Study on the activity of the Cuona-Woka Fault Zone, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, and geological safety risks and prevention methods
-
摘要: 沿青藏高原雅鲁藏布江缝合带修建的高原铁路穿越错那−沃卡活动断裂带,而断裂活动引起同震地表错动造成的工程错断、隧道变形、地质灾害等危害,是铁路运营阶段面临的重要地质安全风险。基于遥感解译、野外调查并结合已有研究成果,分析了穿越高原铁路的错那−沃卡断裂带的发育特征、活动性及其对铁路工程的影响。研究结果表明,错那−沃卡断裂带由5条北东走向的分支断裂组成,其中沃卡盆地西边界断裂(F2-1、F2-2)为晚更新世活动断裂,沃卡盆地东边界断裂(F2-4、F2-5)为全新世活动断裂,盆地内部断裂F2-3为1915年桑日MS 7.0地震的发震断裂。根据断裂活动造成的变形迹象考察以及活动断裂类型来估算断裂影响范围,未来错那−沃卡断裂带的分支断裂发生同震地表错动时,可能对穿越断裂带的藏嘎隧道和桑珠岭隧道造成变形破坏,断裂活动影响范围宽度为16~30 m。因此,建议加强对高原铁路穿越活动断裂区段的强震变形、工程错断等地质安全风险防控对策研究。文章研究结果为指导高原铁路安全运营和防灾减灾,以及为其他铁路线的活动断裂工程影响评价提供参考。Abstract:
Objective The Plateau Railway, constructed along the Yarlung Zangbo suture zone on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, crosses the active Cuona-Woka Fault Zone. Coseismic surface rupture caused by the active fault leads to engineering breaks, tunnel deformation, and geological disasters; it poses a significant geological safety risk during railway operation. Methods Based on remote sensing, field investigation, and published research, this paper analyzes the development characteristics, activity, and impact of the Cuona-Woka Fault Zone on the Plateau Railway that it intersects. Results The study shows that the Cuona-Woka Fault Zone consists of five northeast-trending branch faults. The western boundary faults of the Woka Basin (F2-1, F2-2) show Late Pleistocene activity, the eastern boundary faults of the Woka Basin (F2-4, F2-5) have Holocene activity, and the F2-3 fault within the basin is the seismogenic fault of the 1915 MS 7.0 Sangri earthquake. Based on the deformation signs caused by fault activity and the types of active faults, it is estimated that future coseismic surface ruptures of the branch faults of the Cuona-Woka Fault Zone may cause deformation and damage to the Zangga tunnel and the Sangzhuling tunnel, which cross the fault zone, with an impact width of approximately 16~30 m. Conclusion Therefore, it is recommended to strengthen research on geological safety risk prevention measures for strong seismic deformation and engineering breaks in the sections of the Plateau Railway crossing the active fault zone. [Significance] The results of the study provide guidance for safe operation and disaster prevention and mitigation of the Plateau Railway, as well as a reference for the impact assessment of active fault engineering on other railway lines. -
Key words:
- Plateau Railway /
- Cuona-Woka /
- active faults /
- geological safety /
- engineering breaks /
- risk prevention and control
-
图 1 藏南裂谷系构造特征与研究区域地质概况
ATF—阿尔金断裂;BCF—崩错断裂;BWR—普兰−文布当桑裂谷;CWR—错那−沃卡裂谷;DXR—定结−申扎裂谷;GCF—格仁错断裂;GTR—岗嘎−当惹雍错裂谷;JF—嘉黎断裂;JGR—江曲藏布−改则裂谷;KF—喀喇昆仑断裂;XF—鲜水河断裂;ZTR—仲巴−塔若错裂谷;F1—雅鲁藏布江断裂带;F2—错那−沃卡断裂带;F3—里龙断裂带;F4—东久−米林断裂带;F5—尼洋河断裂带;F6—喇嘛岭断裂带;F7—派区断裂带a—青藏高原板块构造示意图;b—藏南主要活动断裂、裂谷、地震分布图(据高扬等,2024修改);c—研究区域地质概况及交通位置图
Figure 1. Structural characteristics of the southern Xizang(Tibet) rift system and geological overview of the study area
(a) Schematic plate tectonic diagram of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; (b) Distribution map of major active faults, rift valleys, and earthquakes in southern Xizang(Tibet) (modified after Gao et al., 2024); (c) Geological overview and traffic location map of the study area F1—Yarlung Zangbo Fault Zone; F2— Cuona-Woka Fault Zone; F3—Lilong Fault Zone; F4—Dongjiu-Milin Fault Zone; F5—Niyang River Fault Zone; F6—Lamaling Fault Zone; F7—Paiqu Fault ZoneATF—Altun Tagh Fault Zone; BCF—Bengcuo Fault Zone; BWR—Pulan-Wenbudangsang Rift; CWR—Cuona-Woka Rift; DXR—Dingjie -Shenzha Rift; GCF—Gyaring Co Fault Zone; GTR—Gangga-Dangreyongcuo Rift; JF—Jiali Fault Zone; JGR—Jiangquzangbo-Gerze Rift; KF—Karakorum Fault Zone; XF—Xianshuihe Fault Zone; ZTR—Zhongba-Taruocuo Rift
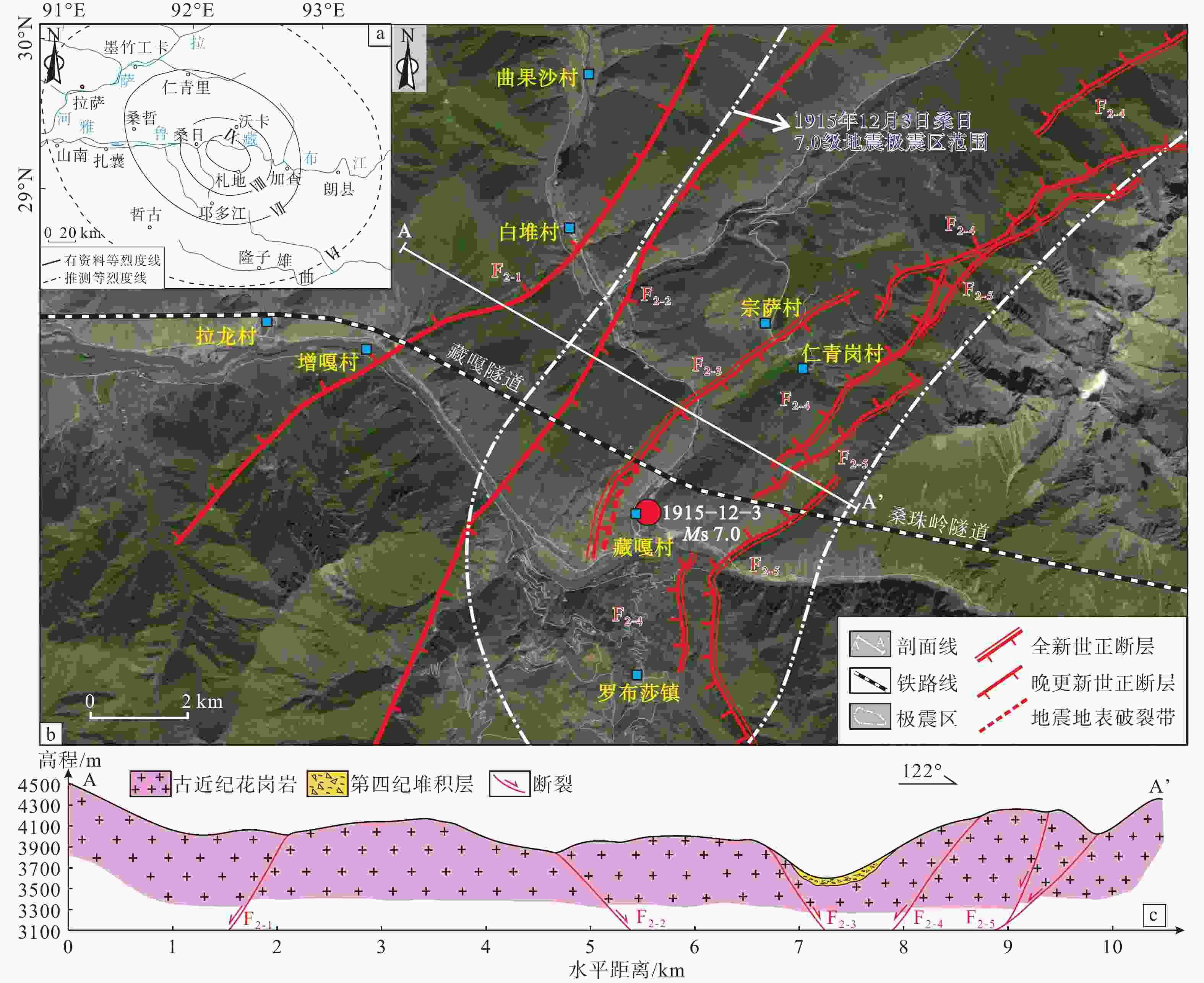
图 2 高原铁路穿越错那−沃卡断裂带遥感解译与空间结构特征
a—1915年西藏桑日地震等烈度线图(据张升林和江在雄,1991修改);b—错那−沃卡断裂带空间展布特征(遥感影像和铁路线位置据国家地理信息公共服务平台(天地图)修改);c—错那−沃卡断裂带地质剖面图
Figure 2. Remote sensing interpretation and spatial structural characteristics of the Plateau Railway crossing the Cuona-Woka Fault Zone
(a) Intensity line diagram of the 1915 Sangri earthquake in Xizang(Tibet) (modified after Zhang and Jiang, 1991); (b) Spatial distribution characteristics of the Cuona-Woka Fault Zone (Remote sensing image and railway location from the National Platform for Common Geo-Spatial Information Services); (c) Geological profile of the Cuona-Woka Fault Zone
图 3 沃卡盆地西边界断裂(F2-1、F2-2)线性地貌特征与活动表现特征
a—增嘎村东侧F2-1断裂线性地貌特征(镜向北东);b—增嘎村雅鲁藏布江北岸F2-1断裂剖面(镜向北东);c—白堆村采石场F2-1断裂剖面(镜向北);d—增曲水电站引水渠东侧F2-2断裂剖面(镜向南东)
Figure 3. Linear geomorphic features and activity characteristics of the western boundary fault (F2-1, F2-2) of the Woka Basin
(a) Linear geomorphic features of F2-1 to the east of Zengga Village (facing NE); (b) Typical profile of F2-1 at the northern bank of the Yarlung Zangbo River in Zengga Village (facing NE); (c) F2-1 fault profile at the Baidui Village quarry (facing N); (d) F2-2 fault profile on the eastern side of the diversion channel of Zengqu hydropower station (facing SE)
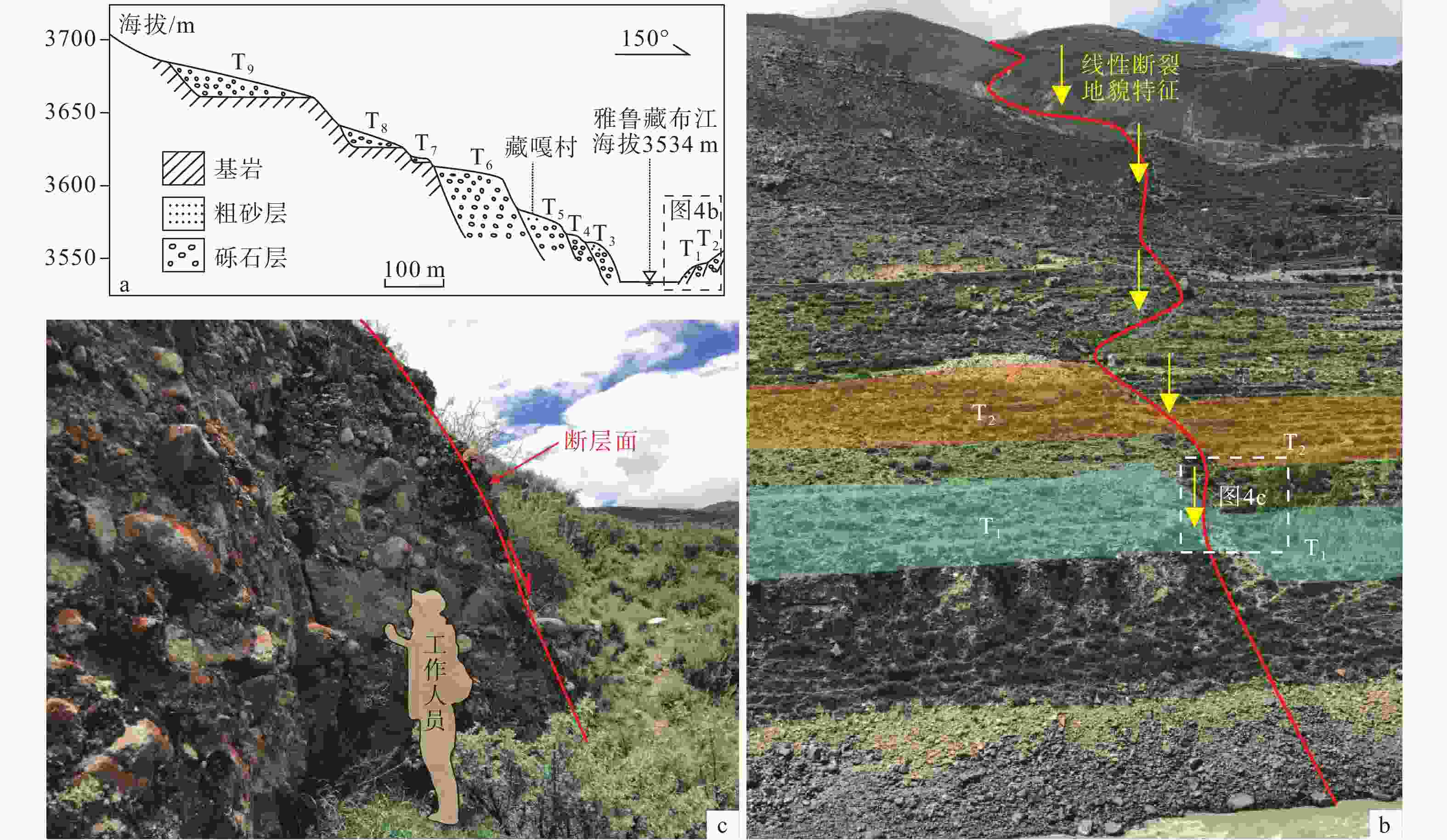
图 4 藏嘎村雅鲁藏布江右岸河流阶地东边界断裂(F2-4)
a—藏嘎村雅鲁藏布江横剖面(祝嵩,2012);b—雅鲁藏布江右岸T1、T2阶地(镜向南西);c—断裂错断阶地断面(镜向南西)
Figure 4. The eastern boundary fault (F2-4) on the river terrace on the right bank of the Yarlung Zangbo River in Zangga Village
(a) Cross-section of the Yarlung Zangbo River in Zangga Village (Zhu, 2012); (b) T1 and T2 terraces on the right bank of the Yarlung Zangbo River (facing SW); (c) Fault-displaced terrace profile (facing SW)
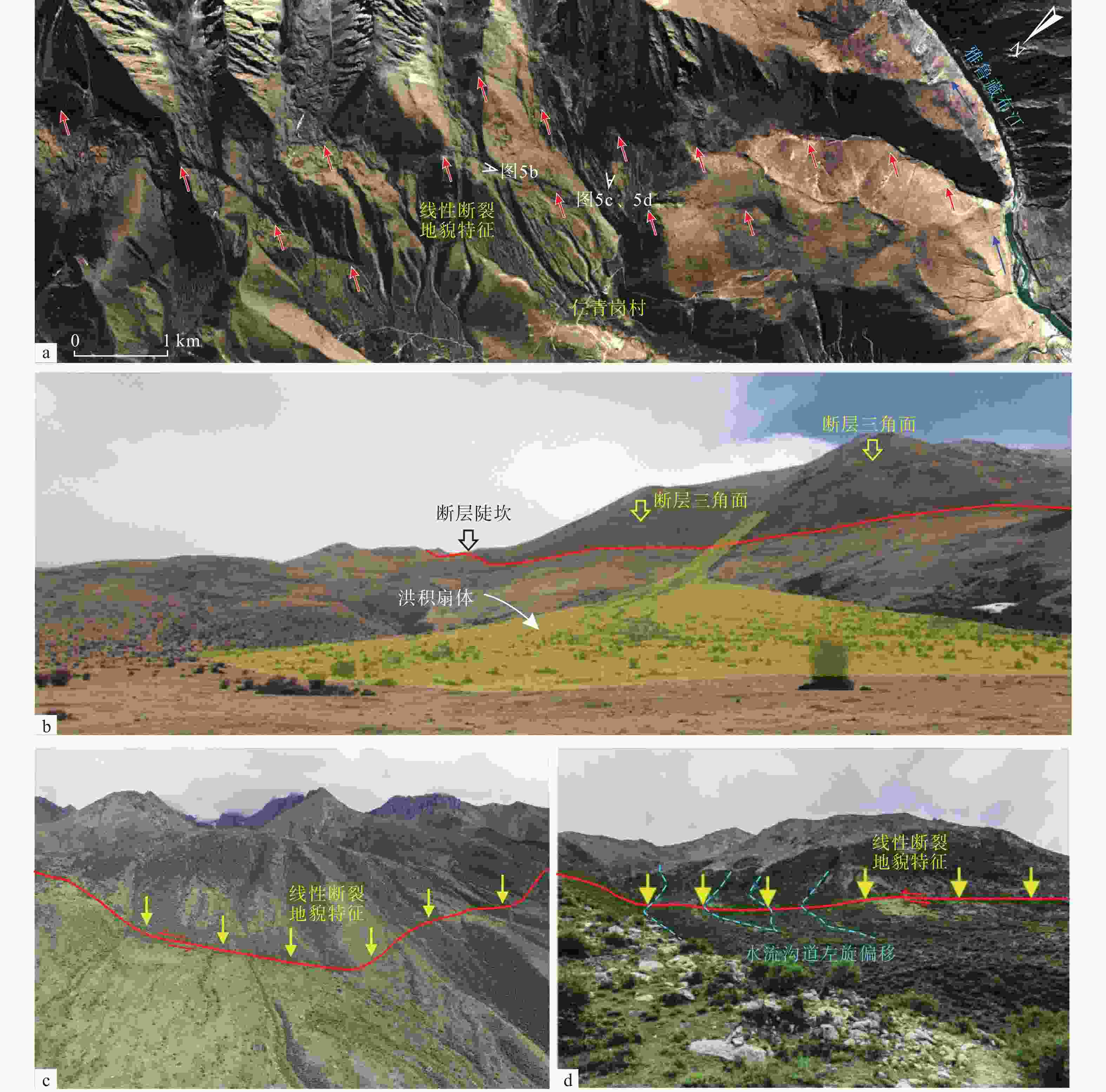
图 5 沃卡盆地东边界断裂断错地貌特征
a—沃卡盆地东边界断裂(F2-4、F2-5)线性地貌特征;b—断裂F2-5沿线断层三角面地貌形态特征(镜向北东);c—仁青岗寺庙东测断裂F2-5穿越导致植被覆盖呈线性特征(镜向南东);d—断裂F2-5导致水流沟道左旋偏移特征(镜向南东)
Figure 5. Geomorphic features of the eastern boundary fault in the Woka Basin
(a) Linear geomorphic features of the eastern boundary faults (F2-4 and F2-5) of the Woka Basin; (b) Geomorphic features of atriangular fault surface along the F2-5 fault (facing NE); (c) Linear features of vegetation coverage caused by the F2-5 fault crossing the east side of the Renqinggang Temple (facing SE); (d) Sinistral deviation of water channels caused by the F2-5 fault (facing SE)
图 6 沃卡盆地盆内断裂(F2-3)活动表现特征
a、b—断裂F2-3穿越藏嘎村西侧形成的地震楔剖面特征(镜向北东);c—断裂F2-3穿越藏嘎村西侧山坡地表破裂带特征(镜向南);d、e—断裂F2-3穿越藏嘎村西侧断裂断错剖面特征(镜向北东)
Figure 6. Activity characteristics of the F2-3 fault in the interior of the Woka Basin
(a)-(b) Characteristics of seismic wedge profiles formed by the F2-3 fault crossing the western side of Zangga Village (facing NE); (c) Characteristics of the surface rupture zone of the F2-3 fault crossing a hillside west of Zangga Village (facing S); (d)-(e) Characteristics of the F2-3 fault profile on the western side of Zangga Village (facing NE)
表 1 错那−沃卡断裂带断层活动对高原铁路工程影响评价表
Table 1. Evaluation of the impact of fault activity on the Plateau Railway project in the Cuona-Woka Fault Zone
断裂名称 编号 产状 断裂
性质活动
时代断裂带宽度/m 变形带宽度/m 影响线路位置 走向 倾向 沃卡盆地西边界断裂 F2-1 由北东向转北北东向 北西向 正断 晚更新世 0 16 藏嘎隧道 沃卡盆地西边界断裂 F2-2 由北东向转南北走向 南东向 正断 晚更新世 0 16 沃卡盆地盆内断裂 F2-3 北东向 南东向 正断 全新世 0 30 沃卡盆地东边界断裂 F2-4 由北东向转南北走向 由北西向转向西 正断 全新世 0 30 桑珠岭隧道 沃卡盆地东边界断裂 F2-5 由北东向转南北走向 由北西向转向西 正断 全新世 0 30 -
[1] BIAN S, YU Z Q, GONG J F, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal distribution and geodynamic mechanism of the nearly NS-trending rifts in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 178-194. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] CHEN P, GENG P, CHEN J, et al., 2023. The seismic damage mechanism of Daliang tunnel by fault dislocation during the 2022 Menyuan Ms6.9 earthquakes based on unidirectional velocity pulse input[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 145: 107047. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107047 [3] DALGIÇ S, 2002. Tunneling in squeezing rock, the Bolu tunnel, Anatolian Motorway, Turkey[J]. Engineering Geology, 67(1-2): 73-96. [4] DENG Q D, ZHANG P Z, RAN Y K, et al., 2003. Basic characteristics of active tectonics of China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(4): 356-372. doi: 10.1360/03yd9032 [5] DOWDING C H, ROZAN A, 1978. Damage to rock tunnels from earthquake shaking[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division, 104(2): 175-191. [6] EISENBERG Y, TREADWELL D D, 2015. San Francisco's southwest ocean outfall[M]. Coastal Engineering: 1982. 2418-2435. [7] GAO Y, WU Z H, ZUO J M, et al., 2024. Spatial-temporal activity of quaternary faults at southern end of Nyalam-Coqen rift, southern Tibet[J]. Earth Science, 49(7): 2552-2569. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] GUO C B, ZHANG Y S, JIANG L W, et al., 2017. Discussion on the environmental and engineering geological problems along the Sichuan-Tibet railway and its adjacent area[J]. Geoscience, 31(5): 877-889. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] HA G H, WU Z H, HE L, 2018. Late Cenozoic sedimentary strata of Qiongduojiang graben, South Tibet: preliminary constraint on the initial rifting age of the SN- trending rift[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(10): 2051-2067. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] HA G H, WU Z H, 2021. Discussion of the seismogenic structure of the 1901 M 6¾ Nyemo earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 218-229. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] HEERMANCE R, SHIPTON Z K, EVANS J P, 2003. Fault structure control on fault slip and ground motion during the 1999 rupture of the Chelungpu Fault, Taiwan[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 93(3): 1034-1050. [12] LING Y C, 2023. Seismic damage characteristics and repair technology of railway tunnels crossing active fault zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 19(3): 1027-1037. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] PENG B Z, YANG Y C, 1996. Physical geography and natural resources in the Nanga Bawa area[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-380. (in Chinese) [14] ROCKWELL T K, BEN-ZION Y, 2007. High localization of primary slip zones in large earthquakes from paleoseismic trenches: observations and implications for earthquake physics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B10): B10304. [15] SHAN X J, LIU J H, MA C, 2004. Preliminary analysis on characteristics of coseismic deformation associated with MS=8.1 western Kunlunshan pass earthquake in 2001[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 26(5): 474-480. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] SONG G Z, ZHANG Y H, 2021. Development types and risk assessment of high-steep dangerous rock mass at the entrance of Lhasa-Linzhi railway tunnel[J]. Railway Engineering, 61(1): 88-92. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] TANG R C, LI T T, LI J C, 1980. Preliminary understanding of the geological and structural background and causes of the Dangxiong 7.5 earthquake[J]. Journal of Seismological Research(1): 87-96. (in Chinese) [18] TAPPONNIER P, MERCIER J L, ARMIJO R, et al., 1981. Field evidence for active normal faulting in Tibet[J]. Nature, 294(5840): 410-414. doi: 10.1038/294410a0 [19] TAPPONNIER P, XU Z Q, ROGER F, et al., 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 294(5547): 1671-1677. [20] TAYLOR M, YIN A, 2009. Active structures of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen and their relationships to earthquake distribution, contemporary strain field, and Cenozoic volcanism[J]. Geosphere, 5(3): 199-214. [21] WANG S, LYU T Y, WU Z H, et al., 2023. Research on the applicability of electron spin resonance dating of the late Quaternary sinter deposits in the rift valley, southern Tibet[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 29(2): 276-289. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] WEI L M, XU X W, LI F, et al., 2023. Theory and application of setback distance from active faults[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 51(12): 69-82. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] WEN Y L, SONG Z P, YU H Y, et al., 2016. Current large earthquake risk on the eastern Himalayan belt and compared to the seismicities before 1950 Motuo M 8.6 earthquake[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 31(1): 103-109. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] WU Z H, ZHANG Y S, HU D G, et al., 2007. Quaternary normal faulting and its dynamics of the Oiga graben in south-eastern Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(10): 1328-1337. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] WU Z H, ZHANG Y S, HU D G, et al., 2008. The quaternary normal faulting of the Cona-Oiga rift[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(1): 144-160. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] WU Z H, 2024. The earthquake-controlling process of continental collision-extrusion active tectonic system around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: a case study of strong earthquakes since 1990[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 30(2): 189-205. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] XIE P, TANG F T, LIANG X H, et al., 2017. Late quaternary movement characteristics of Lilong fault at the west side of Namcha Barwa syntaxis[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 12(3): 480-490. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] XU X W, YU G H, MA W T, et al., 2002. Evidence and methods for determining the safety distance from the potential earthquake surface rupture on active fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 24(4): 470-483. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] XU X W, YU G H, CHEN G H, et al., 2007. Near-surface character of permanent geologic deformation across the mega-strike-slip faults in the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Seismology and Geology, 29(2): 201-217. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] XU X W, WEN X Z, YE J Q, et al., 2008. The Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake surface ruptures and its seismogenic structure[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 597-629. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] XU X W, GUO T T, LIU S Z, et al., 2016. Discussion on issues associated with setback distance from active fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(3): 477-502. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] XU Z Q, LI H B, YANG J S, 2006. An orogenic plateau: the orogenic collage and orogenic types of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(4): 1-17. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] YU H T, CHEN J T, BOBET A, et al., 2016. Damage observation and assessment of the Longxi tunnel during the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 54: 102-116. [34] ZHANG P Z, WANG M, GAN W J, et al., 2003. Slip rates along major active faults from GPS measurements and constraints on contemporary continental tectonics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 81-92. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] ZHANG P Z, DENG Q D, ZHANG Z Q, et al., 2013. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 43(10): 1607-1620. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] ZHANG S L, JIANG Z X, 1991. The 1915 7.0-magnitude Sangri earthquake in Tibet[J]. Northeastern Seismological Research, 7(1): 131-132. (in Chinese) [37] ZHANG W, LI M, JI Y P, et al., 2022. Analysis and enlightenment of typical failure characteristics of tunnels caused by the Menyuan M6.9 earthquake in Qinghai Province[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 44(3): 661-669. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] ZHANG Y S, SUN P, SHI J S, et al., 2010. Investigation of rupture influenced zones and their corresponding safe distances for reconstrution after 5.12 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 18(3): 312-319. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] ZHANG Y S, REN S S, GUO C B, et al., 2019. Research on engineering geology related with active fault zone[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(4): 763-775. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] ZHANG Y S, WU R A, GUO C B, et al., 2022. Geological safety evaluation of railway engineering construction in plateau mountainous region: ideas and methods[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(5): 1736-1751. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] ZHOU Q, XU X W, YU G H, et al., 2010. Width distribution of the surface ruptures associated with the Wenchuan earthquake: implication for the setback zone of the seismogenic faults in postquake reconstruction[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 100(5B): 2660-2668 [42] ZHOU R J, MA S H, GONG Y, et al. , 1997. Recent activity of the fault from Cuona to Zegucuo in Tibet and the Cuonai earthquake with magnitude 7½ in A. D. 1806[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan(3): 35-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] ZHU S, 2012. River landform and geology environment evolution in the Yarlung Zangbo River valley[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Science. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] 卞爽,于志泉,龚俊峰,等,2021. 青藏高原近南北向裂谷的时空分布特征及动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报,27(2):178-194. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.018 [45] 邓起东,张培震,冉勇康,等,2002. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学D辑:地球科学,32(12):1020-1030. [46] 高扬,吴中海,左嘉梦,等,2024. 藏南聂拉木-措勤裂谷南段第四纪正断层作用的时空特征[J]. 地球科学,49(7):2552-2569. [47] 郭长宝,张永双,蒋良文,等,2017. 川藏铁路沿线及邻区环境工程地质问题概论[J]. 现代地质,31(5):877-889. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.05.001 [48] 哈广浩,吴中海,何林,2018. 藏南邛多江地堑的晚新生代沉积地层及对南北向裂谷形成时代的初步限定[J]. 地质学报,92(10):2051-2067. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.10.007 [49] 哈广浩,吴中海,2021. 西藏尼木1901年M 6¾地震的发震构造探讨[J]. 地质力学学报,27(2):218-229. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.021 [50] 令永春,2023. 穿越活动断裂带铁路隧道震害特征及修复技术[J]. 地下空间与工程学报,19(3):1027-1037. [51] 彭补拙,杨逸畴,1996. 南迦巴瓦峰地区自然地理与自然资源[M]. 北京:科学出版社:1-380. [52] 宋国壮,张玉芳,2021. 拉林铁路隧道洞口高位高陡危岩体发育类型及风险评估[J]. 铁道建筑,61(1):88-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2021.01.22 [53] 唐荣昌,李天祒,李介成,1980. 当雄7.5级地震地质构造背景及其成因的初步认识[J]. 地震研究(1):87-96. [54] 王晟,吕同艳,吴中海,等,2023. 藏南裂谷区晚第四纪泉华的ESR测年适用性研究[J]. 地质力学学报,29(2):276-289. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2023016 [55] 魏雷鸣,徐锡伟,李峰,等,2023. 活动断层避让距离确定的理论基础与应用实例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,51(12):69-82. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.11.0768 [56] 吴中海,张永双,胡道功,等,2007. 西藏桑日县沃卡地堑的第四纪正断层活动及其机制探讨[J]. 地质学报,81(10):1328-1337. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.10.003 [57] 吴中海,张永双,胡道功,等,2008. 藏南错那-沃卡裂谷的第四纪正断层作用及其特征[J]. 地震地质,30(1):144-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2008.01.010 [58] 吴中海,2024. 青藏高原陆陆碰撞-挤出活动构造体系控震作用:以1990年以来强震活动为例[J]. 地质力学学报,30(2):189-205. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2023186 [59] 徐锡伟,于贵华,马文涛,等,2002. 活断层地震地表破裂“避让带”宽度确定的依据与方法[J]. 地震地质,24(4):470-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2002.04.001 [60] 徐锡伟,于贵华,陈桂华,等,2007. 青藏高原北部大型走滑断裂带近地表地质变形带特征分析[J]. 地震地质,29(2):201-217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.02.002 [61] 徐锡伟,郭婷婷,刘少卓,等,2016. 活动断层避让相关问题的讨论[J]. 地震地质,38(3):477-502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.03.001 [62] 许志琴,李海兵,杨经绥,2006. 造山的高原:青藏高原巨型造山拼贴体和造山类型[J]. 地学前缘,13(4):1-17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.04.002 [63] 张培震,王敏,甘卫军,等,2003. GPS观测的活动断裂滑动速率及其对现今大陆动力作用的制约[J]. 地学前缘,10(S1):81-92. [64] 张培震,邓起东,张竹琪,等,2013. 中国大陆的活动断裂、地震灾害及其动力过程[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,43(10):1607-1620. [65] 张升林,江在雄,1991. 1915年西藏桑日7.0级地震[J]. 东北地震研究,7(1):131-132. [66] 张威,李明,姬云平,等,2022. 青海门源M6.9地震典型隧道破坏特征分析与启示[J]. 地震工程学报,44(3):661-669. [67] 张永双,孙萍,石菊松,等,2010. 汶川地震地表破裂影响带调查与建筑场地避让宽度探讨[J]. 工程地质学报,18(3):312-319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.03.004 [68] 张永双,任三绍,郭长宝,等,2019. 活动断裂带工程地质研究[J]. 地质学报,93(4):763-775. [69] 张永双,吴瑞安,郭长宝,等,2022. 高原山区铁路工程建设地质安全评价:思路与方法[J]. 地质学报,96(5):1736-1751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.05.014 [70] 中国地震局地质研究所,2013. 川藏铁路拉萨至林芝段工程沿线断裂活动性评价及地震动参数区划报告[R]. 北京:中国地震局地质研究所. [71] 周荣军,马声浩,龚宇,等,1997. 西藏错那—哲古错断裂的新活动与1806年错那7½级地震[J]. 四川地震(3):35-39. [72] 祝嵩,2012. 雅鲁藏布江河谷地貌与地质环境演化[D]. 北京:中国地质科学院. -





 下载:
下载: