Improving the inversion accuracy of shallow shear wave velocity structure based on microtremor method: A case study of Haikou Jiangdong New District
-
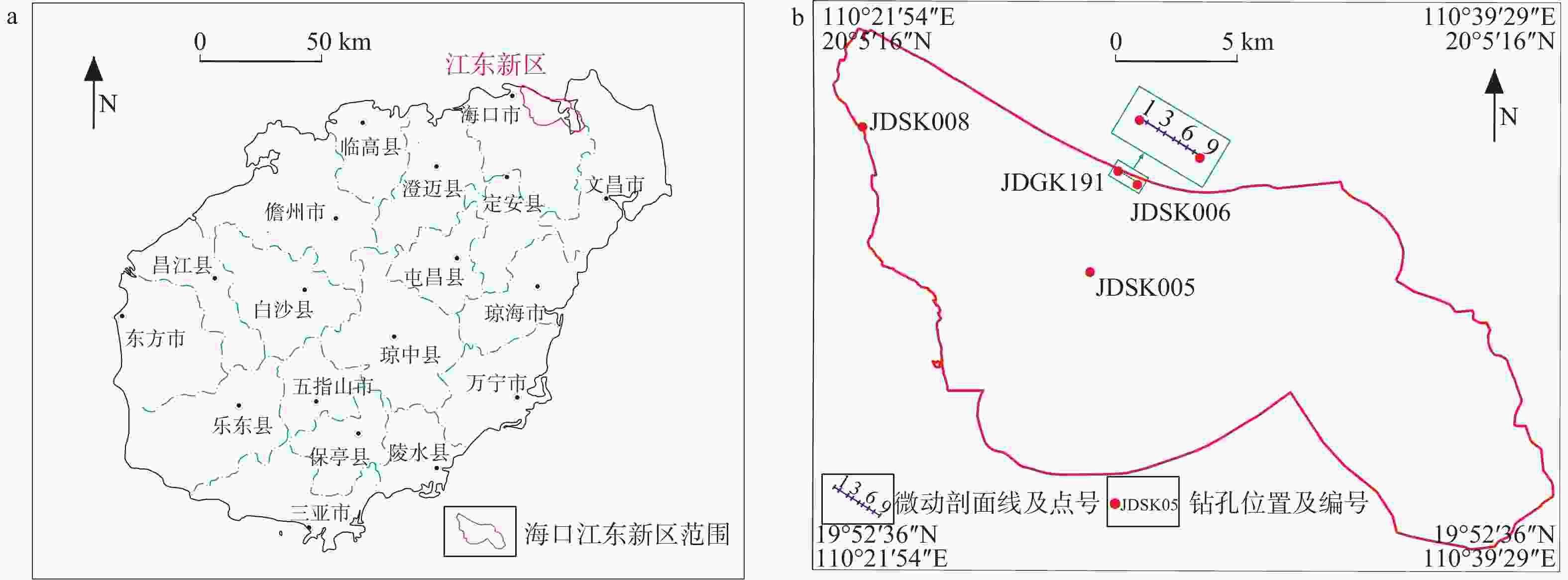
摘要: 微动方法不受地震源时空分布的限制,已成为探测浅层地下横波速度空间结构的重要方法。在海口江东新区开展微动与钻孔、横波测井的对比试验,试验显示:微动反演结果与测井曲线形态一致,对应深度地层的横波速度基本吻合,取得了一定的应用效果;但在分层上微动和钻孔结果并非完全对应,就波速而言,微动结果未反演出一个波速差异较小界面,钻孔结果未区分出一个波速差异较大界面,对两者在微动反演结果中的影响机制进行研究,有助于提高对微动反演模型的认识,获得更合理的反演结果。基于波速差异较小和较大界面,设计物性分层模型、地质分层模型以及组合模型,从频散曲线形态、软弱夹层、分层变化等方面讨论两类界面影响反演结果的规律。结果显示:物性分层模型反演结果能更好地反映出软弱层位置;改变界面主要影响相邻地层,增加波速差异较小和较大界面,分别使相邻地层波速误差增大和减小;波速差异较大界面对相邻层波速的影响程度要小于差异较小界面,误差大幅变化主要是由波速差异较小界面引起,反演对波速差异较小界面更敏感。微动方法在海口江东新区实际应用研究表明,合并模型中波速差异较小界面或增设波速差异较大的界面,不改变地层局部的变化趋势时,有助于提高波速的反演精度。选取实测数据反演得到二维微动横波速度剖面,结合钻孔提供工程基岩面的埋深及起伏信息,为海口江东新区场地条件评价和地下空间利用规划提供可靠依据。Abstract:
Objective The microtremor survey method is not limited by the spatiotemporal distribution of seismic sources and has become an effective method for observing the structure of shallow shear wave velocity. An experiment to compare microtremor, drilling, and shear wave logging was conducted in Jiangdong New District. The experiment showed that the microtremor inversion results were consistent with the logging curve shape, and the shear wave velocities of the strata and the corresponding depths were basically in agreement. Thus, good application results can be achieved. However, it was found that the microtremor inversion strata and the drilled strata did not completely correspond. In terms of wave velocity, the microtremor results could not reveal an interface with a small difference in wave velocity, while the drilling data did not distinguish an interface with a large difference in wave velocity. The study of the influence mechanism of the two factors on the microtremor inversion results is helpful to improve the understanding of the microtremor inversion model and to obtain more reasonable inversion results. Methods On the basis of a small or a large wave velocity difference, a physical stratification model, a geological stratification model, and a combined model are designed. The factors and rules affecting the inversion results are discussed by dispersion curves, low-velocity layers, layer variations, and inversion method. Results The inversion results of the physical property stratification model can better reflect the location of a weak layer. Changing the interface mainly affects the adjacent layers. Adding interfaces with small and large differences in wave velocity increases and decreases the wave velocity errors of the adjacent layers, respectively. The interface with a large velocity difference has less influence on the velocity of the adjacent layers than an interface with a small velocity difference. A large error change is mainly caused by an interface with a small velocity difference, and the inversion is more sensitive to an interface with a small velocity difference. Conclusion The practical application of the microtremor method in Jiangdong New District of Haikou shows that it is helpful to improve the inversion accuracy of the wave velocity by merging the interfaces with smaller wave velocity differences or adding interfaces with larger wave velocity differences, without changing the local trend of the layer velocity. Significance The 2D microtremor shear wave velocity section was obtained by inverting the measured data. Combined with the depth and undulation information of the bedrock surface provided by drilling, it provides a reliable basis for the site condition evaluation and the underground space utilization planning of Haikou Jiangdong New District. -
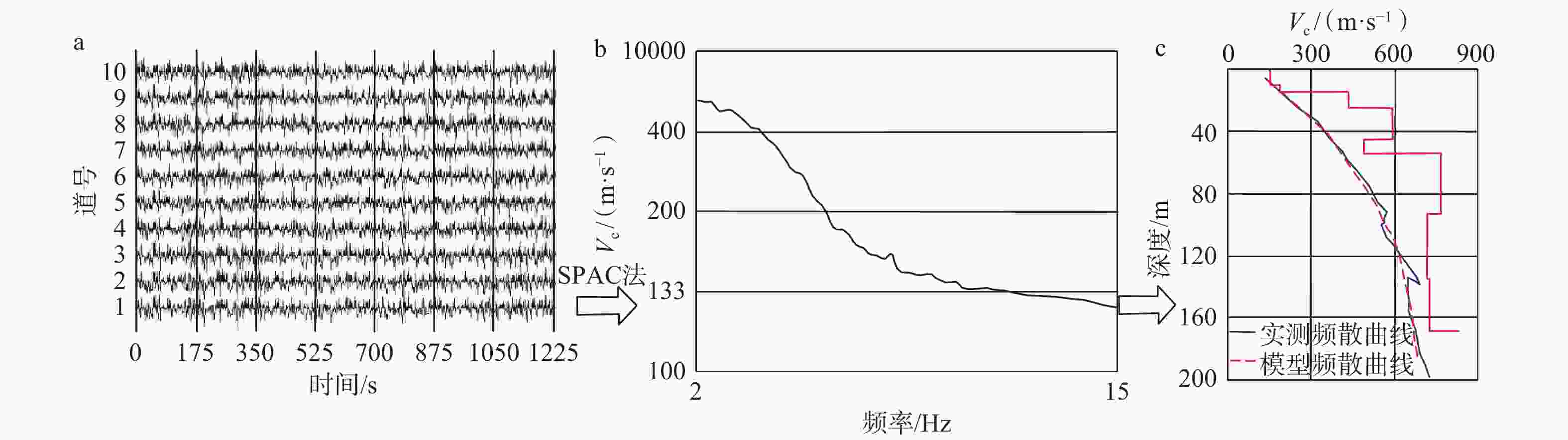
图 4 微动数据主要处理流程(钟宙灿等,2023)
a—微动原始数据;b—频散曲线提取;c—分层反演
Figure 4. Main processing flow of microtremor sound data (Zhong et al.,2023)
(a) Microtremor data; (b) Dispersion curve extraction; (c) Hierarchical inversion
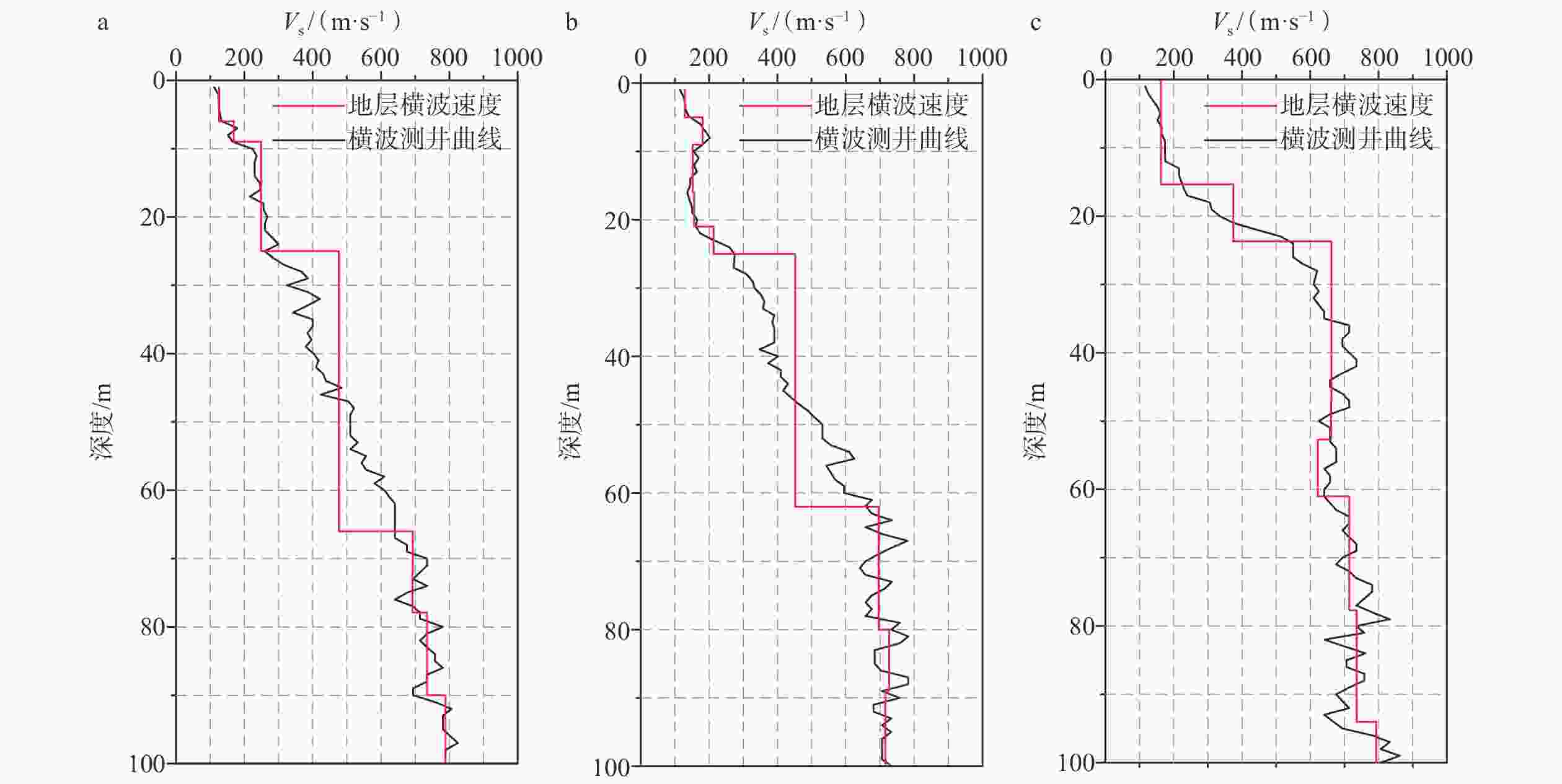
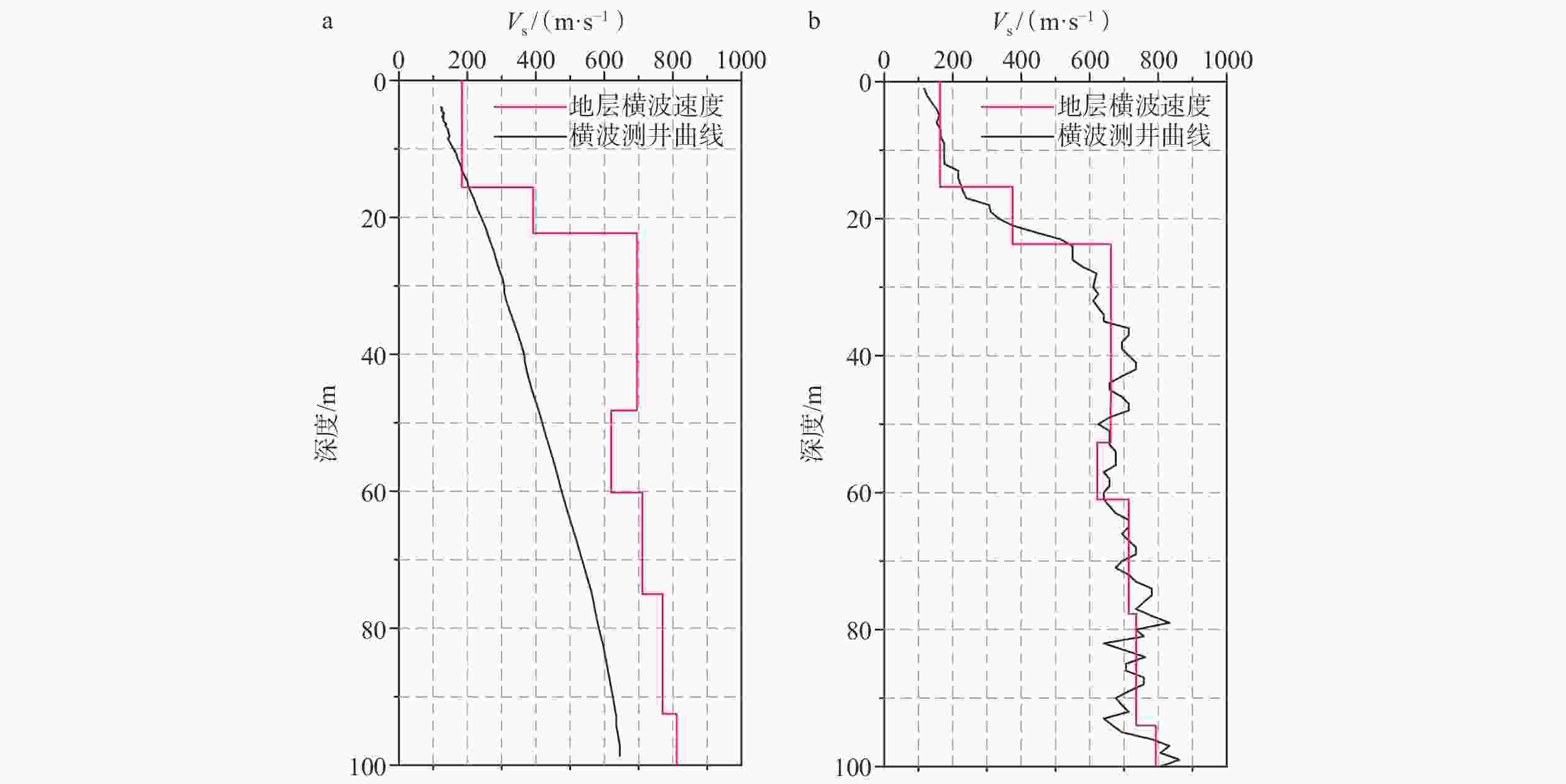
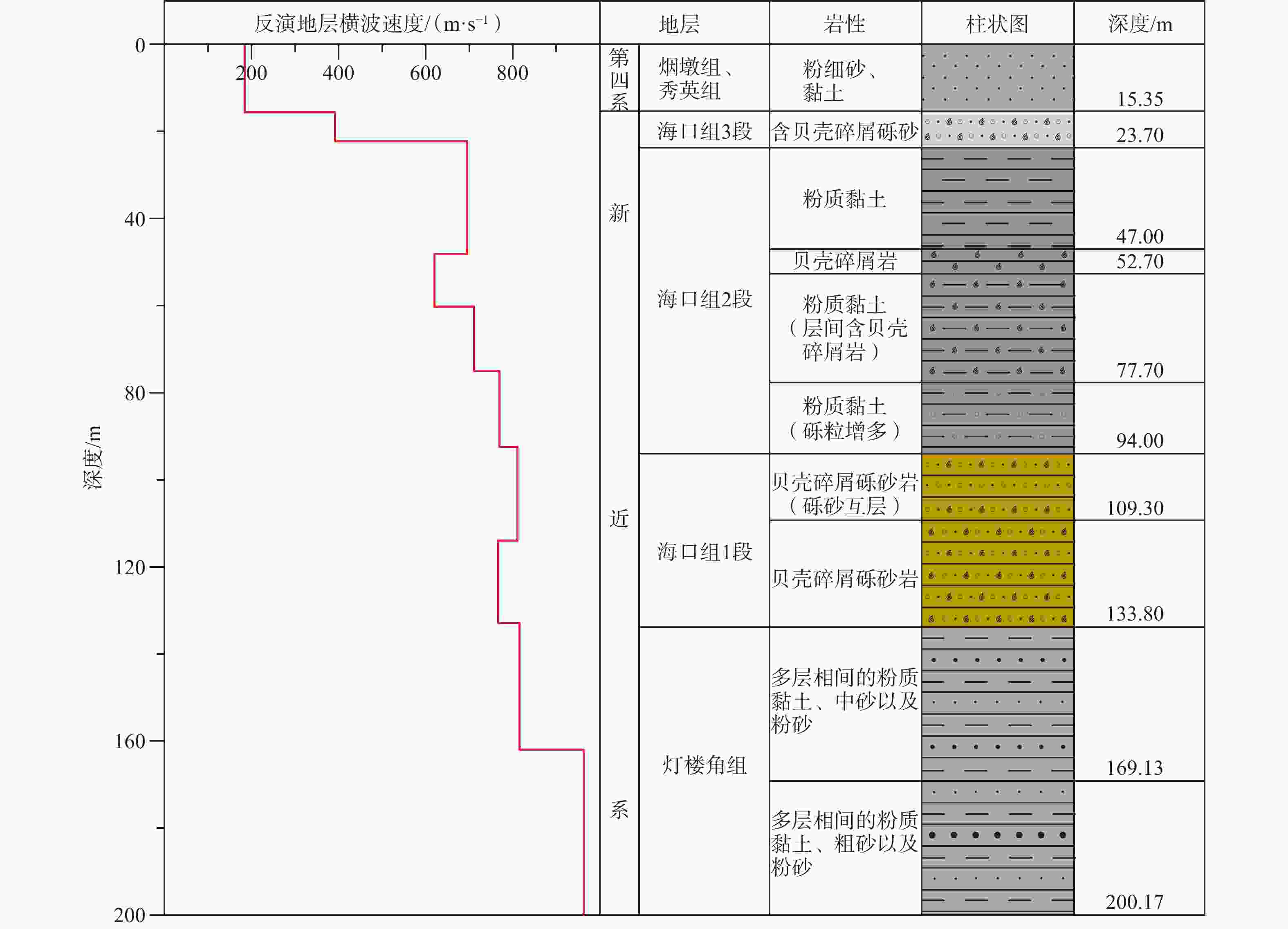
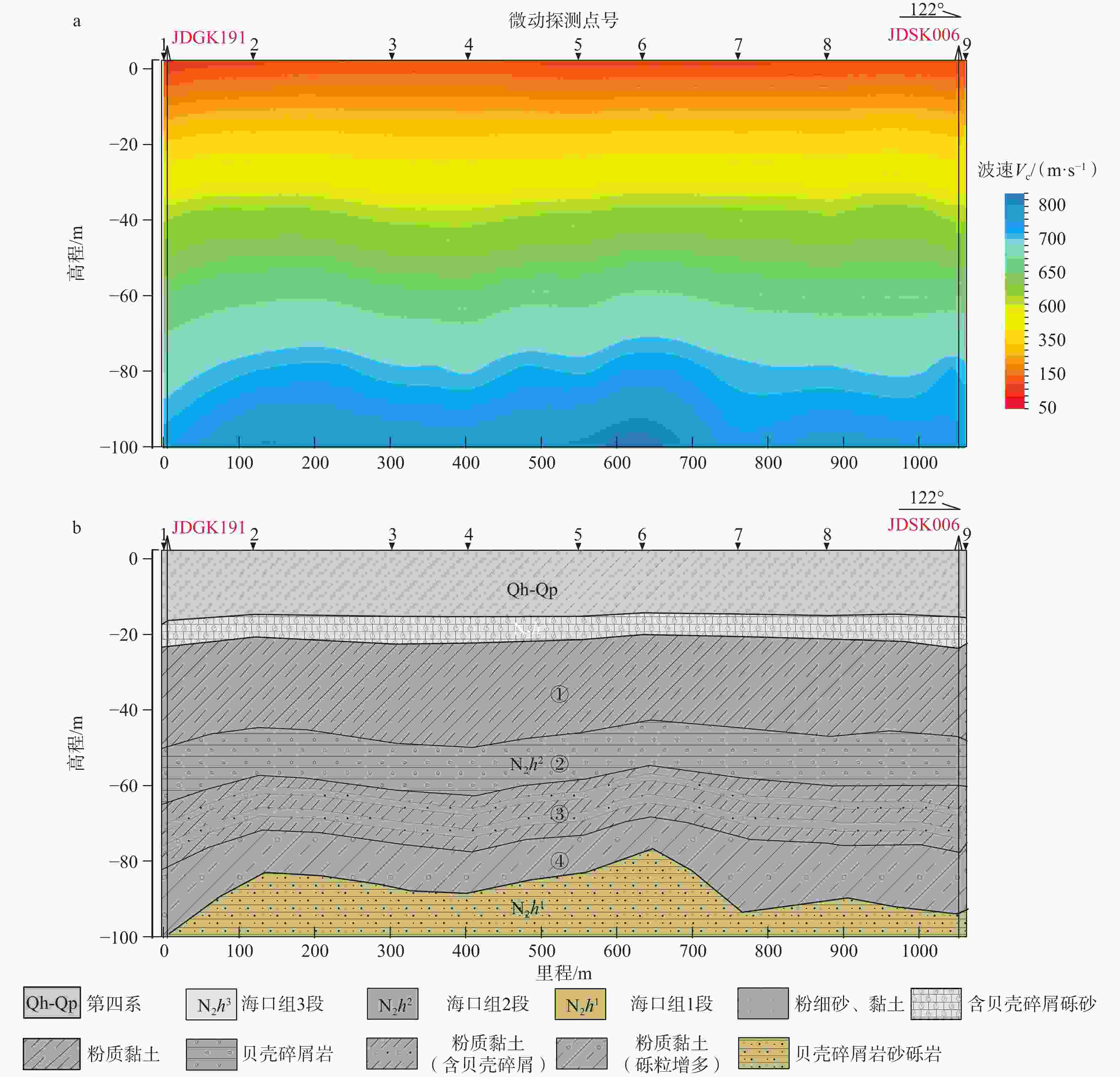
表 1 微动反演结果与JDSK006钻孔钻遇地层、孔中测井结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of microtremor inversion results with geological strata and logging results of borehole JDSK006
钻孔钻遇地层 孔中测井 微动反演结果 底界深度
相对误差/%层速度绝对
误差/(m/s)测井波速
标准差/(m/s)土的
类型时代单元 岩性名称 底界
深度/m层速度/
(m/s)底界
深度/m层速度/
(m/s)第四系烟墩组、秀英组 粉细砂、黏土 15.35 163 15.6 184 1.62 21 30.8 软弱土−
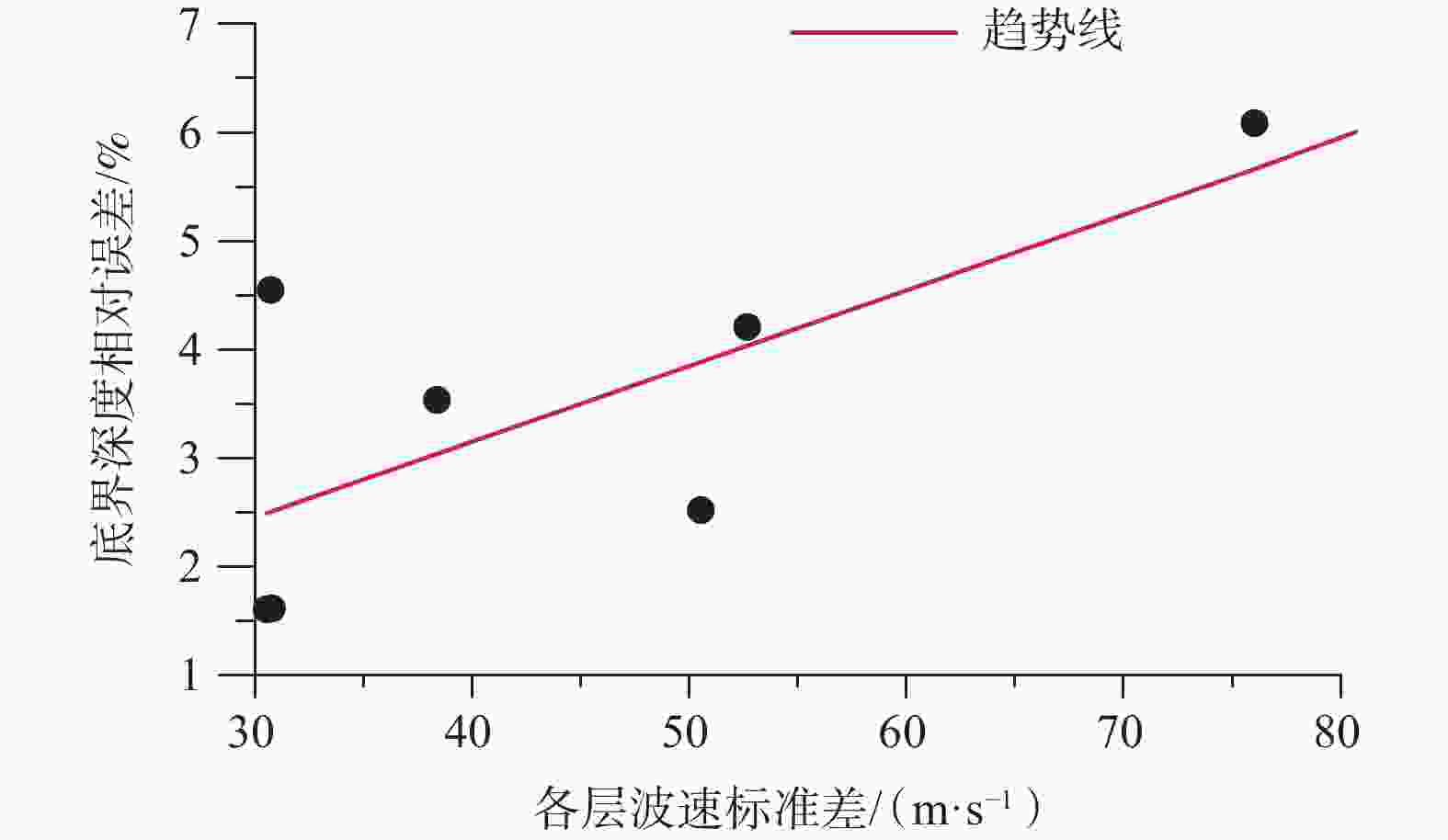
中软土新近系海口组3段 含贝壳碎屑砾砂 23.70 375 22.3 392 6.09 17 76.0 中硬土 新近系海口组2段 粉质黏土 47.00 646 48.2 695 2.52 49 50.5 坚硬土 贝壳碎屑岩 52.70 675 — — — — — 软质岩 粉质黏土
(层间含贝壳碎屑)— 666 60.2 620 4.55 46 30.7 坚硬土 77.70 714 75.0 711 3.54 3 38.4 坚硬土 粉质黏土
(砾粒增多)94.00 736 92.5 770 1.62 34 30.5 坚硬土 新近系海口组1段 贝壳碎屑砂砾岩(砾砂互层) 109.30 793 114.0 811 4.21 18 52.7 较硬岩 贝壳碎屑砂砾岩 133.80 — 133.0 767 0.60 — — 较硬岩 新近系灯楼角组 多层相间的粉质黏土、中砂及粉砂 169.13 — 162.0 816 4.31 — — 坚硬土 多层相间的粉质黏土、粗砂及粉砂 200.17 — 216.0 963 — — — 坚硬土 表 2 模型1—3微动反演结果及误差分析
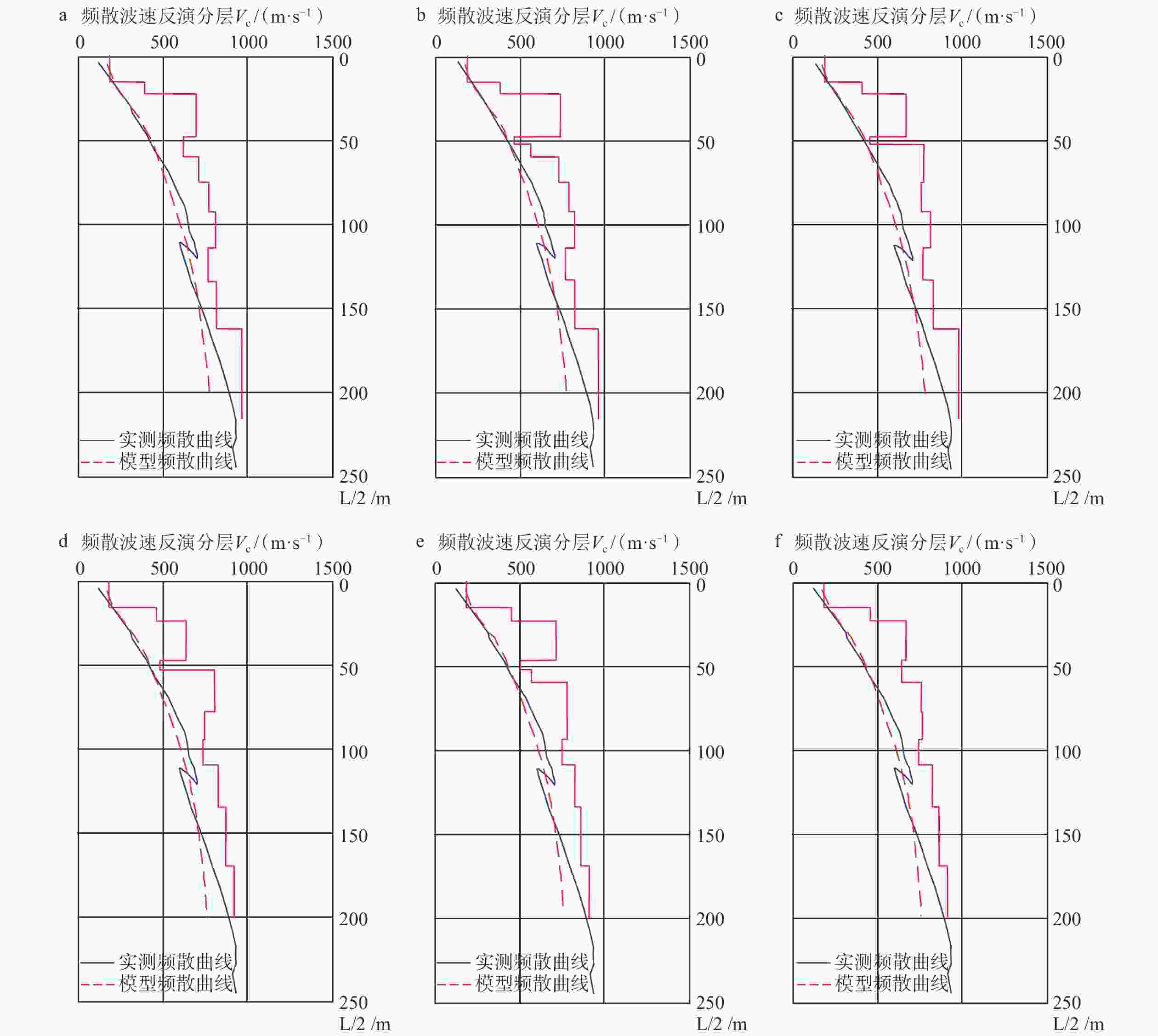
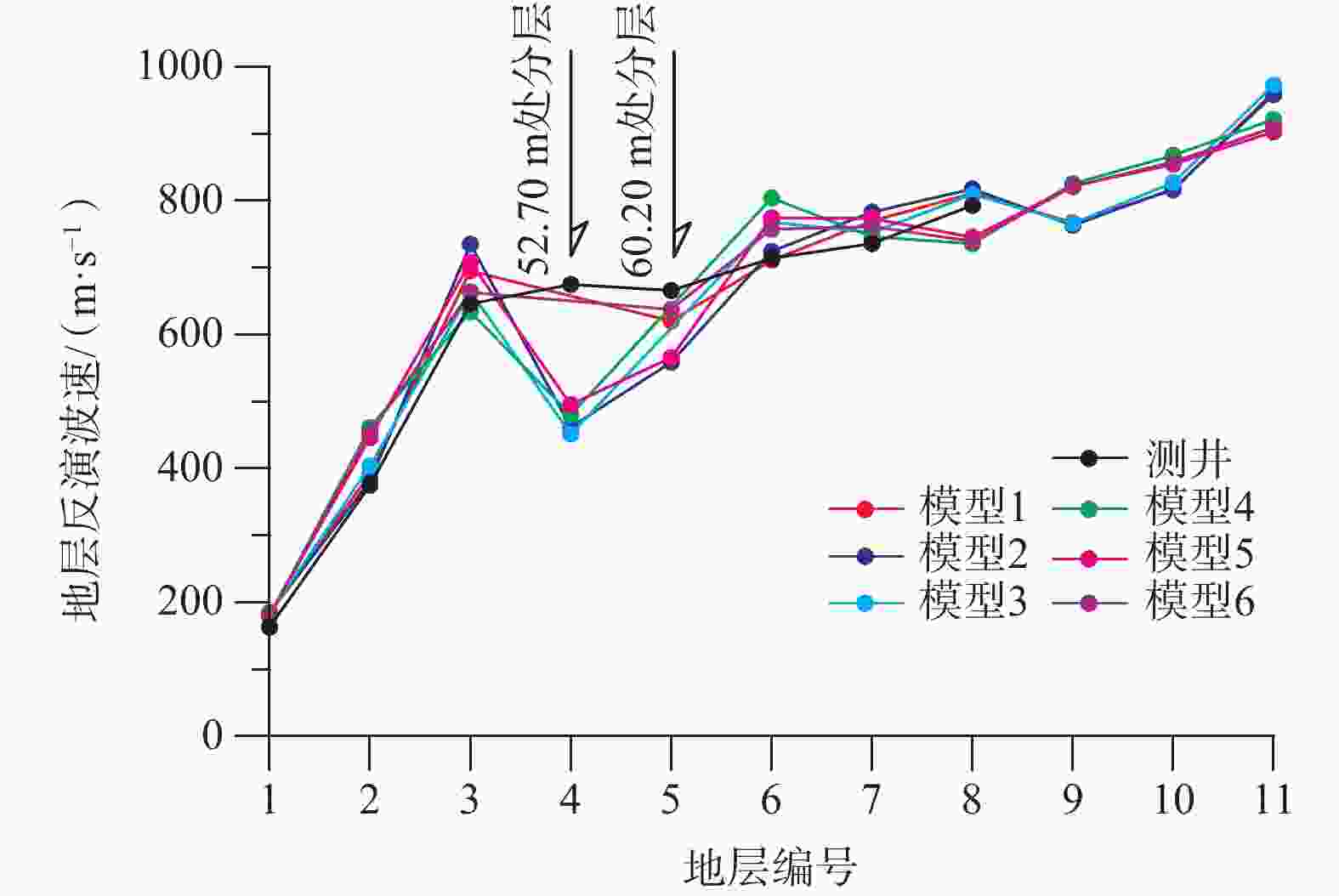
Table 2. Results and error analysis of microtremor inversion in models 1-3
层编号 钻探分层
深度/m测井横波
波速/(m/s)模型1 模型2 模型3 分层深度/
m反演波速/
(m/s)绝对误差/
(m/s)分层深度/
m反演波速/
(m/s)绝对误差/
(m/s)分层深度/
m反演波速/
(m/s)绝对误差/
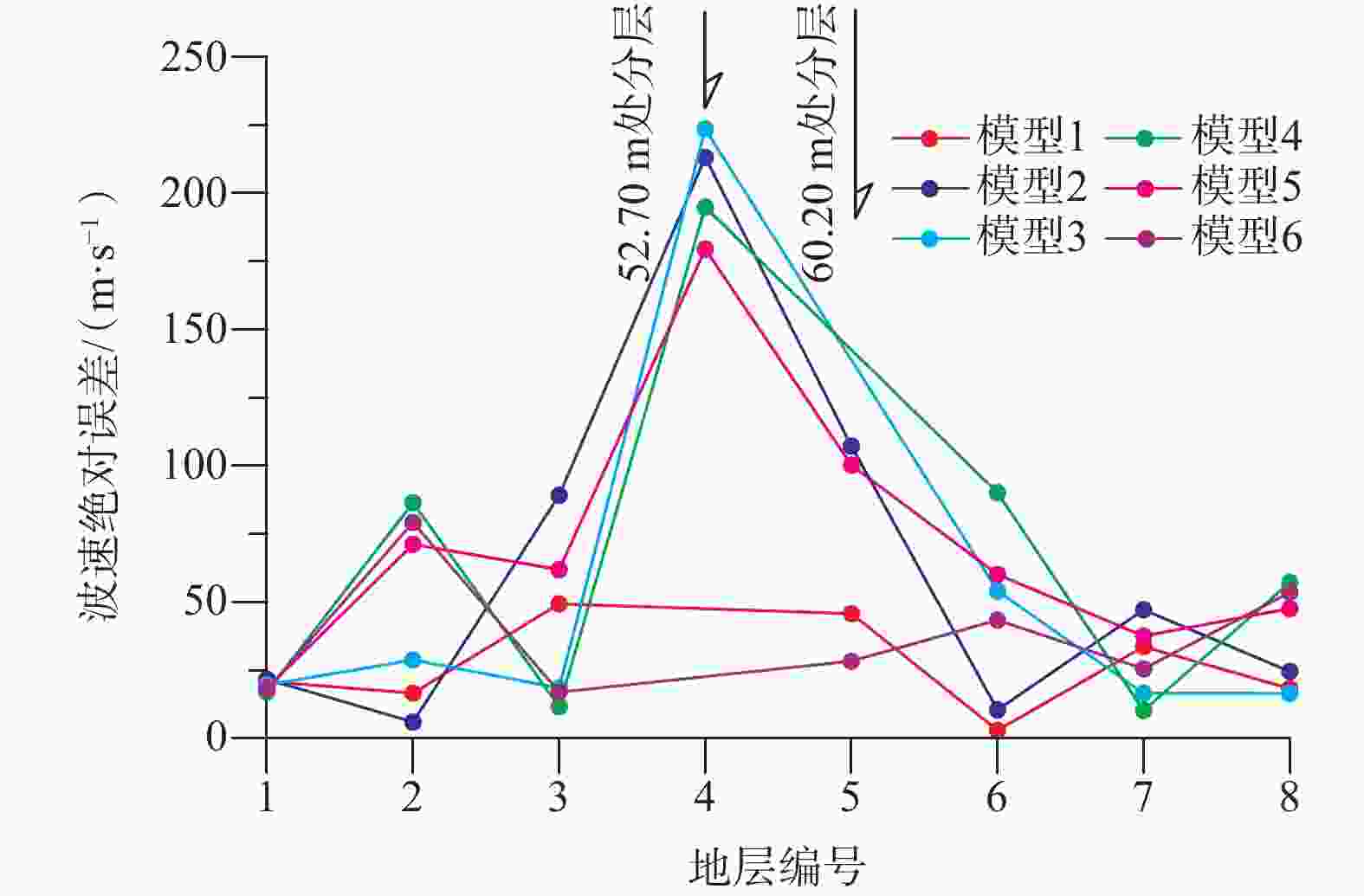
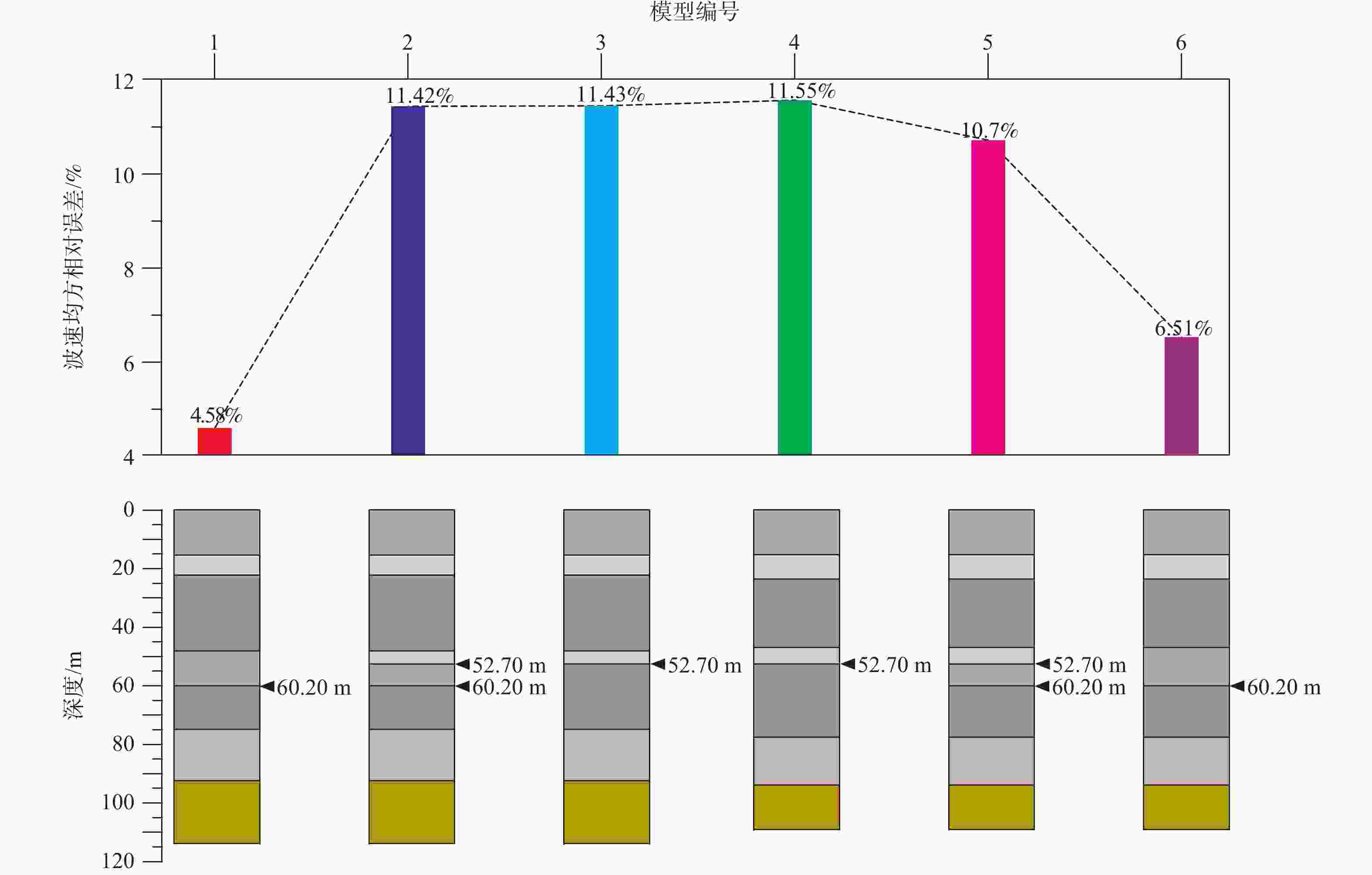
(m/s)1 15.35 163.00 15.60 183.89 20.89 15.60 184.69 21.69 15.60 182.61 19.61 2 23.70 375.00 22.30 391.58 16.58 22.30 381.00 6.00 22.30 403.77 28.77 3 47.00 646.00 48.20 695.34 49.34 48.20 735.18 89.18 48.20 664.50 18.50 4 52.70 675.00 — — — 52.65 461.90 213.10 52.65 451.50 223.50 5 — 666.00 60.20 620.23 45.77 60.20 558.77 107.23 — — — 6 77.70 714.00 75.00 711.01 2.99 75.00 724.49 10.49 75.00 768.07 54.07 7 94.00 736.00 92.50 769.67 33.67 92.60 783.18 47.18 92.40 752.54 16.54 8 109.30 793.00 114.00 811.26 18.26 114.00 817.55 24.55 114.00 809.50 16.50 9 133.80 — 133.80 767.25 — 133.20 763.26 — 133.20 766.27 — 10 169.13 — 162.00 816.04 — 162.00 817.78 — 162.00 827.15 — 11 200.17 — 216.00 962.73 — 216.00 958.50 — 216.00 972.89 — 均方相对误差 4.58% 均方相对误差 11.42% 均方相对误差 11.43% 表 3 模型4—6微动反演结果及误差分析
Table 3. Results and error analysis of microtremor inversion in models 4-6
层编号 钻探分层
深度/m测井横波
波速/(m/s)模型4 模型5 模型6 分层深度/
m反演波速/
(m/s)绝对误差/
(m/s)分层深度/
m反演波速/
(m/s)绝对误差/
(m/s)分层深度/
m反演波速/
(m/s)绝对误差/
(m/s)1 15.35 163.00 15.36 180.05 17.05 15.36 181.40 18.40 15.36 180.90 17.90 2 23.70 375.00 23.70 461.45 86.45 23.70 446.18 71.18 23.70 454.21 79.21 3 47.00 646.00 47.00 634.36 11.64 47.00 707.92 61.92 47.00 662.98 16.98 4 52.70 675.00 52.65 480.12 194.88 52.65 495.54 179.46 — — — 5 — 666.00 — — — 60.20 565.78 100.22 60.20 637.67 28.33 6 77.70 714.00 77.60 804.12 90.12 77.60 774.15 60.15 77.60 757.40 43.40 7 94.00 736.00 94.00 746.26 10.26 94.00 773.53 37.53 94.00 761.50 25.50 8 109.30 793.00 109.25 735.83 57.17 109.25 745.37 47.63 109.25 739.47 53.53 9 133.80 — 133.80 825.48 — 133.80 822.23 — 133.80 821.04 — 10 169.13 — 169.20 867.89 — 169.20 854.44 — 169.20 858.23 — 11 200.17 — 200.00 921.52 — 200.00 902.97 — 200.00 909.55 — 均方相对误差 11.55% 均方相对误差 10.70% 均方相对误差 6.51% -
[1] AKI K, 1957. Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special reference to microtremors[J]. Bulletin of the Earthquake Research Institute, 35: 415-456. [2] AKI K, 1965. A note on the use of microseisms in determining the shallow structures of the earth’s crust[J]. Geophysics, 30(4): 665-666. doi: 10.1190/1.1439640 [3] BEATY K S, SCHMITT D R, SACCHI M, 2002. Simulated annealing inversion of multimode Rayleigh wave dispersion curves for geological structure[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 151(2): 622-631. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2002.01809.x [4] CAI W, SONG X H, YUAN S C, et al., 2018. Inversion of Rayleigh wave dispersion curves based on firefly and bat algorithms[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(6): 2409-2420. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] CHO I, NAKKKANISHI I, LING S, et al., 1999. Application of forking genetic algorithm FGA to an exploration method using microtremors; Bidotansaho heno kotaigun tansaku bunkigata identeki arugorizumu fGA no tekiyo[J]. Geophysical Exploration, 52(3): 227-246. [6] CHAVEZ-GARCIA F J, RODRIDUEZ M, STEPHENSON W R, 2005. Analternative approach to the SPAC analysis of microtremors: exploiting stationarity of noise[J]. Bull. Seism. Soc. Am.,95(1): 277-293. [7] FU W, XU P F, LING S Q, et al., 2012. Application of the microtremor survey method to geothermal exploration[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 33(3): 71-75. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] GAO Y H, HUANG S H, LIU D, et al., 2018. Microtremor detection technology and its new progress in engineering application[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 18(23): 146-155. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] HE Z Q, DING Z F, JIA H, et al., 2007. To determine the velocity structure of shallow crust with surface wave information in microtremors[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(2): 492-498. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] HE Z Q, HU G, LU L Y, et al., 2013. The shallow velocity structure for the Tonghai basin in Yunnan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(11): 3819-3827. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] HORIKE M, 1985. Inversion of phase velocity of long-period microtremors to the S-wave-velocity structure down to the basement in urbanized areas[J]. Journal of Physics of the Earth, 33(2): 59-96. doi: 10.4294/jpe1952.33.59 [12] HUANG H Q, 2011. Research on application of passive suface wave methods in the metallic ore zone[J]. Geology of Fujian, 30(4): 320-326. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] LI Q L, LEI X D, LI C, et al., 2019. Exploring thick overburden structure by microtremor survey: a case study in the subsidiary administrative center[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 34(4): 1635-1643. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] LIANG D Y, XU G Q, XIAO Y, et al., 2021. Neogene-quaternary stratigraphic standard and combined zoning of Haikou Jiangdong new district[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 21(26): 11052-11063. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] LIU H P, BOORE D M, JOYNER W B, et al., 2000. Comparison of phase velocities from array measurements of Rayleigh waves associated with microtremor and results calculated from borehole shear-wave velocity profiles[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 90(3): 666-678. doi: 10.1785/0119980186 [16] LIU Y Z, MEI R W, YE P, et al., 2016. Data acquisition and processing system of WD intelligent natural source surface wave and its application test[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 40(5): 1007-1015. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] LI X Y, CHEN X F, YANG Z T, et al., Application of high-order surface waves in shallow exploration: An example of the Suzhou river, Shanghai[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(1): 247-255. [18] NI S D, LI Z W, SOMERVILLE P, 2014. Estimating subsurface shear velocity with radial to vertical ratio of local P waves[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 85(1): 82-90. doi: 10.1785/0220130128 [19] SONG X H, GU H M, ZHANG X Q, et al., 2008. Pattern search algorithms for nonlinear inversion of high-frequency Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 34(6): 611-624. [20] SONG X H, TANG L, LV X C, et al., 2012. Application of particle swarm optimization to interpret Rayleigh wave dispersion curves[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 84: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2012.05.011 [21] TIAN B Q, DU Y N, YOU Z W, et al., 2019. Measuring the sediment thickness in urban areas using revised H/V spectral ratio method[J]. Engineering Geology, 260: 105223. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105223 [22] TSAI V C, MOSCHETTI M P, 2010. An explicit relationship between time-domain noise correlation and spatial autocorrelation (SPAC) results[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 182(1): 454-460. [23] XIA J H, MILLER R D, PARK C B, 1999. Estimation of near-surface shear-wave velocity by inversion of Rayleigh waves[J]. Geophysics, 64(3): 691-700. doi: 10.1190/1.1444578 [24] XIE P, WANG Q L, LI J G, et al., 2019. Application of SPAC method on stratification of stratigraphic structure in Jianghan Plain[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 41(3): 717-723. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] XU H, WU X P, SHENG Y, et al., 2021. Application of microtremor survey method in detection of urban land subsidence[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 45(6): 1512-1519. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] XU P F, LI C J, LING S Q, et al., 2009. Mapping collapsed columns in coal mines utilizing microtremor survey methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(7): 1923-1930. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] XU P F, LING S Q, LI C J, et al., 2012. Mapping deeply-buried geothermal faults using microtremor array analysis[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 188(1): 115-122. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05266.x [28] XU P F, SHI W, LING S Q, et al., 2012. Mapping spherically weathered “boulders” using 2D microtremor profiling method: a case study along subway line 7 in Shenzhen[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(6): 2120-2128. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] XU P F, LI S H, DU J G, et al., 2013a. Microtremor survey method: a new geophysical method for dividing strata and detecting the buried fault structures[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(5): 1841-1845. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] XU P F, LI S H, LING S Q, et al., 2013b. Application of SPAC method to estimate the crustal S-wave velocity structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(11): 3846-3854. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] XU P F, DU Y N, LING S Q, et al., 2020. Microtremor survey method based on inversion of the SPAC coefficient of multi-mode Rayleigh waves and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(10): 3857-3867. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] XU Y X, ZHANG B L, LUO Y H, et al., 2013b. Surface-wave observations after integrating active and passive source data[J]. The Leading Edge, 32(6): 634-637. doi: 10.1190/tle32060634.1 [33] XU Y X, LUO Y H, 2015. Methods of ambient noise-based seismology and their applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(8): 2618-2636, doi: 10.6038/cjg20150803. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] YANG T C, HE J S, LU S L, et al., 2004a. Dispersion curves of Rayleigh wave in three-layer media[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 28(1): 41-45. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] YANG T C, HE J S, LV S L, et al., 2004b. Multimodes of Rayleigh guided waves and their dispersion and displacement characteristics in three-layer media[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 26(1): 20-26. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] YANG T C, XIAO Q L, 2009. Dispersion characteristics of Rayleigh waves in multilayered media[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 33(3): 299-303. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] ZHANG B X, LU L Y, BAO G S, 2002. A study on zigzag dispersion curves in Rayleigh wave exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 45(2): 263-274. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] ZHAO D, 2010. Passive surface waves: methods and applications[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 34(6): 759-764. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] ZHAO H P, HE D K, HONG Y, 2022. Inversion of microtremor recordings dispersion curve based on geological unit[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 7(6): 662-669. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] ZHONG Z C, CAI S K, LIU Q X, et al., 2023. Application of SPAC method on to the fine division of Neogene-quaternary strata in Haikou Jiangdong new district[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 23(36): 15393-15403. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 蔡伟,宋先海,袁士川,等,2018. 基于萤火虫和蝙蝠群智能算法的瑞雷波频散曲线反演[J]. 地球物理学报,61(6):2409-2420. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0322 [42] 付微,徐佩芬,凌苏群,等,2012. 微动勘探方法在地热勘查中的应用[J]. 上海国土资源,33(3):71-75. [43] 高艳华,黄溯航,刘丹,等,2018. 微动探测技术及其工程应用进展[J]. 科学技术与工程,18(23):146-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.23.020 [44] 何正勤,丁志峰,贾辉,等,2007. 用微动中的面波信息探测地壳浅部的速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报,50(2):492-498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.02.021 [45] 何正勤,胡刚,鲁来玉,等,2013. 云南通海盆地的浅层速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报,56(11):3819-3827. doi: 10.6038/cjg20131123 [46] 黄海清,2011. 被动源面波勘探在金属矿区的应用探索[J]. 福建地质,30(4):320-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3970.2011.04.008 [47] 李巧灵,雷晓东,李晨,等,2019. 微动测深法探测厚覆盖层结构:以北京城市副中心为例[J]. 地球物理学进展,34(4):1635-1643. doi: 10.6038/pg2019CC0128 [48] 李雪燕,陈晓非,杨振涛,等,2020. 城市微动高阶面波在浅层勘探中的应用:以苏州河地区为例[J]. 地球物理学报,63(1):247-255. [49] 梁定勇,许国强,肖瑶,等,2021. 海口江东新区新近纪-第四纪标准地层与组合分区[J]. 科学技术与工程,21(26):11052-11063. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.26.008 [50] 刘云祯,梅汝吾,叶佩,等,2016. WD智能天然源面波数据采集处理系统及其应用试验[J]. 物探与化探,40(5):1007-1015. [51] 谢朋,王秋良,李井冈,等,2019. SPAC法在江汉平原地层结构分层中的应用[J]. 地震工程学报,41(3):717-723. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.03.717 [52] 徐浩,吴小平,盛勇,等,2021. 微动勘探技术在城市地面沉降检测中的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探,45(6):1512-1519. [53] 徐佩芬,李传金,凌甦群,等,2009. 利用微动勘察方法探测煤矿陷落柱[J]. 地球物理学报,52(7):1923-1930. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.028 [54] 徐佩芬,侍文,凌苏群,等,2012. 二维微动剖面探测“孤石”:以深圳地铁7号线为例[J]. 地球物理学报,55(6):2120-2128. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.06.034 [55] 徐佩芬,李世豪,杜建国,等,2013a. 微动探测:地层分层和隐伏断裂构造探测的新方法[J]. 岩石学报,29(5):1841-1845. [56] 徐佩芬,李世豪,凌甦群,等,2013b. 利用SPAC法估算地壳S波速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报,56(11):3846-3854. [57] 徐佩芬,杜亚楠,凌甦群,等,2020. 微动多阶瑞雷波SPAC系数反演方法及应用研究[J]. 地球物理学报,63(10):3857-3867. doi: 10.6038/cjg2020O0148 [58] 徐义贤,罗银河,2015. 噪声地震学方法及其应用[J]. 地球物理学报,58(8):2618-2636 [59] 杨天春,何继善,吕绍林,等,2004a. 三层层状介质中瑞利波的频散曲线特征[J]. 物探与化探,28(1):41-45. [60] 杨天春,何继善,吕绍林,等,2004b. 三层层状介质中的多导波模式及其频散和位移特征[J]. 物探化探计算技术,26(1):20-26. [61] 杨天春,肖巧玲,2009. 多层层状介质的瑞利面波频散特性[J]. 物探与化探,33(3):299-303. [62] 张碧星,鲁来玉,鲍光淑,2002. 瑞利波勘探中“之”字形频散曲线研究[J]. 地球物理学报,45(2):263-274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2002.02.013 [63] 赵东,2010. 被动源面波勘探方法与应用[J]. 物探与化探,34(6):759-764. [64] 赵红鹏,何登科,洪雨,2022. 基于地质单元体的微动信号频散曲线反演[J]. 矿业科学学报,7(6):662-669. [65] 钟宙灿,蔡水库,刘巧霞,等,2023. SPAC法在海口江东新区新近纪-第四纪地层精细划分中的应用[J]. 科学技术与工程,23(36):15393-15403. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2300424 -




 下载:
下载: