Stress field simulation and fracture development prediction of the Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in the Fushun-Yongchuan Block, Sichuan Basin
-
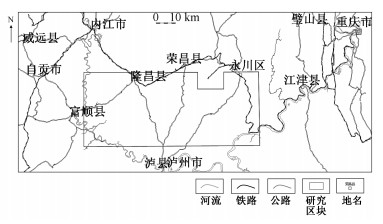
摘要: 岩石中构造裂缝主要受控于地层所处的区域构造应力场,地应力对油气的运移、成藏和分布有着重要的作用。通过应用ANSYS有限元数值模拟方法对四川盆地富顺-永川区块的五峰组-龙马溪组进行应力场模拟及分析研究、应用构造曲率法中的三点法对该层段页岩进行张裂缝发育情况预测研究、综合模拟结果与曲率计算数据对目的区域目的层段进行裂缝发育强度综合预测研究,结果表明富顺-永川区块五峰组-龙马溪组应力高值沿背斜走向分布的规律明显,研究区的东部及西南部的背斜应力值较其他区域背斜高;曲率高值沿背斜走向分布的规律明显,研究区东部及西南部背斜曲率值较其他区域背斜高;在现今应力的作用下,研究区背斜处裂缝发育程度较高,向斜处裂缝发育程度较低,研究区东部及西南部背斜裂缝发育程度较其他区域高。Abstract: The tectonic fractures in rocks are mainly controlled by the regional tectonic stress field where the strata are located. Tectonic stress plays an important role in the migration, accumulation and distribution of oil and gas. The stress field of the Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in the Fushun-Yongchuan Block of the Sichuan Basin was simulated and analyzed by ANSYS finite element software; The three-point method in the method of structural curvature method was used to predict the development of cracks in the shale, and the comprehensive simulation results and curvature calculation data were used to predict the fracture intensity in the target area. The results proved that the distribution of the high stress value of the Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in the Fushun-Yongchuan Block is along the anticline, and the anticline stress values in the eastern and southwestern part of the study area are higher than those in other areas; the distribution of high curvature is along the anticline, and the curvature values of the anticline in the east and southwest of the study area are higher than those in other areas; the fracture in the anticline of the study area has a higher level of development, and it's lower in the syncline, at the same time it's higher in the anticline of the eastern and southwestern part of the study area than other areas under the current stress.
-
Key words:
- curvature method /
- finite element /
- fracture prediction /
- Longmaxi Formation /
- Sichuan Basin
-
图 3 四川盆地古生界(部分)地层综合柱状图(刘文平等,2017)
Figure 3. Comprehensive histogram of the Paleozoic strata (partial) in the Sichuan Basin (Liu et al., 2017)
表 1 四川盆地燕山期主幕水平主应力大小计算表
Table 1. Computation chart of horizontal stress of Yenshanian main curtain in the Sichuan Basin
井号 深度/m σ1/MPa σ3/MPa σ/MPa A井 1585 62.4 35.3 71.69 1594 49.1 31.4 58.28 1599 56.3 36.2 66.93 B井 2451 61.5 47.5 77.70 2470 59.8 46.5 75.75 2490 64.4 49.6 81.28 C井 2940 73.8 42.5 85.16 2934 73.9 45.2 86.62 2980 74.8 45.2 87.39 2986 75.2 47.9 89.15 2991 75.2 44.4 87.32 2998 75.2 44.7 87.48 注:σ1—最大水平主应力;σ3—最小水平主应力;σ—燕山期主幕水平应力 -
AL-RUWAILI S B, CHARDAC O, 2003. 3D model for rock strength & in-situ stresses in the Khuff formation of Ghawar field, methodologies & applications[C]//Middle east oil show. Bahrain: Society of Petroleum Engineers: 206-219. CAO R R, LIU Z Y, 2008. Application of curvature of face-trend surface fitting method in fracture prediction[J]. Computer Applications of Petroleum, 16(3):12-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sygyjsjyy200803006 CHEN Y P, ZHAO C B, LIN G, 2008. Mechanical properties of deep earth rocks and their roles in the investigation of continental deformation processes[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 32(3):276-284. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200803003 CUI F P, HU R L, LIU Z L, et al., 2008. Surfer software platform based complex three-dimensional geological digital models for pre-processing of FLAC3D[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 16(5):699-702. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcdzxb200805023 DING W L, ZENG W T, WANG R Y, et al., 2016. Method and application of tectonic stress field simulation and fracture distribution prediction in shale reservoir[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(2):63-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201602008 DONG D Z, SHI Z S, SUN S S, et al., 2018. Factors controlling microfractures in black shale:a case study of Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Shuanghe Profile, Changning area, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(5):763-774. (in Chinese with English abstract) DU ROUCHET J, 1981. Stress fields, a key to oil migration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 65(1):74-85. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0e6ba4fbef6b0e696c5dd5d50c43ca18&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn FINKBEINER T, BARTON C A, ZOBACK M D, 1997. Relationships among in-situ stress, fractures and faults, and fluid flow:Monterey formation, Santa Maria basin, California[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 81(12):1975-1999. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=482f51a884a748d708619a8ca5d47562&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn GUO K, XU Z Y, NI G S, et al., 1998. Research on the main curvature method and its application to cracky oil-gas deposits[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 20(4):335-337. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800604007 GUO Y H, LI Z F, LI D H, et al., 2004. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Early Silurian in Sichuan area[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 6(1):20-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200401003.htm HUANG S W, JIANG M L, 2017. Analysis on structural fracture characteristics in Ansai Yanhewan Area[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 46(10):973-975. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lnhg201710015 JIANG Y L, ZHANG L, LU X S, et al., 2005. Application of the tectonic stress simulation based on ANSYS in Kelasu region of Kuche depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 25(4):42-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy200504014 LIU G F, LU H J, HE S L, 2009. Application of finite element analysis in reservoir in-situ stress research[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 9(24):7430-7435. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxjsygc200924033 LIU S G, DENG B, ZHONG Y, et al., 2016. Unique geological features of burial and superimposition of the lower Paleozoic shale gas across the Sichuan basin and its periphery[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(1):11-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201601002 LIU T, YANG F P, 2002. Proficient in ANSYS[M]. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press. (in Chinese) LIU W P, ZHANG C L, GAO G D, et al., 2017. Controlling factors and evolution laws of shale porosity in Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 38(2):175-184. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201702005 MOAVENI S, 2003. Finite element analysis: theory and application with ANSYS[M]. 2nd ed. Publishing House of Electronics Industry. MOHTARAMI E, BAGHBANAN A, HASHEMOLHOSSEINI H, 2017. Prediction of fracture trajectory in anisotropic rocks using modified maximum tangential stress criterion[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 92:108-120. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=3514f07f11f2041cf345d2b1149b42c1 MOU C L, GE X Y, XU X S, et al., 2014. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Late Ordovician and its petroleum geological significance in Middle-Upper Yangtze Region[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 16(4):427-440. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201404001 MU L X, 2009. Prediction of reservoir fractures[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press. (in Chinese) NELSON P H, 2011. Pore-throat sizes in sandstones, siltstones, and shales:reply[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 95(8):1448-1453. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0d00afa2ff29de48153e57af9aca4155&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn PETRICCA P, CARAFA M M C, BARBA S, et al., 2013. Local, regional, and plate scale sources for the stress field in the Adriatic and Periadriatic region[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 42:160-181. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d571ede2467ac224d21290fa2f670e51 RAMANDI H L, MOSTAGHIMI P, ARMSTRONG R T, 2017. Digital rock analysis for accurate prediction of fractured media permeability[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 554:817-826. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=eeda458f9900b20e669f1e8b85e71618 SHEN G H, 2008. Application of the finite element numerical simulation method in fracture prediction[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 15(4):24-26, 29. (in Chinese with English abstract). SONG W, MA X J, LV F L, et al., 2017. The two-dimensional plane model study of tectonic ground fissure stress field in Hejian County of Cangzhou city, Hebei Province[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 38(3):83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SHAD201703020.htm SONG Y, JIANG L, MA X Z, 2013. Formation and distribution characteristics of unconventional oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 15(5):605-614. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG T, YANG K M, XIONG L, et al., 2015. Shale sequence stratigraphy of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan and their control on reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 36(8):915-925. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201508003 WEI C G, LEI M S, WAN T F, et al., 2006. Numerical simulation of palaeotectonic stress field of Yingcheng Fm in Gulong-Xujiaweizi area:prediction and comparative study of tectoclase development area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 27(1):78-84, 105. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200601016.htm WU L Q, LIU C L, LI B, et al., 2014. Numerical simulation of tectonic stress field and prediction of oil-favored areas:a case study of the third member of Qingshankou Formation in Guizijing region of Qian'an area, Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 20(4):339-351. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dzlx201404002.htm YAN C N, JIN Z J, ZHAO J H, et al., 2016. Comparison of Marcellus shale in United States and Longmaxi formation shale in southern China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 35(6):122-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201606017 YUE G Y, DU S Q, HUANG J J, et al., 1996. Principle of structural compounding-combine[M]. Chengdu:The Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese) ZHANG S R, WAN T F, CHEN J P, 2004. Tectonic stress field modeling and fracture prediction in strata in Xiaoquan-Xinchang area, western Sichuan depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 25(1):70-74, 80. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz200401013 ZHANG X M, YIN S, SHI C L, 2018. Developmental characteristics and controlling factors of fractures in tight sandstone of Shanxi Formation, southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 23(3):43-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201803005 ZHAO W T, CHEN X Z, 2009. Foundation of finite element method[M]. Beijing:Science Press. (in Chinese) ZHOU C C, 2003. Studies on the structure mode of Baigezhuang region and the identification and prediction of structure fracture of reservoirs[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences3. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZOU C N, DONG D Z, WANG Y M, et al., 2015. Shale gas in China:characteristics, challenges and prospects (I)[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 42(6):689-701. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=23ba24cff51bb6ef40e936a3e748210e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn 曹润荣, 刘宗彦, 2008.面曲率法-趋势面拟合法在裂缝预测中的应用[J].石油工业计算机应用, 16(3):12-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sygyjsjyy200803006 陈运平, 赵崇斌, 林舸, 2008.深部岩石力学性质及其在大陆构造变形过程研究中的作用[J].大地构造与成矿学, 32(3):276-284. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200803003 崔芳鹏, 胡瑞林, 刘照连, 等, 2008.基于Surfer平台的FLAC3D复杂三维地质建模研究[J].工程地质学报, 16(5):699-702. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcdzxb200805023 丁文龙, 曾维特, 王濡岳, 等, 2016.页岩储层构造应力场模拟与裂缝分布预测方法及应用[J].地学前缘, 23(2):63-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201602008 董大忠, 施振生, 孙莎莎, 等, 2018.黑色页岩微裂缝发育控制因素:以长宁双河剖面五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 45(5):763-774. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201805002 郭科, 胥泽银, 倪根生, 1998.用主曲率法研究裂缝性油气藏[J].物探化探计算技术, 20(4):335-337. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800604007 郭英海, 李壮福, 李大华, 等, 2004.四川地区早志留世岩相古地理[J].古地理学报, 6(1):20-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb200401003 黄生旺, 姜萌蕾, 2017.安塞沿河湾地区构造裂缝特征分析[J].辽宁化工, 46(10):973-975. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lnhg201710015 蒋有录, 张乐, 鲁雪松, 等, 2005.基于ANSYS的应力场模拟在库车坳陷克拉苏地区的初步应用[J].天然气工业, 25(4):42-44. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy200504014 刘广峰, 陆红军, 何顺利, 2009.有限元法开展油气储层地应力研究综述[J].科学技术与工程, 9(24):7430-7435. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxjsygc200924033 刘树根, 邓宾, 钟勇, 等, 2016.四川盆地及周缘下古生界页岩气深埋藏-强改造独特地质作用[J].地学前缘, 23(1):11-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201601002 刘涛, 杨凤鹏, 2002.精通ANSYS[M].北京:清华大学出版社. 刘文平, 张成林, 高贵冬, 等, 2017.四川盆地龙马溪组页岩孔隙度控制因素及演化规律[J].石油学报, 38(2):175-184. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201702005 牟传龙, 葛祥英, 许效松, 等, 2014.中上扬子地区晚奥陶世岩相古地理及其油气地质意义[J].古地理学报, 16(4):427-440. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201404001 穆龙新, 2009.储层裂缝预测研究[M].北京:石油工业出版社. 沈国华, 2008.有限元数值模拟方法在构造裂缝预测中的应用[J].油气地质与采收率, 15(4):24-26, 29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yqdzycsl200804007 宋伟, 马学军, 吕凤兰, 等, 2017.沧州河间构造地裂缝应力场二维平面模型研究[J].上海国土资源, 38(3):83-89. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shdz201703020 宋岩, 姜林, 马行陟, 2013.非常规油气藏的形成及其分布特征[J].古地理学报, 15(5):605-614. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb201305003 王同, 杨克明, 熊亮, 等, 2015.川南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩层序地层及其对储层的控制[J].石油学报, 36(8):915-925. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95667X/201508/83898866504849534856484851.html 魏春光, 雷茂盛, 万天丰, 等, 2006.古龙-徐家围子地区营城组古构造应力场数值模拟-构造裂缝发育区带预测及对比研究[J].石油与天然气地质, 27(1):78-84, 105. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz200601013 吴林强, 刘成林, 李冰, 等, 2014.应力场数值模拟与油藏有利区预测:以松辽盆地乾安地区归字井青三段为例[J].地质力学学报, 20(4):339-351. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20140402&journal_id=dzlxxb 颜彩娜, 金之钧, 赵建华, 等, 2016.美国Marcellus页岩与中国南方龙马溪组页岩地质特征对比及启示[J].地质科技情报, 35(6):122-130. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201606017 乐光禹, 杜思清, 黄继钧, 等, 1996.构造复合联合原理:川黔构造组合叠加分析[M].成都:成都科技大学出版社. 张守仁, 万天丰, 陈建平, 2004.川西坳陷孝泉-新场地区须家河组二-四段构造应力场模拟及裂缝发育区带预测[J].石油与天然气地质, 25(1):70-74, 80. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz200401013 张学敏, 尹帅, 史长林, 2018.沁水盆地南部山西组致密砂岩裂缝发育特征及控制因素[J].海相油气地质, 23(3):43-52. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201803005 赵维涛, 陈孝珍, 2009.有限元法基础[M].北京:科学出版社. 周灿灿, 2003.柏各庄地区构造样式及储层构造裂缝识别与预测[D].广州: 中国科学院研究生院(广州地球化学研究所). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y540848 邹才能, 董大忠, 王玉满, 等, 2015.中国页岩气特征、挑战及前景(一)[J].石油勘探与开发, 42(6):689-701. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201506001 -





 下载:
下载: