PETROGENESIS AND TECTONIC IMPLICATIONS OF TWO TYPES EARLY SILURIAN GRANITES IN EAST JUNGGAR
-
摘要: 哈尔里克山西段早志留世二长花岗岩和正长花岗岩呈北西西向带状展布,侵入奥陶系塔水组(O1-2t),LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为438.8±2.3~435.8±3.1 Ma。岩石高硅(SiO2含量73.0%~77.8%)、富钾(K2O含量3.31%~4.26%)、低镁(MgO含量0.03%~0.59%),铝饱和指数A/CNK值1.02~1.08,属高钾钙碱性弱过铝质岩石。二长花岗岩轻重稀土分馏显著,Eu异常中等,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti、P,富集Rb、Ba、K,表现为分异的Ⅰ型花岗岩特征,源区为基性下地壳;正长花岗岩强烈亏损Eu、P、Ti、Sr,不同程度富集Rb、K、Zr、Hf,表现为A型花岗岩特征,其源区为缺水的浅部长英质地壳。结合区域地层不整合资料,认为东准噶尔地区早志留世为后碰撞环境而非岛弧带,后碰撞软流圈上涌带来的热熔融准噶尔年轻地壳形成了岩性丰富的东准噶尔志留纪后碰撞岩浆岩组合。Abstract: The early Silurian monzogranite and syenogranite are located in the western section of Harlik Mountain with a NWW-trending, which intrude into the Ordovician Tashui Formation (O1-2t). The LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating shows their emplacement ages are 438.8±2.3 Ma~435.8±3.1 Ma. The rocks have high contents of silicon (SiO2=73.0~77.8%)and potassium (K2O=3.31~4.26%), and low contents of magnesium (MgO=0.03~0.59%), with moderate aluminum saturation index (A/CNK=1.02~1.08), which show that the rocks are high-K calc-alkaline, weakly peraluminium series. Monzogranites exhibit strongly fractionated REE patterns with moderate negative Eu anomalies, and they are depleted in Nb, Ta, Ti, P, but enriched in Rb, Ba, K, showing notable fractionated Ⅰ-type granitoids with mafic lower continental crust as a potential magma source. Syenogranites show remarkably depletion of Eu, P, Ti and Sr, and enrichment of Rb, K, Zr and Hf, showing A-type granites affinity, whose magma source maybe the dehydrated felsic upper continental crust. Combined with the stratigraphic unconformity in this region, we propose that the East Junggar is in a post-collisional setting rather than arc-related setting during the early Silurian. The upwelling asthenosphere provided enhanced heat flux and triggered the partial melting of the juvenile crust, and resulted in the generation of various Silurian post-collisional granites in East Jungga.
-
Key words:
- Harlik /
- Silurian /
- A-type granite /
- post-collision
-
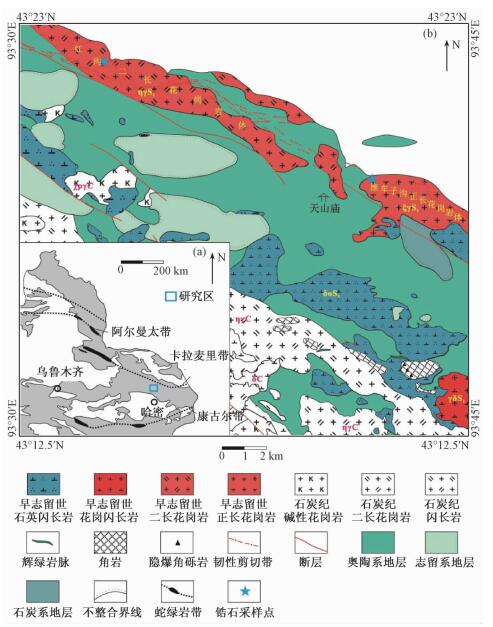
图 1 哈尔里克山西段早志留世酸性侵入岩带地质简图
a-新疆北部主要蛇绿岩带分布图[14];b-哈尔里克山天山庙地质简图
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the early Silurian acid intrusive rock belt in western Harlik
表 1 二长花岗岩及正长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素测定结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb analytical data of monzogranite granite and syenogranite
测试点号 含量/10-6 同位素比值 rho 年龄/Ma 谐和度 TotPb 232Th 238U Th/U 207Pb/U235 1σ 206Pb/U238 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 6-1-1 88 256 175 1.46 0.54530 0.02537 0.07087 0.00096 0.29070 441.9 16.7 441.4 5.8 99% 6-1-2 118 323 279 1.16 0.55938 0.02303 0.07107 0.00081 0.27717 451.1 15.0 442.6 4.9 98% 6-1-3 107 298 328 0.91 0.56076 0.02145 0.06349 0.00064 0.26344 452.0 14.0 396.8 3.9 86% 6-1-4 135 378 267 1.41 0.57805 0.02126 0.07067 0.00093 0.35683 463.2 13.7 440.2 5.6 94% 6-1-5 199 531 454 1.17 0.59651 0.02125 0.07140 0.00070 0.27347 475.0 13.5 444.6 4.2 93% 6-1-6 74 194 228 0.85 0.55959 0.03037 0.07033 0.00119 0.31240 451.3 19.8 438.2 7.2 97% 6-1-7 130 357 292 1.22 0.55107 0.01895 0.07089 0.00077 0.31660 445.7 12.4 441.5 4.7 99% 6-1-8 117 317 253 1.25 0.57510 0.02105 0.07062 0.00087 0.33594 461.3 13.6 439.9 5.2 95% 6-1-9 62 177 149 1.19 0.62054 0.02718 0.07054 0.00103 0.33232 490.2 17.0 439.4 6.2 89% 6-1-10 89 244 275 0.89 0.56684 0.02304 0.06904 0.00091 0.32499 456.0 14.9 430.4 5.5 94% 6-1-11 67 176 191 0.92 0.64106 0.03184 0.07034 0.00109 0.31246 503.0 19.7 438.2 6.6 86% 6-1-12 93 272 255 1.07 0.61367 0.02545 0.07136 0.00094 0.31598 485.9 16.0 444.3 5.6 91% 6-1-13 164 483 440 1.10 0.58525 0.01905 0.06971 0.00064 0.28022 467.8 12.2 434.4 3.8 92% 6-1-14 150 431 399 1.08 0.55626 0.01688 0.07008 0.00076 0.35720 449.1 11.0 436.6 4.6 97% 6-1-15 95 249 287 0.87 0.57430 0.02401 0.07057 0.00088 0.29934 460.8 15.5 439.6 5.3 95% 6-1-16 122 341 267 1.28 0.52404 0.02208 0.07072 0.00094 0.31554 427.8 14.7 440.5 5.7 97% 6-1-17 85 218 274 0.79 0.54034 0.01976 0.06996 0.00102 0.39842 438.6 13.0 435.9 6.1 99% 6-1-18 73 199 251 0.79 0.56191 0.02098 0.06864 0.00098 0.38287 452.8 13.6 428.0 5.9 94% 6-1-19 108 298 356 0.84 0.54723 0.01769 0.06996 0.00077 0.34166 443.2 11.6 435.9 4.7 98% 6-1-20 123 325 334 0.97 0.55780 0.01918 0.07104 0.00079 0.32143 450.1 12.5 442.4 4.7 98% 1458-1-1 126 274 466 0.59 0.58972 0.02053 0.07042 0.00095 0.38903 470.7 13.1 438.7 5.7 92% 1458-1-2 417 932 833 1.12 0.67608 0.01818 0.07141 0.00075 0.38992 524.4 11.0 444.6 4.5 83% 1458-1-3 134 279 518 0.54 0.59189 0.01755 0.06859 0.00059 0.28931 472.1 11.2 427.6 3.6 90% 1458-1-4 244 575 693 0.83 0.58317 0.01724 0.06983 0.00078 0.37580 466.5 11.1 435.1 4.7 93% 1458-1-5 197 385 577 0.67 0.69410 0.02071 0.07035 0.00062 0.29367 535.3 12.4 438.3 3.7 80% 1458-1-6 145 322 518 0.62 0.56713 0.01991 0.06966 0.00084 0.34456 456.2 12.9 434.1 5.1 95% 1458-1-7 117 257 431 0.60 0.57266 0.01803 0.06979 0.00071 0.32382 459.7 11.6 434.9 4.3 94% 1458-1-8 75 164 305 0.54 0.56195 0.01985 0.06912 0.00082 0.33401 452.8 12.9 430.8 4.9 95% 1458-1-9 148 317 509 0.62 0.60223 0.02262 0.07210 0.00108 0.39857 478.6 14.3 448.8 6.5 93% 1458-1-10 142 333 537 0.62 0.53956 0.01780 0.06967 0.00085 0.37077 438.1 11.7 434.2 5.1 99% 1458-1-11 140 322 453 0.71 0.56567 0.02791 0.07215 0.00135 0.37791 455.2 18.1 449.1 8.1 98% 1458-1-12 104 235 395 0.59 0.56548 0.01964 0.06989 0.00105 0.43257 455.1 12.7 435.5 6.3 95% 1458-1-13 128 274 477 0.57 0.52948 0.02016 0.07113 0.00103 0.37913 431.5 13.4 442.9 6.2 97% 1458-1-14 127 278 502 0.55 0.54827 0.02037 0.07091 0.00104 0.39518 443.9 13.4 441.6 6.3 99% 1458-1-15 154 332 555 0.60 0.58246 0.03455 0.06980 0.00089 0.21390 466.0 22.2 435.0 5.3 93% 1458-1-16 104 234 402 0.58 0.52215 0.02313 0.07106 0.00118 0.37456 426.6 15.4 442.5 7.1 96% 1458-1-17 148 291 426 0.68 0.63807 0.02119 0.07073 0.00092 0.39001 501.1 13.1 440.6 5.5 87% 1458-1-18 112 226 382 0.59 0.72545 0.06040 0.07142 0.00093 0.15642 553.9 35.5 444.7 5.6 78% 1458-1-19 436 826 1040 0.79 0.72088 0.02301 0.07399 0.00082 0.34696 551.2 13.6 460.2 4.9 81% 1458-1-20 165 306 493 0.62 0.68070 0.02961 0.07144 0.00110 0.35257 527.2 17.9 444.8 6.6 83% 1458-1-21 234 532 691 0.77 0.56210 0.01530 0.06923 0.00089 0.47121 452.9 9.9 431.5 5.4 95% 表 2 哈尔里克山西段早志留世酸性侵入岩主量元素(%)、微量元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 2. Major and trace element concentrations for the early Silurian acid intrusive rock in western Harlik
样号 岩性 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 LOI Total FeO* Mg# DI A/CNK V Cr Ga Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Ta Th U Pb Cs Hf Ba Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ΣREE (La/Yb)N (La/Sm)N δEu D3540-1H 二长花岗岩 75.3 0.18 12.96 1.38 0.07 0.31 0.85 4.28 3.67 0.04 0.47 99.54 1.24 30.80 92.70 1.03 16 10 13.5 67.4 167 14.9 113 7.0 0.7 11.85 2.26 14 0.27 3.2 977 54.9 5.70 18.3 3.30 0.67 2.70 0.37 2.31 0.48 1.51 0.24 1.74 0.29 122.81 11.77 5.78 0.67 D3540-3H 73.0 0.29 14.02 2.11 0.09 0.59 1.74 3.76 3.94 0.08 1.05 100.69 1.90 35.65 86.67 1.03 34 10 14.5 90.6 305 12.2 150 6.0 0.5 11.00 1.72 15 1.25 3.5 961 53.2 5.41 17.1 2.90 0.75 2.23 0.29 1.86 0.39 1.20 0.20 1.48 0.23 117.84 13.97 6.64 0.87 D2591-4H 77.8 0.15 12.29 1.14 0.04 0.25 0.67 3.99 3.31 0.02 0.63 100.27 1.03 30.29 93.61 1.08 16 10 10.8 49.7 149 12.0 86 6.9 0.6 12.50 2.61 13 0.16 2.4 775 48.8 4.73 14.3 2.44 0.44 1.89 0.25 1.67 0.35 1.09 0.18 1.29 0.20 106.73 15.24 7.51 0.60 D1352-1H 正长花岗岩 76.8 0.08 11.88 1.64 0.02 0.05 0.08 4.19 4.06 < 0.01 0.25 99.02 1.48 5.70 96.96 1.04 7 20 21.6 121.5 37 66.1 278 17.5 1.2 12.35 2.28 12 0.37 8.9 407 103.0 11.05 42.8 10.40 0.88 10.65 1.75 12.15 2.63 8.09 1.28 8.17 1.28 253.73 3.28 2.40 0.25 D1352-2H 76.5 0.09 12.04 1.74 0.03 0.06 0.07 4.55 3.76 < 0.01 0.19 99.02 1.57 6.40 96.94 1.03 8 20 21.7 87.7 44 69.3 357 20.2 1.8 14.90 2.54 12 0.20 11. 369 89.0 8.98 33.6 7.91 0.65 8.36 1.42 10.35 2.30 7.65 1.22 8.35 1.34 213.73 2.64 2.59 0.24 D2591-4H 76.6 0.09 12.04 1.77 0.06 0.03 0.05 4.31 4.26 0.02 0.14 99.41 1.59 3.25 97.18 1.02 6 20 23.2 105.5 23 84.0 313 18.5 1.5 13.15 2.33 15 0.14 8.9 461 105.5 11.85 44.1 10.80 0.91 10.70 1.81 12.60 2.72 8.58 1.28 8.91 1.32 265.98 3.41 2.62 0.26 注:FeO*=0.8998×Fe2O3; 镁值Mg#=molar 100×Mg/(Mg+FeO*); DI=标准矿物(Q+Af+Ab+Ne+Kp+Lc); δEu=2×EuN/(SmN+GdN); A/CNK=Al2O3/(CaO+ Na2O+K2O)分子比; (La/Yb)N代表La和Yb球粒陨石标准化比值 表 3 哈尔里克山西段早志留世酸性侵入岩锆石饱和温度计算结果
Table 3. Values of zircon saturation thermometer for the Early Silurian acid intrusive rock in western Harlik
岩性 样品编号 Na K Ca Al Si Zr M D T/℃ 二长花岗岩 D3540-1 0.0781 0.0441 0.0086 0.1438 0.7091 113 1.37 4389.4 759 D3540-3 0.0684 0.0472 0.0175 0.1551 0.6852 150 1.42 3306.7 779 D2591-4 0.0728 0.0397 0.0068 0.1363 0.7314 86 1.26 5767.4 743 正长花岗岩 D1352-1 0.0770 0.0491 0.0008 0.1327 0.7273 278 1.32 1784.2 842 D1352-2 0.0833 0.0453 0.0007 0.1341 0.7224 357 1.34 1389.4 865 D1352-3 0.0787 0.0512 0.0005 0.1337 0.7217 313 1.36 1584.7 851 -
[1] Badarch G, Dickson Cunningham W, Windley B F. A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia:Implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1):87~110. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00017-2 [2] Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(1):31~47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022 [3] Xiao W J, Han C, Yuan C, et al. Middle Cambrian to Permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of Northern Xinjiang, NW China:Implications for the tectonic evolution of central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(2/4):102~117. [4] Xu Q, Ji J, Zhao L, et al. Tectonic evolution and continental crust growth of Northern Xinjiang in northwestern China:Remnant ocean model[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 126:178~205. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.08.005 [5] 顾连兴, 胡受奚, 于春水, 等.论博格达俯冲撕裂型裂谷的形成与演化[J].岩石学报, 2001(04):585~597. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200104008.htmGU Lian-xing, HU Shou-xi, YU Chun-shui, et al. Initation and evolution of the Bogda subduction-torn-type rift[J]. Acia Petrologica Sinica, 2001(4):585~597. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200104008.htm [6] 冯益民, 朱宝清, 杨军录, 等.东天山大地构造及演化——1:50万东天山大地构造图简要说明[J].新疆地质, 2002, (4):309~314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200204004.htmFENG Yi-min, ZHU Bao-qing, YANG Jun-lu, et al. Tectonics and evolution of the eastern Tianshan Mountains:A brief introduction to tectonic map (1:500000) of the eastern Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2002, (4):309~314. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI200204004.htm [7] 李锦轶.新疆东部新元古代晚期和古生代构造格局及其演变[J].地质论评, 2004, 50(3):304~322. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200403015.htmLI Jin-yi. Late Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic tectonic framework and evolution of eastern Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(3):304~322. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200403015.htm [8] Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China):Implications for the continental growth of Central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(4):370~395. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.4.370 [9] 李锦轶, 王克卓, 孙桂华, 等.东天山吐哈盆地南缘古生代活动陆缘残片:中亚地区古亚洲洋板块俯冲的地质记录[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(5):1087~1102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605004.htmLI Jin-yi, WANG Ke-zhuo, SUN Gui-hua, et al. Paleozoic active margin slices in the southern Turfan-Hami basin:Geological records of subduction of the Paleo-Asian Ocean plate in central Asian regions[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(5):1087~1102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605004.htm [10] 曹福根, 涂其军, 张晓梅, 等.哈尔里克山早古生代岩浆弧的初步确定——来自塔水河一带花岗质岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年的证据[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(8):923~927. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200608004.htmCAO Fu-gen, TU Qi-jun, ZHANG Xiao-mei, et al. Preliminary determination of the Early Paleozoic magmatic arc in the Karlik Mountains, East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China:Evidence from zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of granite bodies in the Tashuihe area[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(8):923~927. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200608004.htm [11] 郭华春, 钟莉, 李丽群.哈尔里克山口门子地区石英闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(8):928~931. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200608005.htmGUO Hua-chun, ZHONG Li, LI Li-Qun. Ziron SHRIMP U-Pb dating of quartz diorite in the Koumenzi area, Karlik Mountains, East Tianshan, Xinjiang, China, and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(8):928~931. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200608005.htm [12] 马星华, 陈斌, 王超, 等.早古生代古亚洲洋俯冲作用:来自新疆哈尔里克侵入岩的锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素证据[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(1):89~104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201501007.htmMA Xing-hua, CHEN Bin, WANG Chao, et al. East Paleozoic subduction of the Paleo-Asian Ocan:Zircon U-Pb geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from the Harlik pluton, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(1):89~104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201501007.htm [13] 徐学义, 李荣社, 陈隽璐, 等.新疆北部古生代构造演化的几点认识[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(6):1521~1534. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201406001.htmXU Xue-yi, LI Rong-she, CHEN Jun-lu, et al. New constrains on the Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the northern Xinjiang area[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(6):1521~1534. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201406001.htm [14] 董连慧, 朱志新, 屈迅, 等.新疆蛇绿岩带的分布、特征及研究新进展[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(10):2894~2904. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201010002.htmDONG Lian-hui, Zhu Zhi-xin, QU Xun, et al. Spatial distribution geological features and latest progress of the main ophiolite zones in Xinjiang NW-China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(10):2894~2904. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201010002.htm [15] 吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(16):1589~1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002WU Yuan-bao, ZHENG Yong-fei. Gensis of zircon and its constraints on the interpretation of U-Pb age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(16):1589~1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 [16] Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63~81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745 [17] Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635~643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2 [18] 邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等.福建北东沿海高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(11):2468~2484. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200811003.htmQIU Jian-sheng, XIAO E, HU Jian, et al. Petrogenesis of fractionated Ⅰ-type granites in the coastal area of northeastern Fujian Province:Constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry, and Nd-Hf isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(11):2468~2484. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200811003.htm [19] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The continental crust:Its composition and evolution[M]. London:Blackwell Scientific, 1986. [20] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt:Implications for mantle composition and processes[M]. London:Geological Society, 1989. [21] 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217~1238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK199001002.htmWU Fu-yuan, LI Xian-hua, YANG Jin-hui, et al. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(6):1217~1238. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK199001002.htm [22] 李献华, 李武显, 李正祥.再论南岭燕山早期花岗岩的成因类型与构造意义[J].科学通报, 2007, 52(9):981~991. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200709000.htmLI Xian-hua, LI Wu-xian, LI Zheng-xiang.[J]. Re-discussion on genesis type and tectonic significance of Early Yanshanian granite in Nanling[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(9):981~991. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200709000.htm [23] Holtz F, Pichavant M, Barbey P, et al. Effects of H2O on liquidus phase relations in the haplogranite system at 2 and 5 kbar[J]. American Mineralogist, 1992, 77(11/12):1223~1241. [24] Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4):407~419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202 [25] 邱检生, 胡建, 王孝磊, 等.广东河源白石冈岩体:一个高分异的Ⅰ型花岗岩[J].地质学报, 2005, 79(4):503~514. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200504010.htmQIU Jian-sheng, HU Jian, WANG Xiao-lei, et al. The Baishigang Pluton in Heyuan, Guangdong Province:A highly fractionated Ⅰ-type granite[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(4):503~514. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200504010.htm [26] Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2):295~304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X [27] Miller C F, McDowell S M, Mapes R W. Hot and cold granites Implications of zircon saturation temperatures and preservation of inheritance[J]. Geology, 2003, 31(6):529~532. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0529:HACGIO>2.0.CO;2 [28] Patiño Douce A E. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8):743. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0743:GOMATG>2.3.CO;2 [29] Castillo Paterno R.埃达克岩成因回顾[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(6):617~627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200606000.htmCastillo Paterno R. Review of the genesis of adakites[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(6):617~627. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200606000.htm [30] Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8~32 kbar:Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4):891~931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891 [31] Conrad W K, NichollsI I A, Wall V J. Water-Saturated and-Undersaturated Melting of Metaluminous and Peraluminous Crustal Compositions at 10 kb:Evidence for the Origin of Silicic Magmas in the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand, and Other Occurrences[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1988, 29(4):765~803. doi: 10.1093/petrology/29.4.765 [32] Küster D, Harms U. Post-collisional potassic granitoids from the southern and northwestern parts of the Late Neoproterozoic East African Orogen:a review[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45(1/4):177~195. [33] Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7):641. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2 [34] Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956~983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 [35] 韩宝福.后碰撞花岗岩类的多样性及其构造环境判别的复杂性[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(3):64~72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200703007.htmHAN Bao-fu. Diverse post-collisional granitoids and their tectonic setting discrimination[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(3):64~72. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200703007.htm [36] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Yuan C, et al. Paleozoic multiple subduction-accretion processes of the southern Altaids[J]. American Journal of Science, 2009, 309(3):221~270. doi: 10.2475/03.2009.02 [37] 董连慧, 屈迅, 赵同阳, 等.新疆北阿尔泰造山带早古生代花岗岩类侵入序列及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(8):2307~2316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201208002.htmDONG Lian-hui, QU Xun, ZHAO Tong-yang, et al. Magmatic sequence of Early Palaeozoic granitic intrusions and its tectonic implications in north Altay orogeny, Xinjiang[J]. 2012, 28(8):2307~2316. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201208002.htm [38] 简平, 刘敦一, 张旗, 等.蛇绿岩及蛇绿岩中浅色岩的SHRIMP U-Pb测年[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(4):439~456. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200311002036.htmJIAN Ping, LIU Dun-yi, ZHANG Qi, et al. SHRIMP dating of ophiolite and leucocratic rocks within ophiolite[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(4):439~456. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200311002036.htm [39] 程裕淇.中国地层典:志留系[M].北京:地质出版社, 1998.CHENG Yu-qi. Stratigraphic lexicon of China:Silurian[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1998. [40] 李亚萍, 李锦轶, 孙桂华, 等.新疆东准噶尔早泥盆世早期花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(12):1885~1893. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.020LI Ya-ping, LI Jin-yi, SUN Gui-hua, et al. Determination of the Early Devonian granite in East Junggar, Xinjiang, China and its geological implications[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(12):1885~1893. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.020 [41] 徐芹芹, 赵磊, 牛宝贵.新疆东准噶尔纸房地区早古生代花岗岩的确定及其地质意义[J].地质力学学报, 2015, 21(4):502~516. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150406&flag=1XU Qin-qin, ZHAO Lei, NIU Bao-gui. Determination of the early Paleozoic granite in Zhifang area, east Junggar, Xingjiang and its geological implications[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2015, 21(4):502~516. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150406&flag=1 -





 下载:
下载: