Provenance study of the Xining loess in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China
-
摘要: 碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学被认为是研究沉积物物源的有效手段。然而,应用碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学对中国黄土高原进行物源研究时却获得了非常复杂的物源信息。西宁黄土沉积于青藏高原东北缘地区,对其开展碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学研究不仅可以获得其物源信息,同时可以为探讨青藏高原北缘碎屑物质对黄土高原的贡献提供重要依据。碎屑锆石形貌学研究结果表明其可能经历了强烈的物理风化以及多次再循环,同时也可能暗示了物源的高度复杂性。来自不同沉积层位的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄结果表明,西宁黄土碎屑物质的最终来源可能是青藏高原北缘和中亚造山带,且物源区自约1.3 Ma以来可能没有显著变化,但是两者对西宁黄土的相对贡献可能在不同的时期具有微弱的差异。西宁黄土与中国黄土高原中、西部典型剖面的碎屑锆石年龄分布具有高度相似性,暗示了两者的物源区可能很大程度上具有一致性,但具少量差异。Abstract: Single-grain U-Pb dating of detrital zircons is regarded as an efficient and effective technique to differentiate the contribution of discrete sources. However, its application to the extensive Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP) yields rather complex information in provenance discrimination. The Xining loess was deposited in the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau (NETP), and the detrital zircon U-Pb chronology study can not only obtain provenance information but also provide an important basis to discuss the contribution of the detrital materials from the Northern Tibetan Plateau (NTP) to the CLP. Results of the detrital zircon morphology suggest that zircons may have undergone intense physical weathering and multiple recirculations, and may also indicate the high complexity of the source. Detrital zircon U-Pb age results from different sedimentary layers of the Xining loess reveal there are no obvious temporal variations in the provenance of the Xining loess since ~1.3 Ma and materials may ultimately be eroded from the NTP and the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB), although the relative contribution of detritus from the two sources may slightly vary through time. The U-Pb age spectra of the Xining loess are highly similar to that of typical loess sites in the western-central CLP, suggesting that the provenance areas of the CLP and the Xining loess may be largely consistent, but the possibility of a small difference of provenance cannot be ruled out.
-
Key words:
- Xining /
- detrital zircon /
- U-Pb ages /
- provenance /
- Chinese Loess Plateau /
- Northeastern Tibetan Plateau
-
图 5 碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄直方图及KDE图(n为锆石数目)
a—黑木沟剖面(Pullen et al., 2011);b—灵台剖面(Bird et al., 2015);c—西峰剖面(Che and Li, 2013);d—渭南剖面(Xiao et al., 2012);e—曹岘剖面(Che and Li, 2013);f—西宁黄土
Figure 5. Detrital zircon U-Pb age histograms and KDE diagrams
(a) The Heimugou section (Pullen et al., 2011); (b) The Lingtai section (Bird et al., 2015); (c) The Xifeng section (Che and Li, 2013); (d) The Weinan section (Xiao et al., 2012); (e) The Caoxian section (Che and Li, 2013); (f) The Xining loess
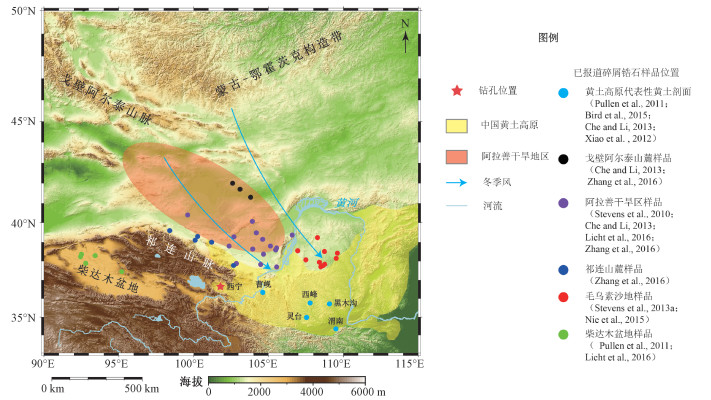
图 6 西宁黄土、黄土高原及潜在物源区沉积物的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄直方图与KDE图(n为锆石数目)
a—西宁黄土样品;b—黑木沟、西峰、灵台、渭南、曹岘5个黄土剖面综合数据;c—祁连山麓沉积物(Zhang et al., 2016);d—柴达木盆地沉积物(Pullen et al., 2011; Licht et al., 2016);e—西毛乌素沙地沉积物(Stevens et al., 2013a; Nie et al., 2015);f—东毛乌素沙地沉积物(Stevens et al., 2010, 2013; Nie et al., 2015);g—阿拉善干旱区(综合的腾格里沙漠、弱水河床沉积物样品数据,引自Stevens et al., 2010; Che and Li, 2013; Licht et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2016);h—戈壁阿尔泰山麓沉积物(Che and Li, 2013; Zhang et al., 2016)
Figure 6. Detrital zircon U-Pb chronology of the Xining loess, the CLP and potential provenances and KDE diagrams
(a) Samples from the Xining loess; (b) Combined data of the five loess sections of the CLP in Figure 4; (c) Sediments from the piedmont of the Qilian mountains (Zhang et al., 2016); (d) Sediments from the Qaidam Basin(Pullen et al., 2011; Licht et al., 2016); (e) Sediments from the western Mu Us desert(Stevens et al., 2013a; Nie et al., 2015); (f) Sediments from the eastern Mu Us desert(Stevens et al., 2010, 2013; Nie et al., 2015); (g) Alxa arid areas (Combined data from the Tengger Desert and the Ruoshui River, after Stevens et al., 2010; Che and Li, 2013; Licht et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2016); (h) Sediments from the piedmont of the Gobi Altay mountains (Che and Li, 2013; Zhang et al., 2016)
表 1 西宁黄土碎屑锆石磨圆度统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of detrital zircon roundness of the Xining loess
棱角状 次棱角状 次圆状 圆状 浑圆状 总数目 DL-1 7.9% 45.3% 31.8% 11.2% 3.7% 267 DL-2 9.0% 27.5% 37.6% 22.0% 3.9% 255 DL-3 5.9% 38.1% 35.9% 14.3% 5.9% 273 DL-4 13.9% 48.7% 24.5% 8.8% 3.3% 271 DL-5 11.4% 38.5% 35.2% 13.6% 1.5% 273 -
ANZ S, 2000. The history and variability of the East Asian paleomonsoon climate[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 19(1-5): 171-187. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00060-8 BIRD A, STEVENS T, RITTNER M, et al., 2015. Quaternary dust source variation across the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 435: 254-264. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.06.024 CHE X D, LI G J, 2013. Binary sources of loess on the Chinese Loess Plateau revealed by U-Pb ages of zircon[J]. Quaternary Research, 80(3): 545-551. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2013.05.007 CHEN J, LI G J, YANG J D, et al., 2007. Nd and Sr isotopic characteristics of Chinese deserts: implications for the provenances of Asian dust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(15): 3904-3914. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.033 CHEN J, LI G J, 2011. Geochemical studies on the source region of Asian dust[J]. Science ChinaEarth Sciences, 54(9): 1279-1301. CHEN Y, FANG X M, SONG C H, et al., 2012. The uplift and erosion of the Tianshan Mountains recorded by detrital zircon geochronology from the Cenozoic sediments in the southern Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(5): 225-233. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHENG Y, LI X Q, ZHAO Z Y, et al., 2018. Detrital zircon U-Pb ages and its provenance significance in the TZK3 core from the Yangtze River delta[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(5): 635-644. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHU H, ZHANG J R, WEI C J, et al., 2013. A new interpretation of the tectonic setting and age of meta-basic volcanics in the Ondor Sum Group, Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(28-29): 3580-3587. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5862-7 FENN K, STEVENS T, BIRD A, et al., 2018. Insights into the provenance of the Chinese Loess Plateau from joint zircon U-Pb and garnet geochemical analysis of last glacial loess[J]. Quaternary Research, 89(3): 645-659. doi: 10.1017/qua.2017.86 GEHRELS G E, YIN A, WANG X F, 2003. Detrital-zircon geochronology of the northeastern Tibetan plateau[J]. GSA Bulletin, 115(7): 881-896. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2003)115<0881:DGOTNT>2.0.CO;2 GENG Y S, WANG X S, SHEN Q H, et al., 2006. Redefinition of the Alxa Group-complex (Precambrian metamorphic basement) in the Alxa area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 33(1): 138-145. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO P, LIU C Y, WANG J Q, et al., 2017. Considerations on the application of detrital-zircon geochronology to sedimentary provenance analysis[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 35(1): 46-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO Z T, LIU T, FEDOROFF N, et al., 1998. Climate extremes in Loess of China coupled with the strength of deep-water formation in the North Atlantic[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 18(3-4): 113-128. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(98)00010-1 HE X Y, FANG T H, BO H T, et al., 2022. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of Late Permian-Middle Triassic granitoids in Guobaoshan, eastern section of the eastern Tianshan mountains: constraints from geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(1): 126-142. JAHN B M, GALLET S, HAN J M, 2001. Geochemistry of the Xining, Xifeng and Jixian sections, Loess Plateau of China: Eolian dust provenance and paleosol evolution during the last 140 ka[J]. Chemical Geology, 178(1-4): 71-94. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00430-7 JI J F, CHEN J, LU H Y, 1999. Origin of illite in the loess from the Luochuan area, Loess Plateau, central China[J]. Clay Minerals, 34(4): 525-532. doi: 10.1180/000985599546398 JIAN P, LIU D Y, KR NER A, et al., 2008. Time scale of an early to mid-Paleozoic orogenic cycle of the long-lived Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia of China: implications for continental growth[J]. Lithos, 101(3-4): 233-259. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.07.005 LI G J, CHEN J, CHEN Y, et al., 2007. Dolomite as a tracer for the source regions of Asian dust[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112(D17): D17201. doi: 10.1029/2007JD008676 LI G J, CHEN J, JI J F, et al., 2009. Natural and anthropogenic sources of East Asian dust[J]. Geology, 37(8): 727-730. doi: 10.1130/G30031A.1 LI G J, PETTKE T, CHEN J, 2011. Increasing Nd isotopic ratio of Asian dust indicates progressive uplift of the north Tibetan Plateau since the middle Miocene[J]. Geology, 39(3): 199-202. doi: 10.1130/G31734.1 LI G J, CHE X D, XIAO G Q, et al., 2013. Zircon ages of Xining loess: implication for the provenance of the loess on Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 33(2): 345-350. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI S Z, YANG Z, ZHAO S J, et al., 2016. Global Early Paleozoic Orogens (Ⅱ): subduction-accretionary-type orogeny[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 46(4): 968-1004. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Z, NIE S R, 1999. Xining loess deposition and its material sources, China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 24(6): 581-584. (in Chinese with English abstract) LICHT A, PULLEN A, KAPP P, et al., 2016. Eolian cannibalism: reworked loess and fluvial sediment as the main sources of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. GSA Bulletin, 128(5-6): 944-956. doi: 10.1130/B31375.1 LIN X, LIU J, WU Z H, et al., 2021. Study on borehole provenance tracing and fluvial sediment diffusion in the Bohai Sea: double constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb age and in-situ geochemical element of apatite grains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 304-316. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU D S, 1985. Loess and the environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-215. (in Chinese) LIU T, DING Z L, 1998. Chinese loess and the paleomonsoon[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 26: 111-145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.26.1.111 LU H Y, WANG X Y, WANG X Y, et al., 2012. Palaeoclimatic changes in northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau revealed by magnetostratigraphy and magnetic susceptibility analysis of thick loess deposits[J]. Natherlands Journal of Geoscience-Geologie en Mijnbouw, 91(1-2): 187-198. MAHER B A, MUTCH T J, CUNNINGHAM D, 2009. Magnetic and geochemical characteristics of Gobi Desert surface sediments: implications for provenance of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geology, 37(3): 279-282. doi: 10.1130/G25293A.1 MAHER B A, PROSPERO J M, MACKIE D, et al., 2010. Global connections between Aeolian dust, climate and ocean biogeochemistry at the present day and at the last glacial maximum[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 99(1-2): 61-97. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2009.12.001 MIAO L C, ZHANG F Q, FAN W M, et al., 2007. Phanerozoic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling orogenic belt in North China: constraints from geochronology of ophiolites and associated formations[M]//ZHAIMG, WINDLEYBF, KUSKYTM, et al. Mesozoic sub-continental lithospheric thinning under eastern Asia. London: Geological Society ofLondon, 280: 233-237. NIE J S, PENG W B, 2014. Automated SEM-EDS heavy mineral analysis reveals no provenance shift between glacial loess and interglacial paleosol on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Aeolian Research, 13: 71-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aeolia.2014.03.005 NIE J S, STEVENS T, RITTNER M, et al., 2015. Loess Plateau storage of Northeastern Tibetan Plateau-derived Yellow River sediment[J]. Nature Communications, 6: 8511. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9511 PULLEN A, KAPP P, MCCALLISTER A T, et al., 2011. Qaidam Basin and northern Tibetan Plateau as dust sources for the Chinese Loess Plateau and paleoclimatic implications[J]. Geology, 39(11): 1031-1034. doi: 10.1130/G32296.1 SONG S G, NIU Y L, SU L, et al., 2013. Tectonics of the North Qilian Orogen, NW China[J]. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1378-1401. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.004 SONG S G, NIU Y L, SU L, et al., 2014. Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continent collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and orogen recycling: the example of the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 129: 59-84. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.11.010 STEVENS T, PALK C, CARTER A, et al., 2010. Assessing the provenance of loess and desert sediments in northern China using U-Pb dating and morphology of detrital zircons[J]. GSA Bulletin, 122(7-8): 1331-1344. doi: 10.1130/B30102.1 STEVENS T, CARTER A, WATSON T P, et al., 2013a. Genetic linkage between the Yellow River, the Mu Us desert and the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 78: 355-368. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.11.032 STEVENS T, ADAMIEC G, BIRD A F, et al., 2013b. An abrupt shift in dust source on the Chinese Loess Plateau revealed through high sampling resolution OSL dating[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 82: 121-132. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.10.014 SU M R, LI Y L, LIU H C, et al., 2020. Paleoproterozoic basement in eastern Central Asia Orogenic Belt: evidence from granite and sedimentary strata in Sino-Mongolia border area[J]. Geology in China, 47(4): 1186-1203. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN J M, DING Z L, XIA X P, et al., 2018. Detrital zircon evidence for the ternary sources of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 155: 21-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.012 SUN Y B, TADA R J, CHEN J C, et al., 2008. Tracing the provenance of fine-grained dust deposited on the central Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(1): L01804. SUN Y B, YAN Y, NIE J S, et al., 2020. Source-to-sink fluctuations of Asian Aeolian deposits since the late Oligocene[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 200: 102963. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102963 TUNG K A, YANG H Y, LIU D Y, et al., 2007a. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of the detrital zircons from the Longshoushan Group and its tectonic significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(10): 1414-1425. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0189-x TUNG K A, YANG H J, YANG H Y, et al., 2007b. SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of the zircons from the Precambrian basement of the Qilian Block and its geological significances[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(10): 2687-2701. VERMEESCH P, 2012. On the visualisation of detrital age distributions[J]. Chemical Geology, 312-313: 190-194. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.04.021 WANG X S, GAO J, KLEMD R, et al., 2014. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Precambrian high-grade metamorphic complex in the Southern Central Tianshan ophiolitic m lange, NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 254: 129-148. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.08.017 WINDLEY B F, ALEXEIEV D, XIAO W J, et al., 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(1): 31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022 WU C L, YANG J S, ROBINSON P T, et al., 2009. Geochemistry, age and tectonic significance of granitic rocks in north Altun, northwest China[J]. Lithos, 113(3-4): 423-436. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2009.05.009 WU C L, CHEN H J, WU D, et al., 2018. Paleozoic granitic magmatism and tectonic evolution of the South Altun block, NW China: constraints from zircon U-Pb dating and Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 160: 168-199. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.04.019 XIA L Q, LI X M, YU J Y, et al., 2016. Mid-Late Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic volcanism and tectonic evolution of the Qilian Mountain[J]. Geology in China, 43(4): 1087-1138. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIAO G Q, ZONG K Q, LI G J, et al., 2012. Spatial and glacial-interglacial variations in provenance of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(20): L20715. XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, HUANG B C, et al., 2009. End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids: implications for the geodynamic evolution, Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6): 1189-1217. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0407-z XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, SUN S, et al., 2015. A tale of amalgamation of Three Permo-Triassic collage systems in central Asia: Oroclines, Sutures, and terminal accretion[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43: 477-507. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105254 XIE J, WU F Y, DING Z L, 2007. Detrital zircon composition of U-Pb ages and Hf isotope of the Hunshandake sandland and implications for its provenance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 523-528. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE J, YANG S L, DING Z L, et al., 2012. Methods and application of using detrital zircons to trace the provenance of loess[J]. Science ChinaEarth Sciences, 55(11): 1837-1846. XIU Q Y, YU H F, LI Q, et al., 2004. Discussion on the petrogenic time of Longshoushan Group, Gansu Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(3): 366-373. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU X W, LI X H, JIANG N, et al. 2015. Basement nature and origin of the Junggar terrane: new zircon U-Pb-Hf isotope evidence from Paleozoic rocks and their enclaves[J]. Gondwana Research, 28(1): 288-310. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.03.011 XU X Y, HE S P, WANG H L, et al. 2008. An Introduction to the geology of Northwest China: Qinling, Qilian and Tianshan regions[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press. YANG H, ZHANG H F, LUO B J, et al., 2015. Early Paleozoic intrusive rocks from the eastern Qilian orogen, NE Tibetan Plateau: Petrogenesis and tectonic significance[J]. Lithos, 224-225: 13-31. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.02.020 YU S Y, ZHANG J X, LI S Z, et al., 2018. Continuity of the North Qilian and North Altun orogenic belts of NW China: evidence from newly discovered Palaeozoic Low-Mg and high-Mg adakitic rocks[J]. Geological Magazine, 155(8): 1684-1704. doi: 10.1017/S0016756817000565 YUAN Y, ZONG K Q, HE Z Y, et al., 2018. Geochemical evidence for Paleozoic crustal growth and tectonic conversion in the Northern Beishan Orogenic Belt, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos, 302-303: 189-202. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.12.026 ZHANG H B, NIE J S, LIU X J, et al., 2021. Spatially variable provenance of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geology, 49(10): 1155-1159. doi: 10.1130/G48867.1 ZHANG H Z, LU H Y, XU X S, et al., 2016. Quantitative estimation of the contribution of dust sources to Chinese loess using detrital zircon U-Pb age patterns[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 121(11): 2058-2099. ZHANG H Z, LU H Y, STEVENS T, et al., 2018. Expansion of dust provenance and aridification of Asia since ~7.2 Ma revealed by detrital zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(24): 13437-13448. ZHANG J X, YU S Y, GONG J H, et al., 2013. The latest Neoarchean-Paleoproterozoic evolution of the Dunhuang block, eastern Tarim craton, northwestern China: evidence from zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic analyses[J]. Precambrian Research, 226: 21-42. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.11.014 ZHANG S, JIAN X, PULLEN A, et al., 2020. Tectono-magmatic events of the Qilian orogenic belt in northern Tibet: new insights from detrital zircon geochronology of river sands[J]. International Geology Review, 63(8): 917-940. ZHANG S H, ZHAO Y, KR NER A, et al., 2009. Early Permian plutons from the northern North China Block: constraints on continental arc evolution and convergent margin magmatism related to the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6): 1441-1467. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0368-2 ZHAO Y, SUN Y, YAN J H, et al., 2015. The Archean-Paleoproterozoic crustal evolution in the Dunhuang region, NW China: constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology and in situ Hf isotopes[J]. Precambrian Research, 271: 83-97. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.10.002 ZHENG R G, WU T R, ZHANG W, et al., 2014. Late Paleozoic subduction system in the northern margin of the Alxa block, Altaids: geochronological and geochemical evidences from ophiolites[J]. Gondwana Research, 25(2): 842-858. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.011 ZUZA A V, WU C, REITH R C, et al., 2017. Tectonic evolution of the Qilian Shan: an early Paleozoic orogen reactivated in the Cenozoic[J]. GSA Bulletin, 130(5-6): 881-925. 陈熠, 方小敏, 宋春晖, 等, 2012. 准噶尔盆地南缘新生代沉积物碎屑锆石记录的天山隆升剥蚀过程[J]. 地学前缘, 19(5): 225-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205023.htm 程瑜, 李向前, 赵增玉, 等, 2018. 长江三角洲地区TZK3孔碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及其物源意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 24(5): 635-644. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.05.064 耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 等, 2006. 内蒙古阿拉善地区前寒武纪变质基底阿拉善群的再厘定[J]. 中国地质, 33(1): 138-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200601014.htm 郭佩, 刘池洋, 王建强, 等, 2017. 碎屑锆石年代学在沉积物源研究中的应用及存在问题[J]. 沉积学报, 35(1): 46-56. 贺昕宇, 方同辉, 薄贺天, 等, 2022. 东天山东段国宝山晚二叠世—中三叠世花岗质岩石成因与构造意义: 年代学和地球化学约束[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(1): 126-142. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.20222807 李高军, 车旭东, 肖国桥, 等, 2013. 西宁黄土碎屑锆石年龄特征及其对黄土高原黄土物源的指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 33(2): 345-350. 李珍, 聂树人, 1999. 西宁黄土沉积及其物质来源[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 24(6): 581-584. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1999.06.006 刘东生, 1985. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 中国海洋出版社. 林旭, 刘静, 吴中海, 等, 2021. 渤海钻孔物源示踪和河流沉积物扩散研究: 碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和磷灰石原位地球化学元素双重约束[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 304-316. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.028 苏茂荣, 李英雷, 刘汇川, 等, 2020. 中亚造山带东段古元古代结晶基底: 来自中蒙边境花岗岩和沉积地层的证据[J]. 中国地质, 47(4): 1186-1203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202004019.htm 夏林圻, 李向民, 余吉远, 等, 2016. 祁连山新元古代中—晚期至早古生代火山作用与构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 43(4): 1087-1138. 谢静, 吴福元, 丁仲礼, 2007. 浑善达克沙地的碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成及其源区意义[J]. 岩石学报, 23(2): 523-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702029.htm 修群业, 于海峰, 李铨, 等, 2004. 龙首山岩群成岩时代探讨[J]. 地质学报, 78(3): 366-373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200403009.htm 徐学义, 何世平, 王洪亮, 等, 2008. 中国西北部地质概论: 秦岭、祁连、天山地区[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. -





 下载:
下载: