DISTRIBUTION OF PRESENT-DAY CRUSTAL STRESS AND TECTONIC ANALYSIS IN THE RONGJIANG CALEDONIAN FOLD BELT, SOUTHEASTERN GUIZHOU
-
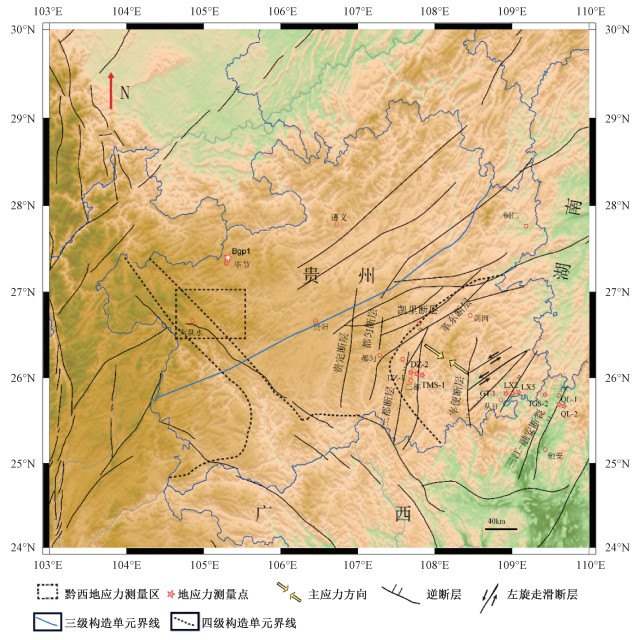
摘要: 贵州东南部位于盖层极不发育的榕江加里东褶皱带内,为查明该区域内的地应力状态,在贵州省黔南州境内进行了7个钻孔的水压致裂地应力测量工作,同时结合贵州西部已有研究结果和贵州西北部1个钻孔的地应力测量资料,对贵州东南部与西部和西北部的地应力分布差异进行了对比研究,最后结合断层的活动性质以及Byerlee准则探讨了测孔区域断层的稳定性,结果表明:水平主应力在研究区占主导地位,最大水平主应力方向表现为北西向;根据安德森断层理论,三向主应力的相对大小有利于逆断层和走滑断层的活动,这与研究区发育的活动断层性质相对应;最大和最小水平主应力的线性拟合结果表明,研究区水平主应力的梯度大于黔西煤层地区、广西盆地东北部和全国的地应力梯度值,最大水平主应力的值在相近深度上大于黔西、黔西北地区和广西盆地东北部;三都断裂带附近存在较高的构造应力,μm值(最大剪应力与平均主应力的比值)较高,表明断层处于摩擦极限平衡状态;而三江-融安断裂两侧的构造作用存在较为明显的差异,西侧的构造作用强于东侧;虽然部分钻孔内的μm值都处于高值,但区域应力方向与断层多以较大角度相交,因此断层是稳定的,这与研究区的地震活动性相吻合。Abstract: Southeastern Guizhou is located in the Rongjiang Caledonian fold belt, which is very undeveloped in caprock. In order to find out the state of crustal stress in this area, the hydraulic fracturing stress measurements of 7 boreholes were carried out. A comparative study was made on the distribution differences of crustal stress in the southeast, west and northwest of southeastern Guizhou, combining with the research results of west Guizhou and crustal measurement data of a borehole in northwestern Guizhou. Finally the fault stability around the sampling borehole area was discussed in association with fault activities and the Byerlee criterion. The results demonstrate that the horizontal principle stress is dominant in the study area, and the maximum horizontal principal stress is in the N-W direction; according to the Anderson fault theory, the relative magnitude of the three-direction principal stress is favorable to the movement of the thrust fault and strike-slip fault, which corresponds to the nature of the active fault developed in the study area; the linear fitting results of the maximum and minimum horizontal principal stresses show that the gradient of horizontal principal stress is larger than that of the coal seam area in western Guizhou, the northeastern Guangxi basin and the whole country, and the maximum horizontal principal stress is larger than that of western Guizhou, northwesternern Guizhou and the northeastern Guangxi basin at the similar depth; there are high tectonic stresses near the Sandu fault zone, and the μm value (the ratio of the maximum shear stress to the average principal stress) is higher, which indicates that the fault is in the state of friction limit equilibrium; the tectonic action on both sides of the Sanjiang-Rongan fault is obviously different, and the tectonic action on the west side is stronger than that on the east side; although μm values are high in some boreholes, the direction of regional stresses intersect with the fault at a larger angle, so the fault is stable, which is consistent with the seismicity in the study area.
-
表 1 地应力测量结果
Table 1. Results of in-situ stress measurement in boreholes
孔号 岩性 序号 深度/m 主应力值/MPa 方位/(°) P0/MPa μm KHmax Ka K′ SH Sh SV DZ-1 泥质灰岩 1 197.00 12.79 7.06 5.21 N28°W 1.93 0.54 2.45 1.90 3.31 泥质灰岩 2 239.40 16.35 9.88 6.33 N32°W 2.35 0.56 2.58 2.07 3.52 泥质灰岩 3 249.60 16.71 10.37 6.6 2.45 0.55 2.53 2.05 3.44 泥质灰岩 4 263.36 17.73 10.26 6.97 N41°W 2.58 0.55 2.54 2.01 3.45 泥质灰岩 5 272.14 17.83 10.3 7.2 2.67 0.54 2.48 1.95 3.35 泥质灰岩 6 293.24 18.85 11.19 7.76 2.87 0.53 2.43 1.94 3.27 DZ-2 炭质页岩 1 284.02 15.29 10.13 7.52 N44°W 1.68 0.40 2.03 1.69 2.33 炭质页岩 2 293.79 16.43 9.88 7.78 2.12 0.43 2.11 1.69 2.53 炭质页岩 3 315.91 15.85 9.10 8.36 2.34 0.38 1.90 1.49 2.24 炭质页岩 4 324.25 17.53 10.38 8.58 N37°W 2.42 0.42 2.04 1.63 2.45 炭质页岩 5 344.29 20.13 11.87 9.11 N53°W 2.62 0.46 2.21 1.76 2.70 TMS-1 砂质板岩 1 108.62 10.20 5.39 2.87 0.44 0.60 3.55 2.72 4.02 砂质板岩 2 152.86 11.1 7.95 4.04 N63°W 0.87 0.53 2.75 2.36 3.23 砂质板岩 3 222.62 11.82 7.63 5.89 N55°W 1.56 0.41 2.01 1.65 2.37 砂质板岩 4 341.31 13.86 7.97 9.03 2.72 0.36 1.53 1.21 1.77 GT-1 石英砂岩 1 148.50 7.52 4.91 3.93 1.09 0.39 1.91 1.58 2.26 石英砂岩 2 162.80 10.83 8.2 4.31 1.23 0.51 2.51 2.21 3.12 石英砂岩 3 249.50 13.78 8.32 6.6 N43°W 2.08 0.44 2.09 1.67 2.59 石英砂岩 4 261.00 14.73 8.96 6.91 N48°W 2.19 0.45 2.13 1.71 2.66 石英砂岩 5 277.60 15.47 9.43 7.35 2.35 0.45 2.10 1.69 2.62 石英砂岩 6 286.90 16.08 10.51 7.59 2.44 0.45 2.12 1.75 2.65 LX2 石英砂岩 1 144.44 8.23 5.06 3.82 1.32 0.47 2.15 1.74 2.76 石英砂岩 2 213.00 14.36 10.69 5.64 2 0.55 2.55 2.22 3.40 石英砂岩 3 277.11 14.42 8.89 7.33 N41°W 2.62 0.43 1.97 1.59 2.51 石英砂岩 4 378.00 15.49 10.83 10 3.61 0.30 1.55 1.32 1.86 石英砂岩 5 425.30 16.75 11.4 11.25 N56°W 4.08 0.28 1.49 1.25 1.77 石英砂岩 6 462.30 18.42 11.93 12.22 N35°W 4.44 0.30 1.51 1.24 1.80 LX5 泥质砂岩 1 200.50 7.91 4.81 5.11 N40°W 1.87 0.35 1.55 1.24 1.86 泥质砂岩 2 220.10 8.75 5.91 5.61 N47°W 2.07 0.31 1.56 1.31 1.89 泥质砂岩 3 228.00 9.37 6.83 5.81 2.14 0.33 1.61 1.39 1.97 泥质砂岩 4 238.80 11.28 7.25 6.06 2.24 0.41 1.86 1.53 2.37 泥质砂岩 5 289.18 10.77 6.43 7.37 N54°W 2.74 0.37 1.46 1.17 1.73 JGS-2 花岗岩 1 119.41 9.68 6.49 3.16 1.17 0.62 3.06 2.56 4.28 花岗岩 2 166.50 10.34 6.41 4.41 1.63 0.52 2.34 1.90 3.13 花岗岩 3 206.00 12.60 7.65 5.45 N35°W 2.02 0.51 2.31 1.86 3.08 花岗岩 4 234.50 15.85 10.4 6.2 2.3 0.55 2.56 2.12 3.47 花岗岩 5 269.30 17.00 10.76 7.13 N52°W 2.64 0.52 2.38 1.95 3.20 花岗岩 6 278.70 17.50 10.92 7.37 N56°W 2.73 0.52 2.37 1.93 3.18 花岗岩 7 288.50 17.69 10.95 7.63 2.83 0.51 2.32 1.88 3.10 Bgp1
(黔西北毕节地区)页岩 1 278.50 7.19 4.73 7.37 1.77 0.22 0.98 0.81 页岩 2 295.00 10.45 6.69 7.81 1.93 0.22 1.34 1.10 页岩 3 358.50 14.37 9.31 10.20 NW50° 2.55 0.21 1.41 1.16 页岩 4 387.80 12.26 7.80 10.26 NW42° 2.84 0.22 1.19 0.98 页岩 5 425.40 12.13 7.77 11.26 3.21 0.22 1.08 0.88 页岩 6 448.60 12.56 8.40 11.87 NW54° 3.44 0.20 1.06 0.88 注:Sv—垂直主应力;P0—静水压力;Ka—平均水平主应力与垂直应力之比;KHmax—最大水平主应力与垂直主应力之比;K′—有效应力条件下的KHmax;μm—最大剪应力与平均主应之比 表 2 地应力随深度变化拟合方程
Table 2. Fitting equation of in-situ stress with depths in different regions
-
[1] HAST N. The state of stress in the upper part of the earth's crust[J]. Tectonophysics, 1969, 8(3): 169-211. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(69)90097-3 [2] BROWN E T, HOEK E. Trends in relationships between measured in-situ stresses and depth[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1978, 15(4): 211-215. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4ce40fe47cc2324742e2ee91f75225d3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] RUMMEL F, MÖHRING-ERDMAN, G, BAUMGÄRTNER J. PAGEOPH. Stress constraints and hydrofracturing stress data for the continental crust[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1986, 124(4-5): 875-895. doi: 10.1007/BF00879616 [4] BYERLEE J. Friction of rocks[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1978, 116(4-5): 615-626. doi: 10.1007/BF00876528 [5] 秦向辉, 陈群策, 孟文, 等.大地震前后实测地应力状态变化及其意义:以龙门山断裂带为例[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(3): 309-320. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180303&journal_id=dzlxxbQIN Xianghui, CHEN Qunce, MENG Wen, et al. Evaluating measured in-situ stress state changes associated with earthquakes and its implications: a case study in the longmenshan fault zone[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(3): 309-320. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180303&journal_id=dzlxxb [6] 陈群策, 孙东生, 崔建军, 等.雪峰山深孔水压致裂地应力测量及其意义[J].地质力学学报, 2019, 25(5): 853-865. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190514&journal_id=dzlxxbCHEN Qunce, SUN Dongsheng, CUI Jianjun, et al. Hydraulic fracturing stress measurements in Xuefengshan deep borehole and its significance[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(5): 853-865. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190514&journal_id=dzlxxb [7] 王艳华, 崔效锋, 胡幸平, 等.基于原地应力测量数据的中国大陆地壳上部应力状态研究[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(9): 3016-3027. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201209020WANG Yanhua, CUI Xiaofeng, HU Xingping, et al. Study on the stress state in upper crust of China mainland based on in-situ stress measurements[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(9): 3016-3027. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201209020 [8] RALEIGH C B, HEALY J H, BREDEHOEFT J D. An experiment in earthquake control at Rangely, Colorado[J]. Science, 1976, 191(4233): 1230-1237. doi: 10.1126/science.191.4233.1230 [9] ZOBACK M D, HICKMAN S. In situ study of the physical mechanisms controlling induced seismicity at monticello reservoir, South Carolina[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1982, 87(B8): 6959-6974. doi: 10.1029/JB087iB08p06959 [10] 李兵, 李兵岩, 张策, 等.广西盆地东北部的地应力分布特征[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(S1): 3475-3484. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSLX2017S1041.htmLI Bing, LI Bingyan, ZHANG Ce, et al. Distribution characteristics of the crustal stress in the northeast of Guangxi Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(S1): 3475-3484. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSLX2017S1041.htm [11] 马杏垣.中国岩石圈动力学地图集[M].中国地图出版社, 1989.MA Xingyuan. Lithspheric dynamics atlas of China[M]. Beijing: China Cartographc Publishing House, 1989. (in Chinese) [12] 高振鲲.贵州高原现今应力场数值模拟及其工程地质意义[D].贵阳: 贵州大学, 2008. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&filename=2008206049.nhGAO Zhenkun. Mathematical simulation research on present tectonic stress field and its engineering geology significance of Guizhou plateau[D]. Guizhou: Guizhou University, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&filename=2008206049.nh [13] 徐宏杰, 桑树勋, 易同生, 等.黔西地应力场特征及构造成因[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 45(6): 1960-1966. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201406029XU Hongjie, SANG Shuxun, YI Tongsheng, et al. Characteristics of in-situ stress field and its tectonic origin in Western Guizhou[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2014, 45(6): 1960-1966. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201406029 [14] 许忠淮, 汪素云, 黄雨蕊, 等.由大量的地震资料推断的我国大陆构造应力场[J].地球物理学报, 1989, 32(6): 636-647. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1989.06.004XU Zhonghuai, WANG Suyun, HUANG Yurui, et al. The tectonic stress field of Chinese continent deduced from a great number of earthquakes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1989, 32(6): 636-647. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1989.06.004 [15] 李细光, 史水平, 黄洋, 等.广西及其邻区现今构造应力场研究[J].地震研究, 2007, 30(3): 235-240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2007.03.006LI Xiguang, SHI Shuiping, HUANG Yang, et al. Current tectonic stress field in Guangxi and vicinity[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 2007, 30(3): 235-240. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2007.03.006 [16] 景锋, 盛谦, 张勇慧, 等.中国大陆浅层地壳实测地应力分布规律研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(10): 2056-2062. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.10.014JING Feng, SHENG Qian, ZHANG Yonghui, et al. Research on distribution rule of shallow crustal geostress in China mainland[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(10): 2056-2062. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.10.014 [17] 李兵, 丁立丰, 王建新, 等.山东蓬莱近海岸的地应力状态及断层稳定性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2019, 25(4): 459-466. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190402&journal_id=dzlxxbLI Bing, DING Lifeng, WANG Jianxin, et al. The state of the in-situ stress and fault stability evaluation of the Penglai coast[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(4): 459-466. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190402&journal_id=dzlxxb [18] HAIMSON B C, CORNET F H. ISRM Suggested Methods for rock stress estimation—Part 3: hydraulic fracturing (HF) and/or hydraulic testing of pre-existing fractures (HTPF)[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003, 40(7-8): 1011-1020. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.08.002 [19] ZOBACK M D. Reservoir geomechanics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010. [20] 李延栋.中国区域地质志, 贵州志[M].北京:地质出版社, 2017.LI Yandong. China regional geological records, Guizhou Zhi[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017. (in Chinese) [21] 谢富仁, 崔效峰, 赵建涛, 等.中国大陆及邻区现代构造应力场分区[J].地球物理学报, 2004, 47(4): 654-662. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.016XIE Furen, CUI Xiaofeng, ZHAO Jiantao, et al. Regional division of the recent tectonic stress field in China and adjacent areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2004, 47(4): 654-662. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.04.016 [22] 李学刚, 杨坤光, 胡祥云, 等.黔东凯里—三都断裂结构及形成演化[J].成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 39(1): 18-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201201003LI Xuegang, YANG Kunguang, HU Xiangyun, et al. Formation and evolution of the Kaili-Sandu fault in East Guizhou, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2012, 39(1): 18-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201201003 [23] 刘志臣, 杜威, 陈坡, 等.贵州从江那哥铅锌多金属矿构造变形特征[J].矿业工程研究, 2012, 27(2): 64-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5876.2012.02.015LIU Zhichen, DU Wei, CHEN Po, et al. Study on deformation characteristics of Nage Pb-Zn-polymetallic sulfide ore deposit in Congjiang County of Guizhou Province[J]. Mineral Engineering Research, 2012, 27(2): 64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5876.2012.02.015 [24] 汤世凯, 马筱, 杨坤光, 等.黔东桂北加里东期两类构造变形特征与成因机制探讨[J].现代地质, 2014, 28(1): 109-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.01.010TANG Shikai, MA Xiao, YANG Kunguang, et al. Characteristics and genesis of two types of tectonic deformation during Caledonian in eastern Guizhou and northern Guangxi[J]. Geoscience, 2014, 28(1): 109-118. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.01.010 [25] RANALLI G, CHANDLER T E. The stress field in the upper crust as determined from in situ measurements[J]. Geologische Rundschau, 1975, 64(1): 653-674. doi: 10.1007/BF01820688 [26] 高莉青, 陈宏德.岩体应力状态的影响因[C]//素国家地震局地壳应力研究所情报室.地应力测量理论研究与应用.北京: 地质出版社, 1987.GAO Liqing, CHEN Hongde. The influence of the stress state of rock mass due to the compiling of the information room of the Institute of crustal stress[C]//National Seismological Bureau. Research and Application of Geostress Measurement Theory and Application. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: