The 2012 Thabeikkjin (Myanmar) M 7.0 earthquake and its surface rupture characteristics
-
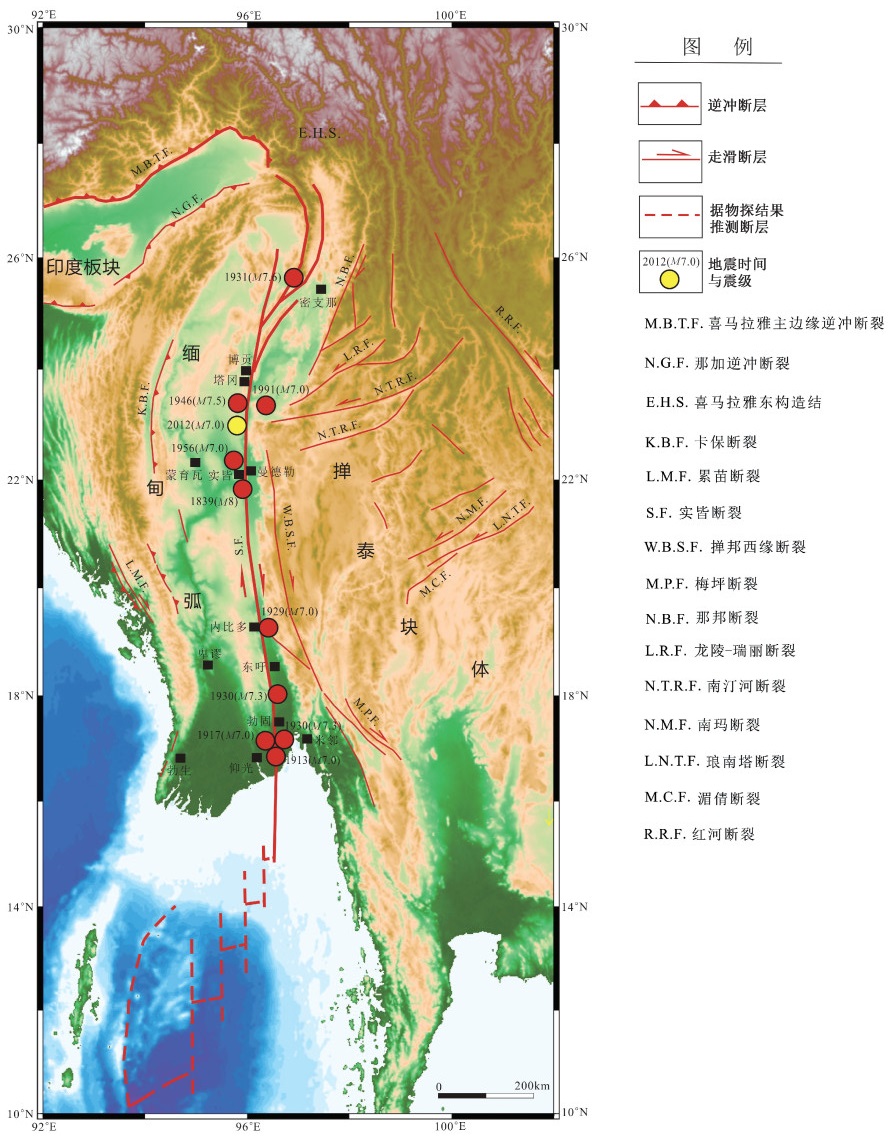
摘要: 文章以地质地貌与地震遗迹野外调查获得的第一手资料为基础,重点介绍了实皆断裂的活动习性、2012年地震产生的建筑物破坏与地震地表破裂带特征。实皆断裂是一条规模宏大,以右旋走滑为主的全新世活动断裂,其水平滑动速率为18~20 mm/a。历史上沿实皆断裂曾发生10余次7级以上强震,迄今保留有1839年曼德勒因瓦M 8、1930年勃固M 7.3、1930年东吁M 7.3等地震遗迹。2012年德贝金M 7.0地震造成了佛塔、民用建筑等严重破坏,形成至少长45 km的地震地表破裂,包括塌岸、滑坡、地震断层等,震中烈度达Ⅸ度。在断层右旋走滑运动作用下,地裂缝呈现出有规律的左阶雁列,与实皆断裂走向的夹角一般为20°~30°;规模较大的地裂缝多呈“S”型。地裂缝有规律的左阶雁列和被断错的地物标志,指示地震地表破裂具明显的右旋走滑性质。2012年地震造成的右旋位错量一般为40~90 cm,最大位错达102 cm。地震地表破裂特征和震源机制解结果一致地表明,此次地震的发震构造为实皆活动断裂。Abstract: Based on the first-hand data obtained from the field survey in terms of geology, landforms, earthquake ruins, this paper focuses on the activity behavior of the Sagaing fault, as well as the damaged buildings and seismic surface rupture zone generated by the 2012 earthquake. The Sagaing fault striking nearly NS is an active large-scale dextral strike-slip fault, with a horizontal slip rate of 18~20 mm/a. Many strong earthquakes more than M 7 have occurred along the Sagaing fault zone historically, and so far, there are still ruins of the earthquakes, such as the 1839 Innwa, Mandalay, M 8 earthquake, the 1930 Bago M 7.3 earthquake and the 1930 Phyu M 7.3 earthquake. The 2012 Thabeikkjin M 7.0 earthquake caused serious damage to pagodas, civil and other buildings, forming an at least 45 km-long seismic surface rupture with bank collapses, landslides, seismic faults and so on. The epicenter intensity of the earthquake is estimated to be IX. Under the dextral strike slip of the fault, the ground fissures show a trend of regular left-step en echelon, and the included angle with the strike of the Sagaing fault is generally 20°~30°; The large-scale ground fissures mostly show a "S" type. The regular left-step en echelon trend of ground fissures and the faulted ground features indicate that the seismic surface fracture are obviously characterized by dextral strike slip. The horizontal dextral displacements caused by the 2012 earthquake are generally between 40~90 cm, and the maximum reaches 102 cm. The surface rupture characteristics and the results of focal mechanism solutions show that the event is caused by the dextral strike-slip of the Sagaing fault.
-
Key words:
- Thabeikkjin /
- earthquake /
- Sagaing fault /
- seismic surface rupture /
- dextral strike-slip
-
图 2 1839年曼德勒因瓦M 8地震中建筑物破坏遗迹
a—亚达纳-希米塔建筑群墙体裂缝;b—亚达纳-希米塔建筑地震后留下的立柱;c—巴加亚修道院墙体裂缝,有的呈X型;d—因震陷而导致的巴加亚修道院围墙变形
Figure 2. Ruins of the buildings destroyed by the 1839 M 8 earthquake in Innwa, Mandalay
(a) Cracks in the walls of Yadana Hsemee Pagoda complex; (b) Columns of Yadana Hsemee Pagoda complex after the earthquake; (c) Cracks in the walls of Bagaya Monastery, and some are X-shaped; (d) Deformation of the wall of Bagaya Monastery caused by earthquake subsidence
图 5 建筑物破坏情况(照片来自缅甸地震委员会; http://searg.rhul.ac.uk/current_research/plate_tectonics/和www.news.cn)
a—马累镇佛塔破坏;b—萨贝纳戈镇佛塔破坏;c—马累镇砖木结构的房屋歪斜;d—德贝金镇砖木结构破坏;e—易欣村寺庙建筑破坏;f—库勒镇钢结构大桥坍塌;g—江心岛上的一座钢筋混凝土庙宇破坏;h—萨贝纳戈镇北佛塔顶部破坏
Figure 5. Damage to the buildings (Photos from Myanmar earthquake Commission; http://searg.rhul.ac.uk/current_research/plate_tectonics/and www.news.cn)
(a) A pagoda in Male town; (b)A pagoda in Sabeanago town; (c) A crooked half-timber house in Male town; (d) A half-timber house in Thabeikkjin town; (e) A temple building in Yee Shin Village; (f) A steel bridge in Kule town; (g) A reinforced concrete temple on an ait; (h) The top of a pagoda in the north of Sabeanago town
图 6 塌岸与滑坡地表破坏(照片引自缅甸地震委员会;http://searg.rhul.ac.uk/current_research/plate_tectonics/)
a—德贝金南伊洛瓦底江塌岸,镜向东;b—上帕那北滑坡,镜向东南;c—萨贝纳戈镇的地震塌陷,镜向东南
Figure 6. River bank collapses and landslides(Photos from Myanmar Earthquake Commission, http://searg.rhul.ac.uk/current_research/plate_tectonics/)
(a) Irrawaddy River bank collapse in the south of Thabeikkjin town, view to east; (b) Landslide in the north of upper Ponna, view to southeast; (c)Earthquake collapse in Sabeanago town, view to southeast
图 7 剪切破裂
a—德贝金左阶斜列的地裂缝,镜向北西;b—德贝金南地裂缝,单条长度4m,镜向东;c—德贝金地裂缝,镜向南东;d—德贝金雁行排列的地裂缝,镜向北西;e—德贝金南拉分盆地边缘雁行排列的地裂缝,一侧拉开下陷,另一侧隆起,镜向南东(米尺长25 cm);f—德贝金地裂缝细部特征,拉张,镜向南(记录本长20 cm);g—德贝金南地裂缝细部特征,拉张,镜向北;h—鼓丘形成机制,镜向北(米尺长25 cm)
Figure 7. Field photos of shear ruptures in Thabeikkjin
(a) The left-step en echelon ground fissures, view to northwest; (b) The ground fissures in the south with each single length of 4 m, view to east; (c) The ground fissures, view to southeast; (d)The en echelon ground fissures, view to northwest; (e) The en echelon ground fissures on the edge of a pull-apart basin in the south, one side is pulled open and sunk while the other is uplifted, view to southeast (Length of the ruler is 25 cm); (f) Detailed features of a pull-apart ground fissure, view to south (Length of the record book is 20 cm); (g) Detailed characteristics of a pull-apart ground fissure in the south, view to north; (h) Formation mechanism of bulge, view to north (Length of the ruler is 25 cm)
图 9 断层产生的右旋位错与地震楔
a—德贝金田埂(宽30 cm)同步右旋位错10 cm,镜向东;b—房屋立柱右旋位错30 cm,镜向东;c—德贝金地裂缝,右旋位错4 cm;d—库勒房屋多条裂缝右旋位错2~3 cm,镜向北;e—德贝金江边地震断层(已钙质充填),总的右旋位错13 cm,镜向东;f—湖边阶地中断层,镜向南;g—湖边阶地中地震楔,镜向南
Figure 9. Field photos showing the dextral dislocations and the seismic wedge produced by seismic fault
(a) An ~10 cm synchronized dextral displacement of ploughed furrows (~30 cm wide), view to east; (b) 30 cm dextral displacement of the house post, view to east; (c) A ground fissure with ~4 cm dextral displacement; (d) Dextral displacements of 2~3 cm occur on multiple house cracks at Kule, view to east; (e) Seismic fault (filled with calcium) at the riverside of Thabeikkjin, with a total dextral displacement of 13 cm, view to east; (f) Fault in lakeside terrace, view to south; (g) Seismic wedge in lakeside terrace, view to south
-
ACHARYYA S K, RAY K K, SENGUPTA S, 1991. The Naga hills and Andaman ophiolite belt, their setting, nature and collisional emplacement history[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 18: 293-315. doi: 10.1016/0079-1946(91)90006-2 AKILAN A, BALAJI S, PADHY S, et al., 2016. The plate kinematics of Burmese micro-plate relative to its surroundings[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(5): 333. doi: 10.1007/s12517-016-2345-6 BERTRAND G, RANGIN C, MALUSKI H, et al., 2001. Diachronous cooling along the Mogok Metamorphic Belt (Shan scarp, Myanmar): the trace of the northward migration of the Indian syntaxis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 19(5): 649-659. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(00)00061-4 CHANG Z F, CHANG H, ZANG Y, et al., 2016. Recent active features of Weixi-Qiaohou fault and its relationship with the Honghe fault[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(3): 517-530. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=671161799 CHANG Z F, CHANG H, LI J L, et al., 2021. Holocene activity and Paleoearthquakes of the Weixi-Qiaohou fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(4): 881-898. (in Chinese with English abstract) CURRAY J R, 2005. Tectonics and history of the Andaman Sea region[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 25(1): 187-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.09.001 GUO S M, JI F J, XIANG H F, et al., 2001. The Honghe active fault zone[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press. (in Chinese) HALL R, 2012. Late Jurassic-Cenozoic reconstructions of the Indonesian region and the Indian Ocean[J]. Tectonophysics, 570-571: 1-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.04.021 HURUKAWA N, MAUNG P M, 2011. Two seismic gaps on the Sagaing Fault, Myanmar, derived from relocation of historical earthquakes since 1918[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(1): L01310. KUNDU B, GAHALAUT V K, 2012. Earthquake occurrence processes in the Indo-Burmese wedge and Sagaing fault region[J]. Tectonophysics, 524-525: 135-146. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.12.031 LE DAIN A Y, TAPPONNIER P, MOLNAR P, 1984. Active faulting and tectonics of Burma and surrounding regions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 89(B1): 453-472. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB01p00453 LICHT A, FRANCE-LANORD C, REISBERG L, et al., 2013. A palaeo Tibet-Myanmar connection? Reconstructing the Late Eocene drainage system of central Myanmar using a multi-proxy approach[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 170(6): 929-939. doi: 10.1144/jgs2012-126 MAURIN T, MASSON F, RANGIN C, et al., 2010. First global positioning system results in northern Myanmar: constant and localized slip rate along the Sagaing fault[J]. Geology, 38(7): 591-594. doi: 10.1130/G30872.1 MITCHELL A H G, 1993. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic events in the Western Myanmar (Burma)-Assam region[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 150(6): 1089-1102. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.150.6.1089 MITCHELL A, HTAY M T, HTUN K M, et al., 2007. Rock relationships in the Mogok metamorphic belt, Tatkon to Mandalay, central Myanmar[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 29(5-6): 891-910. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2006.05.009 MORLEY C K, 2004. Nested strike-slip duplexes, and other evidence for Late Cretaceous-Palaeogene transpressional tectonics before and during India-Eurasia collision, in Thailand, Myanmar and Malaysia[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 161(5): 799-812. doi: 10.1144/0016-764903-124 NIELSEN C, CHAMOT-ROOKE N, RANGIN C, 2004. From partial to full strain partitioning along the Indo-Burmese hyper-oblique subduction[J]. Marine Geology, 209(1-4): 303-327. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.05.001 RAJU K A K, RAMPRASAD T, RAO P S, et al., 2004. New insights into the tectonic evolution of the Andaman basin, northeast Indian Ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 221(1-4): 145-162. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00075-5 RANGIN C, BERTRAND G, CHAMOT-ROOKE N, 2002. Tectonics of the India/Eurasia oblique collision in Myanmar: Evidences from superimposed Cenozoic ductile and brittle fabrics[C]//17th geological HKT workshop. Gangtok. RANGIN C, MAURIN T, MASSON F, 2013. Combined effects of Eurasia/Sunda oblique convergence and East-Tibetan crustal flow on the active tectonics of Burma[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 76: 185-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.05.018 SEARLE M P, NOBLE S R, COTTLE J M, et al., 2007. Tectonic evolution of the Mogok metamorphic belt, Burma (Myanmar) constrained by U-Th-Pb dating of metamorphic and magmatic rocks[J]. Tectonics, 26(3): TC3014, doi: 10.1029/2006TC002083. SEARLE M P, MORLEY C K, 2011. Tectonic and thermal evolution of Thailand in the regional context of SE Asia[M]//RIDD M F, BARBER A J, CROW M J. The geology of Thailand. London: Geological Society of London: 539-572. State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, 2020. The Chinese seismic intensity scale: GB/T 17742-2020[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China. (in Chinese) SOCQUET A, PUBELLIER M, 2005. Cenozoic deformation in western Yunnan (China-Myanmar border)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(4): 495-515. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.03.006 SOCQUET A, VIGNY C, CHAMOT-ROOKE N, et al., 2006. India and Sunda plates motion and deformation along their boundary in Myanmar determined by GPS[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 111(B5): B05406. SONG F M, WANG Y P, YU W X, et al., 1998. The Xiaojiang active fault zone[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press: 16-168. (in Chinese) TSUTSUMI H, SATO T, 2009. Tectonic geomorphology of the Southernmost Sagaing Fault and surface rupture associated with the May 1930 Pegu (Bago) earthquake, Myanmar[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(4): 2155-2168. doi: 10.1785/0120080113 TUN S T, WANG Y, KHAING S N, et al., 2014. Surface ruptures of the Mw 6.8 March 2011 Tarlay earthquake, Eastern Myanmar[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 104(6): 2915-2932. doi: 10.1785/0120130321 VIGNY C, SOCQUET A, RANGIN C, et al., 2003. Present-day crustal deformation around Sagaing fault, Myanmar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B11): 2533. doi: 10.1029/2002JB001999 WALLACE R E, 1998. The geology of earthquakes[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 79(9): 115. WANG Y, SIEH K, TUN S T, et al., 2014. Active tectonics and earthquake potential of the Myanmar region[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 119(4): 3767-3822. doi: 10.1002/2013JB010762 XIANG H F, HAN Z J, GUO S M, et al., 2004. Large-scale dextral strike-slip movement and asociated tectonic deformation along the red-river fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 26(4): 597-610. (in Chinese with English abstract) 常祖峰, 常昊, 臧阳, 等, 2016. 维西-乔后断裂新活动特征及其与红河断裂的关系[J]. 地质力学学报, 22(3): 517-530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.009 常祖峰, 常昊, 李鉴林, 等, 2021. 维西-乔后断裂全新世活动与古地震[J]. 地震地质, 43(4): 881-898. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.009 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会, 2020. 中国地震烈度表: GB/T 17742-2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. 虢顺民, 计凤桔, 向宏发, 等, 2001. 红河活动断裂带[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. 宋方敏, 汪一鹏, 俞维贤, 等, 1998. 小江活动断裂带[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 16-168. 向宏发, 韩竹军, 虢顺民, 等, 2004. 红河断裂带大型右旋走滑运动与伴生构造地貌变形[J]. 地震地质, 26(4): 597-610. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2004.04.006 -





 下载:
下载: