchmap
图 3 危岩带地层中的F4断层角砾岩特征
a—F4断层破碎带全景;b—断层角砾岩破碎特征;c—断层角砾岩,由灰岩角砾和钙质胶结物组成;d、e—断层角砾被后期延伸无规律的张性裂隙切割,裂隙内充填未固结的紫红色泥质条带
Figure 3. Photos of the F4 fault breccia in the unstable rock zone
(a) Panorama of the F4 fault fracture zone; (b) Fregmented fault breccia; (c) Fault breccia composed of limestone breccia and calcareous cement; (d and e) The fault breccia is cut by the later irregular extensional fracture, and the fracture is filled with unconsolidated purplish red argillaceous strip
图 4 灰岩中的溶蚀和淋滤沉积现象
a—灰岩层理面溶蚀形成的瘤状起伏面,表面附着泥质薄膜;b—灰岩裂隙面溶蚀发育的溶沟和石芽;c—横张裂隙内发育的葡萄状钟乳石;d—灰岩淋滤沉积形成的皮壳状钟乳石,内部包裹灰岩角砾核心
Figure 4. Dissolution and leaching deposition in limestone
(a) Nodular undulating surface formed by dissolution of limestone bedding, with argillaceous film attached on the surface; (b) Karst groove and stone bud developed by dissolution of limestone fracture surface; (c) Grape-shaped stalactites developed in transverse fractures; (d) Crust-like stalactites formed by eluviation and sedimentation of limestone, with limestone breccia cores wrapped inside
图 5 岩体结构面特征分析图
S0—原生层理面;S1—纵张节理;S2—横张节理;S3、S4—共轭剪节理;S5—层间剪节理
a—岩体结构面极点图;b—岩体结构面等密度图Figure 5. Characterization plots of the rock mass structural planes
(a) Pole plot of the rock mass structural plane; (b) Contour plot of the rock mass structural plane
S0-Primary bedding plane; S1-Longitudinal joints; S2-Transverse joints; S3 and S4-Conjugate shear joints; S5-Interlayered shear joints图 6 岩体结构面发育特征
a—切割原生层理面(S0)的纵张节理(S1)、横张节理(S2);b—“X”型共轭剪节理(S3、S4);c—背斜南西翼发育的层间剪节理(S5)切割原生层理面(S0)形成缓倾的“Z”型剪切变形;d—纵张节理(S1)与“X”型共轭剪节理(S3、S4)大角度相交,节理内充填网状方解石脉
Figure 6. Photos showing the characteristics of the rock mass structural planes
(a)The longitudinal joint (S1) and the transverse joint (S2) cuts the primary bedding plane (S0); (b) The "X"-type conjugate shear joints (S3 and S4) filled with calcite vein; (c) The interlayered shear joint (S5) developed in the southwest flank of the anticline cuts the primary bedding plane (S0) to form a gentle "Z"-type shear deformation; (d) The longitudinal joint (S1) intersects with the "X"-type conjugate shear joints (S3 and S4) at a large angle, and the joints are filled with reticulate calcite vein
图 9 卡若石灰石矿山采场崩塌形成过程示意图
图件侧重于表达崩塌形成过程,并未按实际厚度比例绘制各地层;同一类型结构面线条厚度的不同表示裂隙宽度的变化
a—崩塌地层沉积建造形成阶段;b—岩体构造破碎阶段早期,区域挤压环境形成褶皱系及相关结构面;c—岩体构造破碎阶段晚期,挤压应力持续,叠加构造体制转换,形成区内断裂系同时,促进了结构面的拓宽、改造与贯通,加剧了岩体结构的破坏;d—崩塌形成阶段Figure 9. Schematic diagram of the rockfall formation process in the Caro limestone mine
(a) Stratum formation process of rockfall; (b) A fold system and associated structural planes developed under regional extrusion stress in the early fracture stage of the rock mass; (c) The extrusion stress continues and the tectonic regime shifts in the late fracture stage, forming a fault stytem within the area, which widens, transforms, and connects the structural planes, accelerating the destruction of the rock structure
The schematic diagram focuses on the rockfall formation process, so the strata are not drawn in proportion to the actual thickness. The difference in line thickness of the same structural plane represents the variation of crack width表 1 结构面产状信息及其统计表/(°)
Table 1. Occurrence information and statistics of the structural plane/(°)
序号 纵张节理S1 横张节理S2 “X”型节理S3 “X”型节理S4 层间剪节理S5 1 22∠74 315∠88 280∠66 175∠82 47∠51 2 32∠85 109∠88 283∠48 169∠74 68∠42 3 25∠78 278∠83 323∠57 158∠87 49∠61 4 47∠77 280∠84 322∠53 166∠72 47∠88 5 42∠75 316∠90 303∠76 164∠77 46∠76 6 32∠77 122∠88 291∠64 157∠82 50∠54 7 39∠75 284∠87 304∠69 165∠73 64∠85 8 23∠87 283∠85 317∠74 156∠52 9 45∠80 282∠82 297∠77 177∠72 10 32∠71 316∠84 319∠51 179∠71 11 27∠79 303∠51 160∠79 12 44∠84 309∠76 175∠62 13 309∠68 175∠52 14 297∠70 164∠75 15 325∠67 170∠84 16 310∠55 178∠88 17 325∠77 155∠74 18 286∠78 166∠55 19 327∠59 151∠63 -
AN Z S, KUTZBACH J E, PRELL W L, et al., 2001. Evolution of Asian monsoons and phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan plateau since Late Miocene times[J]. Nature, 411(6833): 62-66. doi: 10.1038/35075035 BECK R A, BURBANK D W, SERCOMBE W J, et al., 1996. Late Cretaceous ophiolite obduction and Paleocene India-Asia collision in the westernmost Himalaya[J]. Geodinamica Acta, 9(2-3): 114-144. doi: 10.1080/09853111.1996.11105281 CAO D Y, SONG S Y, MA Z K, et al., 2019. Tectonic background of the Qamdo Basin and its structural control on coal forming in the Late Triassic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(2): 169-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN F H, ZHANG J F, LIU J B, et al., 2020. Climate change, vegetation history, and landscape responses on the Tibetan Plateau during the Holocene: a comprehensive review[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 243: 106444. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106444 CHENG P X, LI Z F, 2019. Mechanism of geological hazards in the middle Permian collapse in the Wulingshan mountains of Guizhou province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 38(4): 565-572. (in Chinese with English abstract) DAI F C, TU X B, XU C, et al., 2011. Rock avalanches triggered by oblique-thrusting during the 12 May 2008 Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Geomorphology, 132(3-4): 300-318. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.05.016 DONALDSON D G, WEBB A A G, MENOLD C A, et al., 2013. Petrochronology of Himalayan ultrahigh-pressure eclogite[J]. Geology, 41(8): 835-838. doi: 10.1130/G33699.1 FAN J J, LI C, PENG H, et al., 2014. The discovery of Late Carboniferous-Early Permian oceanic island in the Lungmu Co-Shuanghu-Lancang River suture zone[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(11): 1690-1695. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.11.005 FAN X M, XU Q, SCARINGI G, et al., 2019. The "long" runout rock avalanche in Pusa, China, on August 28, 2017: a preliminary report[J]. Landslides, 16(2): 139-154. FENG Z, LI B, HE K, 2014. Rock collapse mechanism on high-steep slope failure in sub-horizontal thick-bedded mountains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 20(2): 123-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2014.02.003 HAN M M, 2019. Hazard assessment of large collapsed body in limestone area of reservoir area[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAO M, LI Y H, ZHUANG W Q, 2019. Crustal movement and strain distribution in East Asia revealed by GPS observations[J]. Scientific Reports, 9(1): 16797. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53306-y HAO P, LV X J, TIAN Q J, et al., 2012. Contemporary tectonic stress field on boundaries of active tectonic blocks in and around western China[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 34(4): 439-450. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2012.04.002 HARRISON T M, COPELAND P, KIDD W S F, et al., 1992. Raising Tibet[J]. Science, 255(5052): 1663-1670. doi: 10.1126/science.255.5052.1663 HU X L, TANG H M, ZHU L X, 2011. Collapse mode and mechanism of high magmatite rock slope in Wenchuan Epicentral Area[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 36(6): 1149-1154. HUANG Y, ZHANG W J, XU Q, et al., 2012. Run-out analysis of flow-like landslides triggered by the Ms 8.0 2008 Wenchuan earthquake using smoothed particle hydrodynamics[J]. Landslides, 9(2): 275-283. doi: 10.1007/s10346-011-0285-5 JIN Z K, SHI L, GAO B S, et al., 2013. Carbonate facies and facies models[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 31(6): 965-979. (in Chinese with English abstract) KOU L L, LI Z H, DONG X P, et al., 2021. The age sequence of the detrital zircons from the Guanyindian section in Longde, the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(6): 1051-1064. (in Chinese with English abstract) LEECH M L, SINGH S, JAIN A K, et al., 2005. The onset of India-Asia continental collision: early, steep subduction required by the timing of UHP metamorphism in the western Himalaya[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 234(1-2): 83-97. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.038 LI C, 2008. A review on 20 Years′ Study of the Longmu Co-Shuanghu-Lancang river suture zone in Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau[J]. Geological Review, 54(1): 105-119. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.01.012 LI C, XIE Y W, DONG Y S, et al., 2009. The North Lancangjiang suture: the boundary between Gondwana and Yangtze?[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(12): 1711-1719. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.004 LI H, JU N P, ZHENG D, et al., 2013. Mechnisim of rockfall with crock-toppling mode at upstream of Yangshui river basin in Guizhou province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 21(2): 289-296. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.02.015 LI H L, LI G M, LIU H, et al., 2019. Petrogenesis of Paleocene granite porphyry of Daruo area in western Lhasa Block, Tibet: constraints from geochemistry, zircon U-Pb chronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes[J]. Earth Science, 44(7): 2275-2297. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI H L, CHEN L, YANG D, et al., 2022a. Geological genesis of the Juexue red strata landslide in Qamdo, eastern Tibet[J/OL]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology. (2022-05-26). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1593.P.20220525.1537.001.html. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI H L, HUANG H, LI Y L, et al., 2022b. Geohazard effect of plate suture zone along Sichuan-Tibet railway[J/OL]. Earth Science. (2022-08-09). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220808.1704.044.html. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI H L, LI G M, ZHANG Z, et al., 2021. Genesis of Jienagepu gold deposit in Zhaxikang ore concentration area, Eastern Tethys Himalayas: Constraints from He-Ar and in-situ S isotope of pyrite[J]. Earth Science, 46(12): 4291-4315. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2021.12.dqkx202112006 LI X, LI S D, CHEN J, et al., 2008. Coupling effect mechanism of endogenic and exogenic geological processes of geological hazards evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 27(9): 1792-1806. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.09.006 LI X Z, DU D X, WANG Y Z, 1998. The basin range transition and mineralization: examples from the Qamdo Simao Basin and Jinshajiang Ailaoshan orogenic belt in southwestern China[J]. Tethyan Geology, 22(2): 5-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Y H, DU X X, LI T X, 2022. Characterization of the Holocene extensional structures in the Wuwei Basin, northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, and their formation mechanism[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(3): 353-366. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Y S, YI S J, JIANG L W, et al., 2016. Research on the stress deformation and engineering effect of the Lancangjiang fault in Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 33(5): 6-10, 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.05.002 LIN F, FENG L, SUN C, et al., 2015. Formation mechanism of rockfall controlled by intensively developed karst[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 23(3): 408-414. (in Chinese with English abstract) MO X X, ZHAO Z D, DENG J F, et al., 2003. Response of volcanism to the India-Asia collision[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3): 135-148. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.013 MO X X, ZHAO Z D, ZHOU S, et al., 2007. On the timing of India-Asia continental collision[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(10): 1240-1244. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.10.002 MOLNAR P, TAPPONNIER P, 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: effects of a continental collision: features of recent continental tectonics in Asia can be interpreted as results of the India-Eurasia collision[J]. Science, 189(4201): 419-426. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419 PAN G T, LU S N, XIAO Q H, et al., 2016. Division of tectonic stages and tectonic evolution in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(6): 1-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) PAN G T, REN F, YIN F G, et al., 2020. Key zones of Oceanic Plate geology and Sichuan-Tibet railway project[J]. Earth Science, 45(7): 2293-2304. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIN J X, HAN P, CHE X C, et al., 2014. Resuming the Holocene paleoclimate using δ18O and trace elements of travertine in Rongma area, Tibet[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(2): 312-322. (in Chinese with English abstract) QU W, GAO Y, CHEN H L, et al., 2021. Review on characteristics of present crustal tectonic movement and deformation in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China using GPS high precision monitoring data[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 43(1): 182-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) RAN T, WEN B P, SU C, et al., 2012. Analysis of the formation mechanism of the Zhaojiayan rock fall in Wufeng county, Hubei province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 39(6): 114-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) ROYDEN L H, BURCHFIEL B C, VAN DER HILST R D, 2008. The geological evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 321(5892): 1054-1058. doi: 10.1126/science.1155371 SYLVESTER P J, 1998. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites[J]. Lithos, 45(1-4): 29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3 TANG J X, ZHONG K H, LIU Z C, et al., 2006. Intracontinent orogen and metallogenesis in Himalayan epoch: Changdu Large Composite Basin, eastern Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(9): 1364-1376. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.09.012 TAPPONNIER P, ZHIQIN X, ROGER F, et al., 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 294(5547): 1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978 The First Branch of Tibet Institute of Geological Survey, 2007. 1∶250000 regional geological survey report of the Peo'le's Republic of China (Nangqian county, Qamdo County and Janda County) [R]. Lhasa: Tibet Institute of Geological Survey. (in Chinese) WANG Y P, 2016. Study on deformation and failure mechanism of rockfall hazards and monitoring and early warning[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Y Z, WANG E N, SHEN Z K, et al., 2008. GPS-constrained inversion of present-day slip rates along major faults of the Sichuan-Yunnan region, China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(9): 1267-1283. doi: 10.1007/s11430-008-0106-4 WEI J Q, WANG X D, ZHUANG X, et al., 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of diorite among Jicha serpentine and Eza grabbro from Lancangjiang belt, Yunnan province and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6): 1297-1301. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIAO R H, CHEN H Q, LENG Y Y, et al., 2018. Preliminary analysis on the failure process and mechanism of the August 28 collapse in Nayong County, Guizhou province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 29(1): 3-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE F R, ZHANG H Y, CUI X F, et al., 2011. The modern tectonic stress field and strong earthquakes in China[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology(1): 4-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0235-4975.2011.01.003 XU Q, LI W L, 2010. Distribution of large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 18(6): 818-826. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.002 XU Z Q, YANG J S, LI W C, et al., 2013. Paleo-Tethys system and accretionary orogen in the Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(6): 1847-1860. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Z Q, WANG Q, LI Z H, et al., 2016. Indo-Asian collision: tectonic transition from compression to strike slip[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(1): 1-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12639 XUE Y G, KONG F M, SONG Q, et al., 2020. Developmental characteristics and hazard effects of active fault zones along the Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 28(6): 1213-1245. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAN W Z, TAN F W, CHEN M, 2018. Sedimentary-tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon potential in the Qamdo Basin, eastern Xizang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 38(4): 85-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2018.04.009 ZHANG Y S, SHI J S, SUN P, et al., 2009. Coupling between endogenic and exogenic geological processes in the Wenchuan earthquake and example analysis of geo-hazards[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(2): 131-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.003 ZHANG Y S, BA R J, REN S S, et al., 2020. An analysis of geo-mechanism of the Baige landslide in Jinsha River, Tibet[J]. Geology in China, 47(6): 1637-1645. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU D C, WANG Q, CAWOOD P A, et al., 2017. Raising the Gangdese Mountains in southern Tibet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 122(1): 214-223. doi: 10.1002/2016JB013508 ZHU Z M, CUN J H, PANG L F, et al., 2007. Magnetic properties of lacustrine sediments and implications for Paleoclimate in Milin area, Tibet[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32(5): 622-628. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU Y X, DONG J H, LI H J, et al., 2019. Study on cause mechanism and stability of dolomitic Limestone Mountain collapse[J]. Journal of Chengdu University (Natural Science Edition), 38(3): 322-325. (in Chinese with English abstract) 曹代勇, 宋时雨, 马志凯, 等, 2019. 晚三叠世昌都盆地构造背景及对成煤作用的控制[J]. 地学前缘, 26(2): 169-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201902016.htm 程鹏翔, 李宗发, 2019. 贵州武陵山区中二叠统崩塌地质灾害形成机理研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 38(4): 565-572. 范建军, 李才, 彭虎, 等, 2014. 藏北龙木错—双湖—澜沧江板块缝合带发现晚石炭世—早二叠世洋岛型岩石组合[J]. 地质通报, 33(11): 1690-1695. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.11.005 冯振, 李滨, 贺凯, 2014. 近水平厚层高陡斜坡崩塌机制研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 20(2): 123-131. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/article/id/f1129705-db80-46cd-bb93-0310b1caba98 韩明明, 2019. 库区灰岩地区大型崩塌体危险性评价[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学. 郝平, 吕晓健, 田勤俭, 等, 2012. 中国西部及邻区活动地块边界带现代构造应力场[J]. 地震学报, 34(4): 439-450. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2012.04.002 胡新丽, 唐辉明, 朱丽霞, 2011. 汶川震中岩浆岩高边坡破坏模式与崩塌机理[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 36(6): 1149-1154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201106021.htm 金振奎, 石良, 高白水, 等, 2013. 碳酸盐岩沉积相及相模式[J]. 沉积学报, 31(6): 965-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306003.htm 寇琳琳, 李振宏, 董晓朋, 等, 2021. 青藏高原东北缘隆德观音店剖面碎屑锆石年龄序列及地质意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(6): 1051-1064. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.06.085 李才, 2008. 青藏高原龙木错—双湖—澜沧江板块缝合带研究二十年[J]. 地质论评, 54(1): 105-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200801013.htm 李才, 谢尧武, 董永胜, 等, 2009. 北澜沧江带的性质: 是冈瓦纳板块与扬子板块的界线吗?[J]. 地质通报, 28(12): 1711-1719. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200912005.htm 李洪梁, 李光明, 刘洪, 等, 2019. 拉萨地体西段达若地区古新世花岗斑岩成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf同位素的约束[J]. 地球科学, 44(7): 2275-2297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201907007.htm 李洪梁, 陈龙, 杨栋, 等, 2022a. 藏东昌都觉学红层滑坡的地质成因分析[J/OL]. 沉积与特提斯地质. (2022-05-26). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1593.P.20220525.1537.001.html. 李洪梁, 黄海, 李元灵, 等, 2022b. 川藏铁路沿线板块缝合带地质灾害效应研究[J/OL]. 地球科学. (2022-08-09). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220808.1704.044.html. 李洪梁, 李光明, 张志, 等, 2021. 特提斯喜马拉雅东段扎西康矿集区姐纳各普金矿床成因: 黄铁矿He-Ar及原位S同位素约束[J]. 地球科学, 46(12): 4291-4315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202112006.htm 李霍, 巨能攀, 郑达, 等, 2013. 贵州上洋水河流域拉裂—倾倒型崩塌机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 21(2): 289-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201302017.htm 李晓, 李守定, 陈剑, 等, 2008. 地质灾害形成的内外动力耦合作用机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 27(9): 1792-1806. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200809008.htm 李兴振, 杜德勋, 王义昭, 1998. 盆山转换及其成矿作用: 以昌都—思茅盆地和金沙江—哀牢山带为例[J]. 特提斯地质, 22(2): 5-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD800.000.htm 李艺豪, 杜星星, 李天秀, 2022. 青藏高原东北缘武威盆地内部全新世伸展构造特征及其成因机制[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(3): 353-366. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021151 李渝生, 易树健, 蒋良文, 等, 2016. 川藏铁路澜沧江断裂应力形变及工程效应研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 33(5): 6-10, 17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC201605002.htm 林锋, 冯亮, 孙赤, 等, 2015. 强烈岩溶控制型崩塌形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 23(3): 408-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201503006.htm 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 邓晋福, 等, 2003. 印度—亚洲大陆主碰撞过程的火山作用响应[J]. 地学前缘, 10(3): 135-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200303019.htm 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 周肃, 等, 2007. 印度—亚洲大陆碰撞的时限[J]. 地质通报, 26(10): 1240-1244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200710004.htm 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等, 2016. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 23(6): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201606006.htm 潘桂棠, 任飞, 尹福光, 等, 2020. 洋板块地质与川藏铁路工程地质关键区带[J]. 地球科学, 45(7): 2293-2304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202007007.htm 覃建勋, 韩鹏, 车晓超, 等, 2014. 利用荣玛地区温泉钙华δ18O及微量元素重建西藏全新世以来古气候[J]. 地学前缘, 21(2): 312-322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201402030.htm 瞿伟, 高源, 陈海禄, 等, 2021. 利用GPS高精度监测数据开展青藏高原现今地壳运动与形变特征研究进展[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 43(1): 182-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202101013.htm 冉涛, 文宝萍, 苏昌, 等, 2012. 湖北五峰赵家岩崩塌形成机理分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 39(6): 114-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201206024.htm 唐菊兴, 钟康惠, 刘肇昌, 等, 2006. 藏东缘昌都大型复合盆地喜马拉雅期陆内造山与成矿作用[J]. 地质学报, 80(9): 1364-1376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200609012.htm 王延平, 2016. 崩塌灾害变形破坏机理与监测预警研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学. 王阎昭, 王恩宁, 沈正康, 等, 2008. 基于GPS资料约束反演川滇地区主要断裂现今活动速率[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 38(5): 582-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200805006.htm 魏君奇, 王晓地, 庄晓, 等, 2008. 澜沧江缝合带吉岔蛇纹岩中闪长岩和俄咱辉长岩中锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 24(6): 1297-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200806013.htm 西藏自治区地质调查院一分院, 2007. 中华人民共和国1∶25万区域地质调查报告(囊谦县幅、昌都县幅和江达县幅)[R]. 拉萨: 西藏自治区地质调查院. 肖锐铧, 陈红旗, 冷洋洋, 等, 2018. 贵州纳雍"8·28"崩塌破坏过程与变形破坏机理初探[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 29(1): 3-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201801002.htm 谢富仁, 张红艳, 崔效锋, 等, 2011. 中国大陆现代构造应力场与强震活动[J]. 国际地震动态(1): 4-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZT201101004.htm 许强, 李为乐, 2010. 汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 18(6): 818-826. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201006002.htm 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李文昌, 等, 2013. 青藏高原中的古特提斯体制与增生造山作用[J]. 岩石学报, 29(6): 1847-1860. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201306002.htm 许志琴, 王勤, 李忠海, 等, 2016. 印度-亚洲碰撞: 从挤压到走滑的构造转换[J]. 地质学报, 90(1): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201601001.htm 薛翊国, 孔凡猛, 宋茜, 等, 2020. 川藏铁路沿线活动断裂带发育特征与灾害效应研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 28(6): 1213-1245. 占王忠, 谭富文, 陈明, 2018. 藏东昌都盆地沉积构造演化及油气远景分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 38(4): 85-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201804009.htm 张永双, 石菊松, 孙萍, 等, 2009. 汶川地震内外动力耦合及灾害实例[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(2): 131-141. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/article/id/9eaf7ba9-723c-4e6d-9a24-ceec30efda72 张永双, 巴仁基, 任三绍, 等, 2020. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡的地质成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 47(6): 1637-1645. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006004.htm 朱宗敏, 寸金鸿, 庞龙飞, 等, 2007. 西藏米林地区湖积物的磁性特征及其古气候意义[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 32(5): 622-628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200705007.htm 邹银先, 董建辉, 李海军, 等, 2019. 白云质灰岩山体崩塌成因机制及稳定性分析[J]. 成都大学学报(自然科学版), 38(3): 322-325. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDDD201903021.htm -





 下载:
下载: