Estimation of in-situ stress field surrounding the Namcha Barwa region and discussion on the tectonic stability
-
摘要:
南迦巴瓦地区是喜马拉雅东构造结新构造活动最为强烈的区域, 晚第四纪活动断裂发育, 地震活动强烈, 嘉黎断裂带、东久-米林断裂带及墨脱断裂带等活动断裂构造稳定性直接影响该地区工程规划建设。地应力是区域构造稳定性评价的关键性参数, 当前, 关于南迦巴瓦地区地应力场研究成果相对缺乏, 难以满足交通廊道地质安全风险评价实际需求。基于震源机制解数据, 采用应力张量反演方法, 揭示南迦巴瓦地区构造应力场最大主应力方向; 依据断层滑动失稳临界地应力条件, 联合应力形因子和断层摩擦系数反演, 估算南迦巴瓦周边不同区域地应力绝对大小。结果表明: 南迦巴瓦地区现今地应力场最大主应力方向为北东至北北东向; 最大、最小水平主应力大小随深度线性增加梯度分别为0.032~0.0355 MPa/m、0.0227~0.0236 MPa/m, 存在非均匀特征, 估测结果与原位地应力实测值一致性较好; 在当前地应力环境下, 南迦巴瓦周边地区主要活动断裂局部段落存在较大的地震危险性。研究成果可为南迦巴瓦地区工程规划建设提供参考。
Abstract:The Namjag Barwa syntaxis is in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis area with the most intensive neotectonic activity. There are many late Quaternary active fault belts and strong seismicities. The tectonic stability of these active fault belts, such as the Jiali, Dongjiu-Milin, and Motuo fault belts, may influence the project's construction. In-situ stress is a critical parameter for estimating regional tectonic stability. Currently, there is a lack of abundant in-situ stress results about the Namjag Barwa syntaxis. It is challenging to assess geological safety risks for major projects. Based on focal mechanism solutions, the paper reveals the orientation of the maximum principal stress surrounding the Namjag Barwa syntaxis using the stress tensor inversion method. According to the critical condition of fault instability, the magnitudes of principal stresses around the Namjag Barwa syntaxis are also estimated by combining the inversion of the stress shape ratio and the frictional coefficient. The results indicate that the maximum principal stress direction in the Namjag Barwa syntaxis area is NE-NNE. The maximum and minimum horizontal principal stresses increase linearly with depth at a gradient of 0.032~0.0355 MPa/m and 0.0227~0.0236 MPa/m, respectively. Heterogeneous features of the in-situ stress field still exist. Generally, the results estimated in this study are in good concordance with the in-situ stress measurements. They can provide reliable in-situ stress parameters for evaluating the tectonic stability in the Namcha Barwa region.
-
Key words:
- Namcha Barwa /
- in-situ stress /
- focal mechanics solutions /
- tectonic stability
-
图 2 断层滑动失稳力学解析示意图
a—不同走向断裂所处的二维应力状态;b—最优断层摩擦滑动模式;c—断层摩擦滑动应力莫尔圆
σ1—最大主应力;σ3—最小主应力;σn—断层面上正应力;τf—断层面上剪应力;φ—断层内摩擦角;β—断层面外法向与最大主应力方向的夹角Figure 2. Sketch map of mechanical analysis on fault slip instability
(a) Two-dimensional stress state of different fractures; (b) Frictional sliding on an optimally oriented fault; (c) Mohr diagram corresponding to arbitrary sliding fault
σ1-The maximum principal stress; σ3-The minimum principal stress; σn-The normal stress on the fault plane; τf-The shear stress on the fault plane; φ-Internal frictional angel of the fault; β-Angle between the outward normal vector of the fault plane and the direction of σ1图 8 Ⅰ区主应力大小随深度变化特征
σH—最大水平主应力;σv—垂向主应力;σh—最小水平主应力;P0—孔隙水压力;H—深度
Figure 8. Variation characteristics of principal stresses with depth in region Ⅰ
σH-The maximum horizontal principal stress; σv-The vertical principal stress; σh-The minimum horizontal principal stress; P0-The pore pressure; H-The depth
图 9 Ⅱ区主应力大小随深度变化特征
σH—最大水平主应力;σv—垂向主应力;σh—最小水平主应力;P0—孔隙水压力;H—深度
Figure 9. Variation characteristics of principal stresses with depth in region Ⅱ
σH-The maximum horizontal principal stress; σv-The vertical principal stress; σh-The minimum horizontal principal stress; P0-The pore pressure; H-The depth
图 10 Ⅲ区主应力大小随深度变化特征
σH—最大水平主应力;σv—垂向主应力;σh—最小水平主应力;P0—孔隙水压力;H—深度
Figure 10. Variation characteristics of principal stresses with depth in region Ⅲ
σH-The maximum horizontal principal stress; σv-The vertical principal stress; σh-The minimum horizontal principal stress; P0-The pore pressure; H-The depth
图 11 Ⅴ区主应力大小随深度变化特征
σH—最大水平主应力;σv—垂向主应力;σh—最小水平主应力;P0—孔隙水压力;H—深度
Figure 11. Variation characteristics of principal stresses with depth in region Ⅴ
σH-The maximum horizontal principal stress; σv-The vertical principal stress; σh-The minimum horizontal principal stress; P0-The pore pressure; H-The depth
表 1 主应力大小与断层分类
Table 1. Principal stress magnitudes and faulting regimes
断层活动类型 主应力 σ1 σ2 σ3 正断 σv σH σh 逆冲 σH σh σv 走滑 σH σv σh 注:σ1、σ2和σ3分别为最大、中间和最小主应力;σH、σv和σh分别为最大水平、垂向应力和最小水平主应力;σv近似等于上覆岩层的重量(即σv ≈ ρgH,ρ为岩石密度,g为重力加速度,H为岩层厚度) 表 2 南迦巴瓦周边地区主要活动断裂带属性参数
Table 2. Characteristic parameters of the main active fault belts surrounding the Namcha Barwa syntaxis
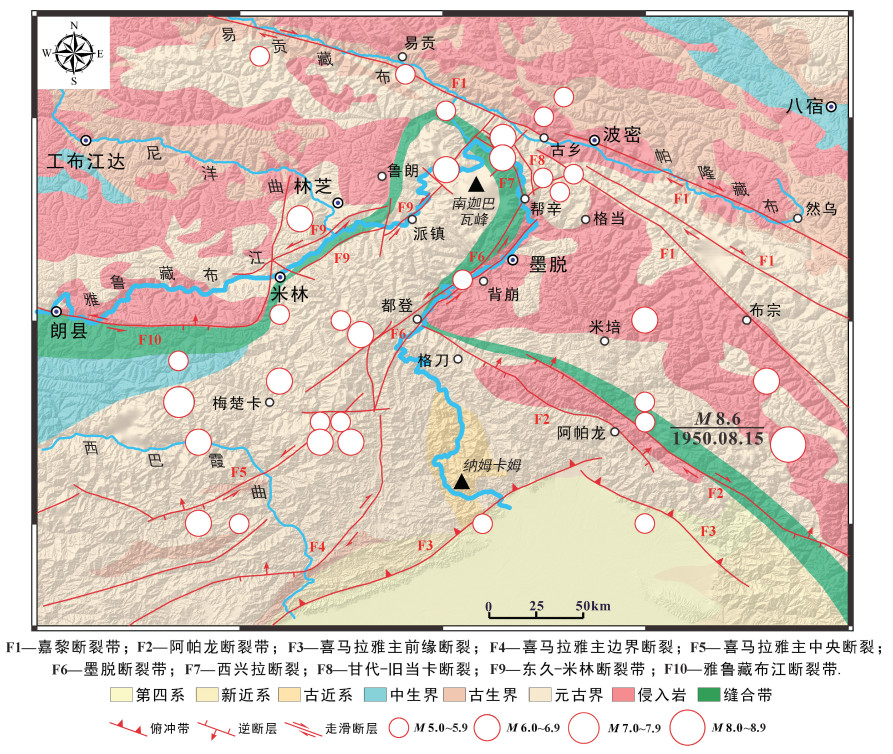
应力分区 断层编码 断层名称 断层参数 走向 倾角 长度/km Ⅰ区 F1-4 嘉黎断裂带 110°±5° 70°±10° 83.08 F7-1 西兴拉断裂带 120°±5° 70°±10° 18.46 F7-2 西兴拉断裂带 120°±5° 70°±10° 20.00 F9-1 东久-米林断裂带 50°±5° 70°±10° 23.08 F9-2 东久-米林断裂带 46°±5° 70°±10° 46.15 F9-3 东久-米林断裂带 40°±5° 70°±10° 26.15 F9-4 未知 138°±5° 70°±10° 21.54 Ⅱ区 F1-1 嘉黎断裂带 112°±5° 60°±10° 56.92 F1-2 嘉黎断裂带 120°±5° 60°±10° 36.92 F1-3 嘉黎断裂带 120°±5° 60°±10° 61.54 F6-9 墨脱断裂带 60°±5° 60°±10° 23.08 Ⅲ区 F2-1 阿帕龙断裂带 120°±5° 45°±10° 53.08 F2-2 阿帕龙断裂带 133°±5° 45°±10° 15.38 F2-3 阿帕龙断裂带 120°±5° 45°±10° 61.54 F6-4 墨脱断裂带 43°±5° 60°±10° 12.31 F6-5 墨脱断裂带 53°±5° 60°±10° 40.00 F6-6 墨脱断裂带 38°±5° 60°±10° 29.23 F6-7 墨脱断裂带 52°±5° 60°±10° 29.23 F6-8 墨脱断裂带 30°±5° 60°±10° 36.92 Ⅴ区 F6-1 墨脱断裂带 50°±5° 65°±10° 68.46 F6-2 墨脱断裂带 18°±5° 65°±10° 33.85 F6-3 墨脱断裂带 40°±5° 65°±10° 21.54 F4-1(北段) 喜马拉雅主边界断裂 10°±5° 65°±10° 10.77 F4-1(中段) 喜马拉雅主边界断裂 350°±5° 65°±10° 10.00 F4-1(南段) 喜马拉雅主边界断裂 355°±5° 65°±10° 16.15 -
BAI L, LI G H, SONG B W, 2017. The source parameters of the M6.9 Mainling, Tibet earthquake and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(12): 4956-4963. (in Chinese with English abstract) BAI L, SONG B W, LI G H, et al., 2019. Seismic activity in the Himalayan Orogenic Belt and its related geohazards[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 34(6): 629-639. (in Chinese with English abstract) BURCHFIEL B C, CHEN Z L, HODGES K V, et al., 1992. The south Tibetan detachment system, Himalayan Orogen: Extension contemporaneous with and parallel to shortening in a collisional mountain belt[M]. Boulder: Geological Society of America: 1-41. CAO J L, SHI Y L, ZHANG H, et al., 2009. Numerical simulation of GPS observed clockwise rotation around the eastern Himalayan syntax in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(8): 1398-1410. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1007/s11434-008-0588-7 CHEN X Q, 2022. Influence of fault fracture zone on initial in-situ stress field in Tongmai tunnel of Sichuan-Tibet traffic corridor[J]. Earth Science, 47(6): 2120-2129. (in Chinese with English abstract) DING L, ZHONG D L, YIN A, et al., 2001. Cenozoic structural and metamorphic evolution of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis (Namche Barwa) [J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letter, 192(3): 423-438. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X01004630 DING L, ZHONG D L, PAN Y S, et al., 1995. Fission track evidence for the Pliocene rapid uplift of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 40(6): 1497-1500. (in Chinese) DONG H W, XU Z Q, CAO H, et al., 2018. Comparison of eastern and western boundary faults of eastern Himalayan Syntaxis, and its tectonic evolution[J]. Earth Science, 43(4): 933-951. (in Chinese with English abstract) ENGLAND P, MOLNAR P, 1997. Active deformation of Asia: from kinematics to dynamics[J]. Science, 278(5338): 647-650. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=434241 FAN Y L, FENG C J, ZHANG P, et al., 2022. Impact of Tohoku-Oki 3.11 M9.0 earthquake on the fault slip potential of the active quaternary faults in Beijing city: new insights from in situ stress monitoring data[J]. Sensors, 22(13): 4888. FENG C J, GAO G L, ZHANG S H, et al., 2022. Fault slip potential induced by fluid injection in the Matouying enhanced geothermal system (EGS) field, Tangshan seismic region, North China[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 22(7): 2257-2287. FENG C J, YANG Y H, MA X D, et al., 2020. Local stress perturbations associated with the 2008 Wenchuan M 8.0 earthquake near the Longmenshan fault zone in the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 200: 104429. FENG X T, JIANG Q, SU G S, 2008. Integrated intelligent stability analysis and dynamic optimization of underground engineering in hard rock with high geostress[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 27(7): 1341-1352. (in Chinese with English abstract) GEPHART J W, FORSYTH D W, 1984. An improved method for determining the regional stress tensor using earthquake focal mechanism data: application to the San Fernando Earthquake Sequence[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 89(B11): 9305-9320. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB11p09305 HAN S, WU Z H, GAO Y, et al. Surface rupture investigation of the 2022 Menyuan Ms 6. 9 earthquake, Qinghai, China: Implications for the fault behavior of the Lenglongling fault and regional intense earthquake risk[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(2): 155-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) HARDEBECK J L, MICHAEL A J, 2006. Damped regional-scale stress inversions: Methodology and examples for southern California and the Coalinga aftershock sequence[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 111(B11): B11310. doi: 10.1029/2005JB004144 HE M C, 2014. The challenges and future of engineering geomechanics[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 22(4): 543-556. (in Chinese with English abstract) HEALY J H, RUBEY W W, GRIGGS D T, et al., 1968. The Denver earthquakes[J]. Science, 161(3848): 1301-1310. https://www.usgs.gov/publications/denver-earthquakes KUMAR S, WESNOUSKY S G, JAYANGONDAPERUMAL R, et al., 2010. Paleoseismological evidence of surface faulting along the northeastern Himalayan front, India: timing, size, and spatial extent of great earthquakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 115(B12): B12422. doi: 10.1029/2009JB006789 LAN H X, ZHANG N, LI L P, et al., 2021. Risk analysis of major engineering geological hazards for Sichuan-Tibet Railway in the phase of feasibility study[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 29(2): 326-341. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI G H, BAI L, DING L, et al., 2020. Source parameters of the 2019 Ms6.3 Medog earthquake and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(3): 1214-1223. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Z Y, WAN Y G, JIN Z T, et al., 2020. The static Coulomb stress influence of the mainling M6.9 earthquake in Tibet on November 18, 2017 to the subsequent earthquakes[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(5): 1091-1108. (in Chinese with English abstract) LU Z, HE C R, 2014. The frictional strength and stability of biotite under hydrothermal conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(4): 1123-1132. (in Chinese with English abstract) LUND B, SLUNGA R, 1999. Stress tensor inversion using detailed microearthquake information and stability constraints: application to Ölfus in southwest Iceland[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 104(B7): 14947-14964. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900111 MARTĺNEZ-GARZÓN P, KWIATEK G, ICKRATH M, et al., 2014. MSATSI: A MATLAB Package for stress inversion combining solid classic methodology, a new simplified user-handling, and a visualization tool[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 85(4): 896-904. MICHAEL A J, 1984. Determination of stress from slip data: faults and folds[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 89(B13): 11517-11526. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB13p11517 NAKATA T, 1989. Active faults of the Himalaya of India and Nepal[M]//MALINCONICO JR L L, LILLIE R J. Tectonics of the western Himalayas. Boulder: Geological Society of America: 243-264. PAN G T, REN F, YIN F G, et al., 2020. Key zones of oceanic plate geology and Sichuan-Tibet railway project[J]. Earth Science, 45(7): 2293-2304. (in Chinese with English abstract) PAN Q, 2021. Measured stress characteristics and route selection strategy of high in-situ stress risk control in Lalin section of Sichuan-Tibet railway[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University. (in Chinese with English abstract) PENG J B, 2006. Some important problems to be addressed in research of active tectonics and environmental disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 14(1): 5-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) PENG X L, WANG D Y, 2013. Tectonic characteristics and the activity of the Yarlung Zangbo River fault zone[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Nat Sci Edit), 10(26): 41-44. (in Chinese) QI S W, LI Y C, SONG S H, et al., 2022. Regionalization of engineering geological stability and distribution of engineering disturbance disasters in Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(3): 599-608. (in Chinese with English abstract) RALEIGH C B, HEALY J H, BREDEHOEFT J D, 1976. An experiment in earthquake control at Rangely, Colorado[J]. Science, 191(4233): 1230-1237. https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/70010885 REN F W, HE C R, 2014. An experimental study of frictional sliding of granitic mylonite under hydrothermal conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(3): 877-883. (in Chinese with English abstract) SAPKOTA S N, BOLLINGER L, KLINGER Y, et al., 2013. Primary surface ruptures of the great Himalayan earthquakes in 1934 and 1255[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(1): 71-76. https://www.nature.com/articles/ngeo1669 SCHELLING D, ARITA K, 1991. Thrust tectonics, crustal shortening, and the structure of the far-eastern Nepal Himalaya[J]. Tectonics, 10(5): 851-862. doi: 10.1029/91TC01011 SHAO C R, 2009. Seismicity of the Yarlung Tsangpo grand canyon region, China[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHI Y L, SUN Y Q, LUO G, et al., 2018. Roadmap for earthquake numerical forecasting in China: reflection on the tenth anniversary of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(19): 1865-1881. (in Chinese with English abstract) SNEE J E L, ZOBACK M D, 2018. State of stress in the Permian Basin, Texas and New Mexico: implications for induced seismicity[J]. The Leading Edge, 37(2): 127-134. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/tle/article-abstract/37/2/127/527282/State-of-stress-in-the-Permian-Basin-Texas-and-New SONG J, TANG F T, DENG Z H, et al., 2011. Study on current movement characteristics and numerical simulation of the main faults around Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(6): 1536-1548. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN X G, JIN X G, LIN Z, et al., 2011. Application of borehole stress relieving method in site stress test at initial location of Galongla tunnel[J]. Technology of Highway and Transport, 8(4): 105-108. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN Y J, GUO C B, WU Z H, et al., 2017. Numerical study of the crustal stress, strain rate and fault activity in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 38(3): 385-392. (in Chinese with English abstract) TANG F T, SONG J, CAO Z Q, et al., 2010. The movement characters of main faults around Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis revealed by the latest GPS data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(9): 2119-2128. (in Chinese with English abstract) TANG F T, YOU H C, LIANG X H, et al., 2019. A Discussion on seismogenic fault of the Milin Ms6.9 earthquake, Tibet, and its tectonic attributes[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 40(1): 213-218. (in Chinese with English abstract) TENG J W, WANG Q S, WANG G J, et al., 2006. Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the 'Himalayas east structural knot'[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(4): 1045-1052. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1002/cjg2.914 TIAN C Y, LAN H X, ZHANG N, et al., 2022. Quantitative prediction of rockburst risk in Sejila Tunel of CZ Railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(3): 621-634. (in Chinese with English abstract) TU J Y, JI J Q, ZHONG D L, et al. The strong activities of the Namula fault zone in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis since Pliocene, constraints from thermochronological data[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(4): 679-690. (in Chinese with English abstract) VAVRYČUK V, 2011. Principal earthquakes: Theory and observations from the 2008 West Bohemia swarm[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 305(3-4): 290-296. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X11001373 VAVRYČUK V, 2014. Iterative joint inversion for stress and fault orientations from focal mechanisms[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 199(1): 69-77. https://academic.oup.com/gji/article/199/1/69/723251 WALSH Ⅲ F R, ZOBACK M D, 2016. Probabilistic assessment of potential fault slip related to injection-induced earthquakes: application to north-central Oklahoma, USA[J]. Geology, 44(12): 991-994. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article-abstract/44/12/991/195082/Probabilistic-assessment-of-potential-fault-slip WAN Y G, 2015. A grid search method for determination of tectonic stress tensor using qualitative and quantitative data of active faults and its application to the Urumqi area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(9): 3144-3156. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG E Q, BURCHFIEL B C, JI J Q, 2001. Estimation of the cenozoic crustal shortening of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis and its geological evidence[J]. Science in China (Series D), 31(1): 1-9. (in Chinese) WANG P, WANG C H, YANG R H, et al., 2019. Preliminary investigation on the deep rock stresses prediction method based on stress polygon and focal mechanism solution[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(11): 4486-4496. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG S J, 2002. Coupling of earth's endogenic and exogenic geological processes and origins on serious geological disasters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 10(2): 115-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG X N, TANG F T, SHAO C R, 2018. The current movement characters of main faults surrounding the Namcha Barwa Syntaxis[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(2): 267-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZZFY201802024.htm WEI W, XIE C, ZHOU B G, et al., 2018. Location of the mainshock and aftershock sequences of the M6.9 Mainling earthquake, Tibet[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(15): 1493-1501. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU C D, ZHU H, DENG Z C, et al., 1990. The structural characteristics of Yarlung zangbo fracture zone[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, (21): 87-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Z H, LONG C X, FAN T Y, et al., 2015. The arc rotational-shear active tectonic system on the southeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau and its dynamic characteristics and mechanism[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(1): 1-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE C, YANG X P, HUANG X N, et al., 2016. Geological evidences of late quaternary activity of Motuo fault in eastern Himalayan Syntaxis[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(4): 1095-1106. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE C, ZHOU B G, LI Z F, 2017. Geomorphic features of eastern Himalayan syntaxis and its tectonic implications[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(2): 276-286. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE F R, CUI X F, ZHAO J T, et al., 2004. Regional division of the recent tectonic stress field in China and adjacent areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(4): 654-662. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG F, SHENG S Z, WAN Y G, et al., 2019. Impact of the stress field in the grid not satisfies the assumption of uniformity on stress field inversion results: the study of stress field in the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis and its surrounding area is an example[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 34(2): 479-488. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG J Y, BAI L, LI G H, et al., 2017. Seismicity in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis and its tectonic implications[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology(6): 12-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) YE J, ZHAO J M, LIU H B, et al., 2020. Aftershocks localization and shallow crustal velocity structure following the Ms6.9 Mainling earthquake in Tibet, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 65(15): 1496-1505. (in Chinese with English abstract) YIN A, 2006. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalayan orogen as constrained by along-strike variation of structural geometry, exhumation history, and foreland sedimentation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(5): 416-515. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825205000565 YIN A, HARRISON T M, 2000. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28: 211-280. YIN F L, HAN L B, JIANG C S, et al., 2018. Interaction between the 2017 M6.9 Mainling earthquake and the 1950 M8.6 Zayu earthquake and their impacts on surrounding major active faults[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(8): 3185-3197. (in Chinese with English abstract) YIN Y P, 2008. Researches on the Geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 16(4): 433-444. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAN H L, BAI L, CHEN Z W, 2023. Source parameters, seismogenic structures of the 1950 Medog-Zayu Ms8.6 earthquake and seismicity in the surrounding areas[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 54(1): 44-55. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG C Y, DU S H, HE M C, et al., 2022. Characteristics of in-situ stresses on the western margin of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis and its influence on stability of tunnel surrounding rock[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 41(5): 954-968. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J J, JI J Q, ZHONG D L, et al., 2003. Discussion on the tectonicframework and forming process of the Namche Barwa terrane, int the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis[J]. Science in China (Series D), 33(4): 373-383. (in Chinese) ZHANG L, LIANG S M, YANG X P, et al., 2020. Landscape evolution of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis based on basin hypsometry and modern crustal deformation[J]. Geomorphology, 355: 107085. ZHANG N, LAN H X, LI L P, et al., 2022. Characteristics and implications of in-situ stresses in southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 30(3): 697-707. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG P, QU Y M, GUO C B, et al., 2017. Analysis of in-situ stress measurement and real-time monitoring results in Nyching of Tibetan Plateau and its response to Nepal Ms8.1 earthquake[J]. Geoscience, 31(5): 900-910. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG P Z, WANG Q, MA Z J, 2002. GPS velocity field and active crustal deformation in and around the Qinghai-Tibet plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 9(2): 442-450. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG W, LI M, JI Y P, et al., 2022. Analysis and enlightenment of typical failure characteristics of tunnels caused by the Menyuan M6.9 earthquake in Qinghai Province[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 44(3): 661-669. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHONG N, GUO C B, HUANG X L, et al., 2021. Late Quaternary activity and paleoseismic records of the middle south section of the Jiali-Chayu fault[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(12): 3642-3659. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU S Y, FENG C J, TAN C X, et al., 2022. Fault slip potential induced by water injection in the Rongcheng deep-seated geothermal reservoir, Xiong'an New Area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 41(S1): 2735-2756. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU S Y, FENG C J, XING L X, et al., 2022. Changes in fault slip potential due to water injection in the Rongcheng deep geothermal reservoir, Xiong'an New Area, North China[J]. Water, 14(3): 410. ZOBACK M D, 2007. Reservoir Geomechanics[M]. New York: Published in the United States of America by Cambridge University Press. ZOBACK M D, HEALY J H, 1992. In situ stress measurements to 3.5 km depth in the Cajon Pass Scientific Research borehole: implications for the mechanics of crustal faulting[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 97(B4): 5039-5057. doi: 10.1029/91JB02175 ZOBACK M L, 1992. First- and second-order patterns of stress in the lithosphere: the World Stress Map Project[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 97(B8): 11703-11728. doi: 10.1029/92JB00132 白玲, 李国辉, 宋博文, 2017. 2017年西藏米林6.9级地震震源参数及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(12): 4956-4963. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201712034.htm 白玲, 宋博文, 李国辉, 等, 2019. 喜马拉雅造山带地震活动及其相关地质灾害[J]. 地球科学进展, 34(6): 629-639. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201906011.htm 曹建玲, 石耀霖, 张怀, 等, 2009. 青藏高原GPS位移绕喜马拉雅东构造结顺时针旋转成因的数值模拟[J]. 科学通报, 54(2): 224-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200902017.htm 陈兴强, 2022. 断层破碎带对川藏交通廊道通麦隧道初始地应力场影响[J]. 地球科学, 47(6): 2120-2129. 丁林, 钟大赉, 潘裕生, 等, 1995. 东喜马拉雅构造结上新世以来快速抬升的裂变径迹证据[J]. 科学通报, 40(16): 1497-1500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199516017.htm 董汉文, 许志琴, 曹汇, 等, 2018. 东喜马拉雅构造结东、西边界断裂对比及其构造演化过程[J]. 地球科学, 43(4): 933-951. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201804002.htm 冯夏庭, 江权, 苏国韶, 2008. 高应力下硬岩地下工程的稳定性智能分析与动态优化[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 27(7): 1341-1352. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200807008.htm 韩帅, 吴中海, 高扬, 等. 2022年1月8日青海门源MS 6.9地震地表破裂考察的初步结果及对冷龙岭断裂活动行为和区域强震危险性的启示[J]. 地质力学学报, 2022, 28(2): 155-168. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2022013 何满潮, 2014. 工程地质力学的挑战与未来[J]. 工程地质学报, 22(4): 543-556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201404004.htm 兰恒星, 张宁, 李郎平, 等, 2021. 川藏铁路可研阶段重大工程地质风险分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 29(2): 326-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202102004.htm 李国辉, 白玲, 丁林, 等, 2020. 2019年西藏墨脱Ms6.3地震震源参数及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(3): 1214-1223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX202003037.htm 李振月, 万永革, 靳志同, 等, 2020. 2017年11月18日西藏米林M6.9地震对后续地震的静态库伦应力的影响[J]. 地震地质, 42(5): 1091-1108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ202005005.htm 路珍, 何昌荣, 2014. 热水条件下黑云母断层泥的摩擦强度与稳定性[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(4): 1123-1132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201404010.htm 潘桂棠, 任飞, 尹福光, 等, 2020. 洋板块地质与川藏铁路工程地质关键区带[J]. 地球科学, 45(7): 2293-2304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202007007.htm 潘前, 2021. 川藏铁路拉林段地应力特征及高地应力风险调控选线策略[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学. 彭建兵, 2006. 中国活动构造与环境灾害研究中的若干重大问题[J]. 工程地质学报, 14(1): 5-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200601001.htm 彭小龙, 王道永, 2013. 雅鲁藏布江断裂带活动构造特征与活动性分析[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 10(26): 41-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201326013.htm 祁生文, 李永超, 宋帅华, 等, 2022. 青藏高原工程地质稳定性分区及工程扰动灾害分布浅析[J]. 工程地质学报, 30(3): 599-608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202203001.htm 任凤文, 何昌荣, 2014. 热水条件下花岗质糜棱岩的摩擦滑动实验研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(3): 877-883. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201403017.htm 邵翠茹, 2009. 雅鲁藏布大峡谷地区地震活动性研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所. 石耀霖, 孙云强, 罗纲, 等, 2018. 关于我国地震数值预报路线图的设想: 汶川地震十周年反思[J]. 科学通报, 63(19): 1865-1881. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201819006.htm 宋键, 唐方头, 邓志辉, 等, 2011. 喜马拉雅东构造结周边地区主要断裂现今运动特征与数值模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(6): 1536-1548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201106014.htm 孙晓光, 靳晓光, 林志, 等, 2011. 嘎隆拉隧道初始地应力钻孔应力解除法在现场测试中的应用[J]. 公路交通技术, (4): 105-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJT201104028.htm 孙玉军, 郭长宝, 吴中海, 等, 2017. 数值模拟探讨青藏高原东部应力应变场及断裂活动性[J]. 地球学报, 38(3): 385-392. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201703008.htm 唐方头, 宋键, 曹忠权, 等, 2010. 最新GPS数据揭示的东构造结周边主要断裂带的运动特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(9): 2119-2128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201009013.htm 唐方头, 尤惠川, 梁小华, 等, 2019. 西藏米林6.9级地震发震断层判定及其构造属性讨论[J]. 地球学报, 40(1): 213-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201901015.htm 滕吉文, 王谦身, 王光杰, 等, 2006. 喜马拉雅"东构造结"地区的特异重力场与深部地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(4): 1045-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200604015.htm 田朝阳, 兰恒星, 张宁, 等, 2022. CZ铁路色季拉山隧道高地应力岩爆风险定量预测研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 30(3): 621-634. 涂继耀, 季建清, 钟大赉, 等. 东构造结那木拉断裂带上新世以来强烈活动的年代学证据[J]. 地质力学学报, 2021, 27(4): 679-690. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.04.056 万永革, 2015. 联合采用定性和定量断层资料的应力张量反演方法及在乌鲁木齐地区的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(9): 3144-3156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201509011.htm 王二七, BURCHFIEL B C, 季建清, 2001. 东喜马拉雅构造结新生代地壳缩短量的估算及其地质依据[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 31(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200101000.htm 王璞, 王成虎, 杨汝华, 等, 2019. 基于应力多边形与震源机制解的深部岩体应力状态预测方法初探[J]. 岩土力学, 40(11): 4486-4496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201911040.htm 王思敬, 2002. 地球内外动力耦合作用与重大地质灾害的成因初探[J]. 工程地质学报, 10(2): 115-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200202000.htm 王晓楠, 唐方头, 邵翠茹, 2018. 南迦巴瓦构造结周边地区主要断裂现今运动特征[J]. 震灾防御技术, 13(2): 267-275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZFY201802024.htm 韦伟, 谢超, 周本刚, 等, 2018. 西藏米林M6.9级地震及其余震序列地震定位[J]. 科学通报, 63(15): 1493-1501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201815011.htm 武长得, 朱红, 邓宗策, 等, 1990. 雅鲁藏布江断裂带的构造特征[J]. 中国地质科学院院报, (21): 87-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB199002008.htm 吴中海, 龙长兴, 范桃园, 等, 2015. 青藏高原东南缘弧形旋扭活动构造体系及其动力学特征与机制[J]. 地质通报, 34(1): 1-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201501002.htm 谢超, 杨晓平, 黄雄南, 等, 2016. 东喜马拉雅构造结墨脱断裂晚第四纪活动地质证据的发现[J]. 地震地质, 38(4): 1095-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201604023.htm 谢超, 周本刚, 李正芳, 2017. 东喜马拉雅构造结地貌形态及其构造指示意义[J]. 地震地质, 39(2): 276-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201702002.htm 谢富仁, 崔效锋, 赵建涛, 等, 2004. 中国大陆及邻区现代构造应力场分区[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(4): 654-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200404016.htm 杨帆, 盛书中, 万永革, 等, 2019. 网格内不满足均匀性假设对应力场反演结果的影响: 以喜马拉雅东构造结及其周边地区应力场研究为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 34(2): 479-488. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201902009.htm 杨建亚, 白玲, 李国辉, 等, 2017. 东喜马拉雅构造结地区地震活动及其构造意义[J]. 国际地震动态(6): 12-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJZT201706004.htm 叶进, 赵俊猛, 刘红兵, 等, 2020. 西藏米林Ms6.9级地震余震定位和地壳浅层速度结构[J]. 科学通报, 65(15): 1496-1505. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB202015010.htm 尹安, 2006. 喜马拉雅造山带新生代构造演化: 沿走向变化的构造几何形态、剥露历史和前陆沉积的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 13(5): 416-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200605016.htm 尹凤玲, 韩立波, 蒋长胜, 等, 2018. 2017年米林6.9级地震与1950年察隅8.6级地震的关系及两次地震对周边活动断层的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(8): 3185-3197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201808008.htm 殷跃平, 2008. 汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 16(4): 433-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200804000.htm 詹慧丽, 白玲, 陈治文, 2023. 1950年西藏墨脱-察隅8.6级地震震源参数、发震构造及周边地震活动性[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 54(1): 44-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXP202301004.htm 张重远, 杜世回, 何满潮, 等, 2022. 喜马拉雅东构造结西缘地应力特征及其对隧道围岩稳定性的影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 41(5): 954-968. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202205008.htm 张进江, 季建清, 钟大赉, 等, 2003. 东喜马拉雅南迦巴瓦构造结的构造格局及形成过程探讨[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(4): 373-383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200304009.htm 张宁, 兰恒星, 李郎平, 等, 2022. 青藏高原东南缘实测地应力特征及意义分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 30(3): 697-707. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202203009.htm 张培震, 王琪, 马宗晋, 2002. 青藏高原现今构造变形特征与GPS速度场[J]. 地学前缘, 9(2): 442-450. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200202035.htm 张鹏, 曲亚明, 郭长宝, 等, 2017. 西藏林芝地应力测量监测与尼泊尔Ms8.1级强震远场响应分析[J]. 现代地质, 31(5): 900-910. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201705003.htm 张威, 李明, 姬云平, 等, 2022. 青海门源M6.9地震典型隧道破坏特征分析与启示[J]. 地震工程学报, 44(3): 661-669. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBDZ202203019.htm 钟宁, 郭长宝, 黄小龙, 等, 2021. 嘉黎-察隅断裂带中南段晚第四纪活动性及其古地震记录[J]. 地质学报, 95(12): 3642-3659. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202112005.htm 朱思雨, 丰成君, 谭成轩, 等, 2022. 雄安容城深热储层回灌注水诱发断层失稳危险性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 41(S1): 2735-2756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2022S1013.htm -





 下载:
下载: