Experimental study on the dynamic rupture of coal and rock caused by high-pressure gas
-
摘要: 为了研究高压气体对煤岩材料变形破坏的作用,自主设计并制造了含高压气体煤岩实验装置,通过测量气体泄压作用诱发的煤岩动力破坏现象,研究了高压气体对煤岩材料变形破坏的作用。实验表明,当气体泄压速率小时,煤岩仅会出现轻微变形;当气体泄压速率大时,煤岩会产生破裂和破碎现象。同时发现煤岩的破坏程度不仅取决于气体的泄压速率,还取决于孔隙气体的压强。当气体泄压速率和气体压强都达到一定临界值时,煤岩才会发生剧烈破碎。通过气体压强与应变之间的关系,确定了煤岩发生破裂和破碎的临界气体压强。Abstract: A special test apparatus has been designed and used to study the effect of high-pressure gas on the deformation and failure of coal and rock. Dynamic ruptures of coal and rock are carried out by gas decompression. The results show that low gas decompression rate only causes deformation of coal specimens slightly while high gas decompression rate leads to fracture and outburst phenomenon. The degree of damage of rocks depends on not only the gas decompression rate but also the gas pressure. Violent fragmentation occurs when gas decompression rate and high saturation pressure reach critical values. According to the relationship between the decompressed gas pressure and strain, the critical gas pressures are determined for the fracture and fragmentation of specimens.
-
Key words:
- gas decompression /
- deformation /
- fracture /
- fragmentation /
- critical gas pressure
-
0. 引言
盾构隧道在砂土地层中施工时开挖面失稳可能性很大,一旦发生会造成极其严重的损失。防止开挖面失稳的关键是合理设置不同盾构支护平衡模式下的支护压应力。针对这一问题,目前主要的研究成果集中在临界状态下开挖面的整体失稳上,如工程中广泛应用的筒仓楔形体模型的极限平衡法[1]和塑性上、下限理论极限分析法[2~3]均是假设开挖面整体失稳。然而,工程实践和模型试验都证明盾构隧道开挖面失稳主要以局部失稳为主。Chambon[4]和Oblozinsky[5]通过三维离心试验发现,与刚性活塞支护模式下全断面失稳不同,静水压应力支护模式下开挖面上半部失稳。Berthoz[6]利用大比例土压盾构模型试验研究发现,土压平衡支护模式下开挖面上半部失稳。这说明,不同支护模式下,开挖面失稳区不同。对于发生这种现象的原因,目前还未见文献报道。随着国内外盾构隧道建设的日益增多,合理确定不同支护模式下盾构支护压应力尤为重要,要确定盾构支护压应力首先必须明确开挖面前方土体对刀盘的压应力分布形式。
不同支护模式下,开挖面前方土体对刀盘的压应力分布模式和大小直接决定了支护压应力的大小和作用效果。盾构掘进遇到障碍物如切削桩基时[7]和双洞盾构[8]近距离施工时,合理的支护压应力对隧道的稳定性起着决定性作用。但长期以来相关学者一直假定楔形体为刚性且开挖面前方土体对刀盘的压应力均匀分布[9~10],不考虑刀盘与松动土体之间的摩擦力,而且水平土压应力系数依赖经验确定。武军等[11]在考虑松动土体内的三维土拱效应和开挖土体与刀盘的摩擦力的基础上,改进了筒仓楔形体模型,并通过与模型试验结果的对比分析,验证了该计算方法的合理性。在此基础上,文章进一步通过理论推导,分析开挖面所受应力的分布形式,研究了不同支护方式下的开挖面稳定性,最后给出了公式的简化计算方法,以方便实际工程运用。
1. 松动区土体对刀盘的压应力
根据武军等[11]的推导,开挖面前方松动土体对刀盘的水平压应力σh为
σh=(fz2+gz+σH)k2 (1) 公式(1)中:z为以计算点与盾构最低点的垂向距离,m;σH为楔形体上覆土压应力,kPa;可由公式(2)求得:
σH=Rγ−ck1tanφ(1−e−k1tanφHR)+σ0e−k1tanφHR (2) 公式(2)中:c为土的粘聚力,kPa;γ为土体容重,kN ·m-3;σ0为地表竖向均布荷载,kPa;φ为土体内摩擦角,(°);H为隧道上覆土厚度,m;R为参数,可按公式(3)确定:
R=BDtanω2(B+Dtanω) (3) 公式(3)中:B=(πD)/4;ω= 45°-φ/2;D为盾构隧道开挖直径,m。当σ0=0且c=Rγ时,σH为负值,此时取σH=0;f, g为计算参数,其表达式分别如下:
f=σH2D2[(a+bD)2−a]−r2D(a+bD) (4) g=r−σH(b+aD) (5) r、a、b为计算参数:
r=γ−2cB (6) a=k2tanδtanω (7) b=2k1tanφB (8) 公式中δ为松动土体与刀盘间的摩擦角,(°);k1, 2[12]为土拱区内的水平土压力系数,其表达式为:
k1,2=3(cos2θ1,2+kasin2θ1,2)3−(1−ka)cos2θ1,2 (9) 公式(9)中:ka为郎肯主动土压力系数,ka=tan2(45°-φ/2);θ1, 2为公式(10)、(11)确定的较大值:
θ1=arctan(1−ka±√(1−ka)2−4tan2δka2tanφka) (10) θ2=arctan(1−ka±√(1−ka)2−4tan2δka2tanδka) (11) 将公式(1)沿隧道直径D积分,求得松动土体对刀盘的平均压应力σah:
σah=(13fD2+12gD+σC)k2 (12) 2. 不同支护模式下支护应力分布
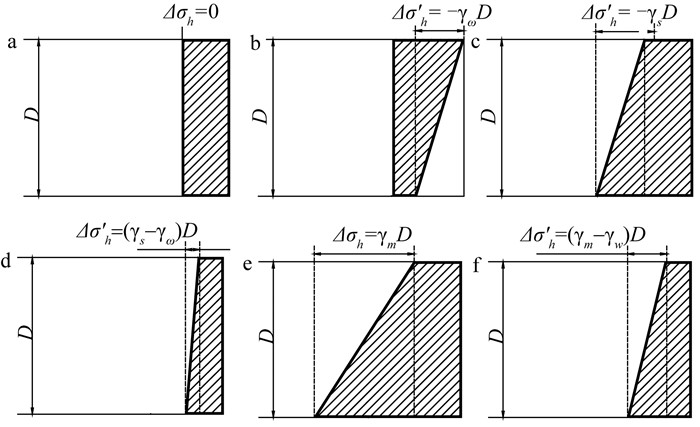
目前常用的盾构支护模式有气压平衡支护、泥水平衡支护和土压平衡支护三种。理论上有效支护压应力均匀分布的只有开挖面在地下水位以上时的气压平衡支护模式,如图 1a所示;当开挖面在地下水位以下时,一部分气压支护力用以平衡地下水压应力,由于水压应力沿深度呈线性分布,因此作用在开挖面上的有效支护压应力呈上大下小的梯形分布,如图 1b所示;在泥水平衡支护模式下,当开挖面在地下水位以上时,支护力沿竖直方向呈上小下大的梯形分布,梯度为γs(γs为泥水容重),如图 1c所示;当开挖面在地下水位以下时,一部分泥水支护力用以平衡地下水压应力,作用在开挖面上的有效支护压应力也呈上小下大的梯形分布,但梯度减小为γs-γw(γw为地下水容重),根据膨润土和含泥量的不同,泥水容重也不同,但一般情况下在11~12 kN ·m-3之间,因此有效泥水支护应力梯度很小,近似于均匀分布,如图 1d所示;在土压平衡支护模式下,由于渣土会被改良为具有流动性的塑形状态,可忽略渣土的剪切强度,因此渣土压应力分布可假设为静水压应力分布,当开挖面在地下水位以上时,支护力沿竖直方向线性分布,梯度为γm(γm为渣土容重),当开挖面在地下水位以下时,有效支护力沿竖直方向线性分布,梯度为γm-γw,一般情况下,土压平衡模式支护力梯度大于泥水平衡模式支护力梯度,如图 1e、1f所示。
3. 不同支护模式下开挖面受力分析
文章假设不考虑渗透力对开挖面稳定性的影响。为不失一般性,取γ=18 kN ·m-3、γ′=10 kN ·m-3、γw=10 kN ·m-3、γs=12 kN ·m-3、γm=18 kN ·m-3。如图 2所示,在三种平衡支护模式下,开挖面失稳均非全断面整体失稳,而是局部失稳。
 图 2 不同支护模式下开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态图a—气压支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;b—气压支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;c—泥水支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;d—泥水支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;e—土压支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;f—土压支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态Figure 2. The distribution of the stress along the depth of the face with compressed air, pressurized slurry and earth pressure balanced shield
图 2 不同支护模式下开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态图a—气压支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;b—气压支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;c—泥水支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;d—泥水支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;e—土压支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态;f—土压支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力沿深度的分布状态Figure 2. The distribution of the stress along the depth of the face with compressed air, pressurized slurry and earth pressure balanced shield气压平衡支护模式下,开挖面在地下水位以上,当φ=0°时,不论粘聚力多大,土体均从刀盘下半部分挤入,开挖面下半部失稳; 当φ>0°时,随着内摩擦角的增大,失稳区逐步从开挖面下半部分向上移动,同时当φ值一定时,随着粘聚力的减小,失稳区逐步上移,如图 2a所示。气压平衡支护模式下,开挖面在地下水位以下时,由于有效气压支护力上大下小分布,开挖面均在下半部分失稳,如图 2b所示。需要说明的是:模型试验中采用的气压支护与实际工程中的并不相同,模型试验中的气体并不直接作用于土体而是被填充在橡胶袋中,通过橡胶薄膜支护开挖面,开挖面局部失稳后,失稳土体挤压橡胶膜,由于橡胶膜的张力使得作用在剩余稳定土体的压应力减小,继而引起失稳部位上部未稳定土体坍塌,所以最终表现为Oblozinsky[5]、Thorpe[14]试验中的整体失稳或上部约3/4断面失稳。实际工程中,开挖面局部土体失稳后形成类似于重力挡土墙的堆积体阻止开挖面的进一步失稳,堆积体的增大,最终能阻止开挖面的失稳。
泥水平衡支护模式下,开挖面在地下水位以上,当φ=0°时,土体从刀盘下半部分挤入,开挖面下半部失稳,但是当φ≠0°时,开挖面均在上半部失稳,如图 2c所示,这与Chambon[4]和Oblozinsky[5]的离心模型试验结果规律性是一致的。开挖面在地下水位以下,当φ=0°时,土体从刀盘下半部分挤入,开挖面下半部失稳,而当φ>0°时,随着内摩擦角的增大,失稳区逐步从开挖面下半部分向上移动,同时当φ值一定时,失稳区随着粘聚力的减小,失稳区逐步上移,如图 2d所示。这与气压平衡支护模式下,开挖面在地下水位以上时,开挖面的失稳规律相同,其原因是该情况下有效泥水支护应力梯度很小,近似于均匀分布。
土压平衡支护模式下,开挖面在地下水位以上时,开挖面均在上半部失稳,如图 2e所示。这与Berthoz[6]的大比例模型试验结果规律性是一致的,造成这种现象的原因是该情况下支护力梯度较大导致开挖面下半部支护压应力大于松动土压应力。土压平衡支护模式下,开挖面在地下水位以下时,由于有效支护力梯度的减小,当φ=0°时,土体从刀盘下半部分挤入,开挖面下半部失稳,而当φ>0°时,随着内摩擦角的增大,失稳区逐步从开挖面下半部分向上移动,同时当φ值一定时,失稳区随着粘聚力的减小,失稳区逐步上移,如图 2f所示,这与图 2a、2d表示的规律相同。
根据武军等[11]的分析,粘聚力不影响开挖土体对刀盘的压应力的分布形式,当C/D≥1.5时,埋深对于松动土体对刀盘的压应力大小和分布形式影响不明显;当φ≥30°时,砂土内摩擦角对于松动土体对刀盘的压应力大小和分布形式影响也不明显;而刀盘与开挖土体间的外摩擦角大小直接影响开挖土体对刀盘的压应力大小和分布形式,因此有必要分析不同支护模式下开挖面失稳和刀盘与开挖土体间外摩擦角的关系。
气压平衡支护模式下,开挖面在地下水位以上时,随着外摩擦角发挥程度的增加,开挖面失稳区逐步从开挖面下半部分向上移动,外摩擦角的发挥程度与地层条件、刀盘开口率有直接关系,如图 3a所示。在透气性小的土体中,气体有可能会在刀盘与土体形成厚度很小的气垫层,减小外摩擦角。刀盘开口率较大时,气体和松动土体直接接触的面积增加,而气体和土体间的摩擦角近似为零,因此开口率增大也会降低外摩擦角。气压平衡支护模式下,开挖面在地下水位以下时,开挖面失稳区位于下半部,与外摩擦的发挥程度关系不大,如图 3b所示。泥水平衡支护模式下,外摩擦角的大小主要与泥膜的质量和厚度有关,泥膜质量好、厚度大,外摩擦角就小。当开挖面在地下水位以上时,外摩擦角的大小对开挖面失稳区域的影响不大,失稳区均位于开挖面上半部分;而开挖面在地下水位以下时,失稳区也位于开挖面上半部分,但失稳程度不同,如图 3c、3d所示。这说明开挖面在地下水位以上时,泥膜的的质量和厚度对开挖面最终的失稳破坏影响不大,但在有地下水的条件下,泥膜的质量和厚度对开挖面最终的失稳破坏程度有较大影响。土压平衡支护模式下,外摩擦角的大小主要与渣土改良的好坏和刀盘开口率的大小有关,渣土改良质量好、刀盘开口率的大,外摩擦角就小。无论开挖面在地下水位以上还是以下,开挖面均在其上部失稳,外摩擦角的大小对其影响不大,如图 3e、3f所示。这说明渣土改良和刀盘开口率的大小对开挖面最终的失稳影响不大。
 图 3 不同支护模式下开挖面合应力与δ的关系图a—气压支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力与δ的关系;b—气压支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力与δ的关系;c—泥水支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力与δ的关系;d—泥水支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力与δ的关系;e—土压支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力与δ的关系;f—土压支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力与δ的关系Figure 3. Change of the resultant pressure distributions on work face with δ with compressed air, pressurized slurry and earth pressure balanced shield
图 3 不同支护模式下开挖面合应力与δ的关系图a—气压支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力与δ的关系;b—气压支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力与δ的关系;c—泥水支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力与δ的关系;d—泥水支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力与δ的关系;e—土压支护模式下地下水位以上开挖面合应力与δ的关系;f—土压支护模式下地下水位以下开挖面合应力与δ的关系Figure 3. Change of the resultant pressure distributions on work face with δ with compressed air, pressurized slurry and earth pressure balanced shield支护压应力设定后,在盾构停机状态下,支护压应力直接通过刀盘上的开口作用于土体,在盾构掘进状态下,支护压应力对土体的作用还受刀盘转动摩擦力和土体进入土舱过程中刀盘对土体产生的向上滑动摩擦力的影响,但是当刀盘旋转切削土体时,土体对刀盘的转动摩擦力合力为一个力偶,该力偶与刀盘扭矩相互平衡,因此土体与刀盘间的转动摩擦力不对开挖面稳定产生影响[11],刀盘对土体产生的向上滑动摩擦力由外摩擦决定。但通过以上分析发现,对于土拱效应明显的砂土地层来说,除气压平衡支护模式下其开挖面在地下水位以上时,外摩擦角对开挖面失稳有较大影响,其余支护模式下,外摩擦角对开挖面失稳影响较小。因此,在砂性地层中,支护压应力的大小设定对防止开挖面失稳最为关键。需要说明的是:由该节分析可知,在各种不同支护模式下,并未发生如筒仓楔形体模型假设的开挖面整体失稳,而是发生了开挖面的局部失稳,而某些局部失稳土体所受的拉应力很大,开挖面的变形随着支护压应力的变小逐步增大,其所受的应力也是逐步变化的,这说明在未到达筒仓楔形体模型所假设的开挖面整体失稳前,开挖面已经发生了局部失稳。这种机理还有待研究,但是对于盾构隧道来说,以筒仓楔形体模型确定的极限稳定支护力是不安全的。
4. 简化设计方法
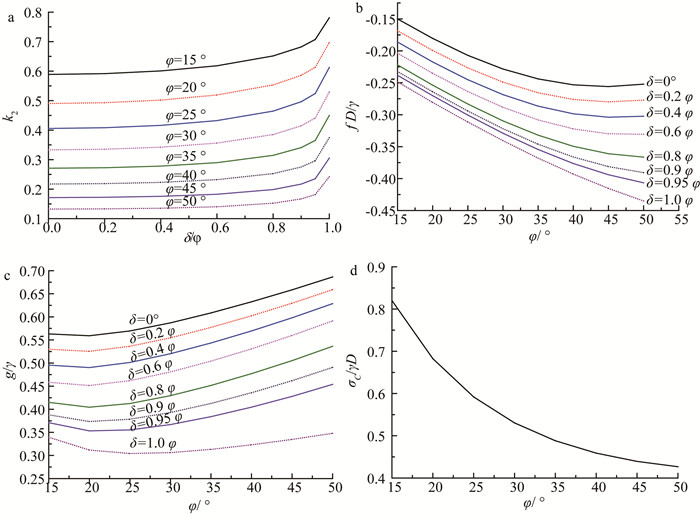
公式(1)和(11)计算过程较为复杂,因此给出C/D=2.0、c=0 kPa时,工程实践中常遇到的土体参数范围内的设计参数k2、f、g、σC无量纲化关系图,如图 4所示,以方便工程设计使用。根据文献[11],当φ≥15°且C/D≥1.5时,粘聚力c和埋深C对松动土体对刀盘压应力的影响不大,因此,图 4也可用于C/D≥1.5、c>0 kPa的情况,且偏于安全。
进一步分析可知,水平土压应力系数k2随着内摩擦角φ的增大而减小,同时当δ/φ≤0.85时,k2随着δ/φ的增加缓慢增大,当δ/φ≥0.85时,k2随着δ/φ的增加快速增大,如图 4a所示。(fD)/γ随着δ/φ的增加而减小,同时当φ≤40°时,(fD)/γ随着φ的增加而快速减小,当φ≥40°时,减小速率变的较为缓慢,如图 4b所示。当φ≤20°时,g/γ随着φ的增大缓慢减小,当φ≥20°时,g/γ随着φ的增大快速增大,如图 4c所示。当φ≤40°时,σC/(γD)随着φ的增大快速减小,当φ≥40°时,减小速率变的较为缓慢,如图 4d所示。
5. 结论
文章通过分析在气压支护模式、泥水支护模式和土压支护三种模式下,盾构隧道开挖面分别在地下水位以上和地下水位以下时所受应力的分布形式以及稳定性,得出如下结论:
(1) 刀盘与松动土体之间的摩擦力对开挖面前方土体对刀盘的压力大小和分布形式有重要的影响,对开挖面稳定性和失稳部位也有重要影响。
(2) 目前工程中广泛使用的建立在开挖面前方土体对刀盘的压力均匀分布和整体失稳基础上的筒仓楔形体模型无法解释模型试验中发现的静水压应力支护模式下开挖面上半部失稳和土压平衡支护模式下开挖面半部失稳的现象,而改进的筒仓楔形体模型能合理解释这一现象,用该改进模型分析开挖面稳定更合理、更安全。
(3) 在气压、泥水和土压平衡支护模式下,开挖面失稳均非全断面整体失稳,而是局部失稳。有效支护应力均匀分布时,除粘土开挖面下部失稳外,其余土体均为开挖面中下部失稳。有效支护压应力呈上小下大的梯形分布时,除软粘土开挖面下部失稳外,其余土体均为开挖面上部失稳。有效支护应力呈上大下小的梯形分布时,所有土体开挖面均为下部失稳。
(4) 对于土拱效应明显的砂土地层来说,除开挖面在地下水位以上其为气压支护模式时,刀盘和土体间的摩擦角发挥程度对开挖面的失稳区域分布有较大影响外,其余支护模式下,刀盘和土体间的摩擦角发挥程度对开挖面的失稳区域分布影响不大。
责任编辑: 范二平 -
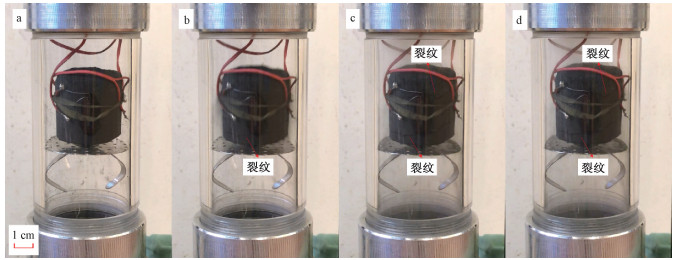
图 2 充入气体压强为0.5 MPa时快速泄压引起的试样破裂(时间间隔16.7 ms)
a—完整试样;b—气体压强差引起破裂开始产生;c—随着气体压强差增大破裂继续扩展;d—随着气体压强差减小破裂停止
Figure 2. Specimen fracture caused by the gas decompression of 0.5 MPa (time interval between two video images is 16.7 ms). (a) Intact specimen. (b) Fractures initiate when the gas pressure gradient occurs. (c) Fractures continue growing with the gas pressure gradient increases. (d) Fractures stop when the gas pressure gradient decreases
图 3 充入气体压强为1.0 MPa时快速泄压引起的试样破裂(时间间隔16.7 ms)
a—完整试样;b—气体压强差引起破裂和破碎;c—随着气体压强差增大破碎继续扩展;d—随着气体压强差减小破碎停止
Figure 3. Specimen fragmentation caused by the gas decompression of 1.0 MPa (time interval between two video images is 16.7 ms). (a) Intact specimen. (b) Fractures and fragmentation initiate when the gas pressure gradient occurs. (c) Fragmentation continues growing with the gas pressure gradient increases. (d) Fragmentation stops when the gas pressure gradient decreases
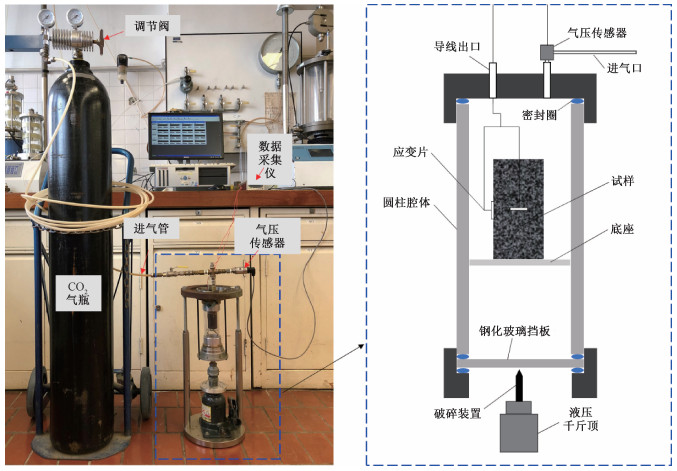
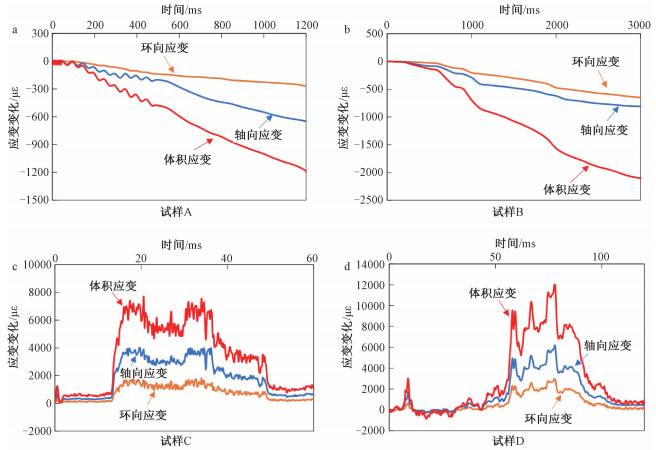
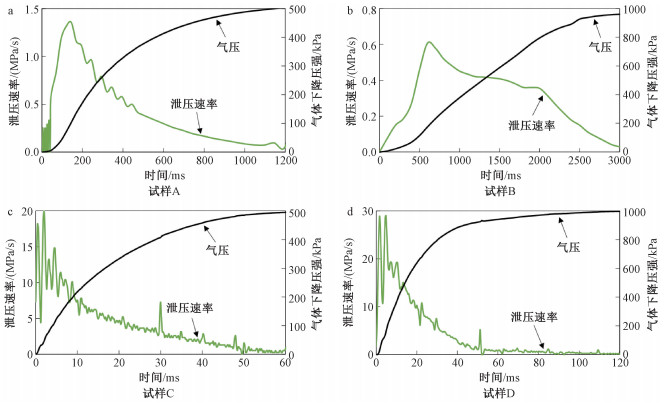
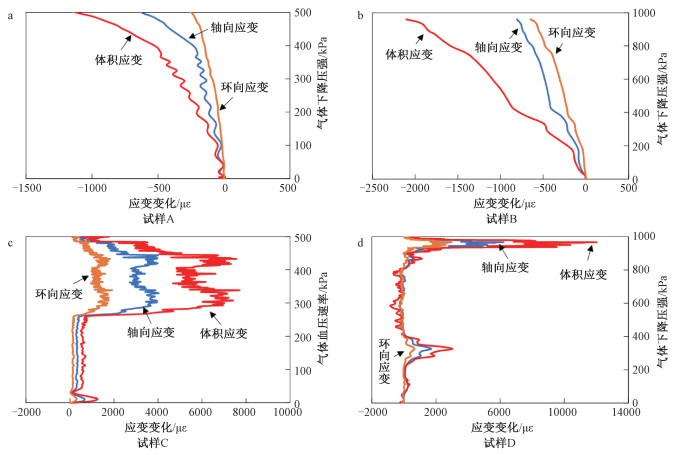
表 1 实验参数与结果
Table 1. Summary of the experimental data and results
编号 初始条件 测试条件 测试结果 尺寸直径×高度/mm 饱和气压*/MPa 平均泄压速率/(MPa/s) 破裂压强/kPa 破碎压强/kPa 充气过程最大体积应变/×10-3 放气过程最大体积应变/×10-3 试样结果 A Φ35.00×35.58 0.5 0.4 - - 4.944 -1.286 完整 B Φ35.00×35.04 1.0 0.3 - - 7.392 -2.104 完整 C Φ35.00×34.96 0.5 6.6 340 - 5.259 7.680 破裂 D Φ35.00×36.16 1.0 8.2 - 960 7.349 12.015 破碎 *注:气体压强数值为高于大气压强的差值 -
ATES Y, BARRON K, 1988. The effect of gas sorption on the strength of coal[J]. Mining Science and Technology, 6(3): 291-300. doi: 10.1016/S0167-9031(88)90287-3 DING Y L, YUE Z Q, 2018. An experimental investigation of the roles of water content and gas decompression rate for outburst in coal briquettes[J]. Fuel, 234: 1221-1228. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.07.143 EVANS I, POMEROY C D, 1966. The strength, fracture and workability of coal[M]. London: Pergamon Press. GUAN P, WANG H Y, ZHANG Y X, 2009. Mechanism of instantaneous coal outbursts[J]. Geology, 37(10): 915-918. doi: 10.1130/G25470A.1 HE M C, MIAO J L, FENG J L, 2010. Rock burst process of limestone and its acoustic emission characteristics under true-triaxial unloading conditions[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 47(2): 286-298. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.09.003 HU QT, ZHANG S T, WEN G C, et al., 2015. Coal-like material for coal and gas outburst simulation tests[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 74: 151-156. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.01.005 HU S B, WANG E Y, LI X C, et al., 2016. Effects of gas adsorption on mechanical properties and erosion mechanism of coal[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 30: 531-538. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2016.02.039 HUANG S, XIA K W, YAN F, et al., 2010. An experimental study of the rate dependence of tensile strength softening of Longyou sandstone[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 43(6): 677-683. doi: 10.1007/s00603-010-0083-8 KONG X G, WANG E Y, HU S B, et al., 2015. Critical slowing down on acoustic emission characteristics of coal containing methane[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 24: 156-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.03.020 LITWINISZYN J, 1994. Rarefaction shock waves in porous media that accumulate CO2, CH4, N2[J]. Shock Waves, 3(3): 223-232. doi: 10.1007/BF01414716 MAJEWSKA Z, MAJEWSKI S, ZIĘTEK J, 2010. Swelling of coal induced by cyclic sorption/desorption of gas: Experimental observations indicating changes in coal structure due to sorption of CO2 and CH4[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 83(4): 475-483. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2010.07.001 PAN Z J, CONNELL L D, 2007. A theoretical model for gas adsorption-induced coal swelling[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 69(4): 243-252. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2006.04.006 PINI R, OTTIGER S, BURLINI L, et al., 2009. Role of adsorption and swelling on the dynamics of gas injection in coal[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 114(B4): B04203. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/255207823_Role_of_adsorption_and_swelling_on_the_dynamics_of_gas_injection_in_coal_-_article_no_B04203 RANJITH P G, JASINGE D, CHOI S K, et al., 2010. The effect of CO2 saturation on mechanical properties of Australian black coal using acoustic emission[J]. Fuel, 89(8): 2110-2117. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.03.025 SAGHAFI A, FAIZ M, ROBERTS D, 2007. CO2 storage and gas diffusivity properties of coals from Sydney Basin, Australia[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 70(1-3): 240-254. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2006.03.006 SKOCZYLAS N, DUTKA B, SOBCZYK J, 2014. Mechanical and gaseous properties of coal briquettes in terms of outburst risk[J]. Fuel, 134: 45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.05.037 TAN T K, KANG W F, 1991. On the locked in stress, creep and dilation of rocks, and the consititutive equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 10(4): 299-312. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX199104000.htm VIETE D R, RANJITH P G, 2006. The effect of CO2 on the geomechanical and permeability behaviour of brown coal: implications for coal seam CO2 sequestration[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 66(3): 204-216. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2005.09.002 VIETE D R, RANJITH P G, 2007. The mechanical behaviour of coal with respect to CO2 sequestration in deep coal seams[J]. Fuel, 86(17-18): 2667-2671. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2007.03.020 WANG C H, GAO G Y, WANG H, et al, 2020. Integrated determination of principal stress and tensile strength of rock based on the laboratory and field hydraulic fracturing tests[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(2): 167-174. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG C J, YANG S Q, YANG D D, et al., 2018. Experimental analysis of the intensity and evolution of coal and gas outbursts[J]. Fuel, 226: 252-262. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.165 WANG G, LI W X, WANG P F, et al., 2017. Deformation and gas flow characteristics of coal-like materials under triaxial stress conditions[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 91: 72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.11.015 WANG S G, ELSWORTH D, LIU J S, 2015. Rapid decompression and desorption induced energetic failure in coal[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 7(3): 345-350. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.01.004 YANG D D, CHEN Y J, TANG J, et al., 2018. Experimental research into the relationship between initial gas release and coal-gas outbursts[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 50: 157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2017.12.015 YIN G Z, JIANG C B, WANG J G, et al., 2016. A new experimental apparatus for coal and gas outburst simulation[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 49(5): 2005-2013. doi: 10.1007/s00603-015-0818-7 YUE Z Q, 2014. Gas inclusions and their expansion power as foundation of rock ""locked in"" stress hypothesis[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 22(4): 739-756. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201404028.htm YUE Z Q, 2015. Expansion power of compressed micro fluid inclusions as the cause of rockburst[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 37(3): 287-294. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_mechanics-engineering_thesis/0201241946771.html ZANG J, WANG K, 2017. Gas sorption-induced coal swelling kinetics and its effects on coal permeability evolution: Model development and analysis[J]. Fuel, 189: 164-177. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.092 ZHANG Q B, ZHAO J, 2014. Quasi-static and dynamic fracture behaviour of rock materials: phenomena and mechanisms[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 189(1): 1-32. doi: 10.1007/s10704-014-9959-z ZHAO Y X, LIU S M, JIANG Y D, et al., 2016. Dynamic tensile strength of coal under dry and saturated conditions[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 49(5): 1709-1720. doi: 10.1007/s00603-015-0849-0 陈宗基, 康文法, 1991. 岩石的封闭应力、蠕变和扩容及本构方程[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 10(4): 299-312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX199104000.htm 王成虎, 高桂云, 王洪, 等, 2020. 利用室内和现场水压致裂试验联合确定地应力与岩石抗拉强度[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(2): 167-174. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20200202&journal_id=dzlxxb 岳中琦, 2014. 奠基岩石""封闭应力""假说的气体包裹体和膨胀能力[J]. 工程地质学报, 22(4): 739-756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201404028.htm 岳中琦, 2015. 岩爆的压缩流体包裹体膨胀力源假说[J]. 力学与实践, 37(3): 287-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXYS201503001.htm 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 彭丽娟,白伟利,李文超,高龙飞. 2022年9月泸定M_S 6.8地震与花莲M_S 6.9地震震害对比分析. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2024(03): 139-144 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术