ENGINEERING GEOLOGICAL EVALUATION ON THE WEST LINE OF THE CROSS-SEA CHANNEL IN THE QIONGZHOU STRAIT
-
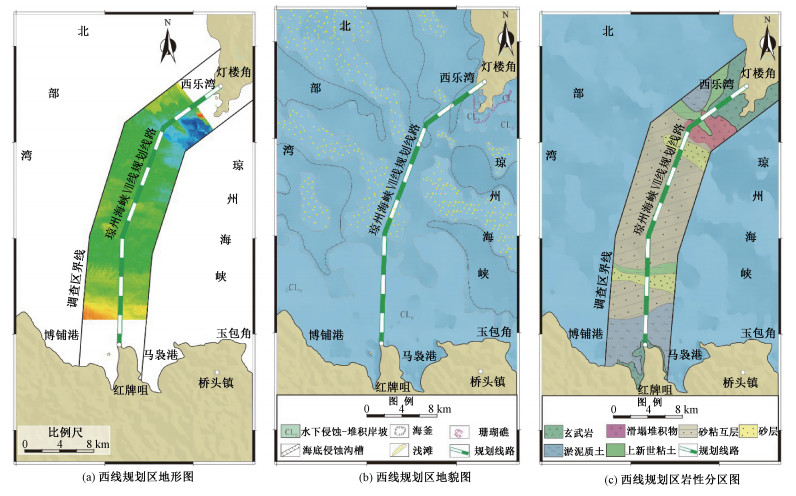
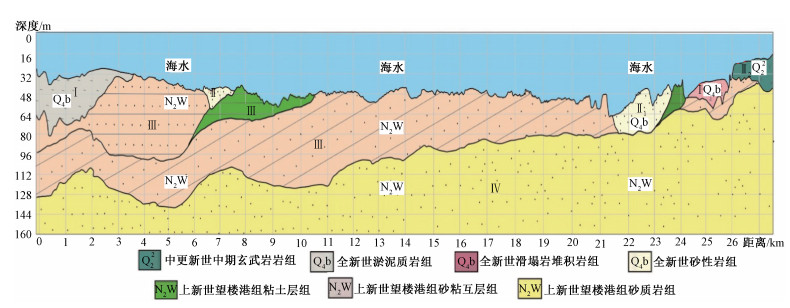
摘要: 为开展琼州海峡跨海通道地壳稳定性评价,避免潜在的地质灾害对跨海通道工程安全性产生不利影响,利用侧扫声纳、单道地震、多波束等地球物理探测方法对琼州海峡海底展开了地形地貌调查,获得了琼州海峡跨海通道工程区海域活动断层分布、西线规划区地形地貌及地质条件等基础地质资料。工程地质评价认为西线线路断裂、地震、火山活动性弱,海底水深小、地形较为平坦、地貌简单,上新世望楼港组低液限粘土及上新世浅海相砂层作为基础持力层,岩土工程力学性质尚可,利于开展跨海通道桥梁方案施工。规划线路穿越1处侵蚀沟槽,影响长度约5 km,地形高差达60 m,且线路东临1处海釜,分布有陡坎,且部分地段分布有滑塌堆积。建议西线线路北段局部西移约1.5 km,同时关注西口潮流侵蚀沟槽、规划区南部淤泥质软土、古河道砂性土沉积、海峡谷底活动沙坡等不良地质作用影响。Abstract: For the crustal stability assessment of the cross-sea channel engineering in the Qiongzhou Strait, geophysical survey methods including side-sweep sonar, single channel seism and multi-beam were applied to investigate the topography and geomorphology of the Qiongzhou Strait. The side sweep sonar images, topographic and the distribution of active faults were obtained. The engineering geological evaluation shows that the fault, earthquake, and volcanic activities in the planned area of the line are weak, the seabed water depth is shallow, the terrain is relatively flat, and the landform is simple. The low liquid limit clay of the formation and the Pliocene neritic facies sand layer could be used as the basic supporting layers, and the mechanical properties of geotechnical engineering are acceptable, which are conducive to the construction of bridges across the sea. Research demonstrates that the planned line passes through an erosion trench, affecting a length of about 5 kilometers, with a terrain height difference of 60 meters and a sea kettle to the east of the line, along with steep slopes as well as slump deposits in some parts of the area. It is proposed that the northern section of the line be partially moved about 1.5 kilometers westward. At the same time, attention will be paid to the erosion of trenches in the West mouth, muddy soft soil in the southern part of the planning area, sandy soil deposits in ancient rivers, and active sand waves at the bottom of the strait.
-
致谢:
本文在编写过程中获中国地质科学院地质研究所张泽明研究员主持的国家自然科学基金项目(40272032)的资助。中国地质大学(武汉)RogerMason教授提供了Ries陨石坑冲击岩的显微照片, 特表谢忱。
责任编辑:范二平
-
表 1 琼州海峡跨海通道前期规划路线方案统计表
Table 1. Statistics of the preliminary route plans for the cross-sea channel in the Qiongzhou Strait
编号 线路 长度/km 最大水深/m 存在问题 Ⅰ线 雷州赤坎—海南白沙角 28 75 海底地形复杂,水深大,受地震和断裂的影响 Ⅱ线 雷州排尾角—海南白沙角 19.7 86 海底地形复杂,水深大,不能避开海峡中的深槽 Ⅲ线 雷州海安港—海南白沙角 25.5 80 海底地形复杂,海峡中有隆起,隆起处水深30~40 m Ⅳ线 雷州三塘—海南新海 19.7 105 海底地形复杂,水深大,海底铺设有海底通讯电缆,为禁止抛锚和捕捞区 Ⅴ线 雷州三塘—海南的天尾 20.3 88 海底地形复杂,水深大,受地震和断裂的影响,南岸有陡坎,优选方案之一。 Ⅵ线 雷州灯楼角—海南玉包角 26.3 60 海底地形复杂,北侧经过一深槽,水深约80 m Ⅶ线(西线) 雷州灯楼角—海南红牌咀 31.8 40 海底较为平坦,平均水深约40 m,但跨海工程长,必须绕避徐闻珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区的核心区。优选方案之一 -
[1] 谭忠盛, 贺维国, 王梦恕.琼州海峡工程地质条件及铁路隧道方案研究[J].隧道建设, 2018, 38(1): 1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdjs201801001TAN Zhongsheng, HE Weiguo, WANG Mengshu. Study of engineering geological conditions and railway tunnel scheme across Qiongzhou strait[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2018, 38(1): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdjs201801001 [2] 詹文欢, 刘以宣.琼州海峡的断裂构造与区域稳定性分析[J].热带海洋, 1989, 8(4): 70-77.ZHAN Wenhuan, Liu Yixuan. A study on faulting and regional stability in Qiongzhou strait[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1989, 8(4): 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 石要红, 郑志昌.跨海通道工程的工程地质调查方法:以琼州海峡跨海工程地质调查为例[J].南海地质研究, 2008, (1): 108-113.SHI Yaohong, ZHENG Zhichang. Engineering geological investigation methods of cross-sea tunnel: a case study of engineering geological investigation of Qiongzhou strait cross-sea engineering[J]. Gresearch of Eological South China Sea, 2008, (1): 108-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 程振廷.跨越琼州海峡铁路隧道施工方案刍议[J].隧道建设, 2008, 28(4): 423-428, 451. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdjs200804007CHENG Zhenting. Preliminary construction plan for tunnel on Qiongzhou Strait crossing railway project[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2008, 28(4): 423-428, 451. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdjs200804007 [5] 谭忠盛, 王梦恕, 罗时祥.琼州海峡铁路隧道方案初步比选分析[J].中国工程科学, 2009, 11(7): 39-44, 85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2009.07.007TAN Zhongsheng, WANG Mengshu, LUO Shixiang. Scheme comparison of Qiongzhou strait railway tunnel[J]. Engineering Science, 2009, 11(7): 39-44, 85. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2009.07.007 [6] 王涵, 贺维国, 袁勇.琼州海峡铁路跨海隧道全寿命风险评价[J].隧道建设, 2018, 38(9): 1513-1519. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdjs201809015WANG Han, HE Weiguo, YUAN Yong. Life-cycle risk evaluation for Qiongzhou strait railway tunnel[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2018, 38(9): 1513-1519. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdjs201809015 [7] 谭忠盛, 王梦恕, 杨小林.海底隧道施工技术及琼州海峡隧道方案的可行性[J].焦作工学院学报(自然科学版), 2001, 20(4): 286-291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9787.2001.04.012TAN Zhongsheng, WANG Mengshu, YANG Xiaolin. Construction technology of undersea tunnel and the feasibility of Qiongzhou Strait tunnel[J]. Journal of Jiaozuo Institute of Technology (Natural Science), 2001, 20(4): 286-291. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9787.2001.04.012 [8] 石新栋, 皇甫明, 谭忠盛, 等.跨琼州海峡隧道方案的探讨[J].隧道建设, 2010, 30(6): 625-628. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdjs201006002SHI Xindong, HUANG Fuming, TAN Zhongsheng, et al. Study on options of Qiongzhou Strait tunnel[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2010, 30(6): 625-628. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdjs201006002 [9] 胡海涛, 殷跃平.区域地壳稳定性评价"安全岛"理论及方法[J].地学前缘, 1996, 3(1-2): 57-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200102001HU Haitao, Yin Yueping. Theory and evaluation methods of regional crust stability "safety island"[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1996, 3(1-2): 57-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200102001 [10] 胡久常.海南岛及其邻区地震活动特征分析[J].华南地震, 1994, 14(4): 29-34.HU Jiuchang. A analysis of seismicity in Hainan Island and its neighboring areas[J]. South China Journal of Seismology, 1994, 14(4): 29-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 谢振福.海南岛及邻区地震活动特征研究[J].震灾防御技术, 2006, 1(4): 326-336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.04.006XIE Zhenfu. Study on Seismic Activity of Hainan peninsular and its adjacent area[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2006, 1(4): 326-336. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.04.006 [12] 徐锡伟.中国城市活动断层概论: 20个城市活动断层探测成果[M].北京:地震出版社, 2015: 381-402.XU Xiwei. Introduction to China's urban activity faults-results of 20 urban activity fault detection[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2015: 381-402. (in Chinese) [13] 李振, 彭华, 马秀敏, 等.琼州海峡古河道及其工程地质评价[J].工程地质学报, 2018, 26(4): 1017-1024. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201804026LI Zhen, PENG Hua, MA Xiumin et al. Paleochannels and engineering geological evaluation along Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(4): 1017-1024. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201804026 [14] 叶春池.琼州海峡沉积与地形发育[J].热带地理, 1986, 6(4): 346-353.YE Chunchi. Distribution of sediments and submarine topography of Qiongzhou Strait[J]. Tropical Geography, 1986, 6(4): 346-353. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 彭学超.琼州海峡地质构造特征及成因分析[J].南海地质研究, 2000, (12): 44-57. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200000876087PENG Xuechao. Geological structure characterics and cause of formation analyzing in Qiongzhou Strait, South China Sea[J]. Gresearch of Eological South, 2000, (12): 44-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200000876087 [16] 吴树仁, 陈庆宣, 孙叶.我国区域地壳稳定性研究的新进展[J].地质力学学报, 1995, 1(1): 31-37. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19950105&journal_id=dzlxxbWU Shuren, CHEN Qingxuan, SUN Ye. Recent progress of the study on regional crustal stability in China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 1995, 1(1): 31-37. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=19950105&journal_id=dzlxxb [17] 丁准泰.广州市区域地壳稳定性评价[J].中山大学研究生学刊(自然科学、医学版), 2009, 30(4): 83-94.DING Zhuntai. The evaluation of regional crustal stability in Guangzhou City[J]. Journal of the Graduates Sun Yat-sen University (Natural Sciences、Medicine), 2009, 30(4): 83-94. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 李振, 彭华, 姜景捷, 等.侧扫声纳在琼州海峡跨海通道地壳稳定性调查中的应用[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(2): 244-252. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180211&journal_id=dzlxxbLI Zhen, PENG Hua, JIANG Jingjie, et al. Application of side scan sonar in the investigation of crustal stability of the cross-sea channel in the Qiongzhou strait[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(2): 244-252. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180211&journal_id=dzlxxb -






 下载:
下载: