Evolution and changes of the ancient Luanhe fluvial fan since the Quaternary in Tangshan, Hebei Province
-
摘要: 古滦河冲积扇研究的关注点更多在全新世,对其更新世的演化与变迁一直没有进行过系统研究。根据古滦河冲积扇上PZK10、PZK20钻孔的磁性地层学、年代地层学、沉积学、测井沉积学、岩芯色度分析等,对古滦河冲积平原的第四纪三维地质结构、冲积扇体的规模以及迁移规律进行综合研究,结果表明: PZK10孔揭露了上新世时沉积的巨厚洪积成因“泥包砾”地层,早更新世时发育两个冲积扇−湖相旋回,中更新世时发育辫状河沉积,晚更新世发育湖相、冲积扇相、辫状河相沉积。PZK20孔上新世沉积了一套巨厚“泥包砾”层,早更新世为扇前平原−辫状河相沉积,中更新世为辫状河−冲积扇相沉积,晚更新世为辫状河沉积。古滦河发育两期冲积扇,第一期为早更新世早期,在沙流河镇一带出山口形成的规模较大的冲积扇;第二期为早更新世中期,古滦河在现今丘庄水库一带发生分流,在丰润区一带出山口形成的冲积扇。中更新世,第一期冲积扇开始萎缩,第二期冲积扇继续发育,形成巨厚砾石层;晚更新世,古滦河在迁西县城以北发生袭夺,东流迁移出研究区,在西峡口进入迁安盆地,形成以西峡口为顶点的冲积扇。Abstract: The study of the ancient Luanhe alluvial fan has focused more on the Holocene, and no systematic study has been conducted on its Pleistocene evolution and variation. We studied the magnetic stratigraphy, chronostratigraphy, sedimentology, logging sedimentology, and core color of the boreholes PZK10 and PZK20 in the ancient Luanshe alluvial fan. Based on that, we carried out a comprehensive study of the Quaternary three-dimensional geological structure, the scale of the alluvial fan body, and the migration pattern of the ancient Luanshe alluvial plain. The borehole PZK10 recorded Brunches, Matuyama, and Gauss polarity chrons; the boundaries between them are 77.42 m and 71.50 m, respectively. The borehole PZK10 also revealed a set of diluvial “mud-gravel” layers deposited in the Pliocene, with two alluvial fan-lake phase cycles in the Early Pleistocene, braided river deposits in the Middle Pleistocene, and lake, alluvial fan and braided river facies in the late Pleistocene. A set of highly thick “mud-gravel” layers was deposited in the Pliocene of the borehole PZK20. The early Pleistocene is the fan-front–plain-braided river facies deposition, the middle Pleistocene is the braided river–alluvial fan facies deposition, and the late Pleistocene is the braided river deposition. Early Pleistocene, the ancient Luanhe River out of the mountain formed a large-scale alluvial fan in Shaliuhe town, which is the first stage of the ancient Luanhe alluvial fan. In the middle of the early Pleistocene, the ancient Luanhe River diverged in the current Qiuzhuang reservoir, and the alluvial fan formed in the Fengrun area, namely the second stage alluvial fan. In the middle Pleistocene, the first alluvial fan began to shrink, while the second alluvial fan continued to develop, forming a vast thick gravel layer. Late Pleistocene, the ancient Luanhe river was captured north of Qianxi county. It flowed eastwards and migrated out of the research area into the Qian’an basin in Xixiakou village, forming the alluvial fan with Xixiakou village as its apex.
-
Key words:
- Quaternary /
- ancient Luanhe alluvial fan /
- borehole /
- paleomagnetic /
- optically stimulated luminescence /
- logging curve
-
0. 引言
华北平原作为半湿润区,山前分布较多的冲积扇,如燕山山前古滦河冲积扇、永定河冲积扇和太行山山前滹沱河冲积扇(林旭等,2021)。滦河发源于内蒙古高原巴延吉尔山北麓,穿燕山山脉进入华北平原,在更新世形成了以滦县为顶点的冲积扇,其主体分布在整个冀东地区。滦河在中游燕山山区受到强烈的断裂控制,多处呈直角拐弯,其中迁西拐弯处对古滦河演化发育尤为重要。迁西以上,滦河由北南流,沿河分布四级阶地;迁西以下,河道转折东流,沿岸有一、二级阶地。拐点上、下游阶地的突然不连续,表明迁西附近是滦河重要的分流点(高善明,1985)。据遥感影像和地形地貌判断,古滦河曾由迁西县顺直往南,经照燕州村,沿还乡河故道南流,经唐山市丰润区出山口,在山前堆积了中、早更新世古老冲积扇(李从先等,2013)。由于燕山山脉新构造运动十分活跃,山脉阶段性不均衡抬升,造成了古滦河改道和变迁,进而控制和影响着古滦河冲积扇演化,以致其阶段性由西向东摆动(吴忱,1984)。
已有的古滦河冲积扇的研究关注点更多在全新世(高善明,1981,1982;李元芳等,1982;李从先等,1984;胡云壮等,2014;薛春汀,2016),对其岩性特征、微体古生物特征、沉积演化模式、地下水循环等都做过系统研究,但缺乏利用钻孔地层特征对晚更新世及以前古滦河冲积扇演化变迁的研究。一些学者通过对滦河在迁西拐弯处的地形地貌、阶地中“珠状砂”以及沉积物成分的研究,普遍认为滦河改道发生在晚更新世之前,沿照燕州村向南出山口形成以丰润区为顶点的冲积扇(吴忱,1984;大港油田地质研究所等,1985;高善明,1985),但这些研究仅仅依靠遥感影像、野外地形地貌等进行判断,证据不够充分。且对古滦河冲积扇规模、沉积厚度、扇体迁移时限等认识不清,没有进行过钻孔岩石地层、年代地层以及磁性地层研究。
文章以唐山西部玉田−丰润一带为研究区,对区内PZK10、PZK20两个全孔取芯标准孔分别进行古地磁、光释光测年、色度与沉积相分析,并与已有研究报道(胡云壮等,2014;秦帮策等,2021)进行对比,确定了古滦河冲积扇第四纪以来的沉积特征以及扇体由西向东迁移时间,建立古滦河冲积平原地区第四纪地层格架,以期为该地区地下水开发利用、地面沉降机理研究、地下空间开发利用、重大工程建设等提供基础地质支撑。
1. 区域地质背景
研究区位于塔里木−华北板块的华北陆块,其所在的三级构造单元为燕山−辽西裂陷带,四级构造单元为马兰峪复式背斜,五级构造单元横跨大钟庄凹陷(鸦鸿桥凹陷)和丰南穹褶(唐山凸起)(河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所,2017;图1)。
 图 1 研究区大地构造位置及古滦河冲积扇地貌遥感影像图a—研究区位置及古滦河冲积扇地貌遥感影像图;b—大地构造位置Figure 1. Geotectonic location of the study area and remote sensing image of the ancient Luanhe fluvial fan landform(a) Location of the study area and remote sensing image of the ancient Luanhe River fluvial fan landform; (b) Geotectonic position
图 1 研究区大地构造位置及古滦河冲积扇地貌遥感影像图a—研究区位置及古滦河冲积扇地貌遥感影像图;b—大地构造位置Figure 1. Geotectonic location of the study area and remote sensing image of the ancient Luanhe fluvial fan landform(a) Location of the study area and remote sensing image of the ancient Luanhe River fluvial fan landform; (b) Geotectonic position研究区新构造运动活跃,以继承性构造活动为主,北部燕山山区呈继承性上升状态,遭受剥蚀,南部平原区为继承性的下降,接受沉积。第四系沉积物主要是以沙流河为顶点的古滦河冲积扇的砂砾石层、中细砂,少量黏土层;鸦鸿桥凹陷和唐山凸起位于研究区南部平原区,二者以丰台−野鸡坨断裂为界。鸦鸿桥凹陷位于丰台−野鸡坨断裂北西侧下降盘,新生界厚度最大超过800 m,第四系沉积物主要以湖泊相、扇三角洲前缘相的暗灰色黏土、粉细砂沉积为主。唐山凸起位于丰台−野鸡坨断裂南东侧上升盘,新生界厚度一般小于200 m,第四系沉积物主要为以丰润为顶点的古滦河冲积扇沉积的砂砾石层,以及辫状河沉积的中粗砂、中细砂(李勇,1987;陈宏强等,2021)。
2. 钻孔地层沉积相分析
2.1 色度样品测试方法
色度样品为每个野外分层取1件,共采集272件样品(PZK10孔)。色度测试在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心实验测试室完成。测试前样品在温室条件下自然风干,在不损坏自然颗粒结构前提下捣碎磨细,过74μm干筛后取少量样平摊纸上,在避光的室内用SPAD-503便携式色度仪测量各样品3次,取其均值,记录样品的红度(a*)、黄度(b*)和亮度(L*)。其中a*值的变化,受控于沉积物中的赤铁矿、磁铁矿等致色矿物的含量,尤以赤铁矿对a*值的贡献最大;b*值主要受控于不同价态铁的氢氧化物的含量。a*值>2.5、b*值>13时为河流或冲积扇相沉积;a*值<2.5、b*值<13为湖相或海相沉积(方小敏等,1997;王乃昂等,1999;沈吉等,2001;吴艳宏和李世杰,2004;徐丽等,2009)。L*值的高低主要与沉积物中碳酸钙、石英、长石等浅色矿物以及有机质的含量多少有关。
2.2 PZK10孔基本情况及沉积特征
PZK10孔(39°51′55″N;117°52′05″E)位于唐山市丰润区张唐庄村,孔口标高17 m,孔深300.15 m,钻孔揭穿新生代地层,底部为蓟县系雾迷山组灰色粉晶灰岩,厚6.3 m(图2)。全孔岩心采取率达94.9%,除砾石、粗砂层不能采样测古地磁外,岩心状况基本满足了磁性地层学研究的要求。
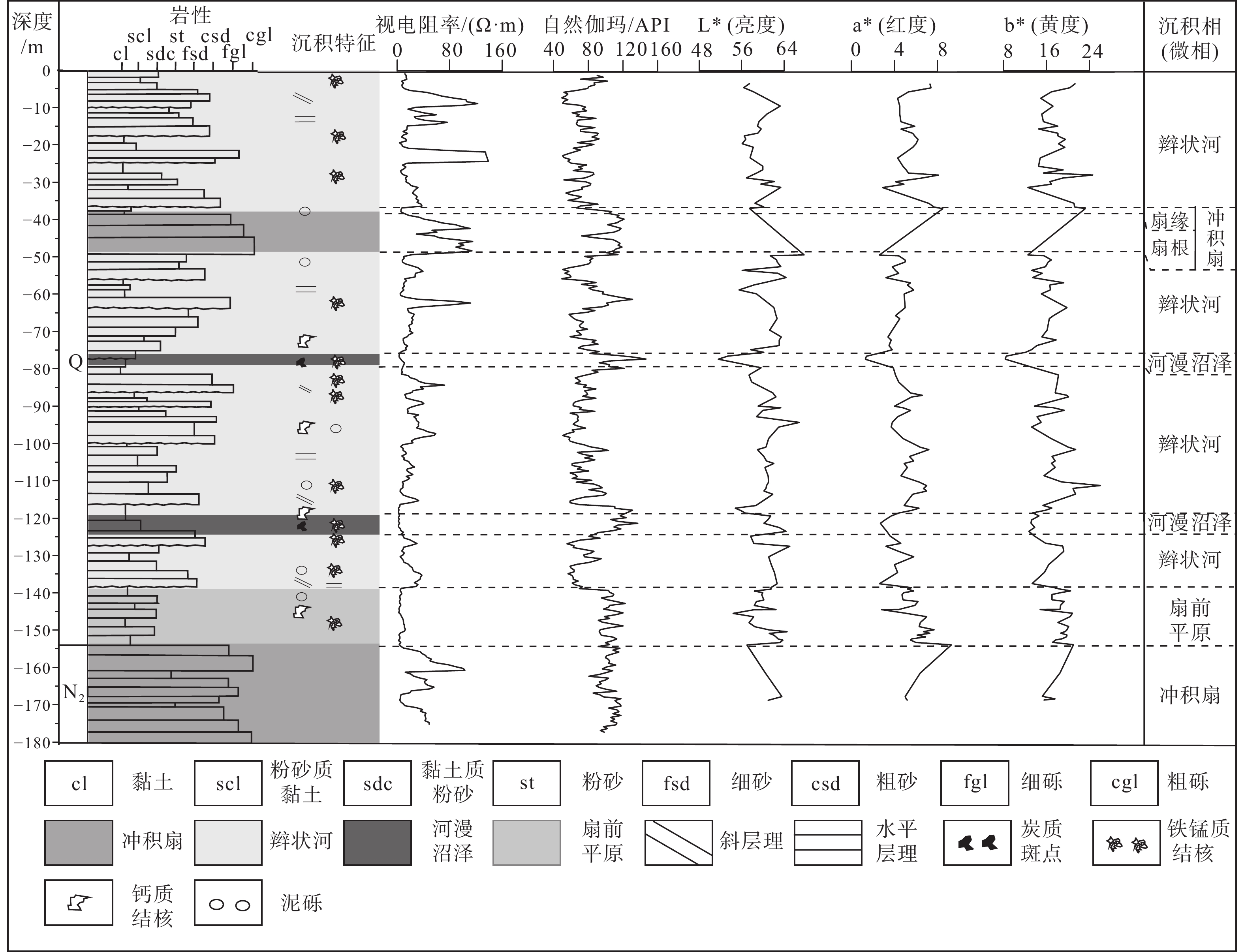
测井曲线中自然伽玛与视电阻率曲线直接反映地层的粒度和泥质含量等特征。通过两种测井曲线特征能反映沉积相特点,以及垂向序列特征,进而达到重建沉积环境的目的。自然伽玛数值越大,表明地层中泥质含量越高;视电阻率数值越大,表明沉积物粒度越粗(王金荣和刘洪涛,2004;宋璠等,2009;赵琳琳等,2016)。根据测井曲线特征(马正,1982)反映的沉积相,结合色度特征,可将研究钻孔划分为5种沉积相(微相)(表1,图3)。
表 1 沉积相特征统计表Table 1. Statistical table of sedimentary facies characteristics沉积相(微相) 色度特征 测井曲线特征 冲积扇相 a*>2.5,b*>13 视电阻率和自然伽玛曲线一般呈高幅箱形,视电阻率数值较高,自然伽玛数值也较高 湖泊相 a*<2.5、b*<13 视电阻率曲线一般呈漏斗形,自然伽玛曲线呈钟形,视电阻率数值较低,自然伽玛数值较高 辫状河相 a*>2.5,b*>13 视电阻率曲线一般呈钟形、箱型;自然伽玛曲线一般呈高幅齿形或呈高幅指形;砂泥比较高 河漫沼泽微相 a*<2.5、b*<13 视电阻率呈低幅箱形,自然伽玛呈高幅指形、箱型,视电阻率数值较低,自然伽玛数值较高 扇前平原微相 a*>2.5,b*>13 视电阻率曲线呈微齿形,自然伽玛曲线呈高幅齿形,齿中线呈水平平行式 189.20~293.85 m层段为冲积扇相,岩性主要为灰绿色、棕红色“泥包砾”层,夹半固结的砂层、黏土层等。砾石磨圆度较好,说明经历了一定距离的搬运;分选较差,表明沉积速度较快,未及分选;砾石直径大多1~5 cm,大者可达10 cm以上,成分复杂,有石英砂岩、安山岩、粗面岩等。黏土层呈强棕色,质密、较硬,局部为半固结状泥岩,且含大量黑色锰质斑点。该层段自然伽玛与视电阻率值均总体偏高,表明砾石间隙充填物主要为黏土,为泥石流沉积的“泥包砾”。
147.90~189.20 m 层段为辫状河相,主体为淡棕色含砾粗砂、粗砂、细砂,夹薄层砾石层,顶部为黏土质细砂和黏土。测井曲线中视电阻率值下部偏高,向上逐渐减小,呈钟形;自然伽玛数值下部较低,向上逐渐变高,表明底部沉积物以砂为主,上部以黏土为主。下部砂和砾石层发育平行层理,上部黏土质粉砂、黏土发育韵律层理,含白色钙质结核。色度a*>2.5、b*>13、 L*>55,表明该层段符合河流相沉积环境特征。
133.00~147.90 m层段为冲积扇相,由砂砾层、棕黄色细砂等组成,视电阻率和自然伽玛值均较高,表明砂砾层内黏土含量较高,具有泥石流沉积特征,应为扇根亚相。上部细砂、粉砂、黏土属扇缘亚相,纵向上发育1个下粗上细的退积型冲积扇旋回。
118.00~133.00 m层段为湖泊相,由深黄棕色、深暗灰棕色黏土、黏土质粉砂、淡棕色含黏土细砂、细砂组成,发育韵律层理,含黑色锰质斑点和灰白色钙质结核。垂向呈下细上粗的反旋回沉积序列,视电阻率曲线呈漏斗形,自然伽玛曲线呈钟形,下部色度指标较低,a*<2.5、b*<13、 L*<50,表明该层段属于湖相环境。
91.80~118.00 m层段为冲积扇相,由砂砾层、棕黄色细砂、粉砂等组成,其中砂砾层内黏土含量较高,视电阻率和自然伽玛值均较高,为“泥砂包砾”,具有泥石流沉积特征,为扇根亚相。上部细砂、粉砂属扇端亚相,发育斜层理,纵向上发育2个下粗上细的退积型冲积扇旋回。色度指标a*>2.5、b*>13,根据色度分析,该层段属于冲积扇相沉积环境。
77.15~91.80 m层段为湖泊相,下部为暗灰绿色黏土、粉砂,向上逐渐过渡为黄色、棕黄色粉砂、细砂,垂向呈逆粒序,发育韵律层理、水平层理,垂向呈下细上粗的反旋回沉积序列;视电阻率曲线呈漏斗形,自然伽玛曲线呈钟形,沉积水体为静水环境,色度a*<2.5、b*<13,据色度分析该层段属于湖相沉积环境。
39.4~77.15 m层段为辫状河相,主体为淡棕色、黄色砂、细砂、砾质粗砂、砂砾及少量含黏土粉砂、含粉砂黏土等,砂泥比较高,砂分选性中等,局部发育斜层理、平行层理。色度指标整体较高,a*>2.5、b*>13 、L*>55,表明为河流相沉积环境。
28.55~39.40 m层段为湖泊相,由暗绿灰色黏土、粉砂组成,发育韵律层理,含黑色锰质斑点;视电阻率值较低,自然伽玛值较高,说明沉积物主要为黏土。由下向上,色度a*<2.5、b*<13,表明其沉积环境属于湖相沉积环境。
21.15~28.55 m层段为冲积扇相,沉积物主要形成于冲积扇环境。底部为砂砾层,砾石磨圆较好,成分复杂,填隙物含较多黏土,对应视电阻率和自然伽玛值均较高,属冲积扇泥石流沉积。
0~21.15 m层段为辫状河相,沉积物主要为黄色细砂、中粗砂,夹少量粉砂、黏土,砂泥比较高,砂粒分选磨圆较好,成熟度高,发育正粒序层理、均匀层理、斜层理。色度指标整体较高,a*>2.5、b*>13、 L*>50,表明该层段为河流相沉积环境。
2.3 PZK20孔基本情况及沉积特征
PZK20孔(39°43′14″N;118°04′29″E)位于唐山市玉田县老庄子镇七王庄村,孔口标高27.3 m,孔深180 m,揭穿第四系(图4,图5),全孔平均取心率>85%。除去砾石、粗砂层不能采样测试古地磁外,该孔取心率和岩心状况基本满足了磁性地层学研究的要求,磁性地层研究参考陈宏强等(2021)研究成果,同时测试了118个色度样品。
 图 4 PZK20孔照片(据陈宏强等,2021修改)Figure 4. Photographs of the borehole PZK20(modified from Chen et al., 2021)
图 4 PZK20孔照片(据陈宏强等,2021修改)Figure 4. Photographs of the borehole PZK20(modified from Chen et al., 2021)154.8~180.0 m层段岩性主要为“泥包砾”,砾石间填隙物主要以泥质成分为主;视电阻率曲线呈现出高幅度指形、漏斗形等变化特征,表明沉积过程中能量变化大,沉积物粒径较粗,该层段应为冲积扇相。
138.3~154.8 m层段为扇前平原微相,物质组成为红色、红黄色黏土、粉细砂,可见黑色锰质斑点;视电阻率曲线呈低阻、微齿形,反映当时沉积环境和沉积物来源较稳定;自然伽玛曲线呈高幅齿形,齿中线呈水平平行式,泥质含量呈匀速变化,表明水动力突发性快速变化。色度指标a*>2.5、b*>13,表明该层段属于冲积扇相沉积。
123.10~138.30 m层段为辫状河相,该段沉积物主要为棕黄色、棕灰色、浅黄色中砂、细砂,夹少量薄层粉砂和黏土,发育斜层理、平行层理,垂向构成正旋回;视电阻率曲线呈现中高幅度钟形、箱形;自然伽玛曲线呈低幅,表明泥质含量很低,结构成熟度高。色度指标a*>2.5、b*>13,表明该层段属于河流相沉积。
116.1~123.1 m层段为河漫沼泽微相,沉积物主要为深灰色、棕灰色黏土,含少量铁质结核和钙质结核。视电阻率曲线呈低幅箱形,自然伽玛曲线呈高幅箱形。色度指标偏低,a*>2.5、b*>13。由于该钻孔位于唐山凸起构造单元,古地势略高,故认为该套沉积物形成于河漫沼泽环境。
78.95~116.10 m层段为辫状河相,由浅棕色、黄棕色中砂、细砂和少量粗砂,夹黄红色、棕红色粉砂、黏土,发育平行层理、斜层理等;中砂、细砂成熟度较高,成分以石英为主,磨圆较好,泥质填隙物极少,表明水动力较强,且具有一定的搬运距离;视电阻率曲线呈箱形—钟形,自然伽玛曲线呈低幅箱形,说明以砂为主,黏土含量较少,砂泥比较高。色度指标a*>2.5、b*>13、 L*>57,表明该层段属于河流相沉积。
74.8~78.95 m层段为河漫沼泽微相,沉积物主要为灰色、暗灰色黏土、有机质黏土,含锰质结核;视电阻率曲线呈低幅箱形,自然伽玛曲线呈高幅指形。色度指标偏低,a*<2.5、b*<13、 L*<55。结合钻孔所处构造单元位置,该层段应形成于河漫沼泽环境。
48.9~74.8 m层段为辫状河相,主要由黄棕色、黄色、浅灰色粗砂、中砂、细砂组成,夹少量粉砂和黏土,发育平行层理、正粒序层理,偶见锰质结核。中砂、细砂成熟度较高,磨圆较好;视电阻率和自然伽玛曲线呈箱形−钟形,局部呈指形,说明黏土含量较少,砂泥比较高。色度指标a*>2.5、b*>13、L*>55,表明该层段属于河流相沉积。
36.5~48.9 m层段为冲积扇相,该段地层下部岩性为浅黄褐色砂砾石层,砾径为1~10 cm为主,岩性主要为粗安岩、花岗岩、石英砂岩,磨圆较好;顶部岩性为棕红色粉砂、黏土,可见黑色锰质结核,直径1~2 mm。砾石层段视电阻率和自然伽玛曲线呈高幅箱形,表明砾石中泥质填隙物含量较高,属冲积扇泥石流沉积;在顶部出现低值,表明该层段为冲积扇退积后的扇前平原沉积。
0~36.5 m层段为辫状河,主要岩性为浅灰色、棕黄色、黄棕色黏土、黏土质粉砂、粉砂、中细砂、砾质粗砂。黏土中可见黑色锰质结核和锈黄色铁质结核;砂分选性好、磨圆度好,发育平行层理,发育平行层理。垂向共发育4个下粗上细的地层结构,代表4次沉积旋回;每个旋回对应的视电阻率曲线均呈钟形;自然伽玛曲线为高幅齿形,局部呈高幅指形。该段水动力由下向上呈减弱趋势,自然伽玛曲线齿中线呈水平平行式,泥质含量呈匀速变化,表明水动力均匀变化。色度指标a*>2.5,b*>13 、L*>55,表明该层段为河流相。
3. 钻孔磁性地层研究
3.1 古地磁样品采集与测试
岩心被劈成两半,按间距0.5~1 m采集手标本,标记顶底方向,室内加工成边长2 cm×2 cm×2 cm的立方体样品。由于砂砾石层无法取样,PZK10钻孔共采集样品215件。
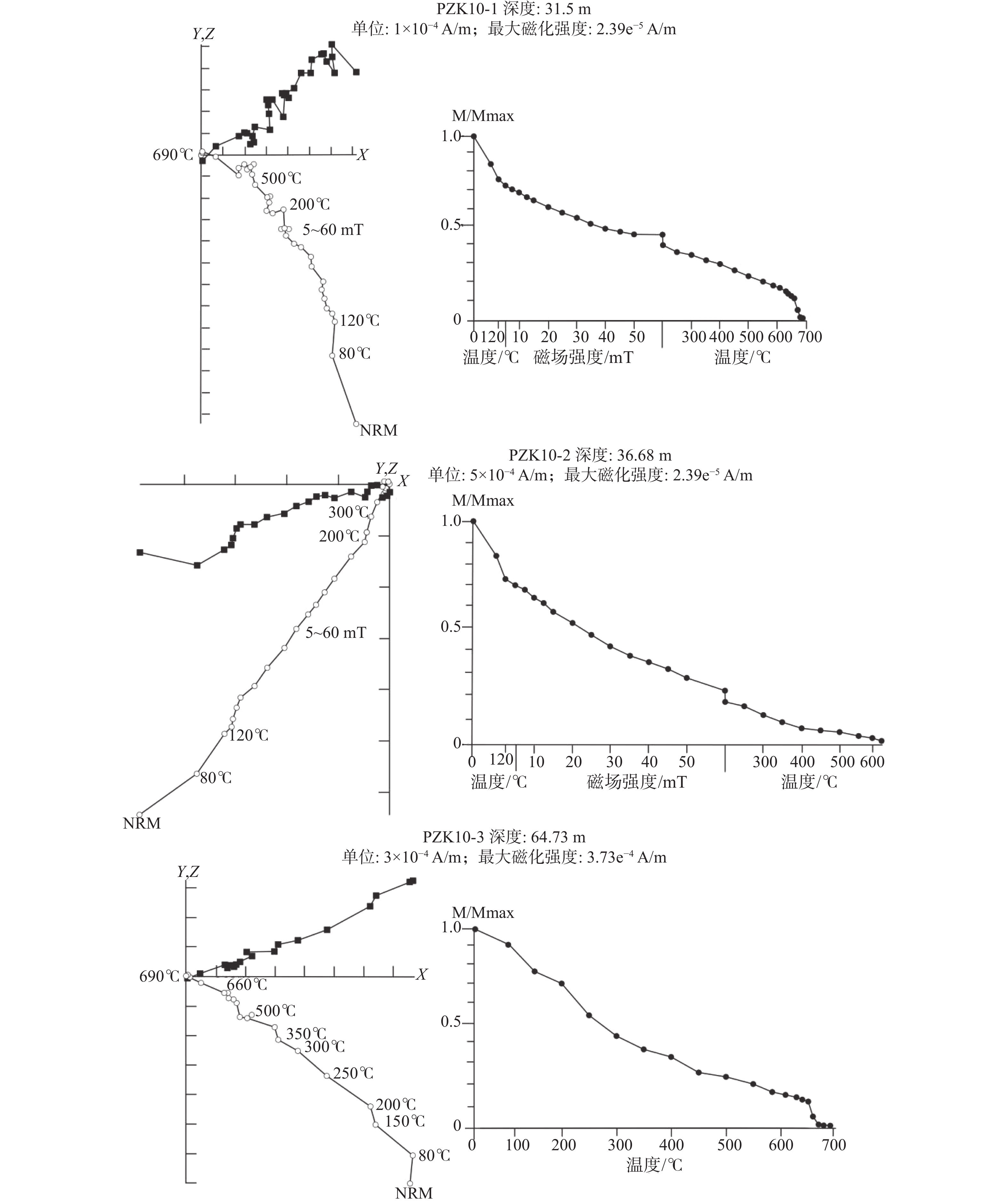
样品测试在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所古地磁实验室完成。PZK10孔样品分别采用混合退磁和热退磁方法,在TD-48热退磁炉中从室温退至120 ℃,转为交变退磁,步长为5~10 mT,最大交变退磁场为70 mT,再转为热退磁,从200 ℃退至690 ℃,温度间隔为10~50 ℃。剩磁在美制2G-760R低温超导磁力仪上进行。热退磁样品剩磁强度衰减曲线显示:多数样品在250℃以下退掉黏滞剩磁,300~690 ℃分离出稳定的特征剩磁;表明磁铁矿和赤铁矿为主要的携磁矿物(图6)。
各样品通过主成分分析法与过原点的线性拟合(Kirschvink,1980),即可获得特征剩磁方向。为此,选择退磁步骤至少为4步的样品,对于最大角偏差(MAD)大于15°的样品予以剔除。继而由PZK10孔150件样品(占全部样品的69.8%)中分离出特征剩磁,并建立了磁性地层序列(图7)。
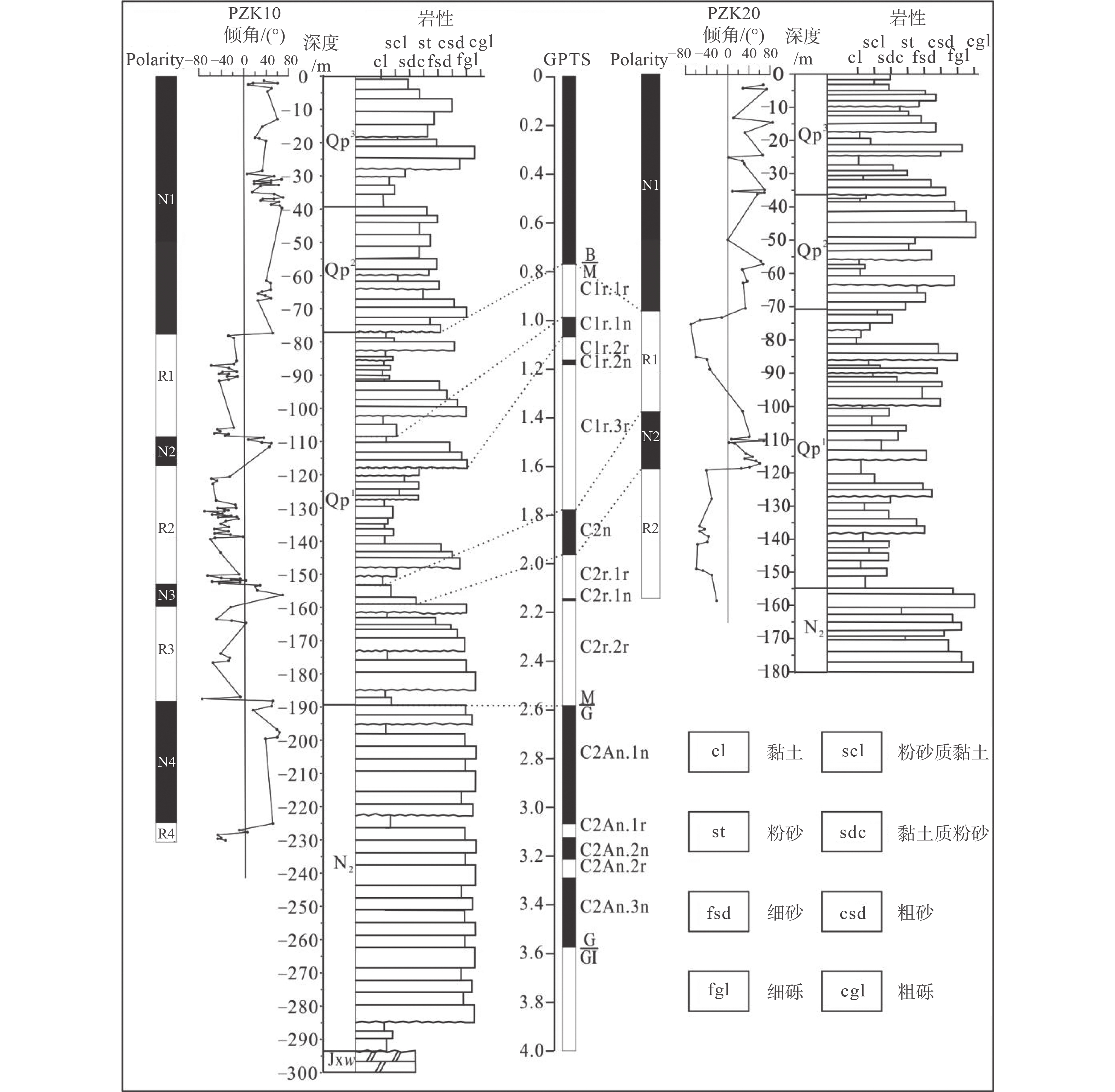
 图 7 PZK10、PZK20孔岩石地层、磁性地层及其地磁极性年表(Cande and Kent,1995)对比图Figure 7. Lithostratigraphy and magnetic stratigraphy of the boreholes PZK10 and PZK20, and their correlations with the geomagnetic polarity timescale(Cande and Kent, 1995)
图 7 PZK10、PZK20孔岩石地层、磁性地层及其地磁极性年表(Cande and Kent,1995)对比图Figure 7. Lithostratigraphy and magnetic stratigraphy of the boreholes PZK10 and PZK20, and their correlations with the geomagnetic polarity timescale(Cande and Kent, 1995)3.2 磁性地层划分
PZK10孔古地磁极性柱可分辨出8个极性带(图7),其中4个正极性带,分别为N1(0~77.42 m)、N2(108.10~118.00 m)、N3(153.35~159.15 m)、N4(189.30~225.50 m);4个负极性带,分别为R1(77.42~108.10 m)、R2(118.00~153.35 m)、R3(159.15~189.30 m)、R4(225.50~229.90 m)。R1、R2、R3均对应Matuyama负极性时,N1对应Brunches正极性时。N2为一套细碎屑沉积物,岩性为棕黄色黏土质粉砂、粉砂质黏土,由于其距离Brunches正极性时较近,认为其应为Jaramillo正极性亚时;Olduvai正极性亚时持续事件长,且强度大,在邻区其他钻孔中均有出现(胡云壮等,2014;陈宏强等,2021),因此推断N3对应Olduvai正极性亚时,N4为 Gauss正极性时,R4为Kaena负极性亚时。
PZK20孔的磁性地层主要依据陈宏强等(2021)对其进行的划分。
4. 钻孔年代地层研究
4.1 光释光样品测试方法
依据区域地层沉积速率结合光释光测年有效年龄范围,在PKZ10孔采集深度约40 m以内粉细砂样品,采样间隔为10~20 m。采样应在岩心未劈开前,在岩心横切面中心,用铁皮罐砸入岩心中避光采取,并及时用黑色塑料袋包装,避免阳光照射。此次工作分别在埋深12.4 m和29.8 m处,采集两个样品,岩性为黄色、淡棕色粉细砂。样品测试在北京光释光实验室科技有限公司完成,在Daybreak 2200(美国)光释光仪上测定。该系统蓝光光源波长为470 nm,半宽5 nm,最大功率为60 mW/cm2;红外光源波长为880 nm,半宽10 nm,最大功率为80 mW/cm2,选择最大功率进行测量。预热温度为260℃ 10秒,试验剂量预热温度220℃ 10秒。需要辐照的测片都是在801E辐照仪中进行的,其90Sr-Yβ放射源的照射剂量率约为0.081432 Gy/Sec。所有样品采用细颗粒简单多片再生法获得等效剂量值,用饱和指数方法进行拟合。
4.2 钻孔年代地层
在12.4 m和29.8 m处获得光释光年龄分别为98.3±9.8 ka和>115.3 ka(表2),粉细砂分选性、磨圆度均较好,样品得到充分曝光,下伏地层为一套湖相沉积地层,埋深为30.6~39.4 m(图3)。区域资料显示(天津市地质调查研究院和河北省地质调查院,2005),渤海湾沿岸晚更新世第一次海侵发生于晚更新世早期,时间为110~70 ka海水沿河流上溯淹没陆地,西至杨柳青,北达黑狼口、八门城,东至黄花店,东到玉田南部、唐山胥各庄至柏各庄南附近,沉积了渤海湾沿岸第Ⅲ海侵层(汪品先等,1981;王强和田国强,1999;王强等,2008;王强和李从先,2009;胥勤勉等,2011)。据此,并结合光释光年龄判断,该套湖相地层对应MIS5阶段沉积,故将PZK10孔上更新统底界置于湖相地层底部,埋深约为39.40 m。PZK20孔的年代地层参照陈宏强等(2021)做的划分,上更新统底界埋深为36.2 m,中更新统底界埋深为73.0 m,第四系底界埋深为155.0 m。
表 2 PZK10钻孔光释光样品信息及测年数据统计表Table 2. OSL sample information and dating data in the borehole PZK10样品编号 埋深/m 等效剂量 /Gy U/×10−6 Th/×10−6 K/% 含水量/% 年龄/ka PZK10-OSL1 12.4 330.9 0.90 4.38 2.42 8.26 98.3±9.8 PZK10-OSL2 29.8 >375.0 0.90 4.01 2.40 17.10 >115.3 5. 古滦河冲积扇的演化与变迁讨论
5.1 冲积扇不同位置钻孔对比
通过查阅资料,收集到研究区4个地质钻孔资料,钻孔位置见图1。胡云壮等(2014)报道了唐山西部丰润七树庄中心小学ZK1钻孔,且进行了详细地层旋回划分。焦2、K6为1980年河北省唐山市丰润新区城市供水项目施工的水文地质钻孔;丰1为冀东平原农田供水项目施工水文地质钻孔。4个钻孔岩心描述详实,测井曲线对岩性特征反应较好,对此次研究工作具有很好的利用价值。现将ZK1钻孔与焦2孔参照此次研究的基准孔进行年代地层划分。
ZK1钻孔位于以沙流河镇出山口的第一期冲积扇上,可与PZK10孔进行对比。孔深约180 m,揭穿晚新生代,底部基岩为灰岩(图8)。自第四纪以来沉积了巨厚的冲积扇相砾石层,总厚度约140 m,直到晚更新世中晚期才沉积了薄层的辫状河砂体。参照PZK10孔按照前述依据测井曲线判断钻孔沉积相的方法结合岩性描述,将钻孔重新划分。ZK1钻孔位于凸起之上,古地形较高,上新世沉积的“泥包砾”层被剥蚀,第四纪沉积物直接不整合覆于基岩上。中更新统底界埋深定为84.25 m,岩性为灰绿色、暗灰色中细砂层,对应PZK10孔77.42 m处湖泊相沉积的暗灰色中细砂,下部均为冲积扇相砾石层;晚更新统底界埋深定为37.75 m,岩性为灰黑色淤泥、黏土层,对应PZK10孔晚更新世底部沉积的湖相地层(28.55~39.40 m)。
 图 8 ZK1、焦2钻孔地层柱状图及测井曲线(胡云壮等,2014)Figure 8. Stratigraphic column and logging curves of the boreholes ZK1 and Jiao-2 (Hu et al., 2014)
图 8 ZK1、焦2钻孔地层柱状图及测井曲线(胡云壮等,2014)Figure 8. Stratigraphic column and logging curves of the boreholes ZK1 and Jiao-2 (Hu et al., 2014)焦2钻孔位于以丰润区出山口的第二期冲积扇上,可与PZK20孔进行对比。孔深约207 m,揭穿晚新生代,底部基岩为灰岩(图8)。早更新世中早期,沉积物以细颗粒为主,岩性为黏土、粉砂;早更新世晚期,沉积了巨厚砾石层,厚约40 m,发育一个完整的冲积扇扇根−扇缘旋回;中更新世发育厚约42 m的砾石层,晚更新世沉积物以辫状河砂体为主。参照PZK20孔对焦2孔年代地层进行划分,两孔孔深相似,底部均沉积了上新世“泥包砾”,厚约11.70 m;中更新统底界为79.80 m,72.40~79.80 m为辫状河沉积的砂砾石层对应于PZK20孔埋深48.90~74.80 m的辫状河相沉积的砂砾石、中细砂等;晚更新世底界埋深为38.40 m,对应于PZK20孔36.50 m处,下部均为冲积扇沉积的砾石层。
5.2 古滦河冲积扇演化与变迁
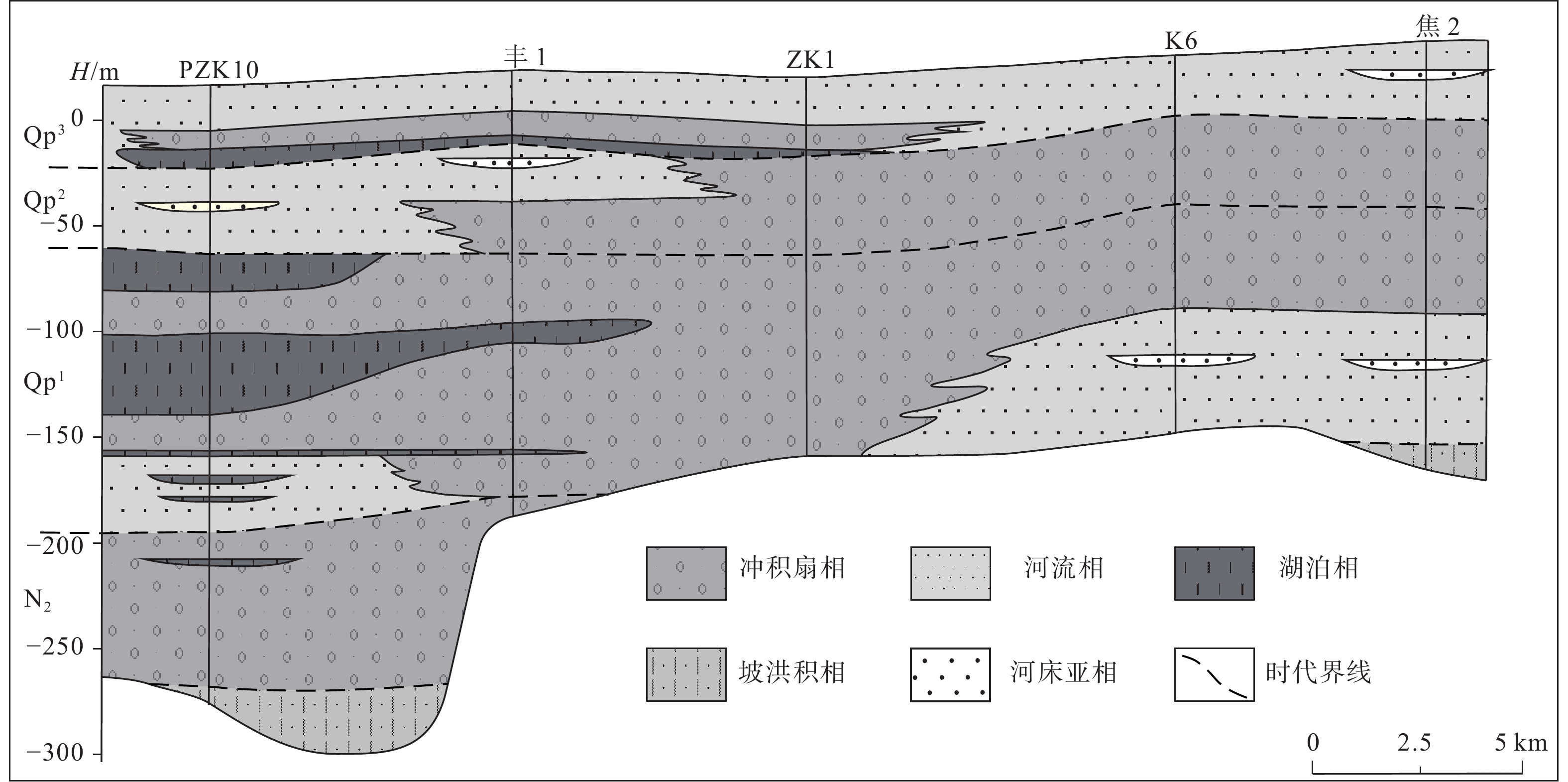
研究区位于滦河冲积扇中北部(图1),区内主要发育2个规模较大的冲积扇,分别是以沙流河镇为顶点的第一期冲积扇,以及以丰润区为顶点的第二期冲积扇,通过PZK10、PZK20钻孔年代地层、磁性地层、沉积相分析等研究结合搜集已有的钻孔(丰1、ZK1钻孔、K6、焦2)组成第四纪联孔剖面图(图1,图9),对第四纪以来古滦河冲积扇在该区的演化进行初步探讨。
早更新世早期,古滦河首先在沙流河镇北部一带出山口形成规模较大的冲积扇,即第一期冲积扇,沉积了厚约90 m砾石层;早更新世中期,在古滦河上游的丘庄水库一带发生分流(吴忱,1984),并在丰润一带出山形成冲积扇,即第二期冲积扇,沉积了厚约40 m砾石层。该套砾石层仅在焦2孔中揭露,未在PZK20孔中发现,推测此时车轴山地区基岩出露面积较大,对冲积扇起到了一定的阻挡作用。
中更新世,为第一期冲积扇向第二期冲积扇过渡阶段。由于燕山山脉阶段性不均衡抬升(徐杰等,2005),以致滦河由西向东的摆动,在丘庄水库一带古滦河改道。此时ZK1孔沉积了厚约20 m的砾石层,而PZK10孔为沉积了冲积扇后的辫状河沉积砂体。这也正好印证了此时水动力正在减弱,冲积扇已无法到达相对海拔较高的PZK10孔。同时第二期冲积扇也正在发育,并且规模较大,焦2孔内沉积了厚约40 m的砾石层。中更新世后期,车轴山基岩出露面积逐渐减少,隔挡作用减弱,PZK20孔沉积了厚约20 m的砾石层。
晚更新世初期(MIS5阶段),气候变暖,渤海湾地区发生海侵。研究区内湖泊扩张,迫使北侧山区第一期冲积扇和第二期冲积扇发生退积,古滦河在迁西县城以北发生袭夺,东流迁移出研究区,在西峡口进入迁安盆地,南流出山区进入平原,形成以西峡口为顶点的冲积扇。随着气候由暖变冷,区域海侵结束,区内湖泊开始萎缩。到晚更新世中期,此时沙流河贯通,形成小规模的沙流河冲积扇,PZK10与ZK1钻孔中泥砾层厚约20 m,晚更新世晚期过渡为辫状河沉积。
6. 结论
(1)通过PZK10的磁性地层,结合光释光测年结果,建立其第四纪年代地层格架。PZK10孔早更新世底界为189.30 m,中更新世底界为77.42 m,晚更新世底界为39.4 m;早更新世时期内分别在108.10~118.00 m处识别出了Jaramillo正极性亚时,153.35~159.15 m处识别出了Olduvai正极性亚时。
(2)对PZK10、PZK20孔岩石组合、测井曲线及色度特征进行研究,结果表明PZK10孔上新世时沉积了巨厚洪积成因“泥包砾”层,早更新世时发育两个冲积扇−湖相旋回;中更新世时发育辫状河,晚更新世发育湖相、冲积扇相、辫状河相地层;PZK20孔上新世与PZK10孔类似,沉积了一套巨厚“泥包砾”层;早更新世为扇前平原−辫状河相沉积,中更新世为辫状河−冲积扇相沉积,晚更新世为辫状河沉积。
(3)古滦河冲积扇自第四纪以来总体呈现出从西向东迁移的规律。早更新世早期,古滦河冲积扇以沙流河镇一带出山口,形成第一期古滦河冲积扇;早更新世中期,古滦河在上游的丘庄水库一带发生分流,并在丰润北部出山口形成冲积扇,形成第二期古滦河冲积扇。两期冲积扇一直持续至中更新世末期,此间呈现出第一期冲积扇向第二期冲积扇过渡的特征。晚更新世初期,古滦河冲积扇向东迁移出研究区,形成以西峡口村为顶点的冲积扇。
-
图 1 研究区大地构造位置及古滦河冲积扇地貌遥感影像图
a—研究区位置及古滦河冲积扇地貌遥感影像图;b—大地构造位置
Figure 1. Geotectonic location of the study area and remote sensing image of the ancient Luanhe fluvial fan landform
(a) Location of the study area and remote sensing image of the ancient Luanhe River fluvial fan landform; (b) Geotectonic position
图 4 PZK20孔照片(据陈宏强等,2021修改)
Figure 4. Photographs of the borehole PZK20(modified from Chen et al., 2021)
图 7 PZK10、PZK20孔岩石地层、磁性地层及其地磁极性年表(Cande and Kent,1995)对比图
Figure 7. Lithostratigraphy and magnetic stratigraphy of the boreholes PZK10 and PZK20, and their correlations with the geomagnetic polarity timescale(Cande and Kent, 1995)
图 8 ZK1、焦2钻孔地层柱状图及测井曲线(胡云壮等,2014)
Figure 8. Stratigraphic column and logging curves of the boreholes ZK1 and Jiao-2 (Hu et al., 2014)
表 1 沉积相特征统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of sedimentary facies characteristics
沉积相(微相) 色度特征 测井曲线特征 冲积扇相 a*>2.5,b*>13 视电阻率和自然伽玛曲线一般呈高幅箱形,视电阻率数值较高,自然伽玛数值也较高 湖泊相 a*<2.5、b*<13 视电阻率曲线一般呈漏斗形,自然伽玛曲线呈钟形,视电阻率数值较低,自然伽玛数值较高 辫状河相 a*>2.5,b*>13 视电阻率曲线一般呈钟形、箱型;自然伽玛曲线一般呈高幅齿形或呈高幅指形;砂泥比较高 河漫沼泽微相 a*<2.5、b*<13 视电阻率呈低幅箱形,自然伽玛呈高幅指形、箱型,视电阻率数值较低,自然伽玛数值较高 扇前平原微相 a*>2.5,b*>13 视电阻率曲线呈微齿形,自然伽玛曲线呈高幅齿形,齿中线呈水平平行式 表 2 PZK10钻孔光释光样品信息及测年数据统计表
Table 2. OSL sample information and dating data in the borehole PZK10
样品编号 埋深/m 等效剂量 /Gy U/×10−6 Th/×10−6 K/% 含水量/% 年龄/ka PZK10-OSL1 12.4 330.9 0.90 4.38 2.42 8.26 98.3±9.8 PZK10-OSL2 29.8 >375.0 0.90 4.01 2.40 17.10 >115.3 -
CANDE S C, KENT D V, 1995. Revised calibration of the geomagnetic polarity timescale for the Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 100(B4): 6093-6095. doi: 10.1029/94JB03098 CHEN H Q, ZHUAN S P, CHEN C, et al. , 2021. Quaternary activity of the Fengtai-Yejituo fault in Tangshan, Hebei Province: evidence from 14C and magnetic stratigraphy[J]. Geology in China, 48(2): 605-617. (in Chinese with English abstract) FANG X M, XI X X, LI J J, et al. , 1997. Discovery of the late Miocene climate change and its significance in Western China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 42(23): 2521-2524. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/csb1997-42-23-2521 GAO S M, 1981. Facies and sedimentary model of the Luan Riverdelta[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 36(3): 303-314. (in Chinese with English abstract) GAO S M, 1982. Supplement new recognition on Luanhe River delta[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 37(4): 424-426. (in Chinese) GAO S M, 1985. Structures and sedimentary environments of the alluvial fan of the Luan River[J]. Geographical Research, 4(1): 54-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) Geological Insititute of Dagang Oil Field, Bureau of Marine Petroleum Exploration, Institute of Marine Geology, Tongji University, 1985. The Luanhe River alluvial fan-delta[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-164. (in Chinese) HU Y Z, ZHANG J Q, BAI Y N, et al. , 2014. Records of regional tectonic and climatic evolution since 3.45 Ma BP at Borehole TD1 of Tangshan in the middle part of Luanhe River fluvial fan[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 16(2): 249-262. (in Chinese with English abstract) KIRSCHVINK J L, 1980. The least-squares line and plane and the analysis of palaeomagnetic data[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 62(3): 699-718. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1980.tb02601.x LI C X, CHEN G, WANG C G, et al. , 1984. On the Luanhe river alluvial fan-delta complex[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 5(4): 27-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI C X, WANG Q, FAN D D, 2013. Oceanic delta[C]//Sedimentology of China. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press: 812-905. (in Chinese) LI Y, 1987. Mechanism of the appearance of Fengrun-Fengtai concealed active fault on Landsat image[J]. Journal of Seismology, 21(1): 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Y F, GAO S M, AN F T, 1982. A preliminary study of the Quaternary marine strata and its Paleogeographic significance in the Luanhe delta region[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 13(5): 433-439. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIN X, LIU J, WU Z H, et al. , 2021. Study on borehole provenance tracing and fluvial sediment diffusion in the Bohai Sea: double constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb age and in-situ geochemical element of apatite grains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 304-316. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA Z, 1982. Utilization of the combination of log shapes for explanation of the sedimentary environment[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 3(1): 25-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIN B C, FANG W X, ZHANG J G, et al. , 2021. Quaternary sedimentary sequence and sedimentary environment restoration in the Jinzhong Basin, Fenhe Rift Valley[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(6): 1035-1050. (in Chinese with English abstract) Regional Geological and Mineral Resources Survey Institute of Hebei Province, 2017. The regional geology of China, Hebei Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-1272. (in Chinese) SHEN J, ZHANG E L, XIA W L, 2001. Records From lake sediments of the Qinghai lake to mirror climatic and environmental changes of the past about 1000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 21(6): 508-513. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG F, HOU J G, ZHANG Z, et al. , 2009. Application of log curves in indicating sedimentary micro-facies of lake facies basins[J]. Well Logging Technology, 33(6): 589-592. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG J R, LIU H T, 2004. Identification of sedimentary microfacies of logging and its application[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 28(4): 18-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG N A, LI J J, CAO J X, et al. , 1999. A preliminary research on the climatic records of lacustrine deposits of Qingtu Lake in the last 6000 years[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 19(2): 119-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG P X, MIN Q B, BIAN Y H, et al. , 1981. Strata of quaternary transgressions in East China: a preliminary study[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 55(1): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Q, TIAN G Q, 1999. The neotectonic setting of late Quaternary transgressions on the Eastern coastal plain of China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 5(4): 41-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Q, LI C X, 2009. The type of quaternary sequence in the East China coastal plain[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 29(4): 39-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Q, ZHANG Y F, YUAN G B, et al. , 2008. Since MIS 3 stage the correlation between transgression and climatic changes in the North Huanghua area, Hebei[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 28(1): 79-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU C, 1984. Surface ancient channels in Hebei Plain[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 39(3): 268-276. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Y H, LI S J, 2004. Significance of lake sediment color for short time scale climate variation[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 19(5): 789-792. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU J, MA Z J, CHEN G G, et al. , 2005. Estimating times of quaternary tectonic episodes in the Bohai sea based on Geomorphic features of surrounding mountainous areas[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 25(6): 700-710. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU L, MIAO Y F, FANG X M, et al. , 2009. Middle Eocene-Oligocene climatic changes recorded by sedimentary colors in the Xining Basin, in northeastern Tibetan Plateau, NW China[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 45(1): 12-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Q M, YUAN G B, ZHANG J Q, et al. , 2011. Stratigraphic division of the late Quaternary strata along the coast of Bohai Bay and its geology significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(8): 1352-1367. (in Chinese with English abstract) XUE C T, 2016. Extents, type and evolution of Luanhe river fan-delta system, China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 36(6): 13-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO L L, XU Q M, YANG J L, et al. , 2016. Sedimentary evolution of BG10 borehole in northern coast of Bohai Bay during Late Cenozoic[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 36(1): 196-207. (in Chinese with English abstract) 陈宏强, 专少鹏, 陈超, 等, 2021. 河北省唐山地区丰台-野鸡坨断裂第四纪活动性—来自14C和磁性地层年代学的证据[J]. 中国地质, 48(2): 605-617. 大港油田地质研究所, 海洋石油勘探局研究院, 同济大学海洋地质研究所, 1985. 滦河冲积扇-三角洲沉积体系[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-164. 方小敏, 奚晓霞, 李吉均, 等, 1997. 中国西部晚中新世气候变干事件的发现及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 42(23): 2521-2524. 高善明, 1981. 全新世滦河三角洲相和沉积模式[J]. 地理学报, 36(3): 303-314. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1981.03.006 高善明, 1982. 对滦河三角洲一些补充和再认识[J]. 地理学报, 37(4): 424-426. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1982.04.009 高善明, 1985. 滦河冲积扇结构和沉积环境[J]. 地理研究, 4(1): 54-62. 河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所, 2017. 中国区域地质志·河北志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-1272. 胡云壮, 张金起, 白耀楠, 等, 2014. 3.45 Ma以来滦河冲积扇中部唐山TD1孔记录的区域构造和气候演化[J]. 古地理学报, 16(2): 249-262. 李从先, 陈刚, 王传广, 等, 1984. 论滦河冲积扇-三角洲沉积体系[J]. 石油学报, 5(4): 27-36. 李从先, 王强, 范代读, 2013. 海洋三角洲[C]//中国沉积学. 北京: 石油工业出版社: 812-905. 李勇, 1987. 丰润-丰台隐伏活动断裂在卫星影象上的表现机制[J]. 地震学刊, 21(1): 39-42. 李元芳, 高善明, 安凤桐, 1982. 滦河三角洲地区第四纪海相地层及其古地理意义的初步研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 13(5): 433-439. 林旭, 刘静, 吴中海, 等, 2021. 渤海钻孔物源示踪和河流沉积物扩散研究: 碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和磷灰石原位地球化学元素双重约束[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 304-316. 马正, 1982. 应用自然电位测井曲线解释沉积环境[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 3(1): 25-40. doi: 10.11743/ogg19820103 秦帮策, 方维萱, 张建国, 等, 2021. 汾河裂谷晋中盆地内第四纪沉积序列与沉积环境恢复[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(6): 1035-1050. 沈吉, 张恩楼, 夏威岚, 2001. 青海湖近千年来气候环境变化的湖泊沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 21(6): 508-513. 宋璠, 侯加根, 张震, 等, 2009. 利用测井曲线研究陆相湖泊沉积微相[J]. 测井技术, 33(6): 589-592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1338.2009.06.020 天津市地质调查研究院, 河北省地质调查院, 2005. 1: 25万天津市幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 王金荣, 刘洪涛, 2004. 测井沉积微相识别方法及应用[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 28(4): 18-20. 王乃昂, 李吉均, 曹继秀, 等, 1999. 青土湖近6000年来沉积气候记录研究: 兼论四五世纪气候回暖[J]. 地理科学, 19(2): 119-124. 汪品先, 闵秋宝, 卞云华, 等, 1981. 我国东部第四纪海侵地层的初步研究[J]. 地质学报, 55(1): 1-13. 王强, 田国强, 1999. 中国东部晚第四纪海侵的新构造背景[J]. 地质力学学报, 5(4): 41-48. 王强, 张玉发, 袁桂邦, 等, 2008. MIS 3阶段以来河北黄骅北部地区海侵与气候期对比[J]. 第四纪研究, 28(1): 79-95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.01.009 王强, 李从先, 2009. 中国东部沿海平原第四系层序类型[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 29(4): 39-51. 吴忱, 1984. 河北平原的地面古河道[J]. 地理学报, 39(3): 268-276. 吴艳宏, 李世杰, 2004. 湖泊沉积物色度在短尺度古气候研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 19(5): 789-792. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.05.016 徐杰, 马宗晋, 陈国光, 等, 2005. 根据周围山地第四纪地貌特征估计渤海第四纪构造活动幕的发生时间[J]. 第四纪研究, 25(6): 700-710. 徐丽, 苗运法, 方小敏, 等, 2009. 青藏高原东北部西宁盆地中始新世-渐新世沉积物颜色与气候变化[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 45(1): 12-19. 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 张金起, 等, 2011. 渤海湾沿岸晚第四纪地层划分及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 85(8): 1352-1367. 薛春汀, 2016. 滦河冲积扇-三角洲的范围和类型及其演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 36(6): 13-22. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2016.06.003 赵琳琳, 胥勤勉, 杨吉龙, 等, 2016. 渤海湾北岸BG10孔晚新生代沉积环境演化过程[J]. 第四纪研究, 36(1): 196-207. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.19 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 石光耀,张运强,张欢,潘志龙,李庆喆,张金龙,张鹏程,吕可欣,闫皓. 河北平原北部蓟州区西南头营剖面地层沉积特征与沉积环境研究. 地质论评. 2024(06): 2113-2126 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:




 百度学术
百度学术









