Discovery of active faults in the southern Beishan area, NW China: Implications for regional tectonics
-
摘要: 在河西走廊北侧、北山南缘新发现属于不同断裂系统的两条晚第四纪活动断裂,分别称之为旧井-板滩断裂和俄博庙断裂。其中,旧井-板滩断裂长约28 km,距玉门市约55 km,由4条分支断裂组成,呈复杂的"Y"字形分布。总体走向北东40°~50°,倾向北西,倾角60°~70°,控制了西侧两个晚新生代盆地的发育。俄博庙断裂长约18 km,距金塔县城约50 km,走向近东西,倾向北西,倾角60°~80°。根据卫星影像解译、断错地貌调查、探槽开挖和光释光测年结果,旧井-板滩断裂断错了一系列山脊、冲沟和阶地,在距今约2万年以来有过活动,以正左旋走滑为主;俄博庙断裂北向逆冲形成清晰的线性陡坎,并左旋断错了冲沟,在距今约3万年以来有过活动,以逆左旋走滑为主。以上两条断裂的新构造活动揭示了青藏高原北缘晚新生代以来的远程应变传递已经进入北山造山带南缘。Abstract: On the north side of the Hexi Corridor, two active faults, which belong to two different fault systems, have been discovered on the southern margin of Beishan, namely the Jiujing-Bantan fault and the Ebomiao fault. The NE-trending (40°~50°) Jiujing-Bantan fault with a NW-trending dip angle of 60°~70° is ~28 km long and ~55 km away from Yumen City. It consists of 4 branches and presents a complex Y-shaped distribution, controlling the development of the two late Pleistocene basins on its west side. The nearly EW-trending Ebomiao fault with a NW-trending dip angle of 60°~80° is ~18 km long and ~50 km away from Jinta County. Base on results from the satellite image interpretation, offset geomorphological survey, trench excavation and optical luminescence dating, we discovered a series of ridges, gullies and terraces offset by the Jiujing-Bantan fault which has been active since ~20 ka ago mostly with normal left-lateral strike-slips. The northward thrusting of the Ebomiao fault formed a clear linear scarp and offset the gullies with left-lateral strike-slips. This fault has been active since ~30 ka ago, mainly with reverse left-lateral strike-slips. The neotectonic activities of these two faults evidences that the long-range strain transmission from the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau has entered into the southern margin of the Beishan orogenic belt since the late Cenozoic.
-
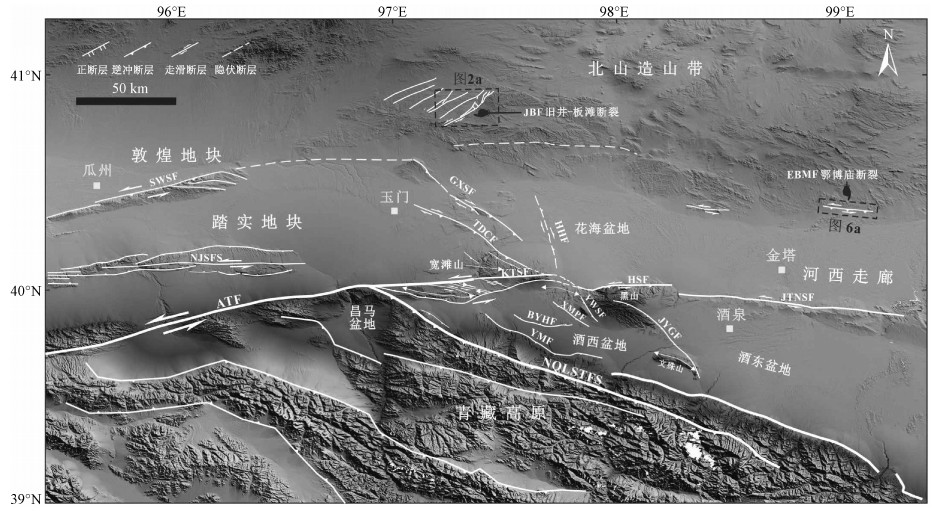
图 1 青藏高原北缘主要活动断裂分布图
JBF—旧井-板滩断裂;EBMF—俄博庙断裂;SWSF—三危山断裂;NJSF—南截山断裂;ATF—阿尔金断裂;GXSF—干峡山断裂;TDCF—塔尔湾-登登山-池家刺窝断裂;HHF—花海断裂;KTSF—宽滩山断裂;HSF—黑山断裂;YWSF—阴洼山断裂;JYGF—嘉峪关断裂;XMPF—新民堡断裂;BYHF—白杨河断裂;YMF—玉门断裂;NQLSTFS—北祁连逆冲断裂系;JTNSF—金塔南山北缘断裂
Figure 1. Distribution of the main faults on the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau.JBF—Jiujing-Bantan fault, EBMF—Ebomiao fault; SWSF—Sanweishan fault; NJSF—Nanjieshan fault; ATF—AltynTagn fault; GXSF—Ganxiashan fault; TDCF—Taerwan-Dengdengshan-Chijiaciwo fault; HHF—Huahai fault; KTSF—Kuantanshan fault; HSF—Heishan fault; YWSF—Yinwashan fault; JYGF—Jiayuguan fault; XMPF—Xinminpu fault; BYHF—Baiyanghe fault; NQLSTFS—Northern Qilianshan thrust fault system; JTNSF—northern Jinta'nanshan fault
图 2 旧井-板滩断裂卫星影像和平面展布图
JBF—旧井-板滩断裂;JBF-1,JBF-2,JBF-3和JBF-4为旧井-板滩断裂的4条分支;JTC-5和JTC-7为两个探槽的编号
Figure 2. Satellite image of the Jiujing-Bantan fault and its interpretation JBF—Jiujing-Bantan fault; JBF-1, JBF-2, JBF-3 and JBF-4 are four branches of the JBF; JTC-5 and JTC-7 are the code numbers of two trenches
图 7 俄博庙断裂断错地貌据(云龙等,2019修改)
a—断错地貌卫片;b—断层陡坎;c—侵蚀陡坎;d—g—断错冲沟
Figure 7. Offset landforms along the Ebomiao fault (modified after Yun et al., 2019). (a) Satellite image of offset landform; (b) Fault scarp; (c) Eroded scarp; (d-g) Offset gully
图 8 探槽ETC-03处地貌和探槽西壁地质剖面图据(云龙等,2019修改)
F1—F4为断层;U1—U8为地层代号
a—断层陡坎;b—探槽局部照片;c—探槽ETC-03解译图Figure 8. Offset landforms and geological interpretation of the western wall of the Trench ETC-03 (modified after Yun et al., 2019). (a) Fault scarp; (b) Partial photo of the trench; (c) Interpretation of the Trench ETC-03 F1-F4 are faults; U1-U8 are the code numbers of strata
图 9 青藏高原北缘主要断裂分布及MT剖面
JBF—旧井-板滩断裂;EBMF—俄博庙断裂;SWSF—三危山断裂;NJSF—南截山断裂;ATF—阿尔金断裂;GXSF—干峡山断裂;TDCF—塔尔湾-登登山-池家刺窝断裂;HHF—花海断裂;KTSF—宽滩山断裂;HSF—黑山断裂;YWSF—阴洼山断裂;JYGF—嘉峪关断裂;XMPF—新民堡断裂;BYHF—白杨河断裂;YMF—玉门断裂;NQLSTFS—北祁连逆冲断裂系;JTNSF—金塔南山北缘断裂
R1—R4—高阻体;C1—C3—低阻体
a—青藏高原北缘卫片及主要活动断裂解译;b—穿越俄博庙断裂的MT剖面(据Yang et al., 2019修改)Figure 9. Distribution of the main faults on the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau and the MT profile. (a) Satellite image and interpretation of the main active faults on the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. (b) The MT profile passing through the Ebomiao fault (modified after Yang et al., 2019).
JBF—Jiujing-Bantan fault; EBMF—Ebomiao fault; SWSF—Sanweishan fault; NJSF—Nanjieshan fault; ATF—AltynTagn fault; GXSF—Ganxiashan fault; TDCF—Taerwan-Dengdengshan-Chijiaciwo fault; HHF—Huahai fault; KTSF—Kuantanshan fault; HSF—Heishan fault; YWSF—Yinwashan fault; JYGF—Jiayuguan fault; XMPF—Xinmingpu fault; BYHF—Baiyanghe fault; YMF—Yumen fault; NQLSTFS—Northern Qilianshan thrust fault system; JTNSF—northern Jinta'nanshan fault R1-R4—high resistance body; C1-C3—low resistance body
表 1 探槽内的光释光测年样品分析结果
Table 1. Analysis results of the OSL dating samples from the trenches
野外编号 埋深/m 环境剂量率/(Gy/ka) 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka F21TC5-1 0.40 2.48 50.00 20.12±1.71 TC7-1 0.28 3.67±0.14 51.24±1.94 13.95±0.75 OSL-14 0.50 2.80±0.20 102.20±1.40 36.40±0.40 OSL-15 0.37 2.40±0.30 8.00±1.80 3.30±2.40 OSL-16 0.50 2.80±0.30 84.50±3.50 30.20±1.20 OSL-17 1.70 2.80±0.30 >300.00 >100.00 注:样品F21TC5-1采自探槽JTC-5;样品TC7-1采自探槽JTC-7;样品OSL-14—OSL-17采自探槽ETC-03 -
AVOUAC J P, TAPPONNIER P, 1993. Kinematic model of active deformation in central Asia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 20(10): 895-898. doi: 10.1029/93GL00128 CHEN B L, WANG C Y, LIU J M, et al., 2006. The activity of the Xinminbao fault from the Late Pleistocene to Holocene[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 27(6): 515-524. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.oalib.com/paper/1557720 CHEN B L, WANG C Y, GONG Y L, 2008. Late Cenozoic activity of t11e Yumen fault in the western segment of the HexiCorridor. NW China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(10): 1709-1719. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/298469098_Late_Cenozoic_activity_of_the_Yumen_fault_in_the_western_segment_of_the_Hexi_Corridor_NW_China CHEN T, LIU Y G, MIN W, et al., 2012. The activity age of Tarwan fault and genesis of the topographic scarp[J]. Seismology and Geology, 34(3): 401-414. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201203005.htm CHENG F, GARZIONE C N, JOLIVET M, et al., 2019a. Initial deformation of the northern Tibetan Plateau: insights from deposition of the Lulehe Formation in the Qaidam Basin[J]. Tectonics, 38(2): 741-766. doi: 10.1029/2018TC005214 CHENG F, GARZIONE C N, MITRA G, et al., 2019b. The interplay between climate and tectonics during the upward and outward growth of the Qilian Shan orogenic wedge, northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 198: 102945. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102945 CUNNINGHAM D, DAVIES S, MCLEAN D, 2009. Exhumation of a Cretaceous rift complex within a Late Cenozoic restraining bend, southern Mongolia: implications for the crustal evolution of the Gobi Altai region[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of London, 166(2): 321-333. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492008-082 CUNNINGHAM D, 2013. Mountain building processes in intracontinental oblique deformation belts: lessons from the Gobi Corridor, Central Asia[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 46: 255-282. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2012.08.010 CUNNINGHAM D, ZHANG J, LI Y F, 2016. Late Cenozoic transpressional mountain building directly north of the AltynTagh Fault in the Sanweishan and Nanjieshan, North Tibetan Foreland, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 687: 111-128. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.09.010 DAI S, FANG X M, SONG C H, et al, 2005. Early Uplift of the Northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(7): 673-683. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/csb2005-50-7-673 DARBY B J, RITES B D, YUE Y J, et al., 2005. Did the AltynTagh fault extend beyond the Tibetan Plateau?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 240(2): 425-435. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.09.011 FANG X M, ZHAO Z J, LI J J, et al., 2005. Magnetostratigraphy of the Late Cenozoic Laojunmiao Anticline in the Northern Qilian Mountains and Its Implications for the Northern Tibetan Plateau Uplift[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 48(7): 1040-1051. doi: 10.1360/03yd0188 GUO Z J, ZHANG Z C, ZHANG C, et al., 2008. Lateral growth of the AltynTagh strike-slip fault atthe north margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Late Cenozoic strike-slip faults and the crustal stability in the Beishan area, Gansu, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(10): 1678-1686. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200810011.htm HU X P, ZANG A, HEIDBACHO, et al., 2017. Crustal stress pattern in China and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 149: 20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.07.005 LEASE R O, BURBANK D W, ZHANG H P, et al., 2012. Cenozoic shortening budget for the northeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau: Is lower crustal flow necessary?[J]. Tectonics, 31: TC3011. http://gateway.proquest.com/openurl?res_dat=xri:pqm&ctx_ver=Z39.88-2004&rfr_id=info:xri/sid:baidu&rft_val_fmt=info:ofi/fmt:kev:mtx:article&genre=article&jtitle=Tectonics&atitle=Cenozoic%20shortening%20budget%20for%20the%20northeastern%20edge%20of%20the%20Tibetan%20Plateau%3A%20Is%20lower%20crustal%20flow%20necessary%3F LEI X L, MA J, KUSEUNOSE K, et al., 1991. Spatial distribution and fractal structure of AE focuses on Inada granite under Triaxial compression[J]. Seismology and Geology, 13(2): 97-106, 114. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZDZ199102001.htm LI A, WANG X X, ZHANG S M, et al., 2016. The slip rate and paleoearthquakes of the Yumen fault in the Northern Qilian Mountains since the Late Pleistocene[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(4): 897-910. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313579408_The_slip_rate_and_paleoearthquakes_of_the_Yumen_fault_in_the_northern_Qilian_mountains_since_the_late_pleistocene LIU M, YANG Y Q, SHEN Z K, et al., 2007. Active tectonics and intracontinental earthquakes in China: the kinematics and geodynamics[M]//STEIN S, MAZZOTTI S. Continental Intraplate Earthquakes: Science, Hazard, and Policy Issues. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 425: 209-318. LIU X W, YUAN D Y, ZUO X B, et al., 2018. Active characteristics of the Sanweishan fault in the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau during late Pleistocene. Seismology and Geology, 40(1): 121-132. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_seismology-geology_thesis/0201253220867.html MIN W, LIU Y G, CHEN T, et al., 2016. The quantative study on activity of Dengdengshan-Chijiaciwo faults since Late Quaternary[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(3): 503-522. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/309530979_The_quantative_study_on_activity_of_Dengdengshan-Chijiaciwo_faults_since_late_quaternary MOLNAR P, TAPPONNIER P, 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: effects of a continental collision[J]. Science, 189(4201): 419-426. doi: 10.1126/science.189.4201.419 MOLNAR P, ENGLAND P, MARTINOD J, 1993. Mantle dynamics, uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the Indian monsoon[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 31(4): 357-396. doi: 10.1029/93RG02030 SHI Z T, YE Y G, ZHAO Z J, et al., 2001. ESR dating of late Cenozoic molassic deposits in the Jiuxi Basin[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 44(S1): 203-209. doi: 10.1007/BF02911988 SONG D F, XIAO W J, WINDLEY B F, et al., 2016. Metamorphic complexes in accretionaryorogens: Insights from the Beishan collage, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 688: 135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.09.012 TAPPONNIER P, XU Z Q, ROGER F, et al., 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 294(5547): 1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978 WANG C S, DAI J G, ZHAO X X, et al., 2014. Outward-growth of the Tibetan Plateau during the Cenozoic: a review[J]. Tectonophysics, 621: 1-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.01.036 WANG F, SU G, JIN P D, 2004. Tectonic deformation and evolution trend of Beishan region, Gansu Province since Late Quaternary[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 27(2): 173-178. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/292278126_Tectonic_deformation_and_evolution_trend_of_Beishan_region_Gansu_province_since_late_Quaternary WANG F, WANG J, FAN H H, et al., 2015. Distribution of Late Quaternary active faults and its tectonic significance in the Beishan Region, Gansu Province, China[J]. Geological Review, 51(3): 250-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225159721_Distribution_of_Tuvaella_brachiopod_fauna_and_its_tectonic_significance WANG M, SHEN Z K, 2020. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 125(2): e2019JB018774. doi: 10.1029/2019JB018774 WU L, XIAO A C, WANG L Q, et al., 2011. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous northern Qaidam Basin, NW China: implications for the earliest Cretaceous intracontinentaltectonism[J]. Cretaceous Research, 32(4): 552-564. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2011.04.002 WU L, XIAO A C, YANG S F, et al., 2012. Two-stage evolution of the AltynTagh Fault during the Cenozoic: new insight from provenance analysis of a geological section in NW Qaidam Basin, NW China[J]. Terra Nova, 24(5): 387-395. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3121.2012.01077.x XIAO Q B, ZHANG J, WANG J J, et al., 2012. Electrical resistivity structures between the Northern Qilian Mountains and Beishan Block, NW China, and tectonic implications[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 200-201: 92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2012.04.008 XIAO Q B, SHAO G H, LIUZENG L, et al., 2015. Eastern termination of the AltynTagh Fault, western China: Constraints from a magnetotelluric survey[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120(5): 2838-2858. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011363 XIAO W J, MAO Q G, WINDLEY B F, et al., 2010. Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional processes of the Beishan orogenic collage[J]. American Journal of Science, 310(10): 1553-1594. doi: 10.2475/10.2010.12 XIE F R, CUI X F, ZHAO J T, et al., 2004. Regional division of the recent tectonic stress field in China and adjacent areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(4): 654-662. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/261529704_Regionalization_of_the_Recent_Tectonic_Stress_Field_in_China_and_Adjacent_Regions XU X W, WANG F, ZHENG R Z, et al., 2005. Late Quaternary sinistral slip rate along the AltynTagh fault and its structural transformation model[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 48(3): 384-397. doi: 10.1360/02yd0436 YAN D P, SUN M, GONG L X, et al., 2020. Composite structure and growth of the Longmenshan foreland thrust belt in the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(5): 615-633. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG H B, YANG X P, ZHAN Y, et al., 2019. Quaternary activity of the Beihewan Fault in the southeastern Beishan Wrench Belt, western China: Implications for crustal stability and intraplate earthquake hazards north of Tibet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 124(12): 13286-13309. doi: 10.1029/2018JB017209 YANG H B, YANG X P, CUNNINGHAM D, et al., 2020. A regionally evolving transpressional duplex along the northern margin of the AltynTagh Fault: New kinematic and timing constraints from the Sanweishan and Nanjieshan, China[J/OL]. Tectonics, 39, e2019TC005749. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019TC005749. YIN A, HARRISON T M, 2000. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28: 211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 YIN A, 2010. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Asia: a preliminary synthesis[J]. Tectonophysics, 488(1-4): 293-325. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.06.002 YU Z Y, MIN W, CHEN T, et al., 2015. Late Quaternary tectonic deformation of the eastern end of the AltynTagh fault[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 89(6): 1813-1834. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12599 YUE Y J, RITTS B D, GRAHAM S A, et al., 2004a. Slowing extrusion tectonics: lowered estimate of post-Early Miocene slip rate for the AltynTagh fault[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 217(1-2): 111-122. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00544-2 YUE Y J, RITTS B D, HANSON A D, et al., 2004b. Sedimentary evidence against large strike-slip translation on the Northern AltynTagh fault, NW China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 228(3-4): 311-323. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.10.008 YUN L, ZHANG J, XU W, et al., 2019. The active characteristics and its significance of the southern margin fault of Beishan Area in Gansu Province[J]. Geological Review, 65(4): 825-838. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLP201904005.htm YUN L, ZHANG J, XU W, et al., 2021. Geometry, kinematics andregional tectonic significance of the Huahai fault in the western Hexi Corridor, NW China[J]. Earth Science, 46(1): 259-271. (in Chinese with English abstract) YUN L, ZHANG J, WANG J, et al., 2020. Active deformation to the north of the AltynTagh Fault: Constraints on the northward growth of the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 198: 104312. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104312 ZHANG B, HE W G, LIU B X, et al., 2020. New activity characteristics and slip rate of the ebomiao fault in the southern margin of Beishan, Gansu Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(2): 455-471. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG P Z, MOLNAR P, DOWNS W R, 2001. Increased sedimentation rates and grain sizes 2-4 Myr ago due to the influence of climate change on erosion rates[J]. Nature, 410(6831): 891-897. doi: 10.1038/35073504 ZHANG P Z, MOLNAR P, XU X W, 2007. Late Quaternary and present-day rates of slip along the AltynTagh Fault, northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 26(5): TC5010. doi: 10.1029/2006TC002014 ZHANG J, CUNNINGHAM D, 2012. Kilometer-scale refolded folds caused by strike-slip reversal and intraplate shortening in the Beishan region, China[J]. Tectonics, 31(3): TC3009. doi: 10.1029/2011TC003050 ZHANG N, ZHENG W J, LIU X W, et al., 2016. Kinematics characteristics of Heishan fault in the western Hexicorridor and its implications for regional tectonic transformation[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 38(2): 245-257. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://jese.chd.edu.cn/en/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=201602010 ZHAO G M, WU Z H, LIU J, et al., 2019. The time space distribution characteristics and migration law of large earthquakes in the Indiam-Eurasian Plate collision deformation area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(3): 324-340. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/333948849_THE_TIME_SPACE_DISTRIBUTION_CHARACTERISTICS_AND_MIGRATION_LAW_OF_LARGE_EARTHQUAKES_IN_THE_INDIAM-EURASIAN_PLATE_COLLISION_DEFORMATION_AREA ZHAO Z J, FANG X M, LI J J, 2001. Late Cenozoic magnetic strata in Jiudong Basin, northern margin of Qilian Mountains[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Science, 31(S1): 195-201. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1007/BF02911987 ZHENG W J, ZHANG P Z, GE W P, et al., 2013. Late Quaternary slip rate of the South Heli Shan Fault (northern Hexi Corridor, NW China) and its implications for northeastward growth of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 32(2): 271-293. doi: 10.1002/tect.20022 ZHENG Y, ZHANG Q, WANG Y, et al., 1996. Great Jurassic thrust sheets in Beishan (North Mountains): Gobi areas of China and southern Mongolia[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 18(9): 1111-1126. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(96)00038-7 ZUZA A V, WU C, REITH R C, et al., 2018a. Tectonic evolution of the Qilian Shan: an early Paleozoic orogen reactivated in the Cenozoic[J]. GSA Bulletin, 130(5-6): 881-925. doi: 10.1130/B31721.1 ZUZA A V, WU C, WANG Z Z, et al., 2018b. Underthrusting and duplexing beneath the northern Tibetan Plateau and the evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Lithosphere, 11(2): 209-231. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/329858498_Underthrusting_and_duplexing_beneath_the_northern_Tibetan_Plateau_and_the_evolution_of_the_Himalayan-Tibetan_orogen 陈柏林, 王春宇, 刘建民, 等, 2006. 新民堡断裂新构造活动特征[J]. 地球学报, 27(6): 515-524. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.06.001 陈柏林, 王春宇, 宫玉良, 2008. 河西走廊盆地西段玉门断裂晚新生代的活动特征[J]. 地质通报, 27(10): 1709-1719. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.10.013 陈涛, 刘玉刚, 闵伟, 等, 2012. 塔尔湾断裂活动时代厘定及地貌陡坎成因分析[J]. 地震地质, 34(3): 401-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.03.002 戴霜, 方小敏, 宋春晖, 等, 2005. 青藏高原北部的早期隆升[J]. 科学通报, 50(7): 673-683. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.07.011 方小敏, 赵志军, 李吉均, 等, 2004. 祁连山北缘老君庙背斜晚新生代磁性地层与高原北部隆升[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 34(2): 97-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200402000.htm 郭召杰, 张志诚, 张臣, 等, 2008. 青藏高原北缘阿尔金走滑边界的侧向扩展: 甘肃北山晚新生代走滑构造与地壳稳定性分析[J]. 地质通报, 27(10): 1678-1686. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.10.010 雷兴林, 马瑾, 楠濑勤一郎, 等, 1991. 三轴压缩下粗晶花岗闪长岩声发射三维分布及其分形特征[J]. 地震地质, 13(2): 97-106, 114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ199102000.htm 李安, 王晓先, 张世民, 等, 2016. 祁连山北缘玉门断裂晚更新世以来的活动速率及古地震[J]. 地震地质, 38(4): 897-910. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.04.008 刘兴旺, 袁道阳, 邹小波, 等, 2018. 青藏高原北缘三危山断裂晚更新世活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 40(1): 121-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.01.010 闵伟, 刘玉刚, 陈涛, 等, 2016. 登登山-池家刺窝断裂晚第四纪活动性定量研究[J]. 地震地质, 38(3): 503-522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.03.002 史正涛, 业渝光, 赵志军, 等, 2001. 酒西盆地晚新生代地层的ESR年代[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 31(S1): 163-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2001S1024.htm 王峰, 苏刚, 晋佩东, 2004. 甘肃北山地区晚第四纪构造变形特征及演化趋势[J]. 地震研究, 27(2): 173-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2004.02.010 王峰, 王驹, 范洪海, 等, 2005. 甘肃北山旧井地区晚第四纪活动断裂分布及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 51(3): 250-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2005.03.004 谢富仁, 崔效锋, 赵建涛, 等, 2004. 中国大陆及邻区现代构造应力场分区[J]. 地球物理学报, 74(4): 654-662. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.016 颜丹平, 孙铭, 巩凌霄, 等, 2020. 青藏高原东缘龙门山前陆逆冲带复合结构与生长[J]. 地质力学学报, 26(5): 615-633. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20200501&journal_id=dzlxxb 云龙, 张进, 徐伟, 等, 2019. 甘肃北山南缘断裂的活动特征及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 65(4): 825-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201904005.htm 云龙, 张进, 徐伟, 等, 2021. 河西走廊西段花海断裂几何学、运动学及区域构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 46(1): 259-271. 张波, 何文贵, 刘炳旭, 等, 2020. 甘肃北山南缘俄博庙断裂的新活动特征及活动速率[J]. 地震地质, 42(2): 455-471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.02.013 张宁, 郑文俊, 刘兴旺, 等, 2016. 河西走廊西端黑山断裂运动学特征及其在构造转换中的意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 38(2): 245-257. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2016.02.012 赵根模, 吴中海, 刘杰, 等, 2019. 印度-欧亚板块碰撞变形区的大地震时空分布特征与迁移规律[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(3): 324-340. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190303&journal_id=dzlxxb 赵志军, 方小敏, 李吉均, 2001. 祁连山北缘酒东盆地晚新生代磁性地层[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 31(S1): 195-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2001S1029.htm -





 下载:
下载: