Geological environment changes during the late Pleistocene-Holocene on the E'mei tableland in the northern Yuncheng basin, Shanxi Province: Implications for the distribution of human settlements
-
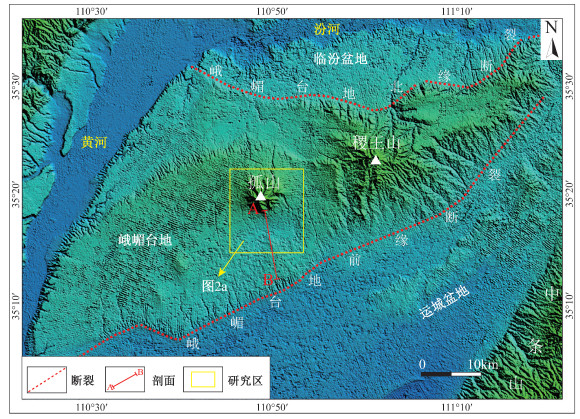
摘要: 新构造运动及自然环境的变化深刻影响着人类聚落的形成与分布。山西运城盆地北部的峨嵋台地中段自北向南发育孤山隆起、埝底洼地、三管高地,现今人类聚落在相对平坦的埝底洼地中较少,而是围绕低洼地带周缘斜坡带分布。野外地质调查发现,研究区广泛分布的马兰黄土之上覆盖着一套冲洪积物、湖相沉积及河流相沉积。文章对不同地貌部位典型剖面开展了详细的野外地质调查及光释光、碳十四年代学研究,结合研究区古人类遗址分布位置及现今人类聚落分布特征,深入分析了晚更新世—全新世峨嵋台地的地质环境变化过程及其对人类聚落迁移的影响。研究结果表明,埝底洼地晚更新世黄土之上湖相沉积底部年龄为距今1.7万年左右,指示该时期峨嵋台地中段形成了低洼地带,并汇水成湖,结合区域构造资料推测该洼地的形成可能与三管高地北侧断裂活动有关。距今约5000年左右的荆村遗址、袁家庄遗址分布位置反映全新世中期湖泊范围可能扩大到了孤山山前,古人类邻水而居。之后随着气候变干,湖泊逐渐萎缩,人类聚落不断向低洼地带迁移。因此,现今人类聚落围绕埝底洼地周缘分布而不进入低洼地带的特征主要延续了全新世中晚期人类聚落邻水而居的形态,这也相应指示了人类聚落分布及演变与自然环境变化之间存在着紧密联系。
-
关键词:
- 山西地堑系 /
- 峨嵋台地 /
- 晚更新世—全新世环境 /
- 古湖泊 /
- 人类聚落
Abstract: Neotectonic movements and the changing natural environment have profoundly influenced human settlements on their formation and distribution. The Gushan uplift, Niandi low-lying area and Sanguan highland developed from north to south in the central section of the E'mei tableland; however, human settlements nowadays distribute on the peripheral slopes around the low-lying area rather than right in the Niandi low-lying area. Our field investigation reveals that the Malan loess is overlied by a set of alluvial-diluvial deposits, lacustrine deposits, and fluvial deposits. This paper mainly presents field evidence and chronological analyses of OSL and 14C for the typical sections of different geomorphic sites to discuss the geological environment evolution of the E'mei tableland during the late Pleistocene-Holocene and its influence on the migration of human settlements. Our field investigation and analysis results show that the formation age of the bottom of the late Pleistocene lacustrine deposits above the loess in the Niandi low-lying area is about 17 ka B.P., indicating a depression had developed in the middle section of the E'mei tableland during this period with water converging in, forming a lake afterwards. Combined with the regional structural data, it is speculated that the formation of this depression was caused by the fault activity on the north side of the Sanguan highland. The location of 5000-year-old ruins of Jingcun Village and Yuanjiazhuang Village shows that the lake may have expanded to the piedmont of Gushan in the middle Holocene. Along with increasing dryness of climate and the shrinkage of lake, human settlements kept migrating to the low-lying lands. Nowadays, villages around the periphery of the Niandi low-lying area carries on the distribution pattern of living by water in the middle-late Holocene, which indicates that the distribution and evolution of human settlements are closely connected with the changes of natural environment. -
图 2 峨嵋台地孤山及周边地区地质特征
a—峨嵋台地孤山及周边地区地质简图(位置见图 1方框);b—地质地貌剖面图(位置见图 1);c—埝底洼地与三管高地相邻部位地貌特征(遥感影像来自Google Earth)
Figure 2. Diagrams showing the geological features of the Gushan in the E'mei tableland and surrounding areas.
(a) Geological sketch of the Gushan and its surrounding areas in the E'mei tableland (Location is shown in Fig. 1). (b) Geological and geomorphic profile (Location is shown in Fig. 1). (c) Geomorphological characteristics of the adjacent parts between the Niandi low-lying area and Sanguan highland (Remote sensing image is from Google Earth)
图 4 焦家营剖面及邻区地层特征
L—黄土;S—古土壤
a—马兰黄土及上覆冲洪积物特征;b—剖面上部冲洪积物特征及采样位置;c—焦家营剖面北西侧冲沟黄土及古土壤特征Figure 4. Photos showing the stratigraphic characteristics of the Jiaojiaying section and the surrounding strata.
(a) Characteristics of the Malan loess and its overlying alluvial and diluvial sediments. (b) Characteristics and the sampling positions of alluvial and diluvial sediments in the upper section. (c) Characteristics of loess and palaeosol in the northwest side of the Jiaojiaying section.
L—loess; S—paleosol图 6 黄家庄剖面晚更新世地层柱状图及野外特征
a—剖面整体特征及采样位置;b—黄色含蜗牛碎片粗砂特征;c—土黄色粉砂特征
Figure 6. Stratigraphic column of the Huangjiazhuang section in the late Pleistocene and field photos.
(a) Overall characteristics of the profile and sampling position. (b) Characteristics of yellow coarse sand containing snail fragments. (c) Characteristics of khaki silt
表 1 光释光样品特征及测试结果
Table 1. Characteristics and test results of the OSL samples
序号 编号 岩性 埋深 实测含水量/% 环境剂量率/(Gy/Ka) 测试粒径/μm 测试方法 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka B.P. 1 D1013-3 灰色粉砂 3.2 m — 4.43 4~11 μm SMAR 105.95±4.73 23.93±2.62 2 D1013-1 土黄色黄土 7.8 m — 4.46 4~11 μm SMAR 179.36±12.11 40.18±4.85 3 PM03-5 灰白色粉砂 4.8 m 12.77 2.93±0.21 4~11 μm SMAR 28.95±1.46 9.89±0.86 4 D1077-2 黄色中砂 2.3 m 1.26 3.00±0.24 4~11 μm SMAR 57.83±2.72 19.31±1.82 5 D1077-1 土黄色粉砂 2.7 m 5.59 2.81±0.21 4~11 μm SMAR 77.48±6.81 27.63±3.17 表 2 碳十四样品特征及测试结果
Table 2. Characteristics and test results of the 14C samples
序号 编号 岩性 埋深 测试对象 测试方法 年龄/a B.P. 1 D1013-4 灰色粉砂 1.6 m 有机土 AMS14C 19620±60 2 PM03-1 棕褐色粘土 0.6 m 有机土 AMS14C 2380±30 3 PM03-4 棕褐色粘土 2.6 m 有机土 AMS14C 3590±30 4 N9-1 棕红色粘土 12.0 m 有机土 AMS14C 17520±60 -
AITKEN M J, 1998. An introduction to optical dating[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press: 39-50. AN C B, WANG L, JI D X, et al., 2006. The temporal and spatial changes of Neolithic cultures in Gansu-Qinghai region and possible environmental forcing[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 26(6): 923-927. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200606006.htm CAO Y F, HUANG C C, PENG J L, 2005. Preliminary studies of wild fire frequency and environmental changes during the Holocene on the alluvial plain of the Yuncheng basin[J]. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 29(4): 692-696. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://europepmc.org/abstract/CBA/536992 CAO Y F, HAN J Q, 2009. Wildfire activity and ecological environment change during Holocene in the Yuncheng basin[J]. Journal of Arid land Resources and Environment, 23(2): 125-129. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/281594898_Wildfire_activity_and_ecological_environment_change_during_Holocene_in_the_Yuncheng_Basin CHEN S Y, QIANG L Y, ZHANG F J, et al., 2020. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of earthen fort ruins in the lower reaches of the Yellow River and their relations with floods[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 40(7): 1202-1209. (in Chinese with English abstract) CLARK P U, DYKE A S, SHAKUN J D, et al., 2009. The last glacial maximum[J]. Science, 325(5941): 710-714. doi: 10.1126/science.1172873 Compilation Group of Human Geography, Editorial Committee of Geography, General Editorial Committee of Encyclopedia of China, Editorial Department of China Encyclopedia Press, 1984. Theory of man-land relationship, Encyclopedia of Chinese Geography: Human Geography[M]. Beijing: Encyclopedia of China Publishing House: 12-14. (in Chinese) FOLK R L, WARD W C, 1957. Brazos River Bar[Texas]; A study in the significance of grain size parameters[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 27(1): 3-26. doi: 10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D GANG C X D, 2001. The settlement structure of Yangshao culture[J]. JIANG B L, QIN X L, trans. Archaeology And cultural Relics(6): 83-91, 93. (in Chinese) GIRAUD J, 2009. The evolution of settlement patterns in the eastern Oman from the Neolithic to the early Bronze age (6000-2000 BC)[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 341(8-9): 739-749. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2009.03.005 GUO C S, 2019. Study on main fault activity and deformation characteristics of related blocks in Yuncheng Basin[D]. Beijing: Institution of Earthquake Forecasting, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese with English abstract) GUO Y Y, MO D W, MAO L J, et al., 2013. The relationship between settlements distribution and environmental changes from the Neolithic to Shang-Zhou periods in north Shandong Province[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 68(4): 559-570. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dlxb-e201304008.aspx HEATON T J, BLACKWELL P G, BUCK C E, 2009. A Bayesian approach to the estimation of radiocarbon calibration curves: The INTCAL09 Methodology[J]. Radiocarbon, 51(4): 1151-1164. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200034214 HOU G L, XU C J, XIAO J Y, 2012. Comparative analysis of prehistoric sites distribution around 4 ka B. P. in Gansu-Qinghai region based on GIS[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 32(1): 116-120. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201201020.htm HU X M, 1997. The change of from Fen river on Emei platform[J]. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science), 20(2): 154-158. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-AHSZ702.012.htm JIANG J Q, MO D W, LV J Q, et al., 2016. Holocene geomorphic evolution of Taiyuan basin in Shanxi Province and its influence on ancient human settlement distribution[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 18(5): 895-904. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201605018.htm KUPER R, KRÖPELIN S, 2006. Climate-controlled Holocene occupation in the Sahara: motor of Africa's evolution[J]. Science, 313(5788): 803-807. doi: 10.1126/science.1130989 LI H, DING J L, 2020. Review of the quantity of excavated Pottery Xun in Jing village site[J]. World of Antiquity(3): 41-43. (in Chinese) LI J J, 1990. The patterns of environment changes since late Pleistocene in northwestern China[J]. Quaternary Sciences(3): 197-204. LI T Y, MO D W, HU K, et al., 2013. The environmental and cultural background of the Taosi site, Xiangfen County, Shanxi Province[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 33(4): 443-449. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285787357_The_environmental_and_cultural_background_of_the_Taosi_site_Xiangfen_county_Shanxi_Province LI Z H, GONG W B, LIANG X, et al., 2019. Geological map of Shangguo(I49E005012)[Z]. China Geological Survey. MENG L C, 2011. Study on the formation mechanism of ground fissures in Shanxi fault basin[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University. (in Chinese with English abstract) NICOLL K, 2004. Recent environmental change and prehistoric human activity in Egypt and Northern Sudan[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 23(5-6): 561-580. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2003.10.004 PENG J B, WANG Q Y, ZHUANG J Q, et al., 2020. Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(5): 714-730. (in Chinese with English abstract) QI Y, XU H B, ZHANG J X, et al., 2011. Geochemistry, geochronology and geological significance of Gufengshan granodiorite in Linfen grabben basin[J]. Geological Review, 57(4): 565-573. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201104013.htm REIMER P J, BAILLIE M G L, BARD E, et al, 2009. INTCAL09 and MARINE09 radiocarbon age calibration curves, 0-50000 Years Cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 51(4): 1111-1150. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200034202 ROSEN A M, 2008. The impact of environmental change and human land use on alluvial valleys in the loess plateau of China during the middle Holocene[J]. Geomorphology, 101(1-2): 298-307. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.05.017 SHI B H, 2013. Influence of hydrological and geomorphic conditions on settlement site selection in Jiaodong peninsula[J]. Huaxia Archaeology(4): 34-45. (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HXKG201304005.htm SHI C X, MO D W, LIU H, et al., 2010. Late Neolithic cultural evolution and environmental changes in northern Jianghan plain east of Hanjiang river[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 30(2): 335-343. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DSJJ201002011.htm SONG Y Q, 2002. A study on the relationship between man and land on the origin of Chinese civilization[M]. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) STUIVER M, BRAZIUNAS T F, 1993. Modeling atmospheric 14C influences and 14C ages of marine samples to 10, 000 BC[J]. Radiocarbon, 35(1): 137-189. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200013874 TALMA A S, VOGEL J C, 1993. A simplified approach to calibrating 14C dates[J]. Radiocarbon, 35(2): 317-322. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200065000 TIAN T T, WU Z H, ZHANG K Q, et al., 2013. Overview of quaternary dating methods and their application in neotectonics and active tectonics research[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 19(3): 242-266. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/334027617_OVERVIEW_OF_QUATERNARY_DATING_METHODS_AND_THEIR_APPLICATION_IN_NEOTECTONICS_AND_ACTIVE_TECTONICS_RESEARCH/download TURNEY C S M, BROWN H, 2007. Catastrophic early Holocene sea level rise, human migration and the Neolithic transition in Europe[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 26(17-18): 2036-2041. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.07.003 WANG H B, MO D W, LI T Y, 2014. Study on the environmental and cultural background of the formation and the location selection of Taosi site[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 21(3): 302-308. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201403058.htm WANG Q, LI C G, TIAN G Q, et al., 2000. The surface system of Yuncheng Basin has changed dramatically since 7. 1Ma and the tectonic setting of salt lake formation[J]. Science in China (Series D), 30(4): 420-428. (in Chinese) WEISS H, BRADLEY R S, 2001. What drives societal collapse?[J]. Science, 291(5504): 609-610. doi: 10.1126/science.1058775 WENTWORTH C K, 1922. A scale of grade and class terms for Clastic sediments[J]. Journal of Geology, 30(5): 377-392. doi: 10.1086/622910 WU C J, 1991. The core of study of geography: man-land areal system[J]. Economic Geography(3): 1-6. (in Chinese) WU F, 2016. The study of the age of the river terraces in the western Yellow River E'mei platform[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU L, WANG X Y, ZHOU K S, et al., 2009. The Transmutation of ancient settlements and environmental changes from the Neolithic age to the Han dynasty in the Chaohu lake basin[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 64(1): 59-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB200901008.htm WU Y H, WU R J, WANG Q, et al., 2001. Palaeoclimatic variation and lake level fluctuation in Yuncheng basin, Shanxi Province since 11ka BP[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 21(2): 83-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=5266196 XU W, GAO Z W, YANG Y Y, 2014. Late quaternary activity research of the northern marginal fault of Emei platform, Shanxi Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 36(4): 1064-1076. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/287913435_Late_quaternary_activity_research_of_the_northern_marginal_fault_of_Emei_Platform_Shanxi_Province YAN J Y, HU J M, GONG W B, et al., 2020. Late Cenozoic magnetostratigraphy of the Yuncheng Basin, central North China Craton and its tectonic implications[J]. Geological Journal, 55(11): 7415-7428. doi: 10.1002/gj.3744 YAN W M, 1965. The periodization of the Yangshao culture at Miaotikou[J]. Acta Archaeologica Sinica(2): 49-78. (in Chinese) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/293138462_The_periodization_of_the_Yangshao_culture_at_Miaodigou YUAN B Y, TONG H W, WEN R L, et al., 2009. The formation mechanism of the Nihewan palro-lake and its relationship with living environment for early ancient humen[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(1): 77-87. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX200901008.htm ZHANG H Y, 2006. Issues of identifying the space-time range of Yangshao culture[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics(5): 66-70. (in Chinese) ZHANG K Q, 2012. Quantitative calculations of environmental dose rate at different influencing factors in luminescence dating[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 18(1): 62-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201201008.htm ZHANG K Q, WU Z H, LÜ T Y, et al., 2015. Review and progress of光释光dating[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(1): 183-203. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Z P. 1997. The Yangshao age-the prosperity of prehistoric society and the transformation towards civilization. World of Antiquity(1): 1-44. (in Chinese) ZHAO J X, REN J J, YU S E, et al, 2009. OSL age of fault collapse wedge in Xinding basin, Shanxi Province and its significance for paleoearthquake events[J]. Geoscience, 23(6): 1022-1029. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200906004.htm ZHAO J X, REN J J, YU S E, et al, 2011. OSL dating of fault collapse wedge using SAR method: taking the Xitian trench of Xinding basin, Shanxi as an example[J]. Geoscience, 25(2): 356-362. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz201102020 ZHOU J, 2015. Yellow River E Mei area landform sedimentary history research[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU J J, ZHANG X M, ZHAO F S, et al, 2019. Research on risk assessment of geological hazards in Qinling-Daba mountain area, south Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(4): 544-553. (in Chinese with English abstract) 安成邦, 王琳, 吉笃学, 等, 2006. 甘青文化区新石器文化的时空变化和可能的环境动力[J]. 第四纪研究, 26(6): 923-927. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.06.006 曹艳峰, 黄春长, 庞奖励, 2005. 运城盆地洪积扇全新世时期的野火与环境变化的初步探讨[J]. 植物生态学报, 29(4): 692-696. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.2005.04.023 曹艳峰, 韩军青, 2009. 运城盆地全新世时期的野火活动与生态环境演变[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 23(2): 125-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH200902023.htm 陈诗越, 强柳燕, 张风菊, 等, 2020. 黄河下游地区堌堆遗址时空分布特征及其与黄河洪水关系[J]. 地理科学, 40(7): 1202-1209. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX202007017.htm 冈村秀典, 2001. 仰韶文化的聚落结构[J]. 姜宝莲, 秦小丽, 译. 考古与文物(6): 83-91, 93. 郭春杉, 2019. 运城盆地主要断裂活动性及其相关块体变形特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地震预测研究所. 郭媛媛, 莫多闻, 毛龙江, 等, 2013. 山东北部地区聚落遗址时空分布与环境演变的关系[J]. 地理学报, 68(4): 559-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB201304014.htm 侯光良, 许长军, 肖景义, 2012. 基于GIS的4kaB.P. 气候事件前后甘青史前遗址分布分析[J]. 地理科学, 32(1): 116-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201201020.htm 胡晓猛, 1997. 古汾河在峨嵋台地上的变迁[J]. 安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版), 20(2): 154-158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHSZ702.012.htm 姜佳奇, 莫多闻, 吕建晴, 等, 2016. 山西太原盆地全新世地貌演化及其对古人类聚落分布的影响[J]. 古地理学报, 18(5): 895-904. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201605018.htm 李辉, 丁金龙, 2020. 荆村遗址出土陶埙数量问题简述[J]. 文物世界(3): 41-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1092.2020.03.013 李吉均, 1990. 中国西北地区晚更新世以来环境变迁模式[J]. 第四纪研究(3): 197-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.03.001 李拓宇, 莫多闻, 胡珂, 等, 2013. 山西襄汾陶寺都邑形成的环境与文化背景[J]. 地理科学, 33(4): 443-449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201304007.htm 李振宏, 公王斌, 梁霞, 等, 2019. 上郭幅(I49E005012)地质图[Z]. 中国地质调查局. 孟令超, 2011. 山西断陷盆地地裂缝成因机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学. 彭建兵, 王启耀, 庄建琦, 等, 2020. 黄土高原滑坡灾害形成动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(5): 714-730. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20200506&journal_id=dzlxxb 齐玥, 徐鸿博, 张竞雄, 等, 2011. 临汾断陷盆地孤峰山花岗闪长岩的地球化学和年代学及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 57(4): 565-573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201104013.htm 史本恒, 2013. 水文和地貌条件对胶东半岛聚落选址的影响[J]. 华夏考古(4): 34-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXKG201304005.htm 史辰羲, 莫多闻, 刘辉, 等, 2010. 江汉平原北部汉水以东地区新石器晚期文化兴衰与环境的关系[J]. 第四纪研究, 30(2): 335-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201002011.htm 宋豫秦, 2002. 中国文明起源的人地关系简论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. 田婷婷, 吴中海, 张克旗, 等, 2013. 第四纪主要定年方法及其在新构造与活动构造研究中的应用综述[J]. 地质力学学报, 19(3): 242-266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.03.002 王海斌, 莫多闻, 李拓宇, 2014. 陶寺古城形成与选址的环境与文化背景研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 21(3): 302-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201403058.htm 王强, 李彩光, 田国强, 等, 2000. 7.1 Ma以来运城盆地地表系统巨变及盐湖形成的构造背景[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 30(4): 420-428. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200004011.htm 吴传钧, 1991. 论地理学的研究核心: 人地关系地域系统[J]. 经济地理(3): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJDL199103002.htm 吴立, 王心源, 周昆叔, 等, 2009. 巢湖流域新石器至汉代古聚落变更与环境变迁[J]. 地理学报, 64(1): 59-68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.01.007 吴艳宏, 吴瑞金, 王强, 等, 2001. 运城盆地11 ka B.P. 以来气候环境变迁与湖面波动[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 21(2): 83-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200102019.htm 武繁, 2016. 黄河峨嵋台地西段河湖阶地的年代学研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学. 徐伟, 高战武, 杨源源, 2014. 山西峨嵋台地北缘断裂晚第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 36(4): 1064-1076. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.04.011 严文明, 1965. 论庙底沟仰韶文化的分期[J]. 考古学报(2): 49-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KGXB196502002.htm 袁宝印, 同号文, 温锐林, 等, 2009. 泥河湾古湖的形成机制及其与早期古人类生存环境的关系[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(1): 77-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2009.01.007 张宏彦, 2006. 关于仰韶文化时空范围的界定问题[J]. 考古与文物(5): 66-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7830.2006.05.008 张克旗, 2012. 释光测年中环境剂量率影响因素研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 18(1): 62-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2012.01.007 张克旗, 吴中海, 吕同艳, 2015. 光释光测年法: 综述及进展[J]. 地质通报, 34(1): 183-203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.015 张忠培, 1997. 仰韶时代: 史前社会的繁荣与向文明时代的转变[J]. 文物世界(1): 1-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WWJK701.000.htm 赵俊香, 任俊杰, 于慎谔, 等, 2009. 山西忻定盆地断层崩积楔光释光年龄及其对古地震事件的指示意义[J]. 现代地质, 23(6): 1022-1029. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2009.06.004 赵俊香, 任俊杰, 于慎谔, 等, 2011. 断层崩积楔单片再生法光释光测年: 以山西忻定盆地西田探槽为例[J]. 现代地质, 25(2): 356-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.02.020 周珺, 2015. 黄河峨嵋台地段地貌沉积历史研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学. 周静静, 张晓敏, 赵法锁, 等, 2019. 陕南秦巴山区地质灾害危险性评价研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(4): 544-553. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190412&journal_id=dzlxxb -





 下载:
下载: