Research on fluid inclusions of the Jiadi gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou
-
摘要: 架底金矿是近年来在黔西南新发现的主要赋存于玄武岩中的大型微细粒浸染型金矿床。为查明其成矿流体特征,探讨流体成矿机制,针对矿床不同成矿阶段采取流体包裹体样品开展工作。根据野外观察和室内分析,架底金矿热液成矿期可分为3个阶段:黄铁矿阶段、烟灰色石英阶段和硫化物阶段,其中烟灰色石英阶段为主要成矿阶段。流体包裹体以NaCl-H2O和CO2-NaCl-H2O型为主,黄铁矿阶段富CO2包裹体,均一温度(Th)为211~231℃,盐度(wt)为2.10~7.60(% NaCl equiv);烟灰色石英阶段见大量NaCl-H2O和CO2-NaCl-H2O型包裹体,均一温度(Th)为182~218℃,盐度(wt)为1.40~5.90(% NaCl equiv);硫化物阶段包裹体均一温度(Th)普遍小于183℃,盐度(wt)为0.90~5.30(% NaCl equiv)。激光拉曼光谱分析显示包裹体中含CO2、CH4、N2、SO2等气相组分,随着成矿流体均一温度、盐度和密度的不断下降,包裹体中气相组分种类也趋于简单。通过计算成矿流体的ρ、P、pH、Eh和fO2等物理化学参数,表明成矿环境具有中低温、低盐度、低密度、近中性、相对还原及低氧逸度的特征。流体包裹体组合变化表明成矿作用发生在流体CO2含量不断降低的过程,主成矿阶段流体混合和区域伸展构造引起流体沸腾作用强烈,大量金属成分(黄铁矿、自然金等)快速沉淀形成金矿体。Abstract: The Jiadi gold deposit, located in southwestern Guizhou Province, is a newly discovered large-scale basalt-hosted and fine-grained disseminated gold deposit. This article focuses on the characteristics of ore-forming fluid in order to discuss the ore-forming mechanism by the fluid inclusion analyses from different mineralization stages of the deposit. Based on the field observations and laboratory analyses, the hydrothermal ore-forming processes of the deposit can be divided into three stages: the pyritization forming-stage (1st stage), the smoky-gray quartz forming-stage (2nd stage) and the sulfide forming-stage (3rd stage), among which the smoky-gray quartz forming-stage is the primary stage. The fluid inclusions are mainly composed of NaCl-H2O and CO2-NaCl-H2O type, and CO2-rich inclusions are frequently observed in the first stage minerals, with homogenization temperature (Th) ranging from 211 to 231℃, and salinity (wt) from 2.10 to 7.60 (%NaCl equiv). There are a lot of NaCl-H2O and CO2-NaCl-H2O type of inclusions in the second stage, with the homogenization temperature (Th) changing from 182 to 218℃, and the salinity (wt) from 1.40 to 5.90 (%NaCl equiv). The homogenization temperature (Th) of the third stage is generally lower than 183℃, with the salinity (wt) varying from 0.90 to 5.30 (%NaCl equiv). The results of laser Raman spectroscopy show that the inclusions generally contain CO2, CH4, N2, SO2 and other gas-phase components. As the homogeneous temperature, salinity and density of the ore-forming fluid continue to decrease, the component types in the inclusions tend to reduce. By calculating the ρ, P, pH, Eh, and ƒO2, the ore-forming environment is characterized by low to moderate temperatures, low salinity, low density, near neutrality, relative reducibility and low oxygen fugacity. The change in fluid inclusion assemblage (FIA) indicates that the mineralization occurred as the fluid CO2 content continued to decrease. The fluid mixing in the main ore-forming stage and the regional extensional structure caused strong fluid boiling, and a large number of metal components (pyrite, natural gold, etc.) were rapidly precipitated to form gold ore bodies.
-
Key words:
- southwestern Guizhou /
- Jiadi deposit /
- fluid inclusions /
- laser Raman spectroscopy /
- ore-forming fluid
-
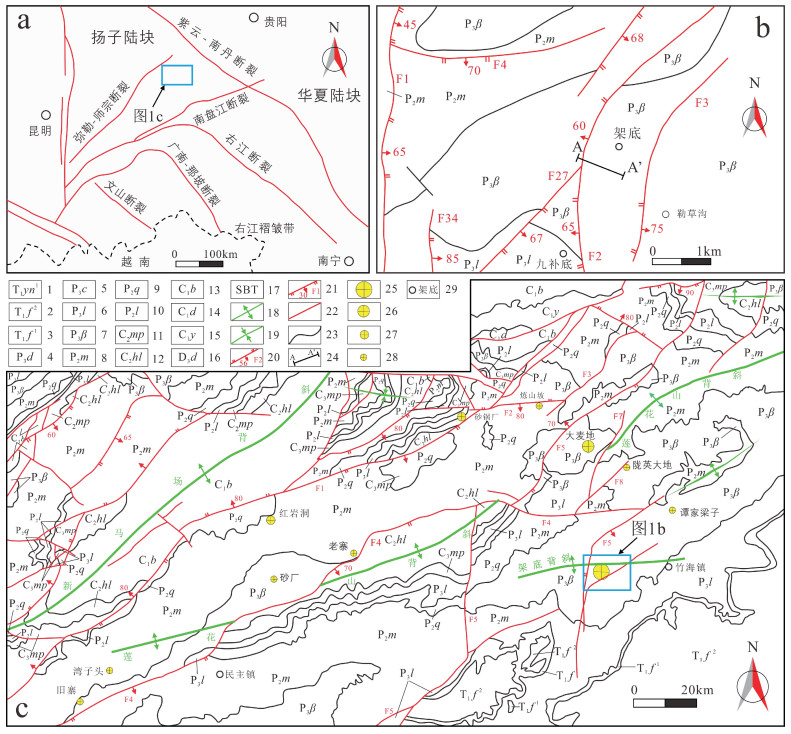
图 1 莲花山背斜地质构造及微细浸染型金矿产地分布示意图(据何金坪等,2018修改)
a—右江盆地构造简图;b—架底金矿床构造地质简图;c—莲花山背斜地质构造及微细浸染型金矿产地分布示意图
1—下三叠统永宁镇组一段;2—下三叠统飞仙关组二段;3—下三叠统飞仙关组一段;4—上二叠统大隆组;5—上二叠统长兴组;6—上二叠统龙潭组;7—上二叠统峨眉山玄武岩组;8—中二叠统茅口组;9—中二叠统栖霞组;10—中二叠统梁山组;11—上石炭统马平组;12—上石炭统黄龙组;13—下石炭统摆佐组;14—下石炭统大塘组;15—下石炭统岩关组;16—上泥盆统代化组;17—构造蚀变体(SBT);18—背斜轴;19—向斜轴;20—逆断层及编号;21—正断层及编号;22—性质不明断层;23—地质界限;24—勘探线位置及编号;25—大型金矿床;26—中型金矿床;27—小型金矿床;28—金矿点;29—地理位置及名称Figure 1. Sketch map of the geologic structure and distribution of disseminated gold deposits and occurrences in the Lianhuashan anticline area(modified from He et al., 2018)
(a)Simplified tectonic map of the Youjiang basin; (b)Structural geologic sketch map of the Jiadi gold deposit; (c)Sketch map of the geologic structure and distribution of disseminated gold deposits in the Lianhuashan anticline area
1-First section of the Yongningzhen Formation; 2-Second section of the Feixianguan Formation; 3-First section of Feixianguan Formation; 4-Dalong Formation; 5-Changxing Formation; 6-Longtan Formation; 7-Emeishan Basalt Formation; 8-Maokou Formation; 9-Qixia Formation; 10-Liangshan Formation; 11-Maping Formation; 12-Huanglong Formation; 13-Baizuo Formation; 14-Datang Formation; 15-Yanguan Formation; 16-Daihua Formation; 17-Structural alteration body(SBT); 18-Synclinal axis; 19-Anticlinal axis; 20-Reverse faults and their numbers; 21-Normal faults and their numbers; 22-Ill-defined fault; 23-Geologic boundary; 24-Exploration line and its number; 25-Large gold deposits; 26-Medium gold deposits; 27-Small gold deposits; 28-Gold occurrence; 29-Geolocation图 2 架底金矿床7号勘探线剖面图(位置见图 1b;据何金坪等,2018修改)
Figure 2. Cross-section of the No.7 exploration line of the Jiadi gold deposit (shown in fig. 1b; modified from He et al., 2018)
图 3 架底金矿床3个成矿阶段矿石手标本及显微镜下照片
a—架底金矿上层矿体露头;b—架底金矿下层矿体(SBT)钻孔岩心松散矿石;c—烟灰色石英阶段石英+黄铁矿细脉;d—蚀变火山角砾岩型矿石中3个阶段热液矿物的分布情况;e—烟灰色石英阶段细脉状黄铁矿;f—烟灰色石英阶段烟灰色含金石英脉;g—显微镜下黄铁矿阶段半自形—他形浸染状黄铁矿;h—显微镜下烟灰色石英阶段团块状黄铁矿;i—显微镜下烟灰色石英阶段细脉状黄铁矿;j—显微镜下硫化物阶段自形黄铁矿;①-、②-、③-分别表示黄铁矿、烟灰色石英和硫化物成矿阶段;Py表示黄铁矿;Q表示石英
Figure 3. Hand specimens and microscopic photographs showing the three ore-forming stages of the Jiadi gold deposit
(a) Photo showing upper ore-body outcrops of the Jiadi gold deposit; (b) Photo showing loose ores in drill core, lower orebody (SBT) of the Jiadi gold deposit; (c) Specimen of Quartz+pyrite vein of the smoky gray quartz stage; (d) Specimen showing the distribution of hydrothermal minerals of the three stages in altered volcanic breccia type ore; (e) Specimen of veined pyrite of the smoky gray quartz stage; (f) Specimen of smoky gray gold-bearing quartz vein of the smoky gray quartz stage; (g) Microscopic photo of subhedral-euhedral disseminated pyrite of the pyrite stage; (h) Microscopic photo of massive pyrite of the smoky gray quartz stage; (i) Microscopic photo of veined pyrite of the smoky gray quartz stage; (j) Microscopic photo of euhedral pyrite of sulfide stage; ①, ②, ③ represent the pyrite, smoky gray quartz and sulfide mineralization stage respectively; Py stands for pyrite; Q stands for quartz
图 5 架底金矿床流体包裹体岩相学特征
FIA表示流体包裹体组合;LH2O表示液相H2O;VH2O表示气相H2O;LCO2表示液相CO2;VCO2表示气相CO2
a—相互穿切的石英脉,脉内可见大量细小金属矿物产出;b—发育良好环带的石英晶体;c—沿石英晶体裂隙分布的次生包裹体;d—红色虚线之间流体包裹体条带为流体包裹体组合(FIA);e—硫化物阶段纯液相包裹体;f—黄铁矿阶段富液相流体包裹体;g—可见硫化物阶段包裹体“卡脖子”现象;h—烟灰色石英阶段含CO2两相包裹体;i—烟灰色石英阶段含CO2三相包裹体Figure 5. Petrographic characteristics of fluid inclusions in the Jiadi gold deposit
(a)Interpenetrating quartz veins with large amounts of fine metallic minerals; (b)Quartz crystal with well zonal texture; (c)Secondary inclusions distributed along the fractures of quartz crystals; (d)The fluid inclusion band between red dotted lines is a fluid inclusion assembly (FIA); (e)Pure liquid inclusions of the sulfide stage; (f)Liquid-rich fluid inclusions of the pyrite stage; (g)"Neck-locked" phenomenon of inclusion in sulfide stage; (h)Two-phase inclusions containing CO2 of smoky gray quartz stage; (i)Three-phase inclusions containing CO2 of smoky gray quartz stage
FIA stands for fluid inclusion assembly; LH2O represents liquid phase H2O; VH2O represents gaseous phase H2O; LCO2 represents liquid phase CO2; VCO2 represents gaseous phase CO2图 7 架底金矿床流体包裹体激光拉曼光谱特征
a—黄铁矿阶段NaCl-H2O型气液两相包裹体;b—烟灰色石英阶段含少量气相组分的NaCl-H2O型气液两相包裹体;c—烟灰色石英阶段含少量CO2三相包裹体;d—硫化物阶段含CO2、CH4、N2两相包裹体
Figure 7. Laser Raman spectroscopy characteristics of fluid inclusions in the Jiadi gold deposit
(a)NaCl-H2O type gas-liquid two-phase inclusions of the pyrite stage; (b)NaCl-H2O type gas-liquid two-phase inclusions containing a small amount of gas-phase components of the smoky gray quartz stage; (c)Three-phase inclusions containing a small amount of CO2 of the smoky gray quartz phase; (d)Two-phase inclusions containing CO2, CH4 and N2 of the sulfide stage
图 8 黔西南主要微细浸染型金矿床与架底金矿成矿流体物理参数图(泥堡数据郑禄林,2017;戈塘数据杜放,2017;烂泥沟数据韩雪,2012)
a—黔西南主要微细浸染型金矿床成矿流体物理参数图;b—架底金矿成矿流体均一温度和盐度散点图
Figure 8. Physical parameters of ore-forming fluids of main fine disseminated gold deposits and the Jiadi gold deposit in Southwestern Guizhou(The data of Nibao from Zheng, 2017; The data of Getang from Du, 2017; The data of Lannigou from Han, 2012)
(a)Map of physical parameters of ore-forming fluids of main fine disseminated gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou; (b)Scatter diagram of homogenization temperature and salinity of ore-forming fluid from the Jiadi gold deposit
表 1 两相NaCl-H2O型流体包裹体参数
Table 1. Parameters of two-phase NaCl-H2O fluid inclusions
样品编号 采样层位及测试矿物 包裹体类型 测温数量 初熔温度/℃ 均一温度/℃ 冰点温度/℃ 盐度/(%NaCl equiv) 密度/(g/cm3) 备注 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 ZK3109-1 SBT(Cal) A2 10 -23.8~-20.3 -22.05 231~206 215.0 -2.3~-4.8 -3.8 7.6~3.9 6.1 0.883~0.903 0.893 黄铁矿阶段 ZK3109-2 P3β2(Cal) A2 7 -24.0~-21.1 -22.55 218~199 208.3 -1.2~-4.7 -3.1 7.4~2.1 5.0 0.878~0.909 0.894 黄铁矿阶段 ZK3109-4 P3β2(Q) A2 7 -21.6~-20.4 -21.00 225~199 209.7 -1.7~-4.5 -3.3 7.2~2.9 5.4 0.877~0.915 0.896 黄铁矿阶段 ZK3109-5 P3β2(Q) A2 7 -24.6~-21.4 -23.00 235~198 213.1 -1.5~-4.0 -2.9 6.4~2.6 4.8 0.867~0.907 0.887 黄铁矿阶段 ZK3109-7 P3β2(Q) A2 7 -22.8~-21.1 -21.95 225~198 209.1 -1.9~-4.2 -2.9 6.7~3.2 4.8 0.868~0.907 0.888 黄铁矿阶段 ZK3109-8 P3β2(Q) A2 9 -23.2~-20.7 -21.95 223~195 212.4 -1.8~-4.3 -3.0 6.9~3.1 5.0 0.871~0.908 0.890 黄铁矿阶段 8 -21.8~-20.5 -21.15 196~177 187.0 -0.8~-3.0 -1.9 5.0~1.4 3.2 0.882~0.926 0.904 烟灰色石英阶段 ZK3109-10 P3β2(Q) A2 9 -24.3~-21.4 -22.85 223~198 211.9 -1.7~-4.7 -2.9 7.4~2.9 4.7 0.872~0.909 0.891 黄铁矿阶段 ZK2725-4 P3β2(Q) A2 9 -22.7~-20.4 -21.55 222~188 205.7 -1.5~-3.5 -2.5 5.7~2.6 4.2 0.860~0.919 0.890 烟灰色石英阶段 ZK2725-5 P3β2(Q) A2 5 -21.9~-20.6 -21.25 218~195 207.0 -1.8~-3.6 -2.6 5.9~3.1 4.4 0.882~0.897 0.890 黄铁矿阶段 ZK2725-9 P3β2(Q) A2 7 -23.1~-21.6 -22.35 215~193 206.9 -1.9~-3.2 -2.7 5.3~3.2 4.4 0.875~0.912 0.894 黄铁矿阶段 ZK2725-12 P3β2(Q) A2 9 -23.7~-21.1 -22.40 217~185 20.1 -2.1~-3.6 -2.9 5.9~3.5 4.6 0.872~0.910 0.891 烟灰色石英阶段 ZK2725-13 P3β2(Q) A2 7 -26.6~-21.0 -23.80 213~195 204.8 -2.2~-3.6 -2.8 5.9~3.7 4.6 0.884~0.970 0.896 黄铁矿阶段 ZK2725-15 P3β2(Q) A2 8 -24.2~-21.9 -23.05 215~196 205.5 -1.7~-3.7 -2.6 6.0~2.9 4.3 0.870~0.908 0.889 黄铁矿阶段 ZK3125-1 P3β2(Q) A2 9 -23.6~-21.7 -22.65 180~162 170.8 -0.5~-1.6 -1.0 2.7~0.9 1.8 0.905~0.930 0.918 硫化物阶段 ZK4204-1 P3β2(Q) A2 7 -24.4~-21.8 -23.10 213~176 197.3 -1.5~-3.2 -2.3 5.3~2.6 3.8 0.871~0.931 0.901 硫化物阶段 ZK4204-2 P3β2(Q) A2 7 -25.1~-20.8 -22.95 223~198 208.1 -2.5~-4.7 -3.7 7.4~4.2 5.9 0.882~0.913 0.898 黄铁矿阶段 表 2 两相CO2-NaCl-H2O型流体包裹体参数
Table 2. Parameters of two-phase CO2-NaCl-H2O fluid inclusions
样品编号 采样层位及测试矿物 包裹体类型 测温数量 初熔温度/℃ 笼形物熔化温度/℃ 均一温度/℃ 冰点温度/℃ 盐度/(%NaCl equiv) 密度/(g/cm3) 备注 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 ZK3109-3 P3β2(Q) B1 7 -59.0~-56.0 57.5 4.0~9.8 6.9 229~197 209.8 -1.0~-4.7 -3.3 6.4~1.7 4.7 0.875~0.961 0.918 黄铁矿阶段 ZK3109-6 P3β2(Q) B1 7 -58.1~57.0 57.6 6.8~8.1 7.5 224~198 210.7 -1.7~-4.5 -3.2 7.2~2.9 5.2 0.845~0.958 0.902 黄铁矿阶段 ZK3109-9 P3β2(Q) B1 10 -58.3~-56.7 57.5 5.3~8.7 7.0 227~197 211.3 -1.5~-4.0 -3.0 6.4~2.6 4.9 0.852~0.928 0.890 黄铁矿阶段 P3β2(Q) B1 8 -57.2~-56.7 57.0 5.3~8.4 6.9 201~179 188.1 -0.7~-3.0 -1.7 5.0~1.2 2.9 0.831~0.930 0.881 烟灰色石英阶段 ZK3109-12 P3β2(Q) B1 9 -58.6~-57.3 58.0 7.4~9.3 6.9 220~179 198.6 -1.8~-4.1 -2.9 6.6~3.1 4.8 0.862~0.918 0.890 黄铁矿阶段 ZK2725-14 P3β2(Q) B1 7 -58.8~-57.1 58.0 7.0~9.4 8.2 224~195 210.3 -2.1~-4.1 -3.2 6.6~3.5 5.2 0.875~0.960 0.918 黄铁矿阶段 寄主矿物:Q—石英,Cal—方解石;采样层位:P3β2—上二叠统峨眉山玄武岩组二段,SBT—下层构造蚀变岩矿石;包裹体类型:A2—两相NaCl-H2O型,B1—两相CO2-NaCl-H2O型 表 3 黔西南主要微细浸染状金矿床成矿流体包裹体物理参数表
Table 3. Physical parameters of ore-forming fluids of prime fine-disseminated gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou
-
CHEN B J, WEN C Q, HUO Y, et al., 2010. Study on fluid inclusion of the Shuiyindong gold deposit, Southwestern Guizhou[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 29(1): 45-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN M H, MAO J W, QU W J, et al., 2007. Re-Os dating of arsenian pyrites from the Lannigou gold deposit, Zhenfeng, Guizhou Province, and its geological significances[J]. Geological Review, 53(3): 371-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) DU F, 2017. Characteristics and significance of fluid inclusions from breccia ore of Getang gold deposit in Anlong, Guizhou Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) FAN H R, XIE Y H, WANG Y L, 1997. Fluid inclusion evidences in the processes and environments of gold deposition[J]. Journal of Precious Metallic Geology, 6(3): 204-213. (in Chinese with English abstract) FAN H R, HU F F, YANG J H, et al., 2005. Fluid evolution and large-scale gold metallogeny during Mesozoic tectonic transition in the eastern Shandong Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(5): 1317-1328. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO J H, 2002. Mineralizing process of micrograin-type gold deposits in Southeastern Yunnan and Northwestern Guangxi[J]. Mineral Deposits, 21(S1): 121-124. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN X, 2012. The study on geologic-geochemical characteristics and causes discusses of the Lannigou Carlin-type gold deposits in Guizhou[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) HE J P, YUAN S F, WANG X Y, et al., 2018. Geochemical Characteristics of the Lianhuashan anticline in the Southwest Guizhou dense area of mineral deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 38(3): 384-387, 397. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU C W, MOU Y Z, 2015. Analysis of Geological features ofmineralization and prospecting potential of the Jiadi gold deposit in Panxian, Guizhou Province[J]. Nonferrous Metals Abstract, 30(3): 42-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU R Z, SU W C, BI X W, et al., 1995. A possible evolution way of ore-Formting hydrothermal fluid for the Carlin-type gold deposits in the Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi triangle area[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 15(2): 144-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Y Z, LIU W H, WANG J J, et al., 2017. Basin-scale structure control of Carlin-style gold deposits in central Southwestern Guizhou, China: insights from seismic reflection profiles and gravity data[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 91: 444-462. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.09.011 HUA R M, CHEN P R, ZHANG W L, et al., 2005. Three major metallogenic events in Mesozoic in South China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(2): 99-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG X Q, CHEN Z L, WANG P A, et al., 2008. Fluid inclusion study of the Shazhou uranium orefield in the Xiangshan deposiţJiangxi[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 14(2): 176-185. (in Chinese with English abstract) LARGE S J E, BAKKER E Y N, WEIS P, et al., 2016. Trace elements in fluid inclusions of sediment-hosted gold deposits indicate a magmatic-hydrothermal origin of the Carlin ore trend[J]. Geology, 44(12): 1015-1018. doi: 10.1130/G38351.1 LEHRMANN D J, PAYNE J L, PEI D H, et al., 2007. Record of the end-Permian extinction and Triassic biotic recovery in the Chongzuo-Pingguo platform, southern Nanpanjiang basin, Guangxi, south China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 252(1-2): 200-217. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.11.044 LI J H, 2021. The study of ore-forming processes of the Jiadi and Damaidi basalt-hosted gold deposits, Southwestern Guizhou Province, China[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU B, DUAN G X, 1987. The density and isochoric formulae for NaCl-H2O fluid inclusions (salinity≤25 WT%) and their applications[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 7(4): 345-352. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU B, 2011. Calculation of pH and Eh for aqueous inclusions as simple system[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(5): 1533-1542. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J M, LIU J J, 1997. Basin fluid genetic model of sediment-hosted microdisseminated gold deposits in the gold-triangle area between Guizhou, Guangxi and Yunnan[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 17(4): 448-456. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J Z, DENG Y M, LIU C Q, et al., 2006. Metallogenic conditions and model of the superlarge Shuiyindong stratabound gold deposit in Zhenfeng County, Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 33(1): 169-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J Z, XIA Y, DENG Y M, et al., 2009. Researches on the Sbt of Shuiyindong gold deposit and significance for regional prospecting[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 17(3): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU X F, NI S Z, SU W C, 1996. Characteristics of isotope geochemistry and plutonic-origin fluid mineralization for Carlin-type gold deposits in the Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 16(4): 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KWYS199604016.htm LIU Y H, 2002. Analysis on the Minerogenetic Geological Condition of the Gold Ore in the Lianhuashan Anticline Western Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 19(4): 231-234. (in Chinese with English abstract) LU H Z, 2008. Role of CO2 fluid in the formation of gold deposits: Fluid inclusion evidences[J]. Geochimica, 37(4): 321-328. (in Chinese with English abstract) LU H Z, 2019. Geofluids and across earth sphere structures[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6): 1003-1012. (in Chinese with English abstract) MAO J W, LI Y Q, 2001. Fluid inclusions of the Dongping gold telluride deposit in Hebei Province, China: involvement of mantle fluid in metallogenesis[J]. Mineral Deposits, 20(1): 23-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) NIE G J, YU H M, HE S, et al., 2020. Physical simulation analysis of the Cenozoic fault activities and structural deformation mechanism of the Youjiang area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(3): 316-328. (in Chinese with English abstract) NIE L Q, ZHOU T F, WANG F Y, et al., 2019. Study of fluid inclusions and H-O-S isotopic compositions of Donggushan tungsten skarn deposit, Anhui Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(12): 3825-3837. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.16 PENG Y W, GU X X, ZHANG Y M, et al., 2014. Source and evolution of ore-forming fluid of the Huijiabao gold field, Southwestern Guizhou: evidences from fluid inclusions and stable isotopes[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 33(5): 666-680. (in Chinese with English abstract) QIU L F, WU D, WU Y, et al., 2019. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids and sources of polymetallic ore-forming materials in deep segment of uranium deposits in Niutoushan area, Xiangshan[J]. Mineral Deposits, 38(2): 291-302. (in Chinese with English abstract) SU W C, XIA B, ZHANG H T, et al., 2008. Visible gold in arsenian pyrite at the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China: implications for the environment and processes of ore formation[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 33(3-4): 667-679. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.10.002 SU W C, ZHANG H T, HU R Z, et al., 2012. Mineralogy and geochemistry of gold-bearing arsenian pyrite from the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China: implications for gold depositional processes[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 47(6): 653-662. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0328-9 TIAN C, ZHANG W G, HE H J, et al., 2021. Mineralogical characteristics of gold-bearing pyrite and gold occurrence regularity of the Jiadi gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 1255-1266. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG D F, LIU J Z, XIONG C J, et al., 2014. A Preliminary Study on Ore Characteristics of the Jiadi Gold Deposit in Panxian, Guizhou[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 31(6): 55-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG D F, 2015. A preliminary study on the geological and geochemical characteristics of the Jiadi gold deposit in Panxian, Guizhou[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU F Y, GE W C, SUN D Y, et al., 2003. Discussions on the lithospheric thinning in eastern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3): 51-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU X H, CHENG P L, XIAO C G, et al., 2013. Metallogenic geologic characteristics of Damaidi gold deposit in basalt distribution area of Western Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 30(4): 283-288. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIA Y, 2005. Characteristics and model for Shuiyindong gold deposit in Southwestern Guizhou, China[D]. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAN D P, ZHOU M F, SONG H L, et al., 2002, Where was south China locatedin the reconstruction of Rodinia?[D]. Eart h Science Frontiers, 9(4): 249-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAO J, 2018. Studies on ore-forming material source and ore genesis of Laozhaiwan fine-disseminated gold deposit, in Yunnan[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZENG G P, 2018. Study on the structurally controlling on the micro-disseminated gold deposits in the western of the Southwest Guizhou gold ore concentration area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). (in Chinese with English abstract) ZENG S G, WANG S H, WU X H, 2014. Metallogenic Mode Disscussion of Microscopic Disseminated Type Gold Deposit in Lianhuashan Area[J]. Guizhou Geology, 31(3): 161-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG L, DU D Q, ZHANG H B, et al., 2012. Study on structural ore control of Huijiapu gold mine field in Southwestern Guizhou: tectonic significance of the "Two-stairs" model[J]. Gold, 33(9): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG R Q, ZHOU Y, WANG X W, et al., 2009. Structural features and tectonic evolution of the Wei-Zi-Luo fault zone in Southwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(2): 178-189. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG T, CHEN Z L, HUANG H Y, et al., 2020. Geochemical characteristics of gold-bearing minerals and its geological significance in the Ashawayi gold deposit in the southwestern Tianshan Orogen[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(3): 443-458. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO F Y, XIAO C G, ZHANG B Q, et al., 2018. REE and isotopic features of the Jiadi gold deposit in Panxian county, Guizhou Province and its ore-forming material source[J]. Geology and Exploration, 54(3): 465-478. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG L L, 2017. Mineralization mechanism and ore-forming process of the Nibao gold deposit in Southwestern Guizhou, China[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU L M, JIN J F, HE M Y, et al., 1997. An initial study of the mineralization of plutonic fluid of the fine disseminated gold deposit in Southwest Guizhou Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 16(3): 173-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHUO Y Z, HU R Z, XIAO J F, et al., 2019. Trace elements and C-O isotopes of calcite from Carlin-type gold deposits in the Youjiang Basin, SW China: constraints on ore-forming fluid compositions and sources[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 113: 103067. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103067 陈本金, 温春齐, 霍艳, 等, 2010. 黔西南水银洞金矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 29(1): 45-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2010.01.007 陈懋弘, 毛景文, 屈文俊, 等, 2007. 贵州贞丰烂泥沟卡林型金矿床含砷黄铁矿Re-Os同位素测年及地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 53(3): 371-382. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2007.03.010 杜放, 2017. 贵州安龙戈塘金矿角砾状矿石流体包裹体特征研究及意义[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学. 范宏瑞, 谢奕汉, 王英兰, 1997. 流体包裹体与金矿床的成矿及勘探评价[J]. 贵金属地质, 6(3): 204-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD703.006.htm 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨进辉, 等, 2005. 胶东中生代构造体制转折过程中流体演化和金的大规模成矿[J]. 岩石学报, 21(5): 1317-1328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200505000.htm 国家辉, 2002. 滇东南桂西北微细粒型金矿成矿作用探讨[J]. 矿床地质, 21(S1): 121-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2002S1038.htm 韩雪, 2012. 贵州烂泥沟卡林型金矿床地质地球化学特征及成因探讨[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学. 何金坪, 苑顺发, 汪小勇, 等, 2018. 黔西南矿集区莲花山背斜区地球化学特征[J]. 四川地质学报, 38(3): 384-387, 397. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2018.03.007 胡瑞忠, 苏文超, 毕献武, 等, 1995. 滇黔桂三角区微细浸染型金矿床成矿热液一种可能的演化途径: 年代学证据[J]. 矿物学报, 15(2): 144-149. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1995.02.005 胡承伟, 牟永忠, 2015. 贵州省盘县架底金矿床成矿地质特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 有色金属文摘, 30(3): 42-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJW201503023.htm 华仁民, 陈培荣, 张文兰, 等, 2005. 论华南地区中生代3次大规模成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 24(2): 99-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.02.002 黄锡强, 陈正乐, 王平安, 等, 2008. 江西相山铀矿田沙洲矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 14(2): 176-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2008.02.009 李俊海, 2021. 贵州西南部架底和大麦地玄武岩中金矿床成矿过程研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学. 刘斌, 段光贤, 1987. NaCl—H2O溶液包裹体的密度式和等容式及其应用[J]. 矿物学报, 7(4): 345-352. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1987.04.010 刘斌, 2011. 简单体系水溶液包裹体pH和Eh的计算[J]. 岩石学报, 27(5): 1533-1542. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105026.htm 刘建明, 刘家军, 1997. 滇黔桂金三角区微细浸染型金矿床的盆地流体成因模式[J]. 矿物学报, 17(4): 448-456. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1997.04.012 刘建中, 邓一明, 刘川勤, 等, 2006. 贵州省贞丰县水银洞层控特大型金矿成矿条件与成矿模式[J]. 中国地质, 33(1): 169-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.01.019 刘建中, 夏勇, 邓一明, 等, 2009. 贵州水银洞Sbt研究及区域找矿意义探讨[J]. 黄金科学技术, 17(3): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2518.2009.03.001 刘显凡, 倪师军, 苏文超, 1996. 滇黔桂微细浸染型金矿同位素地球化学特征与深源流体成矿[J]. 矿物岩石, 16(4): 106-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS199604016.htm 刘远辉, 2002. 贵州莲花山背斜金的成矿地质条件分析[J]. 贵州地质, 19(4): 231-234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2002.04.004 卢焕章, 2008. CO2流体与金矿化: 流体包裹体的证据[J]. 地球化学, 37(4): 321-328. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.04.006 卢焕章, 2019. 地球中的流体和穿越层圈构造[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(6): 1003-1012. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.06.083 毛景文, 李荫清, 2001. 河北省东坪碲化物金矿床流体包裹体研究: 地幔流体与成矿关系[J]. 矿床地质, 20(1): 23-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2001.01.004 聂冠军, 于红梅, 何声, 等, 2020. 右江地区新生代断裂活动及构造变形机制的物理模拟分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(3): 316-328. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.03.029 聂利青, 周涛发, 汪方跃, 等, 2019. 安徽庐枞矿集区东顾山钨矿床成矿流体来源与演化: 来自H、O、S同位素和流体包裹体的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 35(12): 3825-3837. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.16 彭义伟, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 等, 2014. 黔西南灰家堡金矿田成矿流体来源及演化: 流体包裹体和稳定同位素证据[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 33(5): 666-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.05.013 邱林飞, 吴迪, 吴玉, 等, 2019. 相山牛头山地区铀矿床深部多金属成矿流体特征与成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 矿床地质, 38(2): 291-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201902005.htm 田冲, 张文高, 何虎军, 等, 2021. 黔西南架底金矿床载金黄铁矿的矿物学特征及金的赋存规律研究[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 1255-1266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202104022.htm 王大福, 刘建中, 熊灿娟, 等, 2014. 贵州盘县架底金矿矿石特征初步研究[J]. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 31(6): 55-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5269.2014.06.014 王大福, 2015. 贵州盘县架底金矿地质地球化学特征初步研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学. 吴福元, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等, 2003. 中国东部岩石圈减薄研究中的几个问题[J]. 地学前缘, 10(3): 51-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.004 吴小红, 程鹏林, 肖成刚, 等, 2013. 贵州西部玄武岩分布区大麦地金矿成矿地质特征[J]. 贵州地质, 30(4): 283-288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2013.04.008 夏勇, 2005. 贵州贞丰县水银洞金矿床成矿特征和金的超常富集机制研究[D]. 贵阳: 中国科学院研究生院(地球化学研究所). 颜丹平, 周美夫, 宋鸿林, 等, 2002. 华南在Rodinia古陆中位置的讨论: 扬子地块西缘变质-岩浆杂岩证据及其与Seychelles地块的对比[J]. 地学前缘, 9(4): 249-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2002.04.004 姚娟, 2008. 云南老寨湾金矿床成矿物质来源分析及矿床成因探讨[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学. 曾国平, 2018. 黔西南矿集区西段微细浸染型金矿构造控矿作用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉). 张蕾, 杜定全, 张晗彬, 等, 2012. 黔西南灰家堡金矿田的构造控矿模式研究: "两层楼"模式的构造意义[J]. 黄金, 33(9): 13-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201209003.htm 张荣强, 周雁, 汪新伟, 等, 2009. 贵州西南部威-紫-罗断裂带构造特征及演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(2): 178-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.02.007 曾昭光, 王石华, 吴小红, 2014. 莲花山地区微细粒浸染型金矿成矿模式探讨: 以架底金矿为例[J]. 贵州地质, 31(3): 161-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5943.2014.03.001 张涛, 陈正乐, 黄宏业, 等, 2020. 西南天山阿沙哇义金矿载金矿物地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(3): 443-458. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.03.038 赵富远, 肖成刚, 张兵强, 等, 2018. 贵州盘县架底金矿稀土元素和同位素特征及成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 54(3): 465-478. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.03.003 郑禄林, 2017. 贵州西南部泥堡金矿床成矿作用与成矿过程[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学. 朱赖民, 金景福, 何明友, 等, 1997. 初论黔西南微细浸染型金矿床深源流体成矿[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 16(3): 173-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH703.008.htm -





 下载:
下载: