Basic characteristics, dynamic mechanism and development direction of the formation and distribution of deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs in China
-
摘要: 随着油气资源对外依赖度加大,中国的油气勘探已经拓展到深层和超深层领域,并相继在中西部盆地发现了塔河、普光、安岳、靖边、顺北等一批大型油气田,展示出广阔的勘探前景。中国已探明的深层和超深层碳酸盐岩油气藏特征与全球的有很大差异,经典的油气地质理论指导这类油气田勘探遇到了前所未有的重大挑战,需要完善和发展。通过调研和比较全球已探明的碳酸盐岩和砂岩油气藏地质特征,发现它们的油气来源条件、油气藏形成条件、成藏动力、演化过程特征等类同;同时,发现碳酸盐岩和砂岩油气藏的矿物组成、孔隙度和渗透率随埋深变化特征、孔渗结构特征、储层物性下限、油气藏类型等有着很大不同。中国深层和超深层碳酸盐岩油气藏与全球的相比较具有五方面差异:地层年代更老、埋藏深度更大、白云岩储层比率更大、天然气资源比率更高、储层孔渗关系更乱。中国已经发现的深层碳酸盐岩油气藏成因类型可以归为五种:沉积型高孔高渗油气藏、压实成岩型低孔低渗油气藏、结晶成岩型低孔低渗油气藏、流体改造型高孔低渗油气藏、应力改造型低孔高渗油气藏;它们形成的动力学机制分别与地层沉积和浮力主导的油气运移作用、地层压实和非浮力主导的油气运移作用、成岩结晶和非浮力主导的油气运移作用、流体改造介质和浮力主导的油气运移作用、应力改造和浮力主导的油气运移作用等密切相关。中国深层和超深层碳酸盐岩油气藏勘探发展的有利领域和油气藏类型主要有三个:一是低热流盆地浮力成藏下限之上自由动力场形成的高孔高渗常规油气藏;二是构造变动频繁的叠合盆地内外应力和内部流体活动改造而形成的缝洞复合型油气藏;三是构造稳定盆地内局限动力场形成的广泛致密连续型非常规油气藏。改造类非常规致密碳酸盐岩油气藏是中国含油气盆地深层和超深层油气资源的主要类型:它们叠加了早期形成的常规油气藏特征,又具有自身广泛连续分布的非常规特征,还经受了后期构造变动的改造;复杂的分布特征,致密的介质条件和高温高压环境使得这类油气资源勘探开发难度大、成本高。Abstract: With the increasing dependence on external oil and gas resources, China's oil and gas exploration has expanded to deep and ultra-deep areas and discovered a number of large oil and gas fields in the central and western basins successively, such as the Tahe, Puguang, Anyue, Jingbian and Shunbei oilfields, showing a broad prospect of exploration. The proven deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs in China are quite different from those in the world, and the exploration of these oil and gas fields under the guidance of the classical oil and gas geological theories has met unprecedented challenges, which need to be improved and developed. Through the investigation and comparison of the geological characteristics of the proven carbonate and sandstone reservoirs around the world, it is found that their oil and gas source conditions, accumulation dynamics, and evolution processes are similar; however, it is revealed at the same time that the mineral composition of reservoir layers, their porosity and permeability change characteristics with buried depth, porosity and permeability structure characteristics, the lower limit of reservoir physical properties, and oil and gas reservoir types are very different. There are five differences between the deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs in China and other basins in the world, which in China have older formations, greater burial depth, greater dolomite reservoir ratio, higher natural gas resource ratio, and more chaotic relationship between porosity and permeability. The genetic types of deep carbonate reservoirs discovered in China can be classified into five types: sedimentary high-porosity and high-permeability oil/gas reservoirs, compacted diagenetic low-porosity and low-permeability oil/gas reservoirs, crystalline diagenetic low-porosity and low-permeability oil/gas reservoirs, fluid modified high-porosity and low-permeability oil/gas reservoirs, and stress reformed low-porosity and high-permeability oil/gas reservoirs. The dynamic mechanisms of their formation are respectively related to the oil and gas migration dominated by stratigraphic deposition and buoyancy, formation compaction and non-buoyancy, diagenetic crystallization and non-buoyancy, fluid reformed media and buoyancy, stress reformed media and buoyancy. There are mainly three favorable areas and related types of oil and gas reservoirs for the exploration and development of China's deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs. The first is the conventional oil and gas reservoirs with high-porosity and high-permeability, formed in the free oil/gas dynamic field above the hydrocarbon buoyance-driven depth limit in basins with low heat flow. The second is the fracture-cavity compound oil/gas reservoirs, formed by external stress and inner fluids activities in the superimposed basin due to frequent structural changes. The third one is the extensive compacted continuous unconventional tight oil/gas reservoirs, formed by the confined dynamic field in the structurally stable basin. The reformed unconventional tight carbonate oil and gas reservoirs are the main types of future oil and gas resources in the deep and ultra-deep layers of China's petroliferous basins. They both have the characteristics of conventional reservoirs formed in the early stage and their own unconventional characteristics of extensive and continuous distribution, and have undergone structural changes in the later stage. The complex distribution characteristics, dense medium conditions and high temperature and pressure environment make the exploration and development of this kind of oil and gas resources difficult and costly.
-
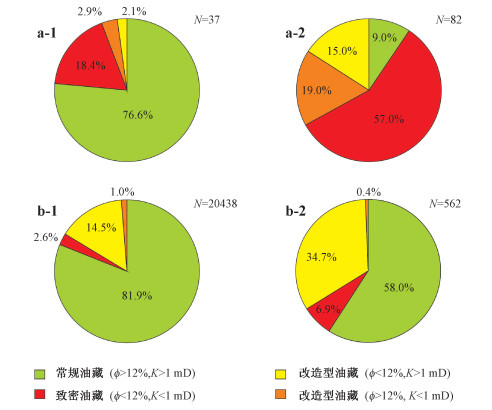
图 1 中国塔里木盆地和全球含油气盆地中浅层和深层已经发现的油气藏储层孔隙度和渗透率结构特征差异性比较
a—中国塔里木盆地油气藏(a-1—储层埋深<4500 m,a-2—储层埋深>4500 m);b—世界含油气盆地油气藏(b-1—储层埋深<4500 m,b-2—储层埋深>4500 m)
Figure 1. Comparison of the structural characteristics of porosity and permeability of oil and gas reservoirs that have been discovered in the middle-shallow and deep layers of the Tarim Basin in China and the global petroliferous basins
图 6 碳酸盐岩油气藏与砂岩油气藏的孔隙度和渗透率结构特征差异性比较
a—塔中地区两种储层物性参数关系图(a-1—碎屑岩储层渗透率与孔喉半径关系,a-2—碎屑岩储层孔隙度与孔喉半径关系,a-3—碎屑岩储层孔隙度与渗透率关系,a-4—碳酸盐岩储层渗透率与孔喉半径关系,a-5—碳酸盐岩储层孔隙度与孔喉半径关系,a-6—碳酸盐岩储层孔隙度与渗透率关系);b—苏里格气田低渗透致密砂岩和靖边气田致密白云岩储层孔-渗关系(b-1—致密砂岩孔隙度—渗透率关系,b-2—低渗透致密白云岩孔隙度-渗透率关系)
Figure 6. Comparison of the structural characteristics of porosity and permeability between carbonate reservoirs and sandstone reservoirs
图 11 a-塔河油田在塔里木盆地平面上分布特征; b-塔河油田在纵向剖面上的分布特征; c-岩心溶蚀孔洞发育特征; d-岩心测试(基质)孔渗特征(d-1—间房组,d-2—鹰山组)
a-塔河油田在塔里木盆地平面上分布特征; b-塔河油田在纵向剖面上的分布特征; c-岩心溶蚀孔洞发育特征; d-岩心测试(基质)孔渗特征(d-1—间房组,d-2—鹰山组)
Figure 11. Geological characteristics of fluid modified high-porosity and low-permeability carbonate reservoirs in Tahe, Tarim Basin
图 13 中国含油气盆地砂岩储层与碳酸盐岩储层中浮力成藏下限对应临界条件差异性比较
a—含油气盆地浮力成藏下限概念模型与控藏特征;b—依据钻探结果确定的砂岩介质中油气浮力成藏下限(b-1—鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格庙石炭系砂岩含气层孔渗特征,b-2—准噶尔盆地二叠系砂岩含油层孔渗特征);c—碳酸盐岩储层介质中的浮力成藏下限(K=1.0 mD, Φ=5±2%;c-1—安岳气田白云岩储层孔渗特征,c-2—普光气田飞仙关组白云岩储层孔渗特征,c-3—塔中油气田砂岩储层孔渗特征)
Figure 13. Comparison of the differences between the lower limits of buoyancy accumulation in sandstone reservoirs and carbonate reservoirs in China's petroliferous basins corresponding to critical conditions
图 14 中国含油气盆地砂岩油气藏和碳酸盐岩油气藏成藏底限研究与对比分析
a—塔里木盆地砂岩油气藏形成底限预测结果(a-1—为砂岩孔隙度随埋深变化及油气水钻探结果,a-2—为油气水钻探结果随埋深的变化,a-3—为油气成藏底限最大埋深判别结果及对应的临界条件;Z=6250 m,K=0.01 mD, Φ=2%±1%,干层比率=100%);b—砂岩和碳酸盐岩储层孔渗关联特征及油气成藏底限对应临界条件(b-1—四川盆地安岳大气田白云岩储层,b-2—塔里木盆地塔中油气田砂岩储层,b-3—四川盆地普光大气田白云岩储层)
Figure 14. Research and comparative analysis of low limits of sandstone reservoirs and carbonate reservoirs in China's petroliferous basins
图 16 深层和超深层常规油气藏形成分布领域(据Pang et al., 2012a, 2020修改)
Figure 16. Formation and distribution fields of deep and ultra-deep conventional oil and gas reservoirs (modified after Pang et al., 2012a, 2020)
图 17 局限动力场内非浮力主导油气运移形成致密非常规碳酸盐岩油气藏
a—非浮力主导油气运移形成三类源外致密非常规油气藏,包括致密非常规常规油气藏、致密非常规深盆油气藏、致密非常规叠复连续油气藏; b—中国深层非浮力主导形成非常规碳酸盐岩油气藏一四川盆地安岳气田周边有利成藏区预测结果(b-1—灯影组灯二段有利勘探区,b-2—灯影组灯四段有利勘探区,b-3—寒武系龙王庙组有利勘探区: Wang et al, 2019a) c—定量预测评价结果与钻探结果吻合度检验(c-1—灯影组成功井吻合率超过88.9%,失利井吻合率超过73.7%,c-2—龙王庙组成功井吻合率超过88.9%,失利井吻合率超过84.2%)
Figure 17. Non-buoyancy dominates oil and gas migration in a limited dynamic field to form tight unconventional carbonate reservoirs
图 18 改造型局限动力场内多动力主导油气运移形成改造类致密非常规碳酸盐岩油气藏
a—多动力主导油气运移形成五类改选类油藏(a-1—裂缝改造类油气藏,a-2—孔洞改造类致密油气藏,a-3—缝洞复合改造类油气藏,a-4—氧压降解改造类稠油沥青,a-5—高温裂解改造类油气藏);b—塔里木盆地塔中下陶统碳酸盐岩多动力油气成藏与形成特征(b-1—剖面上油气钻探结果与分布特征,b-2—平面上油气钻探结果与分布特征)
Figure 18. Multi-power dominates oil and gas migration in a modified limited dynamic field to form reformed tight unconventional carbonate reservoirs
表 1 中国和海外已经发现的最大的前五个碳酸盐岩油气田地质特征比较
Table 1. Comparison of the geological characteristics of the top five largest carbonate oil and gas fields discovered in China and overseas
国家 盆地名称 油气田名称 储量/亿吨 层位 岩性 孔隙度/%/渗透率/mD 埋深/m 中国 四川盆地 普光气田 3.5 二叠系 白云岩 8.1~12/3.24~479.3 >5000 四川盆地 安岳气田 8.4 震旦系 白云岩 3.22/0.5 >5500 塔里木盆地 塔河油田 13.5 奥陶系 灰岩+白云岩 1.15/1.54 >5000 塔里木盆地 顺北油气田 17 奥陶系 灰岩+白云岩 1.96/7.50 >7000 鄂尔多斯盆地 靖边气田 6.9 奥陶系 白云岩 6/2.63 >2500 海外 伊朗扎格罗斯盆地 Gachsaran油田 34.6 中新统 石灰岩 9/15 < 3500 阿联酋波斯湾盆地 Zakum油田 32.1 下白垩统 石灰岩 20/3 < 2500 卡塔尔波斯湾盆地 North Field气田 263 二叠/三叠 白云岩 9.5/300 < 3500 伊朗波斯湾盆地 Pars South气田 130 二叠/三叠 白云岩 20.25/0.94 < 3000 俄罗斯滨里海盆地 Astrak han气田 27.7 上石炭统 灰岩 11/2.3 < 4500 表 2 中国深层和超深层碳酸盐岩油气藏成因特征与动力学分类
Table 2. Genetic characteristics and dynamic classification of deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs in China
碳酸盐岩油气成因分类 形成条件 基本特征 主控因素 动力机制 典型实例 I常规类油气藏 I-1浮力主导常规圈闭油气藏 礁滩沉积鲕粒滩沉积 埋深相对较浅,高孔高渗 沉积作用 沉积成岩+浮力主导(先成岩后成藏) 普光气田威远气田 I-2浮力主导裂缝改造油气藏 构造变动断裂作用 构造变动强,低孔高渗 断裂作用 应力改造+浮力主导(先裂缝后成藏) 顺北油气田 I-3浮力主导孔洞改造油气藏 流体改造次生溶蚀 孔洞发育,高孔低渗 不整合作用 流体改造+浮力主导(先孔洞后成藏) 塔河油田 II非常规类气藏 II-1非浮力主导致密圈闭油气藏 储层深埋压实 埋深相对较浅,低孔低渗 压实作用 浮力主导+压实致密(先成藏后致密) / II-2非浮力主导致密深盆油气藏 深坳区发育储层 埋深相对较大,低孔低渗 源岩排烃 压实+非浮力(先致密后成藏) 安岳气田 III复合类油气藏 III-1多动力主导叠复连续油气藏 储层广泛连续 油气层广泛连续,不受构造控制 源储组合 浮力+成藏+非浮力(成藏后致密再成藏) / III-2多动力主导白云岩化油气藏 灰滩或云滩沉积 埋深较浅,低孔低渗 重结晶作用 结晶+浮力/非浮力(先缝隙后成藏) 靖边气田 -
DENG S, LI H L, HAN J, et al., 2019. Characteristics of the central segment of Shunbei 5 strike-slip fault zone in Tarim Basin and its geological significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 40(5):990-998, 1073. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201905005 GU Y, WAN Y L, HUANG J W, et al., 2019. Prospects for ultra-deep oil and gas in the "deep burial and high pressure" Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 41(2):157-164. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201902002 GUO Y C, PANG X Q, LI Z X, et al., 2017. The critical buoyancy threshold for tight sandstone gas entrapment:Physical simulation, interpretation, and implications to the Upper Paleozoic Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 149:88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.10.004 HOVORKA S D, DUTTON A R, RUPPEL S C, 1994. Sedimentologic and diagenetic controls on aquifer properties, Lower Cretaceous Edwards Carbonate Aquifer, Texas:Implications for aquifer management[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 78(9):1460-1461. doi: 10.1306/a25fee9b-171b-11d7-8645000102c1865d IHS Energy Group, 2018. International petroleum exploration and production database[R]. Englewood, Colorado: IHS Energy Group. KANG Y Z, XING S W, LI H J, et al., 2019. Features of structural systems in northern China and its control on basin and hydrocarbon distribution[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6):1013-1024. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201906002 LI Y T, QI L X, ZHANG S N, et al., 2019. Characteristics and development mode of the Middle and Lower Ordovician fault-karst reservoir in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(12):1470-1484. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYDQ201902019.htm LI Z, HUANG S J, LIU J Q, et al., 2010. Buried diagenesis, structurally controlled thermal-fluid process and their effect on Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in Tahe, Tarim basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 28(5):969-979. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201005014 LIU B Z, 2020. Analysis of main controlling factors of oil and gas differential accumulation in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin-taking Shunbei No.1 and No.5 strike slip fault zones as examples[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 25(3):83-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsykt202003008 LIU D H, XIAO X M, TIAN H, et al., 2009. Evidence of overpressured high-density methane inclusions and fluid pressure simulation calculations in the geological history of the Puguang Gas Field[C]//Proceedings of the 12th National Conference on Organic Geochemistry. Chengdu: Geological Society of China, Petroleum Society of China, Mineral Rock Geochemistry Society of China: 344-346. (in Chinese) LIU S G, SONG J M, ZHAO Y H, et al., 2014. Controlling factors of formation and distribution of Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation high-quality reservoirs in Sichuan basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 41(6):657-670. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201406001 MA Y S, 2007. Generation mechanism of Puguang gas field in Sichuan basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 28(2):9-14, 21. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYXB200702001.htm MA Y S, CAI X Y, GUO T L, 2007. The controlling factors of oil and gas charging and accumulation of Puguang gas field in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(S1):193-200. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-6007-7 MA Y S, CAI X Y, LI G X, 2005. Basic characteristics and concentration of the Puguang gas field in the Sichuan basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(6):858-865. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200506014 PANG X Q, 2014. Alteration and reformation of hydrocarbon reservoirs and simulation of the hydrocarbon loss through major tectonic events[M]. Beijing:Science Press. (in Chinese) PANG X Q, JIA C Z, PANG H, et al., 2018. Destruction of hydrocarbon reservoirs due to tectonic modifications:Conceptual models and quantitative evaluation on the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 91:401-421. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.01.028 PANG X Q, JIA C Z, ZHANG K, et al., 2020. The dead line for oil and gas and implication for fossil resource prediction[J]. Earth System Science Data, 12(1):577-590. doi: 10.5194/essd-12-577-2020 PANG X Q, JIANG Z X, HUANG H D, et al., 2014. Formation mechanisms, distribution models, and prediction of superimposed, continuous hydrocarbon reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 35(5):795-828. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201405001 PANG X Q, LIAO Y, 2016. Genetic mechanism and prediction methodology for overstacked and continuous hydrocarbon accumulations[M]. Beijing:Science Press. (in Chinese) PANG X Q, LIU K Y, MA Z Z, et al., 2012a. Dynamic field division of hydrocarbon migration, accumulation and hydrocarbon enrichment rules in sedimentary basins[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 86(6):1559-1592. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12023 PANG X Q, WANG W Y, WANG Y X, et al., 2015. Comparison of otherness on hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and characteristics between deep and middle-shallow in petroliferous basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(10):1167-1187. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201510001 PANG X Q, ZHOU X Y, YAN S H, et al., 2012b. Research advances and direction of hydrocarbon accumulation in the superimposed basins, China:Take the Tarim Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 39(6):692-699. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(12)60094-9 QIAO B, LIU H F, HE L, et al., 2018. A new method to quantitatively rebuild palaeogeomorphology and its application to Jingbian gasfield Ordos basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 41(4):32-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqktykf201804006 QIU Z, SHI Z S, DONG D Z, et al., 2016. Geological characteristics of source rock and reservoir of tight oil and its accumulation mechanism:A case study of Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusar sag, Junggar basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 43(6):928-939. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.researchgate.net/publication/312129786_Geological_characteristics_of_source_rock_and_reservoir_of_tight_oil_and_its_accumulation_mechanism_A_case_study_of_Permian_Lucaogou_Formation_in_Jimusar_sag_Junggar_Basin SHEN W B, PANG X Q, ZHANG B S, et al., 2015. Physical properties differences and key controlling factors of the clasolite reservoirs and carbonate reservoirs in Tazhong Area[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 21(1):138-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb201501014 TODOROVIC-MARINIC D, CHOPRA S, EDMONDS M, 2011. Advanced seismic techniques help in characterizing a challenging Jean Marie carbonate play, NE British Columbia, Canada-a Case Study[J]. Csegrecorder, 10(1):51-59. http://csegrecorder.com/articles/view/advanced-seismic-techniques-help-in-characterizing-a-challenging-jean-marie WANG X X, CUI D Y, SUN C H, et al, 2019. Characteristics of strike-slip fault and its controlling on oil in block A of the Halahatang oilfield, Tarim basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6):1058-1067. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201906006 WANG W Y, PANG X Q, CHEN Z X, et al., 2019a. Quantitative prediction of oil and gas prospects of the Sinian-Lower Paleozoic in the Sichuan Basin in central China[J]. Energy, 174:861-872. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360544219304220 WANG W Y, PANG X Q, CHEN Z X, et al., 2019b. Statistical evaluation and calibration of model predictions of the oil and gas field distributions in superimposed basins:A case study of the Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation in the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 106:42-61. WEI X S, CHEN J P, LV Q Q, et al., 2019. Quality differences between dolomite and tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 40(2):294-301. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201902009 WU D, ZHU X M, ZHANG H H, et al., 2014. Deposition characteristics and hydrocarbon distribution in medium and large basins of Nansha, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 16(5):673-686. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201405009 XU D Z, 2018. Research on the genetic mechanism of Ordovician reservoirs in Shunbei area[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG C Y, WEN L, WANG T G, et al, 2020. Timing of hydrocarbon accumulation for paleo-oil reservoirs in Anyue gas field in Chuanzhong Uplift[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 41(3):492-502. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz202003007 YANG H, LIU S X, ZHANG D F, 2013. Main controlling factors of gas pooling in Ordovician marine carbonate reservoirs in the Ordos Basin and advances in gas exploration[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 33(5):1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy201305001 ZHANG C L, PANG X Q, TIAN S C, et al., 2014. Oil-Source Correlation of Paleo-reservoir in Ordovician and the Gas Source of Jingbian Gasfield, West Ordos basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 25(8):1242-1251. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201408015 ZHAO R, ZHAO T, LI H L, et al., 2019. Fault-controlled fracture-cavity reservoir characterization and main-controlling factors in the Shunbei hydrocarbon field of Tarim Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 26(5):8-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tzyqc201905002 ZHU G Y, ZHANG S C, 2009. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration potential of deep reservoirs in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 30(6):793-802. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU C N, ZHAI G M, ZHANG G Y, et al., 2015. Formation, distribution, potential and prediction of global conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon resources[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(1):13-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201501002 邓尚, 李慧莉, 韩俊, 等, 2019.塔里木盆地顺北5号走滑断裂中段活动特征及其地质意义[J].石油与天然气地质, 40(5):990-998, 1073. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201905005 顾忆, 万旸璐, 黄继文, 等, 2019. "大埋深、高压力"条件下塔里木盆地超深层油气勘探前景[J].石油实验地质, 41(2):157-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201902002 康玉柱, 邢树文, 李会军, 等, 2019.中国北方地区构造体系控盆作用与控油分布规律[J].地质力学学报, 25(6):1013-1024. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190602&journal_id=dzlxxb 李映涛, 漆立新, 张哨楠, 等, 2019.塔里木盆地顺北地区中-下奥陶统断溶体储层特征及发育模式[J].石油学报, 40(12):1470-1484. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYXB201912005.htm 李忠, 黄思静, 刘嘉庆, 等, 2010.塔里木盆地塔河奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层埋藏成岩和构造-热流体作用及其有效性[J].沉积学报, 28(5):969-979. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201005014 刘宝增, 2020.塔里木盆地顺北地区油气差异聚集主控因素分析:以顺北1号、顺北5号走滑断裂带为例[J].中国石油勘探, 25(3):83-95. 刘德汉, 肖贤明, 田辉, 等, 2009.普光气田地质历史中存在超压的高密度甲烷包裹体证据和流体压力模拟计算[C]//第十二届全国有机地球化学学术会议论文集.成都: 中国地质学会, 中国石油学会, 中国矿物岩石地球化学学会: 344-346. 刘树根, 宋金民, 赵异华, 等, 2014.四川盆地龙王庙组优质储层形成与分布的主控因素[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 41(6):657-670. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201406001 马永生, 2007.四川盆地普光超大型气田的形成机制[J].石油学报, 28(2):9-14, 21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb200702002 马永生, 蔡勋育, 李国雄, 2005.四川盆地普光大型气藏基本特征及成藏富集规律[J].地质学报, 79(6):858-865. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200506014 马永生, 蔡勋育, 郭彤楼, 2007.四川盆地普光大型气田油气充注与富集成藏的主控因素[J].科学通报, 52(S1):149-155. 庞雄奇, 2014.油气藏调整改造与构造破坏烃量模拟[M].北京:科学出版社. 庞雄奇, 姜振学, 黄捍东, 等, 2014.叠复连续油气藏成因机制、发育模式及分布预测[J].石油学报, 35(5):795-828. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201405001 庞雄奇, 廖勇, 2016.叠复连续油气藏成因机制与预测方法:以南哈大气田的勘探与发现为例[M].北京:科学出版社. 乔博, 刘海锋, 何鎏, 等, 2018.鄂尔多斯盆地靖边气田的古地貌定量恢复新方法[J].天然气勘探与开发, 41(4):32-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqktykf201804006 邱振, 施振生, 董大忠, 等, 2016.致密油源储特征与聚集机理:以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 43(6):928-939. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SKYK201606010.htm 沈卫兵, 庞雄奇, 张宝收, 等, 2015.塔中地区碳酸盐岩与碎屑岩储层物性差异及主控因素[J].高校地质学报, 21(1):138-146. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb201501014 王新新, 崔德育, 孙崇浩, 等, 2019.哈拉哈塘油田A地区断裂特征及其控油作用[J].地质力学学报, 25(6):1058-1067. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190606&journal_id=dzlxxb 魏新善, 陈娟萍, 吕奇奇, 等, 2019.白云岩与砂岩致密储集体质量的差异性[J].石油与天然气地质, 40(2):294-301. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201902009 吴冬, 朱筱敏, 张厚和, 等, 2014.中国南沙海域大中型盆地沉积特征与油气分布[J].古地理学报, 16(5):673-686. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201405009 许大钊, 2018.顺北地区奥陶系储层成因机制研究[D].成都: 西南石油大学. 杨程宇, 文龙, 王铁冠, 等, 2020.川中隆起安岳气田古油藏成藏时间厘定[J].石油与天然气地质, 41(3):492-502. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz202003007 杨华, 刘新社, 张道锋, 2013.鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系海相碳酸盐岩天然气成藏主控因素及勘探进展[J].天然气工业, 33(5):1-12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy201305001 张春林, 庞雄奇, 田世澄, 等, 2014.鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系古油藏油源对比与靖边气田气源[J].天然气地球科学, 25(8):1242-1251. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201408015 赵锐, 赵腾, 李慧莉, 等, 2019.塔里木盆地顺北油气田断控缝洞型储层特征与主控因素[J].特种油气藏, 26(5):8-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tzyqc201905002 朱光有, 张水昌, 2009.中国深层油气成藏条件与勘探潜力[J].石油学报, 30(6):793-802. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb200906001 邹才能, 翟光明, 张光亚, 等, 2015.全球常规-非常规油气形成分布、资源潜力及趋势预测[J].石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(1):13-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201501002 -





 下载:
下载: