Research on the applicability of electron spin resonance dating of the late Quaternary sinter deposits in the rift valley, southern Tibet
-
摘要:
藏南裂谷区泉华(硅华和钙华)是受区域构造运动控制的水热活动产物,其形成年代对研究该区域水热活动历史有着重要意义。电子自旋共振(ESR)测年法是一种测定泉华年龄的有效测年手段。但存在硅华样品成分复杂,其ESR测年信号具有混合叠加、相互干扰的现象,影响ESR信号的读取;且应用ESR测年法对藏南的钙华样品研究较少,不利于全面掌握藏南水热活动历史等问题。因此对藏南泉华样品ESR测年适用性的研究将有助于指导藏南地区泉华ESR测年的准确性,同时为开展区域构造活动研究提供扎实的年代学基础。该文选取藏南阿里—日喀则地区搭格架热田区的硅华样品和夏康坚温泉区的钙华样品,开展了泉华样品的ESR信号选取和附加剂量影响、钙华ESR信号热稳定性探究,进而得到相对准确的泉华发育年代。研究结果表明:搭格架热田区第三、四级阶地处硅华分别形成于81±16 ka、177±20 ka,夏康坚温泉区河漫滩和第一级阶地处的钙华分别沉积于106±32 ka、264±26 ka。辐照剂量方面,藏南泉华样品在0~7680 Gy范围内对人工附加剂量响应良好;温度方面,硅华受封闭温度影响较小,钙华g=2.0034心信号在20~250 ℃范围具有良好的稳定性,适合ESR测年。矿物结构方面,藏南钙华的矿物纯度、结晶程度较好,ESR年龄结果相对准确。
Abstract:Sinters in the rift valleys of southern Tibet, including silica sinter and travertine deposits, are the products of hydrothermal activity under regional tectonic movement. Their formation age is significant for studying hydrothermal activity history in this region. Electron spin resonance (ESR) dating is a practical dating method for determining the age of silica sinter and travertine deposits. However, silica sinter's ESR signals vary due to the complex composition. Meanwhile, these ESR signals are mixed, superimposed, and interfere with each other, affecting the ESR signal's measurement. Furthermore, ESR dating has been applied less in travertine samples in southern Tibet, which is not conducive to a comprehensive understanding of the hydrothermal activity history in southern Tibet. Studying the applicability of ESR dating of southern Tibetan silica sinter and travertine deposits helps obtain accurate ESR ages. It lays the chronologic foundation for researching tectonic activities in these rift valleys. This research applied ESR dating to the silica sinter and travertine deposits collected separately from the Targejia thermal field area and the Xiakangjian hot spring area, located in the Ngri-Xigaze area in southern Tibet. We performed ESR dating tests, including how to choose ESR signals, the effect of additional doses, and the thermal stability of ESR signals in travertine. Based on these tests, relatively accurate, reliable ESR ages of silica sinter and travertine were obtained. The results show that: According to the ESR dating results, the silica sinter samples collected from the fourth and third terrace of the Targejia geothermal field were formed at 177±20 and 81±16 ka, respectively, and the travertine deposits collected from the floodplain and first terrace of the Xiakangjian hot spring were formed at 106±32 ka and 264±26 ka, respectively. In terms of irradiation dose, sinter samples collected from southern Tibet respond well to irradiation dose in the range of 0~7680 Gy; In terms of temperature, silica sinter samples are less affected by closure temperature, and the thermal behavior of the ESR signal at g=2.0034 of travertine in southern Tibet is stable in the range of 20 ℃~250 ℃ that is suitable for ESR dating. Regarding mineral structure, The travertine in southern Tibet has better mineral purity and crystallinity; thus, the ESR age results are relatively accurate.
-
Key words:
- ESR Dating /
- sinter /
- silica sinter /
- travertine /
- Southern Tibet /
- g-value /
- Quaternary
-
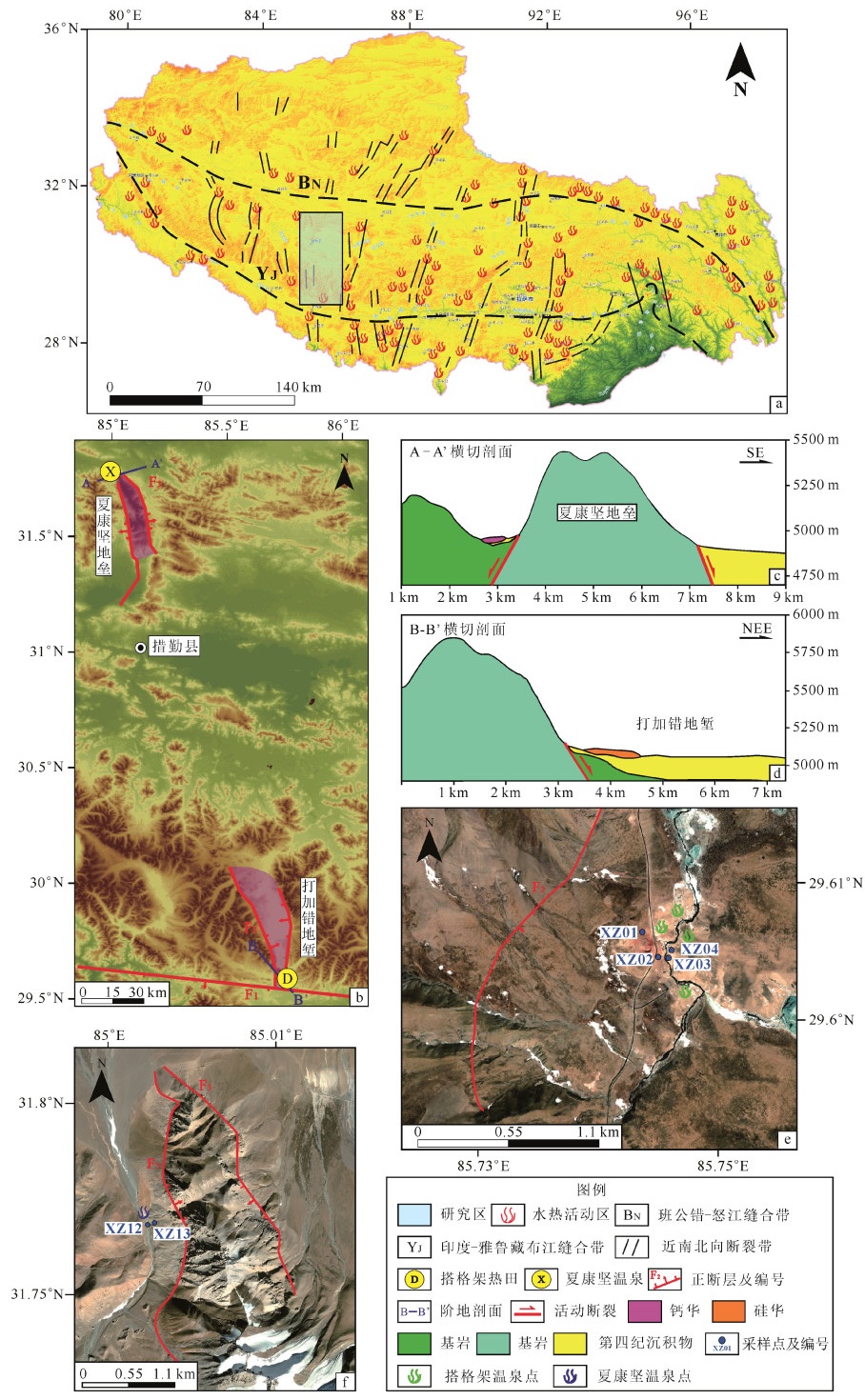
图 1 研究区位置与典型剖面及采样点分布
a—研究区地理位置(据侯增谦等, 2001修改);b—夏康坚地垒和打加错地堑位置;c—夏康坚地垒横切剖面;d—打加错地堑横切剖面;e—搭格架热田区采样点位置;f—夏康坚温泉区采样点位置
Figure 1. Location of the study area and the distribution of the stypical profiles and sampling sites
(a) The location of study area (modified from Hou et al., 2001); (b) The location of the Xiakangjian horst and the Dajiacuo graben; (c) The cross-section of the Xiakangjian horst; (d) The cross-section of the Dajiacuo graben; (e) Sampling sites in the Targejia geothermal field; (f) Sampling sites in the Xiakangjian hot spring
图 2 搭格架、夏康坚泉华分布与采样示意图
a—搭格架热田区河谷阶地剖面与采样点分布(据赵元艺等, 2006修改);b—夏康坚温泉区河谷阶地剖面与采样点分布;c—搭格架热田区部分硅华样品及其镜下照片(Tuf为凝灰岩)
Figure 2. The distribution of silica sinter and travertine deposits in the Targejia and Xiakangjian areas and the sampling sites
(a) The valley terrace profile and sampling sites in the Targejia geothermal field (modified from Zhao et al., 2006); (b) The valley terrace profile and sampling sites in the Xiakangjian hot spring; (c) The travertine samples collected from the Targejia geothermal field and their microscope slices
图 3 代表性泉华样品电子自旋共振(ESR)波谱图
a—硅华样品ESR波谱图;b—钙华样品(XZ12)ESR波谱图;c—钙华样品(XZ13)ESR波谱图
Figure 3. Typical ESR resonance spectra of silica sinter and travertine samples
(a) The ESR spectrum of the silica sinter sample; (b) The ESR spectrum of the travertine sample (XZ12); (c) The ESR spectrum of the travertine sample (XZ13)
图 4 样品在不同辐照条件下的ESR信号强度拟合
a—样品XZ12在不同辐照剂量下的信号强度拟合;b—样品XZ04在不同辐照剂量下的信号强度拟合
Figure 4. ESR signal intensity fitting of samples under different irradiation conditions
(a) The ESR signal intensity fitting of the sample XZ12 under different irradiation conditions; b—The ESR signal intensity fitting of the sample XZ04 under different irradiation conditions
表 1 西藏泉华样品在不同附加剂量下的De值与R2参数
Table 1. The De value and R2 of the samples from the Tibetan travertine deposits in different additional doses
样品名称 De(0~7084 Gy) R2 De(0~3680 Gy) R2 De(0~1961 Gy) R2 XZ01 207±18 >0.99 203±21 >0.99 190±21 >0.99 XZ02 181±30 >0.99 172±49 >0.99 136±55 >0.98 XZ03 44±10 >0.99 42±8 >0.99 37±4 >0.99 XZ04 258±60 >0.99 278±86 >0.98 299±162 >0.96 XZ12 42±10 >0.99 38±11 >0.99 39±11 >0.99 XZ13 105±9 >0.99 103±6 >0.99 90±5 >0.99 表 2 泉华样品ESR测年数据
Table 2. ESR dating results of the silica sinter and travertine samples
样品编号 经纬度 样品类型 U/(ug/g) Th/(ug/g) K/% 等效剂量/Gy 年剂量率/(Gy/ka) ESR年龄/ka XZ01 85.75°E
29.60°N硅华 0.655 3.85 0.549 203±21 1.15±0.05 177±20 XZ02 85.75°E
29.60°N硅华 0.280 0.222 0.096 172±49 0.39±0.03 441±130 XZ03 85.75°E
29.60°N硅华 0.089 0.442 0.267 42±8 0.52±0.03 81±16 XZ04 85.75°E
29.61°N硅华 0.355 2.340 0.424 278±86 0.86±0.04 300±71 XZ12 85.01°E
31.77°N钙华 0.364 0.279 0.039 38±11 0.36±0.03 106±32 XZ13 85.01°E
31.77°N钙华 0.610 0.140 0.018 103±6 0.39±0.03 264±26 -
AITKEN M J, 1985. Thermoluminescence dating[M]. London: Academic Press. BIAN S, YU Z Q, GONG J F, et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal distribution and geodynamic mechanism of the nearly NS-trending rifts in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 178-194. (in Chinese with English abstract) CASS J, KENT R S, MARSHALL S A, et al., 1974. Electron spin resonance absorption spectrum of HCO32- molecule-ions in irradiated single-crystal calcite[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969), 14(2): 170-181. doi: 10.1016/0022-2364(74)90271-6 CHEN Y, GAO J, FENG J, 1993. ESR dating of geyserites from intermittent geyser sites on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 44(1-2): 207-213. doi: 10.1016/0969-8043(93)90221-U CHEN Y J, GAO J C, FENG J J, et al., 1992. A preliminary study on the history of hydrothermal activities occurred in Southern Tibetan[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 19(5): 18-21, 24. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHOI P Y, HWANG J H, BAE H, et al., 2015. Kinematics and ESR Ages for Fault Gouges of the Quaternary Jingwan Fault, Dangjin, western Korea[J]. Journal of the Korean Earth Science Society, 36(1): 1-15. doi: 10.5467/JKESS.2015.36.1.1 DUVAL M, GUILARTE V, 2015. ESR dosimetry of optically bleached quartz grains extracted from Plio-Quaternary sediment: evaluating some key aspects of the ESR signals associated to the Ti-centers[J]. Radiation Measurements, 78: 28-41. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2014.10.002 ENGIN B, GVVEN O, KÖKSAL F, 1999. Thermoluminescence and electron spin resonance properties of some travertines from Turkey[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 51(6): 729-746. doi: 10.1016/S0969-8043(99)00091-3 EULER F K, KAHAN A, 1987. Radiation effects and anelastic loss in germanium-doped quartz[J]. Physical Review B, 35(9): 4351-4359. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.35.4351 GAO L, YIN G M, LIU C R, et al., 2011. ESR dating of fault gouge from the eastern Liupanshan piedmont fault zone[J]. Nuclear Techniques, 34(2): 121-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) GRÜN R, SCHWARCZ H P, FORD D C, et al., 1988. ESR dating of spring deposited travertines[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 7(3-4): 429-432. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(88)90041-8 GRÜN R, 1989. Electron spin resonance (ESR) dating[J]. Quaternary International, 1: 65-109. doi: 10.1016/1040-6182(89)90010-4 GRÜN R, 1991. Potential and problems of ESR dating[J]. International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Part D. Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurements, 18(1-2): 143-153. doi: 10.1016/1359-0189(91)90106-R GRÜN R, 1997. Electron spin resonance dating[M]//TAYLOR R E, AITKEN M J. Chronometric dating in archaeology. New York: Springer: 217-260. HA G H, WU Z H, 2021. Discussion of the seismogenic structure of the 1901 M 6 $ {\scriptstyle{}^{3}\!\!\diagup\!\!{}_{4}\;}$ Nyemo earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 218-229. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN F, XIAO P, LI M Q, et al., 2022. Establishment of the standardized growth curves for ESR dating of fossil teeth[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 42(5): 1401-1409. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE J G, ZHOU Y Z, NIE F J, et al., 2007. Petrologic and geochemical characteristics of the hydrothermal chert in Southern Tibet and its geological significance[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 26(1): 74-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2007.01.011 HENNIG G J, GRÜN R, 1983. ESR dating in quaternary geology[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2(2-3): 157-238. doi: 10.1016/0277-3791(83)90006-9 HOU Z Q, LI Z Q, QU X M, et al., 2001. Uplift processes of the Tibetan Plateau since 0. 5 Ma: evidence from hydrothermal activity in Gangdese belt[J]. Science in China (Series D), 31(S1): 27-33. (in Chinese) HOU Z Q, ZHAO Z D, GAO Y F, et al., 2006. Tearing and dischronal subduction of the Indian Continental Slab: evidence from cenozoic gangdese volcano-magmatic rocks in South Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(4): 761-774. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG P H, PENG Z C, JIN S Z, et al., 1986. Study on the age determination of Quaternary materials by electron spin resonance (ESR)[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 31(6): 453-455. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/csb1986-31-6-453 IKEYA M, 1993. New applications of electron spin resonance: dating, dosimetry and microscopy[M]. Singapore: World Scientific. LAWLESS J L, CHEN R, LO D, et al., 2005. A model for non-monotonic dose dependence of thermoluminescence (TL)[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 17(4): 737-753. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/17/4/016 LI X X, LIU C R, JI H, et al., 2022. Response characteristics of travertine ESR signal to different artificial irradiation dose rates[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 42(5): 1443-1449. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Y W, WEI C Y, LI C A, et al., 2022. Application and evaluation of multiple-centres ESR dating of Pliocene-Quaternary fluvial sediments: a case study from the Zhoulao core from the Jianghan Basin, middle Yangtze River basin, China[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 70: 101297. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2022.101297 LI Z Q, 2002. Present hydrothermal activities during collisional orogenics of the Tibetan Plateau[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Z Q, HOU Z Q, NIE F J, et al., 2005. Characteristic and distribution of the partial melting layers in the upper crust: evidence from active hydrothermal fluid in the South Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(1): 68-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.01.008 LIU C R, YIN G M, GAO L, et al., 2011. Research advances in ESR geochronology of quaternary deposits[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(2): 490-498. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.02.022 LIU X, 1998. ESR dating and its geological significance of travertine in the stone forest, Yunnan province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 17(1): 9-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) MAHMUD H H, MANSOUR A, EZZ-ELDIN F M, 2014. Generation and bleaching of E′-centers induced in a-SiO2 by γ-irradiation[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 302(1): 261-272. doi: 10.1007/s10967-014-3174-2 NIU X S, ZHENG M P, LIU X F, et al., 2017. Sedimentary property and the geological significance of travertines in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science & Technology Review, 35(6): 59-64. (in Chinese with English abstract) PAN G T, MO X X, HOU Z Q, et al., 2006. Spatial-temporal framework of the Gangdese Orogenic Belt and its evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 521-533. (in Chinese with English abstract) PAN Y S, FANG A M, 2010. Formation and evolution of the Tethys in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 45(1): 92-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2010.01.009 PIROUELLE F, BAHAIN J J, FALGUÈRES C, et al., 2007. Study of the effect of a thermal treatment on the DE determination in ESR dating of speleothems[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2(1-4): 386-391. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2006.05.030 PRESCOTT J R, HUTTON J T, 1994. Cosmic ray contributions to dose rates for luminescence and ESR dating: large depths and long-term time variations[J]. Radiation Measurements, 23(2-3): 497-500. doi: 10.1016/1350-4487(94)90086-8 QIU D F, YUN J B, LIU Q Y, et al., 2018. The current research status and prospects of quartz electron spin resonance dating in geology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 53(2): 749-764. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIU S B, WANG F D, DONG D Q, et al., 2022. Sedimentary evolution of the Dawan travertines and their geological environmental significance, Huanglong, China[J]. The Depositional Record, 8(1): 251-265. doi: 10.1002/dep2.165 RINK W J, BARTOLL J, SCHWARCZ H P, et al., 2007. Testing the reliability of ESR dating of optically exposed buried quartz sediments[J]. Radiation Measurements, 42(10): 1618-1626. doi: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2007.09.005 SERWAY R A, MARSHALL S A, 1967. Electron spin resonance absorption spectra of CO3- and CO33- molecule-ions in irradiated single-crystal calcite[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 46(5): 1949-1952. doi: 10.1063/1.1840958 TAO X F, LIU D Z, ZHU L D, et al., 2004. Tectonic landform characteristics and formation mechanism of Xiakangjian Jokul in Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 31(2): 129-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2004.02.004 WANG J H, 1998. Continental hydrothermal sedimentation: a case study of Yunnan Province[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) WANG P, 2013. Study on modern geochemical processes and CO2 source and sink relationship of small watershed of typical hydrothermal area in Southern Tibet collision orogenic belt[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG S L, 1992. Palaeosinters and its significance, Qing-Xizang Plateau[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 19(4): 29-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG X, 2018. The geochemical characteristic and indicating meaning of sinters in the Yangyi geothermal field, Tibet[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) WEN H G, LUO L C, LUO X T, et al., 2019. Advances and prospects of terrestrial thermal spring travertine research[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 37(6): 1162-1180. (in Chinese with English abstract) WIESER A, GÖKSU H Y, REGULLA D F, et al., 1993. ESR and TL dating of travertine from Jordan: complications in paleodose assessment[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 44(1-2): 149-152. doi: 10.1016/0969-8043(93)90210-2 XUAN Y T, ZHAN W H, YAO Y T, et al., 2022. Testing of quartz ESR dating for the marine strata on the northwestern coast of Hainan Island[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 42(3): 123-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.sciengine.com/doi/pdf/D1EAD5A62F7B41368957E65642E6196D YI C L, BI W L, LI J P, 2016. ESR dating of glacial moraine deposits: some insights about the resetting of the germanium (Ge) signal measured in quartz[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 35: 69-76. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2016.06.003 YOU Y X, WEN H G, ZHENG R C, et al., 2019. Advances and prospects of the terrestrial geothermal siliceous sinter research[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 38(1): 68-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG S Q, WU H D, ZHANG Y, et al., 2020. Characteristics of regional and geothermal geology of the Reshuiquan HDR in Guide County, Qinghai Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(5): 1591-1605. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14324 ZHAO W J, KUMAR P, MECHIE J, et al., 2011. Tibetan plate overriding the Asian plate in central and northern Tibet[J]. Nature Geoscience, 4(12): 870-873. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1309 ZHAO Y Y, NIE F J, HOU Z Q, et al., 2006. Geological characteristics and formation age of hot spring cesium deposit in Targejia area, Tibet[J]. Mineral Deposits, 25(3): 281-291. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.03.007 ZHAO Y Y, ZHAO X T, MA Z B, et al., 2010. Chronology of the Gulu hot spring cesium deposit in Nagqu, Tibet and it Geological Significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(2): 211-220. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG M P, WANG Q X, DUO J, et al., 1995. A new type of hydrothermal deposit-cesium-bearing geyserite in Tibet[M]. Beijing: Geology Press. (in Chinese) 卞爽, 于志泉, 龚俊峰, 等, 2021. 青藏高原近南北向裂谷的时空分布特征及动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 178-194. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.018 陈以健, 高钧成, 冯锦江, 等, 1992. 藏南的水热活动历史初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 19(5): 18-21, 24. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.1992.05.009 高璐, 尹功明, 刘春茹, 等, 2011. 六盘山东麓断裂断层泥ESR测年研究[J]. 核技术, 34(2): 121-125. 哈广浩, 吴中海, 2021. 西藏尼木1901年M 6 $ {\scriptstyle{}^{3}\!\!\diagup\!\!{}_{4}\;}$地震的发震构造探讨[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 218-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202202001.htm 韩非, 肖萍, 李梦琪, 等, 2022. 化石电子自旋共振(ESR)测年等效剂量标准生长曲线的构建[J]. 第四纪研究, 42(5): 1401-1409. 何俊国, 周永章, 聂凤军, 等, 2007. 西藏南部热水沉积硅质岩岩石学和地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 26(1): 74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2007.01.011 侯增谦, 李振清, 曲晓明, 等, 2001. 0. 5Ma以来的青藏高原隆升过程: 来自冈底斯带热水活动的证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 31(S1): 27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2001S1004.htm 侯增谦, 赵志丹, 高永丰, 等, 2006. 印度大陆板片前缘撕裂与分段俯冲: 来自冈底斯新生代火山-岩浆作用证据[J]. 岩石学报, 22(4): 761-774. 黄培华, 彭子成, 金嗣炤, 等, 1986. 电子自旋共振法(ESR)测定第四纪物质年龄的研究[J]. 科学通报, 31(6): 453-455. 李新秀, 刘春茹, 姬昊, 等, 2022. 钙华ESR信号对不同人工辐照剂量率的响应特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 42(5): 1443-1449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ202205017.htm 李振清, 2002. 青藏高原碰撞造山过程中的现代热水活动[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院. 李振清, 侯增谦, 聂凤军, 等, 2005. 藏南上地壳低速高导层的性质与分布: 来自热水流体活动的证据[J]. 地质学报, 79(1): 68-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200501007.htm 刘春茹, 尹功明, 高璐, 等, 2011. 第四纪沉积物ESR年代学研究进展[J]. 地震地质, 33(2): 490-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201102027.htm 刘星, 1998. 云南石林地区钙华的ESR测年及其地质意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 17(1): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR801.001.htm 牛新生, 郑绵平, 刘喜方, 等, 2017. 青藏高原钙华沉积属性特征及其地质意义[J]. 科技导报, 35(6): 59-64. 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等, 2006. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 22(3): 521-533. 潘裕生, 方爱民, 2010. 中国青藏高原特提斯的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 45(1): 92-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201001010.htm 邱登峰, 云金表, 刘全有, 等, 2018. 石英电子自旋共振(ESR)的地学研究现状与展望[J]. 地质科学, 53(2): 749-764. 陶晓风, 刘登忠, 朱利东, 等, 2004. 西藏阿里地区夏康坚雪山构造地貌特征及其形成机制[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 31(2): 129-132. 王江海, 1998. 陆相热水沉积作用: 以云南地区为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 王鹏, 2013. 藏南碰撞造山带典型水热区现代地球化学过程与小流域CO2源、汇关系研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学. 王绍令, 1992. 青藏高原古泉华及其意义[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 19(4): 29-31. 王潇, 2018. 西藏羊易地热田泉华地球化学特征及其指示意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院. 文华国, 罗连超, 罗晓彤, 等, 2019. 陆地热泉钙华研究进展与展望[J]. 沉积学报, 37(6): 1162-1180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201906007.htm 禤宇添, 詹文欢, 姚衍桃, 等, 2022. 海南岛西北部更新世海相地层的石英ESR测年探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 42(3): 123-132. 游雅贤, 文华国, 郑荣才, 等, 2019. 陆地热泉硅华研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科技情报, 38(1): 68-81. 张森琦, 吴海东, 张杨, 等, 2020. 青海省贵德县热水泉干热岩体地质-地热地质特征[J]. 地质学报, 94(5): 1591-1605. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202005017.htm 赵元艺, 聂凤军, 侯增谦, 等, 2006. 西藏搭格架热泉型铯矿床地质特征及形成时代[J]. 矿床地质, 25(3): 281-291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200603006.htm 赵元艺, 赵希涛, 马志邦, 等, 2010. 西藏谷露热泉型铯矿床年代学及意义[J]. 地质学报, 84(2): 211-220. 郑绵平, 王秋霞, 多吉, 等, 1995. 水热成矿新类型: 西藏铯硅华矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. -





 下载:
下载: