Discussion on the ore-controlling factors in the Longlin–Xilin Sb–Au mining district of western Guangxi, South China
-
摘要: 华南锑成矿省锑资源储量占全国83%以上,位于成矿省西南部的滇黔桂锑矿带是华南锑成矿省的重要组成部分。文章以滇黔桂锑矿带中部桂西隆林−西林锑金矿集区为例,系统分析了区内82个矿床(点)的赋矿层位、赋矿围岩岩性、容矿构造特征及锑、金矿床共伴生关系,结合3个典型矿床调查及岩浆岩时空分布,探讨锑成矿作用与碎屑岩、岩浆岩的成因联系。研究结果表明:具有高锑背景值的炭质泥页岩和富黄铁矿砂岩是研究区锑成矿的有利岩性,为锑成矿提供了物质来源。岩浆作用对锑成矿既可以起到直接作用(Sb和S来源)也可以起到间接作用(热源),两者均有利于锑矿床的形成。容矿构造分析显示研究区经历了印支期南北向挤压,随后叠加中晚侏罗世北西—南东向挤压。北西西—南东东向和北东—南西向断裂及其交汇处是有利的容矿空间。隆林−西林矿集区锑、金矿床统计显示,区内以独立的锑、金矿床为主,暗示研究区锑、金成矿流体可能多为不同来源流体。在上述研究基础上,文章提出桂西隆林-西林锑金矿集区勘查有利区域:新州背斜核部下泥盆统郁江组炭质泥页岩和富黄铁矿粉砂岩是锑矿勘查的重点层位;隆林县弄桑−石家寨北西西—南东东向断裂带内隐伏岩体周边和西林县北西西—南东东向斗皇−西林断裂与北东—南西向断裂的交汇部位是锑矿勘查的有利区域。以上成果为研究区内锑金矿床成因和成矿规律认识提供新的思考,为区内锑矿床勘查提供方向。Abstract:
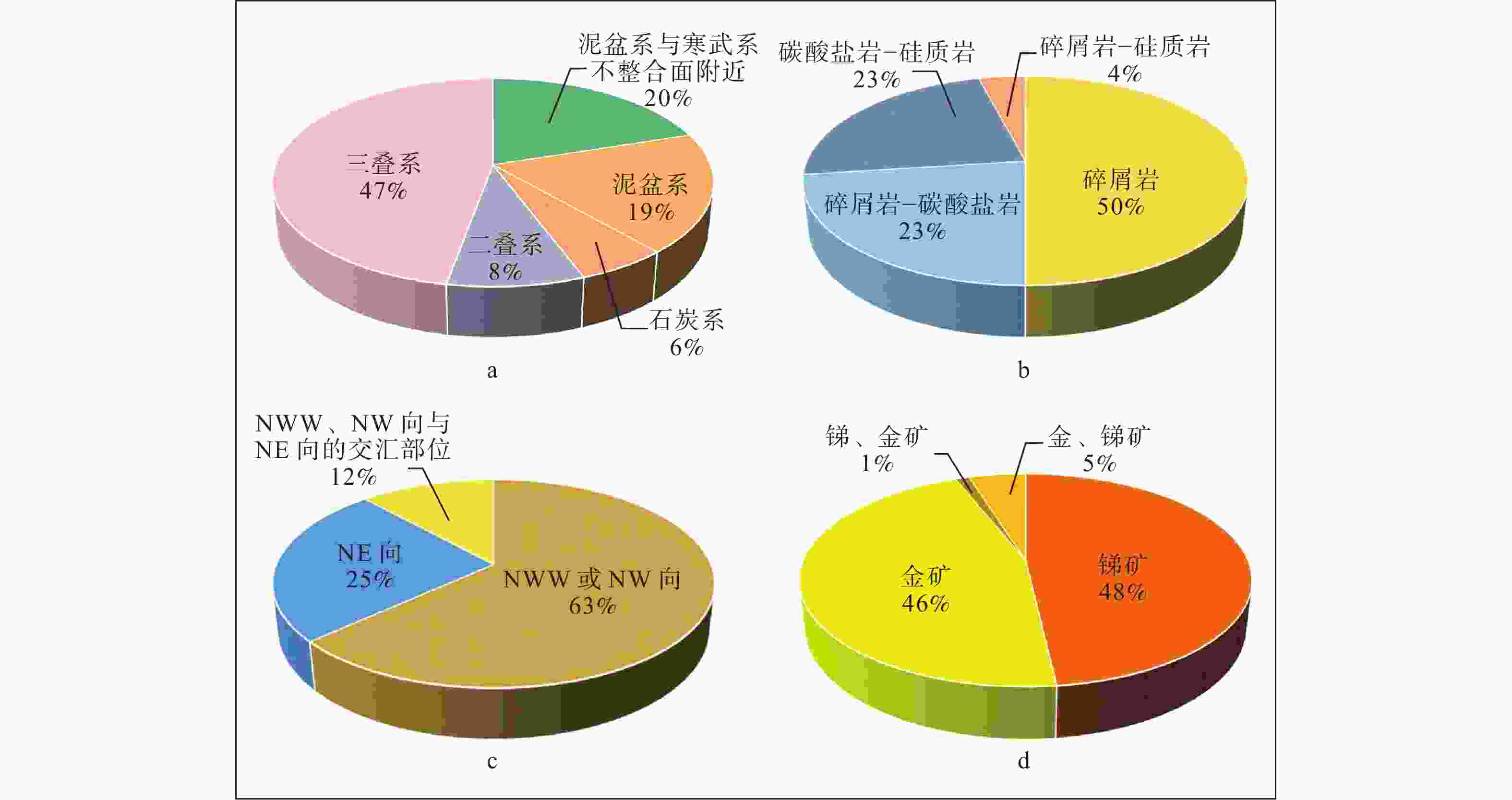
Objective Sb deposits are characterized by simple mineral assemblage. The ore-forming ages, sources of ore-forming materials, and genesis of Sb deposits are controversial owing to the absence of suitable minerals for analysis. Sb resources in the South China Sb metallogenic region account for over 83% of the national total, with the Dian–Qian–Gui Sb belt in the southwest being an significant component of this region. Methods Taking the Longlin–Xilin Sb–Au mining district of western Guixi in the central part of the Dian–Qian–Gui Sb belt as an example, this paper systematically summarizes the ore-bearing strata, lithology of ore-bearing wall rocks, ore-bearing structures, and the coexistence relationship of Au and Sb deposits in 86 ore deposits (points) in the area. Combined with the geological characteristics of three typical deposits (Maxiong, Longtan, and Mahao) and the spatiotemporal distribution of Jurassic felsic intrusions, the inherent connection between Sb mineralization and clastic rocks and felsic intrusions was explored. Results (1) Statistics and field works show that the most favorable ore-bearing stratum in the Longlin–Xilin mining district is the Lower Devonian Yujian Formation (D1y) , followed by the Lower Triassic Luolou Formation (T1Ll) and the Middle Triassic Banna Formation (T2b). The lithologies most conducive to mineralization are carbonaceous shale, pyrite-rich sandstone, and siltstone. The Sb content in these strata or lithologies is tens or even hundreds of times higher than the crustal abundance, which has the potential for Sb mineralization. (2) Within the NWW–SEE trending Nongsang–Shijiazhai fault zone in the Longlin area, the middle and late Jurassic felsic intrusions, which have consistent spatiotemporal occurrences with Sb and Au deposits, can directly contribute to antimony mineralization (as sources of Sb and S) and indirectly influence it (as a heat source), both favoring the formation of antimony deposits. (3) Statistical results show that Sb, Au, and Sb–Au deposits account for 48%, 46%, and 6% in the Longlin–Xilin district, respectively. This suggests that the ore-forming fluids for Sb and Au in the study area may originate from different sources. We also can not rule out the possibility that Sb and Au deposits derive from the same fluid. In the latter case, the precipitation of stibnite consumes H2S in the ore-forming fluid, destabilizing the Au complex in the solution and resulting in localized Au precipitation. This competition between Sb and Au in the fluid for H2S leads to a negative correlation in the grades of Sb and Au in coexisting deposits. (4) The study area experienced NS-striking compression in the Indosinian period, followed by the NW–SE shortening in the middle–late Jurassic. The intersection of NWW–SEE and NE–SW faults is the favorable ore-bearing space. The NWW–SEE faults displayed strike-slip movement in response to the NW–SE shortening, whereas the NE–SW faults exhibited transpression. Consequently, the NE–SW faults are less conducive to Sb mineralization compared to the NWW–SEE faults. The distribution direction of the NWW–SEE Douhuang–Xilin fault aligns with the axial direction of the main folds in the area, with most fault planes trending northward, displaying horizontal scratches, silicification, and extensional characteristics. The intersection of the Dohuang–Xilin fault and the NE–SW fracture exhibits significant Sb anomalies. Conclusion Based on the above studies, the promising areas we propose for Sb prospecting in Longlin–Xilin mining district are (1) Black shale and pyrite-rich siltstones of the Yujiang Formation in the core of the Xinzhou anticline as the key strata; (2) The periphery of the concealed intrusions within the NWW–SEE Nongsang–Shijaizhai fault (Longlin County) and the intersection area of the NWW–SEE Douhuang–Xilin fault and the NE–SW fault as the favorable areas. [ Significance ] The findings provide new insights into the genesis and metallogenic regularities of Sb–Au deposits in the study area, enriching the theoretical understanding of Au mineralization processes. -
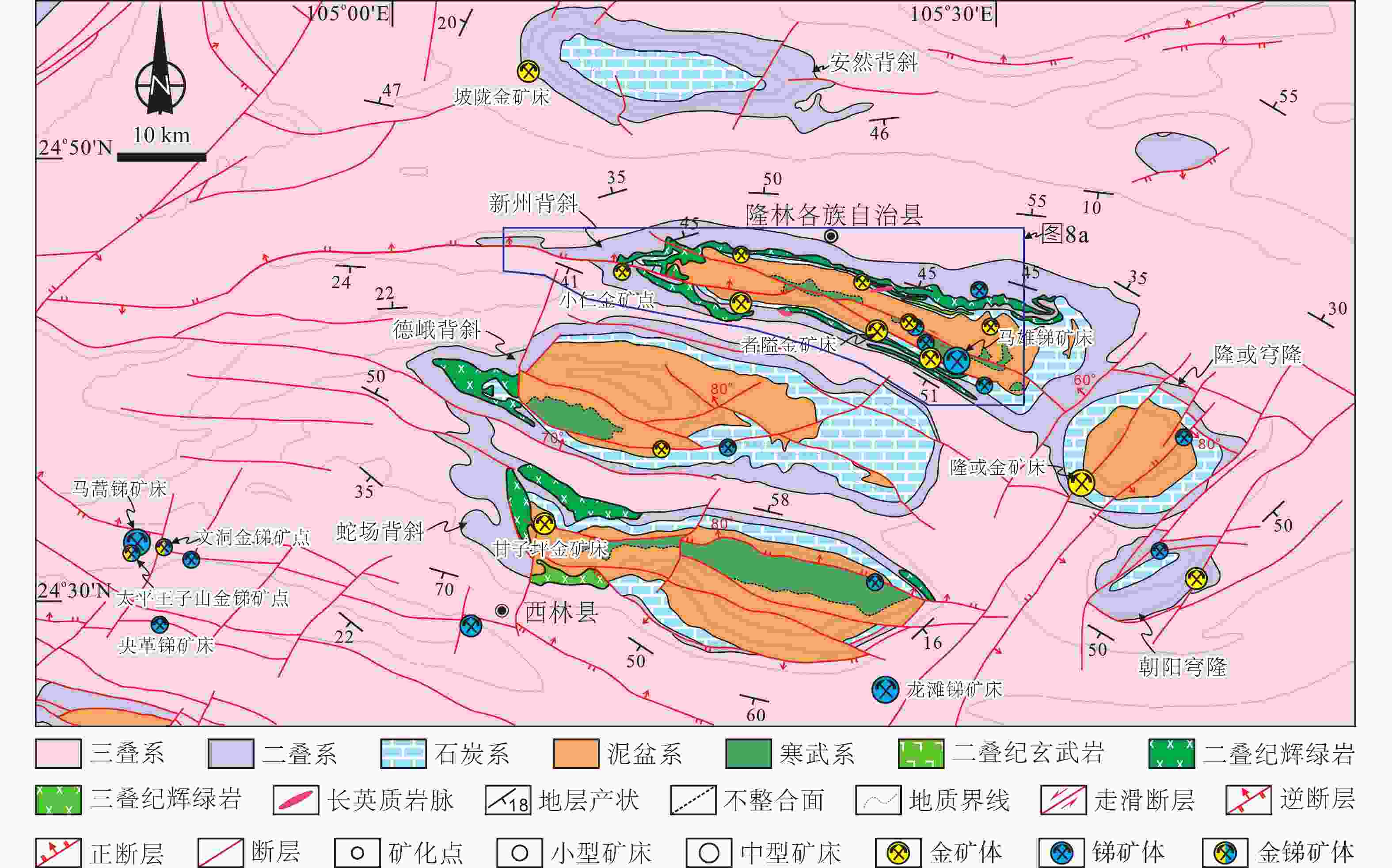
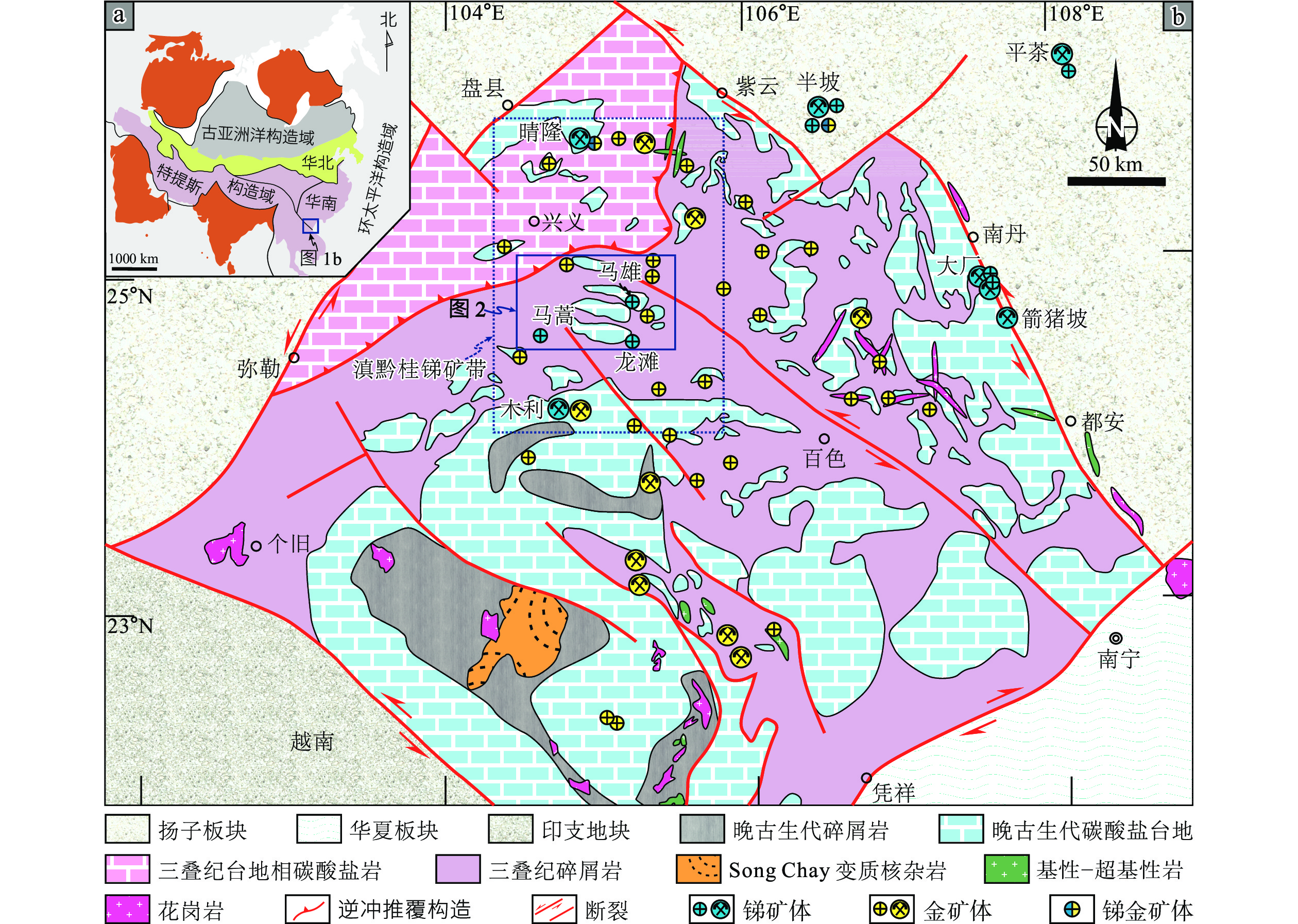
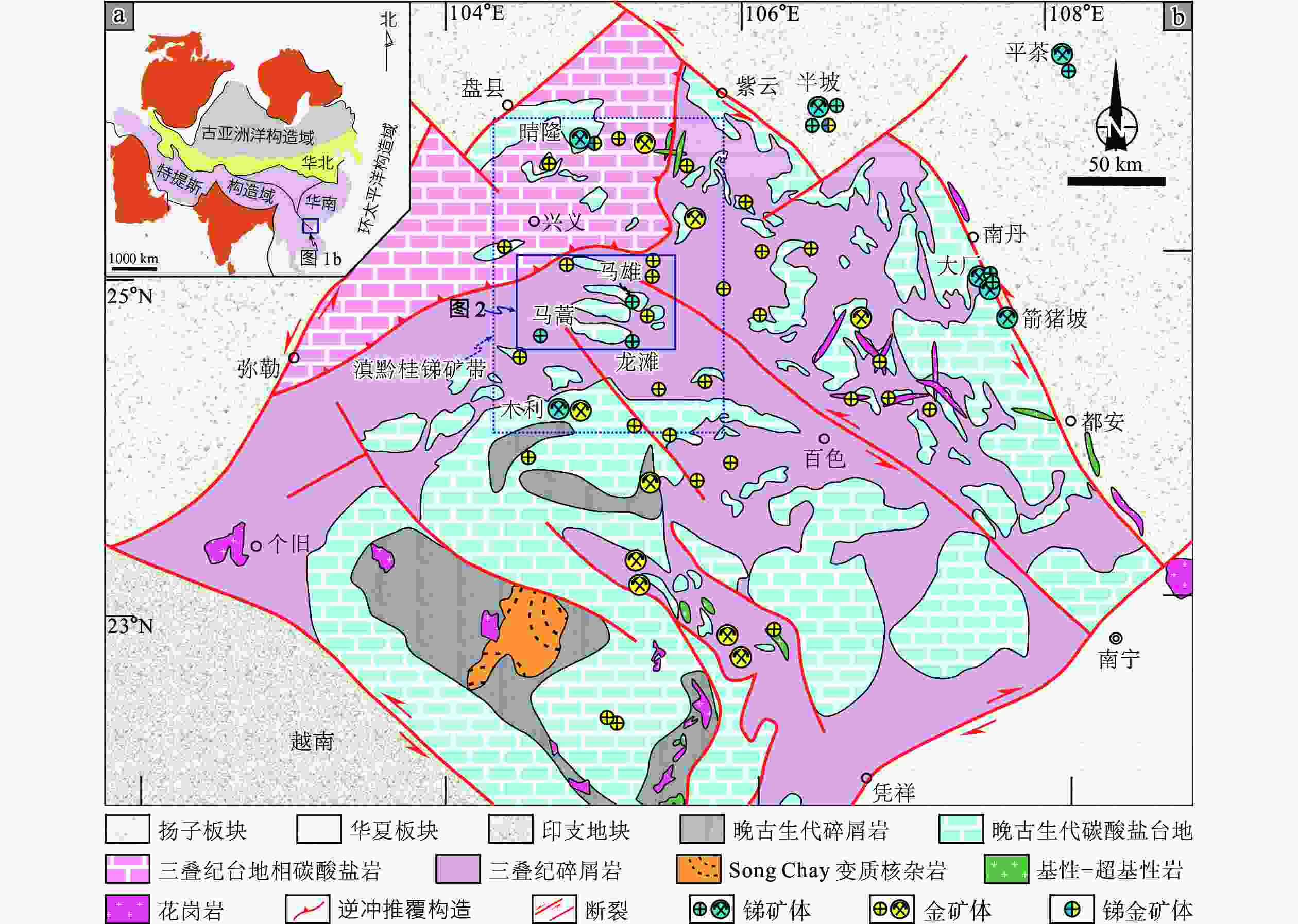
图 1 右江盆地区域地质图
a—研究区大地构造位置图(据胡丽娟等,2023修改);b—右江盆地锑、金矿床分布图(据Xiao et al.,2022修改)
Figure 1. Regional geological map of the Youjiang basin
(a) Tectonic map of Asia showing continental blocks and bounding sutures (modified after Hu et al., 2023); (b) Distribution map of Sb–Au deposits in the Youjiang basin (modified after Xiao et al.,2022)
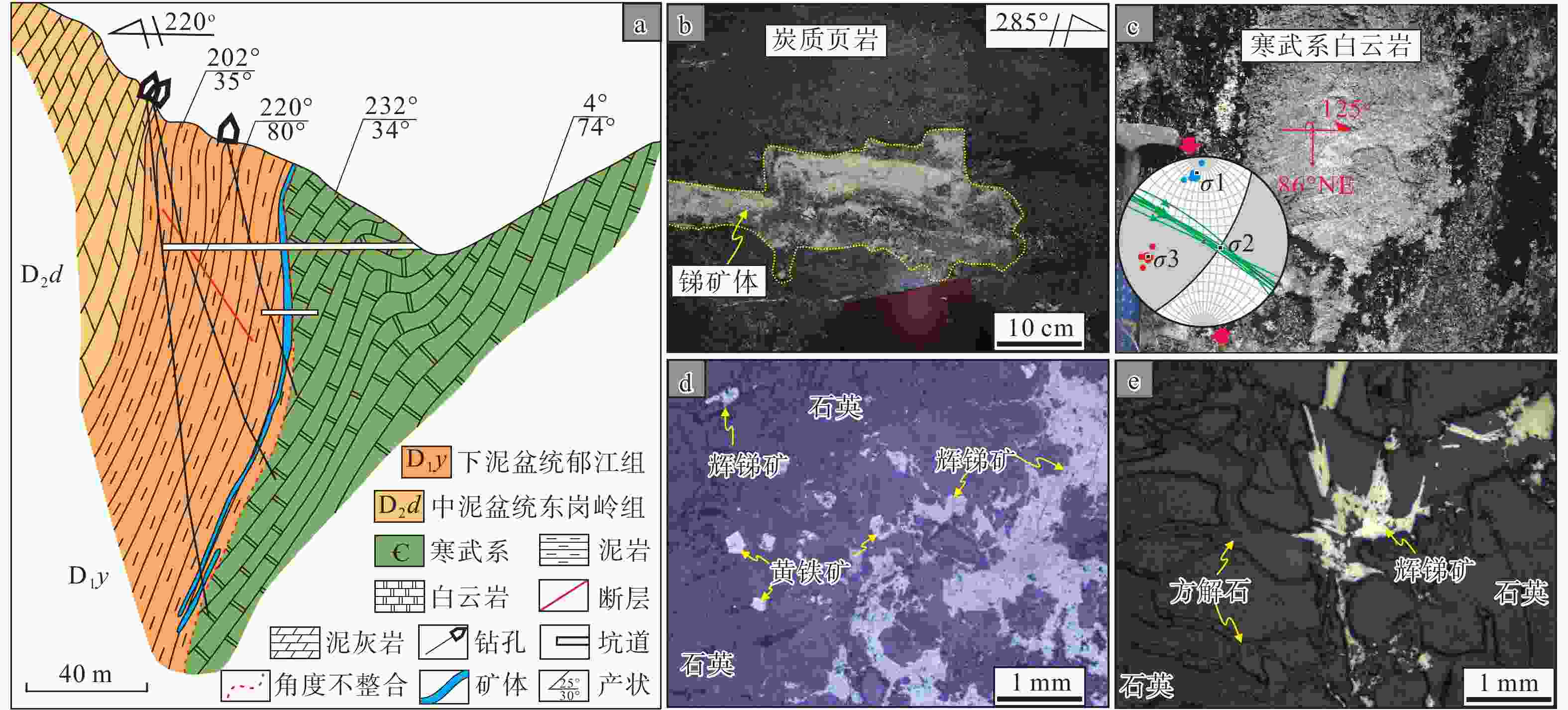
图 3 马雄锑矿床矿体及矿物特征
a—0号勘探线剖面图(据Yan et al.,2022修改);b—主矿体顶部为炭质页岩;c—容矿北西西—南东东向走滑断裂底面水平擦痕产状特征(走滑断裂底面水平擦痕矢量数据反演显示三轴主应力方向σ1为351°/12°、σ2为110°/67°、σ3为256°/20°,指示近南北向挤压应力场);d—脉状矿化的辉锑矿、石英和蚀变围岩中的黄铁矿;e—脉状矿化的辉锑矿、方解石、石英
Figure 3. Ore body and mineral characteristics of the Maxiong antimony deposit
(a) Geological cross-section along the exploration line 0 (modified after Yan et al.,2022); (b) The hanging wall of the main ore body composed of carbonaceous shales; (c) Occurrence characteristics of horizontal scratches on the bottom surface of NWW–SEE strike-slip ore-bearing fault (Inversion of horizontal scratches vector data on the bottom surface of strike-slip fault shows that the triaxial principal stress directions σ1 is 351°/12°, σ2 is 110°/67° and σ3 is 256°/20°, indicating the near NS compressive stress field); (d) Stibnite–quartz vein mineralization and pyrite in altered wall rocks; (e) Stibnite–quartz–calcite vein mineralization
图 4 龙滩锑矿床矿体及矿物特征
a—A12勘探线地质剖面图(据广西壮族自治区二七四地质队,1990修改);b—层状矿体;c—脉状矿体产于北东东—南西西向高角度走滑断裂中(高角度走滑断裂断层面擦痕矢量数据反演显示三轴主应力方向σ1为129°/9°、σ2为28°/53°、σ3为226°/36°,指示北西—南东向挤压应力场);d—方解石−辉锑矿矿石手标本;e—脉状矿化的辉锑矿、方解石
Figure 4. Ore body and mineral characteristics of the Longtan Sb deposit
(a) Geological cross-section along the exploration line A12 (modified after No.274 Team of Guangxi Bureau of Geology, 1990); (b) Stratiform ore body in Luolou Formation sandstones; (c) Vein ore bodies occur in NEE–SWW high angle strike-slip faults (Inversion of the vector data of scratches on the fault plane of high-angle strike-slip fault shows that the triaxial principal stress directions σ1 is 129°/9°, σ2 is 28°/53° and σ3 is 226°/36°, indicating that it was formed in the NW–SE compressive stress field); (d) Calcite–stibnite hand specimen; (e) Stibnite–calcite vein mineralization
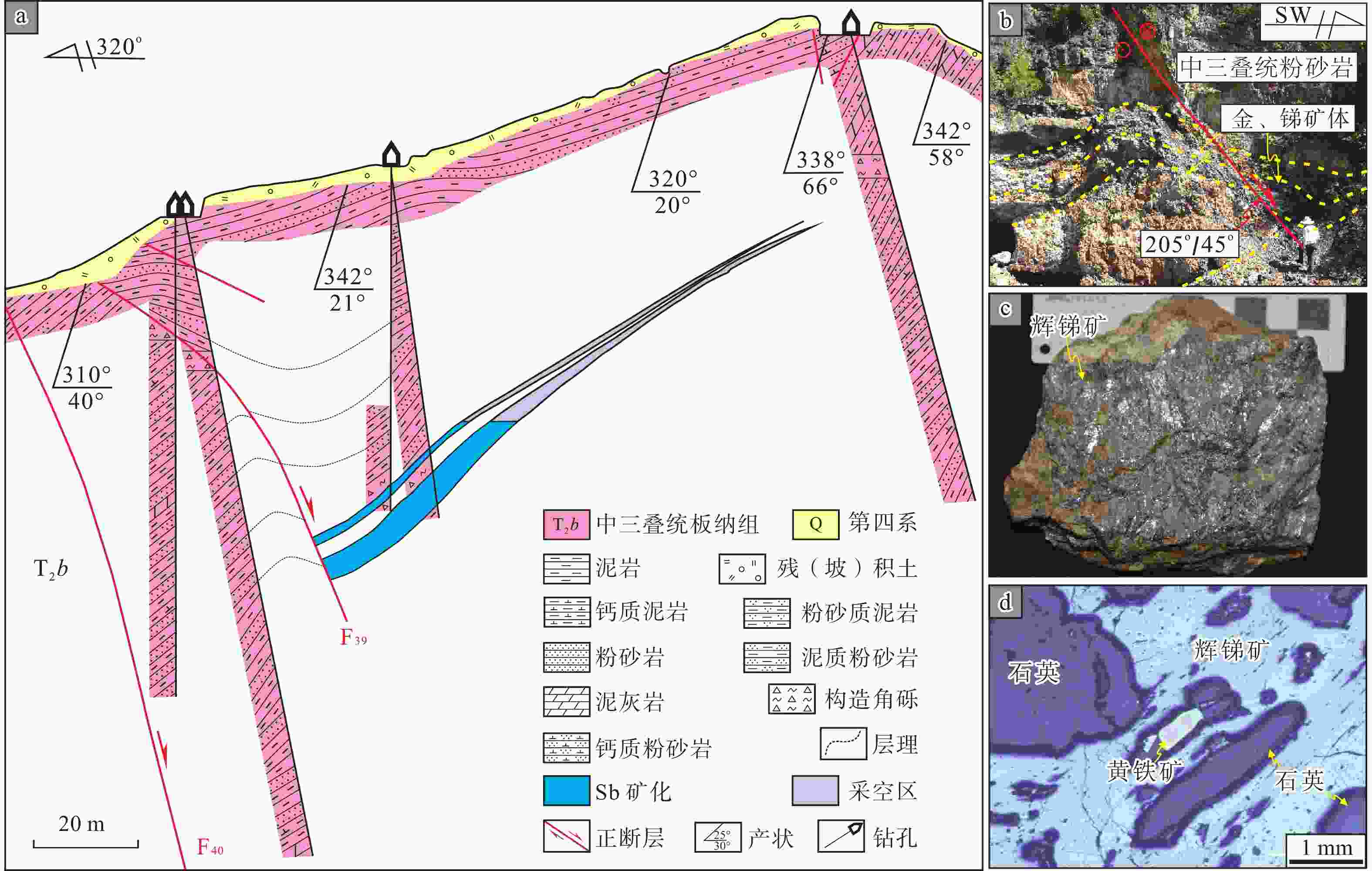
图 5 马蒿锑矿床矿体及矿物特征
a—6号勘探线地质剖面图(据广西金果子矿业有限公司,2011修改);b—马蒿锑矿床文洞矿段容矿断裂具有右行正断特征,金、锑矿体产在断裂下盘牵引褶皱核部虚脱空间;c—辉锑矿矿石手标本;d—辉锑矿−石英脉中石英与辉锑矿、黄铁矿共生
Figure 5. Ore body and mineral characteristics of the Mahao Sb deposit
(a) Geological cross-section along the exploration line 6 (modified after Guangxi Jinguozi Mining Co., Ltd, 2011); (b) The ore-bearing fault in Wendong ore segement of Mahao Sb deposit characterized by right-lateral normal faulting, with the Au (Sb) ore bodies occurring in the core space of traction folds formed by footwall of faults; (c) Stibnite hand specimen; (d) Stibnite coexisting with quartz and pyrite
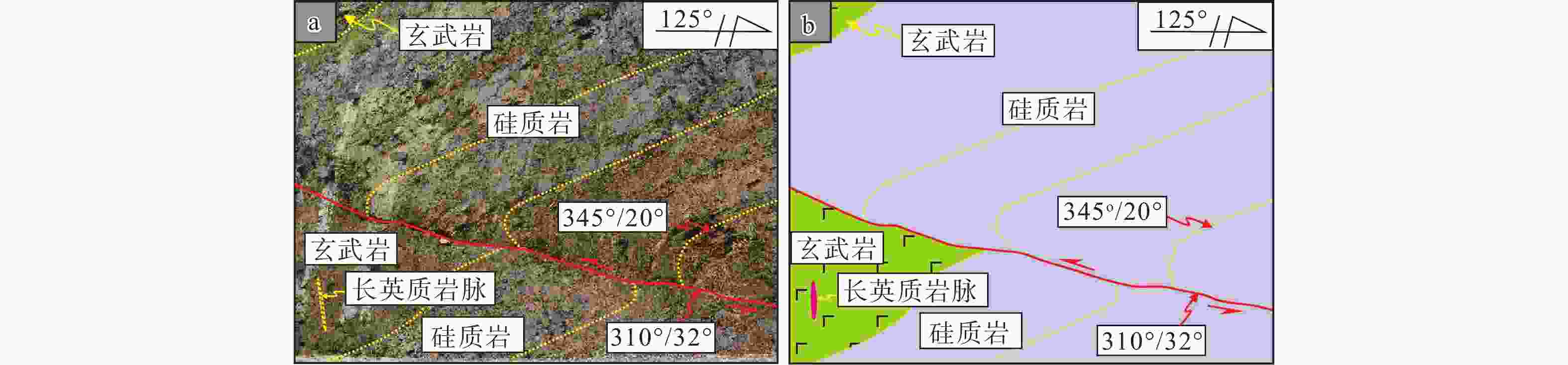
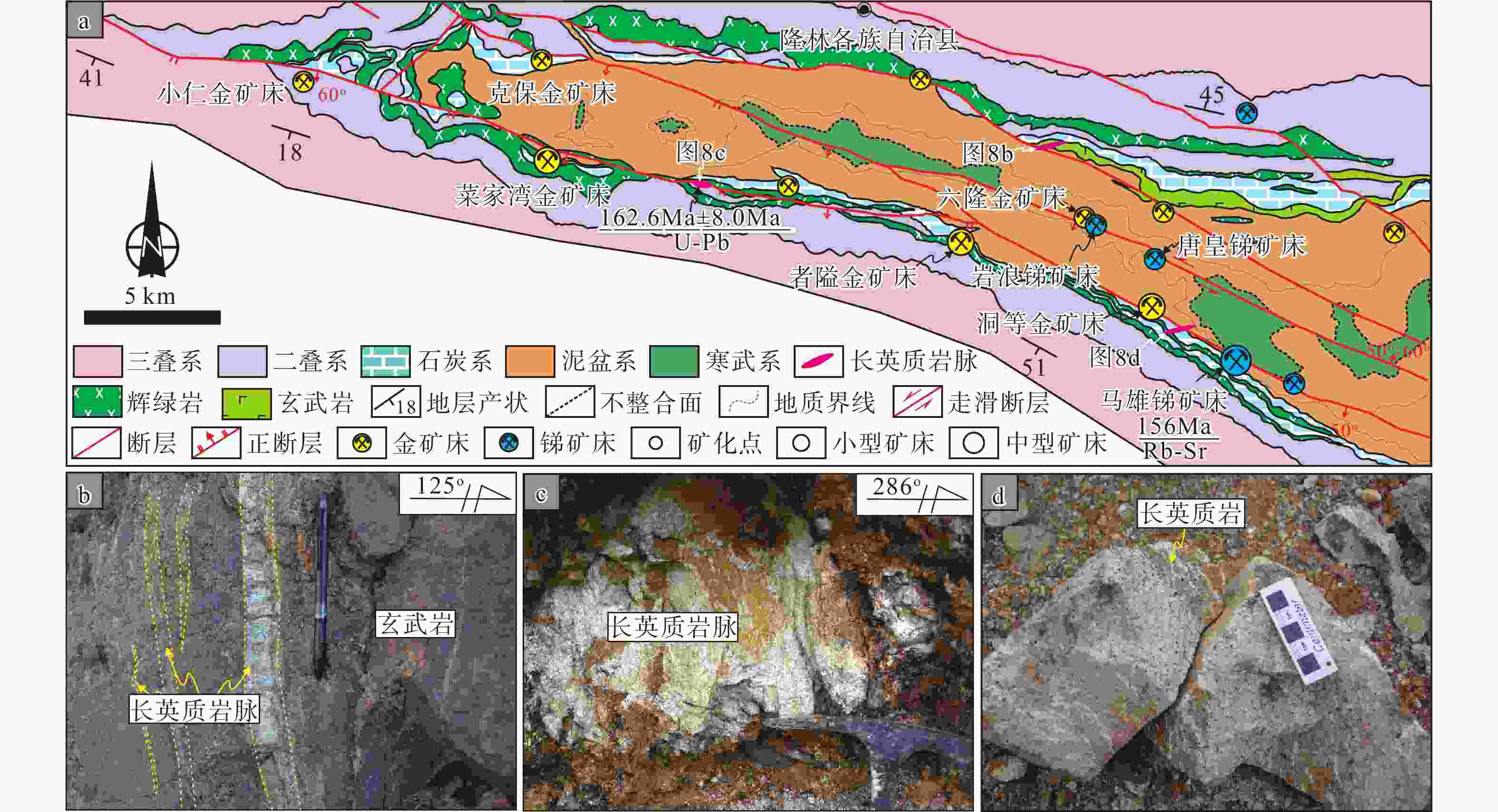
图 8 隆林北西西—南东东向含矿断裂中锑、金矿床及长英质岩脉分布图
a—隆林北西西—南东东向含矿断裂中锑、金矿床及晚侏罗世长英质岩脉分布图;b—大树脚长英质岩脉侵入中二叠世玄武岩;c—弄桑长英质岩脉;d—石家寨长英质岩
Figure 8. Distribution map of antimony deposits, gold deposits, and felsic dikes in NWW–SEE striking faults in Longlin Country
(a) Distribution map of Sb deposit, Au deposits, and Late Jurassic felsic dikes in NWW–SEE ore-bearing faults; (b) Felsic dyke intruded into the Middle Permian basalt at Dashujiao, Longlin Country; (c) Felsic dyke occurred at Nongsang, Longlin Country; (d) Felsic rock occurred at Shijiazhai, Longlin Country
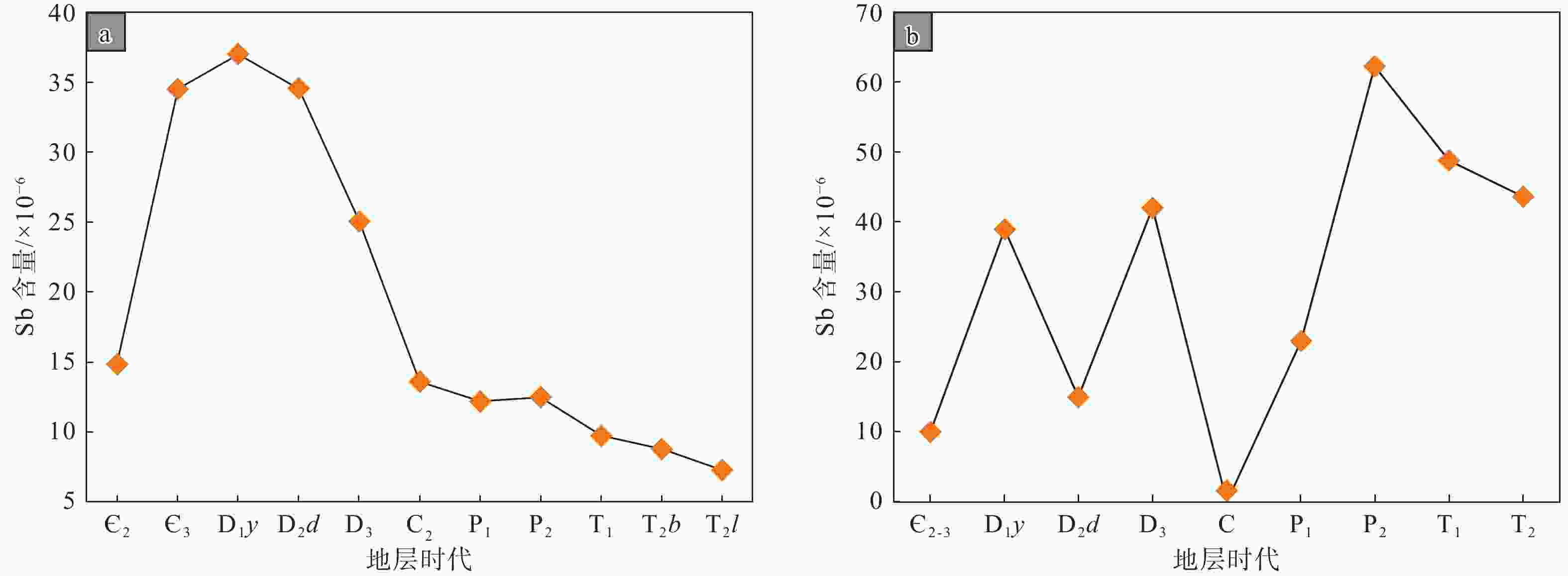
图 9 隆林−西林地区不同时代地层锑丰度
Є2—中寒武统;Є3—上寒武统;D3—上泥盆统;D1y—下泥盆统郁江组;D2d—中泥盆统东岗岭组;C—石炭系;C2—中石炭统;P1—下二叠统;P2—上二叠统;T1—下三叠统;T2—中三叠统;T2b—中三叠统板纳组;T2l—中三叠统兰木组a—隆林地区不同时代地层锑丰度(数据引自杨怀顺,2007);b—三林地区不同时代地层锑丰度(数据引自韦文灼,1993)
Figure 9. Sb abundance in different strata in the Longlin–Xilin area
(a) Sb abundance in stratigraphic units of different ages in the Longlin area (data from Yang, 2007); (b) Sb abundance stratigraphic units of different ages in the Sanlin area (data from Wei, 1993)Є2–the Middle Cambrian; Є3–the Upper Cambrian; D3–the Upper Devonian; D1y–the Yujiang Formation of the Lower Devonian; D2d–the Donggangling Formation of the Middle Devonian; C–the Carboniferous; C2–the Middle Carboniferous; P1–the Lower Permian; P2–the Upper Permian; T1–the Lower Triassic; T2–the Middle Triassic; T2b–the Banna Formation of the Middle Triassic; T2l–the Mulan Formation of the Middle Triassic
表 1 国内外典型锑矿床赋矿围岩岩性
Table 1. Lithology of the surrounding rocks of typical antimony deposits at home and abroad
国家 地区 矿床名称 赋矿围岩主要岩性 参考文献 中国 湖南 锡矿山锑矿床 灰岩、黑色页岩、砂岩 Hu and Peng,2018 贵州 半坡锑矿床 石英砂岩、砂质泥岩、页岩 肖宪国,2014 云南 木利锑矿床 硅质岩、黑色页岩 韩江,2020 西藏 扎西康Sb-Pb-Zn矿床 灰黑色页岩、泥质和钙质页岩 Liang et al.,2018 澳大利亚 Victoria Costerfield Sb-Au矿床 富黄铁矿粉砂岩、炭质页岩 Wilson et al.,2017 New England Orogen Hillgrove锑矿床 页岩、石英砂岩、灰岩 Boyle and Hill,1988 加拿大 New Brunswick The Lake George锑矿床 砂岩、泥岩 Scratch et al.,1984 Newfoundland Beaver Brook锑矿床 黑色页岩、砂岩、砾岩 Lake and Wilton,2006 俄罗斯 The kolyvan-tomsk folded area Semiluzhinskoe Au-Sb矿床 炭质页岩、钙质页岩 Kalinin et al.,2015 美国 California McLaughlin锑矿床 泥岩、粉砂岩、灰岩、砾岩 Sherlock et al.,1995 吉尔吉斯斯坦 — Kadamzhai and Khaidarkan锑矿床 灰岩、灰绿色页岩、黑色页岩 Hnylko et al.,2019 — Atebayue锑矿床 砂岩、粉砂岩 Zhou et al.,2018 西班牙 SAN Antonio, Badajoz Alburquerqu锑矿床 角砾岩、钙质页岩组、硅质层 Gumiel and Vindel,1983 Ciudad Real San Felipe锑矿床 砂质页岩、石英岩 Ciudad Real Nazarena 锑矿床 砂质页岩、石英岩 葡萄牙 Braganca Braganca锑矿床 砾岩、石英岩、黑色板岩 Neiva et al.,2008 Porto Alto do Sobrido锑矿床 黑色泥页岩、砂岩、黑色泥质片岩 Simoes,1997 德国 Rhenish地块北部 Arnsberg锑矿床 富黄铁矿的黑色页岩和硅质灰岩 Wagner and Boyce,2003 表 2 国内外典型锑−金矿床Au-Sb品位
Table 2. Au–Sb ore grade of typical antimony gold deposits at home and abroad
国家 矿床名称 Au品位/×10−6 Sb品位/% 参考文献 中国 湘中沃溪Sb–Au–W矿床 8.1 3.50 陈明辉,2016 湘中龙山Au–Sb矿床 2.51~5.91 1.93~6.63 文琴和刘涛,2019 西藏马扎拉Au–Sb矿床 2~18.6 3.16~41.67 莫儒伟等,2013 西秦岭早子沟Au–Sb矿床 3.34 1.34 耿建珍等,2019 捷克 Krásná Hora Sb–Au矿床 3~5 1.5~3 Němec and Zachariáš,2018 俄罗斯 Sarylakh and Sentachan Au–Sb矿床 8~35 20~30 Bortnikov et al.,2010 俄罗斯 Semiluzhinskoe Au–Sb矿床 2 0.1~21 Kalinin et al.,2015 澳大利亚 Hillgrove Au–Sb 矿床 4~5 3~4 Ashley et al.,2000 -
[1] ASHLEY P M, CREAGH C J, RYAN C G, 2000. Invisible gold in ore and mineral concentrates from the Hillgrove gold-antimony deposits, NSW, Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 35(4): 285-301. doi: 10.1007/s001260050242 [2] BORTNIKOV N S, GAMYNIN G N, VIKENT’EVA O V, et al, 2010. The Sarylakh and Sentachan gold-antimony deposits, Sakha-Yakutia: a case of combined mesothermal gold-quartz and epithermal stibnite ores[J]. Geology of Ore Deposits, 52(5): 339-372. doi: 10.1134/S1075701510050028 [3] BOYLE G O, HILL R L, 1988. The Hillgrove antimony-gold field[J]. New England Orogen Tectonics and Metallogenesis, 235-239. [4] BUCHHOLZ P, OBERTHÜR T, LÜDERS V, et al, 2007. Multistage Au-As-Sb mineralization and crustal-scale fluid evolution in the Kwekwe district, Midlands greenstone belt, Zimbabwe: a combined geochemical, mineralogical, stable isotope, and fluid inclusion study[J]. Economic Geology, 102(3): 347-378. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.102.3.347 [5] CHEN J, HUANG Z L, YANG R D, et al , 2021. Symbiosis and differentiation mechanism of gold and antimony in Nanpanjiang-Youjiang Basin[C]//Proceedings of the first national mineral exploration conference. Hefei: Chinese Geophysical Society: 1067-1071. (in Chinese) [6] CHEN M H, 2016. Pitch of ore bodies and occurrence pattern of the tabular ore body in vein-like W-Tb-Au deposits in western Hunan province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 31(3): 340-345. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] DING J H, ZHANG Y, MA Y B, et al, 2021. Metallogenic characteristics and resource potential of antimony in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 230: 106834. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2021.106834 [8] DU Y S, XU Y J, 2012. A preliminary study on Caledonian event in South China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 31(5): 43-49. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] FU S L, ZAJACZ Z, TSAY A, et al, 2020. Can magma degassing at depth donate the metal budget of large hydrothermal Sb deposits?[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 290: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.08.029 [10] FU S L, HU R Z, PENG J T, et al, 2023. A comprehensive genetic model for the world’s largest Sb deposit (Xikuangshan, China)[J]. GSA Bulletin, 135(3-4): 1074-1088. doi: 10.1130/B36424.1 [11] GAN C S, WANG Y J, BARRY T L, et al, 2020. Late Jurassic high-Mg andesites in the Youjiang Basin and their significance for the southward continuation of the Jiangnan Orogen, South China[J]. Gondwana Research, 77: 260-273. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.06.018 [12] GAN C S, WANG Y J, ZHANG Y Z, et al, 2021. The assembly of the South China and Indochina blocks: constraints from the Triassic felsic volcanics in the Youjiang Basin[J]. GSA Bulletin, 133(9-10): 2097-2112. doi: 10.1130/B35816.1 [13] GAN C S, WANG Y J, ZHANG Y Z, et al, 2022. Petrogenesis of Late Cretaceous granites and implications for W-Sn mineralization in the Youjiang Basin, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 144: 104846. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104846 [14] GENG J Z, HUANG Y Q, JIANG G P, et al, 2019. Zircon U-Pb age and Lu-Hf isotopes of the dacite from Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit, west Qinling, China[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 42(3): 166-173. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] Guangxi Jinguozi Mining Co., Ltd, 2011. Geological Profile of No.6 Exploration Line in Mahao Antimony Deposit [R]. Guangxi: Guangxi Jinguozi Mining Co., Ltd. (in Chinese) [16] Guangxi Institute of Geological Survey, 2019. Report on actually measured and 1: 50000 regional geological survey of Longlin [R]. Guangxi: Guangxi Institute of Geological Survey. (in Chinese) [17] Guangxi Xilin County Hengyuan Mining Development Co., Ltd, 2015. Implementation scheme of gold and antimony exploration in Wendong mining area, Xilin county, Guangxi [R]. Guangxi: Guangxi Xilin County Hengyuan Mining Development Co., Ltd. (in Chinese) [18] Guangxi Xilin County Hengyuan Mining Development Co., Ltd, 2017. Implementation scheme of gold and antimony exploration in Taipingwangzishan mining area, Guzhang Town, Xilin County, Guangxi [R]. Guangxi Xilin County Hengyuan Mining Development Co., Ltd. (in Chinese) [19] GUILLEMETTE N, WILLIAMS-JONES A E, 1993. Genesis of the Sb-W-Au deposits at Ixtahuacan, Guatemala: evidence from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 28(3): 167-180. [20] GUMIEL P, VINDEL E, 1983. Estudio de las mineralizaciones filonianas plomo-antimoníferas de la cobertera en la Sierra de la Demanda. Mina Santa Rufina, Urrez (Burgos)[R]. Madrid: Instituto Geológico y Minero de España. [21] HAGEMANN S G, LÜDERS V, 2003. P-T-X conditions of hydrothermal fluids and precipitation mechanism of stibnite-gold mineralization at the Wiluna lode-gold deposits, western Australia: conventional and infrared microthermometric constraints[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 38(8): 936-952. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0351-6 [22] HAN J, 2020. Discussion on the origin of Muliantin deposit in Guangnan County, Yunnan Province[J]. Gansu Metallurgy, 42(1): 69-71. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] HNYLKO O, TSUKORNYK I, HENERALOVA L, et al, 2019. A Late Carboniferous olistostrome at the front of the southern Tian Shan nappes (Kadamzhai and Khaidarkan deposits, Kyrgyzstan)[J]. Geological Quarterly, 63(2): 407-423. [24] HOU F H, HUANG J X, 1984. Research into the Permian and Triassic volcaniclastic turbidite of Nanpan River Sag: a unique turbidite mode without submarine fan[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2(4): 19-32. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] HU A X, PENG J T, 2018. Fluid inclusions and ore precipitation mechanism in the giant Xikuangshan mesothermal antimony deposit, South China: conventional and infrared microthermometric constraints[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 95: 49-64. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.02.005 [26] HU L J, WU X K, LE X W, et al, 2023. Dating the Deli Pb–Zn deposit, Xidamingshan mining district, South China: implications for regional exploration[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 29(1): 76-86. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] HUANG H, DU Y S, HUANG Z Q, et al, 2013. Depositional chemistry of chert during late Paleozoic from western Guangxi and its implication for the tectonic evolution of the Youjiang Basin[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 56(3): 479-493. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4496-y [28] JIANG W, YAN Q R, DENG L, et al, 2019. Early Jurassic mafic intrusions in the southern Youjiang Basin, SW China: petrogenesis, tectonic and metallogenic implications[J]. Minerals, 9(12): 771. doi: 10.3390/min9120771 [29] KALININ Y A, NAUMOV E A, BORISENKO A S, et al, 2015. Spatial-temporal and genetic relationships between gold and antimony mineralization at gold-sulfide deposits of the Ob-Zaisan folded zone[J]. Geology of Ore Deposits, 57(3): 157-171. doi: 10.1134/S1075701515030022 [30] KETRIS M P, YUDOVICH Y E, 2009. Estimations of Clarkes for Carbonaceous biolithes: world averages for trace element contents in black shales and coals[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 78(2): 135-148. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2009.01.002 [31] KRUPP R E, 1988. Solubility of stibnite in hydrogen sulfide solutions, speciation, and equilibrium constants, from 25 to 350°C[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(12): 3005-3015. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90164-0 [32] LAKE J W L, WILTON D H C, 2006. Structural and stratigraphic controls on mineralization at the Beaver Brook antimony deposit, central Newfoundland[R]. Current Research. Government of Newfoundland and Labrador, Department of Natural Resources, Geological Survey, Report, 6(1): 135-146. [33] LI B L, WANG L Q, ZHANG X G, et al, 2022. Sulfur and lead isotope compositions and their geological significances in the Quzhen Sb mineralization section of the Hamuqu Sb-Au Deposit, Tibet[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 43(2): 202-210. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] LI J H, ZHAO G C, JOHNSTON S T, et al, 2017. Permo-Triassic structural evolution of the Shiwandashan and Youjiang structural belts, South China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 100: 24-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2017.05.004 [35] LI J W, HU R Z, XIAO J F, et al, 2020. Genesis of gold and antimony deposits in the Youjiang metallogenic province, SW China: evidence from in situ oxygen isotopic and trace element compositions of quartz[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 116: 103257. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103257 [36] LI S Z, SUO Y H, ZHOU J, et al, 2022. Tectonic evolution of the South China Ocean-Continent Connection Zone: transition and mechanism of the Tethyan to the Pacific tectonic domains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(5): 683-704. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] LIANG W, HOU Z Q, ZHENG Y C, et al, 2018. The Zhaxikang vein-type Pb-Zn-Ag-Sb deposit in Himalayan Orogen, Tibet: product by overprinting and remobilization processes during post-collisional period[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 92(2): 682-705. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13549 [38] LONG Z Y, QIU K F, SANTOSH M, et al, 2023. Fingerprinting the metal source and cycling of the world’s largest antimony deposit in Xikuangshan, China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 135(1-2): 286-294. doi: 10.1130/B36377.1 [39] MO R W, SUN X M, ZHAI W, et al, 2013. Ore-forming fluid geochemistry and metallogenic mechanism from Mazhala gold-antimony deposit in southern Tibet, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4): 1427-1438. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] NEIVA A M R, ANDRÁŠ P, RAMOS J M F, 2008. Antimony quartz and antimony–gold quartz veins from northern Portugal[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 34(4): 533-546. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.03.004 [41] NĚMEC M, ZACHARIÁŠ J, 2018. The Krásná Hora, Milešov, and Příčovy Sb-Au ore deposits, Bohemian Massif: mineralogy, fluid inclusions, and stable isotope constraints on the deposit formation[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 53(2): 225-244. doi: 10.1007/s00126-017-0734-8 [42] NESBITT B E, MUEHLENBACHS K, MUROWCHICK J B, 1989. Genetic implications of stable isotope characteristics of mesothermal Au deposits and related Sb and Hg deposits in the Canadian Cordillera[J]. Economic Geology, 84(6): 1489-1506. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.84.6.1489 [43] No.274 Geological Team of Guangxi Bureau of Geology, 1990. Geological survey report of Longtan antimony mine area in Longlin county [R]. Guangxi: 274 Team of Guangxi Bureau of Geology. (in Chinese) [44] PENG J T, HU R Z, 2001. Metallogenic Epoch and metallogenic tectonic environment of antimony deposits, South China[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 29(3): 104-108. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] QIAO L, 2016. Tectonic evolution and bauxite metallogenesis in the Youjiang Basin and Adjacent Area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing): 1-165. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] QIU L, YAN D P, YANG W X, et al, 2017. Early to Middle Triassic sedimentary records in the Youjiang Basin, South China: implications for Indosinian orogenesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 141: 125-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.09.020 [47] QIU L, YANG W X, YAN D P, et al, 2019. Geochronology of early Mesozoic diabase units in southwestern China: metallogenic and tectonic implications[J]. Geological Magazine, 156(7): 1141-1156. doi: 10.1017/S0016756818000493 [48] SCRATCH R B, WATSON G P, KERRICH R, et al , 1984. Fracture-controlled antimony-quartz mineralization, Lake George Deposit, New Brunswick; mineralogy, geochemistry, alteration, and hydrothermal regimes[J]. Economic Geology, 79(5), 1159-1186. [49] SHERLOCK R L, TOSDAL R M, LEHRMAN N J, et al, 1995. Origin of the McLaughlin Mine sheeted vein complex: metal zoning, fluid inclusion, and isotopic evidence[J]. Economic Geology, 90(8): 2156-2181. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.8.2156 [50] SIMOES M C, 1997. Mineralogical and geochemical features of metasedimentary rocks associated to Au-Sb vein mineralization in northern Portugal[J]. Comunicaç õ es do Instituto Geológico e Mineiro, 83: 29-46. [51] SOŚNICKA M, DE GRAAF S, MORTEANI, G, et al , 2022. The Schlaining quartz-stibnite deposit, Eastern Alps, Austria: constraints from conventional and infrared microthermometry and isotope and crush-leach analyses of fluid inclusions[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1-17. [52] WAGNER T, BOYCE A J, 2003. Sulphur isotope geochemistry of black shale-hosted antimony mineralization, Arnsberg, northern Rhenish Massif, Germany: implications for late-stage fluid flow during the Variscan orogeny[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 160(2): 299-308. doi: 10.1144/0016-764902-010 [53] WANG G Z, HU R Z, SU W C, et al, 2003. Fluid flow and mineralization of Youjiang Basin in the Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi area, China[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 46(S1): 99-109. doi: 10.1360/03dz9031 [54] WEI W Z, 1993. Geological characteristics of Maxiong antimony deposit[J]. Southwest Mineral Geology, 7(2): 8-16. (in Chinese) [55] WEN Q, LIU T, 2019. Analysis of geological characteristics and genesis of Longshan gold-antimony deposit[J]. World Nonferrous Metals(14): 90-91. (in Chinese with English abstract [56] WILSON C J L, MOORE D H, LUZIN V, et al, 2017. Costerfield antimony-gold deposit, southeast Australia: coupling between brittle deformation and dissolution-precipitation reactions in the Melbourne Zone[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 91: 741-764. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.024 [57] WU Y, ZHANG S, HUANG Z, et al, 2019. Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Nandan-Libo Area, Northwestern Guangxi, China: evidence from Palaeo-tectonic stress fields analyses[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(5): 872-893. (in Chinese with English abstract [58] XIAO C H, LI G J, LIU H, et al, 2016. Characteristics of rare earth and trace elements of stibnite from the Bijiashan antimony deposit, Southwest Yunnan: implications for ore genesis[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(2): 310-324. (in Chinese with English abstract [59] XIAO C H, CHEN Z L, LIU X C, et al, 2022. Structural analysis, mineralogy, and cassiterite U–Pb ages of the Wuxu Sb-Zn-polymetallic district, Danchi Fold-and-Thrust belt, South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 150: 105150. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.105150 [60] XIAO X G, 2014. Geochronology, ore geochemistry and genesis of the Banpo antimony deposit, Guizhou Province, China[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology: 1-138. (in Chinese with English abstract [61] XING L, LI W C, ZHAO X B, et al, 2024. Separation of Au and Sb mineralization in the Qukulekedong intrusion-related deposit, East Kunlun Orogen (NW China): evidence from fluid inclusions, H-O isotopes, and quartz geochemistry[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 164: 105828. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105828 [62] YAN J, FU S L, LIU S, et al, 2022. Giant Sb metallogenic belt in South China: a product of Late Mesozoic flat-slab subduction of paleo-Pacific plate[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 142: 104697. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104697 [63] YANG H S, 2007. Geological characteristics and ore indicators of antimony deposit in northwestern Guangxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 21(1): 52-55. (in Chinese with English abstract [64] YANG J H, CAWOOD P A, DU Y S, et al, 2012. Detrital record of Indosinian mountain building in SW China: provenance of the Middle Triassic turbidites in the Youjiang Basin[J]. Tectonophysics, 574-575: 105-117. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.08.027 [65] ZHANG T Y, LI C Y, SUN S J, et al, 2020. Geochemical characteristics of antimony and genesis of antimony deposits in South China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(1): 44-54. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.06 [66] ZHOU Z J, CHEN Z L, HAN F B, et al, 2018. Fluid inclusion and isotope geochemistry of the Atebayue Sb deposit, South Tianshan Orogen, Kyrgyzstan[J]. Geological Journal, 53(3): 1050-1060. doi: 10.1002/gj.2943 [67] 陈军,黄智龙,杨瑞东,等,2021. 南盘江-右江盆地金、锑共生分异机制[C]//首届全国矿产勘查大会论文集. 合肥:中国地球物理学会:1067-1071. [68] 陈明辉. 2016. 湘西地区脉状钨锑金矿床的矿体侧伏与板柱状赋存规律[J]. 地质找矿论丛,31(3):340-345. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2016.03.004 [69] 杜远生,徐亚军. 2012. 华南加里东运动初探[J]. 地质科技情报,31(5):43-49. [70] 耿建珍,黄雅琪,姜桂鹏,等. 2019. 西秦岭早子沟金锑矿床含矿英安斑岩年代学及其成因[J]. 地质调查与研究,42(3):166-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.03.002 [71] 广西金果子矿业有限公司,2011. 马蒿锑矿床6号勘探线地质剖面图[R]. 广西:广西金果子矿业有限公司. [72] 广西西林县恒源矿业开发有限责任公司,2015. 广西西林县文洞矿区金锑矿勘探实施方案[R]. 广西:广西西林县恒源矿业开发有限责任公司. [73] 广西西林县恒源矿业开发有限责任公司,2017. 广西西林县古障镇太平王子山矿区金锑矿勘探实施方案[R]. 广西:广西西林县恒源矿业开发有限责任公司. [74] 广西壮族自治区地质调查院,2019. 实测及 1∶5 万区域地质调查隆林幅报告[R]. 广西:广西壮族自治区地质调查院. [75] 广西壮族自治区二七四地质队,1990. 隆林县龙滩锑矿区地质普查报告[R]. 广西:广西壮族自治区二七四地质队. [76] 韩江. 2020. 云南省广南县木利锑矿成因及控矿因素探讨[J]. 甘肃冶金,42(1):69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2020.01.021 [77] 侯方浩,黄继祥. 1984. 南盘江断陷区二、三叠系的火山碎屑浊积岩:一种独特的无海底扇浊流沉积模式[J]. 沉积学报,2(4):19-32. [78] 胡利娟,吴祥珂,乐兴文,等. 2023. 广西西大明山矿集区德立铅锌矿床成矿时代及其找矿勘查启示[J]. 地质力学学报,29(1):76-86. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2022034 [79] 李保亮,王立强,张相国,等. 2022. 西藏哈姆曲锑(金)矿床曲珍矿段S、Pb同位素组成及意义[J]. 地球学报,43(2):202-210. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2021.041501 [80] 李三忠,索艳慧,周洁,等. 2022. 华南洋陆过渡带构造演化:特提斯构造域向太平洋构造域的转换过程与机制[J]. 地质力学学报,28(5):683-704. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222809 [81] 莫儒伟,孙晓明,翟伟,等. 2013. 藏南马扎拉金锑矿床成矿流体地球化学和成矿机制[J]. 岩石学报,29(4):1427-1438. [82] 彭建堂,胡瑞忠. 2001. 华南锑矿带的成矿时代和成矿构造环境[J]. 地质地球化学,29(3):104-108. [83] 乔龙,2016. 右江盆地及其周缘地区构造演化及铝土矿成矿作用[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京):1-165. [84] 韦文灼. 1993. 马雄锑矿床地质特征[J]. 西南矿产地质,7(2):8-16. [85] 文琴,刘涛,2019. 龙山金锑矿地质特征及成因浅析[J]. 世界有色金属(14):90-91. [86] 吴玉,张松,黄铮,等. 2019. 桂西北南丹-荔波地区中、新生代构造演化:来自古构造应力场的证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,43(5):872-893. [87] 肖昌浩,李龚健,刘欢,等. 2016. 云南巍山笔架山锑矿床辉锑矿稀土微量元素特征及其矿床成因意义[J]. 地质力学学报,22(2):310-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.02.011 [88] 肖宪国,2014. 贵州半坡锑矿床年代学、地球化学及成因[D]. 昆明:昆明理工大学:1-138. [89] 杨怀顺. 2007. 桂西北地区锑矿地质特征及找矿标志探讨[J]. 矿产与地质,21(1):52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2007.01.012 [90] 张天羽,李聪颖,孙赛军,等. 2020. 锑的地球化学性质与华南锑矿带成因初探[J]. 岩石学报,36(1):44-54. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.06 -




 下载:
下载: