An analysis of dynamic response characteristics of the Yigong Landslide in Tibet under strong earthquake
-
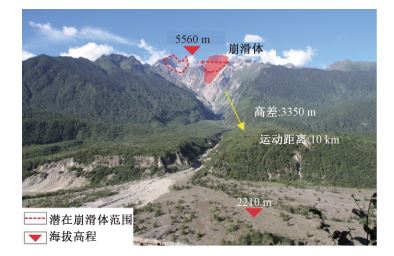
摘要: 西藏雅鲁藏布江大峡谷地区是地震滑坡的高易发区,发生过多期地震滑坡。以西藏易贡滑坡为例,运用FLAC3D有限差分方法,对滑坡所在山体进行频响特征分析,并以此为基础对其地震波作用下的放大效应开展研究,最后对近场强震条件下山顶潜在崩滑体稳定性进行预测。研究结果发现:易贡山体整体卓越频率处于较低值,山顶卓越频率主要集中在1 Hz以下、山顶两侧卓越频率在2~6 Hz之间;在地震波作用下,易贡山体顶部及两侧出现不同程度放大,山体内部沿高度向上呈先增后减、进而再次增大的变化趋势,其计算结果与频响特征分析结果基本一致;静力条件下,潜在崩滑体基本保持稳定,其安全系数为1.27,但地震作用下的计算结果却表明其发生了失稳破坏;在考虑水平向和竖向加速度同时输入的近场强震条件下,崩滑体稳定程度将进一步下降,因此需加强近场强震条件下山体的风险分析及预测。Abstract: The Yarlung Zangbo River Grand Canyon area in Tibet is a highly prone area for earthquake-triggered landslides,where several landslides have occurred before. Taking the Yigong Landslide as an example,this article analyzes the frequency response characteristics of the Yigong Mountain by using the FLAC3D finite difference method. Based on the results,the amplification effect of the Yigong Mountain under seismic waves is discussed and the stability of the Yigong Landslide remnant under the condition of near-field strong earthquakes is predicted. Results show that the overall predominant frequency of the Yigong Mountain is at a low value. The predominant frequencies of the mountain top mainly concentrate below 1 Hz,while that of both sides of the mountain top vary from 2~6 Hz. Under the action of seismic waves,the predominant frequencies of the top and both sides of the mountain appear different degrees of amplification,and that in the mountain interior along the height upward shows the change of first increasing then decreasing,and then increasing again. The calculated results are basically identical with the frequency analysis. Stability analysis shows that the Yigong Landslide remnant keeps stable with a safety factor of 1.27 in static condition; however,the results under the earthquake show the occurrence of instability and failure. Finally,it is predicted that the damage of the Yigong Landslide remnant will obviously increase when considering both horizontal and vertical seismic waves. Therefore,it is necessary to strengthen the risk analysis and prediction of mountains under the condition of near-field strong earthquakes.
-
Key words:
- strong earthquake /
- Yigong Landslide /
- numerical simulation /
- dynamic response /
- stability analysis
-
表 1 不同工况下坡体表面典型监测点加速度值
Table 1. Acceleration values of typical monitoring points on the slope surface under varying working conditions
监测点序号 加速度方向 加速度值/(m·s-2)(两向加速度加载) 加速度值/(m·s-2)(水平向加速度加载) A13 水平向 25.1 15.5 竖向 17.8 10.4 A7 水平向 12.0 9.0 竖向 13.7 5.5 B1 水平向 15.8 11.9 竖向 23.5 12.4 B2 水平向 14.8 10.2 竖向 21.0 10.7 表 2 不同工况下稳定性计算结果
Table 2. Stability analysis under varying working conditions
指标 静力条件 工况1:水平及竖向加速度输入 工况2:水平向加速度输入 塑性区 未贯通 贯通 贯通 剪应变增量最大值 约0.02 约0.14 约0.08 残余变形量/m 无 B1监测点为最大水平0.8;竖向1.0 B1监测点为最大水平0.3;竖向0.6 稳定性 稳定安全系数1.27 失稳残余变形不收敛 失稳残余变形不收敛 -
ASHFORD S A, SITAR N.1997. Analysis of topographic amplification of inclined shear waves in a steep coastal Bluff[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 87(3):692-700. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ef378e49178bc23e2e544de530003502&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn ASHFORD S A, SITAR N, LYSMER J, et al., 1997. Topographic effects on the seismic response of steep slopes[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 87(3):701-709. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/ssa/bssa/article-abstract/87/3/701/120237/Topographic-effects-on-the-seismic-response-of BAI Y J, NI H Y, GE H.2019. Advances in research on the geohazard effect of active faults on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(6):1166-1128. (in Chinese with English abstract) BOURDEAU C, HAVENITH H B.2008. Site effects modelling applied to the slope affected by the suusamyr earthquake (Kyrgyzstan.1992)[J]. Engineering Geology, 97(3-4):126-145. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.12.009 CHEN J C, WANG L M, WANG P, et al., 2020. Dynamic response of loess slopes based on the shake table test[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 42(2):529-535. (in Chinese with English abstract) DI FIORE V.2010. Seismic site amplification induced by topographic irregularity:results of a numerical analysis on 2D synthetic models[J]. Engineering Geology, 114(3-4):109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.05.006 HARP E L, JIBSON R W.2002. Anomalous concentrations of seismically triggered rock falls in Pacoima canyon:are they caused by highly susceptible slopes or local amplification of seismic shaking?[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 92(8):3180-3189. doi: 10.1785/0120010171 Itasca Consulting Group Inc.2005. FLAC (fast Lagrange analysis of continua) slope user's guide (version 5.0)[R]. Minneapolis, Minnesota. LI N, WANG B Q, Men Y M, et al., 2018. Study on dynamic response of landslide supported by pressure-type anchor under earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 24(4):490-497. (in Chinese with English abstract) LIU H D, NIU L F, YUAN F Q, et al., 2018. Test research on the influence of seismic wave frequency on the dynamic response of a layered rock slope[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 45(2):77-83.(in Chinese with English abstract) LIU Z, LI B, HE K, et al., 2020. Research of dynamic response patterns of high steep rock slope under earthquake effects[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 26(1):116-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) LUO Y H.2011. Study on complex slopes response law under earthquake action[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. (in Chinese with English abstract) MEUNIER P, HOVIUS N, HAINES J A.2008. Topographic site effects and the location of earthquake induced landslides[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 275(3-4):221-232. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.07.020 MITANI Y, WANG F W, OKEKE A C, et al., 2013. Dynamic analysis of earthquake amplification effect of slopes in different topographic and geological conditions by using ABAQUS[M]//WANG F W, MIYAJIMA M, LI T L, et al. Progress of Geo-Disaster Mitigation Technology in Asia. Berlin, Heidelberg:Springer:469-490. QI S W.2006. Two patterns of dynamic responses of single-free-surface slopes and their threshold height[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(2):518-523. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1002/cjg2.855 QI S W, WU F Q, SUN J Z.2003. General regularity of dynamic responses of slopes under dynamic input[J]. Science in China Series E (Technological Sciences), 46(S1):28-40. (in Chinese) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=09364f028d5db23ce6a88c12efaf4d16&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn SUN P, YIN Y, CHEN L W.2011. Numerical analysis of the failure mechanism of the Donghekou rockslide in the Wenchuan earthquake region with FLAC[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 38(5):87-91.(in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=66f8778a527b6b19c33f73fb95bfa2d8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn SUN Z L, KONG L W, GUO A G, et al., 2019. Experimental and numerical investigations of the seismic response of a rock-soil mixture deposit slope[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(24):716. doi: 10.1007/s12665-019-8717-y WANG B S, FAN X D, LIU W, et al., 2000. Investigation report of Yigong landslide[R]. Lhasa: Department of Land and Resources of Tibet Autonomous Region. (in Chinese) WANG H Y, XIE L L.2010. Effects of topography on ground motion in the Xishan park, Zigong city[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(7):1631-1638. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2252b8f5c4d67a88873fcadc13649a8d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn WANG W P, LI B, FENG Z, et al., 2019. Failure mechanism of a high-steep rock slope considering site effect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 40(1):297-304, 314. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795217304659 WANG W P, YIN Y P, LI B, et al., 2015. Spectral characteristics of dynamic response of slope with different angles of inclination[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 34(1):121-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=34c3f1086e8d89d284b40af40f46deb5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn XIAO W J, LIAO J M, ZHANG L L.2018. Shaking table test on seismic dynamic responses of isolated mountains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 40(3):582-590. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0267726114002000 YANG G X, WU F Q, DONG J Y, et al., 2012. Study of dynamic response characters and failure mechanism of rock slope under earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 31(4):696-702. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283483745_Study_of_dynamic_response_characters_and_failure_mechanism_of_rock_slope_under_earthquake YIN Y P.2000. The study of Yigong tremendous high-speed landslide in Bomi, Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 11(2):100. (in Chinese) YIN Y P.2008. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 16(4):433-444. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=da929fadbf6811e0a723482473bbdd76&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn YIN Y P, WANG M, LI B, et al., 2012. Dynamic response characteristics of Daguangbao landslide triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 31(10):1969-1982. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d85b9fd040c2f2f9a9ea01bf245bfa2d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn ZHANG Y S, LEI W Z, SHI J S, et al., 2008. General characteristics of 5.12 earthquake-induced geohazards in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 14(2):109-116. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=756d8344d39165db922e2621253266d0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn ZHOU X T, HAN J L, SHI F G, et al., 2014. Numerical simulation for amplification effect of topography and geomorphology to seismic waves[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 22(6):1211-1220. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007%2Fs11430-008-0130-4 ZHU C M, ZHANG C X.2015. Preliminary discussion on treatment of geological hazard in Zhamunong Valley in Tibet[J]. Yangtze River, 46(18):26-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) 白永健, 倪化勇, 葛华.2019.青藏高原东南缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究现状[J].地质力学学报, 25(6):1166-1128. 陈金昌, 王兰民, 王平, 等.2020.基于振动台试验的纯黄土边坡动力响应研究[J].地震工程学报, 42(2):529-535. 李楠, 汪班桥, 门玉明, 等.2018.压力型锚杆支护滑坡的地震动力响应特性研究[J].地质力学学报, 24(4):490-497. 刘汉东, 牛林峰, 袁富强, 等.2018.地震波频率对层状岩质边坡动力响应影响的试验研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 45(2):77-83. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2018.02.12 刘铮, 李滨, 贺凯, 等.2020.地震作用下高陡岩质斜坡动力响应规律研究[J].地质力学学报, 26(1):116-125. 罗永红.2011.地震作用下复杂斜坡响应规律研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学. 祁生文, 伍法权, 孙进忠.2003.边坡动力响应规律研究[J].中国科学E辑技术科学, 33(S1):28-40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9275.2003.z1.004 祁生文.2006.单面边坡的两种动力反应形式及其临界高度[J].地球物理学报, 49(2):518-523. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2006.02.026 孙萍, 殷跃平, 陈立伟.2011.汶川地震区东河口滑坡破坏机制FLAC模拟分析[J].水文地质工程地质, 38(5):87-91. 王保生, 范相德, 刘伟, 等.2000.易贡巨型山体崩塌滑坡调查研究报告[R].拉萨: 西藏自治区国土资源厅. 王海云, 谢礼立.2010.自贡市西山公园地形对地震动的影响[J].地球物理学报, 53(7):1631-1638. 王文沛, 殷跃平, 李滨, 等.2015.不同坡角斜坡动力响应频谱特征研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 34(1):121-128. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.01.013 王文沛, 李滨, 冯振, 等.2019.考虑场地效应的高陡岩质斜坡地震失稳机制[J].岩土力学, 40(1):297-304, 314. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2017.1163 肖文静, 廖佳名, 张亮亮.2018.孤立山体地震动力响应的振动台试验研究[J].地震工程学报, 40(3):582-590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2018.03.582 杨国香, 伍法权, 董金玉, 等.2012.地震作用下岩质边坡动力响应特性及变形破坏机制研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 31(4):696-702. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.04.007 殷跃平.2000.西藏波密易贡高速巨型滑坡概况[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 11(2):100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2000.02.024 殷跃平.2008.汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J].工程地质学报, 16(4):433-444. 殷跃平, 王猛, 李滨, 等.2012.汶川地震大光包滑坡动力响应特征研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 31(10):1969-1982. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.10.003 张永双, 雷伟志, 石菊松, 等.2008.四川5.12地震次生地质灾害的基本特征初析[J].地质力学学报, 14(2):109-116. 周兴涛, 韩金良, 施凤根, 等.2014.地形地貌对地震波放大效应数值模拟研究[J].工程地质学报, 22(6):1211-1220. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2014.06.027 朱成明, 张彩霞.2015.西藏扎木弄沟地质灾害治理初步探讨[J].人民长江, 46(18):26-28. doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2015.18.007 -





 下载:
下载: