Quaternary activity characteristics of the Qionghua–Liantang fault belt in Hainan
-
摘要: 位于琼北福山凹陷与海口隆起边界的琼华−莲塘断裂带,是调节北东向北部湾陆内裂谷不均匀伸展的结果,该断裂带穿过海口市长流新区与环岛高铁重大工程,对海南自贸区规划建设具有直接影响。文章采用构造地貌调查、地球物理探测与钻孔联合剖面等方法,揭露琼华–莲塘断裂带由五源河–道心村断裂、永庄水库断裂及海口砖瓦厂断裂共3条北西向平行展布的高角度活动断裂组成,呈隐伏或半隐伏状态,总体表现为正断层性质。断裂带宽约1.8 km,长度约17 km,第四纪以来断裂垂直位移为8.7~41.6 m,均属于较强活动断裂。3条断裂最新活动时代均为晚更新世,垂直位移速率<0.1 mm/a,其中以海口砖瓦厂断裂错动速率最大。结合琼华–莲塘断裂带的形成构造背景、最新活动时代,及其与第四纪火山活动的关系,文章提出了海南自贸区规划建设及工程避让活动断裂的建议。Abstract: The Qionghua–Liantang fault belt, located at the boundary between the Fushan depression and the Haikou uplift, is the result of the impact of the uneven extension of the NE-trending Beibu Gulf rift. The Qionghua–Liantang fault belt passes through the Changliu New District and the major projects of the island-looping high-speed railway in Haikou, directly impacting the planning and construction of the Hainan Free Trade Zone. The article uses tectonic geomorphic survey, geophysical exploration, and drilling exploration to reveal that the Qionghua–Liantang fault consists of three NW-trending buried and semi-buried normal faults, which are the Wuyuanhe–Daoxincun fault (F1-1), the Yongzhuangshuiku fault (F1-2), and the Haikouzhuanwachang fault (F1-3). The width of the Qionghua–Liantang fault belt is about 1.8 km, and the length is about 17 km. The vertical displacement of the fault belt is 8.7~41.6 m since the Quaternary. The latest active age of these three faults is the late Pleistocene; the vertical activity rate was less than 0.1 mm/a. It is worth noting that the vertical activity rate of the Haikouzhuanwachang fault (F1-3) is higher than the other two faults and has more vigorous activity. Combining the tectonic background, the latest active age of the Qionghua–Liantang fault, and its relationship with Quaternary volcanic activity, this paper puts forward suggestions on the planning and construction of the Hainan Free Trade Zone and building avoidance of active fault.
-
Key words:
- Qionghua–Liantang fault belt /
- fault activity /
- avoidance of active fault /
- Hainan /
- Quaternary period
-
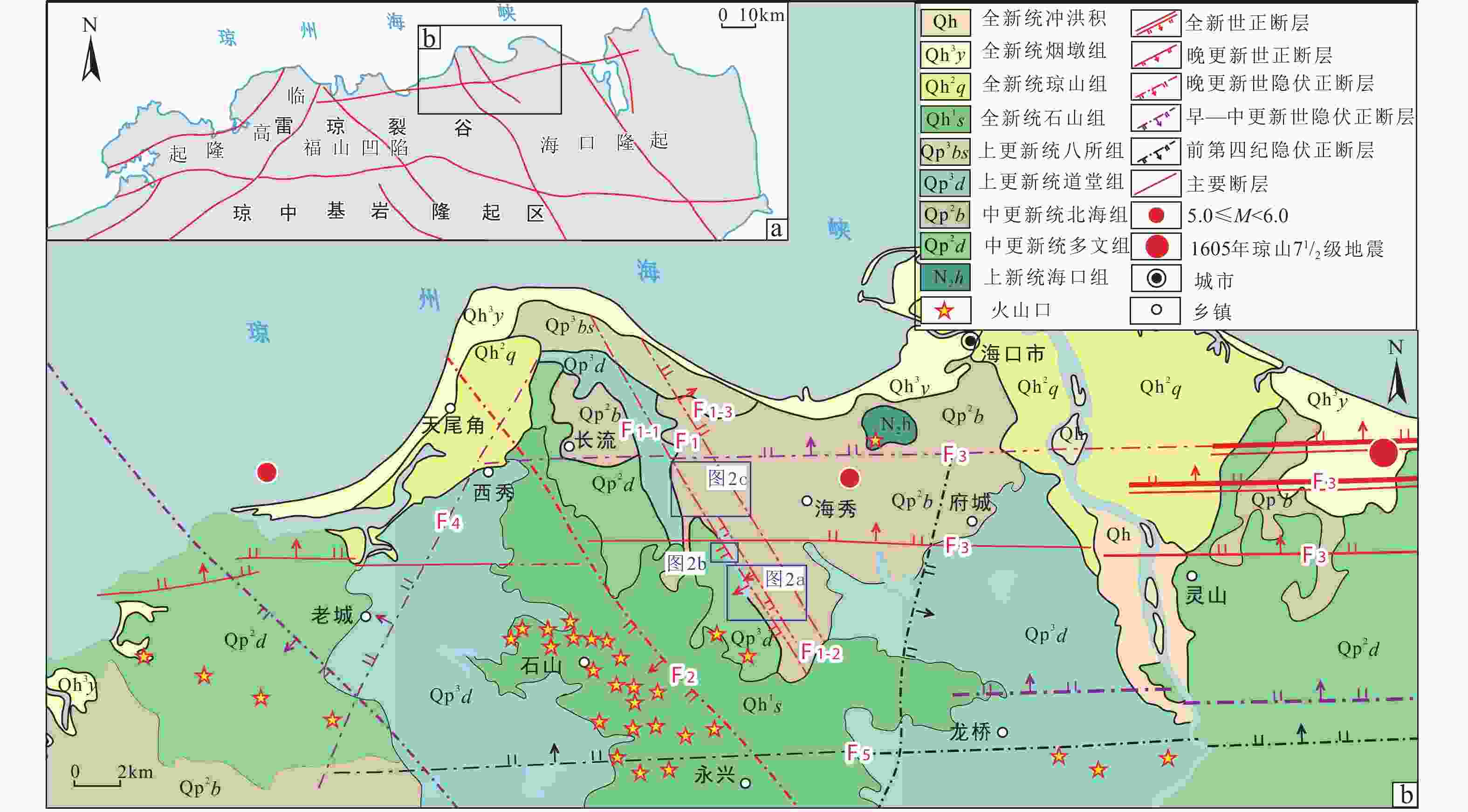
图 1 琼北地区活动断裂分布图
F1—琼华–莲塘断裂带,F1-1—五源河−道心村断裂,F1-2—永庄水库断裂,F1-3—海口砖瓦厂断裂,F2—长流−仙沟断裂带,F3—马袅–铺前断裂带,F4—老城−西秀断裂带,F5—儒关村−云龙断裂带a—琼北地区构造纲要图;b—琼北地区主要活动断裂分布图
Figure 1. Map of active faults in northern Hainan
(a) Sketch map of northern Hainan; (b) Map of main active faults in northern Hainan F1–Qionghua–Liantang fault belt; F1-1–Wuyuanhe–Daoxincun fault; F1-2–Yongzhuangshuiku fault; F1-3–Haikouzhuanwachang fault; F2–Changliu–Xiangou fault belt; F3–Maniao–Puqian fault belt; F4–Laocheng–Xixiu fault belt; F5–Ruguancun–Yunlong fault belt
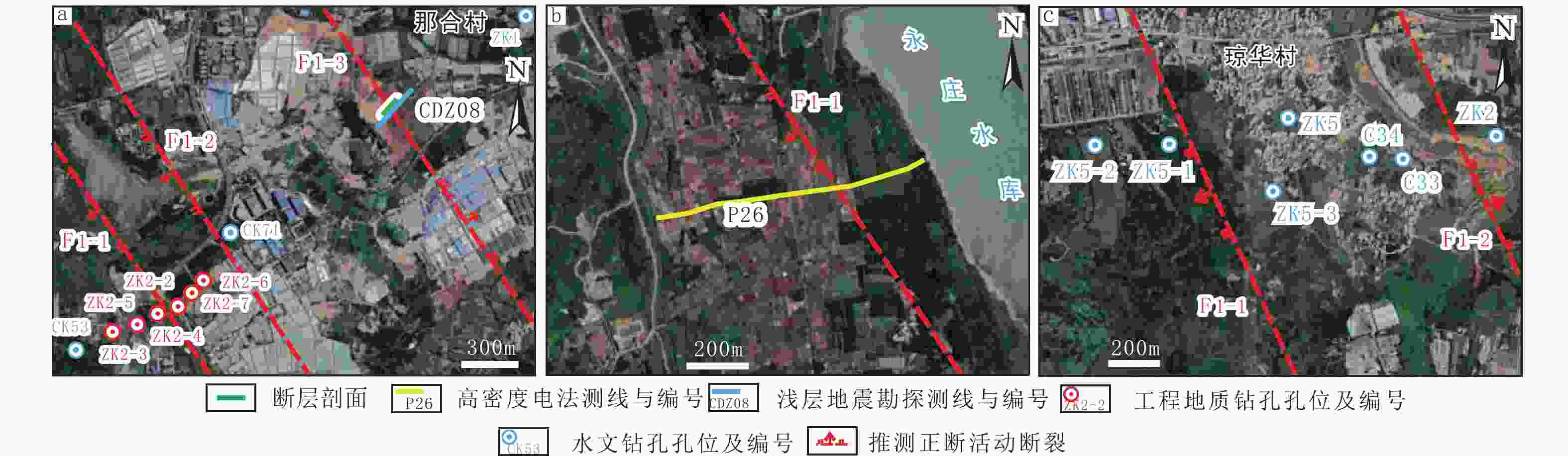
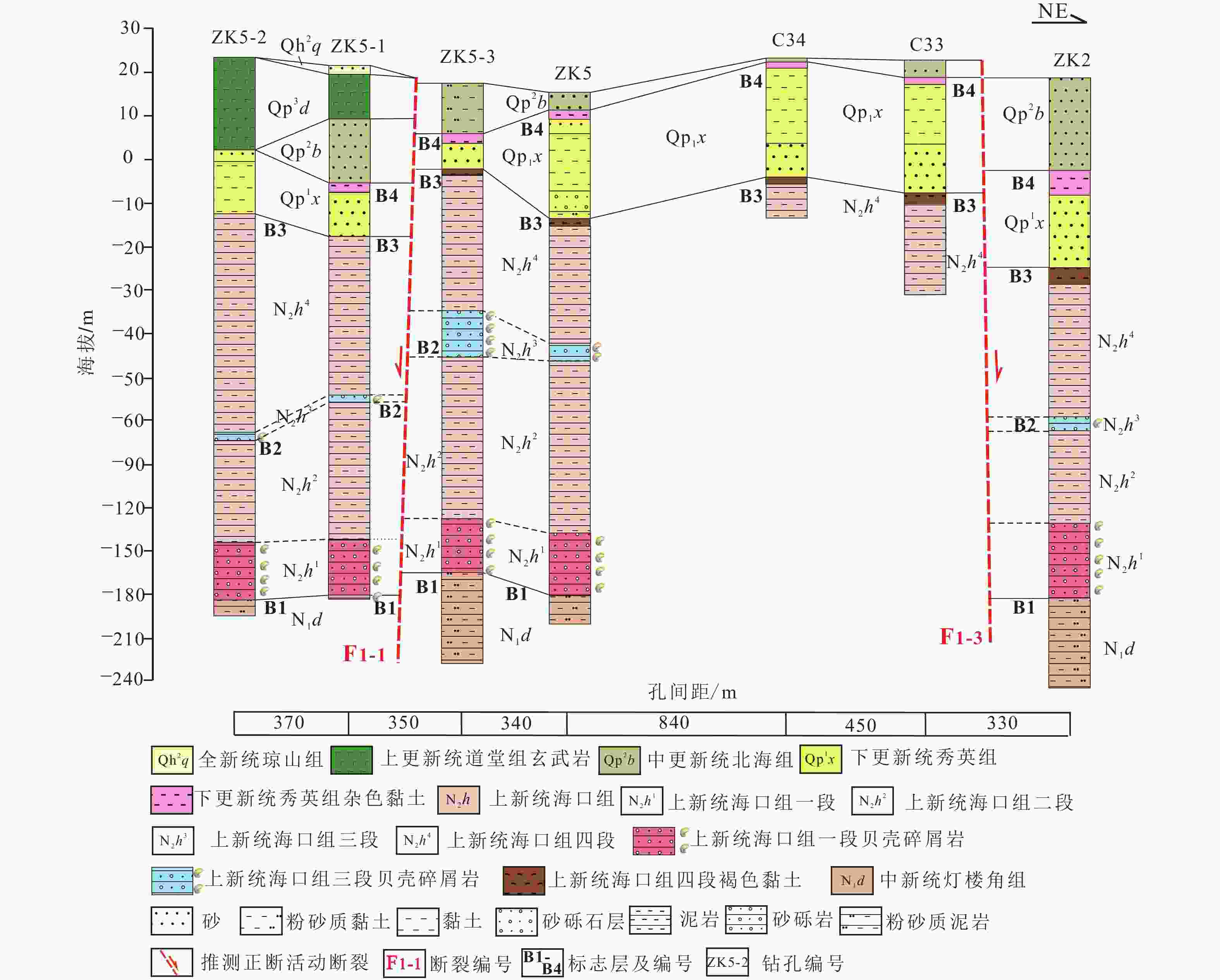
图 2 琼华–莲塘断裂带剖面与地球物理测线及钻孔分布图
a—海口砖瓦厂断层剖面、浅层人工地震测线以及钻孔分布图;b—永庄水库高密度电阻率法测线分布图;c—琼华村钻孔分布图
Figure 2. Profile of the Qionghua–Liantang fault belt and distribution of geophysical survey lines and boreholes
(a) Profile of the Haikouzhuanwachang fault section and distribution of shallow artificial seismic lines and boreholes; (b) Distribution of high-density geophysical survey lines using the electrical method along the Yongzhuangshuiku fault; (c) Borehole distribution in Qionghua village
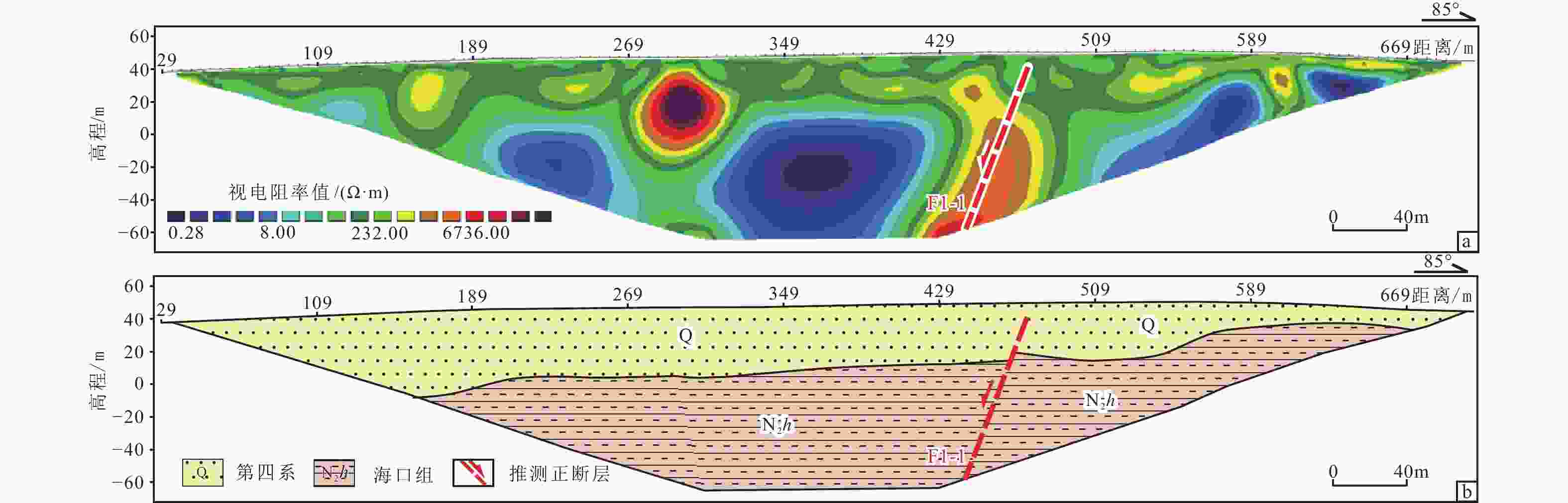
图 3 海口砖瓦厂断裂特征
a—海口砖瓦厂断层剖面;b—海口砖瓦厂断层剖面图; c—F1-3b断层垂直错距0.5 m;d—F1-3a断层垂直错距1.1 m;e—OSL样品采样点;f—F1-3a断层擦痕特征;g—沿F1-3a断层形成的地层牵引变形;h—沿F1-3a断层面发育的铁质结核
Figure 3. Characteristics of the Haikouzhuanwachang fault
(a) Picture of the Haikouzhuanwachang fault section; (b) Schematic diagram of the Haikouzhuanwachang fault section; (c) Characteristics of the secondary fault (F1-3b); vertical offset of this fault is 0.5 m; (d) Characteristics of the secondary fault (F1-3a); vertical offset of this fault is 1.1 m; (e) OSL sampling location; (f) Characteristics of fault slickenside in F1-3a; (g) Characteristics of stratum deformation; (h) Iron concretion along the F1-3a surface
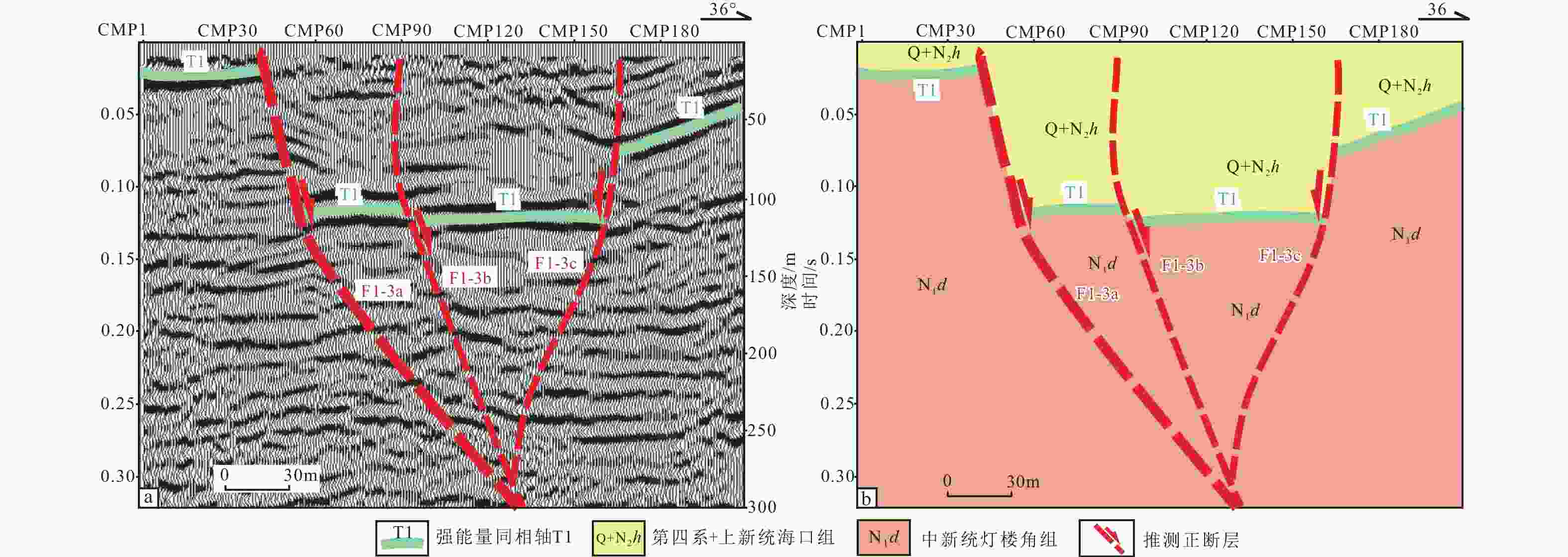
图 5 海口砖瓦厂断裂浅层人工地震勘探剖面
a—浅层人工地震勘探剖面;b—浅层人工地震勘探剖面解译结果
Figure 5. Exploration profile of the Haikouzhuanwachang fault using shallow artificial seismic reflection
(a) Exploration profile of the shallow artificial seismic reflection; (b) Interpretation results of the shallow artificial seismic exploration profile
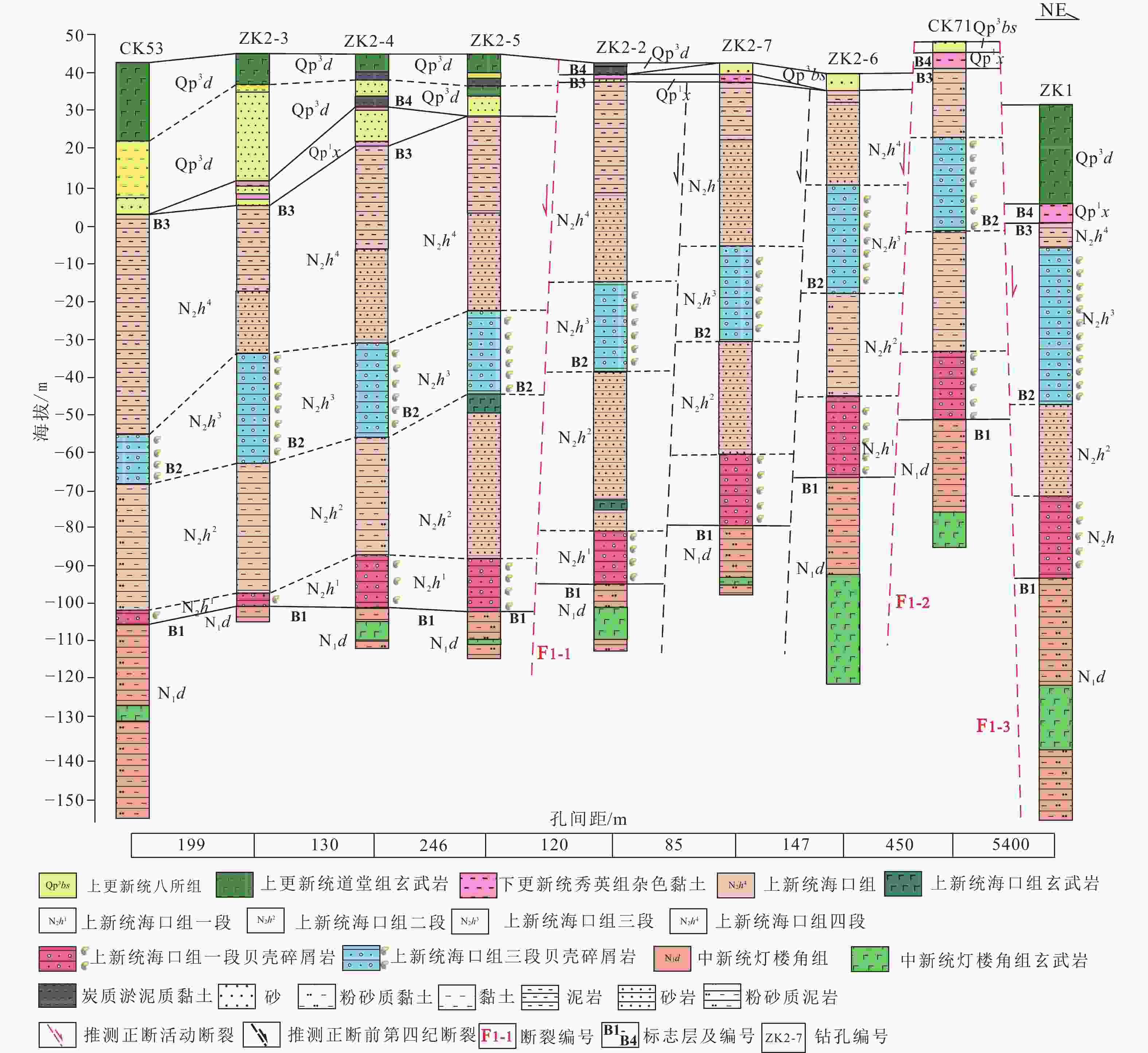
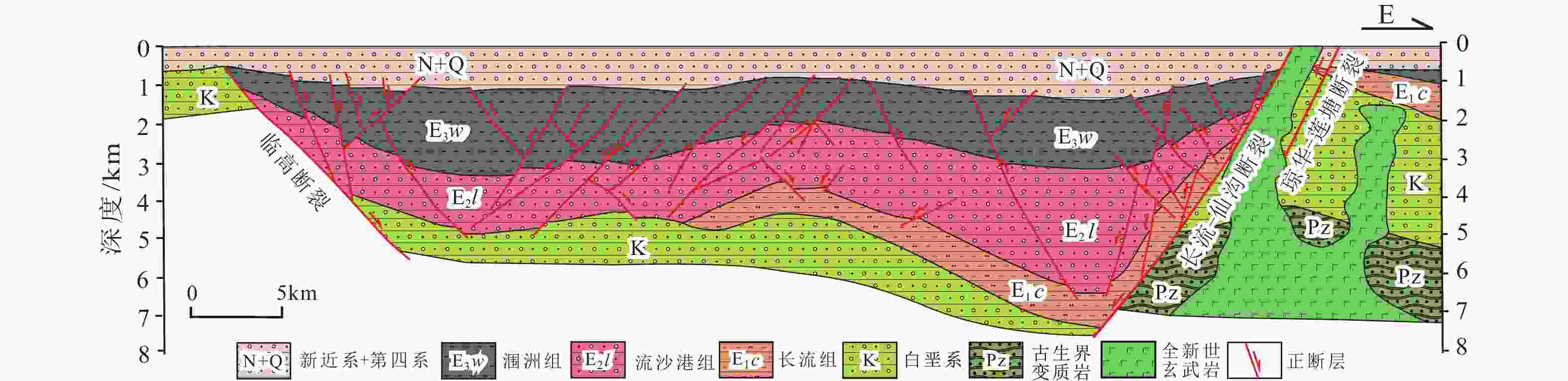
图 8 福山凹陷及琼华−莲塘断裂带剖面图(据Li et al.,2008修改)
Figure 8. Sections of the Fushan depression and the Qionghua–Liantang fault belt (modified from Li et al., 2008)
-
CHEN E M, HUANG Y Y, 1984. A summary of 19 strong earthquakes in South China and the continental margin seismic belt in the northern South China Sea [J]. South China Journal of Seismology, 4(1): 11-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN E M, HUANG Y Y, 1989. Characteristics of the seismic damage and analysis of the seismic structure of the 1605 great earthquake of Qiongzhou, Hainan Island[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 11(3): 319-331. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN W G, ZHANG H N, LI Z Q, et al. , 1987. Some problems of deposition and development of the Beihai formation in northern Hainan Island[J]. Tropical Geography, 7(3): 268-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN W J, GE T M, LI D M, et al. , 1992. K-Ar-Magnetostratigraphic chronology of Cenozoic basalt in Lei-Qiong region [M]//LIU R X. Chronology and geochemistry of Cenozoic volcanic rocks in China. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) DING Y Y, ZHAO X T, HU D G, et al. , 2018. Late Cenozoic fault activity in northeastern Hainan Island and its controlling effect on tectonic subsidence in Dongzhai Port[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 39(2): 155-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) DONG R S, RAN H L, GAO Z, 1993. The relationship between earthquake magnitude and length of active fault in China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 15(4): 395-400. (in Chinese with English abstract) FAN Q C, SUN Q, LI N, et al. , 2004. Periods of volcanic activity and magma evolution of Holocene in North Hainan Island[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3): 533-544. (in Chinese with English abstract) GE T M, FAN L M, XU X, et al. , 1994. Paleomagnetism of Beihai and Zhanjiang formations in Lei-Qiong region[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 14(4): 61-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) HO K S, CHEN J C, JUANG W S, 2000. Geochronology and geochemistry of late Cenozoic basalts from the Leiqiong area, southern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 18(3): 307-324. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00059-0 HUANG Z G, CAI F X, 1994. A new approach to the quaternary volcanicity in the Leiqiong area[J]. Tropical Geography, 14(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) LEI C, REN J Y, PEI J X, et al. , 2011. Tectonic framework and multiple episode tectonic evolution in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan basin, northern continental margin of South China Sea[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 36(1): 151-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI M J, WANG T G, LIU J, et al. , 2008. Occurrence and origin of carbon dioxide in the Fushan Depression, Beibuwan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 25(6): 500-513. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.07.007 LI P, YANG M E, LIU X S, et al. , 1988. Analysis of active fault in the northern Qiongzhou[M]//DING Y Z, LI P, SHI Z L, et al. A collection of earthquake studies in northern Hainan Island. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) LI P C, ZHOU D, ZHANG C M, et al. , 2015. Assessment of the effective CO2 storage capacity in the Beibuwan Basin, offshore of southwestern P. R. China[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 37: 325-339. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.03.033 LI W, JIA L Y, HU D G, et al. , 2019. Late Pleistocene tectonic history of the western segment of Maniao-Puqian fault: evidence from the Laocheng section, northern Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 33(5): 970-978. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU H G, WU X J, LI F, et al. , 2018. Active characteristics of the middle segment of Maniao-Puqian fault in the Holocene[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 13(3): 588-599. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Y, HU D G, XU Y X, et al. , 2019. 3D magnetotelluric imaging of the middle-upper crustal conduit system beneath the Lei-Hu-Ling volcanic area of northern Hainan Island, China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 371: 220-228. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2019.01.013 LIU Y, DU J S, Hu Z W, et al. , 2021. Crustal magma plumbing system beneath the Quaternary volcanic area (northern Hainan Island, China) revealed by magnetotelluric data[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 419: 107362. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2021.107362 LONG W G, LIN Y H, ZHU Y H, et al. , 2006. Establishment of the early-mid Pleistocene Duowen formation on northern Hainan Island, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(3): 408-414. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG C H, SHI G, WU H, et al. , 2021. Application of seismic detection by spark source for concealed faults in Shanghai urban water network area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(6): 938-948. (in Chinese with English abstract) SUN J Z, 1988. Study on Quaternary volcanic activity in northern Hainan Island[M]//DING Y Z, LI P, SHI Z L, et al. A collection of earthquake studies in northern Hainan Island. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) WANG C Q, JIA L Y, HU D G, et al. , 2021. Activity of eastern part of the Maniao-Puqian fault in northern Hainan Island and its evaluation of crustal stability[J]. Geology in China, 48(2): 618-631. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG C Q, JIA L Y, HU D G, et al. , 2022. Quaternary activity characteristics of the Maniao-Puqian fault in the Jiangdong New District of Haikou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(2): 403-417. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIA M M, WANG C Q, HU D G, et al. , 2019. ESR dating of the Basuo formation in the northeastern Hainan Island and its tectonic significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(2): 257-266. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE X N, REN J Y, WANG Z F, et al. , 2015. Difference of tectonic evolution of continental marginal basins of South China Sea and relationship with SCS spreading[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1): 77-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIE Z F, XIE S S, CAI S K, et al. , 2010. Gravity and magnetic field characteristics and regional geological structures of Northern Hainan area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 34(5): 579-582. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU X W, YU G H, RAN Y K, et al. , 2015. An introduction to urban active faults in China[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) XUE W J, 1983. On the age and sedimentation environment of Beihai formation[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 3(3): 31-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAN C G, JIANG W L, 2007. Relationship between the activity of the Changliu-Xiangou fault zone in Late-Quaternary and volcanic activity in North Hainan Island[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2(3): 230-242. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG H, SHI G, WU H, et al. , 2021. Quaternary activity of the Luodian-Zhoupu buried fault in the Shanghai region: integrated exploration and research[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 267-279. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG H N, ZHAO X T, 1984. Characteristics of the neotectonic movement in the Hainan Island and Leizhou peninsula area[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica(3): 276-287. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J J, ZHONG D L, ZHOU Y, 1999. Tectonic evolution of southeast Asia and the Ailao-Honghe tectonic belt[J]. Geological Review, 45(4): 337-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Y Q, 2004. Late Cenozoic squeezing-out tectonism in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its impacts on late hydrocarbon accumulation in rift basins in eastern China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 25(2): 162-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) 陈恩民, 黄咏茵, 1984. 华南十九次强震暨南海北部陆缘地震带概述[J]. 华南地震, 4(1): 11-32. 陈恩民, 黄詠茵, 1989. 1605年海南岛琼州大地震的震害特征和发震构造研究[J]. 地震学报, 11(3): 319-331. 陈伟光, 张虎男, 李子权, 等, 1987. 琼北北海组地层沉积、发育的几个问题[J]. 热带地理, 7(3): 268-275. 陈文寄, 葛同明, 李大明, 等, 1992. 雷琼地区新生代玄武岩的K-Ar-磁性地层年代学[M]//刘若新. 中国新生代火山岩年代学与地球化学. 北京: 地震出版社. 丁莹莹, 赵希涛, 胡道功, 等, 2018. 琼东北晚新生代断裂活动及其对东寨港沉降的控制作用[J]. 地球学报, 39(2): 155-166. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.112601 董瑞树, 冉洪流, 高铮, 1993. 中国大陆地震震级和地震活动断层长度的关系讨论[J]. 地震地质, 15(4): 395-400. 樊祺诚, 孙谦, 李霓, 等, 2004. 琼北火山活动分期与全新世岩浆演化[J]. 岩石学报, 20(3): 533-544. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2004.03.017 葛同明, 樊利民, 徐行, 等, 1994. 雷琼地区湛江组、北海组的古地磁学研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 14(4): 61-70. 黄镇国, 蔡福祥, 1994. 雷琼第四纪火山活动的新认识[J]. 热带地理, 14(1): 1-10. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.000020 雷超, 任建业, 裴健翔, 等, 2011. 琼东南盆地深水区构造格局和幕式演化过程[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 36(1): 151-162. 李玶, 杨美娥, 刘行松, 等, 1988. 琼北地区活动性断裂的研究[M]//丁原章, 李坪, 时振梁, 等. 海南岛北部地震研究文集. 北京: 地震出版社. 李薇, 贾丽云, 胡道功, 等, 2019. 琼北老城剖面记录的马袅—铺前断裂西段晚更新世活动历史[J]. 现代地质, 33(5): 970-978. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2019.05.04 刘华国, 吴小江, 李峰, 等, 2018. 马袅-铺前断裂中段全新世活动特征研究[J]. 震灾防御技术, 13(3): 588-599. doi: 10.11899/zzfy20180310 龙文国, 林义华, 朱耀河, 等, 2006. 海南岛北部第四纪早中更新世多文组的建立[J]. 地质通报, 25(3): 408-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.03.011 宋春华, 施刚, 巫虹, 等, 2021. 上海城市水网地区电火花震源地震探测隐伏断裂的应用探索[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(6): 938-948. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.06.076 孙建中, 1988. 琼北地区第四纪火山活动研究[M]//丁原章, 李坪, 时振梁, 等. 海南岛北部地震研究文集. 北京: 地震出版社. 王超群, 贾丽云, 胡道功, 等, 2021. 海南岛北部马袅-铺前断裂东段活动性与地壳稳定性评价[J]. 中国地质, 48(2): 618-631. 王超群, 贾丽云, 胡道功, 等, 2022. 海口市江东新区马袅-铺前断裂第四纪活动特征[J]. 地质学报, 96(2): 403-417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.02.005 夏蒙蒙, 王超群, 胡道功, 等, 2019. 琼东北八所组ESR年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(2): 257-266. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.02.025 解习农, 任建业, 王振峰, 等, 2015. 南海大陆边缘盆地构造演化差异性及其与南海扩张耦合关系[J]. 地学前缘, 22(1): 77-87. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.01.007 谢振福, 谢顺胜, 蔡水库, 等, 2010. 琼北地区重磁场特征与区域地质构造[J]. 物探与化探, 34(5): 579-582. 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 冉勇康, 等, 2015. 中国城市活动断层概论[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. 薛万俊, 1983. 北海组的地质时代及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 3(3): 31-48. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.1983.03.004 闫成国, 江娃利, 2007. 琼北地区北西方向长流-仙沟断裂带晚第四纪活动及与火山活动关系的讨论[J]. 震灾防御技术, 2(3): 230-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2007.03.002 张浩, 施刚, 巫虹, 等, 2021. 上海罗店-周浦隐伏断裂第四纪活动性综合探测与研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 267-279. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2021.27.02.025 张虎男, 赵希涛, 1984. 雷琼地区新构造运动的特征[J]. 地质科学(3): 276-287. 张进江, 钟大赉, 周勇, 1999. 东南亚及哀牢山红河构造带构造演化的讨论[J]. 地质论评, 45(4): 337-344. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1999.04.001 张岳桥, 2004. 晚新生代青藏高原构造挤出及其对中国东部裂陷盆地晚期油气成藏的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 25(2): 162-169. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2004.02.008 -




 下载:
下载: