| Citation: | PENG Bo, ZHANG Hao, YANG Shenghao, et al., 2020. Logging characterization of Carboniferous fracturedvuggy karst reservoirs in the eastern Qaidam Basin. Journal of Geomechanics, 26 (6): 923-931. DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.06.073 |
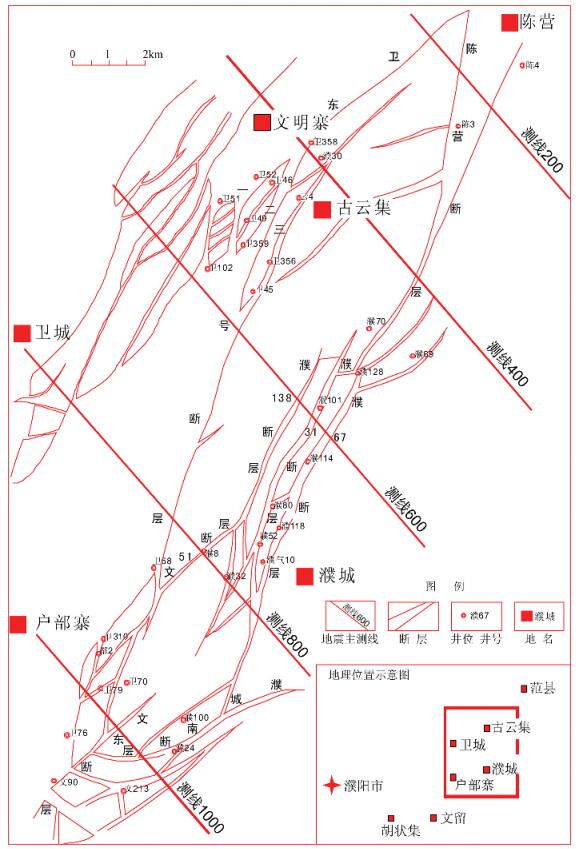
东濮凹陷位于渤海湾盆地西南临清坳陷的南部, 凹陷内发育规模和活动周期不尽相同的断裂, 这些断裂的长期继承性发育不仅控制了东濮凹陷的形成和发育, 也控制了盆地内油气分布与富集[1~7]。濮卫环洼带隶属于东濮凹陷中央隆起带, 为北部卫东-文东断裂系和濮城-陈营断裂系相向下落所形成的“断洼型”负向构造单元, 地质结构复杂, 储层空间展布变化大。目前, 构造高部位的勘探程度较高, 而洼陷带勘探程度还较低。因此, 深入研究该区断裂特征及其对油气运聚的作用, 对滚动勘探开发和隐蔽油气藏勘探具有重要意义。渤海湾及其周缘乃至华北地区油气成藏条件与油气运聚过程研究日亦深入, 已取得许多新成果[8~19]可以借鉴。
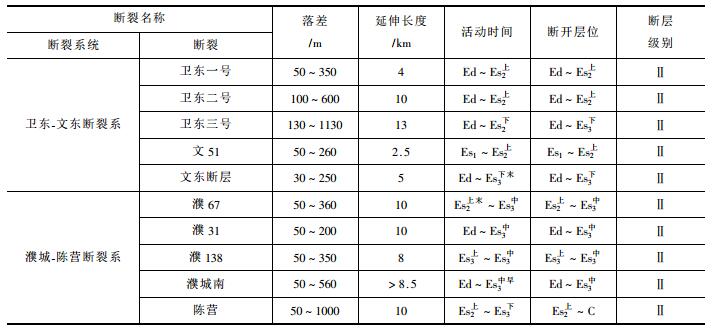
卫东-文东断裂系由复杂的卫东断裂破碎带和文东断层、文51断层等组成(图 1、表 1)。
|
(1) 卫东断层
由3条呈雁行式排列的断层组成, 是一组东倾的滑脱性大断层, 北起古云集地区, 南至卫70井附近消失。断层在沙二下亚段沉积晚期产生, 至东营组沉积末期停止活动。断层走向NNE, 倾向SEE, 倾角15~50°, 落差为50~1130m。剖面上, 在沙三段盐层顺层滑动, 并在盐层内消失, 向下不切割基底。卫东断层下降盘伴生一系列反向“Y”字型次级断层, 从深层到浅层多期发育, 明显控制沙二段、沙一段及东营组等地层的沉积。
(2) 文东断层
文东断层是环洼带南部的西界断层, 向南断层落差逐渐增大。在研究区内, 断层走向NE、倾向SE, 延伸长度5km, 剖面上表现为上缓下陡, 落差为30~250m, 沙三下亚段沉积末期开始活动, 沙三中沉积期强烈活动, 至东营组沉积末期停止活动。
(3) 文51断层
属于卫东断层的伴生断层, 与卫东断层斜交, 呈反“ Y”形, 断层走向NEE, 倾向NWW, 倾角10~40°, 落差50~260m, 南大北小, 延伸长度约2.5km, 于沙二上至沙一期活动, 沙二上沉积期对沉积的控制作用明显。
濮城-陈营断裂系展布于濮城和陈营地区, 发育濮城南断层、濮67断层、濮31断层、濮138断层和陈营断层(见图 1、表 1)。
(1) 濮城南断层
断层走向NE, 倾向NW, 倾角25~60°, 落差50~560m, 延伸长度大于8.5km。断层活动时间为沙三中亚段早期至东营组沉积期。
(2) 濮67断层
濮67断层位于濮城-陈营断裂系的中段, 与濮城南断层和陈营断层首尾相接, 走向NNE, 倾向NWW, 延伸长度约10km。剖面上具有上陡下缓的特点, 倾角20~60°, 断层落差为50~360m, 北大南小。产生于沙三中亚段沉积期, 结束于沙二上亚段沉积末期。
(3) 濮31断层
濮31断层断面下陡上缓, 为濮67断层的伴生断层, 从沙三中后期一直活动至东营组沉积期。断层走向NNE、倾向NWW, 倾角40~60°, 落差50~200m, 延伸长度约10km。
(4) 濮138断层
位于濮31断层的西侧, 断层走向NNE向, 倾向NWW, 倾角40~60°, 落差为50~350m, 延伸长度约8km。剖面上, 向深部交接到濮67断层上。断层活动时间为沙三中-上亚段沉积期。
(5) 陈营断层
陈营断层是一条切割基底的区域性控制沉积断层, SN走向、倾向正西, 断层落差为50 ~1000m, 南端小、北端大, 延伸长度约10km。断裂活动开始于沙三下亚段沉积早期, 结束于沙二上亚段沉积晚期, 沙三下-中期剧烈活动。陈营断层与濮67断层呈雁行式排列, 向北斜交于古云集的云3断层。
目前主要采用断层生长指数、断层落差、断层活动速率等参数来定量表示断层的活动性[20~22]。濮卫环洼带主要断层生长指数和断层落差统计表明, 同一条断层的不同部位、甚至同一部位的不同时期, 其活动性都存在着较大的差异。
卫东断层是卫东-文东断裂系的主体, 沙二上亚段至东营组沉积期间, 持续较强的断裂活动, 是一条长期活动的控洼断层。卫东三号断层活动范围最广泛, 活动强度大, 断层最大落差高达1130m。东营组沉积期, 卫东断层的活动性最强, 断层中段生长指数高达3.5, 在601测线上断层落差达518m。沿走向分段性明显, 断层中段活动强度最大, 向两端活动性减弱(图 2a、b)。
濮城南断层位于濮城-陈营断裂系南端, 活动时间较长, 但整体活动性较弱, 最大落差为560m。沙三中-上亚段沉积期是该断裂主要活动期, 活动范围最广泛, 最大生长指数为1.8, 901测线上的断层落差达460m。沙二下开始活动强度逐渐减弱, 活动范围也缩小至中南部, 至东营期仅在1001测线附近活动, 落差为60m (图 2c、d)。
濮67断层活动时间相对较短, 沙三中-上亚段沉积时期断层活动最为强烈, 沙二下次之, 沙二上活动强度最小。沙三中-上亚段沉积时期, 在701~801测线附近活动性最强, 断层生长指数近1.8, 最大落差达360m, 为濮卫环洼带早期的控洼断裂之一(图 2e、f)。
濮31断层活动时间长, 不同时期、不同部位的断层活动强度变化较大。从断层生长指数来看, 沙三中-上沉积期断层活动性最强, 沙二下开始断层活动相对减弱, 沙一和东营期仅在741测线附近活动, 断层活动微弱。(图 2g)。
濮138断层活动时间较短, 沙三中亚段沉积期断层活动强度弱, 至沙三上亚段沉积期断层活动较为强烈, 且向西南方向活动性增强(图 2h)。
断层和连通砂体是濮卫环洼带最主要的运移通道, 二者共同构成了断层型、断-砂组合型油气输导体系, 它们在平面分布以及成藏模式上均具有较大的差异。
(1) 断层输导体系
该输导体系类型分布较为局限, 仅分布于文明寨的主体高部位、濮城断阶带和卫城卫东断层附近, 其中以文明寨主体部位最具代表性。文明寨主体构造位置较高, 自身生烃能力差, 区内断裂发育, 由于卫东断层沟通了烃源岩和储集层, 油气沿断层面向上垂向运移, 在适当部位聚集成藏, 油气的垂向运移距离远远大于侧向运移距离。
据地层水矿化度对比分析, 濮卫环洼带沙二段地层水具有异常高矿化度, 其值与下部沙三段地层水矿化度较接近。平面上, 异常高矿化度的CaCl2型地层水主要沿濮31、濮城南、卫东断层分布(图 3), 表明这些断层是流体运移的主要通道, 它们沟通了深部的地层, 使高矿化度地层水沿断裂带向上运移。
然而, 断层输导体系若输送大量的油气, 往往需要断层沟通有效烃源岩, 且在烃源岩层系内存在大量的砂体, 这些砂体可以汇聚生烃层系的油气, 然后借助于断层的沟通作用向上部垂向运移, 运移至地层倾角不大的地层进入断层面两侧砂体中形成油气藏。
(2) 断-砂复合输导体系
断层与砂体相互配置构成了濮卫环洼带运载油气的主要输导体系, 分布范围较广, 在卫城和濮城的主体部位最具代表性。目前已经发现的濮城油田、濮城南地区的文213含油气区等, 均具有此类运聚特征。
濮卫环洼带砂岩厚度较大, 断-砂匹配关系良好, 构成了良好的输导体系。该区域的多套砂岩储层呈层状分布于洼陷内及斜坡带, 纵向上每套输导层之上均有泥岩和盐岩盖层封隔, 以侧向输导为主(图 4)。此时, 砂体主要起运移通道的作用, 而断层主要起阻挡油气, 并调节油气运移层系和方向的作用。因此, 随着油气运移层系的不断变浅, 运移动力具有明显的衰减, 在断层活动停止、封堵条件较好的地区聚集成藏, 形成主断层附近的构造-地层油气藏和远离主断层的边部岩性油气藏。
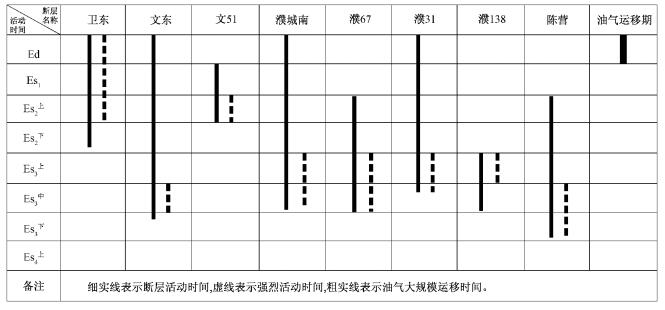
断层活动时间与大规模油气运聚时间的匹配关系, 决定了断层在油气运移成藏中的贡献, 同时也决定了油气藏的分布特征[23]。濮卫环洼带烃源岩生排烃史、油气藏饱和压力及流体包裹体分析表明, 东营组沉积期沙三段烃源岩已经进入生烃门限, 是油气生成和成藏高峰期。东营组地层的剥蚀, 使烃源岩热演化生烃受到抑制甚至停止。新近纪以来研究区再次下沉接受沉积, 至新近纪晚期发生明显的二次生烃作用, 但此时构造活动弱, 生排烃量相对较小①。故该地区成藏关键时期是在东营组沉积时期[24]。
① 高平.濮卫洼陷岩性油气藏成藏规律与精细勘探[R].河南濮阳:中原油田分公司勘探开发科学研究院, 2008.
濮卫环洼带主要断层活动时间与油气运移期对比分析表明(表 2), 卫东断层活动时间长, 油气大规模运移时期强烈活动, 与成藏时间匹配好, 是油气从深层向浅层运移的重要通道。文东、濮31及濮城南等断层活动强度微弱, 活动范围局限, 但与油气大规模运移时间相匹配, 可充当油气运移的有效通道。文51、濮67、濮138和陈营等断层活动时间较早, 东营期已经停止活动或基本停止活动, 主要对油气的聚集成藏起圈闭遮挡的作用。
|
此外, 断层本身活动的不均衡性也使油气运聚成藏情况复杂化。同一条断层(或断层的某一段)在不同时期或不同部位, 由于活动强度的不一致, 对油气成藏所起的作用也不尽相同, 某一时期作为油气运移的通道, 输导油气, 另一时期则成为阻止油气运移的屏障, 使油气在断层附近聚集成藏。
(1) 濮卫环洼带主要发育卫东-文东断裂系和濮城-陈营断裂系, 均为较大规模的二级断裂。卫东-文东断裂系由复杂的卫东断裂破碎带和文东断层、文51断层等组成, 濮城-陈营断裂系自东而西发育陈营断层、濮67断层、濮城南断层、濮31断层和濮138断层。
(2) 卫东、文东、濮城南及濮31等断层活动时间较长, 活动强度不一致, 与成藏时间匹配好, 是油气从深层向浅层运移的重要通道, 文东、濮31及濮城南等断层可充当油气运移的有效通道。
(3) 断层和连通砂体构成了断层型、断-砂组合型油气输导体系。断层型输导体系沟通了烃源岩和储集层, 增强了油气垂向运移能力, 断-砂组合型油气输导体系以侧向输导为主, 断层主要起阻挡油气, 并调节油气运移层系和方向的作用。这些结论对本区油气田滚动勘探开发有重要意义。
|
BAI D Y, JIA B H, ZHONG X, et al., 2012. Study on the deformation of Indosinian Movement in Southeastern Hunan[J]. Geological Review, 58(1):19-29.(in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91067X/201201/40556730.html
|
|
CHEN A Q, CHEN H D, HOU M C, et al., 2011. The Middle-Late Triassic Event sediments in Ordos Basin:Indicators for EpisodeⅠof the Indosinian Movement[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(10):1681-1690. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_acta-geologica-sinica_thesis/0201252706567.html
|
|
CHEN S, 2007. The research on characteristics of Ordovician palaeokarst and reservoir in Tahe Oilfield[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
|
CHEN X G, WU H X, LI Y, et al., 2019. Influences of Indosinian structures on later structural deformation and sedimentation in Piedmont of Western Kunlun Mountains[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 40(1):27-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XJSD201901005.htm
|
|
CUI L, 2019. Logging response characteristics of karst formation in upper Ordovician assemblage of Daniudi gas field[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 33(5):26-30, 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYHN201905007.htm
|
|
DAI X F, ZHANG M, JIANG Q C, et al., 2017. Karst reservoirs seismic prediction of Lower Permian Maokou Formation in central Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(1):79-88. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(17)30010-1
|
|
De JOUSSINEAU G, BARREIT K R, ALESSANDRONI M, et al., 2016. Organization, flow impact and modeling of natural fracture networks in a karstified carbonate bitumen reservoir:An example in the Grosmont Formation of the Athabasca Saleski leases, Alberta, Canada[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 64(2):291-308. doi: 10.2113/gscpgbull.64.2.291
|
|
DING Z W, WANG R J, CHEN F F, et al., 2020. Origin, hydrocarbon accumulation and oil-gas enrichment of fault-karst carbonate reservoirs:A case study of Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in South Tahe area of Halahatang oilfield, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(2):306-317. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60048-9
|
|
GAO Z Q, FAN T L, 2015. Unconformities and their influence on lower Paleozoic petroleum reservoir development in the Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 133:335-351. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.06.015
|
|
HE J, FANG S X, HOU F H, et al., 2013. Vertical zonation of weathered crust ancient karst and the reservoir evaluation and prediction-A case study of M55-M51 sub-members of Majiagou Formation in gas fields, central Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(5):534-542. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s1876380413600750
|
|
HUANG S P, JIANG Q C, FENG Q F, et al., 2019. Type and distribution of Mid-Permian Maokou Formation karst reservoirs in southern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 46(2):293-300. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(19)60009-1
|
|
KANG Y Z, 2020. New theory of marine oil formation and discover of tahe oilfield, northern tarim basin[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 8(3):201-206. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020302&flag=1
|
|
LI Y, KANG Z J, XUE Z J, et al., 2018. Theories and practices of carbonate reservoirs development in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(4):669-678. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s1876380418300740
|
|
LI Z X, GAO J, ZHENG C, et al., 2015. Present-day heat flow and tectonic-thermal evolution since the late Paleozoic time of the Qaidam basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(10):3687-3705. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201510021.htm
|
|
LI Z X, QIU N S, MA Y S, et al., 2017. The tectono-thermal evolution in the eastern Qaidam Basin, Northwest China since the Paleozoic[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 24(3):157-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/317829118_The_tectono-thermal_evolution_in_the_eastern_Qaidam_Basin_Northwest_China_since_the_Paleozoic
|
|
LIU K, LI Z X, SHI X B, et al., 2020. Late Hercynian-Indosinian denudation and uplift history in the eastern Qaidam Basin:constraints form multiple thermometric indicator sand sedimentary evidences[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(4):1403-1421. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
|
LUAN S L, 2018. Sedimentary characteristics of Carboniferous in Chengqianggou-Ximeigou area in Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Shengli College, China University of Petroleum, 32(1):16-18.(in Chinese)
|
|
LUO B, YANG Y, LUO W, et al., 2017. Controlling factors of Dengying Formation reservoirs in the central Sichuan paleo-uplift[J]. Petroleum Research, 2(1):54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ptlrs.2017.06.001
|
|
LUO S C, 2015. Restoration and significance of karst paleogeomorphology of Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University. (in Chinese)
|
|
MA Y S, YIN C M, LIU C L, et al., 2014. Evaluation of oil and gas potential of carboniferous in Qaidam Basin[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing of House, 129-147. (in Chinese)
|
|
PENG B, LIU C L, LI Z X, et al., 2016a. The discovery and genetic analysis of grape-shaped hole of the Carboniferous in Eastern Qaidam Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(5):66-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DXQY201605008.htm
|
|
PENG B, LIU C L, LI Z X, et al., 2016b. Discovery of Palaeozoic karsts in the Qaidam Basin and their oil and gas prospects[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 90(5):1919-1920. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12832
|
|
RUSSEL-HOUSION, GRAY K, 2014. Paleokarst in the Grosmont formation and reservoir implications, Saleski, Alberta, Canada[J]. Interpretation, 2:SF29-SF50. doi: 10.1190/INT-2013-0187.1
|
|
SHEN A J, ZHAO W Z, HU A P, et al., 2015. Major factors controlling the development of marine carbonate reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 42(2):597-608.
|
|
TAN Y J, QIU R Z, XIAO Q H, et al., 2014. Indosinian Movement characteristics and its significance in China and neighboring areas[J]. Coal Geology of China, 26(8):8-14, 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT201408004.htm
|
|
WANG L, LI Z X, LIU C L, et al., 2019.The carboniferous source rock maturity evolution in the delingha depression in the qaidam basin, northwest china[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 25(3):370-381. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190307&flag=1
|
|
WANG X X, CUI D Y, SUN C H, et al., 2019.Characteristics of strike-slip fault and its controlling on oil in block a of the halahatang oilfield, Tarim basin[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6):1058-1067. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190606&flag=1
|
|
WEI X H, REN J F, ZHAO J X, et al., 2018. Paleogeomorphy evolution of the Ordovician weathering crust and its implication for reservoir development, eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Research, 3(1):77-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ptlrs.2018.03.004
|
|
WEI X J, MA Y S, LI Z X, et al., 2018. High-frequency alternations and driving mechanisms of clastic-carbonate successions in the Upper Carboniferous, northern Qaidam Basin[J].Journal of Palaeogeography, 20(3):409-422. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GDLX201803005.htm
|
|
XIAO D, TAN X C, XI A H, et al., 2016. An inland facies-controlled eogenetic karst of the carbonate reservoir in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation, southern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 72:218-233. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.001
|
|
YIN Z W, LI J L, 2013. The prediction method of ancient weatnering crust karst reservoir in Leikoupo Formation of YB Area[J]. Computing Technology for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 35(3):331-337. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-WTHT201303014.htm
|
|
YU H Z, 2019.Characteristics and influencing factors of carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in hashan area, northwestern margin of the Junggar basin[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 25(2):206-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190206&flag=1
|
|
ZENG X, TIAN J X, ZHANG G Q, et al., 2018. Main types and hydrocarbon exploration direction of the paleo-uplifts in the qaidam basin[J].Journal of Geomechanics, 24(3):381-390. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180309&flag=1
|
|
ZHANG S D, REN X G, LUO L, et al., 2019. Logging-based identification and evaluation of karst fractures in the eastern Right Bank of the Amu Darya River, Turkmenistan[J]. Natural Gas Endustry B, 6(1):58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2019.01.008
|
|
ZHAO J L, GONG Z W, LI G, et al., 2012. A review and perspective of identifying and evaluating the logging technology of fractured carbonate reservoir[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 27(2):537-547. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
|
ZHAO W Z, SHEN A J, PAN W Q, et al., 2013. A research on carbonate karst reservoirs classification and its implication on hydrocarbon exploration:Cases studies from Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(9):3213-3222. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_acta-petrologica-sinica_thesis/0201252019573.html
|
|
ZHU D Y, JIN Z J, ZHANG R Q, et al., 2014. Characteristics and developing mechanism of Sinian Dengying Formation dolomite reservoir with multi-stage karst[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(6):335-345. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286819423_Characteristics_and_developing_mechanism_of_Sinian_Dengying_Formation_dolomite_reservoir_with_multi-stage_karst
|
|
柏道远, 贾宝华, 钟响, 等, 2012.湘东南印支运动变形特征研究[J].地质论评, 58(1):19-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.01.002
|
|
陈安清, 陈洪德, 侯明才, 等, 2011.鄂尔多斯盆地中-晚三叠世事件沉积对印支运动Ⅰ幕的指示[J].地质学报, 85(10):1681-1690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201110012.htm
|
|
陈胜, 2007.塔河油田奥陶系古岩溶及储层特征研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学.
|
|
程晓敢, 吴鸿翔, 李勇, 等, 2019.西昆仑山前印支运动期构造对后期构造和沉积的影响[J].新疆石油地质, 40(1):27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201901005.htm
|
|
崔璐, 2019.大牛地气田奥陶系上组合岩溶地层测井响应特征[J].石油地质与工程, 33(5):26-30, 35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201905007.htm
|
|
何江, 方少仙, 侯方浩, 等, 2013.风化壳古岩溶垂向分带与储集层评价预测:以鄂尔多斯盆地中部气田区马家沟组马五5-马五1亚段为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 40(5):534-542. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201305005.htm
|
|
康玉柱, 2002.海相成油新理论与塔河大油田的发现[J].地质力学学报, 8(3):201-206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2002.03.002
|
|
刘奎, 李宗星, 施小斌, 等, 2020.柴达木盆地东部晚海西-印支期剥蚀量与隆升历史:多种古温标与沉积学证据的制约[J].地球物理学报, 63(4):1403-1421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX202004013.htm
|
|
李阳, 康志江, 薛兆杰, 等, 2018.中国碳酸盐岩油气藏开发理论与实践[J].石油勘探与开发, 45(4):669-678. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201804013.htm
|
|
李宗星, 高俊, 郑策, 等, 2015.柴达木盆地现今大地热流与晚古生代以来构造-热演化[J].地球物理学报, 58(10):3687-3705. doi: 10.6038/cjg20151021
|
|
李宗星, 邱楠生, 马寅生, 等, 2017.柴达木盆地东部古生代以来构造-热演化[J].地学前缘, 24(3):157-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201703018.htm
|
|
栾守亮, 2018.柴达木盆地城墙沟-石灰沟地区石炭系沉积特征[J].中国石油大学胜利学院学报, 32(1):16-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5935.2018.01.004
|
|
罗思聪, 2015.四川盆地灯影组岩溶古地貌恢复及意义[D].成都: 西南石油大学.
|
|
马寅生, 尹成明, 刘成林, 等, 2014.柴达木盆地石炭系油气资源潜力评价[M].北京:地质出版社:129-147.
|
|
彭博, 刘成林, 李宗星, 等, 2016.柴达木盆地东部石炭系葡萄状灰岩缝洞的发现及成因分析[J].地学前缘, 23(5):66-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201605008.htm
|
|
谭永杰, 邱瑞照, 肖庆辉, 等, 2014.中国及邻区印支运动特征及其意义[J].中国煤炭地质, 26(8):8-14, 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2014.08.03
|
|
王利, 李宗星, 刘成林, 等, 2019.柴达木盆地德令哈坳陷石炭系烃源岩成熟度演化史[J].地质力学学报, 25(3):370-381. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190307&flag=1
|
|
王新新, 崔德育, 孙崇浩, 等, 2019.哈拉哈塘油田A地区断裂特征及其控油作用[J].地质力学学报, 25(6):1058-1067. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190606&flag=1
|
|
魏小洁, 马寅生, 李宗星, 等, 2018.柴达木盆地北缘上石炭统碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩高频转换过程及驱动机制[J].古地理学报, 20(3):409-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201803005.htm
|
|
尹正武, 李金磊, 2013. YB地区雷口坡组古风化壳岩溶储层预测方法[J].物探化探计算技术, 35(3):331-337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2013.03.15
|
|
于洪洲, 2019.准西北缘哈山地区石炭系火山岩储层特征及影响因素[J].地质力学学报, 25(2):206-214. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190206&flag=1
|
|
曾旭, 田继先, 张国卿, 等, 2018.柴达木盆地古隆起主要类型及油气勘探方向[J].地质力学学报, 24(3):381-390. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180309&flag=1
|
|
赵军龙, 巩泽文, 李甘, 等, 2012.碳酸盐岩裂缝性储层测井识别及评价技术综述与展望[J].地球物理学进展, 27(2):537-547. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.1004-2903.2012.02.017
|
|
赵文智, 沈安江, 潘文庆, 等, 2013.碳酸盐岩岩溶储层类型研究及对勘探的指导意义:以塔里木盆地岩溶储层为例[J].岩石学报, 29(9):3213-3222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201309020.htm
|
|
朱东亚, 金之钧, 张荣强, 等, 2014.震旦系灯影组白云岩多级次岩溶储层叠合发育特征及机制[J].地学前缘, 21(6):335-345. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201406038.htm
|


|

|