Plunge law and mechanical mechanisms of fault-controlled ore bodies (clusters) in hydrothermal deposits
-
摘要: 热液矿床中,矿体(群)的侧伏规律是构造−流体耦合成矿系统在三维空间的具体表现,但确定其侧伏向和侧伏角一直是找矿预测的难题之一。文章聚焦矿体(群)侧伏规律及其力学机制研究中存在的主要问题(多期构造叠加造成的矿体侧伏识别难、矿体群侧伏控制机制不清、深部矿体侧伏模型实证研究不足等),基于矿田地质力学理论与方法,突破多期构造识别、矿体群侧伏控制机制等瓶颈,研究总结了压扭性、张扭性/扭张性、剪切带/扭性为主断裂带及复合构造控制的矿体(群)的侧伏规律,并解析其力学机制,提出矿体(群)侧伏确定方法。研究表明,成矿断裂构造的力学、运动学及其倾向、倾角共同控制矿体(群)侧伏产状,其侧伏向与成矿断裂下降盘运动方向一致,侧伏角受成矿构造应力场水平分量或成矿构造运动方向与断裂走向夹角的大小控制;不同级序构造控制的矿体群与单个矿体的侧伏规律不完全一致。在此基础上,认为成矿构造解析、矿化蚀变分带趋势追索、矿柱中心点投影及勘查工程数据三维空间分析是推断隐伏矿体(群)侧伏的主要方法,构造地球化学和地球物理异常分析等方法,可显著提升深部隐伏矿体(群)侧伏预测的可靠性,有望打开深部找矿新局面,取得事半功倍之功效。该研究在指导矿山深部和外围找矿预测与勘查区矿产评价、优化勘查工程部署、深化热液矿床成矿动力学机制及准确估算资源储量等方面具有重要意义。Abstract:
Objective Hydrothermal mineral deposits provide a representative example of tectonic–fluid coupled metallogenic systems, and the lateral plunge law of ore bodies or ore body clusters constitutes their three-dimensional expression in geological space, yet the determination of pitching direction and pitching angle has long been one of the most difficult problems in prospecting prediction. Methods This study aims to address the major challenges in understanding plunge law and mechanical mechanisms, namely the difficulty of identifying ore body pitching under multiphase tectonic superposition, the lack of clarity in the control mechanisms of ore body cluster pitching, and the insufficiency of empirical studies on deep ore body pitching models. Based on Theory and Methods of Orefield Geomechanics, breakthroughs were achieved in multiphase structural recognition and the identification of control mechanisms, allowing systematic summarization of plunge law associated with compressional–shear, extensional–shear or transtensional, ductile shear zone or brittle shear belt, and composite structural controls, together with detailed analysis of their mechanical mechanisms and the proposal of practical methods for determining pitching. Results The results indicate that in hydrothermal deposits, ore body pitching is strictly controlled by the mechanical properties, kinematic behavior, and spatial configuration of the dominant ore-controlling structures during mineralization: the pitching direction of ore bodies or clusters is consistent with the movement of the hanging wall of the controlling fault, while the pitching angle is governed by the fault dip, the proportion of shear components, the undulatory amplitude of fault planes, and the orientation of the regional principal stresses. Ore bodies controlled by transpressional or transtensional faults exhibit more pronounced pitching than those associated with simple compressional–shear or extensional–shear structures; for single ore bodies or vein clusters, pitching direction may coincide with that of the cluster in transpressional or compressional–shear systems, or conversely oppose it in transtensional or extensional–shear systems; where ductile shear zones control mineralization, pitching is parallel to stretching lineations, while brittle shear belts produce pitching that follows extension–compression directions; in composite structural systems, the determination of pitching requires careful analysis of inherited, superimposed, or transformed tectonic elements to establish the effective mode of control. Mechanically, the pitching direction corresponds to the orientation of maximum permeability of metallogenic fluids within the ore-controlling stress field: in compressional–shear or transpressional faults, pitching is constrained by the sense of shear displacement; in transtensional faults, it is determined by the orientation of dominant fluid channels; and in ductile shear zones, it follows the X-axis of the strain ellipsoid. Conclusion These findings confirm that the mechanics and kinematics of ore-controlling structures are the primary factors dictating the occurrence of pitching in ore bodies and clusters, but they also highlight that the regularities differ between structural hierarchies, with the behavior of ore body clusters not entirely identical to that of single ore bodies, and that the observed patterns reflect the combined action of the metallogenic stress field, fluid dynamics, and the physical properties of host rocks. On this basis, several methods are recognized as effective for inferring the pitching of concealed ore bodies, including structural analysis of mineralizing faults, tracing zoning trends of mineralization and alteration, projection of ore column centroids, and three-dimensional spatial analysis of exploration engineering data, while the integration of structural geochemical and geophysical anomaly analyses can significantly enhance the reliability of pitching prediction in deep concealed settings, thereby opening new avenues for deep ore prospecting and achieving high efficiency in exploration. [Significance] The significance of this study lies not only in its practical applications—guiding deep and peripheral prospecting, improving mineral resource evaluation in exploration areas, optimizing the deployment of exploration projects, and enabling more accurate estimation of reserves—but also in its theoretical contributions, particularly in advancing the understanding of the metallogenic dynamics of hydrothermal deposits by linking structural mechanics, stress fields, fluid migration, and rock physical properties in a unified framework for explaining ore body pitching. -
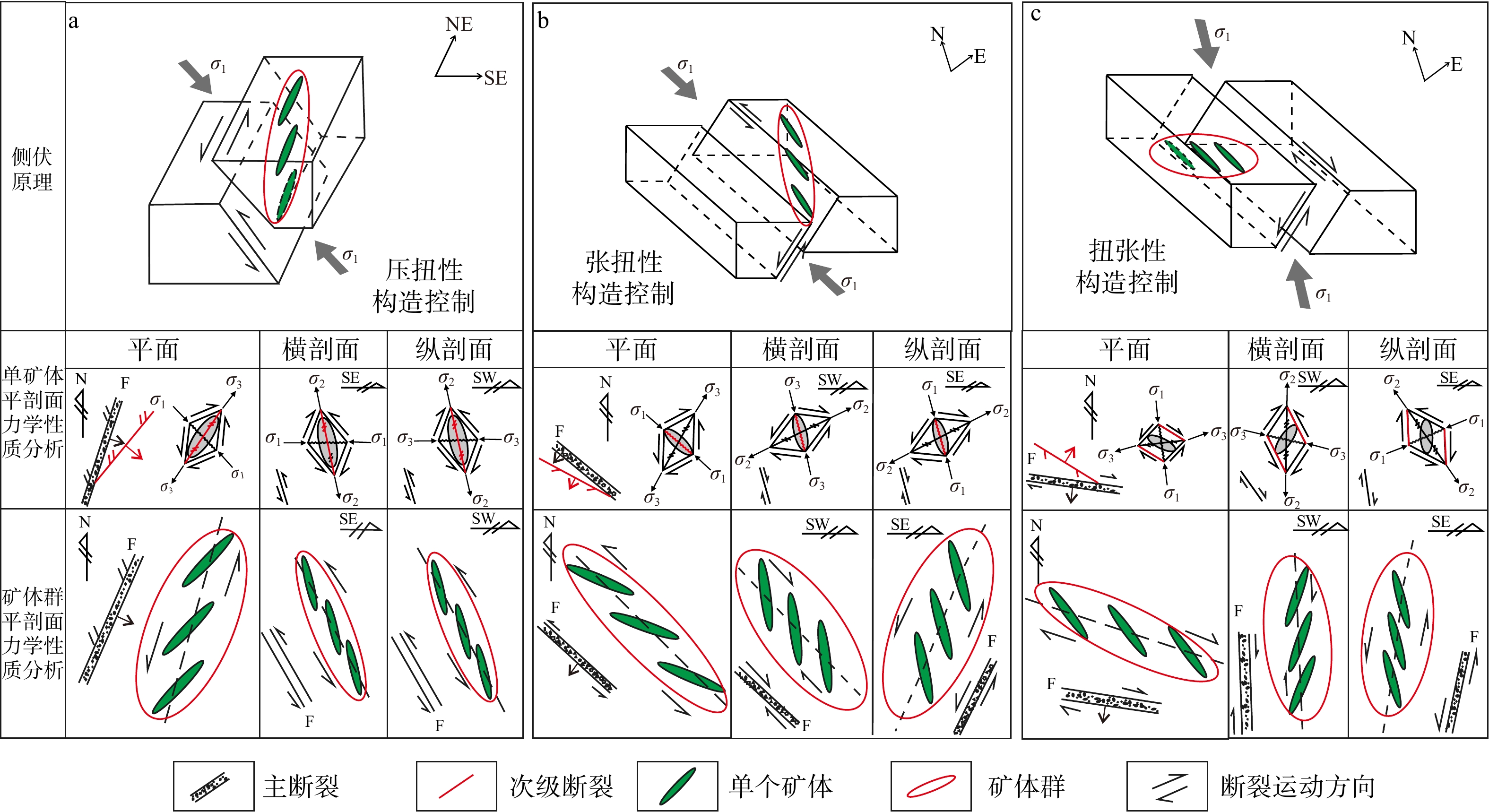
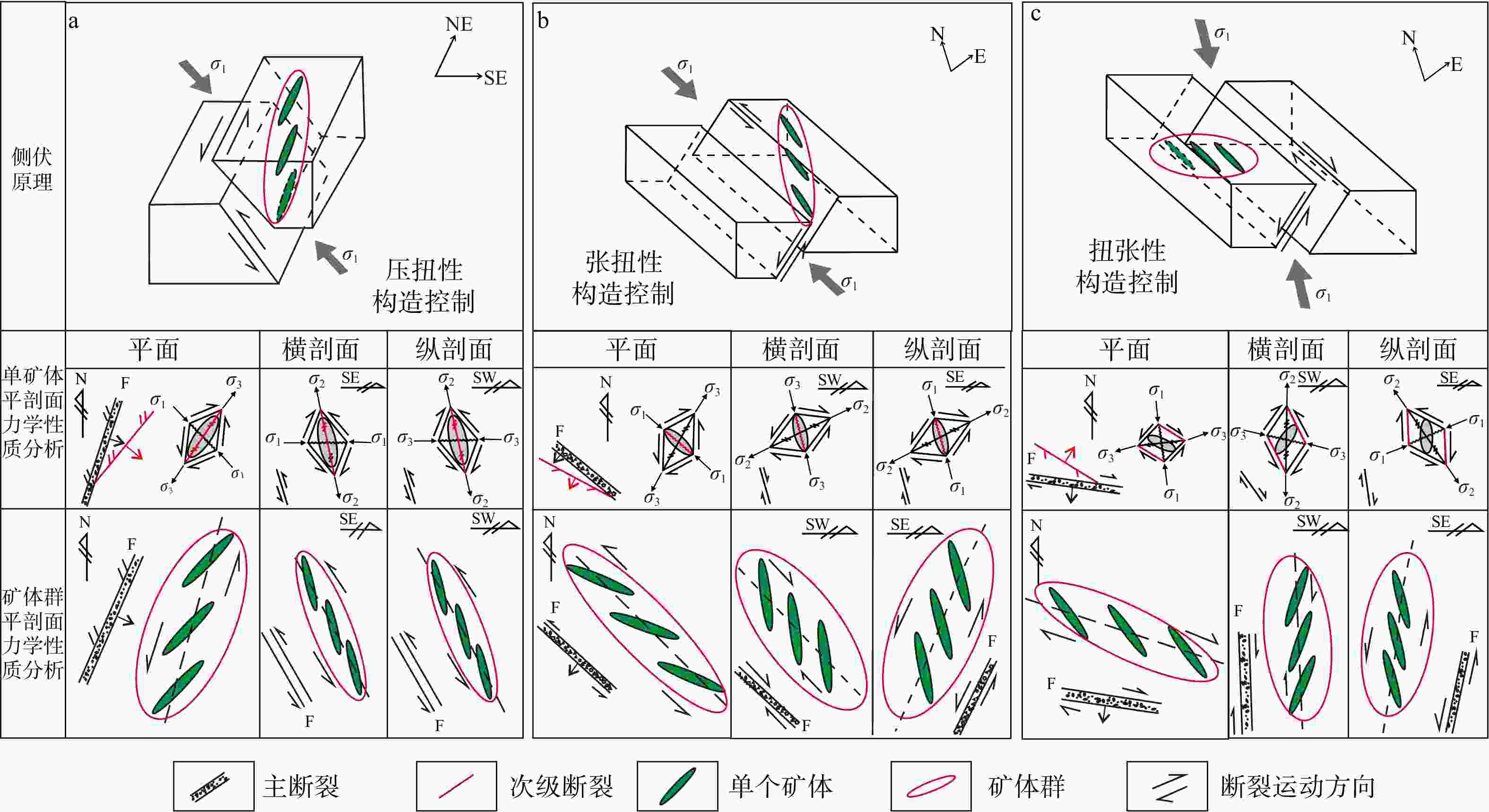
图 1 不同类型断裂带控制的矿体(群)侧伏规律和力学机制示意图
a—压扭性断裂控制的矿体(群)侧伏规律和力学机制示意图;b—张扭性断裂控制的矿体(群)侧伏规律和力学机制示意图;c—扭张性断裂控制的矿体(群)侧伏规律和力学机制示意图
Figure 1. Schematic diagrams of ore body (cluster) plunge law and mechanical mechanisms controlled by different types of fault zones
(a) Schematic diagrams of ore body (cluster) plunge law and mechanical mechanisms controlled by compresso–shear fault structure; (b) Schematic diagrams of ore body (cluster) plunge law and mechanical mechanisms controlled by tensional-shear fault structure; (c) Schematic diagrams of ore body (cluster) plunge law and mechanical mechanisms controlled by shear-tensional fault structure
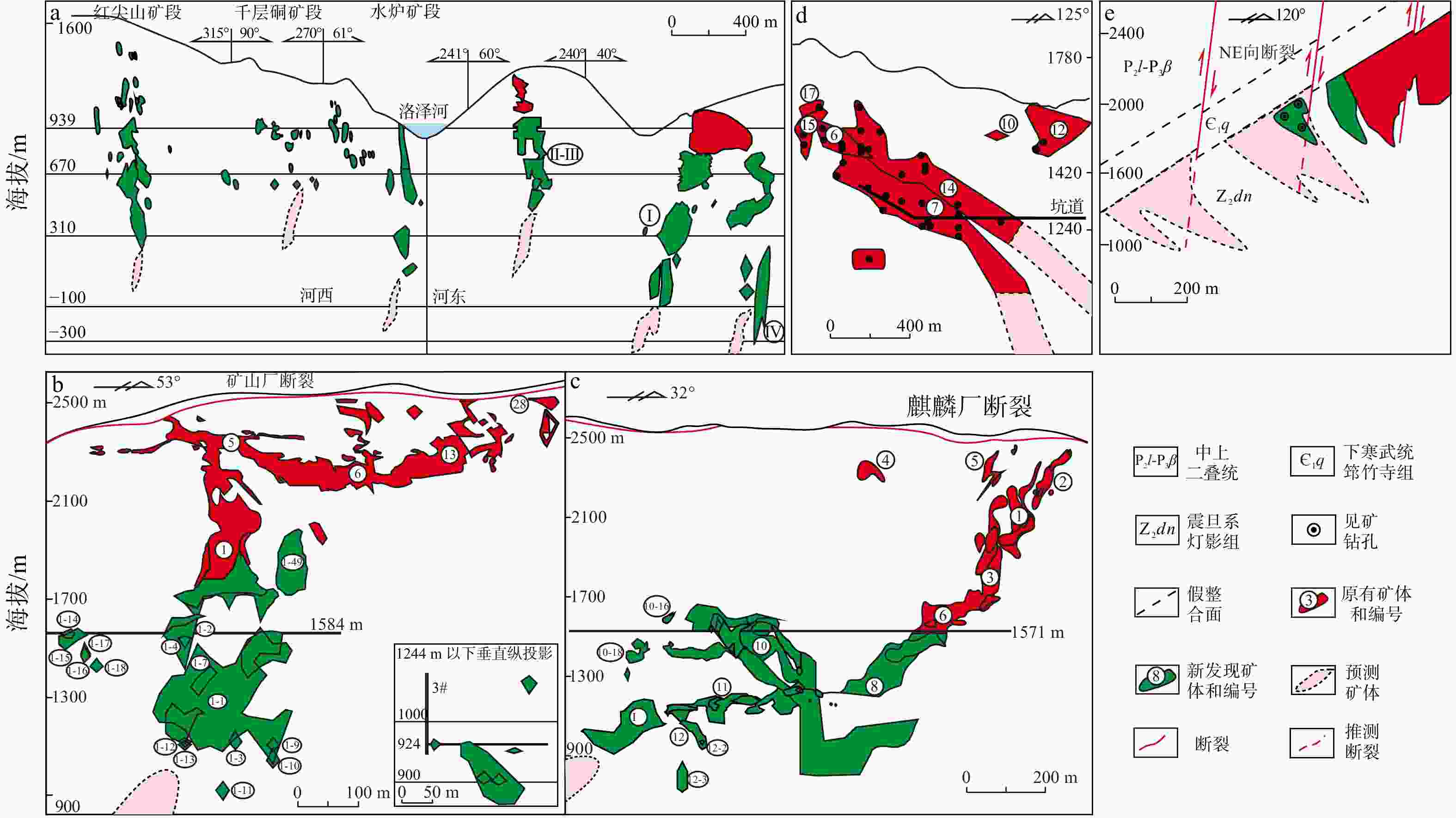
图 2 川滇黔典型铅锌矿床的矿体(群)纵投影图(据韩润生和张艳,2025修改)
a—毛坪铅锌矿床的矿体(群)纵投影图;b—会泽矿山厂铅锌矿床的矿体(群)纵投影图;c—会泽麒麟厂铅锌矿床的矿体(群)纵投影图;d—杉树林铅锌矿床的矿体(群)纵投影图;e—大梁子铅锌矿床的矿体(群)纵投影图a—c为压扭性断裂控制的矿体群侧伏典例,d为张扭性断裂控制的矿体群侧伏典例,e为扭张性断裂控制的矿体群侧伏典例
Figure 2. Longitudinal projection of ore bodies (clusters) in typical lead-zinc deposits in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou region (modified from Han and Zhang, 2025)
(a) Longitudinal projection of ore bodies (clusters) in the Maoping lead-zinc deposits; (b) Longitudinal projection of ore bodies (clusters) in the Kuangshanchang lead-zinc deposits in Huize; (c) Longitudinal projection of ore bodies (clusters) in the Qilinchang lead-zinc deposits in Huize; (d) Longitudinal projection of ore bodies (clusters) in the Shanshulin lead-zinc deposits; (e) Longitudinal projection of ore bodies (clusters) in the Daliangzi lead-zinc deposits(a)–(c) show typical examples of plunging ore body clusters controlled by compresso-shear faults; (d) shows typical examples of plunging ore body clusters controlled by tensional-shear faults; (e) shows typical examples of plunging ore body clusters controlled by shear-tensional faults.
表 1 不同类型断裂构造控制的矿体(群)侧伏规律
Table 1. Ore body (cluster) plunge law of various fault structure types
控矿构造类型 主导控制因素 主要侧伏规律 矿产勘探意义 压扭性/
扭压性
断裂带断裂力学性质和扭动方向(右行/左行)及剪切分量 右行扭动→右侧伏;左行扭动→左侧伏 压扭性断裂控制的矿体侧伏规律清晰且普遍,
是侧伏预测的主要依据张扭性/扭张性断裂带 断裂力学性质和扭动方向及剪切分量 张扭性构造控制的矿体(群)侧伏规律性较弱,矿体(群)斜列侧伏或沿通道倾斜延深;扭张性断裂带控制的矿体(群)侧伏规律性较强 结合局部成矿构造与主次断裂力学、
运动学分析剪切带与扭性为主断裂 拉伸线理方向、剪切带伸长方向/扭性为主断裂运动方向 侧伏方向与线理方向一致;侧伏角=线理倾伏角;主断裂及其派生的次级断裂的力学性质、运动学控制矿体(群)侧伏 线理测量、构造力学性质、运动学判断是关键 复合
构造成矿期主导构造 需精细解析继承性、叠加性或转换构造,确定其侧伏方式 划分构造活动和成矿期次,确定成矿期
主控构造是关键表 2 矿体群侧伏的力学机制小结
Table 2. Summary of mechanical mechanisms for ore (body) cluster plunge
成矿构造 主导应力 扩容空间形成机制 侧伏向决定因素 参考文献 压扭性断裂带 压扭应力 断裂扭动在舒缓波状面产生张性阶步、
断裂在剖面变缓扩容区断裂扭动方向
(右行→右侧伏)Sibson,1987;
韩润生等,2001张扭性或扭张性断裂带 张扭应力或扭张应力 高角度连通裂隙形成流体优势通道 优势通道倾斜方向 Curewitz and Karson,1997 韧性剪切带 简单剪切 X轴方向强应变区渗透性增强 拉伸线理方向 (X轴投影) Groves et al.,1998 表 3 矿体侧伏确定方法适用性及其精度对比
Table 3. Comparison of applicability and accuracy for ore body (cluster) Plunge determination methods
确定方法 适用阶段 数据需求 精度 主要局限 成矿构造解析法 预查—普查、
深部勘查地质填图 中 深部控矿构造可能变化 矿体中心点投影法 详查—勘探 ≥3个中段工程数据 高 部分揭露矿体 等值线趋势法 勘探—开发 密集网格工程 中—高 受矿体形态复杂性影响 构造地球化学异常法 普查—勘查、
勘探≥3个中段工程数据 中—高 受矿体分布和工程布局影响 物探异常确定方法 勘查—勘探 剖面数据 中 受地形、构造和矿体分布影响 -
[1] CHEN G D, 1978. Research method of ore-forming structures[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) [2] CLINE J S, HOFSTRA A H, MUNTEAN J L, et al. , 2005. Carlin-type gold deposits in Nevada: critical geologic characteristics and viable models[M]//HEDENQUIST J W, THOMPSON J F H, GOLDFARB R J, et al. One hundredth anniversary volume. Littleton, CO: Society of Economic Geologists: 451-484. [3] COX S F, KNACKSTEDT M A, BRAUN J, 2001. Principles of structural control on permeability and fluid flow in hydrothermal systems[M]//RICHARDS J P, TOSDAL R M. Structural controls on ore genesis. Society of Economic Geologists: 1-10. [4] COX S F, RUMING K, 2004. The St Ives mesothermal gold system, Western Australia—a case of golden aftershocks?[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 26(6-7): 1109-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2003.11.025 [5] CUREWITZ D, KARSON J A, 1997. Structural settings of hydrothermal outflow: fracture permeability maintained by fault propagation and interaction[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 79(3-4): 149-168. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0273(97)00027-9 [6] DAVIES A J, HAGEMANN S G, WITT W K, et al., 2025. Structural controls on Au–Co mineralisation at the Juomasuo deposit, an example of Paleoproterozoic Au–Co–Cu–REE systems in the Karelian belts of Scandinavia[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 72(5-6): 732-762. doi: 10.1080/08120099.2025.2522879 [7] DENG J, YANG L Q, GE L S, et al., 2006. Research advances on the tectonic regime of the Jiaodong mineral concentration area formation[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 16(5): 513-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] GAO Q B, FAN Y X, WANG K Y, et al., 1998. The main geological means of deep metallogenetic prognosis of gold deposits[J]. Gold Geology, 4(2): 22-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] GROVES D I, GOLDFARB R J, GEBRE-MARIAM M, et al., 1998. Orogenic gold deposits: a proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 13(1-5): 7-27. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7 [10] GROVES D, VEARNCOMBE J, 2020. Introduction: thematic issue of Mineralium deposita on orogenic gold deposits[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 187-188. doi: 10.1007/s00126-019-00951-y [11] HAN R S, CHEN J, LI Y, et al., 2001. Ore-controlling tectonics and prognosis of concealed ores in Huize Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 21(2): 265-269. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] HAN R S, CHEN J, WANG F, et al., 2015. Analysis of metal-element association halos within fault zones for the exploration of concealed ore-bodies: a case study of the Qilinchang Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ge) deposit in the Huize mine district, northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 159: 62-78. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.08.006 [13] HAN R S, 2017-01-04. Large-scale alteration lithofacies positioning and predicating method for hydrothermal deposit: CN, 104156601B[P]. (in Chinese) [14] HAN R S, ZHANG Y, WANG F, et al. , 2019. Metallogenic mechanism and concealed ore location prediction of germanium-rich lead-zinc deposits in northeastern Yunnan ore concentration area[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [15] HAN R S, WANG M Z, JIN Z G, et al., 2020. Ore-controlling mechanism of NE-trending ore-forming structural system at Zn-Pb polymetallic ore concentration area in northwestern Guizhou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(3): 850-868. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] HAN R S, ZHAO D, 2022. Research methods for the deep extension pattern of rock/ore-controlling structures of magmatic-hydrothermal ore deposits: a preliminary study[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29(5): 420-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] HAN R S, WU P, ZHANG Y, et al., 2022. New research progress in metallogenic theory for rich Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ge) deposits in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Triangle (SYGT) area, southwestern Tethys[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(2): 554-573. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] HAN R S, ZHAO D, LIU F, et al. , 2023a-10-27. Method for determining deep extension pattern of rock and ore control structure of magma hydrothermal polymetallic ore field or ore deposit: CN, 115128698B[P]. (in Chinese) [19] HAN R S, ZHANG Y, ZHOU G M, et al. , 2023b-08-18. Determination method for ore control structure depth extension pattern of structure-controlled metatherm ore deposit: CN, 115016015B[P]. (in Chinese) [20] HAN R S, ZHAO D, WANG M Z, 2023c-07-28. Method for determining lateral volt orientation and spatial positioning of deep ore body of hydrothermal polymetallic deposit: CN, 115113297B[P]. (in Chinese) [21] HAN R S, WU J B, ZHANG Y, et al., 2024. Oblique distribution patterns and the underlying mechanical model of orebody groups controlled by structures at different scales[J]. Scientific Reports, 14(1): 4591. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55473-z [22] HAN R S, ZHANG Y, 2025. A preliminary discussion on the mineral exploration system theory: control-mapping exploration system architecture for hydrothermal deposits[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 32(5): 1-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] HAN R S, LIU F, ZHANG Y, 2025a. Discussion on ore-controlling roles of structural system in hydrothermal metallogenic system[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 32(2): 371-389. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] HAN R S, WU J B, CHEN Q, et al. , 2025b-03-18. Structure-controlled hydrothermal deposit hidden ore body space skew determination and deep prospecting target determination method: CN, 117784281B[P]. (in Chinese) [25] HAN R S, ZHANG Y, CHEN Q, et al. , 2025c-03-18. Method for rapidly determining the existence of deep concealed ore bodies in hydrothermal deposits and delineating their occurrence location: CN, 2024 1 0551556.3[P]. (in Chinese) [26] HAN R S, ZHANG Y, LI W Y, et al. , 2025d-01-21. A characteristic element combination anomaly derivative method for determining the occurrence of deep tabular blind ore bodies in hydrothermal deposits: CN, 2024 1 0551629.9[P]. (in Chinese) [27] HODGSON C J, 1989. The structure of shear-related, vein-type gold deposits: a review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 4(3): 231-273. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(89)90019-X [28] HUA R M, CHEN P R, ZHANG W L, et al., 2005. Three major metallogenic events in Mesozoic in South China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(2): 99-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] KNOX-ROBINSON C M, 2000. Vectorial fuzzy logic: a novel technique for enhanced mineral prospectivity mapping, with reference to the orogenic gold mineralisation potential of the Kalgoorlie Terrane, Western Australia[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 47(5): 929-941. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0952.2000.00816.x [30] LUTZ B M, 2023. Orogenic gold in the Blue Mountains, eastern Oregon, USA[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 154: 105310. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105310 [31] MAUGHAN D T, KEITH J D, CHRISTIANSEN E H, et al., 2002. Contributions from mafic alkaline magmas to the Bingham porphyry Cu-Au-Mo deposit, Utah, USA[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 37(1): 14-37. doi: 10.1007/s00126-001-0228-5 [32] PASSCHIER C W, TROUW R A J, 2005. Microtectonics[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. [33] SIBSON R H, 1987. Earthquake rupturing as a mineralizing agent in hydrothermal systems[J]. Geology, 15(8): 701-704. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1987)15<701:ERAAMA>2.0.CO;2 [34] SIBSON R H, 1996. Structural permeability of fluid-driven fault-fracture meshes[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 18(8): 1031-1042. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(96)00032-6 [35] SUN J C, HAN R S, 2016. Theory and method of Orefield geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) [36] VEARNCOMBE J R, 2023. Function and status of structural geology in the Resource industry[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 70(7): 908-931. doi: 10.1080/08120099.2023.2214928 [37] WANG J C, WANG R R, ZHOU Y, et al., 2006. Regularity and geological significance for lateral trending of orebodies[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 26(3): 305-309. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] WOODALL R, 1994. Empiricism and concept in successful mineral exploration[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 41(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1080/08120099408728107 [39] WU J B, HAN R S, ZHANG Y, et al., 2024. Porosity-permeability characteristics and mineralization-alteration zones of the Maoping germanium-rich lead-zinc deposit in SW China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 12: 1347243. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1347243 [40] XUAN D N, TRONG T P, HAI S T, et al., 2024. 3D models for hydrothermal copper ore bodies at Sin Quyen deposit, North Vietnam: a case report for ore reserves and prediction of hidden mineral resource potential[J]. Heliyon, 10(12): e33017. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33017 [41] ZHANG L, YE Z W, HUANG M Q, et al., 2019. Characteristics of bituminous coal permeability response to the pore pressure and effective shear stress in the Huaibei coalfield in China[J]. Geofluids, 2019: 5489051. [42] 陈国达, 1978. 成矿构造研究法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [43] 邓军, 杨立强, 葛良胜, 等, 2006. 胶东矿集区形成的构造体制研究进展[J]. 自然科学进展, 16(5): 513-518. [44] 高秋斌, 范永香, 王可勇, 等, 1998. 金矿床深部成矿预测的主要途径[J]. 黄金地质, 4(2): 22-26. [45] 韩润生, 陈进, 李元, 等, 2001. 云南会泽铅锌矿床构造控矿规律及其隐伏矿预测[J]. 矿物学报, 21(2): 265-269. [46] 韩润生, 2017-01-04. 一种热液矿床的大比例尺蚀变岩相定位预测方法: 中国, 104156601B[P]. [47] 韩润生, 张艳, 王峰, 等, 2019. 滇东北矿集区富锗铅锌矿床成矿机制与隐伏矿定位预测[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [48] 韩润生, 王明志, 金中国, 等, 2020. 黔西北铅锌多金属矿集区成矿构造体系及其控矿机制[J]. 地质学报, 94(3): 850-868. [49] 韩润生, 赵冻, 2022. 初论岩浆热液成矿系统控岩控矿构造深延格局研究方法[J]. 地学前缘, 29(5): 420-437. [50] 韩润生, 吴鹏, 张艳, 等, 2022. 西南特提斯川滇黔成矿区富锗铅锌矿床成矿理论研究新进展[J]. 地质学报, 96(2): 554-573. [51] 韩润生, 赵冻, 刘飞, 等, 2023a-10-27. 确定岩浆热液型多金属矿田或矿床控岩控矿构造深延格局的方法: 中国, 115128698B[P]. [52] 韩润生, 张艳, 周高明, 等, 2023b-08-18. 受构造控制的后生热液矿床控矿构造深延格局的确定方法: 中国, 115016015B[P]. [53] 韩润生, 赵冻, 王明志, 2023c-07-28. 确定热液型多金属矿床深部矿体侧伏向和空间定位的方法: 中国, 115113297B[P]. [54] 韩润生, 张艳, 2025. 初论矿产勘查系统理论: 热液矿床控制: 映射勘查系统架构[J]. 地学前缘, 32(5): 1-27. [55] 韩润生, 刘飞, 张艳, 2025a. 论热液成矿系统中构造体系控矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 32(2): 371-389. [56] 韩润生, 吴建标, 陈青, 等, 2025b-03-18. 受构造控制的热液矿床隐伏矿体空间斜列判定和深部找矿定靶的方法: 中国, 117784281B[P]. [57] 韩润生, 张艳, 陈青, 等, 2025c-03-18. 快速判定热液矿床深部隐伏矿体存在性和圈定其赋存部位的方法: 中国, 202410551556.3[P]. [58] 韩润生, 张艳, 李文尧, 等, 2025d-01-21. 一种确定热液矿床深部板状盲矿体产状的特征元素组合异常导数法: 中国, 202410551629.9[P]. [59] 华仁民, 陈培荣, 张文兰, 等, 2005. 论华南地区中生代3次大规模成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 24(2): 99-107. [60] 孙家骢, 韩润生, 2016. 矿田地质力学理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. [61] 汪劲草, 王蓉嵘, 周瑶, 等, 2006. 矿体的侧伏规律及其地质意义[J]. 桂林工学院学报, 26(3): 305-309. -




 下载:
下载: