Characteristics of ore-controlling structures and ore-prospecting of the Xitieshan lead-zinc deposit, northern edge of the Qaidam basin, NW China
-
摘要: 锡铁山矿床是中国西部的超大型铅锌矿产地之一,产于柴北缘晚奥陶世滩间山群的大理岩和片岩之中,是与海相火山喷流-沉积有关的矿床。很多学者已经从地球化学、岩石学、同位素测年等对该矿床的成矿时代、成矿流体性质、矿床成因等开展了研究,但对于锡铁山矿区构造控矿特征一直存在争议,普遍认为褶皱构造对矿区的控矿作用明显。文章主要以详实的野外观测为基础,分析了矿区的褶皱和断裂构造特征,探讨了构造对矿(床)体的控制作用,为矿区找矿勘查工作部署提供依据。通过详实的野外实测和综合对比分析表明,锡铁山矿区总体上为单斜层,不发育大型的褶皱构造,但是层内褶皱发育,包括A型褶皱和B型褶皱。发育在滩间山群a段内的A型褶皱,其褶皱枢纽与拉伸线理倾向南东,与矿区矿体的总体倾伏方向一致;而在滩间山群d段内的A型褶皱,其枢纽倾向北西;矿区内发育了多条北西西走向的大型断裂,其编号为F1—F6;分析表明,F1断层发育在早期塑性变形基础之上,晚期叠加了叠瓦逆冲推覆作用,造成了矿体及赋矿围岩的局部倒转;F2断裂大规模的左行走滑-逆冲作用导致了矿区滩间山群不同岩性段地质体的拼合接触,造成了矿区部分含矿地质体的缺失;野外填图揭示出,左行走滑的F3断裂从北西往南东,走向从330°逐渐转变为290°方向,并在南东侧末端,发育了一系列分支的左行走滑-正断层,组成"马尾状"构造,截切了矿体与围岩,并发生了横向错移。以此构造控矿特征为基础,结合矿床成因分析,进一步分析了锡铁山矿区深部的找矿方向,认为矿区南东侧深部具有良好的找矿空间;并以07号勘探线为例,根据F3及其分支断层的错移情况,分析了矿体可能被错移的位置。Abstract: The Xitieshan deposit,one of the large-size lead-zinc deposits located at the northern edge of the Qaidam basin in western China,is related to marine Volcanic-Sedimentary Hosted Massive Sulfur deposit (VSHMS). Most prior researches are focused on the mineralization age,the nature of ore-forming fluid,and the genesis of the deposit by the method of petrology,geochemistry,and isotopic dating. However,the characteristics of ore-controlling structures,which are essential to prospecting and expanding the mining resources,have been controversial for long time,and it is generally believed that it was the fold that controlled the production of ore bodies in the deposit. This paper mainly presents field evidences to discuss the characteristics of folds and faults and its controlling roles to the distribution of ore bodies,and further to provide the basis for the mining prospecting exploration. Our field investigation and comparative analysis showed that there was no large-scale syncline or anticline in the deposit and only a monocline composed of the Ordovician Tanjianshan Group in general,although some interlayered folds were well developed,including A-and B-type. Both the fold hinge and the strench lineation of A-type fold in a-segment of the Ordovician Tanjianshan Group are dipping to SE-ward,consistent with the dipping tendency of the whole ore-bodies in the deposit,but different with those in d-segment of the Tanjianshan Group as dipping to NW-ward. There are six large-scale NWW-trending faults in the deposit,named as F1 to F6 from the northeast to southwest. The F1 fault in the deposit probably developed on the base of ductile deformation in early stage. And the latterly nappe thrusting of the fault resulted in the reverse of ore-bodies and host rocks near the fault. Large-scale sinistral strike-slipping faulting of the F2 fault played important roles on the convergence together of different segments of the Tanjianshan Group,and also the missing of some ore-bearing geological bodies. Field mapping between the Zhongjiangou and Wuminggou areas revealed that the orientation of the F3 fault gradually changed from 330-trending in northwest to 290-trending in southeast. And several branch sinistral strike-slipping and normal faults were identified in the southeastern end area,composing a pattern of horsetail structure in the shape,which truncated ore-bodies and host rocks. Therefore,ore-prospecting directions were proposed based on the ore-controlling structures together with the metallogenic models of the deposit,suggesting that the deep region in the southeastern side should be one of most favorable ore potential areas,and the dislocation places of ore-bodies by the F3 fault and its branch sinistral-normal faults in the prospecting Line 07 were further forecasted for example.
-
0. 引言
近断层大地震(如: 1994年美国North Ridge地震、1995年日本Kobe地震、1999年中国台湾集集地震、1999年土耳其Kocaeli地震、2003年伊朗Bam地震)独特的运动特征及其对工程结构的严重影响引起了地震工程界的密切关注[1~6]。Somerville等的研究表明,由于近断层地震动经常包含强烈的动态长周期脉冲和永久地面位移,其运动特征与远场地震动明显不同[1~2]。
汶川“5.12”震后调查表明:地震断裂带附近大量建筑物发生了破坏[7~13],断层上下盘的建筑物在地震时的破坏程度不同,而且即使位于断层同一侧,由于与断层位置关系的差异,地表建筑物的破坏情况也不尽相同。因此,研究断层在地震作用下对地表建筑物的灾害效应,揭示地表破裂的致灾机理对抗震设计和灾害预防具有重要的理论意义和实用价值。
1. 地震引发的建筑物差异性破坏
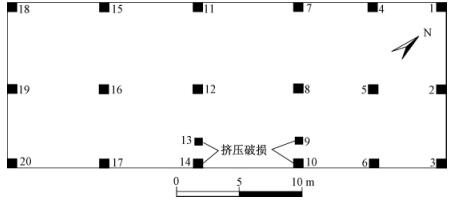
汶川“5.12”地震在汶川县水磨镇西侧斜坡上形成了产状为331°∠54°的地表破裂(断层),同时使位于断层上盘的硅业公司主楼(距离断层约25 m)发生了差异性破坏现象,近断层一侧和远离断层一侧的破坏程度明显不同。
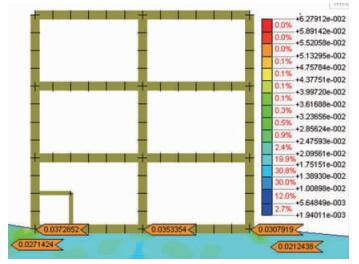
水磨镇硅业公司主楼走向北东—南西向,长35 m,宽12 m,高12 m,楼梯位于中部东南侧,厂房平面图见图 1,其受地震的破坏表现为西北侧的梁、柱破坏较轻,仅一个柱(图 1中18号柱)发生向东南方向错动,最大错动距离约3 cm (见图 2); 而东南侧的梁、柱破坏严重,其中4个钢筋混凝土柱(图 1中9、10、13和14号柱)受到垂向挤压破坏并发生水平剪切,钢筋弯曲(见图 3、图 4)。
本文基于对位于断层上盘的汶川县水磨镇硅业公司的实地调查,采用数值模拟方法研究了水磨镇硅业公司主楼在地震动作用下的动力响应特点,并分析了楼体破坏与断裂的关系。
2. 研究区地质概况
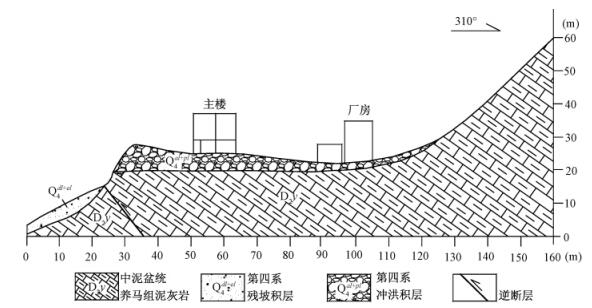
汶川县水磨镇硅业公司位于龙门山构造带中南段的北端、水磨河河谷西北岸的高阶地上,其西北侧紧邻一个高度约35 m斜坡的坡脚。场地出露的地层有:泥盆系养马坝组(D2y)泥灰岩,厚度为89~137 m; 第四系冲洪积物,覆盖于养马坝组之上,厚度为0~7.3 m,由砂、砾石组成,其与基岩的接触界面倾向东南侧; 第四系残坡积物,位于厂房东南侧的陡坎下部,厚度为0~2.9 m。场地地质剖面图见图 5。
3. 研究模型的建立
3.1 基本假设
在建立模型时假设: ①平面应变状态; ②周围岩石为均匀的弹性各向同性材料; ③断裂为无厚度的接触面; ④岩石服从摩尔-库仑破坏准则,楼房梁单元为弹性。
3.2 模型的几何形状和边界条件
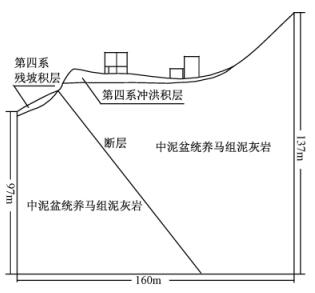
模拟采用二维模型,模型走向为310°。根据现场实地观测,考虑到边界影响以及模拟的目的,建立地质模型见图 6。模型底部宽160 m,右侧高137 m,左侧高97 m,房高12 m,宽12 m (图中所示为楼房的侧剖面),楼梯高2 m,距房主梁2 m。模型中断层倾角54°。
模拟分为两个阶段:特征值分析和地震动力分析。在进行特征值分析时,通过点弹簧定义弹性边界,模型的左右两侧及底部边界均为弹簧边界。对于动力分析,采用Lysmer和Wass (1972)提出的粘性边界(viscous boundary)。鉴于该模拟的目的是研究断裂在地震作用时对地表建筑物的破坏作用,模拟时只对模型加载地震波时程荷载,不施加其他应力边界条件。
3.3 材料参数及地震动参数
本研究区的岩性为泥盆系养马坝组(D2y)泥灰岩,表层为第四系冲洪积物和残坡积物。参考《工程地质手册(1992) 》并结合前人大量的数值模拟经验,采用工程地质类比法,确定材料的力学参数如表 1。
表 1 材料参数Table 1. Parameters of the materials
地震动的数值模拟是通过输入地震记录(加速度时程记录)来实现的。该区选择距离最近的卧龙地震台在龙门山发生地震时的监测资料进行动力模拟。地震作用全过程历时135 s。
4. 模拟结果分析
4.1 最大主应力分布规律
模拟结果表明:最大主应力值沿断层自下而上逐渐降低,但在断层上盘,厂房下伏的基岩(泥质灰岩)中出现增大的现象。而在厂房下地基(第四系冲洪积物)中应力值出现明显的减小趋势,这是由于第四系冲洪积物与基岩泥质灰岩的材料参数相差很大,在地震时有减震的作用。
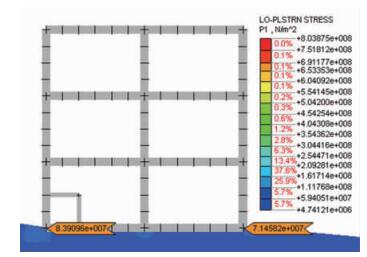
厂房左侧(靠近断层一侧)梁底部平面应变单元节点的最大主应力值大于右侧,左侧为83.9 MPa,右侧为71.4 MPa,两者数值相差12.5 MPa (见图 7)。
但是在房屋左侧(靠近断层一侧)第四系冲洪积物的厚度为4.6209 m,右侧(远离断层一侧)第四系冲洪积物厚度为4.5364 m。按照抗震设计理论,左侧梁单元受到的主应力值应该小于右侧,但是模拟结果却相反。这是因为房屋左侧梁与断层的垂直距离为24.8556 m,右侧梁与断层的垂直距离为84.4065 m,这也就解释了左侧梁单元的主应力大于右侧梁单元主应力值的原因。
4.2 剪应力分布规律
断层上盘剪应力值大于下盘,远离断层,剪应力值逐渐减小。
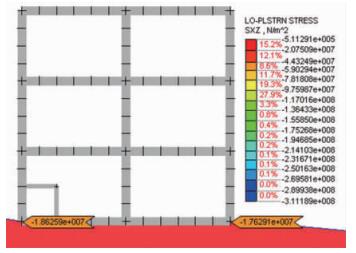
地基中,厂房左侧(靠近断层一侧)的剪应力值大于右侧,左侧为18.626 MPa,右侧为17.629 MPa (见图 8)。
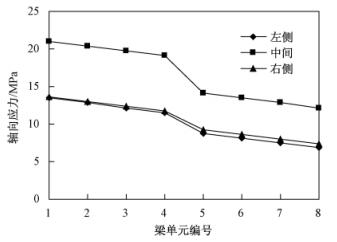
从梁单元轴向应力曲线图(见图 9)可以看出,梁单元(图中梁单元由下至上编号,每楼层分为4个单元,下同)底部所受的轴向应力最大,且梁单元的轴向应力自下而上减小,到第二层上部时已经减小到底部的约二分之一,这与厂房底部柱体发生挤压破坏(见图 3、图 4)、而上部柱体没有破坏的特征相对应。
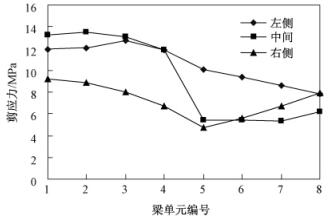
从梁单元剪应力曲线图(见图 10)可以看出,左侧梁单元剪应力最大值出现在楼梯与主体梁相交处(3号梁单元处),由12.008 MPa急剧增大到12.769 MPa,向上至第一层顶部(4号梁单元处)时又急剧减小到11.905 MPa。梁单元剪应力的这种变化规律与图 3显示的破坏特征一致。同时,可以看出,剪应力均为正值,反映其剪切方向为顺时针转动,与图 2-图 4显示的柱体剪切破坏特征相对应。根据梁单元轴向应力和剪应力特征及变化趋势,地震时楼体主梁的破坏是轴向应力和剪应力同时作用造成的。
4.3 剪应变特征
断层附近剪应变发生较为复杂的变化,断层上盘和下盘的剪应变值有明显的差别,从地面上剪应变的分布看,厂房区域剪应变值较大。
从厂房底部的最大剪应变图(见图 11)可以看出,在梁的底部出现应变集中区,而且左侧(靠近断层一侧)大于右侧,左侧为0.03728,右侧为0.03079。
4.4 加速度特征
4.4.1 断裂带上节点水平向加速度特征
断层带上节点水平向加速度值在断层底部最小(-4.457 cm/s2),由底部向上增大,增大的幅度逐渐减小。断层位置的加速度明显增大,断层顶部的加速度最大值达638.7 m/s2 (卧龙台记录到的最大水平加速度为949.979 cm/s2)。
4.4.2 不同岩性中节点水平向加速度特征
泥灰岩中一节点的最大水平加速度值为313.2 m/s2,冲洪积层中一节点最大水平加速度值为472.6 m/s2,残坡积物中一节点最大水平加速度值为637.8 m/s2,表明在软岩中,加速度明显增大。
5. 结论
(1) 位于断层上盘的厂房,靠近断层一侧的最大主应力值大于远离断层一侧。
(2) 断层上盘剪应力值大于下盘,远离断层,剪应力值逐渐减小; 厂房左侧(靠近断层一侧)的剪应力值大于右侧。
(3) 断层附近剪应变发生较为复杂的变化,断层上盘和下盘的剪应变值有明显的差别,厂房底部出现应变集中区,而且左侧(靠近断层一侧)大于右侧。
(4) 加速度值在断层底部最小,由底部向上增加。断层位置的加速度明显增大,断层顶部的加速度最大值达637.8 m/s2。在软岩中,加速度有明显的放大。
(5) 厂房所受的轴向应力在底部最大,向上逐渐减小,与厂房底部柱体发生挤压破坏的特征相对应; 厂房所受的剪应力值和剪切方向与柱体剪切破坏特征相对应。
(6) 断层的形成改变了局部的应力场条件和加速度特征,从而使位于断层上盘的楼房发生差异性破坏,紧邻断层一侧破坏强烈。地震时楼体主梁的破坏是轴向应力和剪应力同时作用造成的。
责任编辑:吴芳 -
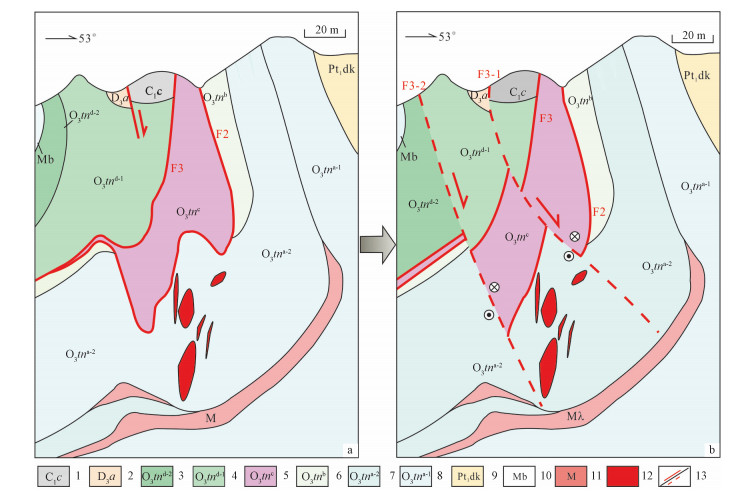
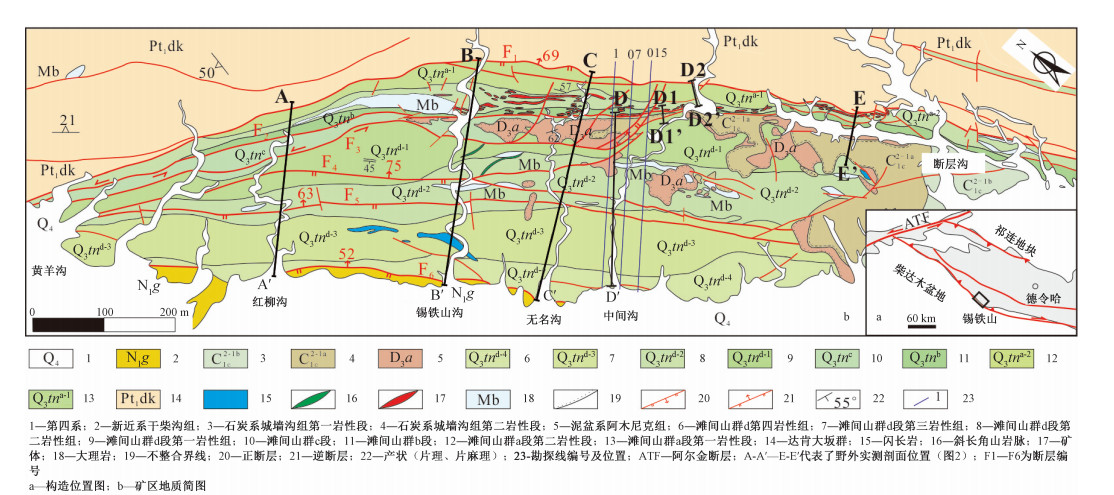
图 1 锡铁山铅锌矿矿区地质构造简图(据魏俊浩等,2015修改)
Figure 1. Simplified geological and structural map of the Xitieshan deposit (modifed after Wei et al, 2015)
图 2 锡铁山矿区实测地质剖面图
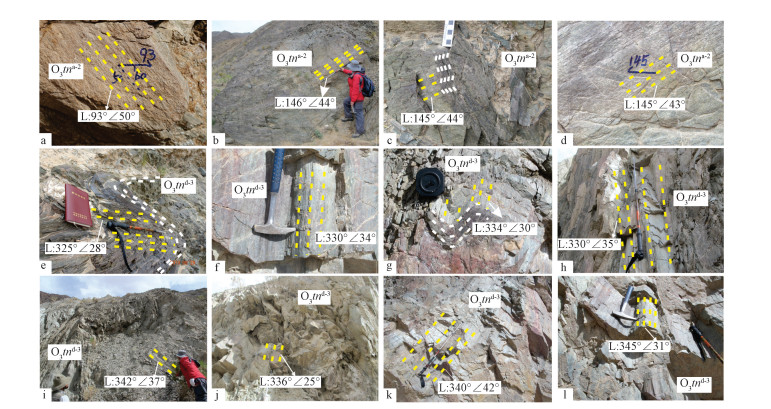
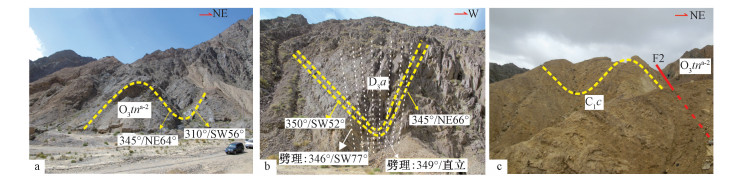
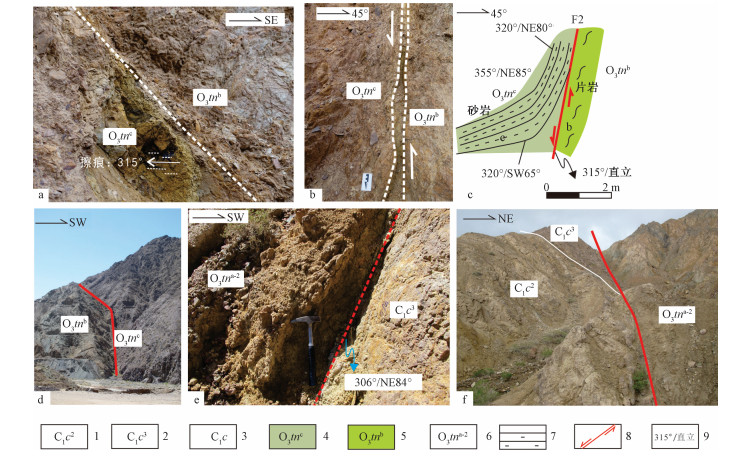
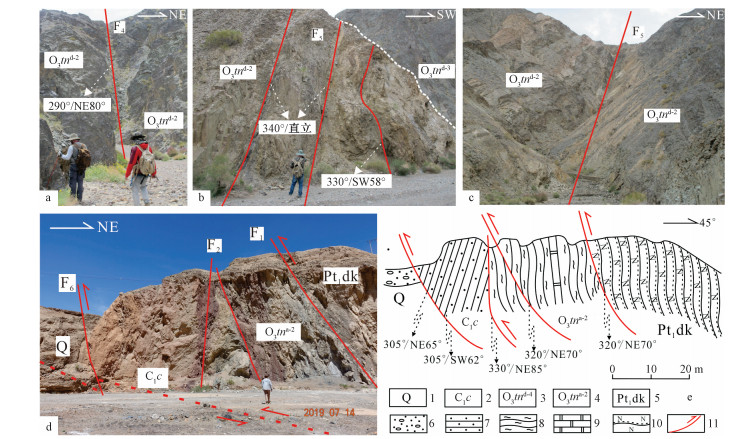
1-干柴沟组;2-城墙沟组;3-阿木尼克组;4-滩间山群d第四岩性组;5-滩间山群d段第三岩性组;6-滩间山群d段第二岩性组;7-滩间山群d段第一岩性组;8-滩间山群c段;9-滩间山群b段;10-滩间山群a段第二岩性段;11-滩间山群a段第一岩性段;12-达肯大坂群;13-矿体;14-斜长片麻岩;15-斜长角闪片麻岩;16-绿泥石片岩;17-绿帘石片岩;18-变玄武岩;19-变流纹岩;20-大理岩;21-含砾砂岩;22-粉砂岩;23-砂岩;24-砾岩;25-逆冲断层;26-走滑断层;A-A′ -E-E′实测剖面位置见图 1;F1-F6为断层编号
Figure 2. Field measured geological cross-sections in the Xitieshan deposit
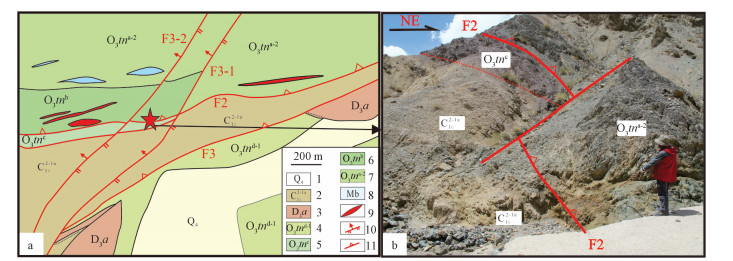
图 11 锡铁山矿区07号勘探线中的矿体被F3分支断层错移示意图
1-城墙沟组;2-阿木尼克组;3-滩间山群d段第二岩性段;4-滩间山群d段第一岩性段;5-滩间山群c段;6-滩间山群b段;7-滩间山群a段第二岩性段;8-滩间山群a段第一岩性段;9-达肯大坂群;10-变流纹岩;11-矿体;12-大理岩;13-左行-正断层;14-示意为大理岩型矿体;15-示意为片岩型矿体
Figure 11. Schematic diagram showing the dislocation of ore bodies by the branch faults of the F3 fault in Line 07 for example
-
BETTS P G, LISTER G S, 2002. Geodynamically indicated targeting strategy for shale-hosted massive sulfide Pb-Zn-Ag mineralisation in the Western Fold Belt, Mt Isa terrane[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 49(6):985-1010. BRADSHAW G D, ROWINS S M, PETER J M, et al., 2008. Genesis of the Wolverine volcanic sediment-hosted massive sulfide deposit, Finlayson Lake district, Yukon, Canada:Mineralogical, mineral chemical, fluid inclusion, and sulfur isotope evidence[J]. Economic Geology, 103(1):35-60. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/247864661_Genesis_of_the_Wolverine_Volcanic_Sediment-Hosted_Massive_Sulfide_Deposit_Finlayson_Lake_District_Yukon_Canada_Mineralogical_Mineral_Chemical_Fluid_Inclusion_and_Sulfur_Isotope_Evidence CHEN Z L, CHEN B L, 2012. Thinking, steps and practice of research on orefield structure in geomechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 34(4):208-215. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zrzz201204004 CHENG C, HAN R S, WANG L, et al., 2019. The generation, development and ore-controlling of structures of the Fulaichang Lead-Zinc deposit, northeastern Guizhou[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(1):90-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201901010 DENG D W, KONG H, XI X S, 2003. Geochemisrry of the hydrothermal sedimentary Xitieshan Pb-Zn deposit, Qinghai Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 22(4):310-313. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb200304005 DENG J N, 1999. Fold structure and prodiction for prospecting in the Xitieshan ore filed, Qinghai[J]. Geological Exploration for Non-Ferrous Metals, 8(5):283-288. (in Chinese with English abstract) DENG J N, 2002. Research progress on geological prospecting of lead-zinc deposits in Xitieshan area[R]. Internal Information of Western Mining Corporation. (in Chinese) DOYLE M G, ALLEN R L, 2003. Subsea-floor replacement in volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 23(3-4):183-222. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b320e2defc885364b6aa33d745590042 DU G H, LI S B, 1982. Geological characteristics of Xitieshan polymetallic deposit in Qinghai[J]. Northwestern Geology(4):27-34. (in Chinese) FAN J C, LI F, 2006. Revision on Tanjianshan Group in the Xitieshan Mine, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 42(6):21-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzykt200606005 FENG Z H, LI S Y, CHEN R Q, 1997. The ore-controlling structural model and its characteristics in the Xitieshan Pb-Zn Mine of Qinghai Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 21(2):167-172. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700038825 FENG Z X, SUN H S, WU G B, et al., 2010. A discussion on type of the Xitieshan Pb-Zn ore deposit, Qinghai[J]. Geological Review, 56(4):501-512. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201004005 FOUQUET Y, VON STACKELBERG U, CHARLOU J L, et al., 1993. Metallogenesis in back-arc environments:the Lau Basin example[J]. Economic Geology, 88(8):2154-2181. FU J G, LIANG X Q, WANG C, et al., 2014. Timing and characteristic of provenance of the C formation in the Tanjianshan Group, Xitieshan, North Qaidam[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(6):1081-1092. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201406012 FU J G, LIANG X Q, WANG C, et al., 2015. Study on the characteristics of volcanic-sedimentary massive sulfide deposits (VSHMS):Taking the Xitianshan lead-zinc deposit as an example[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 35(S1):1001. (in Chinese) FU J G, LIANG X Q, WANG C, et al., 2016. Characteristics and muscovite 40Ar/39Ar Age of Ductile Shear Zone in the Xitieshan Area, North Qaidam[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(1):14-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201601002 FU J G, LIANG X Q, WANG C, et al., 2017. The Xitieshan volcanic sediment-hosted massive sulfide deposit, North Qaidam, China:Geology, structural deformation and geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 80:923-946. GAO X F, XIAO P X, JIA Q Z, 2011. Redetermination of the Tanjianshan Group:Geochronological and Geochemical Evidence of Basalts from the Margin of the Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(9):1452-1463. (in Chinese with English abstract) GERMAN C R, PARSON L M, HEAT SCIENTIFIC TEAM, et al., 1996. Hydrothermal exploration near the Azores Triple Junction:tectonic control of venting at slow-spreading ridges?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 138(1-4):93-104. GLASBY G P, NOTSU K, 2003. Submarine hydrothermal mineralization in the Okinawa Trough, SW of Japan:an overview[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 23(3-4):299-339. GROVES D I, BIERLEIN F P, 2007. Geodynamic settings of mineral deposit systems[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(1):19-30. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b97ee35147c98364d61209c662760d3c GUO J J, 2000. Structural analysis of the Tanjianshan Group in the north margin of Qaidam Block, China and its implication[J]. Progress in Precambrian Research, 23(3):147-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) HAN F, SUN H T, 1999. Sedex type metallogenic system[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(1):139-162. (in Chinese) HUANG Z W, PI D H, 2013. Zircon of volcanic rocks in the d-1 section of the Xitieshan lead-zinc deposit U-Pb age and its geological significance[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica(S2):588-589. (in Chinese) KNORSCH M, DEDITIUS A P, XIA F, et al., 2020. The impact of hydrothermal mineral replacement reactions on the formation and alteration of carbonate-hosted polymetallic sulfide deposits:A case study of the Artemis prospect, Queensland, Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 116:103232. LAI S C, DENG J F, YANG J J, et al., 1993. Large ductile shear zone discovered in the northern margin of Qaidam[J]. Geoscience, 7(1):125. (in Chinese) LARGE R R, 1992. Australian volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits; features, styles, and genetic models[J]. Economic Geology, 87(3):471-510. LARGE R R, BULL S W, MCGOLDRICK P J, 2000. Lithogeochemical halos and geochemical vectors to stratiform sediment hosted Zn-Pb-Ag deposits:part 2. HYC deposit, McArthur River, Northern Territory[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 68(1-2):105-126. LEACH D L, SANGSTER D F, KELLEY K D, et al., 2005. Sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits: A global perspective[C]//100th Anniversary Volume. Littleton, Colorado: Society of Economic Geologists: 561-607. LEACH D L, BRADLEY D C, HUSTON D, et al., 2010. Sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits in Earth history[J]. Economic Geology, 105(3):593-625. doi: 10.2113-gsecongeo.105.3.593/ LI F, WU Z L, LI B Z, et al., 2006. Revision of the Tanjianshan Group on the Northern Margin of the Qaidam Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 39(3):83-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200603012 LI F, WU Z L, LI B Z, 2007. Recognition on formation age of the Tanjianshan Group on the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin and its geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 31(2):226-233. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200702012 LI H, XI X S, 2015. Sedimentary fans:A new genetic model for sedimentary exhalative ore deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 65:375-389. LI P, LI Y B, WANG H F, et al., 2019. Structural characteristics and ore-controlling law of Xitieshan lead-zinc mine in North Qaidam Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 38(4):108-123. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb201904012 MAO J W, ZHANG Z H, WANG Y T, et al., 2012. Types, characteristics and prospecting of major foreign deposits[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House:302-370. (in Chinese) MUKHERJEE I, LARGE R, 2017. Application of pyrite trace element chemistry to exploration for SEDEX style Zn-Pb deposits:McArthur Basin, Northern Territory, Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 81:1249-1270. NIU Y L, 1984. On the genesis of the Xitieshan Multimetal ore deposit[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University, 20(4):105-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) Qinghai Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, 1988. Regional geological survey report (1: 50, 000 Xitieshan, Quanjihe)[R]. 54-137. (in Chinese) Qinghai Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, 1991. Regional geology of Qinghai province[M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House:662. (in Chinese) SAWKINS F J, 1972. Sulfide ore deposits in relation to plate tectonics[J]. The Journal of Geology, 80(4):377-397. doi: 10.1086-627762/ SCHARDT C, LARGE R R, 2009. New insights into the genesis of volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits on the seafloor from numerical modeling studies[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 35(3-4):333-351. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4a91f232b65bfbfff82d1db57ecd36b2 SLACK J F, DUMOULIN J A, SCHMIDT J M, et al., 2004. Paleozoic sedimentary rocks in the Red Dog Zn-Pb-Ag district and vicinity, western Brooks Range, Alaska:Provenance, deposition, and metallogenic significance[J]. Economic Geology, 99(7):1385-1414. doi: 10.2113-99.7.1385/ SUN H S, ZHAO L J, WU G B, et al., 2012. Metallogenic tectonic setting and ore-finding potential of Xitieshan massive sulfide lead-zinc deposit:Evidence from lithochemistry and geochemistry of ore-hosted volcanic strata, Tanjianshan Group[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(2):652-664. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201202023 SUN H S, et al., 2017. Prospecting research on the deep and peripheral prospecting of Xieshan lead-zinc deposit in Qinghai[R]. (in Chinese) SUN H S, LI H, EVANS N J, et al., 2017. Volcanism, mineralization and metamorphism at the Xitieshan Pb-Zn deposit, NW China:Insights from zircon geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 88:289-303. SUN J P, YIN C M, CHEN S Y, et al., 2016. An analysis of Late Carboniferous sedimentary tectonic setting and provenance of North Qaidam area:Evidence from Well Shiqian 1[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(2-3):302-311. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZQYD2016Z1012.htm TANG J R, 2006. The study of mineralization by relay structure of normal fault on typical metal ore deposit[D]. Changsha: Central South University. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG G H, RAN S M, LI M, 2001. The characteristics of Neogene Sertengshan Xietieshan oblique thrust fault in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 7(3):224-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200103005 WANG H C, LU S N, YUAN G B, et al., 2003. Tectonic setting and age of the "Tanjianshan Group" on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(7):487-493. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200307005 WANG J C, PENG E S, SUN Z J, 2000. Tectonic reconstruction of the Xitieshan Pb-Zn deposit after spout sedimentation, Qinghai Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 24(2):163-169. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200002009 WANG L J, ZHU X Y, WANG J B, et al., 2008. Study on fluid inclusions of the sedimentary-exhalative system (SEDEX) in Xitieshan lead-zinc deposit[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(10):2433-2440. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.oalib.com/paper/1472726 WANG L J, PENG Z G, ZHU X Y, et al., 2009. Source and evolution of ore-fluid of the Xitieshan sedimentary-exhalative lead-zinc system, Qinghai province:Evidence from fluid inclusion and isotope geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11):3007-3015. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG M Z, HAN R S, ZHOU W, et al., 2019. Ore-forming structure analysis of the Liangyan lead-zinc mining area in northwestern Guizhou deposit concentration district, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(2):187-197. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201902005 WEI J H, et al., 2015. Contrastive comprehensive study of metallogenic geological conditions and target area prediction in the Xichaishan lead-zinc deposit area of Dachaidan, Qinghai Province[R]. (in Chinese) WU C Z, GU L X, FENG H, et al., 2008. Genetic types of orebodies in the Xitieshan lead-zinc deposit, Qinghai Province, Western China[J]. Geology in China, 35(6):1185-1196. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200806015 WU G B, SUN H S, FENG Z X, et al., 2010. The paleotectonic setting of Xitieshan lead-zinc deposit[J]. Geochimica, 39(3):229-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx201003003 WU G G, 1998. Orefield structure and metallogenic prediction[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 4(2):1-4. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkx201703007 WU J R, 1985. Geological characteristics of the Xitieshan massive sulfide deposit, Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 4(2):1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU J R, REN B C, ZHANG M, et al., 1987. The genetic type and geological characteristics of the Xitieshan massive Sulphide deposit, Qinghai[J]. Northwest Geoscience, 20(6):1-81, 83-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzxb-e200104004 XU Z Q, YANG J S, WU C L, et al., 2003. Timing and Machanism of formation and exhumation of the Qaidam ultra-pressure metamorphic belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(2):163-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) XUE W, ZHANG D, LI C Y, et al., 2019. Structural ore-controlling model and prospecting research for the Dulong Sn-Zn-In polymetallic deposit, southeastern Yunnan[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(1):77-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201901009 YUAN K R, XIAO C B, CHEN R Q, 1996. Prediction of Xitieshan hidden deposit in Qinghai[M]. Changsha:Central South University of Technology Press. (in Chinese) ZAPPETTINI E O, RUBINSTEIN N, CROSTA S, et al., 2017. Intracontinental rift-related deposits:A review of key models[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 89:594-608. ZHAI Y S, 2002. A brief retrospect and prospect of study on ore-forming structures[J]. Geological Review, 48(2):140-146. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000005771 ZHANG D Q, WANG F C, LI D X, et al., 2005. Two types of massive sulfide deposits on northern margin of Qaidam basin, Qinghai Province:Ⅰ. Xitieshan style SEDEX lead-zinc deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(5):471-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG J X, YANG J S, MENG F C, et al., 2006. U-Pb isotopic studies of eclogites and their host gneisses in the Xitieshan area of the North Qaidam mountains, western China:new evidence for an early Paleozoic HP-UHP metamorphic belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 28(2-3):143-150. ZHANG Z J, XIA W H, FENG Z W, et al., 1994. Structure and structure of the Xitianshan lead-zinc deposit in Qinghai-the relationship between organic fluid and mineralization[J]. Mineral Deposits, 13(S1):82-83. (in Chinese) ZHAO F Q, GUO J J, LI H K, 2003. Geological characteristics and isotopic age of Tanjianshan Group along northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(1):28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200301005 ZHONG Y S, SUN H S, GE F J, et al., 2018. Identification of the submarine exhalative conduct and its significances for ore-controlling, genesis and ore-finding, Xitieshan Pb-Zn Deposit, Qinghai Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 37(5):154-161. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201805021 ZHU X Y, DENG J N, WANG J B, et al., 2006. The exhalation-sedimentary system of Xitieshan lead-zinc deposit, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 42(3):18-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200603005.htm ZHU X Y, WANG L J, ZHU G C, et al., 2010a. Characteristics of sulfur isotope geochemistry of Xitieshan lead-zinc deposit, Qinghai:The mixing of sulfurs from hydrothermal and seawater[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(3):657-666. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHU X Y, WANG L J, ZHU G C, et al., 2010b. The genesis of the Xitieshan SEDEX lead-zinc deposit in Qinghai Province:lead isotope evidence[J]. Geology in China, 37(6):1682-1689. (in Chinese with English abstract) 陈正乐, 陈柏林, 2012.地质力学矿田构造研究思路、步骤与实践[J].自然杂志, 34(4):208-215. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zrzz201204004 成晨, 韩润生, 王雷, 等, 2019.黔西北福来厂铅锌矿床构造成生发展及其控矿作用[J].地质力学学报, 25(1):90-104. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190109&journal_id=dzlxxb 邓达文, 孔华, 奚小双, 2003.青海锡铁山热水沉积型铅锌矿床的地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 22(4):310-313. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb200304005 邓吉牛, 1999.青海锡铁山矿区褶皱构造及其找矿预测[J].有色金属矿产与勘查, 8(5):283-288. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199901110091 邓吉牛, 2002.锡铁山地区铅锌矿床地质找矿研究进展[R].西部矿业公司内部资料. 杜光辉, 李树冰, 1982.青海锡铁山多金属矿床的地质特征[J].西北地质(4):27-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XBDI198204003.htm 樊俊昌, 李峰, 2006.青海锡铁山矿区滩间山群新认识[J].地质与勘探, 42(6):21-25. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt200606005 冯佐海, 李少游, 陈儒庆, 1997.青海锡铁山铅锌矿构造控矿型式与特征[J].大地构造与成矿学, 21(2):167-172. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700038825 冯志兴, 孙华山, 吴冠斌, 等, 2010.青海锡铁山铅锌矿床类型刍议[J].地质论评, 56(4):501-512. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201004005 付建刚, 梁新权, 王策, 等, 2014.柴北缘锡铁山滩涧山群c岩性组的时代归属及其物源特征[J].地质学报, 88(6):1081-1092. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201406012 付建刚, 梁新权, 王策, 等, 2015.火山-沉积型块状硫化物矿床(VSHMS)特征研究:以锡铁山铅锌矿床为例[J].矿物学报, 35(S1):1001. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9132303 付建刚, 梁新权, 王策, 等, 2016.柴北缘锡铁山韧性剪切带的基本特征及其形成时代[J].大地构造与成矿学, 40(1):14-28. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201601002 高晓峰, 校培喜, 贾群子, 2011.滩间山群的重新厘定:来自柴达木盆地周缘玄武岩年代学和地球化学证据[J].地质学报, 85(9):1452-1463. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201109005 郭进京, 2000.柴北缘锡铁山地区滩间山群构造变形分析[J].前寒武纪研究进展, 23(3):147-152. 韩发, 孙海田, 1999. Sedex型矿床成矿系统[J].地学前缘, 6(1):139-162. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy199901012 黄志伟, 皮道会, 2013.锡铁山铅锌矿床矿区d-1岩段火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].矿物学报(S2):588-589. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8301453 赖绍聪, 邓晋福, 杨建军, 等, 1993.柴达木北缘发现大型韧性剪切带[J].现代地质, 7(1):125. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HBDX199306003.htm 李峰, 吴志亮, 李保珠, 等, 2006.柴达木盆地北缘滩间山群新厘定[J].西北地质, 39(3):83-90. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdz200603012 李峰, 吴志亮, 李保珠, 2007.柴达木北缘滩间山群时代及其地质意义[J].大地构造与成矿学, 31(2):226-233. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx200702012 李鹏, 李义邦, 王海丰, 等, 2019.柴北缘锡铁山铅锌矿床构造变形特征及其地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 38(4):108-123. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb201904012 毛景文, 张作衡, 王义天, 等, 2012.国外主要矿床类型、特点及找矿勘查[M].北京:地质出版社:302-370. 牛跃龄, 1984.青海锡铁山多金属矿床成因之初步分析[J].兰州大学学报, 20(4):105-115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LDZK198404012.htm 青海省地矿局, 1988.区域地质调查报告(1: 5万锡铁山幅、全集河幅)[R]. 54-137. 青海省地矿局, 1991.青海省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社:662. 孙华山, 赵立军, 吴冠斌, 等, 2012.锡铁山块状硫化物铅锌矿床成矿构造环境及矿区南部找矿潜力:来自滩间山群火山岩岩石化学、地球化学证据[J].岩石学报, 28(2):652-664. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201202023 孙华山, 等, 2017.青海锡铁山铅锌矿深部及外围找矿预测研究[R].中国地质大学(武汉)内部报告. 孙娇鹏, 尹成明, 陈世悦, 等, 2016.柴达木盆地北缘晚石炭世构造环境及物源:以石浅1井为例[J].地质通报, 35(2-3):302-311. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201602012 汤静如, 2006.典型金属矿床正断层中继构造控矿作用研究[D].长沙: 中南大学. 王根厚, 冉书明, 李明, 2001.柴达木盆地北缘赛什腾-锡铁山左行逆冲断裂及地质意义[J].地质力学学报, 7(3):224-230. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20010305&journal_id=dzlxxb 王惠初, 陆松年, 袁桂邦, 等, 2003.柴达木盆地北缘滩间山群的构造属性及形成时代[J].地质通报, 22(7):487-493. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200307005 汪劲草, 彭恩生, 孙振家, 2000.青海锡铁山铅锌矿床喷流沉积后的构造再造过程[J].大地构造与成矿学, 24(2):163-169. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx200002009 王莉娟, 祝新友, 王京斌, 等, 2008.青海锡铁山铅锌矿床喷流沉积系统(SEDEX)成矿流体研究[J].岩石学报, 24(10):2433-2440. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200810024 王莉娟, 彭志刚, 祝新友, 等, 2009.青海省锡铁山sedex型铅锌矿床成矿流体来源及演化:流体包裹体及同位素地球化学证据[J].岩石学报, 25(11):3007-3015. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200911029 王明志, 韩润生, 周威, 等, 2019.黔西北矿集区亮岩铅锌矿区成矿构造解析[J].地质力学学报, 25(2):187-197. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190204&journal_id=dzlxxb 魏俊浩, 等, 2015.青海省大柴旦锡铁山铅锌矿区成矿地质条件对比综合研究及靶区预测[R]. 吴昌志, 顾连兴, 冯慧, 等, 2008.青海锡铁山铅锌矿床的矿体成因类型讨论[J].中国地质, 35(6):1185-1196. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi200806015 吴冠斌, 孙华山, 冯志兴, 等, 2010.锡铁山铅锌矿床成矿构造背景[J].地球化学, 39(3):229-239. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201003003 吴淦国, 1998.矿田构造与成矿预测[J].地质力学学报, 4(2):1-4. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19980214&journal_id=dzlxxb 邬介人, 1985.青海锡铁山块状硫化物矿床地质特征[J].矿床地质, 4(2):1-12. 邬介人, 任秉琛, 张莓, 等, 1987.青海锡铁山块状硫化物矿床的类型及地质特征[J].西北地质科学, 20(6):1-81, 83-88. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001800062 许志琴, 杨经绥, 吴才来, 等, 2003.柴达木北缘超高压变质带形成与折返的时限及机制[J].地质学报, 77(2):163-176. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200302004 薛伟, 张达, 李成远, 等, 2019.滇东南都龙锡锌铟多金属矿床构造控矿模式及找矿方向[J].地质力学学报, 25(1):77-89. https://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190108&journal_id=dzlxxb 袁奎荣, 肖垂斌, 陈儒庆, 1996.青海锡铁山隐伏铅锌矿床预测[M].长沙:中南工业大学出版社. 翟裕生, 2002.成矿构造研究的回顾和展望[J].地质论评, 48(2):140-146. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp200202003 张德全, 王富春, 李大新, 等, 2005.柴北缘地区的两类块状硫化物矿床-I.锡铁山式SEDEX型铅锌矿床[J].矿床地质, 24(5):471-480. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=20854637 赵风清, 郭进京, 李怀坤, 2003.青海锡铁山地区滩间山群的地质特征及同位素年代学[J].地质通报, 22(1):28-31. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz200301005 钟永生, 孙华山, 葛风建, 等, 2018.青海锡铁山铅锌矿床喷流管道相识别、控矿作用及其对矿床成因和找矿勘查意义[J].地质科技情报, 37(5):154-161. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201805021 祝新友, 邓吉牛, 王京彬, 等, 2006.锡铁山铅锌矿床的找矿潜力与找矿方向[J].地质与勘探, 42(3):18-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt200603004 祝新友, 王莉娟, 朱谷昌, 等, 2010a.青海锡铁山铅锌矿床硫同位素地球化学研究:深源与海水硫的混合[J].岩石学报, 26(3):657-666. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201003002 祝新友, 王莉娟, 朱谷昌, 等, 2010b.锡铁山SEDEX铅锌矿床成矿物质来源研究:铅同位素地球化学证据[J].中国地质, 37(6):1682-1689. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201006014 -






 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载: