Quantitative prediction of mineral resources in typical gold deposits in Guangxi, China using a fuzzy weights of evidence method
-
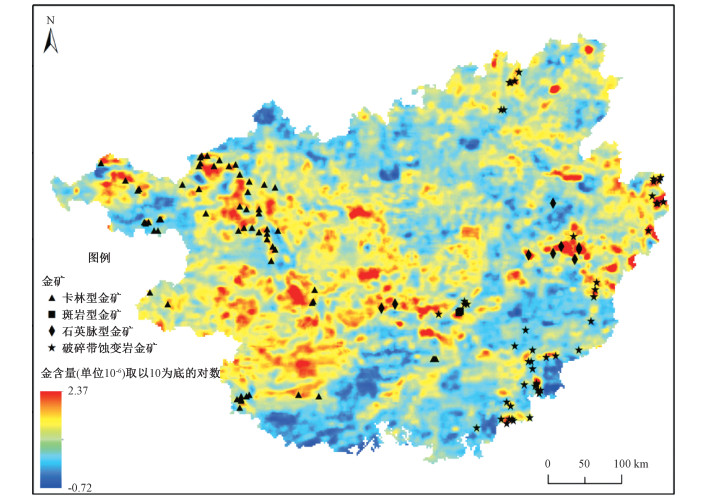
摘要: 多信息融合的矿产资源定量预测是当前资源潜力预测的前缘课题,不同地质背景信息与地球化学数据的深度挖掘是当前该领域急需解决的关键问题。文章通过总结广西各构造单元地质背景和成矿控制要素,在ArcGIS、GeoDAS等软件平台基础上,分析了广西全区60767个地球化学样品中Au、Ag、Mn、Cu、Pb、Zn、Sn、Sb等主要成矿及伴生元素的空间分布特征。基于GeoDAS平台,通过IDW插值、S-A异常分解、主成分分析等技术,选取地球化学组合元素异常、重磁异常以及岩浆岩与断层交点缓冲区数据,通过模糊证据权模型,重点选取卡林型金矿和破碎带蚀变金矿2种典型矿产类型,编制了成矿后验概率图,圈定了金成矿有利地段。该研究对应用新的成矿理论和评价技术方法在广西开展矿产资源潜力评价以及区划工作具有重要的参考意义。Abstract: Quantitative prediction of mineral resources based on multi-information fusion is the leading topic of resource potential prediction, in which the deep mining of different geological background information and geochemical data is the key problem and still challenging. In this study, we analyzed the spatial distribution characteristics of main metallogenic and associated elements such as Au, Ag, Mn, Cu, Pb, Zn, Sn and Sb in 60767 geochemical samples on the platforms like ArcGIS and GeoDAS, by summerzing the geological background information and metallogenic controlling factors of each tectonic unit in Guangxi. Based on the GeoDAS paltform, through IDW interpolation, S-A anomaly decomposition, principal component analysis and other technologies, the data from the layers with geochemical component element anomaly, gravity and aeromagnetic anomaly and the buffers at the intersection of magmatic rock and fault were used as the training points for the utilization of the fuzzy weights of evidence. A posteriori probability map was drawn up to delineate the favorable metallogenic areas for Carlin-type gold deposit and fracture zone altered gold deposit. This study is of great significance to the application of new metallogenic theories and evaluation techniques in the evaluation or zoning of mineral resources potential.
-
图 10 布格重力异常图层隶属度函数v-t图解及模糊证据权重的选择示意图(红色点表示与成矿密切相关的点、蓝色点表示与成矿关系不密切的点)
Figure 10. V-T diagram of membership function of Bouguer gravity anomaly layer and selection of fuzzy evidence weights (red points indicate points closely related to mineralization, blue points indicate points not closely related to mineralization)
图 11 采用模糊证据权法计算的金的后验概率图及资源潜力远景区预测
I-桂中加里东地槽褶皱带(I1-桂北隆起;I2-柳州坳陷;I3-桂东北过渡带;I4-大瑶山隆起;I5-云开隆起);II-桂南海西地槽褶皱带;III-桂西印支地槽褶皱(III1-都阳山隆起III2-右江坳陷;III3-西大明山隆起;III4-十万大山坳陷);1-四堡断裂2-平珮岭断裂;3-三江-融安断裂;4-寿城断裂;5-龙胜-永福断裂;6-资源断裂;7-陆川-岑溪断裂;8-博白-梧州断裂;9-灵山-藤县断裂;10-峒中-小董断裂带;11-高屏-新黑断裂;12-凭祥-大黎断裂带;13-荔浦断裂;14-下雷-灵马断裂;15-那坡断裂带;16-右江断裂带;17-田林-巴马断裂带;18-南丹-昆仑关断裂带;19-白石断裂;20-栗木-马江断裂;21-富川断裂;22-桂林-来宾断裂带;23-观音阁断裂带;24-宜山-柳城断裂带a-依据PCA1背景与异常分解后卡林型金矿预测后验概率图; b-依据PCA3背景与异常分解后破碎带蚀变型金矿预测后验概率图
Figure 11. Posterior probability map of Au and target areas for gold deposits delineated by the fuzzy weights of evidence method. (a) Carlin-type gold deposits predicted by PCA1 background and anomaly decomposition. (b) Altered type gold deposits predicted by PCA3 background and anomaly decomposition I-Caledonian geosynclinal fold belt in Central Guangxi (I1-Northern Guangxi uplift; I2-Liuzhou depression; I3-Northeast Guangxi transitional zone; I4-Dayaoshan uplift; I5-Yunkai uplift); II-Hercynian geosynclinal fold belt in southern Guangxi; III-Indosinian geosynclinal fold in Western Guangxi (III1-Duyangshan uplift; III2-Youjiang depression; III3-Xidamingshan uplift; III4-Shiwandashan depression); 1-Sipu fault, 2-Pingpeiling fault; 3-Sanjiang-rong′an fault; 4-Shoucheng fault; 5-Longsheng-Yongfu fault; 6-Ziyuan fault; 7-Luchuan-Cenxi fault; 8-Bobai-Wuzhou fault; 9-Lingshan-Tengxian fault; 10-Dongzhong-Xiaodong fault zone; 11-Gaoping-Xinhei fault; 12-Pingxiang-Dali fault zone; 13-Lipu fault; 14-Xialei-Lingma fault; 15-Napo fault zone; 16-Youjiang fault zone; 17-Tianlin-Bama fault zone; 18-Nandan-Kunlunguan fault zone; 19-Baishi fault; 20-Limu-Majiang fault; 21-Fuchuan fault; 22-Guilin-Laibin fault zone; 23-Guanyin′ge fault zone; 24-Yishan-Liucheng fault zone
图 13 卡林型金矿预测靶区与广西有色金属成矿带分布
I-丹池锡-铜-铅-锌-银-锑-汞成矿带;II-桂北锡-钨-铜-镍-铅-锌成矿带;III-桂东北锡-钨-铜-铅-锌-金-银成矿带;IV-大明山钨-铜-金成矿带;V-大瑶山铜-铅-锌-金成矿带;VI-云开大山铅-锌-钨-金成矿带;VII-西大明山铜-铅-锌-银成矿带;VIII-桂西金-锑成矿带;IX-靖西-平果铝成矿带
Figure 13. Distribution of Carlin-type gold deposits predicted target area and Guangxi nonferrous metal metallogenic belts I-Danchi metallogenic belt of Sn-Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag-Sb-Hg; II-Northern Guangxi metallogenic belt of Sn-W-Cu-Ni-Pb-Zn; III-Northeastern Guangxi metallogenic belt of Sn-W-Cu-Pb-Zn-Au-Ag; IV-Damingshan metallogenic belt of W-Cu-Au; V-Dayaoshan metallogenic belt of Cu-Pb-Zn-Au; VI-Yunkaidashan metallogenic belt of Pb-Zn-W-Au; VII-West Damingshan metallogenic belt of Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag; VIII-Western Guangxi metallogenic belt of Au-Sb; IX-Jingxi-Pingguo metallogenic belt of Al
图 14 证据权法破碎带蚀变岩型金矿预测与广西有色金属成矿带分布图
I-丹池锡-铜-铅-锌-银-锑-汞成矿带;II-桂北锡-钨-铜-镍-铅-锌成矿带;III-桂东北锡-钨-铜-铅-锌-金-银成矿带;IV-大明山钨-铜-金成矿带;V-大瑶山铜-铅-锌-金成矿带;VI-云开大山铅-锌-钨-金成矿带;VII-西大明山铜-铅-锌-银成矿带;VIII-桂西金-锑成矿带;IX-靖西-平果铝成矿带
Figure 14. Prediction map of altered rock type gold deposits in fracture zone by the weights of evidence method and the distribution of Guangxi nonferrous metal metallogenic belts I-Danchi metallogenic belt of Sn-Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag-Sb-Hg; II-Northern Guangxi metallogenic belt of Sn-W-Cu-Ni-Pb-Zn; III-Northeastern Guangxi metallogenic belt of Sn-W-Cu-Pb-Zn-Au-Ag; IV-Damingshan metallogenic belt of W-Cu-Au; V-Dayaoshan metallogenic belt of Cu-Pb-Zn-Au; VI-Yunkaidashan metallogenic belt of Pb-Zn-W-Au; VII-West Damingshan metallogenic belt of Cu-Pb-Zn-Ag; VIII-Western Guangxi metallogenic belt of Au-Sb; IX-Jingxi-Pingguo metallogenic belt of Al
-
AGTERBERG F P, 1989. Computer programs for mineral exploration[J]. Science, 245(4913): 76-81. doi: 10.1126/science.245.4913.76 AGTERBERG F P, CHENG Q M, 2002. Conditional independence test for weights-of-evidence modeling[J]. Natural Resources Research, 11(4): 249-255. doi: 10.1023/A:1021193827501 AGTERBERG F P, 2011. Modified weights-of-evidence method for regional mineral Resource estimation[J]. Natural Resources Research, 20(2): 95-101. doi: 10.1007/s11053-011-9138-0 BONHAM CARTER G, 1994. Geographic information systems for geoscientists: modelling with GIS[M]. New York: Pergamon Press: 398. BONHAM CARTER G, CHENG Q M, 2001. Spatially weighted principal component analysis[J]. Presented at IAMG 2001 Meeting. Cancún Mexico September 6-12. CARRANZA E J M, 2008. Handbook of exploration and environmental geochemistry[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier: 1-368. CHEN M, 2016. Analysis of the Guangxi gold deposit ore-controlling tectonic characteristics and prospecting prospect[J]. World Nonferrous Metals(12): 119-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-COLO201612050.htm CHEN Y Q, XIA Q L, HUANG J N, et al., 2007. Application of the weights-of-evidence method in mineral resource assessments in the southern segment of the "Sanjiang metallogenic zone" southwestern China[J]. Geology in China, 34(1): 132-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200701018.htm CHENG Q M, 1999. Multifractality and spatial statistics[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 25: 949-961. doi: 10.1016/S0098-3004(99)00060-6 CHENG Q M, AGTERBERG F P, BALLANTYNE S B, 1994. The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 51(2): 109-130. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(94)90013-2 CHENG Q M, ZHANG S Y, 2002. Fuzzy weights of evidence method implemented in GeoDAS GIS for information extraction and integration for prediction of point events. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference of geosciences and remote sensing (IGARSS02), Toronto, Canada, Jun 3, 24-28. CHENG Q M, AGTERBERG F P, 1999. Fuzzy weights of evidence method and its application in mineral potential mapping[J]. Natural Resources Research, 8(1): 27-35. doi: 10.1023/A:1021677510649 CHENG Q M, CHEN Z J, KHALED A, et al., 2007. Application of fuzzy weights of evidence method in mineral resource assessment for gold in Zhenyuan District, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32(2): 175-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200702004 CHENG Q M, 2012. Singularity theory and methods for mapping geochemical anomalies caused by buried sources and for predicting undiscovered mineral deposits in covered areas[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 122: 55-70. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.07.007 DAYA A A, 2015. Comparative study of C-A, C-P, and N-S fractal methods for separating geochemical anomalies from background: A case study of Kamoshgaran region, northwest of Iran[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 150: 52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.12.015 DENG M F, 2010. Binary pattern recognition in the presence of correlated multiple dependent variables[J]. Natural Resources Research, 19(4): 269-278. doi: 10.1007/s11053-010-9128-7 GONG H S, HAN R S, LI Z T, et al, 2020. Element association anomaly of tectonites and prediction of concealed deposit in the Xiaozhuqing exploration area on the periphery of Huize lead-zinc mine area, northeastern Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(3): 419-431, doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.03.036. HE Q L, ZHANG H C, SONG P, et al., 2013. Geological Characteristics and Prospecting Criteria of Paoli Carlin-Type Gold Deposits in Guangxi Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 21(6): 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-HJKJ201306020.htm HONG H Y, TSANGARATOS P, ILIA I, et al., 2018. Application of fuzzy weight of evidence and data mining techniques in construction of flood susceptibility map of Poyang County, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 625: 575-588. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.256 LI B B, LIU B L, GUO K, et al., 2019. Application of a maximum entropy model for mineral prospectivity maps[J]. Minerals, 9(9): 556. doi: 10.3390/min9090556 LI C M, 2010. Distribution regularity and metallogenic characteristics of gold deposits in Guangxi[J]. Mineral Deposits, 29(S1): 951-952. (in Chinese) LIN J H, LUO Y Y, SHU G., et al., 2015. Regionalore-forming regularity and division of minerogeneticseriesin Guangxi[J]. Mineral Deposits, 34(6): 1270-1294. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201506014.htm LIU S F, 2017. Fractal analysis on geochemical distribution and anomaly separation in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing). (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Y P, ZHU L X, ZHOU Y Z, et al., 2020. Experimental research on big data mining and intelligent prediction of prospecting target area: application of convolutional neural network model[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 44(2): 192-202, doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2020.02.003. (in Chinese with abstract). SHI J, ZHU W W, WANG X, et al., 2017. Bibliometrics analysis on the trend of international earth sciences in recent 5 Years[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 91(12): 2881-2888. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/ http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DZXE201712021&dbcode=CJFD&year=2017&dflag=pdfdown SUN T, LI H L, WU K X, et al., 2020. Data-driven predictive modelling of mineral prospectivity using machine learning and deep learning methods: a case study from southern Jiangxi province, China[J]. Minerals, 10(2): 102. doi: 10.3390/min10020102 WANG Z W, WANG L, HUANG G W, et al, 2020. Research on multi-source heterogeneous data fusion algorithm of landslide monitoring based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(4): 575-582, doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.050. (in Chinese with English abstract) WILLIAMS N D, ELLIOTT B A, KYLE J R, 2020. A predictive geospatial exploration model for mississippi valley type Pb-Zn mineralization in the southeast missouri lead district[J]. Natural Resources Research, 29(1): 285-310. doi: 10.1007/s11053-020-09618-2 WU R H, PANG B C, TAN J, et al., 2012. Preliminary analysis of distribution regularity and prospecting direction of gold deposits in Guangxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 26(4): 291-298. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201204005.htm XIAO K Y, DING J H, LOU D B, 2009a. Quantitative assessment of porphyry copper in eastren Tianshan[J]. Geology and Exploration, 45(6): 637-644. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200906003.htm XIAO K Y, DING J H, LOU D B, 2009b. A tentative discussion on theory of minerogenetic series and mineral resource assessment[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(3): 357-365. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200903012.htm YANG B, PENG S L, LI S R, et al., 2007. Metallogenic Series and Metallogenic Belt of Nonferrous Metals in Guangxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 21(1): 8-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD200701001.htm ZHAI Y S, DENG J, WANG J P, et al., 2004. Researches on deep ore prospecting[J]. Mineral Deposits, 23(2): 142-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200402002.htm ZHANG S Y, CHENG Q M, ZHANG S P, et al., 2012. Improvement of weighted weights of evidence and its applications in Sn-Cu mineral potential mapping in Gejiu, Yunnan province, China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 37(6): 1175-1182. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHAO P D, 2007. Quantitative mineral prediction and deep mineral exploration[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200705002.htm ZHOU Y Z, WANG J, ZUO R G, et al., 2018. Machine learning, deep learning and Python language in field of geology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(11): 3173-3178. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB201811002.htm ZHOU Y Z, CHEN C, ZHANG Q, et al., 2020. Introduction of tools for geological big data mining and their applications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 44(2): 173-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Z C, WU Z, 2016. Distribution law and prospecting direction of gold deposit in Guangxi[J]. World Nonferrous Metals(18): 84-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-COLO201618035.htm ZHU G Q, LI H L, WEN R X, et al., 2010. The report of Guangxi concealed rockmass and deep ore prospecting[R]. Guangxi Geophysical Investigation Institute. (in Chinese) ZUO R G, WANG J, XIONG Y H, et al., 2021. Progresses of researches on geochemical exploration data processing during 2011-2020[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 40(1): 81-92. (in Chinese with English abstract) 陈敏, 2016. 分析广西金矿床控矿构造特征及找矿前景[J]. 世界有色金属(12): 119-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201612050.htm 陈永清, 夏庆霖, 黄静宁, 等, 2007. "证据权"法在西南"三江"南段矿产资源评价中的应用[J]. 中国地质, 34(1): 132-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.01.019 成秋明, 陈志军, KHALED A, 等, 2007. 模糊证据权方法在镇沅(老王寨)地区金矿资源评价中的应用[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 32(2): 175-184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2007.02.004 贺秋利, 张红晨, 宋鹏等, 2013. 广西袍里卡林型金矿床地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 黄金科学技术, 21(6): 48-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2518.2013.06.014 龚红胜, 韩润生, 李孜腾, 等, 2020. 滇东北会泽铅锌矿区外围小竹箐勘查区构造岩元素组合异常及隐伏矿预测[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(3): 419-431, doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.03.036. 李昌明, 2010. 广西金矿床分布规律及成矿特点[J]. 矿床地质, 29(S1): 951-952. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1476.htm 林建辉, 罗允义, 树皋, 等, 2015. 广西区域成矿规律综述及成矿系列划分[J]. 矿床地质, 34(6): 1270-1294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201506014.htm 刘舒飞, 2017. 广西地球化学区带规律与异常分布分形解析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京). 刘艳鹏, 朱立新, 周永章, 等, 2020. 大数据挖掘与智能预测找矿靶区实验研究: 卷积神经网络模型的应用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 44(2): 192-202, doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2020.02.003. 王智伟, 王利, 黄观文, 等, 2020. 基于BP神经网络的滑坡监测多源异构数据融合算法研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(4): 575-582, doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2020.26.04.050. 吴荣华, 庞保成, 谭杰, 等, 2012. 广西金矿床的分布规律及找矿方向浅析[J]. 矿产与地质, 26(4): 291-298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2012.04.005 肖克炎, 丁建华, 娄德波, 2009a. 东天山斑岩铜矿资源潜力评价[J]. 地质与勘探, 45(6): 637-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200906003.htm 肖克炎, 丁建华, 娄德波, 2009b. 试论成矿系列与矿产资源评价[J]. 矿床地质, 28(3): 357-365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200903012.htm 杨斌, 彭省临, 李水如, 等, 2007. 广西有色金属成矿系列与成矿区带[J]. 矿产与地质, 21(1): 8-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2007.01.002 翟裕生, 邓军, 王建平, 等, 2004. 深部找矿研究问题[J]. 矿床地质, 23(2): 142-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.02.003 张生元, 成秋明, 张素萍, 等, 2012. 改进的加权证据权模型及其在个旧锡铜矿产资源预测中的应用[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 37(6): 1175-1182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200902008.htm 赵鹏大, 2007. 成矿定量预测与深部找矿[J]. 地学前缘, 14(5): 1-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.05.001 周永章, 王俊, 左仁广, 等, 2018. 地质领域机器学习、深度学习及实现语言[J]. 岩石学报, 34(11): 3173-3178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201811002.htm 周永章, 陈川, 张旗, 等, 2020. 地质大数据分析的若干工具与应用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 44(2): 173-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202002001.htm 周泽昌, 吴钊, 2016. 广西金矿床的分布规律以及找矿方向[J]. 世界有色金属(18): 84-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COLO201618035.htm 朱国器, 黎海龙, 温融湘, 等, 2010. 广西隐伏岩体与深部找矿研究报告[R]. 广西地球物理勘察院内部科研报告. 左仁广, 王健, 熊义辉, 等, 2021. 2011-2020年勘查地球化学数据处理研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 40(1): 81-92. -





 下载:
下载: