The applicability assessment of Sentinel-1 data in InSAR monitoring of the deformed slopes of reservoir in the mountains of southwest China: A case study in the Xiluodu Reservoir
-
摘要: Sentinel卫星凭借其超高的辐射分辨率、稳定的轨道系统、较大的覆盖能力、较短的重返时间、可免费下载的数据,在斜坡灾害识别监测方向上有广泛的应用。自1963年意大利瓦伊昂特大滑坡发生以来,岸坡地质灾害一直是峡谷区水库关注的主要问题之一。以金沙江上游溪洛渡水库区为例,结合PALSAR-2、TerraSAR-X数据,评价Sentinel-1 SAR数据在西南山区水库变形斜坡InSAR监测中的适用性,以理论结合实际结果分析Sentinel-1数据是否可以在一定条件下替代其他商业数据,为今后相关行业应用提供参考。结果显示:Sentinel-1数据在研究区可解译的变形斜坡约200处,类型有滑坡、危岩体和塌岸;经现场核查,Sentinel-1数据解译的最小变形斜坡投影面积约为2400 m2,约35 m(长)×77 m(宽)大小,共16个变形像元聚集。高山峡谷区叠掩、阴影现象严重,通过对雷达常用观测模式下的SAR数据的比较,在SAR数据交集区域,有效观测面积为Sentinel-1升轨70.3%,Sentinel-1降轨68.9%,PALSAR-2升轨70.4%,PALSAR-2降轨67.6%,TerraSAR-X降轨52.5%,在不考虑分辨率的情况下,在库区Sentinel-1数据与其他两种SAR数据观测能力相比持平或更优秀。6月至11月初是溪洛渡水库的水位上升期,周边植被发育较好,造成数据相干性较差,2017年后Sentinel-1A(1B)双星拍摄获取的SAR数据量增加,高频观测可使相干性提高,利用2017年后该卫星数据可有效识别水库蓄—排水周期内的区域性变形斜坡发育变化情况。当长时间缺失SAR数据时,会造成最近一对SAR数据间的某些像元测量的变形超过其InSAR最大量程,解缠时丢失相位周期。Sentinel-1数据由于连续性较好,监测斜坡的变形趋势较为连续,因此更适合连续小变形的趋势识别。
-
关键词:
- Sentinel-1 /
- PALSAR-2 /
- TerraSAR-X /
- 水库变形斜坡 /
- 监测能力
Abstract: Sentinel satellite is widely used in deformed slope identification and monitoring due to its high resolution, stable orbit system, large coverage capacity, short repetition time, and free data download. Since the 1963 catastrophic landslide of Vaiant in Italy, the geologic hazard on bank slopes has been one of the main problems of the reservoir in the mountainous area. Taking the Xiluodu reservoir in the upper reaches of the Jinsha River as the study area, the applicability of the Sentinel-1 SAR data in InSAR monitoring of deformed slopes of reservoir in mountainous areas was evaluated by combining PALSAR-2 and TerraSAR-X data. The results were used to evaluate whether Sentinel-1 data could replace other commercial SAR data under certain conditions. It provides a reference for future applications in related researches. The results show that: About 200 deformed slopes were interpreted by the Sentinel-1 data in the study area, including landslide, rockfall, and bank collapse. According to field investigations, the minimum projected area of deformed slope based on the Sentinel-1 data is about 2400 m2, a size of 35 m (length)×77 m (width), gathered by 16 high-value raster pixels. Overlapping mask shadow phenomenon is severe in the alpine valley area. By comparing SAR data in common satellite radar observation modes, the effective observation area is 70.3% of the ascending Sentinel-1 orbit, 68.9% of the descending Sentinel-1 orbit, 70.4% of the ascending PALSAR-2 orbit, 67.6% of the descending PALSAR-2 orbit, and 52.5% of the descending TerraSAR-X orbit in the intersection area of all SAR data used. Without considering the resolution, it can be concluded that the Sentinel-1 data in the reservoir area has an equal or more excellent observation ability than the other two SAR data. The water level rises from June to early November, and the currounding vegetation develops well, resulting in poor data coherence. Since 2017, the amount of SAR data acquired by Sentinel-1A (1B) has increased, and high-frequency observations can improve the coherence. Therefore, the SAR data can be used to effectively identify the development and change of regional deformed slopes during the water fluctuation cycle. When the SAR data is lacking for a long time, the deformation measured by some pixels between the nearest pair of SAR data could exceed the maximum InSAR measurement range, and the phase period will be lost during the unwrapping. Sentinel-1 SAR data is more suitable for trend identification of continuous small deformations due to its good continuity.-
Key words:
- Sentinel-1 /
- PALSAR-2 /
- TerraSAR-X /
- deformed slopes of reservoir /
- monitoring capacity
-
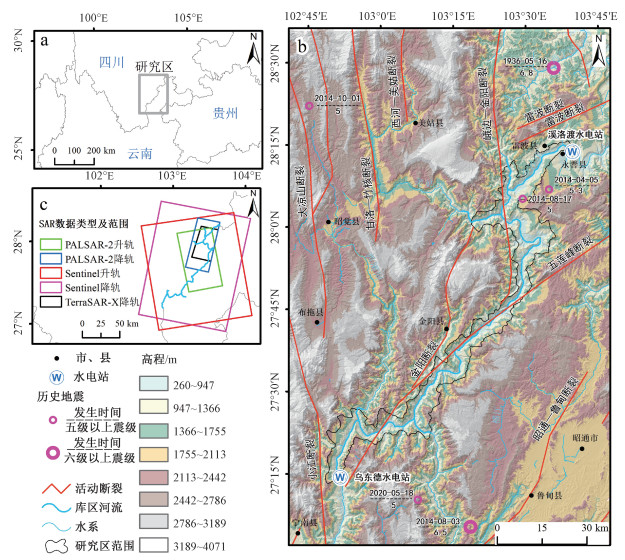
图 1 研究区地理位置、地质背景及SAR数据范围
a—研究区地理位置;b—溪洛渡水库区高程及活动断裂;c—SAR数据类型及拼接裁剪后的实际处理范围
Figure 1. The location and the geological background of the study area, and the SAR data ranges
(a) The location of the study area; (b) The elevation and active faults; (c) The SAR data types, and InSAR processing ranges after images being spliced and clipped
图 7 研究区不同SAR卫星在SAR数据交集区域的有效观测比例
a—Sentinel-1升轨数据有效观测面积;b—Sentinel-1降轨数据有效观测面积;c—PALSAR-2升轨数据有效观测面积;d—PALSAR-2降轨数据有效观测面积;e—TerraSAR-X降轨数据有效观测面积;f—SAR数据交集区域地形阴影
Figure 7. Proportion of effective observations by different SAR satellites in the intersection area of SAR data
(a) The effective observation area of the Sentinel-1 ascending image; (b) The effective observation area of the Sentinel-1 descending image; (c) The effective observation area of the PALSAR-2 ascending image; (d) The effective observation area of the PALSAR-2 descending image; (e) The effective observation area of the TerraSAR-X descending image; (f) The hill shade
图 10 库区翌子村滑坡多源SAR数据D-InSAR结果对比
a—Sentinel-1升轨干涉图; b—Sentinel-1降轨干涉图;c—PALSAR-2升轨干涉图;d—PALSAR-2降轨干涉图;e—TerraSAR-X降轨干涉图;f—光学遥感影像及变形边界
Figure 10. Comparison of D-InSAR results based on the multi-source SAR data of the Yizicun landslide in the reservoir
(a) The interference figure of the Sentinel-1 ascending image; (b) The interference figure of the Sentinel-1 descending image; (c) The interference figure of the PALSAR-2 ascending image; (d) The interference figure of the PALSAR-2 descending image; (e) The interference figure of the TerraSAR-X descending image; (f) The optical image and the deformation boundary
表 1 星载SAR传感器基本参数及特征表
Table 1. Basic parameters and characteristics of Spaceborne SAR sensors
星载SAR系统 所属国家/机构 发射时间 波段(波长/cm) 入射角/(°) 多视数,分辨率(距离向×方位向)/m×m 所用模式 重访周期/天 主要优点 主要缺点 Sentinel-1 欧空局 2014年4月 C(5.6) 37.74 9×1,10.48×13.99 干涉宽幅模式 12(双星6) 免费、覆盖范围广、重复周期短、存档数据多 干涉用模式分辨率低,一般不接受编程预定 PALSAR-2 日本 2014年5月 L(25) 升轨:39.66降轨:38.74 2×2,2.86×4.43 聚束模式 14 覆盖范围广、重复周期短、波段长 需购买,编程数据经常因卫星执行其他任务拍不到 TerraSAR-X 德国 2017年6月 X(3.1) 26.58 3×3,2.73×5.89 聚束模式 11 轨道精度高、数据质量好、重返周期短 需购买,存档数据较少 -
CHEN H K, ZHOU X H, 2016. Study on Identification Method on Failure Mode of Reservoir Landslide: Taking Qingshi Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir as an Example[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University (Natural Science), 33(5): 37-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN T Z, DAI F C, 2018. Exploring the Landslide Deformation Regular Based After the Impoundment in the Xiluodu Reservoir[J]. Industial Construction, 48(Sup): 634-639. (in Chinese with English abstract) China Geological Disaster Prevention Engineering Industry Association, 2018. Guideline of InSAR Monitoring for Geo-hazard, T/CAGHP 013-2018 [S]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences Press. (in Chinese) DENG H Y, WANG C H, 2011. Engineering Geological Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of Old Landslide of Reservoir Bank of Xiluodu Reservoir Areas[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, (5): 59-62. (in Chinese) DONG J, ZHANG L, LI M H, et al., 2018. Measuring precursory movements of the recent Xinmo landslide in Mao county, China with sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 datasets[J]. Landslides, 15(1): 135-144. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0914-8 GAO G P, YANG J H. 2003. Application of GIS in geologic disaster research [J]. Yangtze River, 34(6): 32-33. (in Chinese) GAO L, ZENG QM, 2007. Terrain deformation monitoring in Three Gorges Area using Permanent Scatterers SAR Interferometry[C]//ScanGIS′2007-Proceedings of the 11th Scandinavian Research Conference on Geographical Information Science, s, Norway, 5-7 September 2007: 261-267. INTRIERI E, RASPINI F, FUMAGALLI A, et al., 2018. The Maoxian landslide as seen from space: detecting precursors of failure with Sentinel-1 data[J]. Landslides, 15(1): 123-133. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0915-7 JIANG M, LI Z W, DING X L, et al., 2009. A study on the maximum and minimum detectable deformation gradients resolved by InSAR[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(7): 1715-1724. (in Chinese with English abstract) JIA H Y, WANG Y J, GE D Q, et al., 2020. Improved offset tracking for predisaster deformation monitoring of the 2018 Jinsha River landslide (Tibet, China) [J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 247: 111899. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.111899 HENDRON JR A J, PATTON F D., 1987. The Vaiont slide. a geotechnical analysis based on new geologic observations of the failure surface [J]. Engineering Geology, 24(1-4): 475-491. doi: 10.1016/0013-7952(87)90080-9 HERRERA G, FERNÁNDEZ-MERODO J A, et al., 2009. A landslide forecasting model using ground based SAR data: the portalet case study[J]. Engineering Geology, 105(3-4): 220-230. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.02.009 HU J, LI Z W, DING X L, et al., 2014. Resolving three-dimensional surface displacements from InSAR measurements: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 133: 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.02.005 KANKAKU Y, SAGISAKA M, Suzuki S. (2014). PALSAR-2 launch and early orbit status[C]//. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE geoscience and & remote sensing symposium. Quebec City, QC, Canada: IEEE: 3410-3412. LIAO M S, TANG J, WANG T, et al., 2012. Landslide monitoring with high-resolution SAR data in the Three Gorges region[J]. Sci China Earth Sci, 42(22): 217-229. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIAO M S, WANG T, 2014. Time series InSAR technology and application[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) LIU G X, CHEN Q, LUO X J, et al., 2019. Principle and application of InSAR[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) LIU X H, YAO X, ZHOU Z K, et al, 2018. Study of the technique for landslide rapid recognition by InSAR[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(2): 229-237. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI B, ZHANG Q, WANG W P, et al, 2020. Geohazard monitoring and risk management of high-steep slope in the Wudongde dam area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 556-564. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI L J, YAO X, Yao J M, et al., 2019a. Analysis of deformation characteristics for a reservoir landslide before and after impoundment by multiple D-InSAR observations at Jinshajiang River, China[J]. Natural Hazards, 98(2): 719-733. doi: 10.1007/s11069-019-03726-w LI M H, ZHANG L, SHI X G, et al., 2019b. Monitoring active motion of the Guobu landslide near the Laxiwa Hydropower Station in China by time-series point-like targets offset tracking[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 221: 80-93. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.11.006 LI X E, ZHOU L, SU F Z, et al., 2021. Application of InSAR technology in landslide hazard: Progress and prospects[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 25(2): 614-629. (in Chinese with English abstract) MASSONNET D, FEIGL K L, 1998. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth's surface[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 36(4): 441-500. doi: 10.1029/97RG03139 OUYANG L X, LI X Q, HUI F M, et al., 2017. Sentinel-1A Data Products Characteristics and the Potential Applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 29(2): 286-295. (in Chinese with English abstract) REN Y, 2013. Research on Layover and Shadow Detecting in InSAR[D]. Changsha National University of Defense Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) STROZZI T, LUCKMAN A, MURRAY T, et al., 2002. Glacier motion estimation using SAR offset-tracking procedures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 40(11): 2384-2391. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.805079 SINGLETON A, LI Z, HOEY T et al., 2014. Evaluating sub-pixel offset techniques as an alternative to D-InSAR for monitoring episodic landslide movements in vegetated terrain[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 147: 133-144. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.03.003 SHI X G, ZHANG L, BALZ T, et al., 2015. Landslide deformation monitoring using point-like target offset tracking with multi-mode high-resolution TerraSAR-X data[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 105: 128-140. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.03.017 SHI X G, LIAO M S, LI M H, et al., 2016. Wide-Area Landslide Deformation Mapping with Multi-Path ALOS PALSAR Data Stacks: A Case Study of Three Gorges Area, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 8(2): 136. doi: 10.3390/rs8020136 SCOTT H, ROLAND B, BRENT D, et al., 2016. Three-dimensional surface deformation derived from airborne interferometric uavsar: application to the slumgullion landslide[J]. Journal of geophysical research. Solid earth: JGR, 121(5): 3951-3977. doi: 10.1002/2015JB012559 TANG X S, ZHENG Y R, TANG H M, et al., 2013. Numerical researches on deformation characteristics and prediction of reservoir landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 35(5): 940-947. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG G J, XIE M W, QIU C, et al., 2011. Experiment research of D-InSAR technique on identifying landslide moving in a wide area[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 33(2): 131-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Z Y, ZHANG J Z, 2013. Landslides Monitoring Based on InSAR Technique[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 33(3): 87-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU S, WANG S X, NIU R Q, 2020. Identification of the Potential Landslide in Wushan—Fengjie in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area Based on InSAR Technology[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 27(1): 32-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU W B, LI Z W, DING X L, et al., 2011. Interpolating atmospheric water vapor delay by incorporating terrain elevation information[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 85(9): 555-564. doi: 10.1007/s00190-011-0456-0 YOU X Z, LI S S, YANG S M, et al., 2001. InSAR Investigation in the Early Stage of the Three Gorges Project on the Yangtze River[J]. Crustal Deformation and Earthquake, 21(4): 58-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHONGCUN H Z, 1990. Discussion on reservoir landslide[J]. WANG G X, trans. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 10(1): 53-64. (in Chinese) ZHANG M, ZHANG C S, YANG W M, et al, 2014. The formation conditions and stability of Chahandusi Reservoir landslide in Xunhua Country, Qinghai Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 20(3): 274-284. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAN W J, LI Z W, WEI J C, et al., 2015. A strategy for modeling and estimating atmospheric phase of SAR interferogram[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(7): 2320-2329. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG F, 2018. Study and Engineering Implementation on Problem Areas Detection Technology for Spaceborne InSAR[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG T T, YANG H L, LI DM, et al., 2019. Identification of layover and shadows regions in SAR images: taking Badong as an example[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (11): 85-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHENG J H, HUANG B L, ZHANG Q, et al, 2020. Study on the surge induced by the collapse of dangerous rock mass in Longmen Village in Three Gorges reservoir area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 533-543. (in Chinese with English abstract) 陈洪凯, 周晓涵, 2016. 库岸滑坡破坏模式识别方法研究—以三峡水库青石滑坡为例[J]. 重庆师范大学学报(自然科学版), 33(5): 37-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQSF201605008.htm 陈廷照, 戴福初, 2018. 溪洛渡库区蓄水后滑坡时空分布特征分析[J]. 工业建筑, 48(Sup): 634-639. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GYJZ201806003157.htm 邓宏艳, 王成华, 2011. 溪洛渡库区库岸老滑坡工程地质特征及成因机制分析[J]. 中国水土保持, (5): 59-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2011.05.023 高改萍, 杨建宏, 2003. GIS在地质灾害研究中的应用[J]. 人民长江, 34(6): 32-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2003.06.011 蒋弥, 李志伟, 丁晓利, 等, 2009. InSAR可检测的最大最小变形梯度的函数模型研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(7): 1715-1724. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.07.006 廖明生, 唐婧, 王腾, 等, 2012. 高分辨率SAR数据在三峡库区滑坡监测中的应用[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 42(2): 217-229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201202009.htm 廖明生, 王腾, 2014. 时间序列InSAR技术与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 刘国祥, 陈强, 罗小军, 等, 2019. InSAR原理与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 刘星洪, 姚鑫, 周振凯, 等, 2018. 滑坡灾害InSAR应急排查技术方法研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 24(2): 229-237. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2018.24.02.024 李滨, 张青, 王文沛, 等, 2020. 金沙江乌东德水电站坝区高陡边坡地质灾害监测预警研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 556-564. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.048 李晓恩, 周亮, 苏奋振, 等, 2021. InSAR技术在滑坡灾害中的应用研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 25(2): 614-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB202102008.htm 欧阳伦曦, 李新情, 惠凤鸣, 等, 2017. 哨兵卫星Sentinel-1A数据特性及应用潜力分析[J]. 极地研究, 29(2): 286-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDYZ201702013.htm 任云, 2013. InSAR叠掩与阴影检测技术[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学. 唐晓松, 郑颖人, 唐辉明, 等, 2013. 水库滑坡变形特征和预测预报的数值研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 35(5): 940-947. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201305023.htm 王桂杰, 谢谟文, 邱骋, 等, 2011. 差分干涉合成孔径雷达技术在广域滑坡动态辨识上的实验研究[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 33(2): 131-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201102000.htm 王志勇, 张金芝, 2013. 基于InSAR技术的滑坡灾害监测[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 33(3): 87-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201303019.htm 徐帅, 王尚晓, 牛瑞卿, 2020. 基于InSAR技术的三峡库区巫山—奉节段潜在滑坡识别[J]. 安全与环境工程, 27(1): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ202001006.htm 游新兆, 李澍荪, 杨少敏, 等, 2001. 长江三峡工程库首区InSAR测量的初步研究[J]. 地壳形变与地震, 21(4): 58-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2001.04.008 中村浩之, 1990. 论水库滑坡[J]. 王恭先, 译, 水土保持通报, 10(1): 53-64. 张淼, 张春山, 杨为民, 等, 2014. 青海循化县查汗都斯水库滑坡形成条件与稳定性分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 20(3): 274-284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2014.03.006 占文俊, 李志伟, 韦建超, 等, 2015. 一种InSAR大气相位建模与估计方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(7): 2320-2329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201507010.htm 张芳, 2018. 星载InSAR问题区域检测技术研究以及工程化实现[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学. 中国地质灾害防治工程行业协会, 2018. 地质灾害InSAR监测技术指南: T∕CAGHP 013-2018 [S]. 北京: 中国地质大学出版社. 张同同, 杨红磊, 李东明, 等, 2019. SAR影像中叠掩与阴影区域的识别—以湖北巴东为例[J]. 测绘通报, (11): 85-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHTB201911017.htm 郑嘉豪, 黄波林, 张全, 等, 2020. 三峡库区龙门寨危岩体崩塌产生涌浪研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 533-543. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.046 -





 下载:
下载: