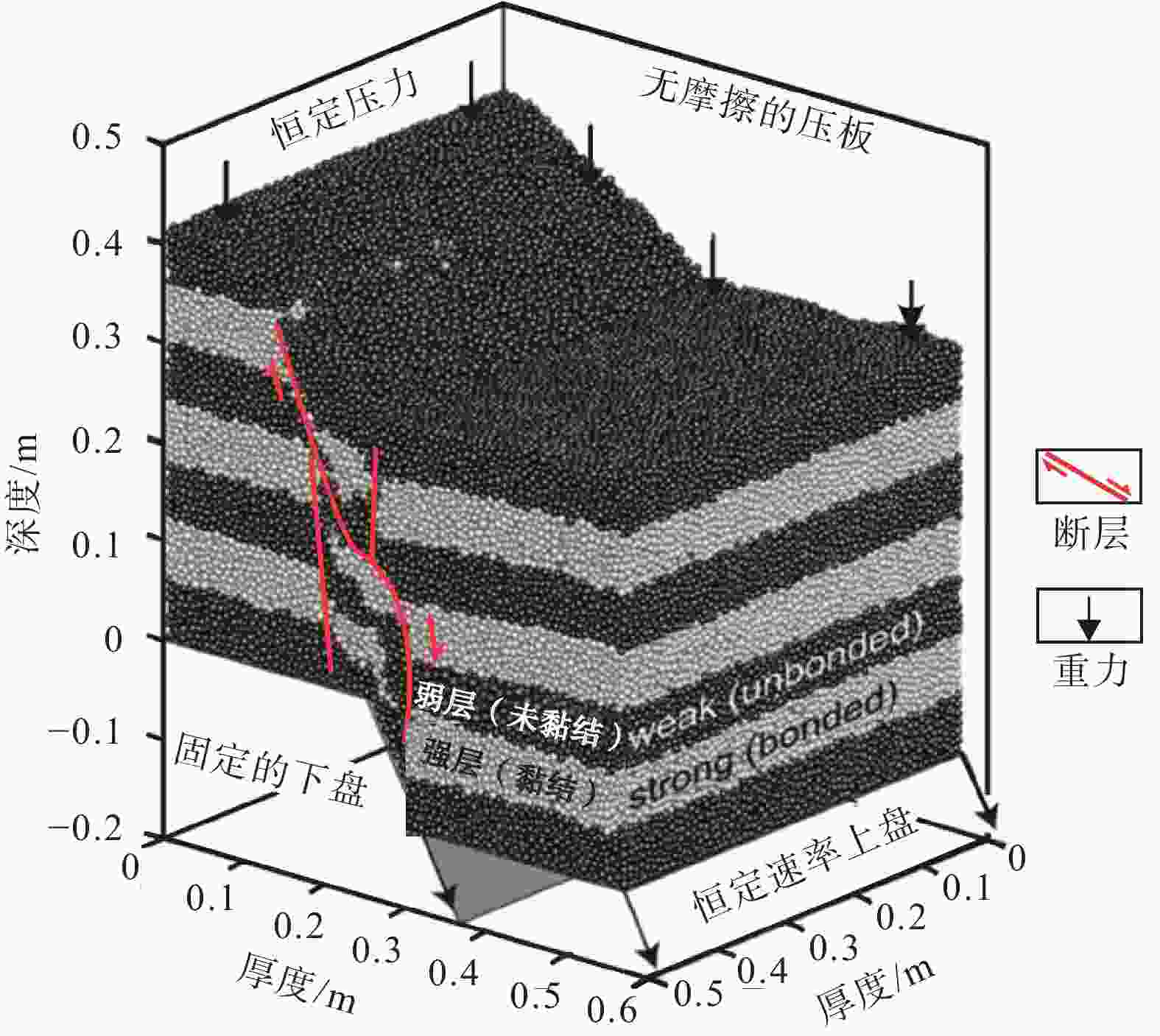
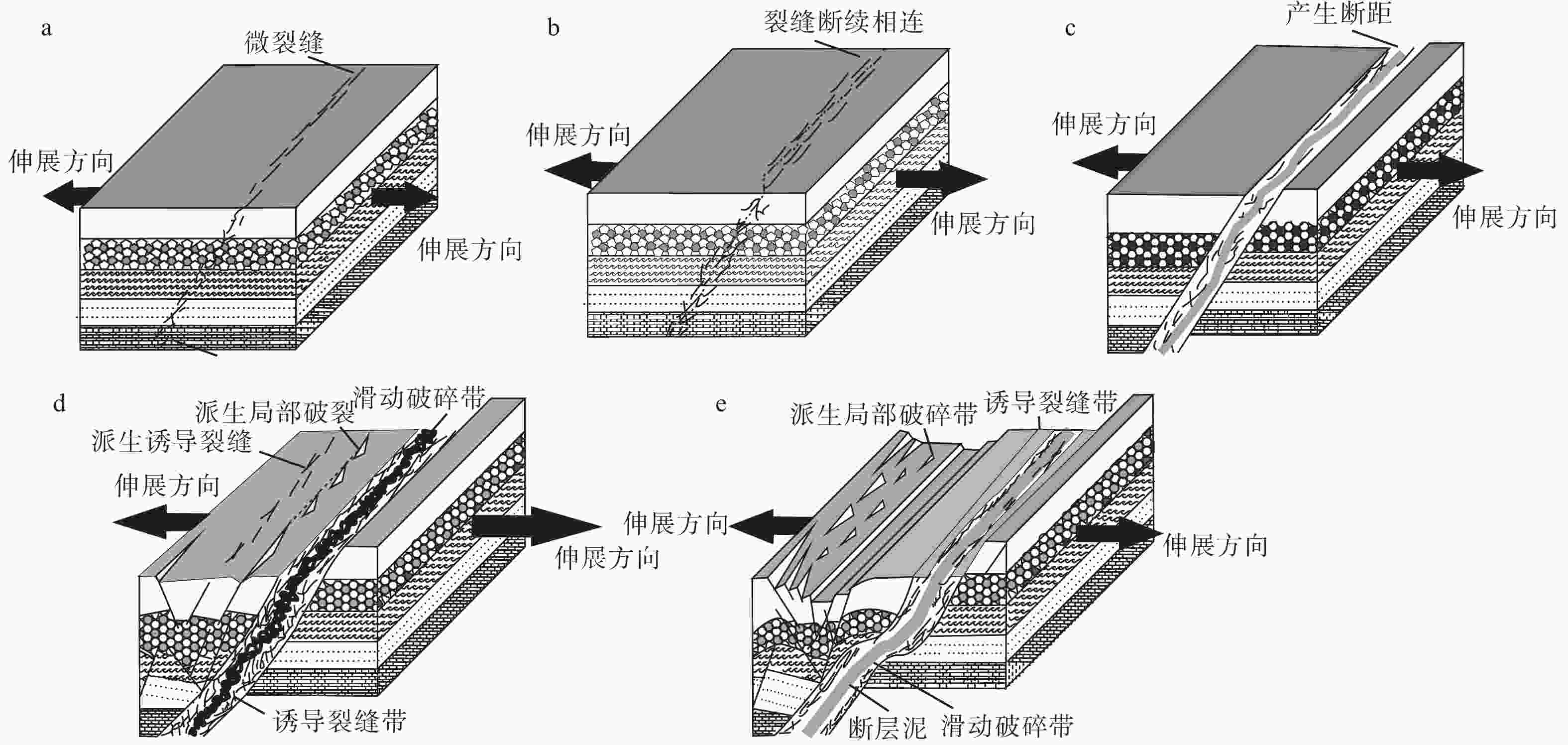
Characteristics of life-cycle stages and reservoir control in the development of extensional faults in the Dongying Sag
-
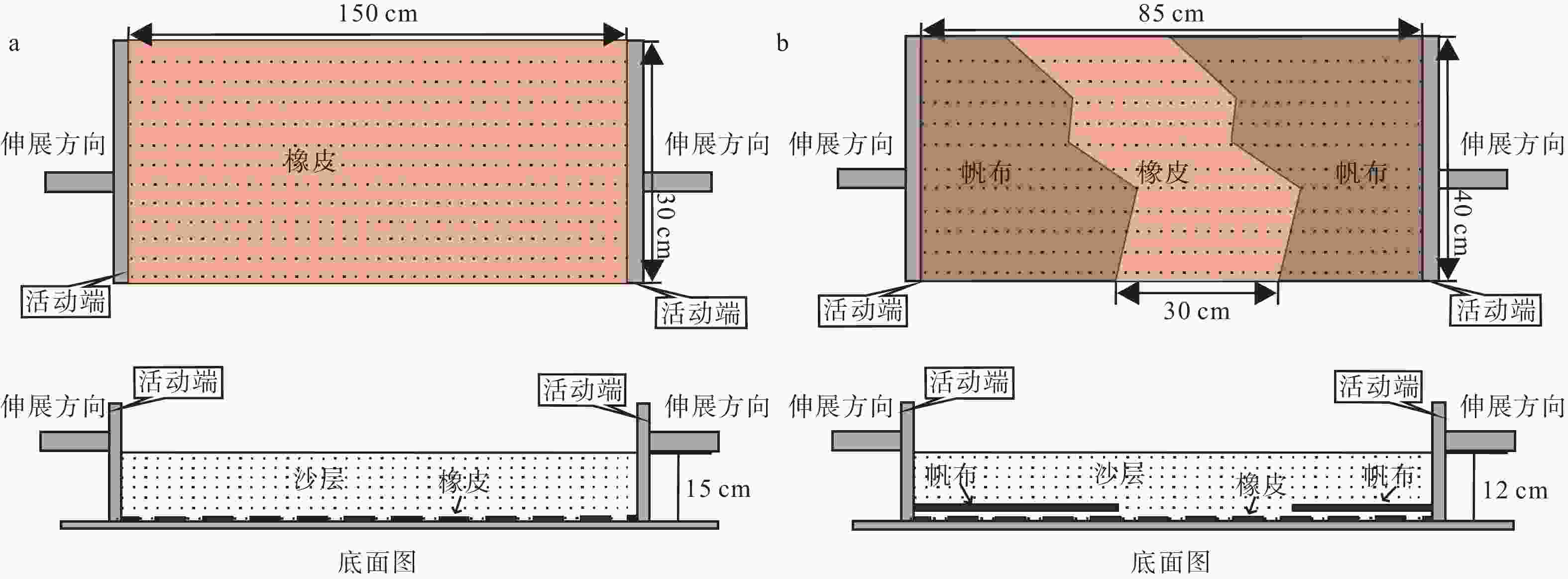
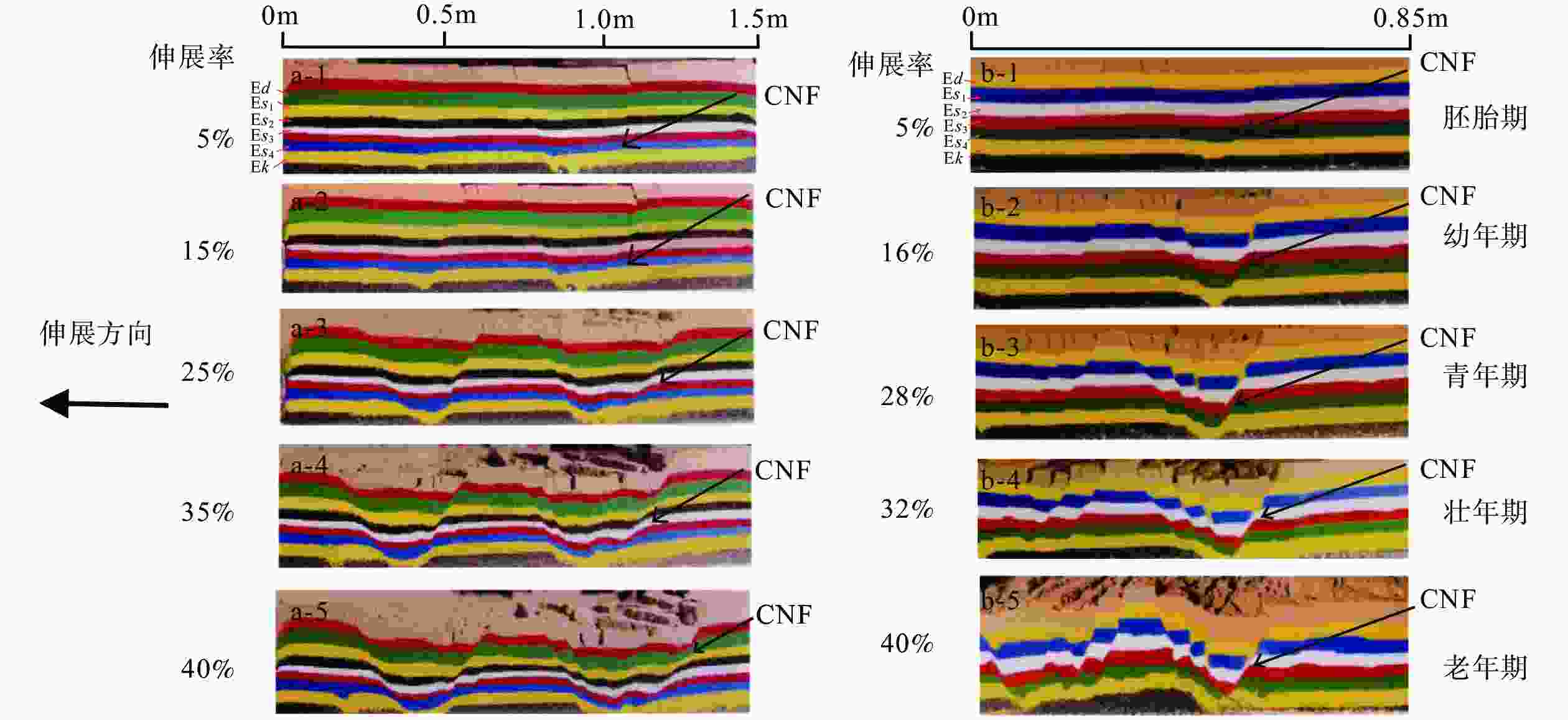
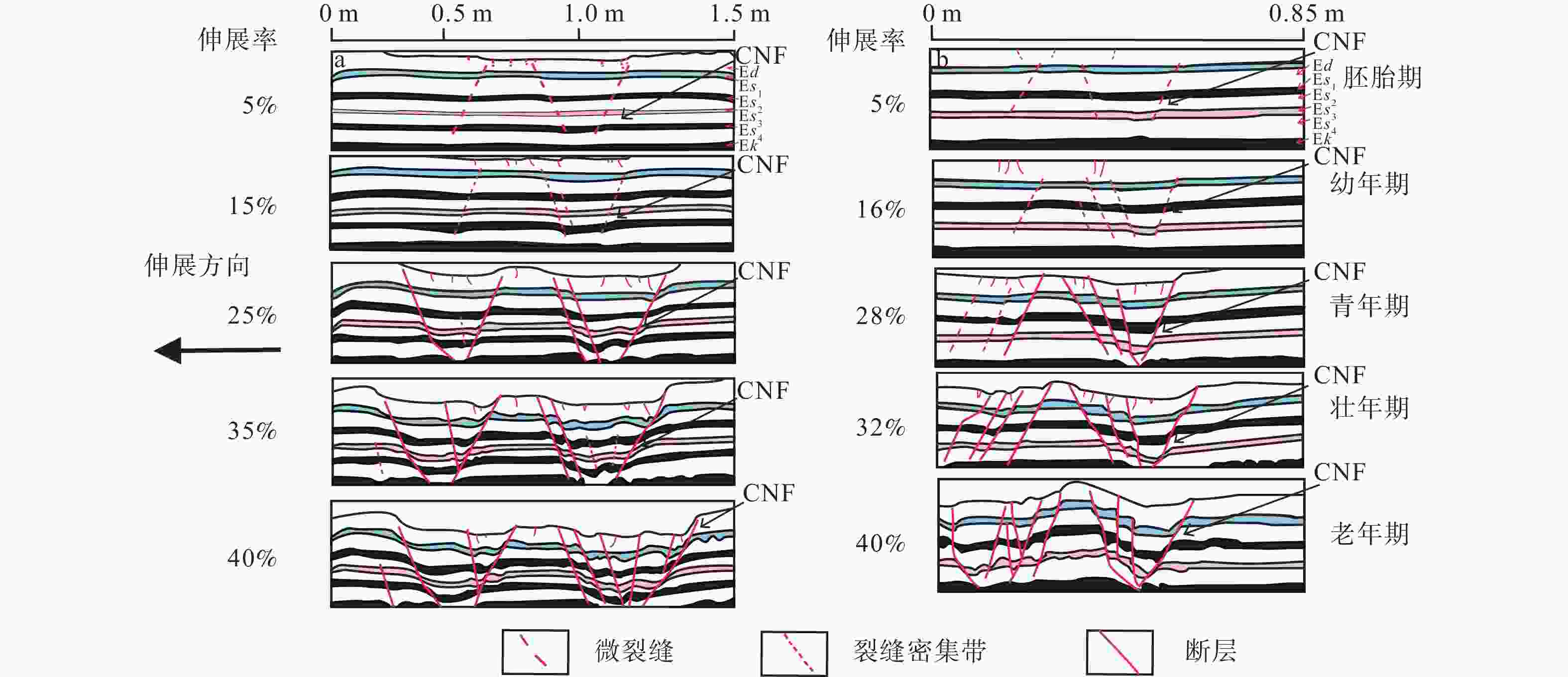
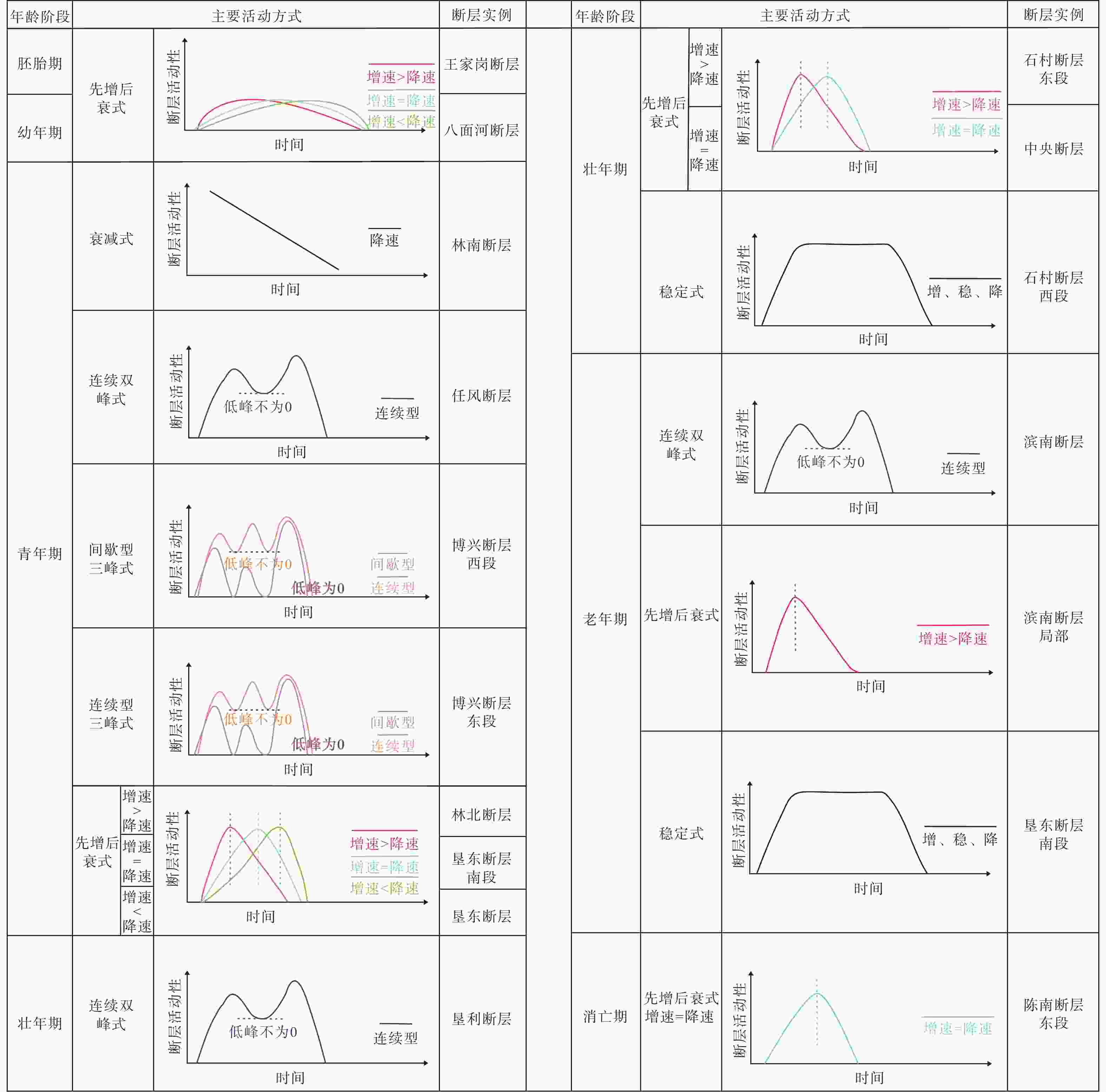
摘要: 断层从无到有的形成过程具有隐性、显性等多个演化阶段,而断层由隐性阶段的胚胎期到显性阶段末期的老年期等各个成长阶段的判别难度很大。针对这一问题,以渤海湾盆地东营凹陷为研究对象,应用物理模拟、数值模拟等方法重现控盆边界断层−陈南断层胚胎期到老年期的全生命阶段演化过程及各阶段的固有特征;在此基础上,定性、定量判识东营凹陷主要断层的相对年龄(Relative Age,RA)以及各年龄阶段的断层活动方式,建立其控藏模式。研究结果表明:东营凹陷张扭性断层可以划分为胚胎期(0<RA≤1,微裂缝或诱导裂缝带)、幼年期(1<RA≤2,断层核形成、裂面断续相连)、青年期(2<RA≤3,板状主断面贯通、清晰断距)、壮年期(3<RA≤4,断层核两侧破碎带形成、板状−铲式断面)、老年期(4<RA≤5,坡坪式断面、派生构造复杂)和消亡期(5<RA≤6,断层停止活动或者发生反转)6个阶段;断层的活动方式与断层年龄的持续时间和活动强度有着密切的关系,稳定、持续、高强度的断层活动方式有利于断层向老年期发展。断层控藏作用研究表明:胚胎期、幼年期断层主要控制油气圈闭,青年期断层主要控制砂体和储层分布,壮年期、老年期断层控制着烃源岩的总体展布范围以及油气的运移、聚集和逸散等过程。结合优势控藏要素、油气富集程度和油气聚集规模等因素进行断层控藏能力评价,陈南断层控藏能力等级为“强”。从断层生命发育演化阶段重新认识断层的控藏能力,将有力地推动和提升断层控藏的理论研究与成熟探区的勘探水平。Abstract:
Objective Faults are among the most prevalent geological structures in oil and gas basins. Because of their significant connection to oil and gas resources, they have consistently attracted the attention of experts and scholars in the field, making them a hot research topic. Although previous researchers delved tirelessly into the correlation between faults, oil, and gas, new theoretical breakthroughs have been steadily emerging and have been used to promote advancements in oil and gas exploration. Nonetheless, there continues to be a dearth of thorough investigations into the underlying links between faults and the formation and distribution of oil and gas reservoirs, as well as methods for comprehensively and quantitatively defining the connections between faults and oil and gas. Methods The formation of a fault from inception encompasses multiple stages of development, including implicit and explicit stages, and differentiating the diverse growth stages of a fault, ranging from the initial embryonic stage to the terminal stage, poses a significant challenge. To address this issue, the Dongying Sag in the Bohai Bay Basin was selected as the focal point of this study. By employing physical and numerical simulation techniques, the researchers sought to replicate the entire life cycle evolution of the Chennan Fault, a basin-controlling boundary fault, from its embryonic stage to its terminal stage while elucidating the distinct characteristics of each stage. Building upon this foundation, the relative ages of the primary faults in the Dongying Depression and the various modes of fault activity at different stages were qualitatively and quantitatively determined, leading to the establishment of a reservoir-control model. Results The research findings indicate that normal faults tend to grow in six distinct stages: the embryonic stage (0 < RA (relative age) ≤ 1), characterized by microfractures or induced fracture zones; juvenile stage (1 < RA ≤ 2), with an intermittent connection of fault geometry; mature stage (2 < RA ≤ 3), marked by the connection of plate-like fault geometry and clear fault throw; declining stage (3 < RA ≤ 4), in which induced fracture zones form on both sides of the fault core, resulting in a shovel-like fault geometry; terminal stage (4 < RA ≤ 5), ramp-flat fault geometry, which has complex derived structures; and death stage (5 < RA ≤ 6), in which fault movement stops or undergoes inversion. The activity pattern of a fault is intricately linked to the duration and intensity of its age. Stable continuous, and high-intensity fault activity promotes the evolution of faults into their terminal stage. Research on reservoir control traps indicates that faults can create reservoirs at all stages of their development. However, as faults age, their ability to control reservoir formation strengthens. The types of traps influenced by faults transition from individual, isolated structures to a variety of arrangements. Moreover, the diversity of oil and gas reservoirs evolves from singular to multifaceted, and the size of these reservoirs expands from small to large. The embryonic and juvenile stage faults primarily influence closure; the mature stage faults predominantly impact sand and reservoir; and the declining stage and terminal stage faults primarily govern the overall distribution range of source rocks, as well as the migration, accumulation, and dissipation of oil and gas. Conclusion The reservoir control potential of the Chennan Fault was assessed by considering factors such as reservoir control advantages, the degree of oil and gas enrichment, and the scale of oil and gas accumulation. The reservoir control capacity of the Chennan Fault was classified as “strong.” Reevaluation of the fault’s reservoir control potential from the perspective of its developmental and evolutionary stages significantly enhances and elevates theoretical research on fault reservoir control and also advances exploration efforts in established mature areas. [Significance] Identifying the formation age and evolutionary patterns of extensional faults has immense theoretical and practical importance for comprehending alterations in the fault’s reservoir control capabilities. Moreover, it offers crucial guidance for oil and gas exploration, particularly for enhancing the reserves in existing exploration areas. -
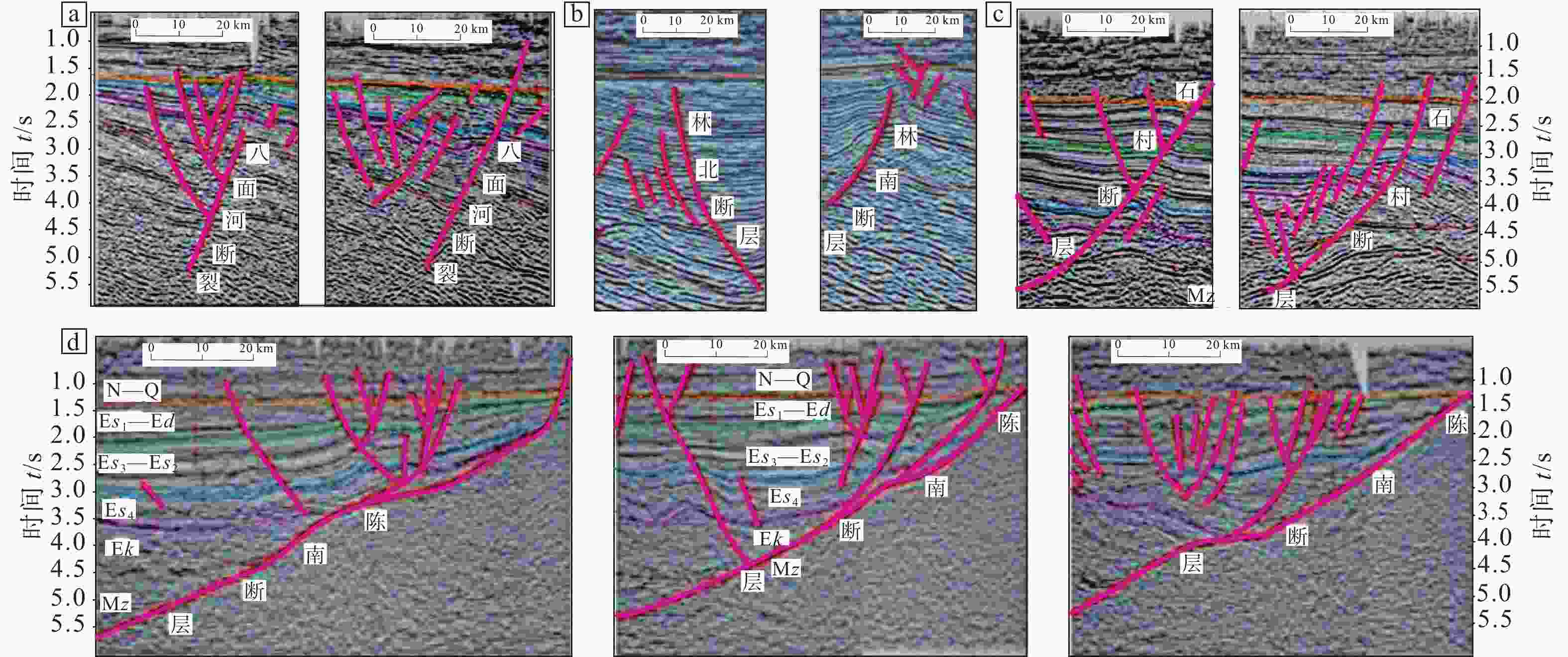
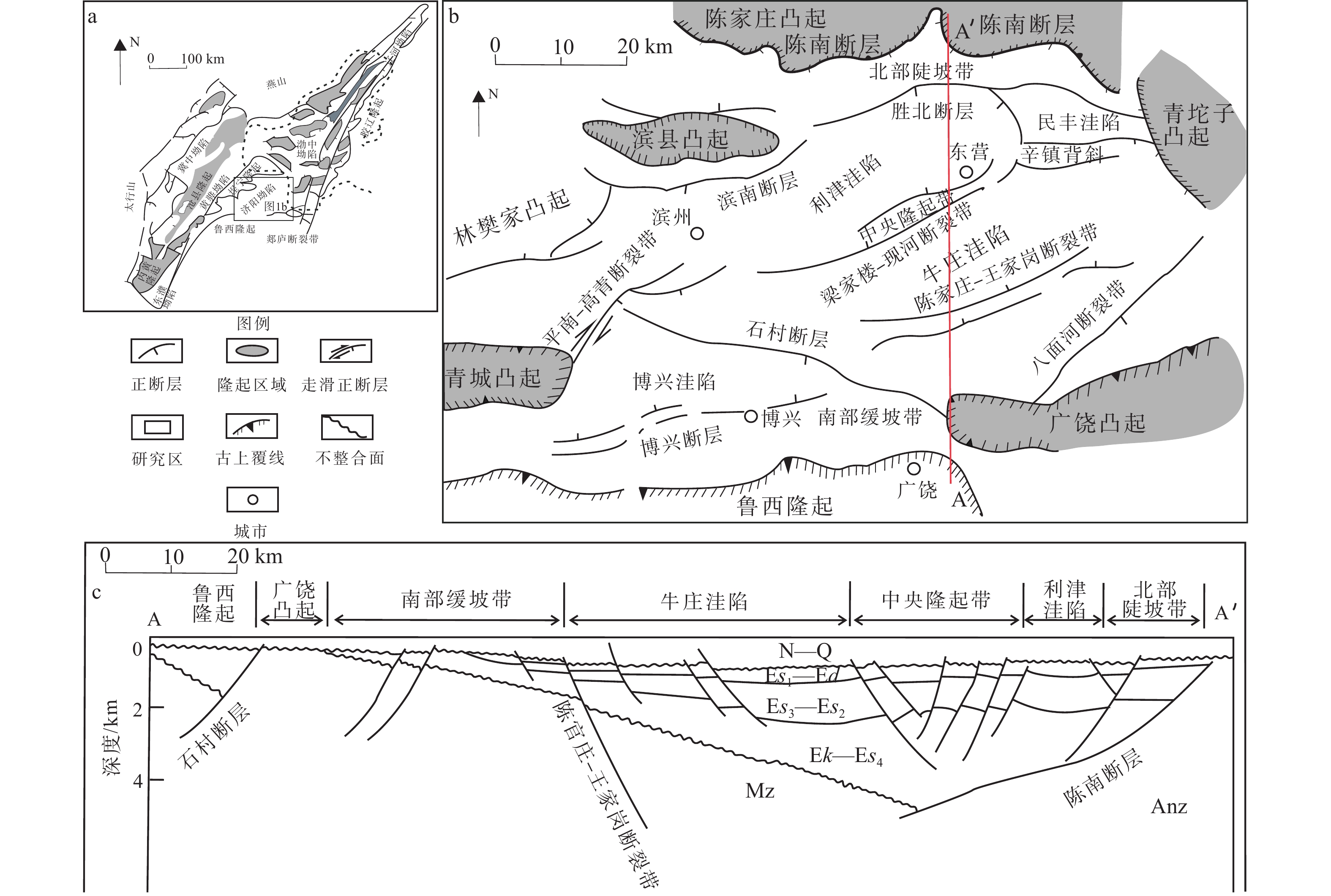
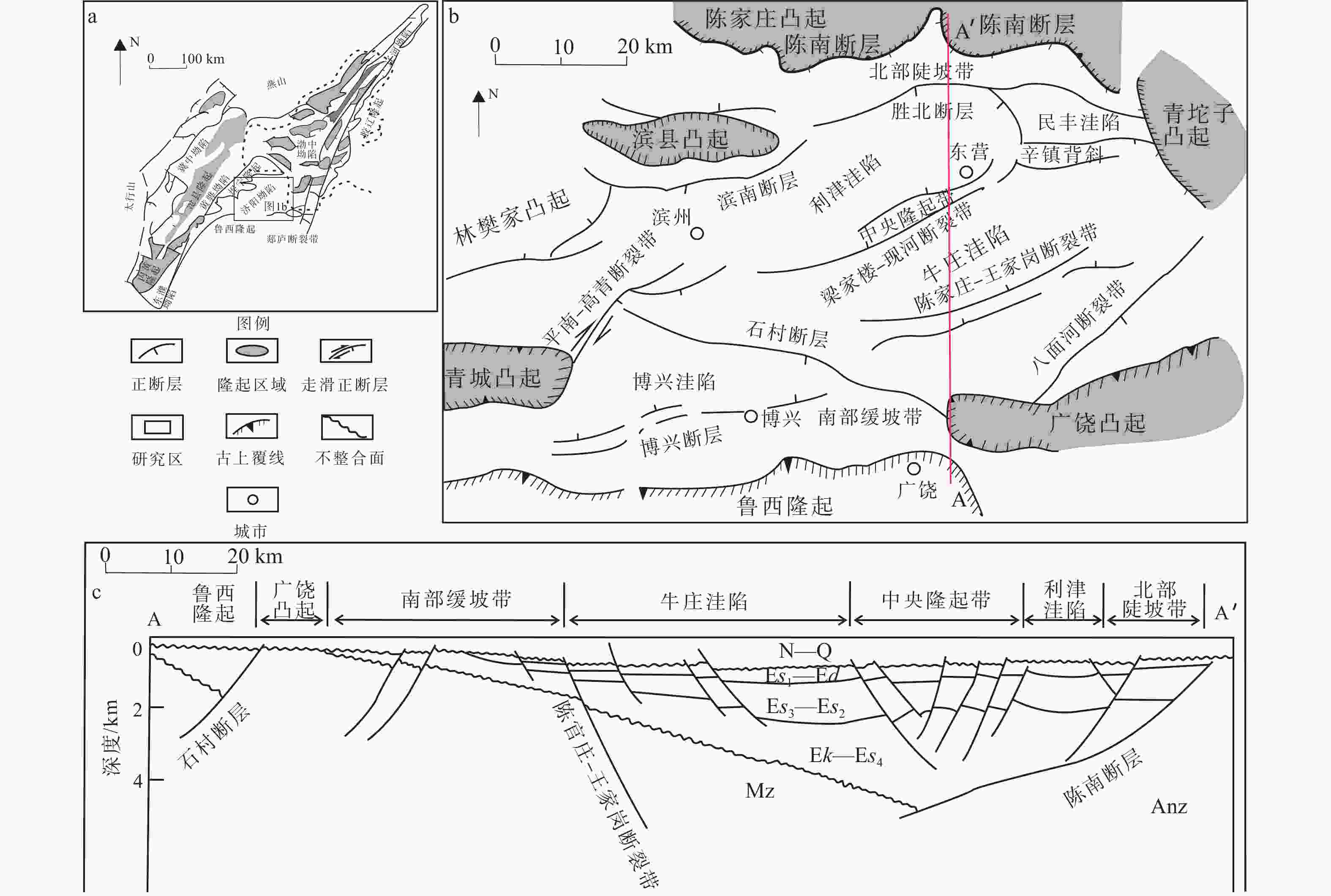
图 1 渤海湾盆地构造简图及研究区位置
N—Q—新近系—第四系;${\mathrm{E}}s_{1} $—Ed—沙河街组一段—东营组;${\mathrm{E}}s_{3} $—${\mathrm{E}}s_{2} $—沙河街组三段—沙河街组二段;Ek—${\mathrm{E}}s_{4} $—孔店组—沙河街组四段;Mz—中生界;Anz—前震旦系 a—渤海湾盆地区域图;b—东营凹陷区域图;c—东营凹陷剖面图
Figure 1. Simple tectonic map of Bohai Bay Basin and the location of the study region
(a) Map of the Bohai Bay Basin; (b) Map of the Dongying Sag; (c) Cross section of the Dongying Sag
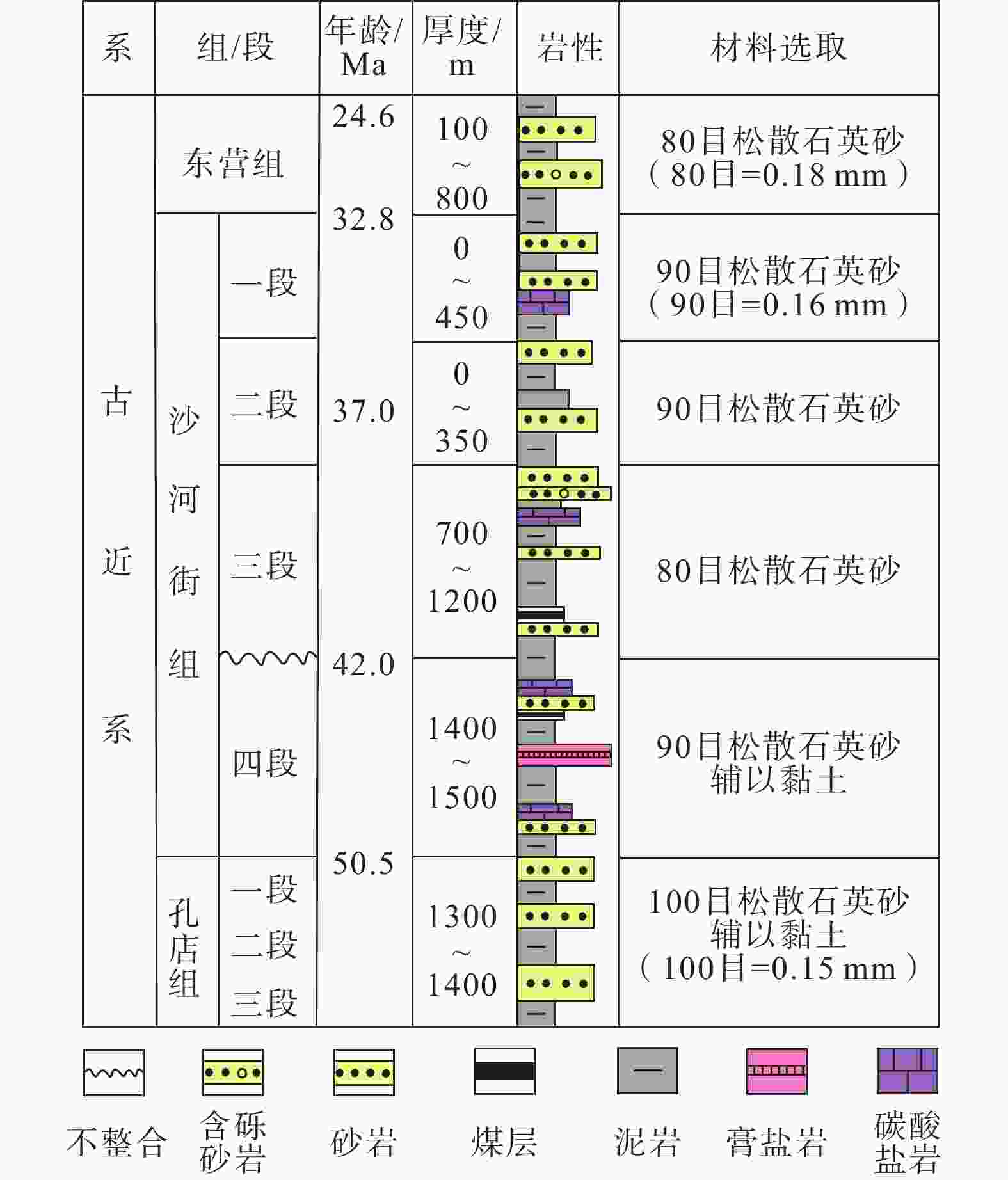
表 1 正断层年龄阶段判别标准
Table 1. Criteria for determining the age stage of normal faults
赋值 1 2 3 4 5 6 断层演化阶段 胚胎期 幼年期 青年期 壮年期 老年期 消亡期 RA(相对年龄) (0,1] (1,2] (2,3] (3,4] (4,5] (5,6] 断距/切割深度 0 0~6 6~9 9~12 >12 反转 切割深度/长度 0~0.4 0~0.8 0~1.2 1.2~1.6 >1.6 断面形态 无 板状 轻微铲状,倾角>60° 铲状,倾角<60° 铲状/坡坪状,倾角<45° 派生构造 无 无 派生破裂 派生破裂或极少断层 复杂派生构造 断层带结构 裂缝 破裂/贯通 滑动破碎带 滑动破碎带+诱导裂缝带 滑动破碎带+诱导裂缝带+断层泥 表 2 东营凹陷主要断层年龄阶段判别结果
Table 2. Results of age stage determination of major faults in the Dongying Sag
断层名称 走向 断层长度/
km新生代
断距/m切割深度/
km切割深度/
断距赋值 长度/切割深度 赋值 断面形态 赋值 断层描述 赋值 相对年龄(RA)/阶段 石村断层 北西向 90 1280.73 6000 4.68 2 1.50 4 轻微铲状 3 较为复杂 4 3.25 壮年期 陈南断层东段 北西向 50 反转 坡坪式 6 复杂 6 6.00 消亡期 林北断层 北东东向 30 640 6000 9.37 4 0.50 2 轻微铲状 3 少数破裂 2 2.75 青年期 林南断层西段 北东东向 60 702 3590 5.11 2 1.67 5 轻微铲状 3 少数破裂 2 3.00 青年期 林南断层东段 北东东向 60 735 3590 4.88 2 1.67 5 铲状 4 破裂 3 3.50 壮年期 高青断层西段 近东西向 70 1206 5000 坡坪状 5 复杂 5 5.00 消亡期 高青断层东段 近东西向 70 1238 5000 铲状 5 复杂 5 5.00 消亡期 滨南断层 近东西向 35 2091 7500 5.59 3 1.47 4 坡坪状 5 复杂 5 4.25 老年期 陈南断层西段 近东西向 80 3319 7500 2.26 1 1.07 3 坡坪状 5 派生复杂 5 3.50 老年期 任风断层 近东西向 100 3590 2.79 5 板状 2 复杂 5 3.00 青年期 无南断层西段 近东西向 75 916 3590 2.86 1 12.00 5 坡坪状 5 复杂 5 4.00 老年期 无南断层东段 近东西向 75 948 3590 3.26 2 12.00 5 坡坪状 5 复杂 5 4.25 老年期 垦东断层南段 近东西向 50 514 3600 7.00 3 1.39 4 裂缝 3 无 1 2.75 青年期 垦东断层北段 近东西向 50 断续相连 2 无 2 2.00 幼年期 王家岗断层带 近东西向 60 裂缝 1 无 1 1.00 胚胎期 胜永断层 近东西向 60 854 7500 8.78 4 0.80 2 轻微铲状 3 较为复杂 4 3.25 壮年期 中央断层 近东西向 80 516 6000 11.63 4 1.33 4 铲状 2 较为复杂 4 3.50 壮年期 八面河断层 近东西向 60 0 4600 6.27 3 1.30 4 断续相连 2 较为复杂 2 2.25 幼年期 博兴断层 近东西向 40 1174 6000 5.11 2 0.67 2 板状 2 无 1 1.75 青年期 孤东断层 近东西向 50 无 1 无 1.00 胚胎期 表 3 东营凹陷断层控藏要素分类与控藏能力评价
Table 3. Classification of fault reservoir-forming elements and evaluation of reservoir-controlling capabilities in the Dongying Sag
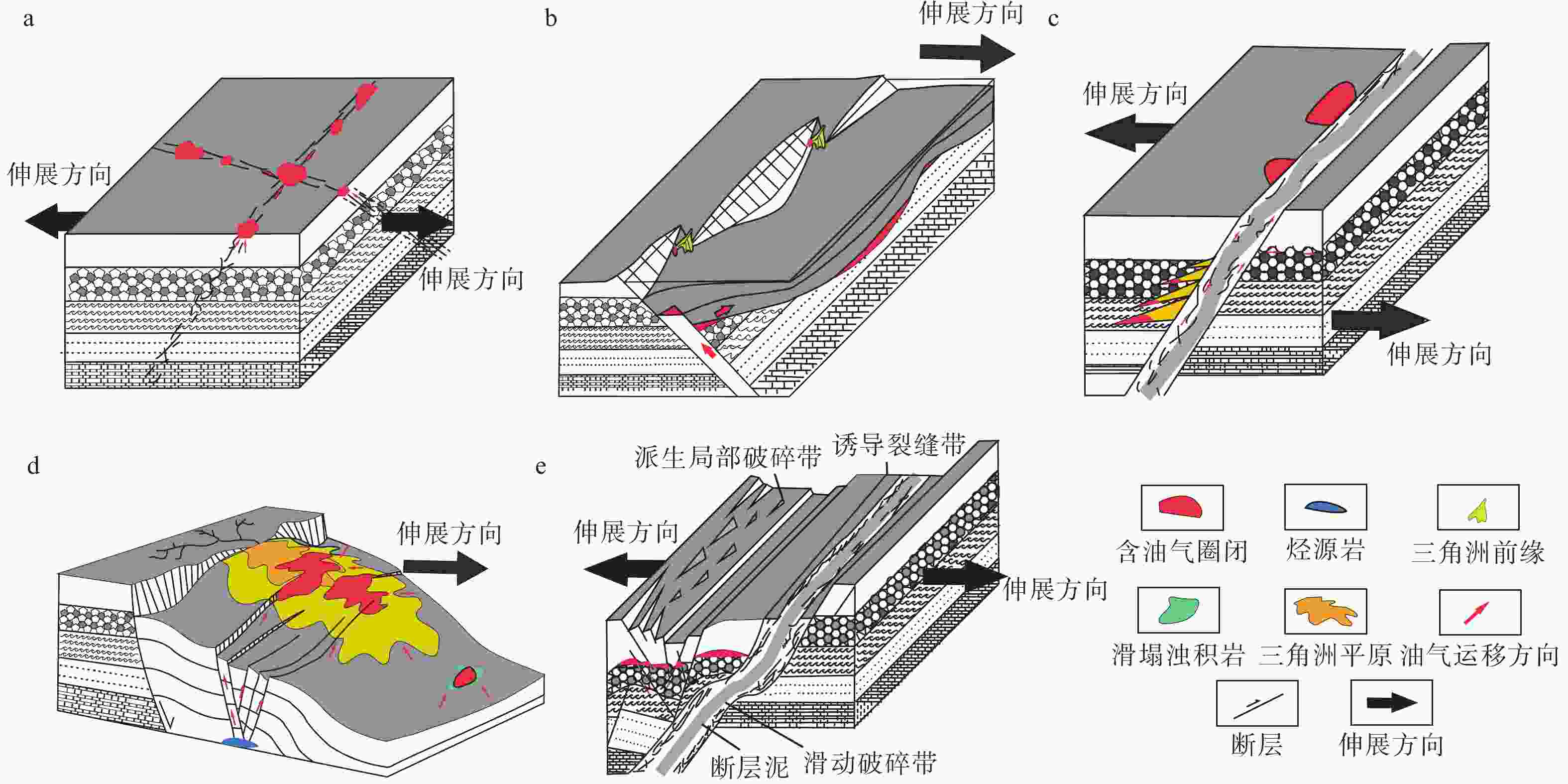
控藏能力 强 中 弱 烃源岩 影响大,主控 影响一般 影响较小 储层 影响大,控扇为主 影响一般、控砂为主 影响较小 输导体系 影响 影响大,主控 影响一般 影响较小 活动方式 双峰、三峰式、增速式、匀速式 稳定式、单峰式 衰减式 圈闭 类型多,规模大 类型少,规模小 影响较小 -
[1] ALAM A, AHMAD S, BHAT M S, et al., 2016. Response to the commentary by Shah, A. A. (2015) and further evidence supporting the dextral strike–slip pull-apart evolution of the Kashmir basin along the central Kashmir fault (CKF)[J]. Geomorphology, 253: 558-563. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.06.017 [2] BURK K, DEWEY J F, 1974. Two plates in Africa during the Cretaceous?[J]. Nature, 249(5455): 313-316. doi: 10.1038/249313a0 [3] CARTWRIGHT J A, MANSFIELD C S, TRUDGIL B D, 1996. Fault growth by segment linkage[M]//BUCHANAN P C, NIEUWLAND D A. Modem developments in structural interpretations, Vol. 99. Geological Society, London, Special Publications: 163-177. [4] CHEN D X, ZHANG F Q, CHEN H L, et al., 2015. Structural architecture and tectonic evolution of the Fangzheng sedimentary basin (NE China), and implications for the kinematics of the Tan-Lu fault zone[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 106: 34-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.02.028 [5] CHEN G, JIANG Y P, ZHOU J X, et al., 2008. The paleo-drop method was used to study the intensity of fault activity in the Shacheng area[J]. Small Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 13(2): 7-10. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] CHILDS C, HOLDSWORTH R E, JACKSON C A L, et al., 2017. Introduction to the geometry and growth of normal faults[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 439(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1144/SP439.24 [7] CHOI J H, YANG S J, HAN S R, et al., 2015. Fault zone evolution during Cenozoic tectonic inversion in SE Korea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 98: 167-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.009 [8] COWIE P A, GUPTA S, DAWERS N H, 2000. Implications of fault array evolution for synrift depocentre development: insights from a numerical fault growth model[J]. Basin Research, 12(3-4): 241-261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2000.00126.x [9] DAVIS G H, 1983. Shear-zone model for the origin of metamorphic core complexes[J]. Geology, 11(6): 342-347. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1983)11<342:SMFTOO>2.0.CO;2 [10] DENG L J, WU K Y, JIAO H Y, et al., 2022. Paleogene fault system in the Xianhe Mining Area, Dongying Sag, Bohai bay basin and its evolution[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(3): 480-491. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] DU H F, SUN X, WANG C W, et al., 2023. Study on mud logging interpretation and evaluation method of geological and engineering sweet spots for shale oil in Dongying sag[J]. Mineral Exploration, 14(3): 480-490. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] FINCH E, HARDY S, GAWTHORPE R, 2003. Discrete element modelling of contractional fault-propagation folding above rigid basement fault blocks[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 25(4): 515-528. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00053-6 [13] FINCH E, HARDY S, GAWTHORPE R, 2004. Discrete‐element modelling of extensional fault‐propagation folding above rigid basement fault blocks[J]. Basin Research, 16(4): 467-488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2004.00241.x [14] FU X F, XU P, WEI C Z, et al., 2012. Internal structure of normal fault zone and hydrocarbon migration and conservation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(6): 200-212. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] FU X F, SUN B, WANG H X, et al., 2015. Fault segmentation growth quantitative characterization and its application on sag hydrocarbon accumulation research[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 44(2): 271-281. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] FU X F, SONG X Q, WANG H X, et al., 2021. Comprehensive evaluation on hydrocarbon-bearing availability of fault traps in a rift basin: a case study of the Qikou Sag in the Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(4): 677-686. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] HOFFMAN P, DEWEY J F, BURKE K. 1974. Aulacogens and their genetic relation to geosynclines, with a Proterozoic example from Great Slave Lake, Canada[J]. [18] JENSEN E, CEMBRANO J, FAULKNER D, et al., 2011. Development of a self-similar strike-slip duplex system in the Atacama Fault system, Chile[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 33(11): 1611-1626. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2011.09.002 [19] JIANG S, 2019. The distinguishing of fault age stage and its controling on hydrocarbon accumulation in Jiyang depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China). (in Chinese with English abstract [20] JIANG Y L, LIU P, SONG G Q, et al., 2015. Late cenozoic faulting activities and their influence upon hydrocarbon accumulations in the Neogene in Bohai Bay basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 36(4): 525-533. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] LIU F J, 2011. Study on reservoir features and oil pool forming regularity of paleogene in the south slope of Dongying depression[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract [22] LUO Q, 1999. An outline of theory of fracture-controlling hydrocarbon[J]. Petroleum Explorationist, 4(3): 8-14. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] LUO Q, 2007. The fault controlling hydrocarbon theory and its significance[C]//Proceedings of the symposium on geological elements of oil and gas accumulation in China Yangtze and peripheral margins. Zhongxiang: 15-29. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] LUO Q, 2010. Concept, principle, model and significance of the fault controlling hydrocarbon theory[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 37(3): 316-324. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60035-3 [25] MA H, 2005. The characters and control of tectonics on sequence stratigraphy of the lower tertiary in Jiyang basin[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] MA S Z, 2007. The study of paleogene tectonic-sedimentary evolution and hydrocarbon reservoir formation model in Huimin sag[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract [27] MARQUES F O, MATEUS A, TASSINARI C, 2002. The Late-Variscan fault network in central–northern Portugal (NW Iberia): a re-evaluation[J]. Tectonophysics, 359(3-4): 255-270. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00514-0 [28] PEACOCK D C P, SANDERSON D J, 1991. Displacements, segment linkage and relay ramps in normal fault zones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 13(6): 721-733. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(91)90033-F [29] PEACOCK D C P, SANDERSON D J, 1994. Geometry and development of relay ramps in normal fault systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 78(2): 147-165. [30] PEACOCK D C P, NIXON C W, ROTEVATN A, et al., 2017. Interacting faults[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 97: 1-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2017.02.008 [31] QU T, HUANG Z L, WANG R, et al.,2021. Development characteristics and controlling factors of coal-measure source rocks in the global Tethys region[J]. Coal geology & exploration,49(5):114-131. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] REILLY C, NICOL A, WALSH J J, et al., 2015. Evolution of faulting and plate boundary deformation in the Southern Taranaki Basin, New Zealand[J]. Tectonophysics, 651-652: 1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.02.009 [33] ROTEVATN A, JACKSON C A L, TVEDT A B M, et al., 2019. How do normal faults grow?[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 125: 174-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2018.08.005 [34] RUBINAT C M, 2012. Basement fault influence on the Bicorb-Quesa salt wall kinematics, insights from magnetotelluric and paleomagnetic techniques on salt tectonics[J]. [35] SIBSON R H, 1977. Fault rocks and fault mechanisms[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 133(3): 191-213. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.133.3.0191 [36] SONG G Z, WANG H, GAN H J, et al., 2013. Slope-break and its control on sequence, sedimentation and hydrocarbon accumulation of upper Es4 in Zhengnan area, Dongying sag[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 44(8): 3415-3424. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] SONG Y D, 2010. Study on structural characteristics and the favorable exploration zones of the middle-northern area in Raoyang sag[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China). (in Chinese with English abstract [38] SU Z F, 2006. Regional sequence stratigraphic correlation and predication of favorable lithologic & stratigraphic traps zones for palaeogene in Jiyang depression[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract [39] SU Z F, XUE Y M, DENG H W, et al., 2008. Construction styles, distribution features and genetic dynamics of the paleogene sequence boundaries in Jiyang depression[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29(4): 459-468. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] TONG M H, NIE J Y, MENG L J, et al., 2009. The law of basement pre-existing fabric controlling fault formation and evolution in rift basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(4): 97-104. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] WANG W F, ZHOU W W, ZHOU J, et al., 2014. Formation mechanism and distribution of buried fault zones in the Jinhu sag[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(5): 1395-1405. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] WANG W F, ZHOU W W, SHAN X J, et al., 2015. Characteristics of hidden fault zone and its significance in geology in sedimentary basin[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 46(6): 2236-2243. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] WANG W F, ZHOU W W, XU S L, 2017. Formation and evolution of concealed fault zone in sedimentary basins and its significance in hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Earth Science, 42(4): 613-624. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] WU Z P, CHEN W, XUE Y, et al., 2010. Structural characteristics of faulting zone and its ability in transporting and sealing oil and gas[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(4): 570-578. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] XU C G, DU X F, PANG X J, et al., 2022. The source-sink system and its control on large-area lithologic reservoirs of the lower Minghuazhen Formation in the southern Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 728-742. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] XUE Y A, LI H Y, XU P, et al., 2021a. Recognition of oil and gas accumulation of Mesozoic covered buried hills in Bohai sea area and the discovery of BZ 13-2 oilfield[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 33(1): 13-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [47] XUE Y A, LV D Y, HU Z W, et al., 2021b. Tectonic development of subtle faults and exploration in mature areas in Bohai Sea, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 48(2): 233-246. (in Chinese with English abstract [48] YANG Y Y, 2008. Growth and development: the whole process of human development[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House. (in Chinese) [49] ZHANG D M, WANG P, ZANG D G, et al., 2023. Pre-Stack Reservoir Prediction of Tight Sandstone of the Fifth Member of Xujiahe Formation in the Wubaochang Area of Northeastern Sichuan[J]. Geology and Exploration, 59(6): 1356-1365. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] ZHAO Y J, 2007. The research of basin structure and filling characteristics of palaeogene in Dongying depression[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract [51] ZHOU J L, 2008. Migration and accumulation of oil-gas in Shengtuo areas of Dongying depression, Bohai Bay basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 19(5): 587-592. (in Chinese with English abstract [52] ZHOU W W, DONG Y P, XIAO C A, et al., 2023. Effect of Strike-Slip Activity of Basement Faults on Hydrocarbon Accumulation in Dongying Sag[J]. Earth Science, 48(07): 2718-2732. (in Chinese with English abstract [53] ZHOU W W, WANG W F, AN B, et al., 2014. Identification of potential fault zones and its geological significance in Bohai Bay basin[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 39(11): 1527-1538. (in Chinese with English abstract [54] ZHOU W W, 2015. Characteristic of concealed fault zone and its significance in hydrocarbon accumulation in Bohai Bay basin[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China). (in Chinese with English abstract [55] ZHOU W W, Zhao C Q, Chang H. Effect of intensity of sedimentary cover deformation on hydrocarbon accumulation in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 677. [56] 陈刚,蒋弋平,周建新,等,2008. 用古落差法研究沙埝地区断层活动强度[J]. 小型油气藏,13(2):7-10. [57] 邓路佳,吴孔友,焦红岩,等,2022. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷现河矿区古近系断裂体系及形成演化[J]. 地质力学学报,28(3):480-491. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021139 [58] 杜焕福,孙鑫,王春伟,等,2023. 东营凹陷页岩油双甜点录井解释评价方法研究[J]. 矿产勘查,14(3):480-490. [59] 付晓飞,许鹏,魏长柱,等,2012. 张性断裂带内部结构特征及油气运移和保存研究[J]. 地学前缘,19(6):200-212. [60] 付晓飞,孙兵,王海学,等,2015. 断层分段生长定量表征及在油气成藏研究中的应用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,44(2):271-281. [61] 付晓飞,宋宪强,王海学,等,2021. 裂陷盆地断层圈闭含油气有效性综合评价:以渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,48(4):677-686. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.04.01 [62] 姜帅,2019. 济阳坳陷断裂年龄阶段判别及控藏作用研究[D]. 青岛:中国石油大学(华东). [63] 蒋有录,刘培,宋国奇,等,2015. 渤海湾盆地新生代晚期断层活动与新近系油气富集关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质,36(4):525-533. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150401 [64] 罗群,1999. “断裂控烃理论”概要[J]. 勘探家,4(3):8-14. [65] 罗群,2007. 断裂控烃理论的提出及其意义[C]//中扬子及周缘油气成藏地质要素学术研讨会论文集. 钟祥:湖北省石油学会地质专业委员会:15-29. [66] 罗群,2010. 断裂控烃理论的概念、原理、模式与意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发,37(3):316-324. [67] 马晖,2005. 济阳坳陷下第三系构造特征及其对层序的控制作用[D]. 广州:中国科学院广州地球化学研究所. [68] 屈童, 黄志龙, 王瑞, 等,2021. 全球特提斯域煤系烃源岩发育特征及其控制因素[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,49(5):114-131 [69] 宋广增,王华,甘华军,等,2013. 东营凹陷郑南地区沙四上亚段坡折带对层序、沉积与油气成藏控制[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),44(8):3415-3424. [70] 苏宗富,2006. 济阳坳陷古近系区域层序地层对比与岩性—地层圈闭有利区带预测[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京). [71] 苏宗富,薛艳梅,邓宏文,等,2008. 济阳坳陷古近系层序界面构建样式、分布特征及其成因动力学分析[J]. 地球学报,29(4):459-468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.04.008 [72] 童亨茂,聂金英,孟令箭,等,2009. 基底先存构造对裂陷盆地断层形成和演化的控制作用规律[J]. 地学前缘,16(4):97-104. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.04.010 [73] 王伟锋,周维维,周杰,等,2014. 金湖凹陷隐性断裂带形成机制及分布[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),44(5):1395-1405. [74] 王伟锋,周维维,单新建,等,2015. 沉积盆地隐性断裂带特征及其地质意义[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),46(6):2236-2243. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.06.035 [75] 王伟锋,周维维,徐守礼,2017. 沉积盆地断裂趋势带形成演化及其控藏作用[J]. 地球科学,42(4):613-624. [76] 吴智平,陈伟,薛雁,等,2010. 断裂带的结构特征及其对油气的输导和封堵性[J]. 地质学报,84(4):570-578. [77] 徐长贵,杜晓峰,庞小军,等,2022. 渤海南部明化镇组下段源-汇体系及其对大面积岩性油气藏的控制作用[J]. 地质力学学报,28(5):728-742. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222813 [78] 薛永安,李慧勇,许鹏,等,2021a. 渤海海域中生界覆盖型潜山成藏认识与渤中13-2大油田发现[J]. 中国海上油气,33(1):13-22. [79] 薛永安,吕丁友,胡志伟,等,2021b. 渤海海域隐性断层构造发育特征与成熟区勘探实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发,48(2):233-246. [80] 杨云衣,2008. 生长与发育:人类发展全过程[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社. [81] 张德明,王鹏,臧殿光,等,2023. 川东北五宝场地区须五段致密砂岩叠前储层预测[J]. 地质与勘探,59(6):1356-1365. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2023.06.020 [82] 赵延江,2007. 东营凹陷古近系盆地结构与充填特征研究[D]. 广州:中国科学院广州地球化学研究所. [83] 周建林,2008. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷胜坨地区油气运聚与成藏研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,19(5):587-592. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.05.587 [84] 周维维,董有浦,肖安成,等,2023. 东营凹陷基底断裂走滑活动对油气成藏的影响[J]. 地球科学,48(7):2718-2732. [85] 周维维,王伟锋,安邦,等,2014. 渤海湾盆地隐性断裂带识别及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报,39(11):1627-1638. [86] 周维维,2015. 渤海湾盆地断裂趋势带特征及控油作用[D]. 青岛:中国石油大学(华东). -




 下载:
下载: