ENGINEERING CHARACTERISTICS AND START-UP MECHANISM OF SLAG CLASTIC FLOW IN ZHAOCHUAN DISTRICT, XUANHUA
-
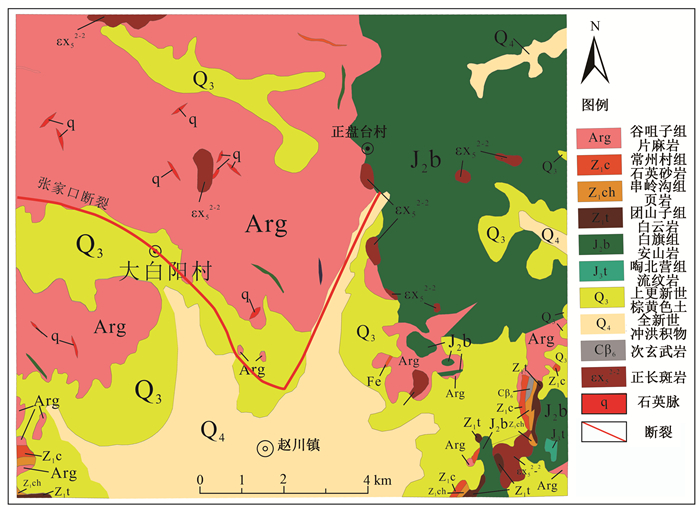
摘要: 张家口宣化地区存在大量具有潜在危险的松散矿渣堆积体,文章以该地区具有代表性的响水沟松散矿渣堆积体为研究对象,对矿渣的颗粒组成、矿物成分、力学性质等进行详细的室内试验研究,结果表明:矿渣堆积体属砾质砂土,粘粒含量少,且级配不良,松散易流动。同一干密度下,随含水率增加,矿渣抗剪强度先增大后减小,当含水率为15%时,其粘聚力最低,表明响水沟矿渣堆积体失稳启动下滑的界限含水率可能在15%左右。综合以上分析结果,拟合得到粘聚力与含水率关系公式,初步预测矿渣碎屑流启动下滑的临界含水率。这一认识对该区矿渣堆积体的稳定性评价及碎屑流灾害预警有重要意义。Abstract: There are a large number of potentially dangerous loose slag accumulation bodies in Xuanhua area of Zhangjiakou. The representative Xiangshuigou loose slag accumulation bodies in the area is taken as the research object, and the laboratory tests are made on particle composition, mineral composition and mechanical properties. The test results show that the slag accumulation bodies belong to gravel sand with less clay content and poor gradation, loose and easy to flow. At the same dry density, the shear strength of slag increases first and then decreases with the increase of moisture content. When the moisture content is 15%, the cohesive force is the lowest, indicating that the limit moisture content of the slag accumulation bodies in Xiangshuigou may be around 15% at the beginning of the decline of instability. Based on the above analysis results, the formula of the relationship between cohesive force and water content is obtained by fitting, and the limit water content of the initial slide of clastic flow is predicted. This conclusion is of great significance to the stability evaluation of slag accumulation body and the early warning of clastic flow in this area.
-
Key words:
- slag accumulation body /
- clastic flow /
- water content /
- shear strength /
- engineering property
-
表 1 宣化赵川地区大型矿渣堆积体统计
Table 1. Statistics of large slag accumulation bodies in Zhaochuan district, Xuanhua
矿渣堆积位置 分布面积/km2 平面形态 展布方向 河阳沟村北东 0.675 不规则状 北东向 小古城南 0.590 不规则状 北东向 辛丈子村东 0.437 不规则状 北东向 河阳沟村南 0.357 不规则状 北西向 张家窑南西 0.350 纺锤状 北西向 四台咀村南西 0.328 不规则状 北西向 响水沟北 0.308 不规则状 北东向 韩家沟北 0.292 蠕虫状 北西向 小古城西 0.270 矩形 北西向 涧河口村北西 0.262 三角形 北东向 行人马沟北 0.250 不规则状 北东向 小蛤蟆口村南 0.201 蠕虫状 北东向 红庙湾村北 0.194 棱角状 北西向 河阳口村南西 0.187 三角形 北西向 关底村南 0.183 不规则状 北西向 杨家营村北 0.179 蠕虫状 北东向 响水沟内 0.176 不规则状 北西向 南窝铺南东 0.168 不规则状 北西向 四台咀村南 0.167 菱形 北东向 黄土坡村北西 0.162 不规则状 北西向 -
[1] 陈廷方, 崔鹏, 刘岁海, 等.矿产资源开发与泥石流灾害及其防治对策[J].工程地质学报, 2004, 13(2):179-182. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200502007CHEN Tingfang, CUI Peng, LIU Suihai, et al. Anthropogenic debris flow disasters and mitigation countermeasures in mineral resources exploitation in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2004, 13(2):179-182. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb200502007 [2] 陈华清, 徐友宁, 张江华, 等.小秦岭大湖峪矿渣型泥石流的物源特征及其危险度评价[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(8):1292-1298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.08.028CHEN Huaqing, XU Youning, ZHANG Jianghua, et al. Source characters and risk assessments of mine slag-type debris flows in the Dahu valley, Xiaoqinling, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(8):1292-1298. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.08.028 [3] 陈循谦.滇东北因民沟"84.5.27."泥石流灾害[J].地理学与国土研究, 1986, 2(1):23-25.CHEN Xunqian. Yin Min Ditch in the Northeastern part of Yunnan Province "84.5.27." Debris Flow Disaster[J]. Geography and Land Research, 1986, 2(1):23-25. (in Chinese) [4] 莫志柏.矿山泥石流形成机理及治理方法研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2003.MO Zhibai. Mine debris flow formation mechanism and governance methods[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2003. (in Chinese) [5] 杨敏.影响小秦岭金矿区矿渣型泥石流形成的主要因素研究[D].西安: 长安大学, 2010.YANG Min. Study on the key control factors of mine waste debris flows initiation in Xiaoqinlin gold mine area[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 徐友宁, 何芳, 张江华, 等.矿山泥石流特点及其防灾减灾对策[J].山地学报, 2010, 28(4):463-469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2010.04.010XU Youning, HE Fang, ZHANG Jianghua, et al. Characteristics and strategy for prevention and reduction of mine debris flow[J]. Journey of Mountain Science, 2010, 28(4):463-469. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2010.04.010 [7] 谢洪, 游勇, 钟敦伦.长江上游一场典型的人为泥石流[J].山地研究, 1994, 12(2):125-128. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400402509XIE Hong, YOU Yong, ZHONG Dunlun. A typical man-made debris flow in the upper reaches of Changjiang river[J]. Mountain Research, 1994, 12(2):125-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400402509 [8] 张树轩, 杨为民, 孟华君, 等.京张地区区域地壳稳定性评价[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(1):70-77. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180108&journal_id=dzlxxbZHANG Shuxuan, YANG Weimin, MENG Huajun, et al. Regional crustal stability evaluation in Beijing-Zhangjiakou area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(1):70-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20180108&journal_id=dzlxxb [9] 周月玲, 尤惠川.张家口断裂第四纪构造变形与活动性研究[J].震灾防御技术, 2010, 5(2):157-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2010.02.002ZHOU Yueling, YOU Huichuan. Research on quaternary deformation and activities of Zhangjiakou Fault, Hebei Province[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2010, 5(2):157-166. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2010.02.002 [10] 邓华锋, 原先凡, 李建林, 等.土石混合体直剪试验的破坏特征及抗剪强度取值方法研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(S2):4065-4072. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2013z2133DENG Huafeng, YUAN Xianfan, LI Jianlin, et al. Research on failure characteristics and determination method for shear strength of earth-rock aggregate in direct shear tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(S2):4065-4072. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb2013z2133 [11] 何蕾.矿物成分与水化学成分对粘性土抗剪强度的控制规律及其应用[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.HE Lei. Impact of mineral logical composition and water chemistry on the shear strength of clay and its application[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014. (in Chinese) [12] 徐彬, 殷宗泽, 刘述丽.膨胀土强度影响因素与规律的试验研究[J].岩土力学, 2011, 32(1):45-50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201101008XU Bin, YIN Zongze, LIU Shuli. Experimental study of factors influencing expansive soil strength[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(1):45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201101008 [13] 谭晓慧, 辛志宇, 沈梦芬, 等.湿胀条件下合肥膨胀土土-水特征研究[J].岩土力学, 2014, 35(12):3353-3369. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201412002TAN Xiaohui, XIN Zhiyu, SHEN Mengfen, et al. Study of soil-water characteristics of Hefei expansive soil under moisture-expansion condition[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(12):3353-3369. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201412002 [14] 顾成权, 孙艳.土体内聚力随含水量、粘粒含量及干密度变化关系探讨[J].水文地质工程地质, 2005, 32(1):34-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.01.008GU Chengquan, SUN Yan. Discussion on the cohesion of soil changing with water content, cohesive soil content and dry density[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2005, 32(1):34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.01.008 [15] 申春妮, 方祥位, 王和文, 等.吸力、含水率和干密度对重塑非饱和土抗剪强度影响研究[J].岩土力学, 2009, 30(5):1347-1351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.028SHEN Chunni, FANG Xiangwei, WANG Hewen, et al. Research on effects of suction, water content and dry density on shear strength of remolded unsaturated soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(5):1347-1351. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.05.028 [16] 许成顺, 尹占巧, 杜修力, 等.黏性土的抗剪强度特性试验研究[J].水利学报, 2013, (12):1433-1438. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slxb201312006XU Chengshun, YIN Zhanqiao, DU Xiuli, et al. Experimental study of shear strength of clay[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2013, (12):1433-1438. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/slxb201312006 [17] 方华.文家沟泥石流源地土体直剪强度特征试验研究[J].工程地质学报, 2011, 19(S1):147-151. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7624770FANG Hua. Study on strength behaviour of debris flow source region soil in Wenjiagou Ravine[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(S1):147-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7624770 [18] 吴瑞安, 张永双, 王献礼, 等.汶川地震区崩滑堆积体强度现场直剪试验研究[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(1):105-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.01.006WU Ruian, ZHANG Yongshuang, WANG Xianli, et al. In-situ direct shearing test on landslide accumulation body intensity of Wenchuan earthquake region[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(1):105-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.01.006 [19] 张岩, 耿济世, 毛磊, 等.珠江三角洲海相沉积软土压缩和剪切变形特性试验研究[J].地震工程学报, 2018, 40(4):745-751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2018.04.745ZHANG Yan, GENG Jishi, MAO Lei, et al. Compression and shear deformation properties of marine soft soil deposits in the Pearl River Delta[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2018, 40(4):745-751. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2018.04.745 [20] 杨为民, 吴树仁, 张永双, 等.降雨诱发坡面型泥石流形成机理[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(6):197-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.06.025YANG Weimin, WU Shuren, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. Preparation mechanism of debris flow induced by rainfall[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(6):197-204. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.06.025 [21] 杨为民, 吴树仁, 张永双, 等.陕西宁陕县城坡面型泥石流形成条件及其诱发机制[J].地质力学学报, 2006, 12(2):219-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2006.02.015YANG Weimin, WU Shuren, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. Formation conditions of slope type mudflow in Ningshaan County, Southern Shaanxi, and its inducing mechanism[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2006, 12(2):219-226. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2006.02.015 [22] 冯振, 李滨, 赵超英, 等.三峡库区山区城镇重大地质灾害监测预警示范研究[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(3):685-694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.022FENG Zhen, LI Bin, ZHAO Chaoying, et al. Geological hazards monitoring and application in mountainous town of three gorges reservoir[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(3):685-694. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.022 [23] 胡凯衡, 马超.泥石流启动临界土体含水量及其预警应用[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 36(2):73-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2014.02.010HU Kaiheng, MA Chao. Critical soil moisture for debris flow initiation and its application in forecasting[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2014, 36(2):73-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2014.02.010 -





 下载:
下载: