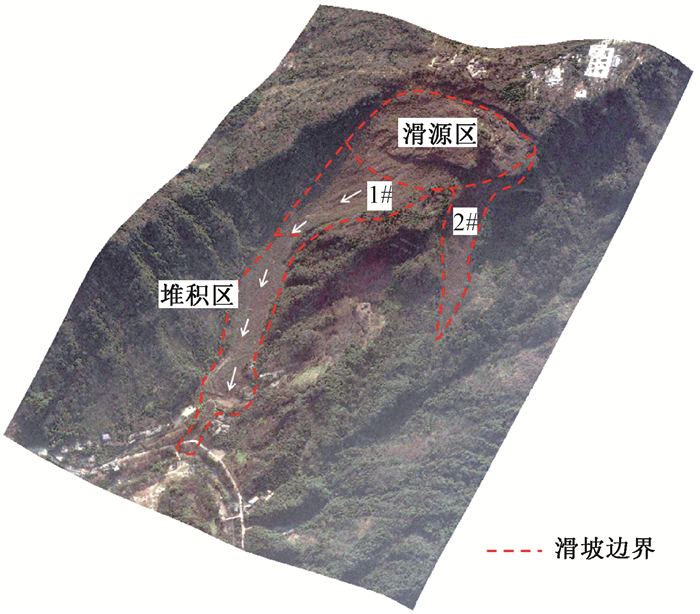
ACCUMULATION CHARACTERISTICS AND ENERGY CONVERSION OF HIGH-SPEED AND LONG-DISTANCE LANDSLIDE ON THE BASIS OF DEM: A CASE STUDY OF SANXICUN LANDSLIDE
-
摘要: 高速远程滑坡-碎屑流运动速度、堆积特征和能量转化是研究其致灾机制的重要因素,而模型试验、野外调查并不能全面揭示其成灾机理。文章以三溪村滑坡为例,采用PFC3D离散元模拟方法,揭示滑坡运动过程中的前部、中部和后部岩土体的速度演化分布、堆积特征和能量转化关系。研究结果表明:三溪村滑坡的残余摩擦系数为0.2时,模拟结果与实际堆积特征一致。前部、中部、后部岩土体到峰值速度存在差异,前部岩土体速度分布表现为显著的单峰型特征,而后部岩土体速度分布为双峰型特征。滑坡不同部位的岩土体堆积呈现层序分布;滑坡重力势能的转化中,摩擦耗能占总能量的52%,动能峰值时刻仅有15%的重力势能转化为动能。研究结果可为高速远程滑坡的运动机理分析和防灾减灾治理工程提供重要参考。Abstract: The velocity, accumulation characteristics and energy conversion are important factors in the study of the disaster-causing mechanism of high-speed and long-stance landslide; however, model test and field investigation can't fully reveal the mechanism. In this study, the landslide in Sanxicun was simulated by PFC3D to reveal that the velocity evolution distribution, accumulation characteristics and energy conversion relationship of frent, middle and rear rock and soil during the landslide movement process. The results show that, when the residual friction coefficient of Sanxicun landslide is 0.2, the simulation results are consistent with the actual accumulation characteristics. When the front, middle and rear rock and soil achieve peak velocity, the time distribution is Sfront < Smiddle < Srear. The velocity distribution of the front rock mass shows significant unimodal characteristic, while that of the rear rock mass is bimodal. The accumulation of rock and soil mass presents sequence distribution. In the transformation of gravitational potential energy of the landslide, friction energy accounts for 52% of the total energy, and only 15% of the gravitational potential energy at the peak of kinetic energy is converted into kinetic energy. The research results can provide reference for the analysis of the disaster-causing mechanism of high-speed and long-stance landslide and the project of disaster prevention and reduction.
-
表 1 数值模型微观参数
Table 1. The numerical micro-parameters of the PFC model
参数名称 单轴数值实验参数 微观参数取值 颗粒半径/m 0.0006~0.0015 0.975~2.437 球颗粒密度/(kg/m3) 2300 2300 球颗粒刚度比/(kn/ks) 1 1 球-球接触模量/GPa 1.48 1.48 平行粘结刚度比 1 1 球颗粒摩擦系数 0.677 0.1~0.4 平行粘结法向强度/Pa 6e6 6e6 平行粘结切向强度/Pa 6e6 6e6 正向临界阻尼比 0.22 0.22 切向临界阻尼比 0.2 0.2 -
[1] 陈自生.高位滑坡的运动转化形式[J].山地研究, 1992, 10(4):225-228. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA199204004.htmCHEN Zisheng. Motion transformation of high-locality landslide[J]. Mountain Research, 1992, 10(4):225-228. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA199204004.htm [2] 许强, 董秀军, 邓茂林, 等. 2010年7·27四川汉源二蛮山滑坡-碎屑流特征与成因机理研究[J].工程地质学报, 2010, 18(5):609-622. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.05.003XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, DENG Maolin, et al. The Ermanshan rock slide-debris flow of July 27, 2010 in Hanyuan, Sichuan:characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(5):609-622. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.05.003 [3] 殷跃平, 刘传正, 陈红旗, 等. 2013年1月11日云南镇雄赵家沟特大滑坡灾害研究[J].工程地质学报, 2013, 21(1):6-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.01.002YIN Yueping, LIU Chuanzheng, CHEN Hongqi, et al. Investigation on catastrophic landslide of January 11, 2013 at Zhaojiagou, Zhenxiong Country, Yunnan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(1):6-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.01.002 [4] 殷跃平, 朱继良, 杨胜元.贵州关岭大寨高速远程滑坡-碎屑流研究[J].工程地质学报, 2010, 18(4):445-454. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.04.002YIN Yueping, ZHU Jiliang, YANG Shengyuan. Investigation of a high speed and long run-out rockslide-debris flow at Dazhai in Guanling of Guizhou province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(4):445-454. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.04.002 [5] 许强, 李为乐, 董秀军, 等.四川茂县叠溪镇新磨村滑坡特征与成因机制初步研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(11):2612-2628. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb201711002XU Qiang, LI Weile, DONG Xiujun, et al. The Xinmocun landslide on June 24, 2017 in Maoxian, Sichuan:characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics & Engineering, 2017, 36(11):2612-2628. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb201711002 [6] 程谦恭, 张倬元, 黄润秋.高速远程崩滑动力学的研究现状及发展趋势[J].山地学报, 2007, 25(1):72-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007CHENG Qiangong, ZHANG Zhuoyuan, HUANG Runqiu. Study on dynamics of rock avalanches:state of the art report[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2007, 25(1):72-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.01.007 [7] 杨龙伟, 魏云杰, 王文沛, 等.新疆伊宁县喀拉亚尕奇滑坡动力学特征研究[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(5):699-705. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201805013YANG Longwei, WEI Yunjie, WANG Wenpei, et al. Research on dynamic characteristics of the Kalayagaqi landslide in Yining country, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 24(5):699-705. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201805013 [8] 胡晓波, 樊晓一, 马新.高速远程滑坡加速运动过程能量消耗评判研究[J].人民长江, 2019, 50(2):191-196. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rmcj201902034HU Xiaobo, FAN Xiaoyi, MA Xin. Energy consumption evaluation of high-speed and long-distance landslide in accelerated motion[J]. Yangtze River, 2019, 50(2):191-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rmcj201902034 [9] 鲁晓兵, 王义华, 王淑云, 等.碎屑流沿坡面运动的初步分析[J].岩土力学, 2004, 25(S2):598-600. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx2004z2127LU Xiaobing, WANG Yihua, WANG Shuyun, et al. The Primary analysis on the castic gain fow[J]. Rock & Soil Mechanics, 2004, 25(S2):598-600. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx2004z2127 [10] FAN X Y, TIAN S J, ZHANG Y Y. Mass-front velocity of dry granular flows influenced by the angle of the slope to the runout plane and particle size gradation[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2016, 13(2):234-245. doi: 10.1007/s11629-014-3396-3 [11] 郝明辉, 许强, 杨兴国, 等.高速滑坡-碎屑流颗粒反序试验及其成因机制探讨[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(3):472-479. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb201503004HAO Minghui, XU Qiang, YANG Xingguo, et al. Physical modeling tests on inverse grading of particles in high speed landslide debris[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics & Engineering, 2015, 34(3):472-479. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb201503004 [12] 王玉峰, 程谦恭, 朱圻.汶川地震触发高速远程滑坡-碎屑流堆积反粒序特征及机制分析[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(6):1089-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.06.002WANG Yufeng, CHENG Qiangong, ZHU Qi. Inverse grading analysis of deposit from rock avalanches triggered by Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics & Engineering, 2012, 31(6):1089-1106. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.06.002 [13] HUNGR O, MCDOUGALL S. Two numerical models for landslide dynamic analysis[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2009, 35(5):978-992. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0210974739/ [14] 孙新坡, 何思明, 高成凤, 等.牛圈沟滑坡离散元数值分析[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 53(1):48-53. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lzdxxb201701007SUN Xinpo, HE Siming, GAO Chengfeng, et al. Discrete element numerical analysis of Niujuangou landslide[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2017, 53(1):48-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lzdxxb201701007 [15] 唐昭荣, 胡植庆, 罗佳明, 等.剧变式山崩之PFC3D模拟初探-以草岭与小林村为例[J].地工技术, 2009, (122):143-152.TANG Chaolung, HU Jyrching, LUO Chiaming, et al. The catastrophic 1999 Tsaoling and 2009 Hsiaoling landslides:Preliminary study from 3-D distinct element modeling[J]. Sino-Geotechnics, 2009, (122):143-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 殷志强, 徐永强, 赵无忌.四川都江堰三溪村"7·10"高位山体滑坡研究[J].工程地质学报, 2014, 22(2):309-318. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.02.022YIN Zhiqiang, XU Yongqiang, ZHAO Wuji. Sanxi Village landslide in Dujiangyan, Sichuan province on July 10, 2013[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(2):309-318. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.02.022 [17] 孟华君, 姜元俊, 张树轩, 等.汶川地震前后都江堰山区滑坡滑动距离影响因素变化分析[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(6):904-913. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170611&flag=1MENG Huajun, JIANG Yuanjun, ZHANG Shuxuan, et al. Analysis on the change of influence factors on slipping displacement of landslides in Dujiangyan area before and after the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(6):904-913. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20170611&flag=1 [18] CUNDALL P A, STRACK O D L. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies[J]. Géotechnique, 1979, 29(1):47-65. doi: 10.1680/geot.1979.29.1.47 [19] ITASCA. PFC3D (Particle Flow Code in 3 Dimensions) version 5.0, Minneapolis, MN, USA:Itasca Consulting Group Inc, 2018:205-215. [20] TANG C L, HU J C, LIN M L, et al. The Tsaoling landslide triggered by the Chi-Chi earthquake, Taiwan:Insights from a discrete element simulation[J]. Engineering Geology, 2009, 106(1-2):1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.02.011 [21] LO C M, LIN M L, TANG C L, et al. A kinematic model of the Hsiaolin landslide calibrated to the morphology of the landslide deposit[J]. Engineering Geology, 2011, 123(1-2):22-39. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.07.002 [22] 常士骠, 张苏民.工程地质手册[M]. 4版.北京:中国建筑工业出版社, 2007:167-168.CHANG Shibiao, ZHANG Sumin. Engineering geological manual[M]. 4thed. Beijing:China Architecture & Building Press, 2007:167-168. (in Chinese) [23] 杜国梁, 张永双, 姚鑫, 等.都江堰市五里坡高位滑坡-碎屑流成因机制分析[J].岩土力学, 2016, 37(S2):493-501. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTLX2016S2064.htmDU Guoliang, ZHANG Yongshuang, YAO Xin, et al. Formation mechanism analysis of Wulipo landslide-debris flow in Dujiangyan city[J]. Rock & Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(S2):493-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTLX2016S2064.htm -





 下载:
下载: