Considerations on the application of in-situ stress measurement and real-time monitoring in deep underground engineering in strong tectonic activity region
-
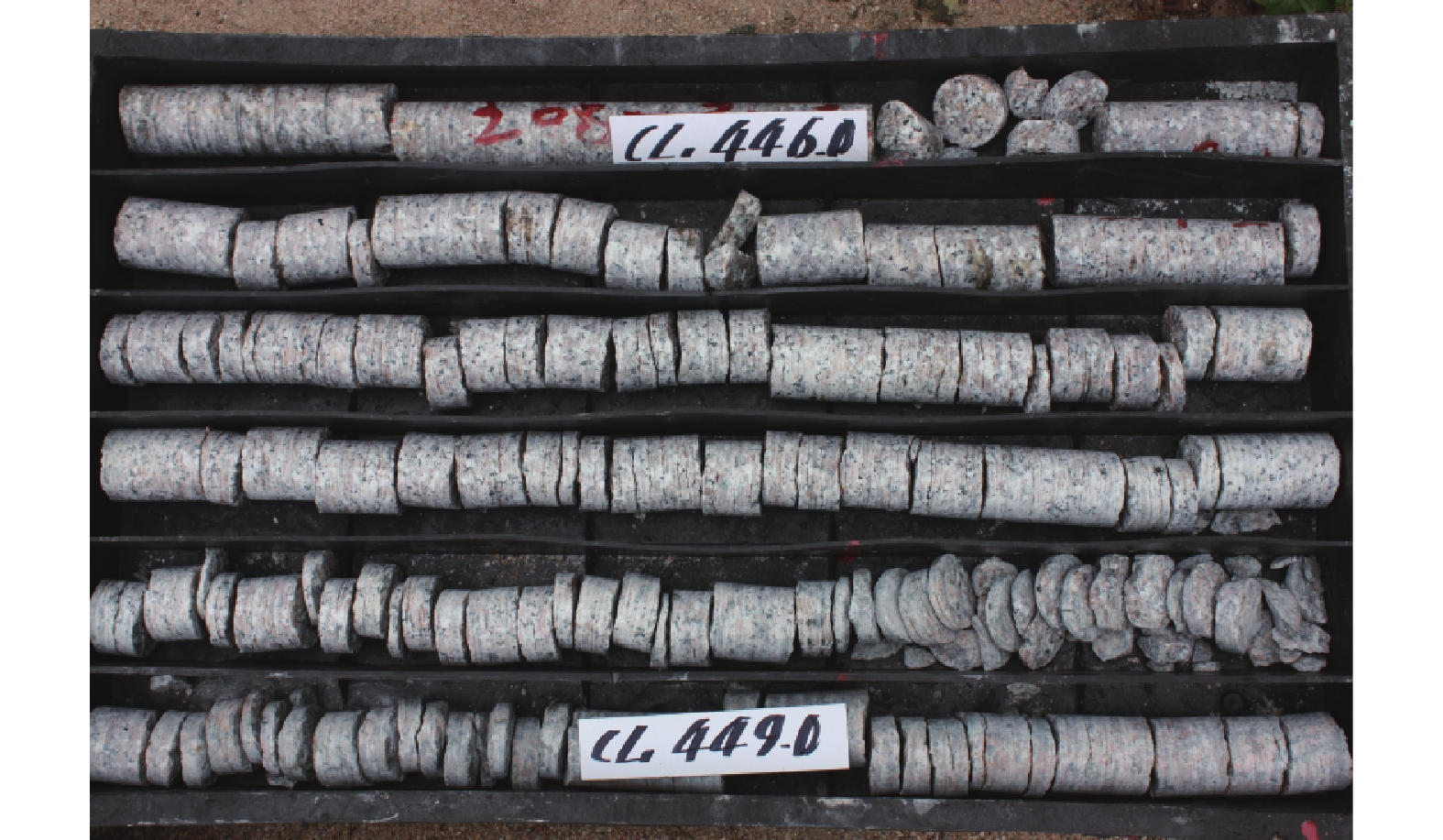
摘要: 强构造活动区,因其原位地应力集中突出、变化复杂、各向异性显著,已成为亟待解决的重大工程地质安全问题和挑战。文章首先分析了原位地应力测量在强构造活动区深埋地下工程应用的经验和不足,然后研究了原位地应力实时监测在强构造活动区深埋地下工程中的应用方法、技术及作用,最后给出了原位地应力测量与实时监测在强构造活动区深埋地下工程中应用建议。研究表明在强构造活动区,不能仅仅依据有限深孔地应力测量结果确定深埋地下工程总体地应力设计参数,而应开展三维地应力场综合研究,揭示其三维地应力场空间分布特征,针对深埋地下工程不同位置采用不同的地应力设计参数,避免因地应力设计参数偏大或偏小造成工程建设浪费或工程病害;在强构造活动区,饼状岩芯密度与地应力测量大小成反比,在饼状岩芯发育深度范围之下未来会形成但仍未形成饼状岩芯的深度范围往往地应力最高、应力最为集中,深埋地下工程应避免该深度范围;原位地应力实时监测可以动态揭示某一构造部位地应力大小的相对变化趋势和演化过程,并可计算地应力实时监测期间不同时域地应力状态绝对值,当大地震或重大工程地质问题发生后,不用开展新的地应力绝对测量,就可以快速评价区域地壳稳定性、深埋地下工程地质安全风险等,为深埋地下工程损毁修复提供量化设计地应力参数及预防变形破坏应力应变预留阈值,评价断层活动危险性。研究成果可为强构造活动区重大工程规划建设和安全运维提供科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 强构造活动区 /
- 饼状岩芯 /
- 原位地应力测量 /
- 压磁电感法地应力实时监测 /
- 应力应变预留阈值
Abstract: The concentration, complexity, and significant anisotropy of in-situ stress make it a pressing and challenging issue in engineering geology safety in strong tectonic activity areas. This paper firstly analyzes the application and existing problems of in-situ stress measurement in deep-buried underground engineering in strong tectonic activity areas. Then, it focuses on the application method, technology, and roles of real-time in-situ stress monitoring in deep underground engineering within tectonically active regions. Finally, it discusses the problems that need to be considered in the application of in-situ stress measurement and real-time monitoring. The results show that in the strong tectonic activity area, relying solely on limited deep hole in-situ stress measurements to determine overall stress design parameters for deep underground engineering is inadequate. A comprehensive study of the three-dimensional in-situ stress field is necessary to reveal its spatial distribution characteristics. Different in-situ stress design parameters should be used for different positions of the deep-buried underground project to avoid engineering waste or engineering damages caused by large or small in-situ stress design parameters. In the strong tectonic activity area, the disk core density is inversely proportional to the measured magnitude of the in-situ stress, and the depth range that has yet to form in the cake-shaped core often has the highest in-situ stress and the most concentrated stress, and the deep underground engineering should avoid this depth range. While a major earthquake or major engineering geological problem occurs, real-time monitoring of in-situ stress can dynamically reveal the relative change trend and evolution process of the in-situ stress magnitude of a specific structural site. It can calculate the absolute value of the in-situ stress state in different time domains during the real-time monitoring period without carrying out new absolute in-situ stress measurements. Regional crust stability and deep-buried engineering geological safety risks can be quickly evaluated, and quantitative in-situ stress design parameters and the stress-strain reserved threshold for preventing deformation and breaking can be provided for the damage repair of deep-buried engineering and the risk of fault activity can also be assessed. The research results will offer geological security for the planning, construction, and safe operation and maintenance of major projects in strong tectonic activity areas. -
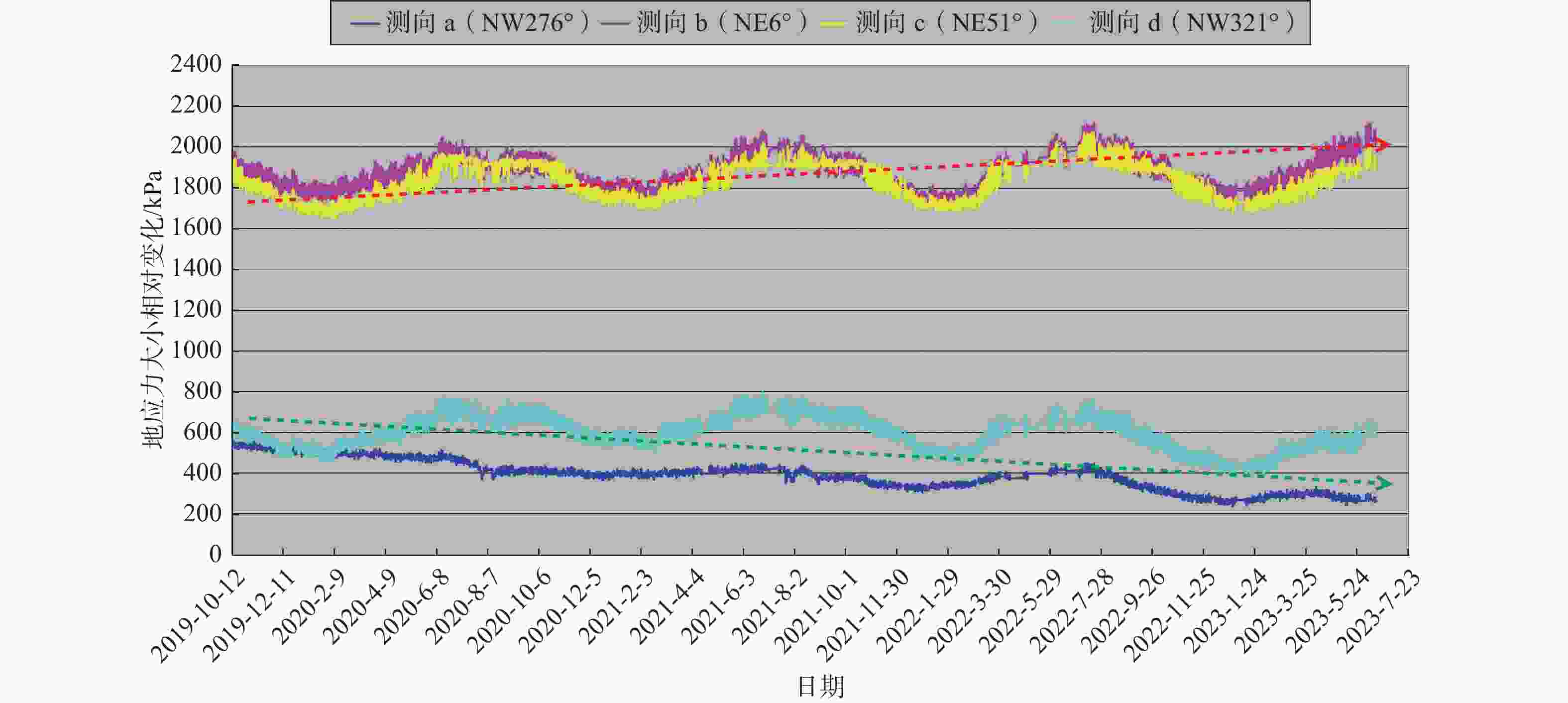
图 6 西藏山南地区乃东县地应力实时监测结果
红色箭头点线表示北东方向地应力呈长期缓慢积累增大趋势;绿色箭头点线表示北西方向地应力呈长期缓慢松弛减小趋势
Figure 6. In-situ stress real-time monitoring results in Naidong County, Shannan region, Tibet
The red arrow dotted line indicates a long-term slow and cumulative increase trend of the NE in-situ stress, while the green arrow dotted line indicates a long-term slow and relaxed decrease trend of the NW in-situ stress.
表 1 地应力判定划分标准
Table 1. Standard for determining in-situ stress classification
应力级别 强度应力比σc/σmax σmax/MPa 陶振宇法:SHmax/Sv 杨子文法:R/σmax 国外 国内 法国隧
道协会日本应用
地质协会苏联顿
巴斯矿区日本国
铁隧规岩土工程
国家标准铁路工程
行业标准公路工程
行业标准水电工程
国家标准低地应力 >4 >4 >4 >6 >7 >7 >7 >7 <10 1.0~1.5 10~100 中等地应力 2~4 2~4 2.2~4 4~6 4~7 10~20 1.5~2.0 4~10 高地应力 <2 <2 <2.2 <4 4~7 4~7 4~7 2~4 20~40 >2 2~4 极高地应力 <4 <4 <4 <2 ≥40 <2 注:σc为岩石饱和单轴抗压强度,MPa;σmax为最大地应力,MPa;SHmax为最大水平主应力,MPa;Sv为垂向主应力,MPa; R=245×(σc/300)0.99Kw0.99,Kw为岩体的完整性系数 -
[1] BAI S W, LI G Y, 1982. Research on stress field around dam area of Ertan hydropower station[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1(1): 45-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] CHEN C J, LIU Z X, LIU J Y, 2016. Study on deformation and failure characteristics of surrounding rock of Jinping Class I hydropower station under high geostress conditions[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station, 32(3): 5-10, 64. (in Chinese) [3] CHENG H, ZHANG G X, LIAO J X, et al. , 2020. Analysis on characteristics and influencing factors of valley deformation of high arch dam[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 51(5): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] FAN Y L, TAN C X, ZHANG P, et al. , 2020. A study of current in-situ stress state and its influence on tectonic stability in the Xiongan New Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 41(4): 481-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] FAN Y L, ZHANG P, GAO Y, et al. , 2021. Study of in-situ stress state and tectonic stability of Liyang seismic area in the Yangtze River Delta region[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 36(5): 1842-1852. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] FAN Y L, FENG C J, ZHANG P, et al. , 2022a. Impact of Tohoku-Oki 3.11 M9.0 earthquake on the fault slip potential of the active Quaternary faults in Beijing city: new insights from in situ stress monitoring data[J]. Sensors, 22(13): 4888. doi: 10.3390/s22134888 [7] FAN Y L, ZHANG P, FENG C J, et al. , 2022b. Analysis of fault slip potential of active faults in Tangshan seismic region after the Tohoku-Oki 3.11 M9.0 earthquake based on in situ stress monitoring data[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10: 970595. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.970595 [8] FENG C J, ZHANG P, SUN W F, et al. , 2014. The application of in situ stress measuring and real-time monitoring results to analyzing the fault activity hazard at Ming tombs borehole in Changping District, Beijing[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 35(3): 345-354. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] GAO K J, ZHAO W G, WANG R K, et al. , 2018. Influence of valley contraction on deformation and stress state of high arch dam[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 18(16): 92-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] GUO C B, ZHANG Y S, JIANG L W, et al. , 2017. Discussion on the environmental and engineering geological problems along the Sichuan-Tibet railway and its adjacent area[J]. Geoscience, 31(5): 877-889. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] GUO Q L, WU F Q, QIAN W P, et al. , 2006. Study on relationship between deformation of surrounding rock and in-situ stress in Wushaoling deep-buried railway tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 25(11): 2194-2199. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] GUO Q L, WANG C H, MA H S, et al. , 2009. In-situ hydro-fracture stress measurement before and after the Wenchuan Ms8.0 earthquake of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(5): 1395-1401. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] HOEK E, BROWN E T, 1997. Practical estimates of rock mass strength[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 34(8): 1165-1186. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(97)80069-X [14] HOEK E, MARINOS P, BENISSI M, 1998. Applicability of the geological strength index (GSI) classification for very weak and sheared rock masses. The case of the Athens schist formation[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 57(2): 151-160. doi: 10.1007/s100640050031 [15] HUANG S L, DING X L, LIAO C G, et al. , 2014. Initial 3D geostress field recognition of high geostress field at deep valley region and considerations on underground powerhouse layout[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 33(11): 2210-2224. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] LI G L, LI N, DING Y J, 2020. Research on key prevention and control technologies for large-deformation high geostress soft rock tunnel[J]. China Railway(12): 69-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] LI H, AN Q M, WANG H Z, et al. , 2006. Study on in-situ stress measurement in V-shaped river valley[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 25(S1): 3069-3073. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] LIANG K, HE Z T, JIANG W L, et al. , 2022. Surface rupture characteristics of the Menyuan Ms6.9 earthquake on January 8, 2022, Qinghai Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 44(1): 256-278. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] LIAO C T, SHI Z X, 1983. In-situ stress measurements and their application to engineering design in the Jinchuan mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2(1): 103-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] LIAO C T, ZHANG C S, WU M L, et al. , 2003. Stress change near the Kunlun fault before and after the Ms 8.1 Kunlun earthquake[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(20): 2027. [21] LIN W R, SAITO S, SANADA Y, et al. , 2011. Principal horizontal stress orientations prior to the 2011 Mw 9.0 Tohoku-Oki, Japan, earthquake in its source area[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(7): L00G10. [22] LIN W R, CONIN M, MOORE J C, et al. , 2013. Stress state in the largest displacement area of the 2011 Tohoku-Oki earthquake[J]. Science, 339(6120): 687-690. doi: 10.1126/science.1229379 [23] LIU G, ZHANG F Y, LI X Z, et al. , 2005. Research on large deformation and its mechanism of Muzhailing tunnel[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 24(S2): 5521-5526. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] MARTIN C D, KAISER P K, CHRISTIANSSON R, 2003. Stress, instability and design of underground excavations[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 40(7-8): 1027-1047. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00110-2 [25] PENG J B, CUI P, ZHUANG J Q, 2020. Challenges to engineering geology of Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 39(12): 2377-2389. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] QIN X H, TAN C X, SUN J Z, et al. , 2012. Experimental study of relation between in-situ crustal stress and rock elastic modulus[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 33(6): 1689-1695. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] QIN X H, CHEN Q C, MENG W, et al. , 2023. Determination of the current in-situ stress field of the Tongmai-Bomi section in the northern margin of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 97(7): 2126-2140. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] QIU Z H, 2010. A review of component borehole observation of stress-strain in China[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 30(5): 42-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) [29] SHEOREY P R, 1994. A theory for in situ stresses in isotropic and transverseley isotropic rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 31(1): 23-34. [30] SONG S W, FENG X M, LIAO C G, et al. , 2016. Measures for controlling large deformations of underground caverns under high in-situ stress condition-A case study of Jinping I hydropower station[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 8(5): 605-618. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.06.002 [31] SUN W F, GUO C B, ZHANG G Z, et al. , 2021. In-situ stress measurement of Guodashan tunnel horizontal borehole in West Sichuan and the engineering significance[J]. Geoscience, 35(1): 126-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] SUN X M, ZHAO C W, TAO Z G, et al. , 2021. Failure mechanism and control technology of large deformation for Muzhailing Tunnel in stratified rock masses[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 80(6): 4731-4750. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02222-5 [33] SUN Y C, XIN M G, WANG Y, et al. ,2022. Measurement and Regression Analysis of the Tunnel Geostress of a Heavy Haul Railway. Railway Investigation and Surveying, 48(1): 16-20, 44. (in Chinese with English abstract) [34] TAN C X, SUN Y, WANG L J, 2003. Some problems of in-situ crustal stress measurements[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 9(3): 275-280, 260. (in Chinese with English abstract) [35] TAN C X, WANG R J, Sun Y, et al. , 2004. Numerical modelling estimation of the ‘tectonic stress plane’ (TSP) beneath topography with quasi-U-shaped valleys[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 41(2): 303-310. doi: 10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00096-0 [36] TAN C X, SHI L, SUN W F, et al. , 2004. Research on tectonic stress plane[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 23(23): 3970-3978. (in Chinese with English abstract) [37] TAN C X, SUN W F, SUN Y, et al. , 2006. A consideration on in-situ crustal stress measuring and its underground engineering application[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(10): 1627-1632. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] TAN C X, ZHANG P, ZHEN H H, et al. , 2008. An analysis on in-situ crustal stress measurements and major engineering geology issues at the dam site area of Jinping first stage hydropower station[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 16(2): 162-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) [39] TAN C X, ZHANG P, FENG C J, et al. , 2014. An approach to deep borehole crustal stress measuring and real-time monitoring and its application in seismogeology research in capital Beijing region[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(8): 1436-1452. (in Chinese with English abstract) [40] TAN C X, HU Q Y, ZHANG P, et al. , 2015. Present tectonic stress adjustment process before and after Japan Mw9.0 earthquake in North and Northeast China and its research significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1): 345-359. (in Chinese with English abstract) [41] TAN C X, ZHANG P, LU S L, et al. , 2019. Significance and role of in-situ crustal stress measuring and real-time monitoring in earthquake prediction research[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 866-876. (in Chinese with English abstract) [42] TAN C X, YANG W M, ZHANG C S, et al. , 2020. Study on active structure and regional crustal stability in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Collaborative Development Area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) [43] TANG H, LI T B, MENG L B, et al. , 2015. Back analysis of ground-stress field for Erlangshan deep buried tunnel on Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Railway Engineering(3): 65-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) [44] WANG C H, GUO Q L, DING L F, et al. , 2009. High in-situ stress criteria for engineering area and a case analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 30(8): 2359-2364. (in Chinese with English abstract) [45] WANG C H, GUO Q L, JIA L, 2011a. Theoretical analysis of high stress criterion based on the Hoek-Brown criterion[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 32(11): 3325-3332. (in Chinese with English abstract) [46] WANG C H, ZHANG Y S, GUO Q L et al. , 2011b. New integrated analysis method to analyze stress regime of engineering area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 33(10): 1562-1568. (in Chinese with English abstract) [47] WANG C H, XING B R, CHEN Y Q, 2014. Prediction of stress field of super-long deep-buried tunnel area and case analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 36(5): 955-960. (in Chinese with English abstract) [48] WANG C H, GAO G Y, YANG S X et al. , 2019. Analysis and prediction of stress fields of Sichuan—Tibet railway area based on contemporary tectonic stress field zoning in western China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 38(11): 2242-2253. (in Chinese with English abstract) [49] WANG D, LI T B, JIANG L W, et al. , 2017. Analysis of the stress characteristics and rock burst of ultra deep buried tunnel in Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 34(4): 46-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) [50] WANG L J, PAN L Z, LIAO C T, et al. , 1991. In-situ stress measurement and its application in engineering[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. (in Chinese) [51] WANG Q W, JU N P, HUANG J, et al. , 2016. Regression analysis of initial geostress field of Sangzhuling super-long tunnel[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 16(25): 137-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) [52] WANG Q W, JU N P, DU L L, et al. , 2018. Three dimensional inverse analysis of geostress field in the Sangri–Jiacha section of Lasa–Linzhi railway[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 39(4): 1450-1462. (in Chinese with English abstract) [53] WEI P , REN X H, JIAO H X, et al. Study on optimization inversion of initial in-situ stress field within slate area [ J] . Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2022, 53(1): 190- 198. (in Chinese with English abstract) [54] WU M L, MA Y, LIAO C T, et al. , 2008. Study on recent state of stress in depth 1 000 m of Jinchuan mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 27(S2): 3785-3790. (in Chinese with English abstract) [55] XU A, QUAN X J, WANG B, et al. ,2022.Inverse Analysis of the Initial Stress Field in High Ground Stress Soft and Hard Rock Tunnels[J]. Railway Standard Design, 66(8): 137-142..(in Chinese with English abstract) [56] XUE S Y, XIE H, YUAN D Y, et al. , 2022. Seismic disaster characteristics of the surface rupture of Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake in 2022[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 44(2): 458-467. (in Chinese with English abstract) [57] XUE Y G, KONG F M, YANG W M, et al. , 2020. Main unfavorable geological conditions and engineering geological problems along Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 39(3): 445-468. (in Chinese with English abstract) [58] YAN J, HE C, WANG B, et al. , 2019. Inoculation and characters of rockbursts in extra-long and deep-lying tunnels located on Yarlung Zangbo suture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 38(4): 769-781. (in Chinese with English abstract) [59] YANG J X, HUANG S L, LIU Z X, 2019. Relationship between deformation failure and strength-to-stress ratio of surrounding rock of large-scale underground hard rock caverns under high geo-stress[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 36(2): 63-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) [60] YANG Q, PAN Y W, CHENG L, et al. , 2015. Mechanism of valley deformation of high arch dam and effective stress principle for unsaturated fractured rock mass[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 34(11): 2258-2269. (in Chinese with English abstract) [61] ZHANG B, CHENG H H, SHI Y L, 2015. Calculation of the co-seismic effect of MS8.1 earthquake, April 25, 2015, Nepal[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(5): 1794-1803. (in Chinese with English abstract) [62] ZHANG C Y, WU M L, LIAO C T, 2013. In-situ stress measurement and study of stress state characteristics of Jinchuan No. 3 mine[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 34(11): 3254-3260. (in Chinese with English abstract) [63] ZHANG C Y, DU S H, HE M C, et al. , 2022. Characteristics of in-situ stresses on the western margin of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis and its influence on stability of tunnel surrounding rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 41(5): 954-967. (in Chinese with English abstract) [64] ZHANG G Z, JIA Z Q, FENG J, et al. , 2022. Definition for dual-index high geostress and classification standard for rock burst and large deformation in railway tunnels[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 39(8): 53-58, 65. (in Chinese with English abstract) [65] ZHANG P, SUN Z G, WANG Q N, et al. , 2017a. In-situ stress measurement and stability analysis of surrounding rocks in the north section of deep buried tunnel in Muzhailing[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 23(6): 893-903. (in Chinese with English abstract) [66] ZHANG P, QU Y M, GUO C B, et al. , 2017b. Analysis of in-situ stress measurement and real-time monitoring results in Nyching of Tibetan plateau and its response to Nepal MS8.1 earthquake[J]. Geoscience, 31(5): 900-910. (in Chinese with English abstract) [67] ZHANG W X, ZHANG J G, TANG S W, et al. , 2013. Ground stress characteristics and their influence on tunnel deformation: case study on Muzhailing tunnel[J]. Tunnel Construction, 33(2): 116-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) [68] ZHANG Y, XIAO P X, DING X L, et al. , 2012. Study of deformation and failure characteristics for surrounding rocks of underground powerhouse caverns under high geostress condition and countermeasures[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 31(2): 228-244. (in Chinese with English abstract) [69] ZHANG Y X. 2021. Characteristics of current in-situ stress field about Sejila mountain traffic corridor[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 29(2): 394-403. (in Chinese with English abstract) [70] ZHANG Y F, YUAN K, ZHOU W J, et al. , 2023. Study on structural deformation characteristics and surface crack distribution of girder tunnel across Lenglongling fault caused by Menyuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 42(5): 1055-1069. (in Chinese with English abstract) [71] ZHU S, ZHAN W, LIANG H B, et al. , 2022. Coseismic deformation characteristics before the Menyuan, Qinghai M 6.9 earthquake from GNSS observation data[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 44(2): 370-379. (in Chinese with English abstract) [72] ZOU X M, ZHONG J F, CHEN Z, et al , 2022. Numerical simulation method-based study on causation of sudden change of seismicity after impoundment of Xiluodu Reservoir [J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 53( 10) : 186-19 [73] 白世伟, 李光煜, 1982. 二滩水电站坝区岩体应力场研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1(1): 45-56. [74] 陈长江, 刘忠绪, 刘建友, 2016. 高地应力条件下锦屏一级水电站地下厂房围岩变形破坏特征研究[J]. 水电站设计, 32(3): 5-10, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9805.2016.03.002 [75] 程恒, 张国新, 廖建新, 等, 2020. 高拱坝谷幅变形特征及影响因素分析[J]. 水利水电技术, 51(5): 65-70. [76] 范玉璐, 谭成轩, 张鹏, 等, 2020. 雄安新区现今地应力环境及其对构造稳定性影响研究[J]. 地球学报, 41(4): 481-491. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.040603 [77] 范玉璐, 张鹏, 高研, 等, 2021. 长三角溧阳震区地应力环境及构造稳定性分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 36(2): 1842-1852. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0368 [78] 丰成君, 张鹏, 孙炜锋, 等, 2014. 北京昌平十三陵钻孔地应力测量与实时监测在断层活动危险性分析中的应用探讨[J]. 地球学报, 35(3): 345-354. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.03.10 [79] 高克静, 赵文光, 王仁坤, 等, 2018. 谷幅收缩对高拱坝变形及应力状态的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 18(16): 92-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.16.015 [80] 郭长宝, 张永双, 蒋良文, 等, 2017. 川藏铁路沿线及邻区环境工程地质问题概论[J]. 现代地质, 31(5): 877-889. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.05.001 [81] 郭啟良, 伍法权, 钱卫平, 等, 2006. 乌鞘岭长大深埋隧道围岩变形与地应力关系的研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 25(11): 2194-2199. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.11.005 [82] 郭啟良, 王成虎, 马洪生, 等, 2009. 汶川Ms8.0级大震前后的水压致裂原地应力测量[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(5): 1395-1401. [83] 黄书岭, 丁秀丽, 廖成刚, 等, 2014. 深切河谷区水电站厂址初始应力场规律研究及对地下厂房布置的思考[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 33(11): 2210-2224. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.11.006 [84] 李国良, 李宁, 丁彦杰, 2020. 高地应力软岩大变形隧道防控关键技术研究[J]. 中国铁路(12): 69-73. [85] 李宏, 安其美, 王海忠, 等, 2006. V型河谷区原地应力测量研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 25(S1): 3069-3073. [86] 梁宽, 何仲太, 姜文亮, 等, 2022. 2022年1月8日青海门源Ms6.9地震的同震地表破裂特征[J]. 地震地质, 44(1): 256-278. [87] 廖椿庭, 施兆贤, 1983. 金川矿区原岩应力实测及在矿山设计中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2(1): 103-112. [88] 刘高, 张帆宇, 李新召, 等, 2005. 木寨岭隧道大变形特征及机理分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 24(S2): 5521-5526. [89] 彭建兵, 崔鹏, 庄建琦, 2020. 川藏铁路对工程地质提出的挑战[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 39(12): 2377-2389. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0446 [90] 秦向辉, 谭成轩, 孙进忠, 等, 2012. 地应力与岩石弹性模量关系试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 33(6): 1689-1695. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2012.06.005 [91] 秦向辉, 陈群策, 孟文, 等, 2023. 喜马拉雅东构造结北缘通麦-波密段现今地应力场特征研究[J]. 地质学报, 97(7): 2126-2140. [92] 邱泽华, 2010. 中国分量钻孔地应力-应变观测发展重要事件回顾[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 30(5): 42-47. [93] 孙炜锋, 郭长宝, 张广泽, 等, 2021. 川西郭达山隧道水平孔地应力测量与工程意义[J]. 现代地质, 35(1): 126-136. [94] 孙元春, 辛明高, 汪洋, 等, 2022.某重载铁路隧道地应力测试与反演分析. 铁道勘察, 48(1): 16-20, 44. [95] 谭成轩, 孙叶, 王连捷, 2003. 地应力测量值得注意的若干问题[J]. 地质力学学报, 9(3): 275-280, 260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2003.03.010 [96] 谭成轩, 石玲, 孙炜锋, 等, 2004. 构造应力面研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 23(23): 3970-3978. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.23.010 [97] 谭成轩, 孙炜锋, 孙叶, 等, 2006. 地应力测量及其地下工程应用的思考[J]. 地质学报, 80(10): 1627-1632. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.10.018 [98] 谭成轩, 张鹏, 郑汉淮, 等, 2008. 雅砻江锦屏一级水电站坝址区实测地应力与重大工程地质问题分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 16(2): 162-168. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.02.003 [99] 谭成轩, 张鹏, 丰成君, 等, 2014. 探索首都圈地区深孔地应力测量与实时监测及其在地震地质研究中应用[J]. 地质学报, 88(8): 1436-1452. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2014.08.006 [100] 谭成轩, 胡秋韵, 张鹏, 等, 2015. 日本Mw9.0级大地震前后华北和东北地区现今构造应力作用调整过程与研究意义探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 22(1): 345-359. [101] 谭成轩, 张鹏, 路士龙, 等, 2019. 原位地应力测量与实时监测在地震预报研究中的作用和意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(5): 866-876. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.05.071 [102] 谭成轩, 杨为民, 张春山, 等, 2020. 京津冀协同发展区活动构造与区域地壳稳定性研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [103] 唐浩, 李天斌, 孟陆波, 等, 2015. 川藏铁路二郎山深埋隧道的地应力场反演分析[J]. 铁道建筑(3): 65-69. [104] 王成虎, 郭啟良, 丁立丰, 等, 2009. 工程区高地应力判据研究及实例分析[J]. 岩土力学, 30(8): 2359-2364. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.08.029 [105] 王成虎, 郭啟良, 贾龙, 2011a. 基于Hoek-Brown强度准则的高应力判据理论分析[J]. 岩土力学, 32(11): 3325-3332. [106] 王成虎, 张彦山, 郭啟良, 等, 2011b. 工程区地应力场的综合分析法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 33(10): 1562-1568. [107] 王成虎, 邢博瑞, 陈永前, 2014. 长大深埋隧道工程区地应力状态预测与实例分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 36(5): 955-960. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201405021 [108] 王成虎, 高桂云, 杨树新, 等, 2019. 基于中国西部构造应力分区的川藏铁路沿线地应力的状态分析与预估[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 38(11): 2242-2253. [109] 王栋, 李天斌, 蒋良文, 等, 2017. 川藏铁路某超深埋隧道地应力特征及岩爆分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 34(4): 46-50. [110] 王连捷, 潘立宙, 廖椿庭, 等, 1991. 地应力测量及其在工程中的应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. [111] 王庆武, 巨能攀, 黄健, 等, 2016. 桑珠岭特长隧道初始地应力场反演分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 16(25): 137-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.25.023 [112] 王庆武, 巨能攀, 杜玲丽, 等, 2018. 拉林铁路桑日至加查段三维地应力场反演分析[J]. 岩土力学, 39(4): 1450-1462. [113] 魏鹏, 任旭华, 焦红星, 等. 板岩区初始地应力场优化反演研究[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文) , 2022, 53(1): 190-198. [114] 吴满路, 马宇, 廖椿庭, 等, 2008. 金川二矿深部1 000 m中段地应力测量及应力状态研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 27(S2): 3785-3790. [115] 徐安, 全晓娟, 汪波, 等. 2022. 高地应力软硬岩隧道初始应力场反演分析. 铁道标准设计, 66(8): 137-142. [116] 薛善余, 谢虹, 袁道阳, 等, 2022. 2022门源MS6.9地震地表破裂带震害特征调查[J]. 地震工程学报, 44(2): 458-467. [117] 薛翊国, 孔凡猛, 杨为民, 等, 2020. 川藏铁路沿线主要不良地质条件与工程地质问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 39(3): 445-468. [118] 严健, 何川, 汪波, 等, 2019. 雅鲁藏布江缝合带深埋长大隧道群岩爆孕育及特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 38(4): 769-781. [119] 杨静熙, 黄书岭, 刘忠绪, 2019. 高地应力硬岩大型洞室群围岩变形破坏与岩石强度应力比关系研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 36(2): 63-70. [120] 杨强, 潘元炜, 程立, 等, 2015. 高拱坝谷幅变形机制及非饱和裂隙岩体有效应力原理研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 34(11): 2258-2269. [121] 张贝, 程惠红, 石耀霖, 2015. 2015年4月25日尼泊尔MS8.1大地震的同震效应[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(5): 1794-1803. [122] 张重远, 吴满路, 廖椿庭, 2013. 金川三矿地应力测量及应力状态特征研究[J]. 岩土力学, 34(11): 3254-3260. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2013.11.029 [123] 张重远, 杜世回, 何满潮, 等, 2022. 喜马拉雅东构造结西缘地应力特征及其对隧道围岩稳定性的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 41(5): 954-967. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2021.0502 [124] 张广泽, 贾哲强, 冯君, 等, 2022. 铁路隧道双指标高地应力界定及岩爆大变形分级标准[J]. 铁道工程学报, 39(8): 53-58, 65. [125] 张鹏, 孙治国, 王秋宁, 等, 2017a. 木寨岭深埋隧道北段地应力测量与围岩稳定性分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 23(6): 893-903. [126] 张鹏, 曲亚明, 郭长宝, 等, 2017b. 西藏林芝地应力测量监测与尼泊尔MS8.1级强震远场响应分析[J]. 现代地质, 31(5): 900-910. [127] 张文新, 张建国, 唐绍武, 等, 2013. 木寨岭隧道地应力特征及对隧道变形影响的研究[J]. 隧道建设, 33(2): 116-121. [128] 张勇, 肖平西, 丁秀丽, 等, 2012. 高地应力条件下地下厂房洞室群围岩的变形破坏特征及对策研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 31(2): 228-244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.02.002 [129] 张玉芳, 袁坤, 周文皎, 等, 2023. 门源地震对跨冷龙岭断层的大梁隧道结构变形特征和地表裂缝分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 42(5): 1055-1069. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2022.0609 [130] 张玉玺, 2021. 色季拉山交通廊道现今地应力场特征研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 29(2): 394-403. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2021-0126 [131] 朱爽, 占伟, 梁洪宝, 等, 2022. 青海门源6.9级地震同震及震前GNSS变形特征分析[J]. 地震工程学报, 44(2): 370-379. doi: 10.20000/j.1000-0844.20220215008 [132] 邹旭明, 钟菊芳, 陈竹, 等. 基于数值模拟方法的溪洛渡水库蓄水后地震活动性突变原因分析[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文), 2022, 53(10): 186-197. -





 下载:
下载: