Characteristics of the Mianhuakeng fault and Youdong fault and their relation to uranium mineralization in the Changjiang uranium ore field, northern Guangdong
-
摘要: 长江铀矿田位于广东仁化县,是中国华南地区最重要的硬岩型铀矿田。铀矿田内发育北北西(近南北)向含矿构造和北东东向棉花坑断裂及北西西向油洞断裂。棉花坑断裂、油洞断裂与铀成矿的关系涉及到矿田控矿构造格局构建和进一步找矿预测等关键问题。通过精细野外地质调查,重点研究棉花坑断裂、油洞断裂与北北西(近南北)向含矿断裂的相互关系,特别是断裂构造发育的特点和相互配套关系,取得如下认识:棉花坑断裂为脆性断裂破碎带,以未胶结的含有磨圆的花岗岩角砾的构造角砾岩和断层泥为特征,线性构造和负地貌特征明显,属于成矿后压扭性断裂,断错铀矿体和铀矿化带,但位移不大;油洞断裂为脆性破碎带,具有线性构造和负地貌特征,为北北西(近南北)向控矿构造的伴生张扭性断裂,并局部被其后的基性岩脉充填,它不是高级序控矿断裂,仅仅起局部含矿构造作用;油洞断裂带附近的韧性变形不是油洞断裂的连续韧性变形带,而是油洞岩体内小规模、零星不规则、多方向韧性变形的一部分;基于含矿构造呈北北西(近南北)向的展布特征,矿田内进一步的找矿方向不是沿着棉花坑断裂或油洞断裂的方向,而是沿着北北西(近南北)向含矿构造及现有矿化带的走向和倾向深部,在现有矿带间空白区的深部也很可能存在隐伏矿带。Abstract: The Changjiang uranium ore field, located in Renhua county of Guangdong province, is the most important granite-type uranium ore field in southern China. There developed the NNW-trending (nearly SN-trending) ore-bearing fault structures, NEE-trending Mianhuakeng fault and NWW-trending Youdong fault. Understanding the characteristics of the Mianhuakeng fault and the Youdong fault and their relation to uranium mineralization is conducive to the building of ore-controlling structure system and further prospecting for uranium deposits. We carried out detailed field investigations, and focused on the analysis of the correlation between the Mianhuakeng fault, Youdong fault and NNW-trending (nearly SN-trending) ore-bearing faults, especially the development characteristics of fault structures and their combination with each other. Our key findings are as follows. (ⅰ) The Mianhuakeng fault is a brittle fracture belt, characterized by uncemented tectonic breccia and fault gouge containing well-rounded granite rubbles. It has obvious linear structures and negative geomorphic features, belonging to a post-mineralization compresso-shear fault, and it dislocates uranium ore body and uranium mineralization zone with small displacement; (ⅱ) The Youdong fault is a brittle fracture zone with linear structures and negative landforms. It is a tensional-torsional fault associated with NNW-trending (nearly SN-trending) ore-controlling structure and partially filled by subsequent mafic dikes. It is not a high degree ore-controlling fault and only plays a role of local ore-bearing structure; (ⅲ) There are several small ductile deformations near the Youdong fault, not that they formed a continuous ductile deformation belt resulting from the Youdong fault, but that they are ductile deformations inner the Youdong granite body with small scale, different strike and sporadic occurrence. (ⅳ) Based on the distribution of NNW-trending (nearly SN-trending) ore-bearing fault structures, the further prospecting for uranium deposits should be not along the Meihuakeng fault and Youdong fault, but along the NNW-trending (nearly SN-trending) fault belt, concentrated on the strike extending area and dipping deep area. In the meantime, there is a good chance for concealed ore zone at the surface and shallow parts of the vacancy for prospecting between existing ore zones.
-
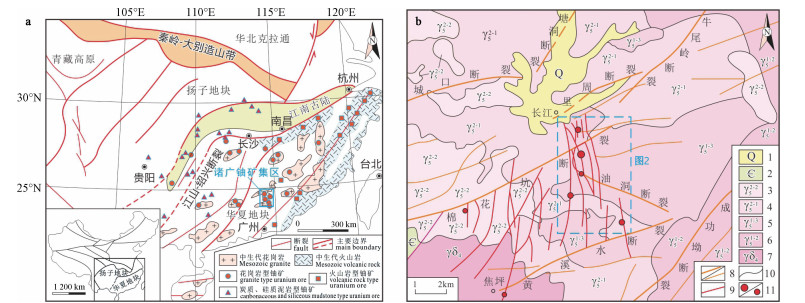
图 1 长江铀矿田大地构造与区域构造图
a—大地构造图(据Hu et al., 2008);b—长江铀矿田区域构造图(1—第四系;2—寒武系浅变质碎屑岩;3—燕山早期晚阶段花岗岩;4—燕山早期早阶段花岗岩;5—印支晚期花岗岩;6—印支早期花岗岩;7—海西期花岗闪长岩;8—主干断裂/次级断裂;9—铀矿带;10—地质界线;11—铀矿床;据黄国荣等,2012修改)
Figure 1. Tectonic and regional geologic map of the Changjiang uranium ore field
(a) Tectonic map of the Changjiang uranium ore field (Hu et al., 2008); (b) Regional geologic map of the Changjiang uranium ore field (1-Quaternary system; 2-Epimetamorphic clastic rock of Cambrian; 3-Granite of late stage of early Yanshanian epoch; 4-Granite of early stage of early Yanshanian epoch; 5-Granite of late Indo-Chinese epoch; 6-Granite of early Indo-Chinese epoch; 7-Granodiorite of Variscan epoch; 8-Main fault/secondary fault; 9-Uranium belt; 10-Geologic boundary; 11-Uranium deposit; modified from Huang et al., 2012)
图 2 粤北长江铀矿田地质图(据核工业北京地质研究院(2021)报告编制)
1—第四系;2—燕山晚期细粒二云母花岗岩;3—燕山晚期花岗斑岩;4—燕山晚期闪斜煌斑岩;5—燕山早期第三阶段细粒黑云母花岗岩;6—燕山早期第一阶段不等粒黑云母花岗岩;7—燕山早期第一阶段中粒黑云母花岗岩;8—印支期第三阶段中粒小斑状二云母花岗岩;9—印支期第二阶段中粒斑状黑云母二长花岗岩;10—碱交代岩;11—主要断层;12—次级断层;13—碱性岩脉;14—地质界线;15—岩性界线;16—铀矿带编号;17—大型铀矿床;18—中/小型铀矿床
Figure 2. Geologic map of the Changjiang uranium ore field, northern Guangdong (adapted from Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, 2021)
1- Quaternary system; 2-Fine grained micaceous granite of late Yanshanian epoch; 3-Granite porphyry of late Yanshanian epoch; 4-Spessartite of late Yanshanian epoch; 5-Fine grained biotite granite of third stage of early Yanshanian epoch; 6-Unequal-grained biotite granite of first stage of early Yanshanian epoch; 7-Medium-grained biotite granite of first stage of early Yanshanian epoch; 8-Medium-sized small porphyritic biotite granite of third stage of Indo-Chinese epoch; 9-Medium-grained porphyritic biotite adamellite of second stage of Indo-Chinese epoch; 10-Alkali netasomatic rock; 11-Main fault; 12-Second-order fracture; 13-Alkaline dike; 14-Geologic boundary; 15-Lithologic boundary; 16-Number of uranium belt; 17-Large uranium deposit; 18-Medium/small sized uranium deposit
图 4 棉花坑断裂旁侧次级裂隙构造特征平面照片
a—棉花坑断裂旁侧的北东向裂隙,仅为简单裂隙,未见矿化蚀变,Z74点;b—c—棉花坑断裂旁侧的近南北向裂隙,Z74点;d—f—棉花坑断裂北旁侧近南北向裂隙,可见有猪肝色硅化及晚期白色石英脉,Z29点
Figure 4. Pictures showing the second-order fracture on the side of the Mianhuakeng fault
(a) Picture showing the simple NE-trending fracture approaching the Mianhuakeng fault with non-alteration at Point Z74; (b-c) Pictures showing the nearly SN-trending fracture approaching the Mianhuakeng fault at Point Z74; (d-f) Pictures showing the nearly SN-trending fracture on the north side of the Mianhuakeng fault with purplish red silicification and late white calcite vein at Point Z29
图 5 棉花坑断裂破碎带剖面图(Z76点)
1—第四系残坡积;2—花岗岩;3—压扭性构造角砾岩;4—片理化带;5—断层;6—硅化带(石英脉)
Figure 5. Section of fracture zone of the Mianhuakeng fault in the Changjiang uranium ore field, northern Guangdong(Point Z76)
1-Quaternary residual slope; 2-Granite; 3-Compresso-shear tectonic breccia; 4-Foliated belt; 5-Fault; 6-Silicified zone(quartz vein)
图 6 油洞村北东电站旁油洞断裂旁侧裂隙与铀矿化特征(Z28点,57号铀矿带)
1—花岗岩;2—石英脉;3—节理裂隙;4—微细石英脉;5—伽玛异常及异常值/ (nC/ (kg ·h));6—产状
Figure 6. Sketch showing the fracture and uranium mineralization near the Youdong fault
1-Granite; 2-Quartz vein; 3-Joint and fracture; 4-Fine quartz vein; 5-Gamma anomaly and its value/ (nC/ (kg ·h)); 6-Attitude
图 7 油洞断裂旁侧铀矿化地质剖面图(Z67点)
1—碎裂花岗岩;2—节理;3—黄褐色硅化带;4—猪肝色硅化带;5—伽玛异常值/nC/ (kg ·h);6—产状
Figure 7. Sketch showing the fracture and uranium mineralization near the Youdong fault (Point Z67)
1-Cataclastic granite; 2-Joint; 3-Tawny silicified zone; 4-Purplish red silicified zone; 5-Gamma anomaly and its value/nC/ (kg ·h); 6-Attitude
图 8 油洞断裂旁侧铀矿化地质剖面图(Z23点)
1—碎裂花岗岩;2—晚期石英脉;3—节理;4—伽玛异常等值线;5—硅化;6—弱铀矿化黄褐色硅化带(30 nC/ (kg ·h)≤伽玛值≤40 nC/ (kg ·h));7—强铀矿化(伽玛值≥40 nC/ (kg ·h))猪肝色硅化带;8—伽玛异常值/ (nC/ (kg ·h));9—产状;10—水池
Figure 8. Sketch showing the fracture and uranium mineralization near the Youdong fault (Point Z23)
1-Cataclastic granite; 2-Late quartz vein; 3-Joint; 4-Gamma anomaly isoline; 5-Silicification; 6-Tawny silicified zone with weak uranium mineralization(30 nC/ (kg ·h)≤gamma value≤40 nC/ (kg ·h)); 7-Purplish red silicified zone with intensive uranium mineralization; 8-Gamma anomaly value/ (nC/ (kg ·h)); 9-Attitude; 10-Cistern
图 9 油洞村油洞断裂及基性岩脉与铀矿化的关系平面素描图(Z32点)
1—花岗岩;2—基性岩脉;3—石英脉;4—片理化;5—断层;6—裂隙节理;7—赤铁矿化界线;8—赤铁矿化;9—裂隙产状;10—放射性异常辐射值/ (nC/ (kg ·h));11—弱铀矿化(50 < γ≤200 nC/ (kg ·h));12—中等铀矿化(200 < γ≤300 nC/ (kg ·h));13—强铀矿化(300 < γ≤800 nC/ (kg ·h))
Figure 9. Picture and sketch showing the relation of the Youdong fault and basic dike to uranium mineralization
1-Granite; 2-Basic dike; 3-Quartz vein; 4-Foliation; 5-Fault; 6-Joint and fracture; 7-Range of hematite mineralization; 8-Hematite mineralization; 9-Attitude of fracture; 10-Gamma Anomaly value/ (nC/ (kg ·h)); 11-Weak uranium mineralization (50 < γ≤200 nC/ (kg ·h)); 12-Moderate uranium mineralization (200 < γ≤300 nC/ (kg ·h)); 13-Intensive uranium mineralization (300 < γ≤800 nC/ (kg ·h))
图 10 长江铀矿田油洞岩体内不同方向的局部韧性变形
a—学堂垇一带,近南北向韧性变形带,原岩为花岗岩,镜头指向西下,D2100点;b—学堂垇一带,近东西向韧性变形带,原岩为花岗岩,镜头指向南下,D2100点北;c—学堂垇一带,近东西向韧性变形带,原岩为花岗岩,镜头指向南下,D2100点北;d—长江1号科学钻孔,68回次,陡倾角韧性变形带;e—图d局部放大;f—9号带南段ZK15-3钻孔220 m附近缓倾角韧性变形带
Figure 10. Pictures showing ductile deformations of different directions in several places of the Youdong granite body
(a) Picture showing the nearly SN-trending ductile deformation developed in the granite at Point D2100, Xuetang' ao; (b) Picture showing the nearly EW-trending ductile deformation developed in the granite at the north of Point D2100, Xuetang' ao; (c) Picture showing the nearly EW-trending ductile deformation developed in the granite at point D2100, Xuetang' ao; (d) Picture showing steep-dip ductile deformation developed in the granite ore from the 68th drilling trip of the Changjiang No.1 scientific drilling hole; (e) Local magnification of Fig. 10d; (f) Picture showing gentle-dip ductile deformation developed in the granite ore from 220-m drilling depth of the ZK15-3 drilling hole, southern part of No.9 uranium ore belt
图 11 长江铀矿田构造演化图
1—含矿断裂;2—铀矿带;3—基性岩脉;4—断层(不含矿);5—压性断裂/压扭性断裂;6—张性断裂/张扭性断裂;7—主应力及其方向
Figure 11. Evolution model of the structures in the Changjiang uranium ore field
1-Ore-bearing fault; 2-Uranium ore belt; 3-Basic dike; 4-Fault (ore-free); 5-Compressive/compresso-shear fault; 6-Extensional/tenso-shear fault; 7-Principal stress and its direction
-
Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology. 2021. Study on prediction and resources enlargement in the deep and peripheral area of granite-type uranium deposit, southern Zhuguang[R]. Beijing, Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, 1-194. (in Chinese) BONNETTI C, LIU X D, MERCADIER J, et al., 2018. The genesis of granite-related hydrothermal uranium deposits in the Xiazhuang and Zhuguang ore fields, north Guangdong province, SE China: insights from mineralogical, trace elements and U-Pb isotopes signatures of the U mineralisation[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 92: 588-612. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.12.010 CAI M H, LI Z S, ZHANG S J, 2011. Study on the ore-forming structure in Changjiang area, Renhua county, Guangdong province[R]. Shaoguan: Research institute No. 290, China National Nuclear Corporation. (in Chinese) CAO H J, HUANG G L, XU L L, et al., 2013. The Ar-Ar age and geochemical characteristics of diabase dykes of the Youdong fault zone in south of Zhuguang granite pluton[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(7): 957-966. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN B L, 2020. Development process of fault structure and formation and evolution of ore-controlling structure: a case study of the Zoujiashan uranium deposit[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(3): 285-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN B L, GAO Y, SHEN J H, et al., 2021. Analysis of ore-controlling structure of Changjiang Uranium ore field, Northern Guangdong[J/OL]. Earth Science. (2021-05-25). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.p.20210524.1725.006.html. (in Chinese with English abstract) DENG P, REN J S, LING H F, et al., 2011. Yanshanian granite batholiths of southern Zhuguang Mountian: SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb dating and tectonic implications[J]. Geological Review, 57(6): 881-888. (in Chinese with English abstract) FENG H S, YIN Z P, XU W X, et al., 2009. Minerogenetic charactetristic and prospecting potential of the deeping of Mianhuakeng Uranium deposit in Southern Zhuguang Granite batholith[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 32(2): 101-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) FU L W, SUN L Q, LING H F, et al., 2016. Study on the source of ore-forming fluid and ore-forming material of the 302 uranium deposit in northern Guangdong province: evidence from H-O-Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 22(1): 43-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) GAO X, SHEN W Z, LIU L L, et al., 2011. Geochemical characteristics and causes of wall rock alteration in the No. 302 uranium deposit, northern Guangdong[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30(1): 71-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO C Y, XU H, BAI Y, et al., 2013. A discussion on the rules of structural ore-controlling of the Changjiang uranium ore field, northern Guangdong[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 33(S2): 207-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO G L, LIU X D, PAN J Y, et al., 2010. Study of fluid inclusion from uranium deposit No. 302 in north Guangdong[J]. Uranium Geology, 26(6): 350-354, 368. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU R Z, BI X W, ZHOU M F, et al., 2008. Uranium metallogenesis in south China and its relationship to crustal extension during the Cretaceous to Tertiary[J]. Economic Geology, 103(3): 583-598. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.103.3.583 HUANG G L, CAO H J, LING H F, et al., 2012. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Age, geochemistry and genesis of the Youdong granite in Northern Guangdong[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(4): 577-586. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG G L, LIU X Y, SUN L Q, et al., 2014. Zircon U-Pb dating, geochemical characteristic and genesis of the Changjiang granite in northern Guangdong[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(5): 836-849. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG G L, CAO H J, XU W X, et al., 2015. Vertical zoning model and prospecting potential in depth of Mianhuakeng uranium deposit in Zhuguang[J]. Uranium Geology, 31(3): 355-362. (in Chinese with English abstract) LEE J S, 1973. Introduction to geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-136. LI J, ZHANG W L, GAO M Q, et al., 2019. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb isotopic dating age of fine-grained granite in Lujing uranium field and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 33(3): 489-495, 501. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI S Z, CAO X Z, WANG G Z, et al., 2019. Meso-cenozoic tectonic evolution and plate reconstruction of the pacific plate[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 642-677. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J G, LI Z Y, NIE J T, et al., 2019. Study on structural properties and prospecting significance of Youdong fault in Changjiang Uranium orefield, South Zhuguang[J]. Uranium Geology, 35(4): 199-205. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU J L, QIN M K, CAI Y Q, et al., 2019. Fluid inclusion studies of the Changpai area in Zhuguang mountain, northern Guangdong province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 38(2-3): 388-396. (in Chinese with English abstract) LUO Q, XU Y, FU S C, et al., 2020. Uranium metallogenic geological characteristics and prospecting potential in Zhuguang Changjiang ore field[J]. Mineral Exploration, 11(2): 276-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) PANG Y Q, XU W X, KUANG Z P, et al., 2015. Geochemical characteristics of primary halo and predicting indications for deep exploration in Mianhuakeng uranium deposit, northern Guangdong province[J]. Uranium Geology, 31(6): 582-588. (in Chinese with English abstract) PANG Y Q, FAN H H, GAO F, et al., 2019. Helium and argon isotopic compositions of fluid inclusions and tracing to the source of ore-forming fluids for the southern Zhuguang uranium ore field in northern Guangdong Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2765-2773. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.09 QI J M, ZHU B, WU J Y, et al., 2019. The evolution of ore-forming fluid and its constraint on mineralization process in Mianhuakeng uranium deposit, northern Guangdong, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(9): 2711-2726. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.09.06 SHEN W Z, LING H F, DENG P, et al., 2010. Study on isotope geochemistry of uranium deposit 302 in northern Guangdong province[J]. Uranium Geology, 26(2): 80-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) XIA Y L, 2019. Geochronology of uranium mineralization in China[M]. Beijing: China Atomic Energy Press: 1-301. (in Chinese) XU H, ZHANG C, PANG Y Q, et al., 2018. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids of the Changpai Uranium deposit in Guangdong province[J]. Geoscience, 32(5): 902-912. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU W X, TAN Z Y, LUO C W, et al., 2014. Geochemical characteristic and ore forming geological significance of fine crystalline granite in Mianhuakeng uranium deposit, northern Guangdong[J]. Uranium Geology, 30(6): 345-355. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU W X, FU S C, XU Y, et al., 2017. Analysis of prospecting potential in the depth of Shulouqiu uranium deposit in southern Zhuguangshan pluton[J]. Mineral Exploration, 8(5): 782-788. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU X W, NIU L, HONG T, et al., 2019. Tectonic dynamics of fluids and metallogenesis[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) YAO Z K, 1983. The geotectonic types and their main character of uranium deposits in China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 7(2): 117-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) YE S X, XU Y, 2019. Characteristics of fault structure in Changjiang ore contrated area and it's relation to uranium ore-forming, southern Zhuguang area[J]. Science & Technology Vision(12): 107-108, 64. (in Chinese) ZENG G Q, LIU N, CHEN B L, 2021. Influence of fluid flow on rheological behavior of rocks: a case study of Tangdong ductile shear zone in northern Guangdong[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 41(2): 247-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG A, LIU C D, YU Z L, et al., 2009. The features and geochronology of alkali metasomatic rock in southern Zhuguang uranium mineralization area[J]. Journal of East China institute of Technology, 32(3): 209-212. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG C, CAI Y Q, XU H, et al., 2016. Mineralization mechanism of 302 Uranium deposit, north Guangdong province: evidence from fluid inclusions[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology, 39(2): 156-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG C, CAI Y Q, Xu H, et al., 2017. Mechanism of mineralization in the Changjiang uranium ore field, South China: Evidence from fluid inclusions, hydrothermal alteration, and H-O isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 86: 225-253. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.01.013 ZHANG G Q, HU R Z, BI X W, et al., 2007. REE geochemical characteristics of the No. 302 Uranium deposit in northern Guangdong, South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 26(4): 425-433. doi: 10.1007/s11631-007-0425-8 ZHONG F J, PAN J Y, QI J M, et al., 2018. New in-situ LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages of Uraninite from the Mianhuakeng Uranium deposit, Northern Guangdong province, China: constraint on the metallogenic mechanism[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 92(2): 852-854. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13558 ZHONG F J, PAN J Y, WU J H, et al., 2019a. Petrogenesis and its relationship with uranium mineralization of gabbro-diorite in Changjiang Uranium ore-field, Northern Guangdong province, China[J]. Earth Science, 44(9): 3042-3059. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHONG F J, PAN J Y, ZHANG W M, et al., 2019b. Magmation, tectonic activity and uranium mineralization events of southern Zhuguang uranium ore-concentrated district, northern Guangdong, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(S1): 108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU H B, PAN J Y, ZHONG F J, et al., 2018. Genesis of fine grained biotite granite in the Changjiang uranium ore field, northern Guangdong of China, and its relation with uranium mineralization[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 38(1): 10-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) 蔡明海, 李钟枢、张丗佳, 2011. 广东省仁化县长江地区成矿构造研究[R]. 韶关: 核工业290研究所. 曹豪杰, 黄国龙, 许丽丽, 等, 2013. 诸广花岗岩体南部油洞断裂带辉绿岩脉的Ar-Ar年龄及其地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 87(7): 957-966. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.07.005 陈柏林, 2020. 断裂构造发育过程与控矿构造形成演化: 以邹家山铀矿床为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(3): 285-298. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.03.027 陈柏林, 高允, 申景辉, 等, 2021. 粤北长江铀矿田控矿构造解析[J/OL]. 地球科学. (2021-05-25). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.p.20210524.1725.006.html. 邓平, 任纪舜, 凌洪飞, 等, 2011. 诸广山南体燕山期花岗岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 57(6): 881-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201106011.htm 冯海生, 尹征平, 徐文雄, 等, 2009. 诸广山棉花坑铀矿深部矿化特征及找矿前景[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 32(2): 101-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2009.02.001 傅丽雯, 孙立强, 凌洪飞, 等, 2016. 粤北302铀矿床成矿流体与成矿物质来源研究: H、O、Sr、Nd同位素证据[J]. 高校地质学报, 22(1): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201601004.htm 高翔, 沈渭洲, 刘莉莉, 等, 2011. 粤北302铀矿床围岩蚀变的地球化学特征和成因研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 30(1): 71-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.01.007 郭春影, 徐浩, 白芸, 等, 2013. 粤北长江铀矿田构造控矿规律初探[J]. 矿物学报, 33(S2): 207-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2013S2116.htm 郭国林, 刘晓东, 潘家永, 等, 2010. 粤北302铀矿床流体包裹体研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 26(6): 350-354, 368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2010.06.005 核工业北京地质研究院. 2021. 诸广南部花岗岩型铀矿深部及外围资源预测与扩大研究[R]. 北京: 核工业北京地质研究院, 1-194. 黄国龙, 曹豪杰, 凌洪飞, 等, 2012. 粤北油洞岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其成因研究[J]. 地质学报, 86(4): 577-586. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.04.004 黄国龙, 刘鑫扬, 孙立强, 等, 2014. 粤北长江岩体的锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及其成因研究[J]. 地质学报, 88(5): 836-849. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201405003.htm 黄国龙, 曹豪杰, 徐文雄, 等, 2015. 诸广棉花坑铀矿床垂向分带模式及深部找矿潜力[J]. 铀矿地质, 31(3): 355-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0658.2015.03.001 李嘉, 张万良, 高梦奇, 等, 2019. 鹿井铀矿田细粒花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及意义[J]. 矿产与地质, 33(3): 489-495, 501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201903018.htm 李三忠, 曹现志, 王光增, 等, 2019. 太平洋板块中-新生代构造演化及板块重建[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(5): 642-677. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.05.060 李四光, 1973. 地质力学概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-136. 刘佳林, 秦明宽, 蔡煜琦, 等, 2019. 粤北诸广山岩体南部长排矿区流体包裹体研究[J]. 地质通报, 38(2-3): 388-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2019Z1019.htm 刘军港, 李子颖, 聂江涛, 等, 2019. 诸广南长江铀矿田油洞断裂性质及其找矿意义研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 35(4): 199-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201904002.htm 罗强, 许幼, 伏顺成, 等, 2020. 诸广长江矿田铀矿地质特征及找矿潜力[J]. 矿产勘查, 11(2): 276-285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS202002012.htm 庞雅庆, 徐文雄, 匡正平, 等, 2015. 粤北棉花坑铀矿床原生晕地球化学特征与深部找矿预测标志[J]. 铀矿地质, 31(6): 582-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201506006.htm 庞雅庆, 范洪海, 高飞, 等, 2019. 粤北诸广南部铀矿田流体包裹体的氦氩同位素组成及成矿流体来源示踪[J]. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2765-2773. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201909009.htm 祁家明, 朱捌, 吴建勇, 等, 2019. 粤北仁化棉花坑铀矿床成矿热液演化及其对成矿过程的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 35(9): 2711-2726. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201909006.htm 沈渭洲, 凌洪飞, 邓平, 等, 2010. 粤北302铀矿床同位素地球化学研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 26(2): 80-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201002003.htm 夏毓亮, 2019. 中国铀成矿地质年代学[M]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社: 1-301. 徐浩, 张闯, 庞雅庆, 等, 2018. 广东长排铀矿床成矿流体特征[J]. 现代地质, 32(5): 902-912. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201805004.htm 徐文雄, 谭忠银, 罗春梧, 等, 2014. 棉花坑铀矿床花岗质脉岩地球化学特征及其与铀成矿的关系[J]. 铀矿地质, 30(6): 345-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201406005.htm 徐文雄, 伏顺成, 许幼, 等, 2017. 诸广山岩体南部书楼丘铀矿床深部找矿潜力分析[J]. 矿产勘查, 8(5): 782-788. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201705008.htm 徐兴旺, 牛磊, 洪涛, 等, 2019. 流体构造动力学与成矿作用[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(1): 1-8. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.01.001 姚振凯, 1983. 我国铀矿床的大地构造类型及其主要特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 7(2): 117-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK198302002.htm 叶松鑫, 许幼, 2019. 诸广南部长江矿集区断裂构造特征及其与铀成矿关系[J]. 科技视界(12): 107-108, 64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJSJ201917051.htm 曾广乾, 刘南, 陈柏林, 2021. 流体作用对岩石流变行为的影响: 以粤北塘洞韧性剪切带为例[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 41(2): 247-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLGX202102001.htm 张爱, 刘成东, 余志灵, 等, 2009. 诸广南部铀矿区碱交代岩特征及同位素年代学研究[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 32(3): 209-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ200903004.htm 张闯, 蔡煜琦, 徐浩, 等, 2016. 粤北302铀矿床成矿机制探讨: 来自流体包裹体的证据[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 39(2): 156-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201602009.htm 钟福军, 潘家永, 巫建华, 等, 2019a. 粤北长江铀矿田辉长闪长岩的岩石成因及其与铀成矿的关系[J]. 地球科学, 44(9): 3042-3059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201909020.htm 钟福军, 潘家永, 张伟盟, 等, 2019b. 粤北诸广南铀矿聚集区岩浆、构造与铀成矿活动[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(S1): 108-114. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.S1.018 周航兵, 潘家永, 钟福军, 等, 2018. 粤北长江铀矿田细粒黑云母花岗岩的成因及其与铀成矿关系[J]. 矿物岩石, 38(1): 10-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201801003.htm -





 下载:
下载: