ANALYSIS ON THE CHANGE OF INFLUENCE FACTORS ON SLIPPING DISPLACEMENT OF LANDSLIDES IN DUJIANGYAN AREA BEFORE AND AFTER THE WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE
-
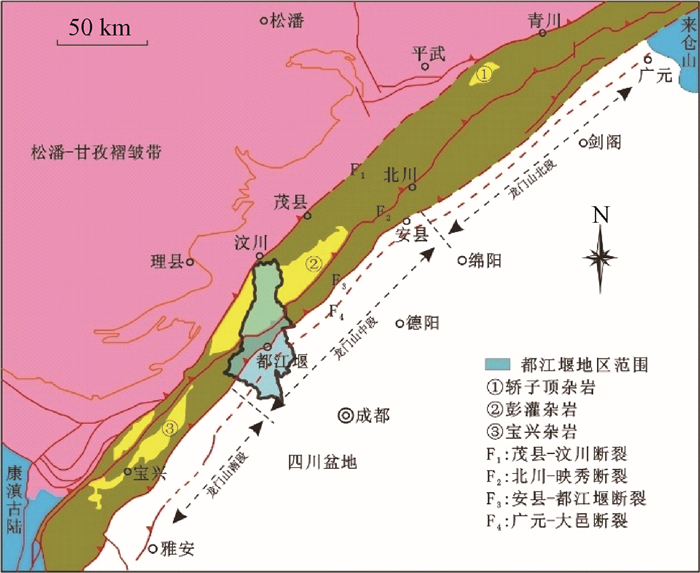
摘要: 滑坡滑动距离作为滑坡防灾减灾的主要评价指标之一,不仅受滑坡体积和落差的影响,还与滑坡运动的地质环境作用相关。本文在对都江堰地区51个地震滑坡、16个降雨滑坡详细调查编目的基础上,采用数理统计方法分析了斜坡原始坡度、滑坡前后缘高差、滑坡平面形态、体积、滑体平均厚度及坡面摩擦系数等6个因素与滑坡水平滑动距离的相关性,借此厘清了汶川Ms8.0级大地震前后不同因素对不同类型滑坡运动的贡献大小,进而构建了不同成因类型滑坡的滑动距离预测关系式,可为龙门山区的滑坡防灾减灾工作提供参考。研究表明:影响都江堰地区地震滑坡运动距离的主要因素有滑坡体积(lgV)、斜坡原始坡度(α)、滑坡平面形态(R)和滑坡前后缘高差(ΔH);而控制降雨滑坡运动距离的主要因素为滑坡前后缘高差(ΔH)、滑坡体积(lgV)、斜坡坡度(α)和斜坡表面摩擦系数(μ);汶川地震后,影响该地区降雨滑坡滑动能力的因素发生了变异,各因素与滑坡滑动距离的相关性较弱,显示出其贡献率在急剧减弱,仅滑坡体积(lgV)与滑动距离的相关性较强。Abstract: Slipping displacement of landslide is one of the most important assessment indexes for prevention and mitigation of landslide disaster, which is not only controlled by landslide volume and drop but also related to the influence of topographical environment.On the basis of detailed field investigation and inventory for 51 seismic-induced landslides and 16 rainfall-induced landslides seated in Dujiangyan area, the correlation between six factors and horizontal slipping displacement of landslides are analyzed through mathematical statistic method, factors including depositional gradient of slope, ridge height difference before and after the earthquake, plane shape, volume, and average thickness of landslide mass and friction coefficient of slope surface. Afterwards, the influence of different factors on different types of landslides before and after Wenchuan earthquake are sort out, and the predictive formulas of slipping displacement due to different causes are built which may support the disaster mitigation in the future. The preliminary conclusions reveal that slipping displacements of seismic-induced landslides are mainly affected by landslide volume(lgV), depositional gradient of slope(α), plane shape(R) and ridge height difference before and after the earthquake(ΔH); while rainfall-induced landslides are mainly affected by ridge height difference before and after the earthquake(ΔH), landslide volume(lgV), depositional gradient of slope(α) and friction coefficient of slope surface(μ). After the Wenchuan earthquake, the factors affecting the sliding of rainfall-induced landslides are changing with a relatively low correlation with slipping displacement, showing that their influence are decreasing and only landslide volume(lgV) still stays a strong correlation.
-
图 6 滑坡滑动距离参数定义示意图
(据文献[29]改)
Figure 6. Sketch of landslide deposit and failing mass and definition of the parameters H, L, Hmax and Lmax
表 1 地震滑坡基本信息表
Table 1. Basic information of earthquake-induced landslides
编号 名称 坡度/° ΔH/m L/m R h/m lgV 发生时间 1 虹口乡夏家坪滑坡 45 356 282.84 2.35 3 5.18 2008.5.12 2 虹口乡寨子坡滑坡 66 55 40.67 0.67 2 4.35 2008.5.12 3 虹口乡乱草坟滑坡 60 22 15 0.25 2 3.73 2008.5.12 4 虹口乡水响沟滑坡 60 15 15 0.25 2 3.73 2008.5.12 5 虹口乡黑泥湾1号滑坡 38 40 63.04 0.53 9 4.91 2008.5.12 6 虹口乡黑泥湾2号滑坡 42 32 44.59 0.43 10 4.8 2008.5.12 7 虹口乡塔子坪滑坡 35 250 491.49 4.29 20 6.1 2008.5.12 8 虹口乡虹口坪滑坡 57 17 24.51 0.67 4 3.94 2008.5.12 9 虹口乡甜竹坪1号滑坡 42 20 36.41 0.61 3 3.94 2008.5.12 10 虹口乡甜竹坪2号滑坡 36 30 64.72 0.5 4 4.58 2008.5.12 11 虹口乡黄金坪滑坡 45 155 148.49 1.24 5 5.13 2008.5.12 12 虹口乡木瓜园滑坡 25 50 108.76 0.34 6 5.28 2008.5.12 13 虹口乡陈家坪滑坡 34 28 49.74 0.67 4 4.2 2008.5.12 14 龙池镇汤家沟滑坡 51 65 64.82 1.2 4 4.42 2008.5.12 15 龙池镇半边街滑坡 68 38 14.98 0.2 3 4.26 2008.5.12 16 龙池镇川主坪滑坡 40 50 153.21 0.95 5 5.2 2008.5.12 17 龙池镇蜂桶岩南部滑坡 62 60 35.21 1.67 2 3.7 2008.5.12 18 龙池镇关门石1号滑坡 45 40 56.57 0.27 8 5.16 2008.5.12 19 龙池镇桂花树1号滑坡 21 30 65.35 0.32 8 4.96 2008.5.12 20 龙池镇桂花树2号滑坡 35 26 98.3 0.86 8 5 2008.5.12 21 龙池镇河边楼外楼滑坡 45 40 49.5 1.4 3 3.89 2008.5.12 22 龙池镇李家山1号滑坡 32 80 127.21 1.25 3 4.61 2008.5.12 23 龙池镇李家山2号滑坡 42 16 81.75 0.61 7 5.02 2008.5.12 24 龙池镇临桥院滑坡 60 25 40 0.8 2 4.08 2008.5.12 25 龙池镇沙子坡1号滑坡 42 25 96.61 0.48 15 5.33 2008.5.12 26 龙池镇吴家坡滑坡 46 120 222.29 2.13 7 5.4 2008.5.12 27 龙池镇大树子1号滑坡 45 62 21.21 0.38 4 3.86 2008.5.12 28 龙池镇大树子2号滑坡 45 50 42.43 2 3 3.62 2008.5.12 29 龙池镇大树子3号滑坡 45 105 95.46 0.68 5 5.01 2008.5.12 30 龙池镇干沟口滑坡 45 10 10.61 0.21 3 3.38 2008.5.12 31 龙池镇老房子滑坡 40 50 114.91 0.79 5 5.03 2008.5.12 32 龙池镇老龙溪场滑坡 45 60 21.21 0.43 5 3.9 2008.5.12 33 龙池镇楠木槽滑坡 50 60 64.28 0.5 10 5.18 2008.5.12 34 龙池镇小湾3号滑坡 30 70 147.22 0.63 5 5.24 2008.5.12 35 向峨乡白岩山2号滑坡 40 30 137.89 0.51 7 5.52 2008.5.12 36 向峨乡木瓜园滑坡 44 50 43.16 0.75 8 4.46 2008.5.12 37 向峨乡龙竹村小学滑坡 42 80 111.47 1.88 2 4.26 2008.5.12 38 向峨乡薛家坡滑坡 50 70 96.42 1.88 8 4.86 2008.5.12 39 向峨乡火烧山滑坡 55 70 74.56 1.3 12 5.06 2008.5.12 40 向峨乡狮子山滑坡 44 75 129.48 1.2 12 5.39 2008.5.12 41 向峨乡苏家梁滑坡 40 295 153.21 1.67 8 5.16 2008.5.12 42 向峨乡张飞山2号滑坡 38 50 94.56 1.09 7 4.84 2008.5.12 43 向峨乡张飞山滑坡 42 90 163.49 2.75 15 5.3 2008.5.12 44 紫平铺镇大沟边2号滑坡 40 140 268.12 1.3 12 5.93 2008.5.12 45 紫平铺镇雷打石碑滑坡 45 50 49.5 1.4 2 3.72 2008.5.12 46 紫平铺镇梨树坪滑坡 24 40 82.22 1.8 5 4.22 2008.5.12 47 紫平铺镇石厂湾滑坡 19 9 73.75 2.6 3 3.71 2008.5.12 48 紫平铺镇白果树滑坡 32 80 127.21 1.07 8 4.98 2008.5.12 49 紫平铺镇杆杆桥滑坡 43 50 58.51 1.33 6 4.33 2008.5.12 50 紫平铺镇和尚岩滑坡 29 80 120.7 1.15 12 5.17 2008.5.12 51 紫平铺镇紫坪村水子地滑坡 38 80 94.56 1.2 3 4.43 2008.5.12 表 2 降雨滑坡基本信息表
Table 2. Basic information of rainfall-induced landslides
编号 名称 坡度/° ΔH/m H: L R h/m lgV 水平滑距L/m 发生时间 1 大观镇高家坪滑坡 26 50 0.397 2.00 10 4.869 125.831 2005 2 灌口镇灵岩村3组滑坡 32 190 0.605 1.15 10 5.948 313.778 2003 3 灌口镇鲜家沟滑坡 31 80 0.583 1.45 12 5.200 137.147 2003 4 灌口镇竹林寺2号滑坡 36 30 0.674 0.50 4 4.255 44.496 2004 5 灌口镇万张沟滑坡 30 40 0.659 1.16 2 3.806 60.622 2003 6 蒲阳镇小石槽沟滑坡 33 17 0.579 1.75 2 3.000 29.353 2005 7 蒲阳镇磨刀沟滑坡 35 80 0.651 0.75 3 4.813 122.873 2002 8 蒲阳镇石槽沟滑坡 37 24 0.667 0.37 3 4.079 35.939 2005 9 青城山镇刘家大湾滑坡 34 90 0.904 2.40 1.5 3.829 99.485 2003 10 青城山镇戴家桥滑坡 38 45 0.951 0.85 2 3.806 47.281 2002 11 青城山镇泰安寺滑坡 42 20 0.538 1.25 2 3.477 37.157 2008.5.12 12 青城山镇五里村边坡滑坡 55 15 0.087 3.75 3 4.732 172.073 2008.5.12 13 向峨乡石瓮河滑坡 40 145 0.901 1.10 20 5.777 160.869 2008.5.12 14 紫坪铺镇大沟边滑坡 40 50 0.858 1.81 4 3.964 58.219 2008.5.12 15 虹口乡黑泥湾滑坡 40 176 1.573 0.42 20 5.954 111.842 2013.7.4 16 虹口乡千丈林滑坡 37 150 1.016 1.24 23 5.845 147.564 2013.7.4 -
[1] Kent P E. The transport mechanism in catastrophic rock falls[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1966, 74(1):79~93. doi: 10.1086/627142 [2] Shreve R L. The Blackhawk Landslide[M]. Boulder, CO:Geological Society of America, 1968, 1~48. [3] Shreve R L. Leakage and fluidization in air-layer lubricated avalanches[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1968, 79(5):653~658. http://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/79/5/653.abstract [4] Erismann T H. Mechanisms of large landslides[J]. Rock Mechanics, 1979, 12(1):15~46. doi: 10.1007/BF01241087 [5] 邢爱国, 殷跃平, 齐超, 等.高速远程滑坡气垫效应的风洞模拟试验研究[J].上海交通大学学报, 2012, 46(10):1642~1646. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT201210020.htmXING Aiguo, YIN Yueping, QI Chao, et al. Study on the wind tunnel testing of air cushion effect of high-speed and long-runoutlandslide[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012, 46(10):1642~1646. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT201210020.htm [6] 程谦恭, 王玉峰, 朱圻, 等.高速远程滑坡超前冲击气浪动力学机理[J].山地学报, 2011, 29(1):70~80. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90138A/201101/37188918.htmlCHENGQiangong, WANGYufeng, ZHUQi, et al. Dynamics of the airblasts generated by rock avalanches[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2011, 29(1):70~80. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90138A/201101/37188918.html [7] Eisbacher G H. Cliff collapse and rock avalanches (sturzstroms) in the Mackenzie Mountains, Northwestern Canada[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1979, 16(2):309~334, doi: 10.1139/t79-032. [8] Davies T R, McSaveney M J, Hodgson K A. A fragmentation-spreading model for long-runout rock avalanches[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1999, 36(6):1096~1110, doi: 10.1139/t99-067. [9] Okura Y, Kitahara H, Sammori T, et al. The effects of rockfall volume on runoutdistance[J]. Engineering Geology, 2000, 58(2):109~124. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00049-1 [10] HsüK J. Catastrophic Debris Streams (Sturzstroms) generated by rockfalls[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1975, 86(1):129~140. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1975)86<129:CDSSGB>2.0.CO;2 [11] Davies T R H. Spreading of rock avalanche debris by mechanical fluidization[J]. Rock Mechanics, 1982, 15(1):9~24. doi: 10.1007/BF01239474 [12] Sassa K. Geotechnical model for the motion of landslides[A]. Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Landslides[C].Publrotterdam:A Abalkema, 1988, 37~55. [13] Abele G, ErismannTH, HeubergerH. Rockslide movement supported by the mobilization of groundwater-saturated valley floor sediments[J]. ZeitschriftfurGeomorphologie, 1997, 41(1):1~20. [14] Deline P. Interactions between rock avalanches and glaciers in the Mont Blanc massif during the late Holocene[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(11/12):1070~1083. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S027737910800293X [15] 王玉峰, 程谦恭, 张柯宏, 等.高速远程滑坡裹气流态化模型试验研究[J].岩土力学, 2014, 35(10):2775~2786. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201410006WANG Yufeng, CHENG Qiangong, ZHANG Kehong, et al. Study of fluidized characteristics of rock avalanches undereffect of entrapped air[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(10):2775~2786. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201410006 [16] 张明, 殷跃平, 吴树仁, 等.高速远程滑坡-碎屑流运动机理研究发展现状与展望[J].工程地质学报, 2010, 18(6):805~817. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_gcdzxb201006001.aspxZHANG Ming, YIN Yueping, WU Shuren, et al. Development status and prospects of studies on kinematics of longrunoutrockavalanches[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(6):805~817. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_gcdzxb201006001.aspx [17] 李秀珍, 孔纪名. "5·12"汶川地震诱发滑坡的滑动距离预测[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2010, 42(5):243~249. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scdxxb-gckx201005034LIXiuzhen, KONG Jiming. Runout distance estimation of landslides triggered by"5·12"Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2010, 42(5):243~249. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/scdxxb-gckx201005034 [18] 樊晓一, 乔建平, 韩萌, 等.灾难性地震和降雨滑坡的体积与运动距离研究[J].岩土力学, 2012, 33(10):3051~3058. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94551X/201210/43556250.htmlFAN Xiaoyi, QIAO Jianping, HAN Meng, et al. Volumes and movement distances of earthquake and rainfall-inducedcatastrophic landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(10):3051~3058. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94551X/201210/43556250.html [19] 樊晓一, 乔建平. "坡"、"场"因素对大型滑坡运动特征的影响[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(11):2337~2347. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=35933243FAN Xiaoyi, QIAO Jianping. Influence of landslide and ground factors on large-scale landslide movement[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(11):2337~2347. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=35933243 [20] 樊晓一, 冷晓玉, 段晓冬.坡脚型与偏转型地震滑坡运动距离及地形因素作用[J].岩土力学, 2015, 36(5):1380~1388. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201505021FAN Xiaoyi, LENGXiaoyu, DUAN Xiaodong. Influence of topographical factors on movement distances of toe-typeand turning-type landslides triggered by earthquake[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(5):1380~1388. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201505021 [21] 孟华君, 姜元俊, 张向营, 等.地震扰动区碎石土滑坡滑动能力分析及预测[J].人民长江, 2017, 48(14):45~49, 54. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91504X/201714/672738947.htmlMENG Huajun, JIANG Yuanjun, ZHANGXiangying, et al. Landslide sliding ability analysis and forecast of gravel soil landslide in seismic zone[J]. YangtzeRiver, 2017, 48(14):45~49, 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91504X/201714/672738947.html [22] Scheidegger A E. On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides[J]. Rock Mechanics, 1973, 5(4):231~236. doi: 10.1007/BF01301796 [23] 张永双, 石菊松, 孙萍, 等.汶川地震内外动力耦合及灾害实例[J].地质力学学报, 2009, 15(2):131~141. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090203&flag=1ZHANG Yongshuang, Shi Jusong, Sun Ping, et al. Coupling between endogenic and exogenic geological processes in the Wenchuan earthquake and example analysis of geo-hazards[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 15(2):131~141. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090203&flag=1 [24] 张永双, 雷伟志, 石菊松, 等.四川5·12地震次生地质灾害的基本特征初析[J].地质力学学报, 2008, 14(2):109~116. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080211&flag=1ZHANG Yongshuang, LEI Weizhi, SHI Jusong, et al. General characteristics of 5·12 earthquake-induced geohazards in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2008, 14(2):109~116. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080211&flag=1 [25] 何宏林, 孙昭民, 魏占玉, 等.汶川Ms8.0地震地表破裂带白沙河段破裂及其位移特征[J].地震地质, 2008, 30(3):658~673. doi: 10.1360/N972015-00602HEHonglin, SUNZhaomin, WEIZhanyu, et al. Ruptureofthe Ms 8.0 Wenchuanearthquake along Baishaheriver[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2008, 30(3):658~673. doi: 10.1360/N972015-00602 [26] 许强, 裴向军, 黄润秋, 等.汶川地震大型滑坡研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 2009, 2~18.XU Qiang, PEI Xiangjun, HUANG Runqiu, et al. Large-Scale Landslides Induced by the WenchuanEarthquake[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2009, 2~18. (in Chinese) [27] 孟华君, 乔建平, 田宏岭, 等.小区域地震地质灾害空间分布特点分析方法探讨[J].工程地质学报, 2014, 22(1):14~23. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98122X/201401/49934125.htmlMENG Huajun, QIAO Jianping, TIAN Hongling, et al. Method discussion on spatial distribution analysis of earthquake induced geohazards in small region[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(1):14~23. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98122X/201401/49934125.html [28] Yin Y P, Cheng Y L, Liang J T, et al. Heavy-rainfall-induced catastrophic rockslide-debris flow at Sanxicun, Dujiangyan, after the WenchuanMs 8.0 earthquake[J]. Landslides, 2016, 13(1):9~23. doi: 10.1007/s10346-015-0554-9 [29] Legros F. The mobility of long-runoutlandslides[J]. Engineering Geology, 2002, 63(3/4):301~331. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0013795201000904 [30] 黄润秋.汶川地震地质灾害研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010.HUANG Runqiu. Geohazard Assessment of the Wenchuan Earthquake[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2010. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: