Application of integrated model based on EEMD-CNN-LSTM for landslide-displacement prediction
-
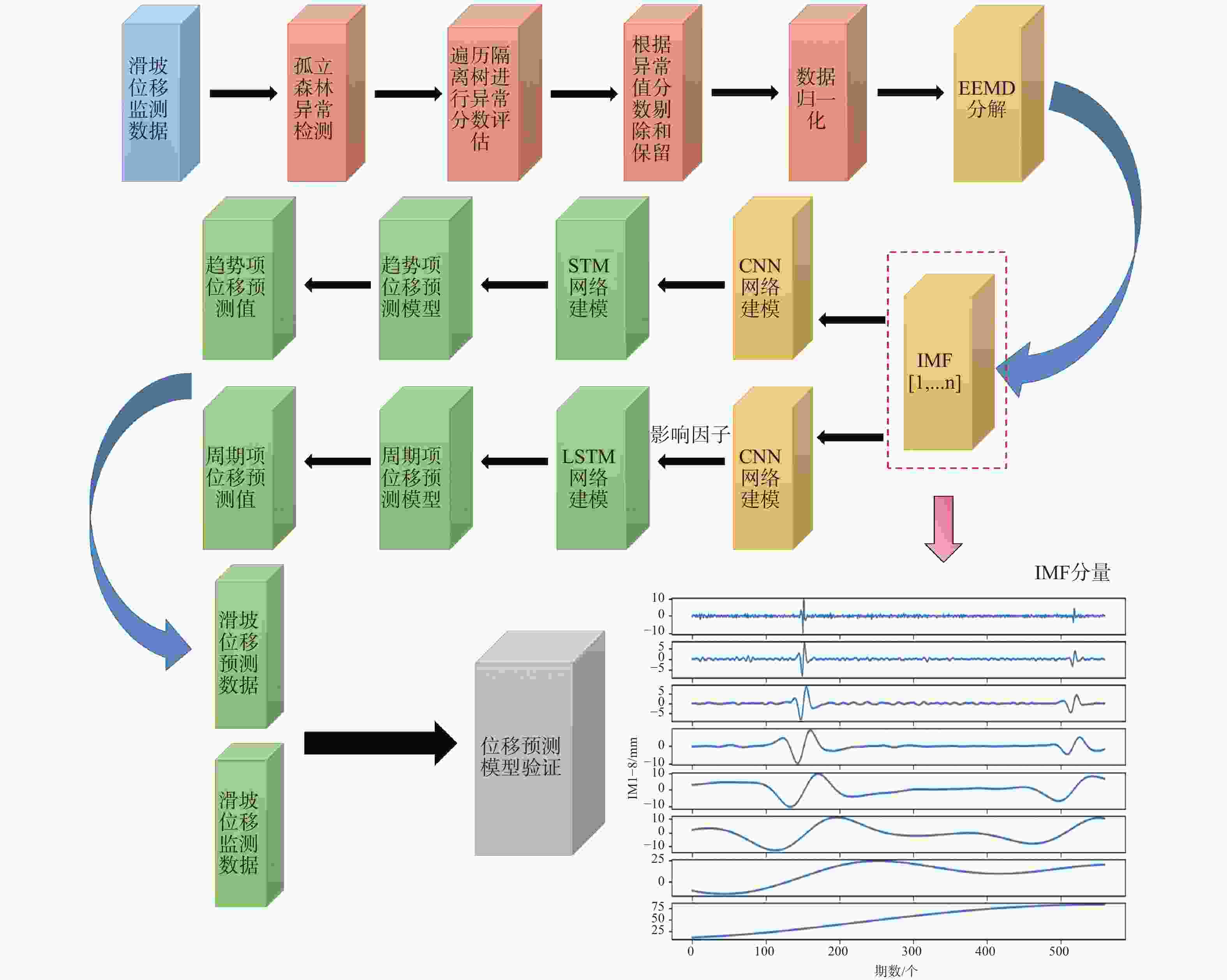
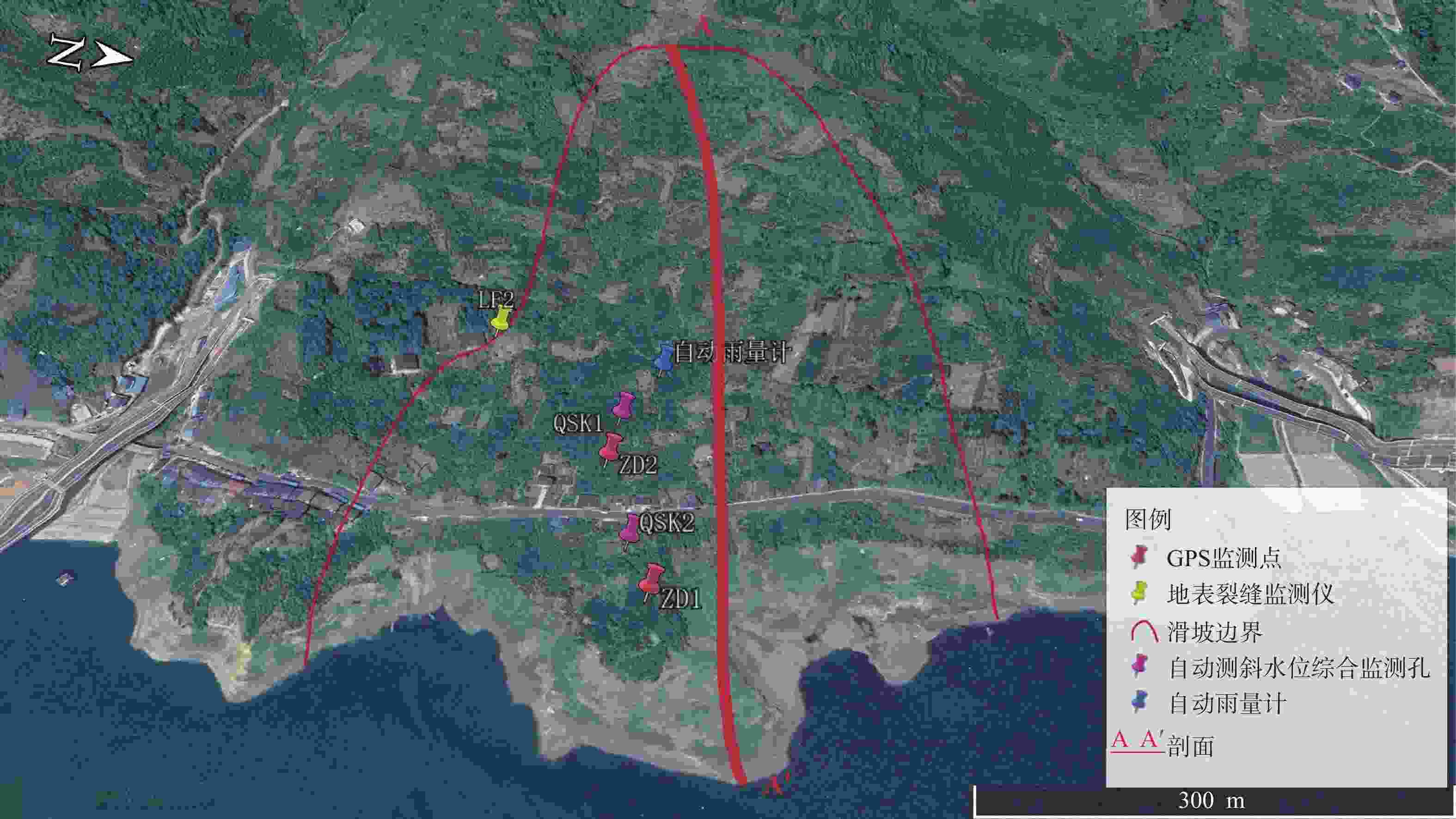
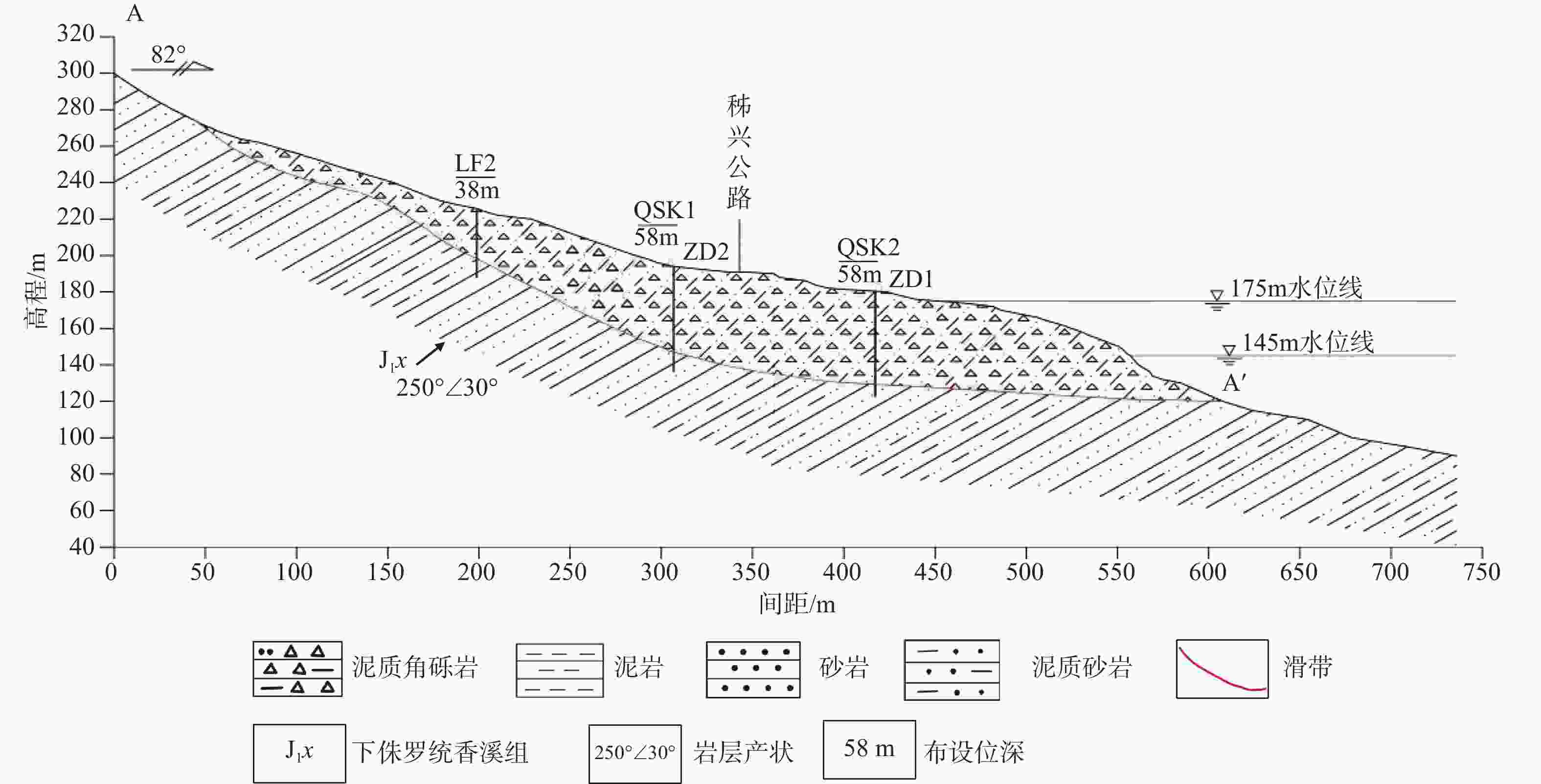
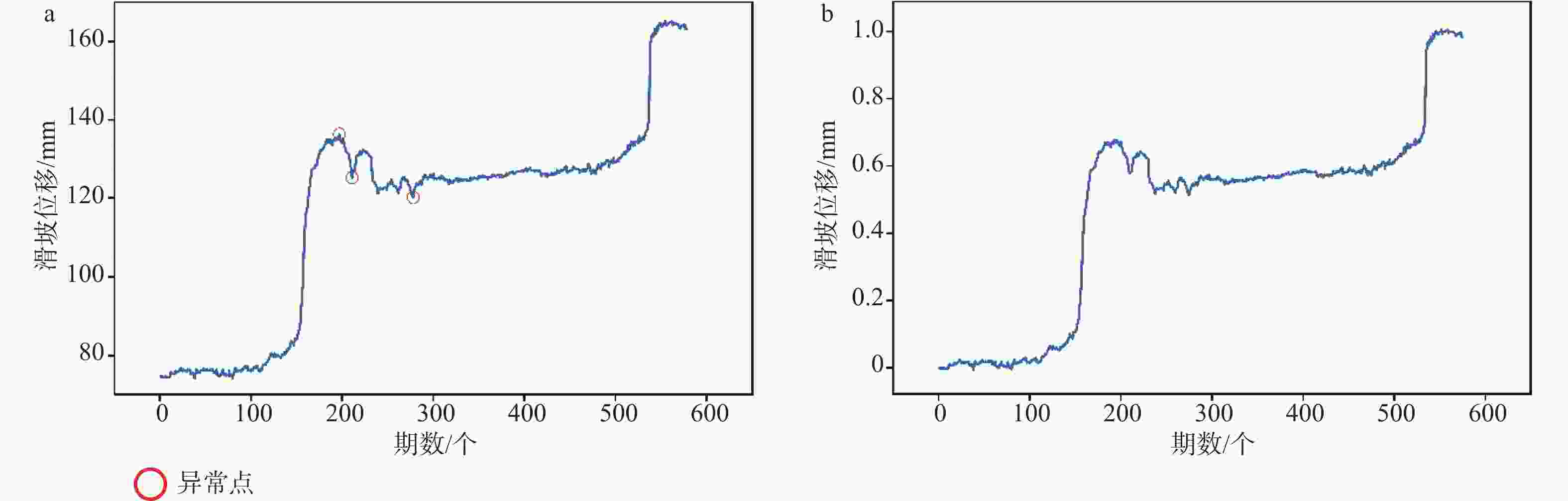
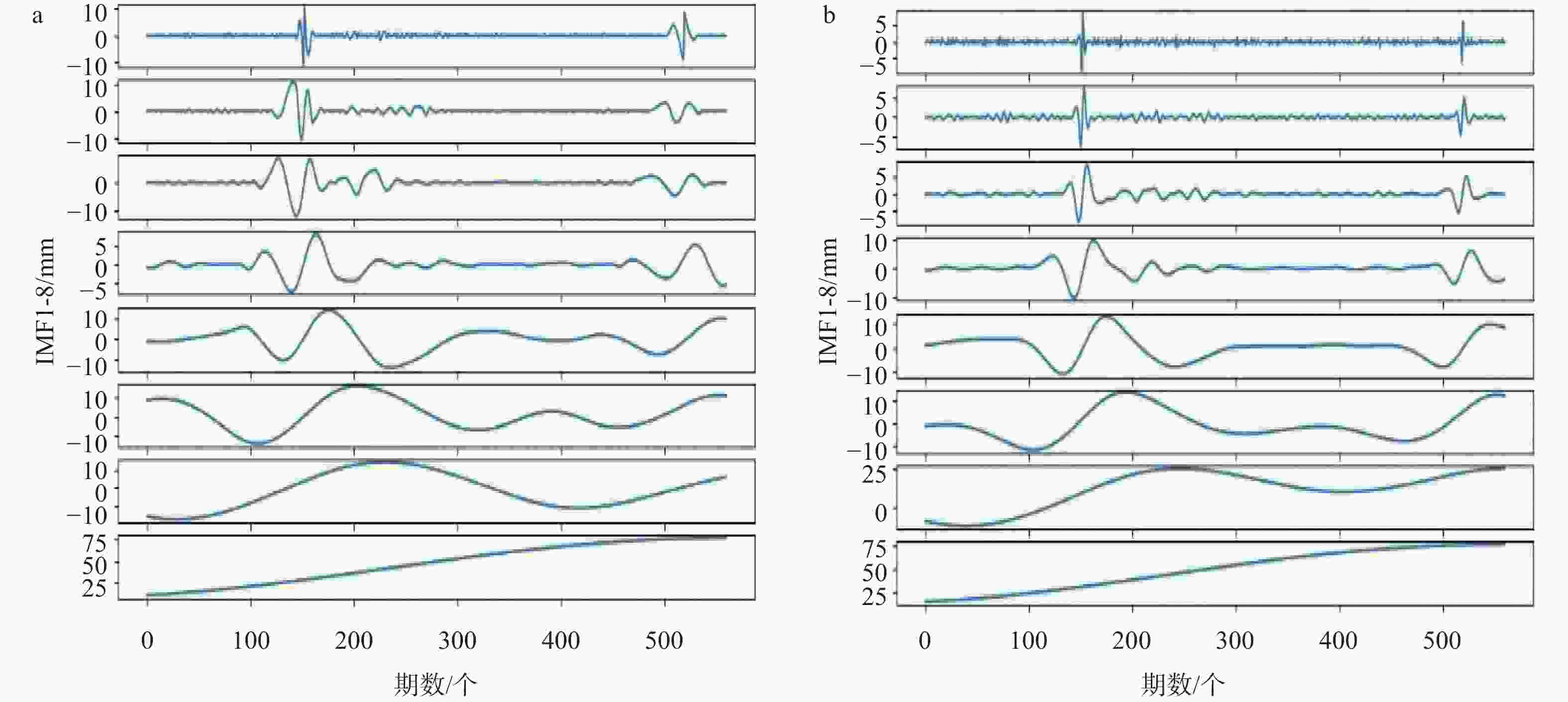
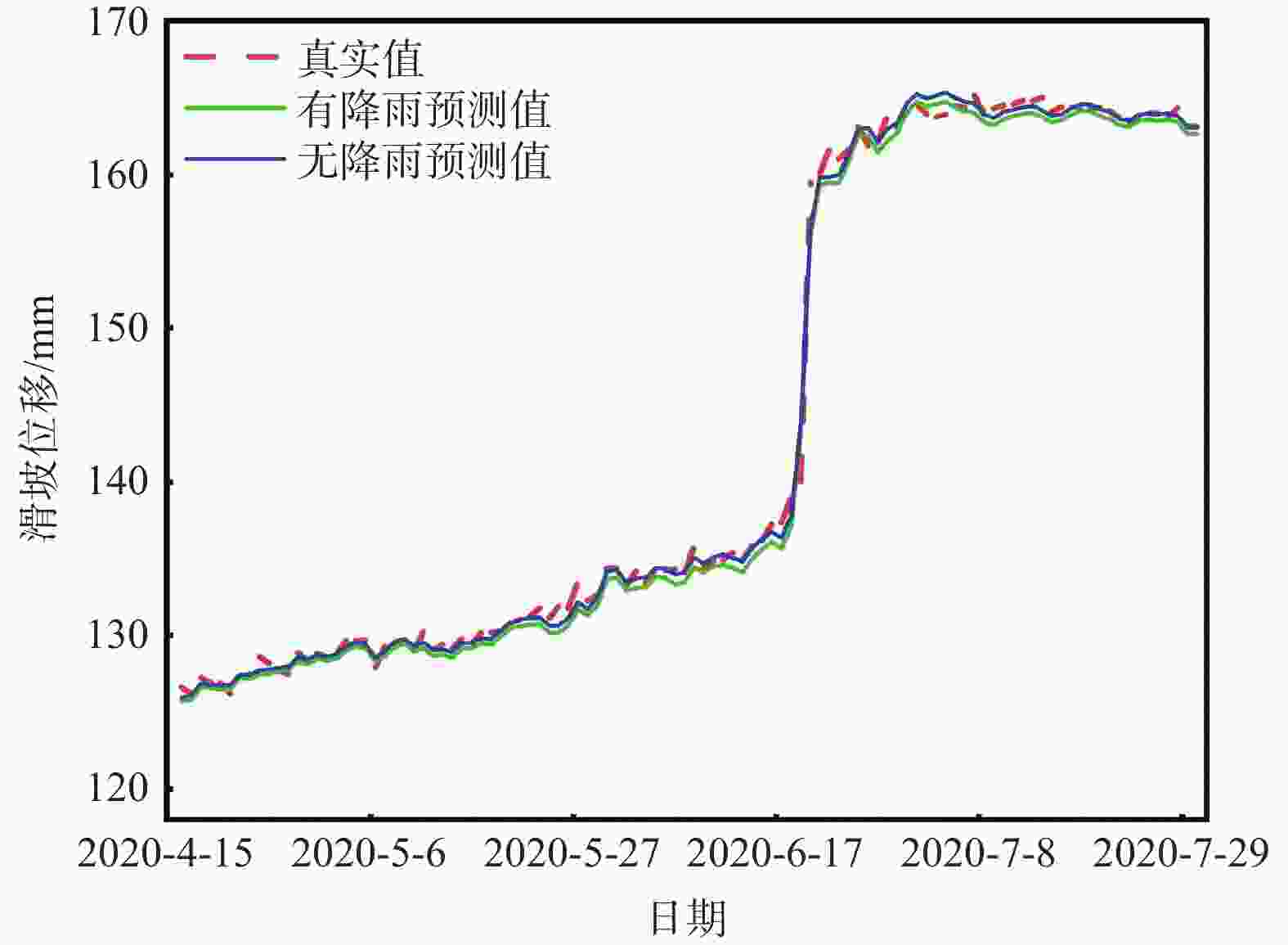
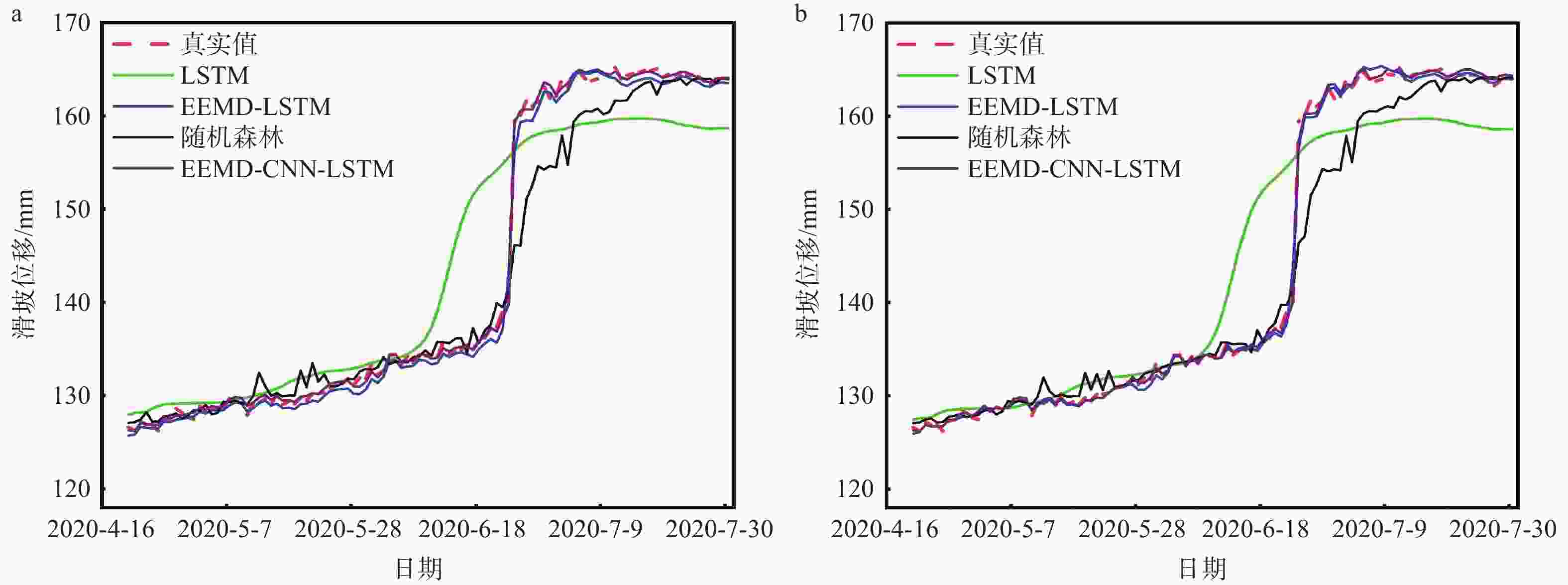
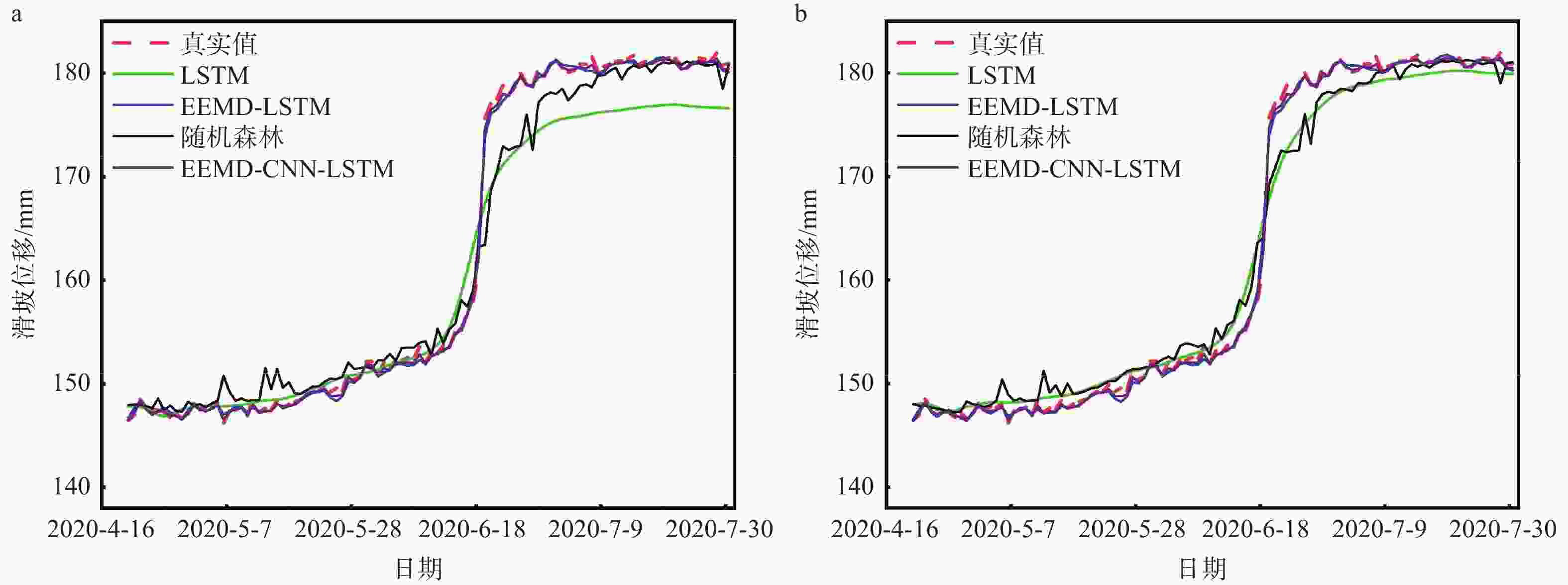
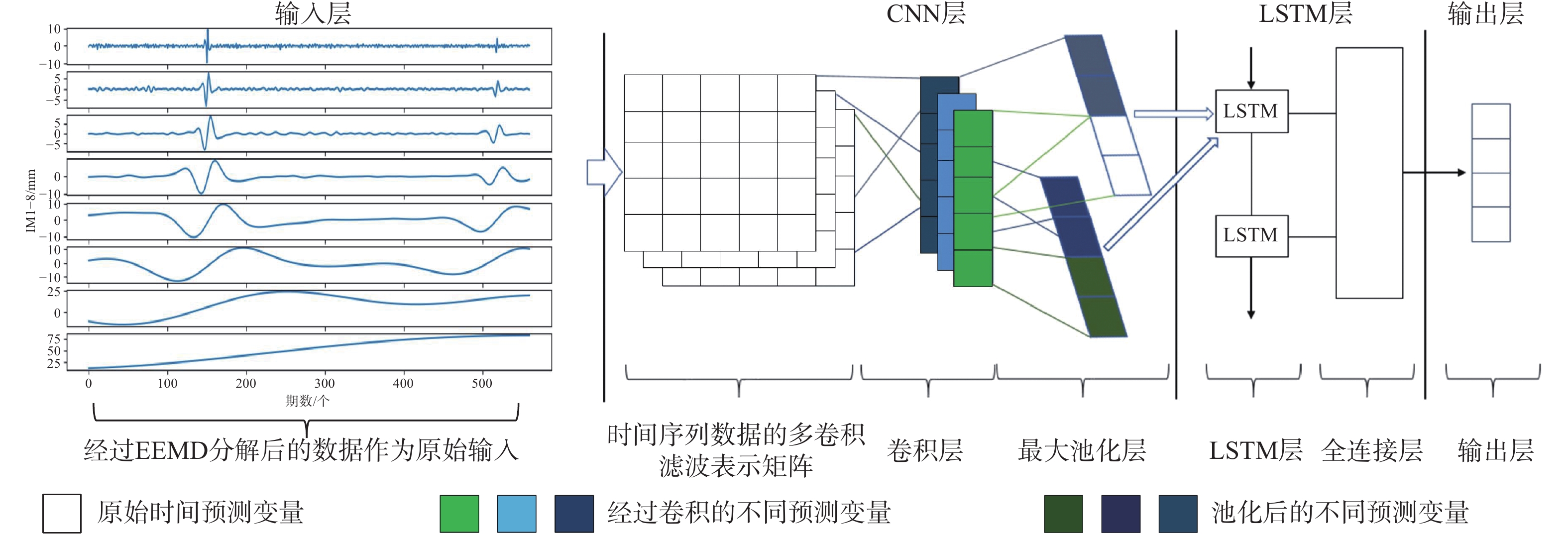
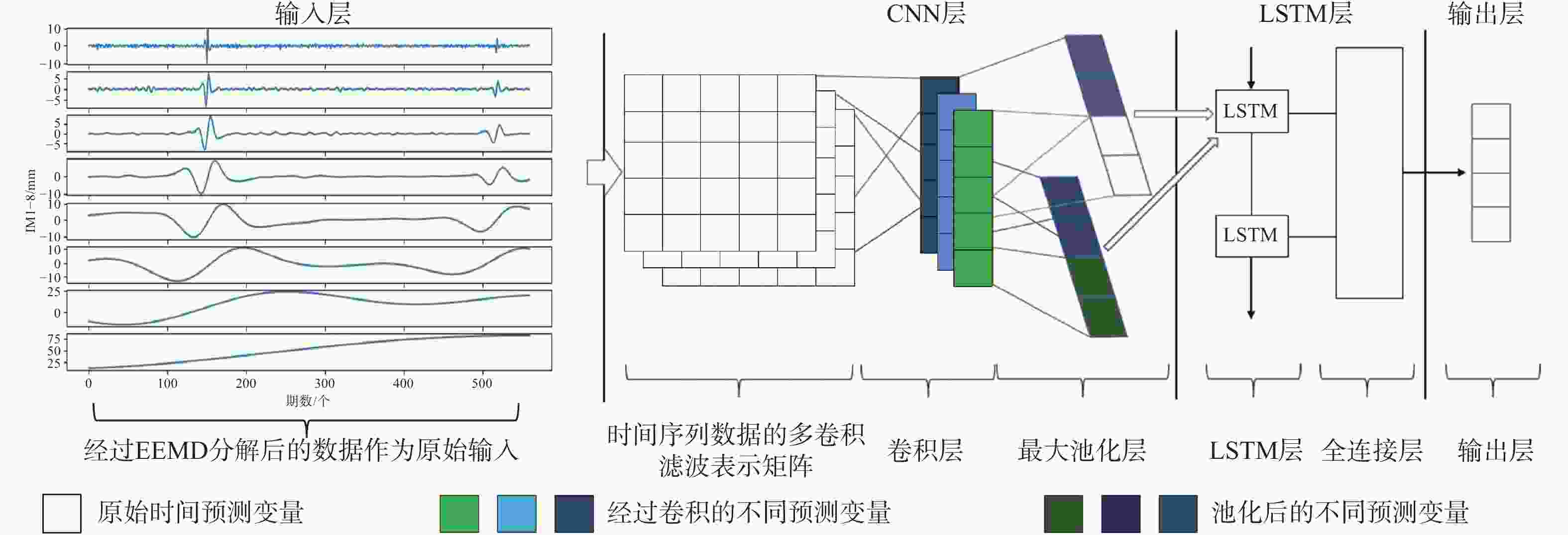
摘要: 滑坡位移预测是滑坡稳定性评价的重要环节。尽管基于深度学习范式的时间序列方法预测滑坡位移取得了一定的成果,但由于滑坡位移数据的非平稳性、周期性和趋势性变化特征,导致当前时间序列模型的滑坡位移的多变量预测容易过拟合。为解决这一问题,针对滑坡位移数据的波动性和由周期项与趋势项位移叠加组成的特性,提出一种基于孤立森林(Isolation Forest,IF)异常检测、集成经验模态分解(Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition,EEMD)、卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Networks,CNN)和长短期记忆神经网络(Long Short-Term Memory,LSTM) 相结合的滑坡位移预测模型。选择三峡库区以降雨为影响因子的阶跃型白家包滑坡为研究对象,引入IF算法对滑坡原始位移数据进行异常检测,使用EEMD方法提取滑坡趋势项和周期项位移,通过CNN捕捉局部周期项和趋势模式,并基于LSTM模型预测总体位移。结果表明,EEMD-CNN-LSTM在预测降雨情况时滑坡总体位移的均方根误差(RMSE)、平均绝对误差(MAE)、评价绝对百分比误差(MAPE)和决定系数(R2)4种指标分别为0.4190、0.3139、0.2379和0.9997,前3种精度评价指标较现有模型分别提升32.3%、25.1%、7.3%。相较于传统的LSTM模型、随机森林方法和EEMD-LSTM方法,EEMD-CNN-LSTM模型在有、无降雨这一外部影响因素下具有显著优势,能够较大地降低过拟合,提高预测的准确性。Abstract:
Objective Landslide-displacement prediction is critical when evaluating landslide stability. Despite the achievements of time-series methods based on deep-learning paradigms in predicting landslide displacement, the nonstationary, periodic, and trending characteristics of landslide displacement data cause multivariate predictions of current time-series models to easily overfit. Existing studies primarily focus on improving single models, whereas systematic studies pertaining to multimodel integration methods are scarce. This study aims to develop an integrated model that addresses these challenges and improves prediction accuracy. Methods Considering the volatility of landslide-displacement data and the combined characteristics of their periodic and trending displacement components, a landslide-displacement prediction model combining isolation forest (IF) anomaly detection, ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and long short-term memory (LSTM) neural networks is proposed. The stepped Baijiabao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, which is affected by rainfall, is investigated in this study. First, the IF algorithm is introduced to detect anomalies in the original landslide-displacement data. This enables outliers, which can distort the prediction results, to be identified and excluded. Subsequently, EEMD is adopted to decompose the displacement data into intrinsic mode functions (IMFs), which represent the underlying periodic and trend components. This decomposition allows one to analyze the inherent characteristics of the data more comprehensively. Next, a CNN is employed to capture local periodic and trend patterns within the IMFs. CNNs are particularly effective in recognizing spatial patterns and features, thus rendering them suitable for identifying complex patterns in the displacement data. Finally, the overall displacement is predicted using the LSTM model, which is suitable for accommodating sequential data and capturing long-term dependencies. These techniques are integrated to leverage their respective strengths, thereby improving the prediction accuracy. Result The results indicate that the root-mean-square error(RMSE), mean absolute error(MAE), absolute percentage error in evaluation (MAPE), and determination coefficient(R2)indices of the EEMD-CNN-LSTM model for predicting the overall landslide displacement under rainfall conditions are 0.4190, 0.3139, 0.2379, and 0.9997, respectively, which signify improvements in the accuracy of the first three evaluation indices by 32.3%, 25.1%, and 7.3%, respectively, compared with those of existing models. This significant improvement demonstrates the model’s robustness in accommodating the complexities of landslide-displacement data under varying conditions. For predictions without rainfall, the RMSE, MAE, MAPE, and R2 indices are 0.4302, 0.2908, 0.2431, and 0.9996, respectively, which signify improvements in the accuracy of the first three indices by 31.2%, 31.7%, and 8.7%, respectively, compared with those of existing models. These results highlight the model’s high generalizability across different scenarios, as it can maintain high prediction accuracies regardless of external influencing factors such as rainfall. Compared with conventional LSTM, random forest, and EEMD-LSTM models, the EEMD-CNN-LSTM model offers significant advantages under the influence of rainfall and without rainfall, thus significantly reducing overfitting and improving the prediction accuracy. The hybrid approach effectively captures the intricate patterns in the data, which cannot be achieved by single models. Conclusion In summary, the multimodel integration method based on IF anomaly detection, EEMD decomposition, local-feature capturing by the CNN, and overall prediction by LSTM significantly improves the accuracy of landslide-displacement prediction, particularly under the influence of rainfall. The integrated model not only addresses the overfitting issues typically encountered in time-series prediction models but also enhances the model’s robustness and reliability. The combination of IF for anomaly detection ensures that outliers do not skew the prediction results, whereas EEMD facilitates the decomposition of data into meaningful components. The CNN’s ability to capture local patterns, coupled with the LSTM’s strength in modeling long-term dependencies, enables the establishment of a comprehensive framework that can effectively accommodate the complexities of landslide displacement data.[ Significance ]This study provides an effective multimodel integration method for landslide-displacement prediction, which addresses the overfitting issues in existing models as well as offers substantial scientific significance and practical value. The proposed model’s ability to accurately predict landslide displacement under varying conditions is extremely beneficial to the stability evaluation of landslide-prone areas, thereby contributing to disaster prevention and mitigation efforts. The innovation is based on the systematic integration of anomaly detection, data decomposition, and advanced neural-network techniques, which results in a robust framework that outperforms conventional methods. The findings of this study are applicable to real-world scenarios, thereby enhancing the accuracy and reliability of landslide monitoring systems and supporting informed decision-making in hazard management and infrastructure development. -
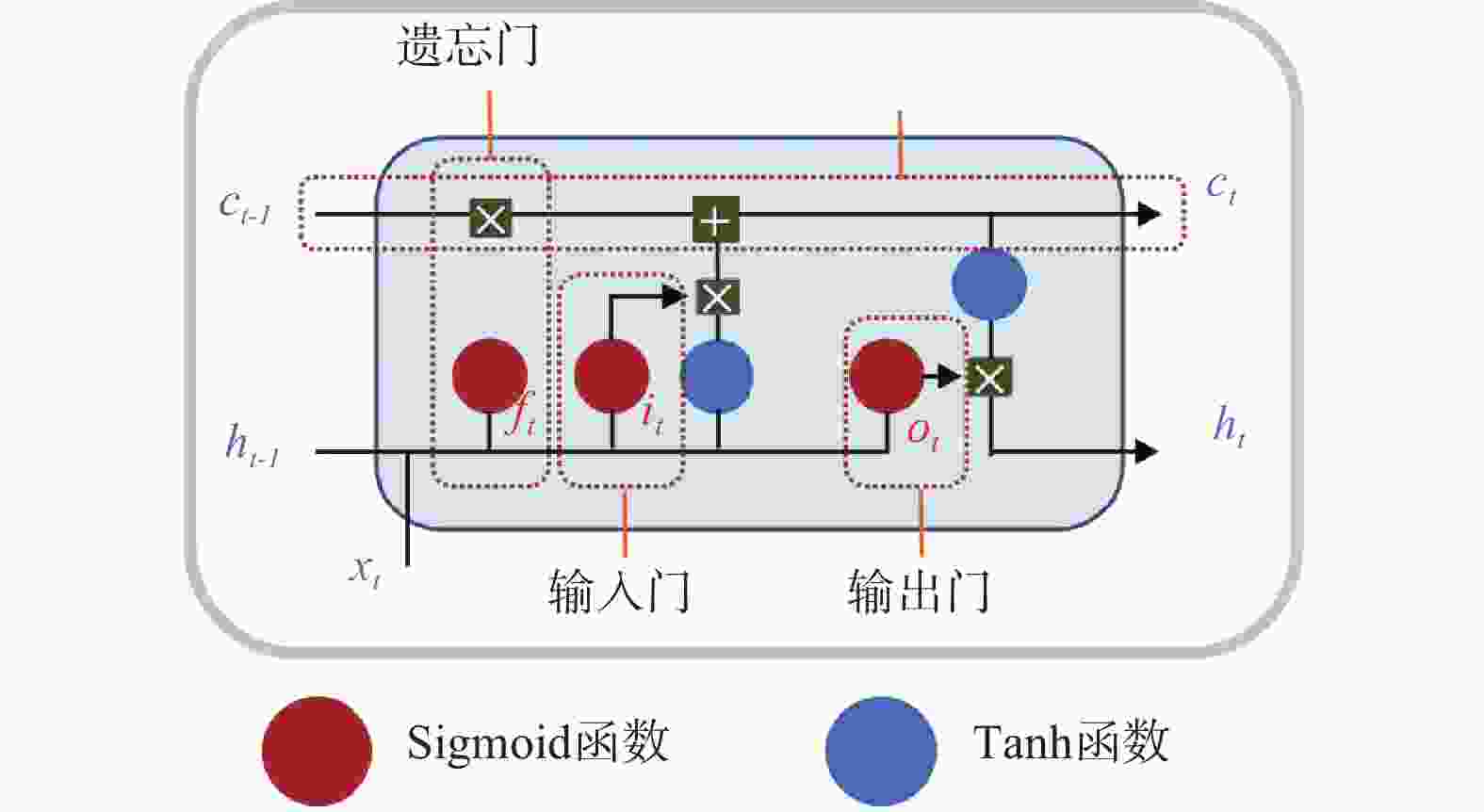
图 2 LSTM网络结构
注:ht-1—上一时刻的输出;ht—当前时刻的输出;ct-1—上一时刻状态;ct—当前状态;xt—当前输入;it—输入门;ft—遗忘门;ot—输出门
Figure 2. LSTM network architecture
Note:ht-1−output of previous moment; ht−output of current moment; ct-1−previous-moment-status; ct−current status; xt−current input; it−input gate; ft−forget gate; ot−output gate.
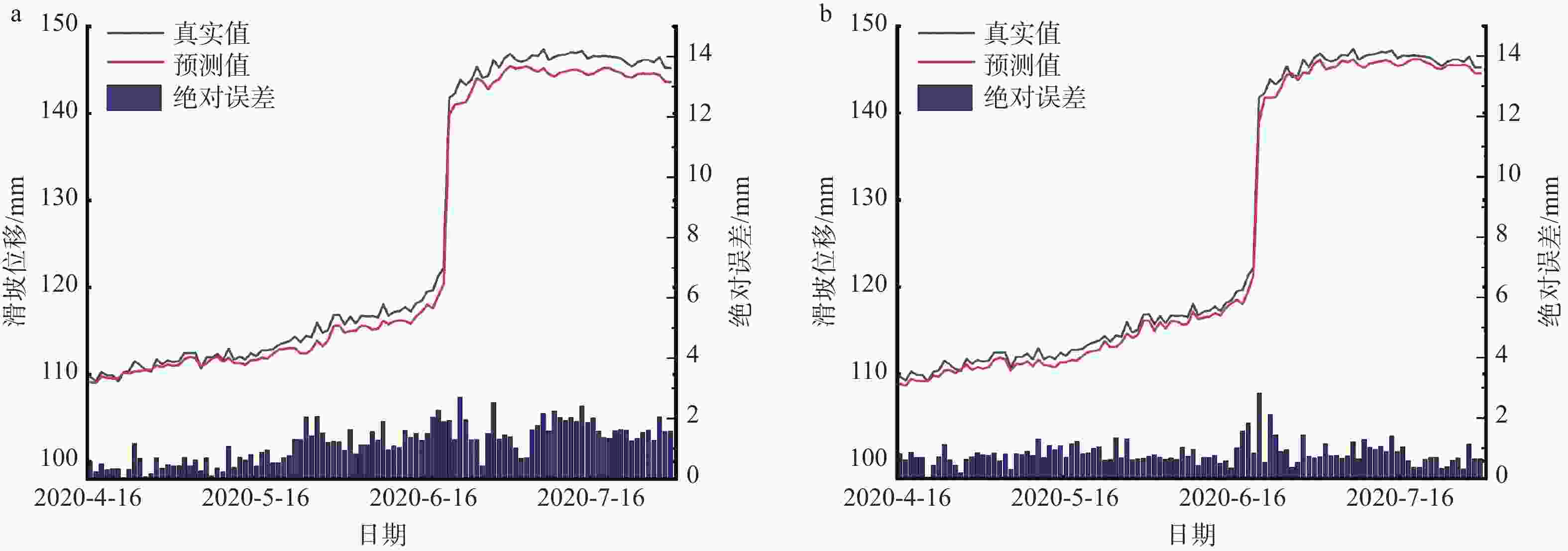
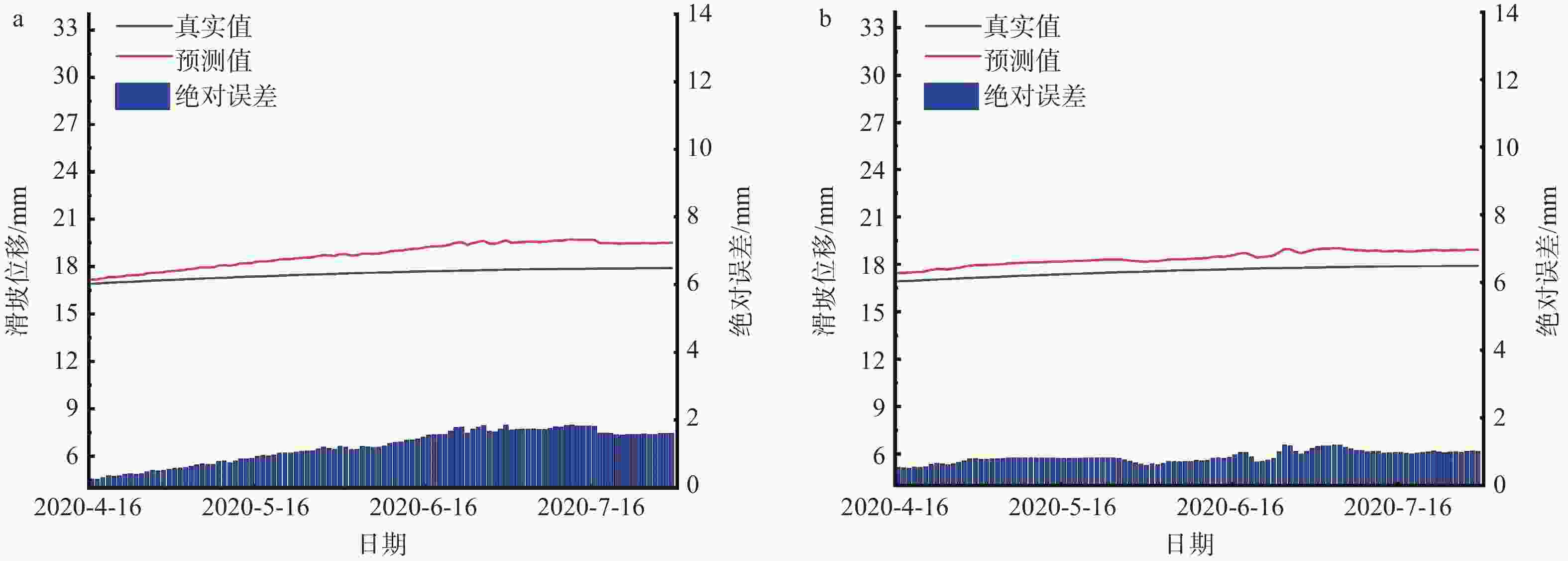
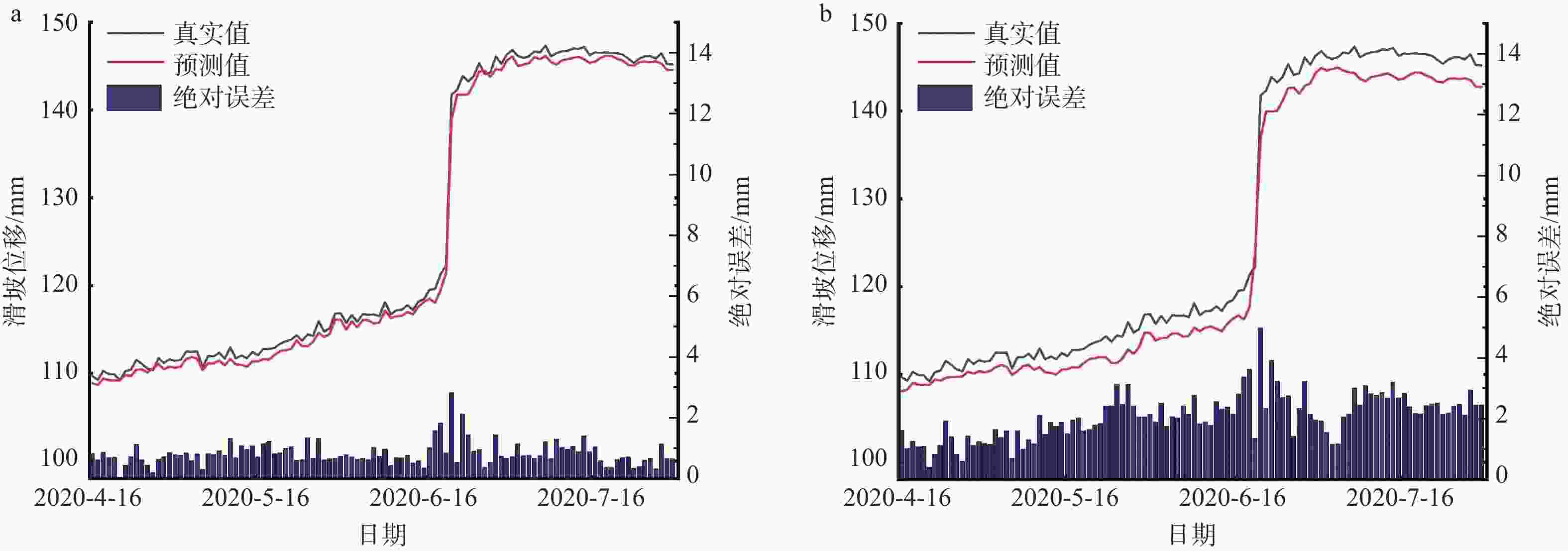
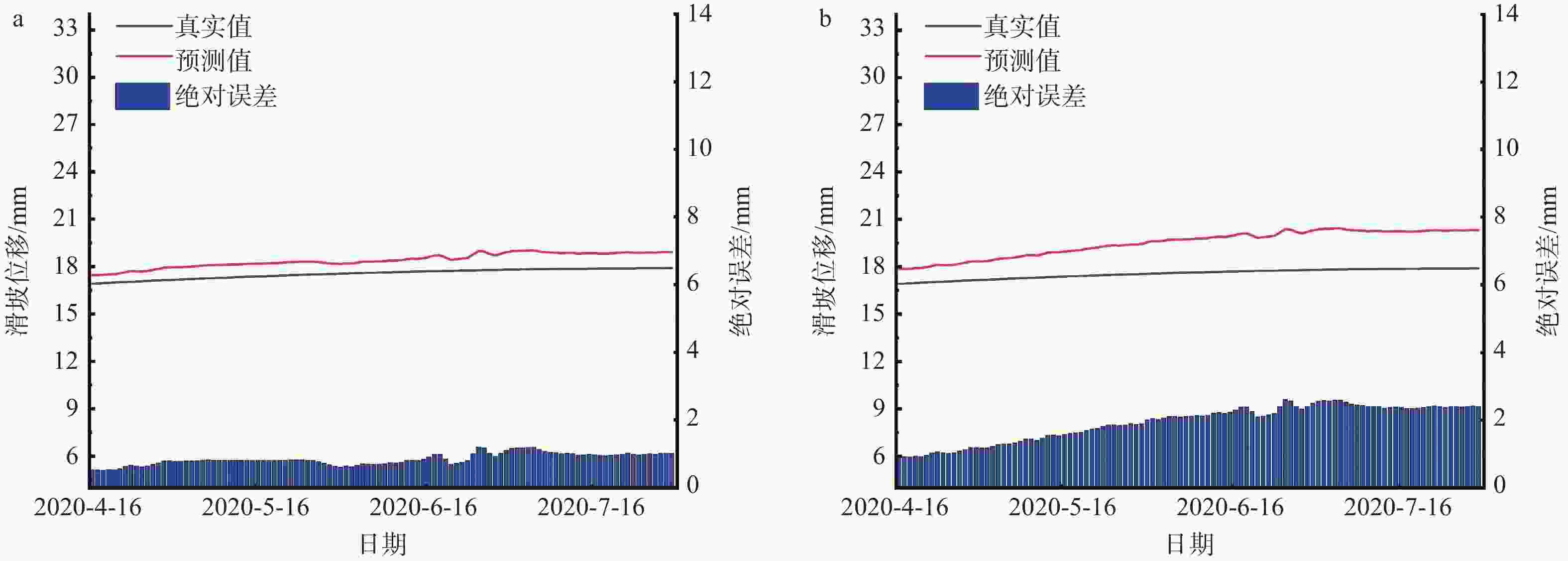
表 1 ZD2监测点EEMD-CNN-LSTM模型、EEMD-LSTM模型、LSTM模型和随机森林模型对滑坡位移预测结果的性能评价
Table 1. Performance evaluation of ZD2 prediction results for EEMD-CNN-LSTM, EEMD-LSTM, LSTM, and random-forest models (with/without rainfall)
模型类型 RMSE/mm MAE/mm MAPE/% R2 EEMD-CNN-LSTM 0.4302/0.4190 0.2908/0.3139 0.2431/0.2379 0.9996/0.9997 EEMD-LSTM 0.6249/0.6187 0.4259/0.4193 0.2642/0.2567 0.9983/0.9983 LSTM 1.9925/3.4102 1.3365/2.7297 0.7888/1.5778 0.9812/0.9449 随机森林 0.8391/1.0329 0.6365/0.7316 0.5078/0.5762 0.9890/0.9885 注:“/”前为降雨下的结果;“/”后为无降雨下的结果 -
[1] AN D, SONG K, YI Z, et al., 2021. A prediction model for reservoir landslide step-like displacements using combined EEMD and RFR method[J]. Mountain Research, 39(1): 143-150. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] BINIYAZ A, AZMOON B, SUN Y, et al., 2022. Long short-term memory based subsurface drainage control for rainfall-induced landslide prevention[J]. Geosciences, 12(2): 64. doi: 10.3390/geosciences12020064 [3] FENG Y, ZENG H N, TU P F, 2023. A time series decomposition method for landslide displacement based on sliding detection algorithm[J]. Journal of Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute, 41(3): 126-133, 147. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] FU W T, HU D M, WANG S H, et al. , 2020. Landslide displacement prediction based on EEMD-GM-ELM model[C]//Proceedings of the 11th China satellite navigation annual conference: S01 satellite navigation industry application. Beijing: Academic Exchange Center of China Satellite Navigation System Management Office: 89-93. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] HAN S, LIU M J, WU J B, et al., 2022. Risk assessment of slope disasters induced by typhoon-rainfall in the southeast coastal area, China: A case study of the Shiyang north slope[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(4): 583-595. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] HARIRI S, KIND M C, BRUNNER R J, 2021. Extended isolation forest[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 33(4): 1479-1489. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2019.2947676 [7] JIANG H W, LI Y Y, ZHOU C, et al., 2020. Landslide displacement prediction combining LSTM and SVR algorithms: a case study of Shengjibao landslide from the three gorges reservoir area[J]. Applied Sciences, 10(21): 7830. doi: 10.3390/app10217830 [8] KANG E S, ZHAO Z X, MENG H D, 2022. Displacement prediction of dump slope based on EEMD-HW-PSO-ELM coupling model[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 30(4): 594-602. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] KATTENBORN T, LEITLOFF J, SCHIEFER F, et al., 2021. Review on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in vegetation remote sensing[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 173: 24-49. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.12.010 [10] KRKAČ M, ŠPOLJARIĆ D, BERNAT S, et al., 2017. Method for prediction of landslide movements based on random forests[J]. Landslides, 14(3): 947-960. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0761-z [11] Aggarwal A, Alshehri M, Kumar M, et al., 2020. Landslide data analysis using various time-series forecasting models[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 88: 106858. [12] LEI Y G, LIN J, HE Z J, et al., 2013. A review on empirical mode decomposition in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 35(1-2): 108-126. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2012.09.015 [13] LI H J, XU Q, HE Y S, et al., 2018. Prediction of landslide displacement with an ensemble-based extreme learning machine and copula models[J]. Landslides, 15(10): 2047-2059. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1020-2 [14] LI L J, YAO X, ZHOU Z K, et al., 2022. The applicability assessment of Sentinel-1 data in InSAR monitoring of the deformed slopes of reservoir in the mountains of southwest China: A case study in the Xiluodu Reservoir[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(2): 281-293. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] LIAN C, ZENG Z G, YAO W, et al., 2013. Displacement prediction model of landslide based on a modified ensemble empirical mode decomposition and extreme learning machine[J]. Natural Hazards, 66(2): 759-771. doi: 10.1007/s11069-012-0517-6 [16] LIU F T, TING K M, ZHOU Z H, 2008. Isolation forest[C]//2008 Eighth IEEE international conference on data mining. Pisa: IEEE: 413-422. [17] MA Y, YU B, HE Y X, et al., 2023. Rainfall Threshold and Development Characteristics of Shallow Landslides Induced by Rainfall: A Case Study of the "June 10th, 2019" Disaster in the Dajishan Area, Quannan County, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 59(5): 1065-1073. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] NAN X C, LIU J F, ZHANG Y X, et al., 2023. Dynamic prediction of landslide displacement based on multi-source time series[J]. Pearl River, 44(4): 54-62. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] PAK U, KIM C, RYU U, et al. , 2018. A hybrid model based on convolutional neural networks and long short-term memory for ozone concentration prediction[J]. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 11(8): 883-895. [20] PENG L, NIU R Q, 2011. Analysis on deformation characteristics and influential factors of Baijiabao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 22(4): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] QU J L, WANG X F, GAO F, et al., 2014. Noise assisted signal decomposition method based on complex empirical mode decomposition[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 63(11): 110201. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7498/aps.63.110201 [22] SHANG M, XIONG D B, ZHANG H Q, et al., 2022. Landslide displacement prediction model based on time series and mixed kernel function SA-SVR[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(2): 575-588. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] SHI X L, HAN X D, YANG X Y, et al., 2023. Factors inducing the Xigouwan landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area and the influence of antecedent precipitation[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 29(2): 253-263. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] SINGH P, KEYVANLOU M, SADHU A, 2021. An improved time-varying empirical mode decomposition for structural condition assessment using limited sensors[J]. Engineering Structures, 232: 111882. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.111882 [25] SUN D L, CHEN D L, MI C L, et al., 2023. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in the gentle hill-valley areas based on the interpretable random forest-recursive feature elimination model[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 29(2): 202-219. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] SUN N K, WANG Y, JI Z C, 2022. Anomaly detection method of electrical power consumption based on deep autoencoder[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 34(12): 2557-2565. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] WANG C H, ZHAO Y J, GUO W, et al., 2022. Displacement prediction model of landslide based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and support vector regression[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 51(10): 2196-2204. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] WANG Y K, TANG H M, HUANG J S, et al., 2022. A comparative study of different machine learning methods for reservoir landslide displacement prediction[J]. Engineering Geology, 298: 106544. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106544 [29] WU J N, 2021. Research on landslide geological disaster prediction method based on deep learning[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] WU Z H, HUANG N E, 2009. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 1(1): 1-41. doi: 10.1142/S1793536909000047 [31] XU S L, NIU R Q, 2018. Displacement prediction of Baijiabao landslide based on empirical mode decomposition and long short-term memory neural network in Three Gorges Area, China[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 111: 87-96. [32] XU Z H, YANG X, SUN Q C, et al. , 2022. Step-type landslide deformation prediction based on multivariable self-optimizing dynamic neural network[J]. Metal Mine(3): 74-82. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] YAN S J, TANG H M, XIANG W, 2007. Effect of rainfall on the stability of landslides[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 34(2): 33-36. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] YANG B B, YIN K L, DU J, 2018. A model for predicting landslide displacement based on time series and long and short term memory neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 37(10): 2334-2343. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] YANG B B, YIN K L, LACASSE S, et al., 2019. Time series analysis and long short-term memory neural network to predict landslide displacement[J]. Landslides, 16(4): 677-694. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-01127-x [36] YAO W M, LI C D, ZUO Q J, et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal deformation characteristics and triggering factors of Baijiabao landslide in three gorges reservoir region, China[J]. Geomorphology, 343: 34-47. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.06.024 [37] YUAN W, SUN R F, ZHONG H Y, et al., 2023. Research on comprehensive deformation prediction and monitoring and early warning methods for step-type like landslide[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 54(4): 461-473. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] ZHOU C, YIN K L, CAO Y, et al., 2018. A novel method for landslide displacement prediction by integrating advanced computational intelligence algorithms[J]. Scientific Reports, 8(1): 7287. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25567-6 [39] 安冬,宋琨,仪政,等,2021. 一种基于EEMD-RFR的水库滑坡台阶状位移预测模型[J]. 山地学报,39(1):143-150. [40] 冯谕,曾怀恩,涂鹏飞,2023. 一种滑动检测算法下的滑坡位移时序分解方法[J]. 长江科学院院报,41(3):126-133,147. [41] 付文涛,胡丁梅,王守华,等,2020. 基于EEMD-GM-ELM模型的滑坡位移预测[C]//第十一届中国卫星导航年会论文集:S01卫星导航行业应用. 北京:中国卫星导航系统管理办公室学术交流中心:89-93. [42] 韩帅,刘明军,伍剑波,等,2022. 东南沿海台风暴雨型单体斜坡灾害风险评价:以泰顺仕阳北坡为例[J]. 地质力学学报,28(4):583-595. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021168 [43] 康恩胜,赵泽熙,孟海东,2022. 基于EEMD-HW-PSO-ELM耦合模型的排土场边坡位移预测模型[J]. 黄金科学技术,30(4):594-602. [44] 李凌婧,姚鑫,周振凯,等,2022. Sentinel-1数据在西南山区水库变形斜坡InSAR监测中的适用性评价:以溪洛渡水库为例[J]. 地质力学学报,28(2):281-293. [45] 马 煜,余 斌,何元勋,等,2023. 降雨激发浅层滑坡发育特征与阈值研究:以江西省全南县大吉山“2019.6. 10”灾害为例[J]. 地质与勘探,59(5):1065-1073. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2023.05.012 [46] 南骁聪,刘俊峰,张永选,等,2023. 基于多源时间序列的滑坡位移动态预测[J]. 人民珠江,44(4):54-62. [47] 彭令,牛瑞卿,2011. 三峡库区白家包滑坡变形特征与影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,22(4):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2011.04.001 [48] 曲建岭,王小飞,高峰,等,2014. 基于复数据经验模态分解的噪声辅助信号分解方法[J]. 物理学报,63(11):110201. doi: 10.7498/aps.63.110201 [49] 尚敏,熊德兵,张惠强,等,2022. 基于时间序列与混合核函数SA-SVR的滑坡位移预测模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,30(2):575-588. [50] 史学磊,韩旭东,杨秀元,等,2023. 三峡库区溪沟湾滑坡的诱发因素及前期降雨影响[J]. 地质力学学报,29(2):253-263. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2022049 [51] 孙德亮,陈丹璐,密长林,等,2023. 基于随机森林-特征递归消除模型的可解释性缓丘岭谷地貌滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质力学学报,29(2):202-219. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2022128 [52] 孙宁可,王艳,纪志成,2022. 基于深度自编码器的电力能耗异常检测方法[J]. 系统仿真学报,34(12):2557-2565. [53] 王晨辉,赵贻玖,郭伟,等,2022. 滑坡位移EEMD-SVR预测模型[J]. 测绘学报,51(10):2196-2204. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220291 [54] 吴俊男,2021. 基于深度学习的滑坡地质灾害预测方法研究[D]. 成都:电子科技大学. [55] 徐志华,杨旭,孙钱程,等,2022. 基于多变量自优化动态神经网络的“阶跃型”滑坡变形预测[J]. 金属矿山(3):74-82. [56] 严绍军,唐辉明,项伟,2007. 降雨对滑坡稳定性影响过程分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,34(2):33-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2007.02.008 [57] 杨背背,殷坤龙,杜娟,2018. 基于时间序列与长短时记忆网络的滑坡位移动态预测模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,37(10):2334-2343. [58] 袁维,孙瑞峰,钟辉亚,等,2023. 阶跃型滑坡综合变形预测及监测预警方法研究[J]. 水利学报,54(4):461-473. -




 下载:
下载: